Masters Degree Dissertation Assignment Sample
Question
This is a vital part of your Programme and will contribute substantially to your personal development. Your MSc Dissertation is worth 40 Credits (two times as much as a taught Module). You will be expected to demonstrate where appropriate your skills in providing:
(a) A synthesis of the literature.
(b) An analysis of quantitative and/or qualitative information.
(c) A summary of empirical results whether found by experimentation, observation, survey
or interview.
(d) The implications of the findings.
Each Dissertation should involve all of the following:
(a) Problem identification
(b) Problem resolution
(c) Information search
(d) Application of methods developed in your Programme
(e) Drawing appropriate conclusions.
Note: The Dissertation is a piece of applied academic research and must be more than a mere technical account.
Writing the matlab dissertation help can seem like a major obstacle as it is likely to be the biggest single piece of academic work you will have undertaken. However, if you have a clear idea of the structure and nature of the research you have done or are doing then it makes it much easier to have a clear plan for the structure of the Dissertation.
Structure
The structure of the final Dissertation is to be presented as follows:
First inside page - Title, your name and year (2021, 2022, etc.)
(see Appendix III for an example of the FRONT page and the FIRST inside page)
• Declaration
• Abstract
• Acknowledgements
• Contents page
• List of Tables & Figures
• First Chapter - Introduction (research purpose and objectives)
• Chapters 2, 3, 4 etc.
• Final Chapter – Conclusions and Recommendations
• References
• Appendices
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Your opening chapter is extremely important as it sets the scene on what is about to come in the rest of the Dissertation. You should therefore aim for this to be a clear and concise piece of assignment help work that provides all the key information required for the reader to understand the background to the work and how you will conduct the research in the pages that follow.
Chapter 2 - Literature Review
The Literature Review chapter is the longest in terms of number of words and also the time taken to complete. This is because you must spend a considerable amount of time identifying, searching for, accessing, reading and discussing material from a wide variety of sources. Overall, this chapter will account for 25-40% of the total word count, meaning that most students will be expected to write around 4,000-5,000 words.
Chapter 3 - Research Methods
Once you have completed the previous chapter you will have a very good idea about the options open to you regarding how you will conduct your own study. Many of the journal articles that you will have discussed in the previous chapter will have provided you with detailed information on the best way to research your topic and also whether there are likely to be any problems with your planned research approach.
In the early stages of this chapter it is important that you identify and set out the key questions and/or hypotheses that you wish to test. This can only really be done after you have a thorough understanding of the types of questions and/or hypotheses that need to be asked based on your review of previous studies in the area.
Once these have been discussed, you need to explain how you will go about answering these questions or testing these hypotheses. For the vast majority of students this will involve the collection of primary data. For some students it may be more appropriate (or indeed the only option open to them) to gather and then analyse only secondary data. There is no problem with this approach but it limits your ability to show us that you are an effective researcher in terms of designing a data collection tool and then using this to gather information for the first time.
Chapter 4 - Data Description
Having completed the collection of data for your Dissertation you should spend some time describing the characteristics of that information before then going on to conduct more detailed analysis. Depending on the type of research you are involved in, this may be relatively short as far as chapter length is concerned, or may be a substantial part of your work if you are investigating more theoretical or complex issues.
Either way, it is important that the reader becomes familiar with the characteristics of the data so that they will then be able to understand the analysis and results that you will discuss in the following chapter.
Chapter 5 - Data Analysis
This is a critical part of the whole study and is where any new discoveries will be made. You need to set this chapter out in a logical manner and the most appropriate way to do this is to systemically address the research objectives, questions and/or hypotheses that you set out in previous chapters.
You may have a purely qualitative study, in which case much of the discussion here will be based on your own interpretation of information that you have gathered (such as through interviews, focus groups, observation studies etc.). It is perfectly acceptable to include direct quotes in this stage to highlight specific issues or get a particular point across. In any event, you should not identify any individual by name or other identifying characteristic. Similarly, in most studies at this level the names of organisations should be omitted from your written work unless you have the express permission of the owner/custodian to use their name.
In a quantitative study you will be presenting numerical data and this must be analysed using appropriate methods, in most cases using specific statistical tests.
Most quantitative data can be analysed using a variety of different tests but you must choose the single test that is appropriate for your objectives and hypotheses and stick to the results you generate. It is unethical to reanalyse data with a variety of statistical tests until you find a result or answer that you had hoped for.
SOLUTION
The role of cultural differences in influencing different marketing strategies in MNCs
Abstract
The dissertation focuses on the role of cultural differences in influencing different marketing strategies in MNCs. The aim of the dissertation is to identify the different cultures and its differences in influencing the varied marketing strategies that are undertaken by the MNCs. From the identified literature it can be stated that the cultural diversity is important in bringing about a considerable understanding of the areas that are necessary for the marketing strategies to take place. The benefits as well as the challenges involved in the marketing strategies along with the cultural benefits are to be identified in this case. The research methods that are followed for this dissertation include collecting data from primary sources and interpreting it in the form of qualitative analysis. Interview method is conducted which can be regarded to have an extensive overview of the managers. 6 managers belonging to different MNCs are targeted to gain clear concept of the topic. The interpretation provides an analysis of the ways with which the cultural factors are important for the MNCs and the concept that is understood in the market. It also helps in bringing about a considerable approach in building strong recommendations for the MNCs to be associated with the cultural diversity. Recommendations in the form of being aware of the local language and identifying cultural differences as the main external threats are provided so that the MNCs can bring about considerable success within the different markets upon expansion.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
In an era of globalisation, various cultural people work together to attain a common goal. In this way, one of the important aspects that are to be developed is the ways with each group of people can be brought together to provide the ultimate success story with which the organisations can succeed. Marketing strategies undertaken by the MNCs help in ensuring that these cultural groups work together by depending on one another and maintain prolific success strategy that can help in bringing about improvement. The focus of the dissertation is to bring about an identification of those marketing strategies that are essential for bringing about the success of the MNCs by identifying different marketing strategies that are important for influencing the cultural differences. In this chapter, the background of the research is provided along with the aims, objectives and questions that can help the researcher maintain a proper guide to the research.
1.2 Background
The marketing mix strategy is hugely influenced by differences in the cultural practices on the global market. The technological revolution has been effective for modern organisations to expand their business on international markets with more effectiveness. The business strategy on an international level is influenced by culture and for this reason understanding of cultural differences on international background needs to be analysed. The globalisation of business organisations has accelerated the development of the economic aspects of the organisations. Technological development has also affected the financing model of international business organisations and revolutionary aspects are visible in current marketing strategies (tradewindfinance.com, 2022). The advancement of technological tools has changed marketing strategies of international organisations because cultural aspects are effectively analysed by technology before proceeding with creating marketing strategies.
International organisations have emphasized their business approaches to reach out to a huge number of international consumers with more effective business strategies. On another side, economic agreements of a particular region have a huge influential impact that determines business strategies. Multiple cultural policies have increased complexity for the international organisations for creating a marketing strategy (worldbank.org, 2018). Economical aspects of a particular culture need to be analysed by management of international organisations so that marketing business strategy could perform more beneficial for the Marketing Programme of the organisation.
The pricing strategy of services and products are hugely impacted by the financial agreement of selected region and for this reason, organisational management needs to analyse the economic agreement. Organisational management needs to understand local cultural practices because knowledge about local culture increases effectiveness in marketing strategy. On another side, local language and local cultural aspects are major aspects that determine marketing practices of organisational management (fm-magazine.com, 2019). Management needs to understand local languages before initiating marketing strategy because acute knowledge about the local language increases efficiency for effectiveness to market services and products in forming markets.
The standardized approach of international markets by the management of Mcdonald's has been ineffective because it has negatively impacted organisational financial conditions on a higher level. The failure in the foreign markets have negatively impacted the brand value of its products and for this reason, it has been incapable of developing its situation even in its home ground market (Feng et al., 2019). After the huge loss of ineffective foreign marketing strategy management of this organisation has decided to empower local authorities so that they could be able to create effective marketing strategies in their particular regions because local authorities can evaluate all cultural aspects that have a higher potential to influence the marketing of its products and services.
It has been an effective approach by its management and for this reason, it has successfully captured a higher rank in the international market. This digital potential allows these firms to communicate their marketing strategies in a locally-specific language across different regions. Further, as observed by Ottman (2017), green marketing has emerged as an important strategic tool that enables multinationals to adopt a sustainable marketing approach and formulate a responsible brand name for all categories of consumers.
The needs of consumers are different from each other and it is mainly because of the cultural differences and practices performed by different cultural communities (ama.org, 2020). Cultural practices determine consumer behaviour and for this reason understanding, cultural identity has been most important for organisational management for expanding their business on foreign markets with more effectiveness.
1.3 Research Aim
The aim of the research is to identify the different cultures and its differences in influencing the varied marketing strategies that are undertaken by the MNCs. The dissertation can help in providing evidence about the roles played by the individuals of varied cultures to bring about success for the MNCs.
1.4 Research Objectives
The objectives of this research work include the following:
• To understand the importance of culture for MNCs
• To understand what is meant by cultural differences at MNCs
• To examine the cultural differences that occur in MNCs and how they are managed
• To evaluate the role of cultural difference as an important factor in the formulation of Global Marketing Strategies
1.5 Research Questions
The research questions include:
• What is the importance of culture for MNCs?
• What is meant by cultural differences at MNCs?
• How do cultural differences occur in MNCs and how are they managed?
• Why is cultural difference an important factor in the formulation of Global Marketing Strategies?
1.6 Research hypothesis
H1: There is a huge influence of cultural differences in different marketing strategies adopted by MNCs
H0: There is no influence of cultural differences in different marketing strategies adopted by MNCs
1.7 Research Rationale
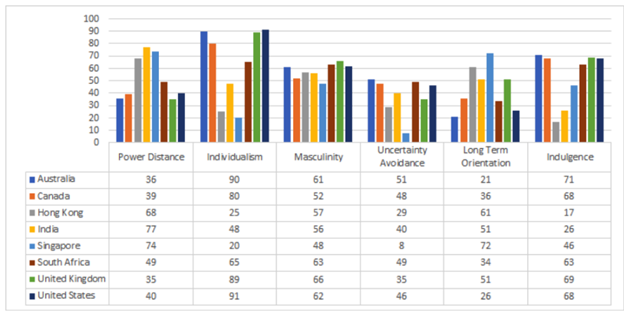
Figure 1: Differences in the cultural aspects in the different countries
(Source: Guzman et al., 2018)
Cultural aspects are different in each country and for this reason, organisational management needs to understand the different cultural aspects of foreign countries so that they could be able to create an effective marketing strategy. The differences in power politics emphasized differentiation in the different marketing strategies that are helpful for organisational management to market their products and services more effectively. Cultural ethnicity differs community members to adopt different lifestyles and consumers adopt products as per their needs to maintain their initiated lifestyle. In order to maintain the active participation of organisational management for successful globalisation, management has to proceed with a higher effective marketing strategy.
Otherwise, organisational management has to face a huge amount of financial loss that could be the reason for their devastation. Numerous organisations have faced a lot of issues after initiating their business to foreign markets due to their ineffective marketing strategy. Employees of different organisations play a major role in practising different business ventures and due to this reason, organisational management needs to understand the individual characteristics of local employees for a successful business model.
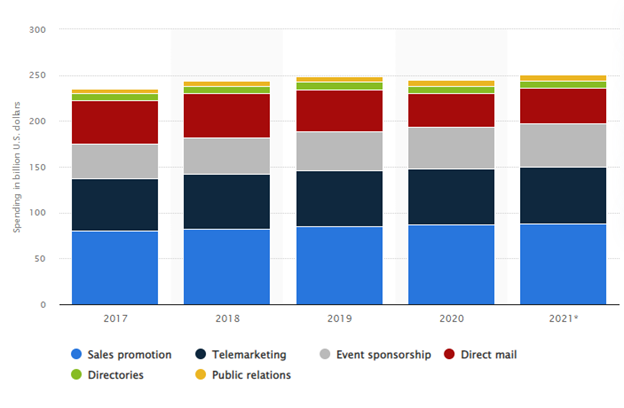
Figure 2: Marketing spending are increasing dramatically
(Source: statista.com, 2021)
In order to promote services and products to foreign markets, organisational management has to practice a higher amount of expense. In the 2020 financial year, the United States has devoted 61.4 billion dollars only for telemarketing. But this marketing spending has increased to 244.7 billion dollars for overall marketing strategies (statista.com, 2021). Organisational managements invest a huge amount in their marketing system that includes directories, telemarketing, public relations, sales promotions and others. Such a higher amount of product promotional investment organisational management has increased the price of their services and products. The organisational management needs to decrease their costs for the promotional activities that would help the organisational management to develop their sustainability power for critical situations. Immediate research on this particular topic is necessary that would help organisational management to develop their understanding of different aspects of the marketing strategies.
This research would enlighten all aspects of the marketing strategy of MNCs that are interrelated with cultural norms of different regions. This particular research would be effective for the organisational management to develop their understanding of different impactful influences of cultural aspects on organisational managements for initiating marketing strategy in foreign countries. The major aspect of this paper is to shed light on different cultural practices that have a higher potential to influence marketing strategies of the MNCs. On another side, this paper would also help numerous organisational managements for initiating an impactful footstep in succeeding with the increasing trend of globalisation. Management of organisational would to helpful by this particular research paper for analysing important aspects of culture foreign countries so that expansion of business would have higher potential to achieve success.
1.8 Research Significance
The significance of this research is that it evaluates the impact of social and cultural patterns on marketing and looks at marketing theory from a wider social perspective. The rising number of multinational organisations across the world and their ability to spread across global markets has made it particularly important to evaluate the impact of different cultures on their marketing strategies. According to recent reports, there have been close to 213 million organisations that have their operational bases all across the world in 2020 (statista.com, 2021). This implies that these firms would be motivated to take account of the cultural demands of consumers across the different countries within which they operate. This research has also been effective in understanding the importance of consumer engagement and heightened consumer knowledge on the business strategies of firms. In addition, it also sheds light on the influence of internal managerial strategies, including a diverse employee and leadership culture and their impact on the unique marketing approach adopted by MNCs.
1.9 Structure of The Dissertation
The dissertation consists of five chapters each dedicated to bring about the achievement of the set objectives. The first chapter provides an introduction, which forms the background of the research. It sets up the aims, objectives and questions that are essential in bringing about quality application of the concepts and theories throughout the dissertation. The second chapter provides the critical explanation of the existing concepts and theories along with the variables that are associated with the topic. Works of scholars along with the counter arguments are presented in the chapter. The third chapter provides an analysis of the data that is to be collected and the method of analysis for meeting the objectives. The fourth chapter helps in interpreting the data collected and align it with the evidence found in the literature review. The final chapter helps in the conclusion of research. Recommendations are also provided if needed.
1.10 Summary
This section has outlined the rationale and significance of this research, which include the need to evaluate the impact of culture and understand cultural distinctions in marketing. The objectives of this work include an assessment of different cultural elements and their influence on the marketing approach of MNCs. Further, it has also addressed aspects like the challenges associated with cultural differences in marketing, along with strategies adopted by firms to mitigate these challenges.
CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
The literature review provides an analysis of the concepts and the theories that are to be applied so that extensive research on the topic can take place. It is necessary to understand the existing literature so that an overall identification of the strategies that is to be undertaken can take place. One of the important areas in this case is the fact that argument as well as counter argument associated with topic along with that of the variables is made. Different opinion of scholars is highlighted in the chapter to provide an opportunity to maintain an extensive research that can provide identification of the topic.
2.2 Concept of Cultural Differences
Cultural differences involve the ways with which integrated system of socially acquired values are undertaken in bringing together an identification of the beliefs and values that exist for a system to be functional. The overall application of the cultural differences can be distinguished between the social groups that exist in the market. According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), one of the important aspects of the cultural differences that can be taken into consideration is the way it brings about variety of choices among an organisation. In terms of decision making and forming strategies cultural differences are regarded to have a steady implication in the overall business strategy that is to take place among an organisation. Hence, as stated by Gherasim and Gherasim (2018) the concept is of utmost value in bringing together people from different groups and promoting globalisation in a way that can allow each of the organisations and the employees to have a severe positive impact on the existing market.
2.3 Theory
Social Exchange Theory (SET)
This work is based on an evaluation of the relationship between marketing and cultural difference, which can be understood through an application of theories like the social exchange theory. This is an important theory for understanding cross-cultural communication, in which social behaviour is largely seen as an immediate result of the exchange and interaction between different groups. In this context, the effectiveness of these social interactions is understood by weighing the positive and negative outcomes that result from these interactions.
Social Interaction
In the theory, it is stated that a person will weigh the cost of the social interaction against the reward of that social interaction. For this reason, it can be stated that risks and benefits can be identified as potential metaphors so that the prediction of the behaviour of the individuals in the society can be put in place. In the words of Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017) one of the important applications of the theory is that it can help in understanding the clarity of relationships that exist in bringing about different cultural trends and help in maintaining the communication level between the people.
Communication
This implies that within the process of communication, people usually expect reciprocal behaviours that emerge from their interactions with other people. This suggests that the element of rewards and costs are important factors for judging different social interactions within group processes (Cropanzano et al., 2017). This theory can be suitably applied to marketing by underlining that consumers would judge the effectiveness of different marketing methods in terms of the possible rewards that these would generate for them. This implies that cultural difference is an important criterion for understanding marketing methods as they influence the relative value attached to the marketing communication by consumers.
Culture
Without an analysis of the culture, determination of the areas that require improvement cannot be made. This theory can be applied among companies that aim to seek expansion in foreign nations. According to Kotler (2019), the overall application of the expansion strategies need to be associated with the cultural phenomenon in a way that can allow these aspects to have a complete understanding of the behaviour of each people. Thus, as stated by Feng et al. (2019) the application of the social exchange theory for organisations is regarded as a way to bring about effective and efficient analysis of the market along with the application of the impact that might exist in the current situation of the market.
2.4 Cultural Differences Model
Geert Hofstede’s cultural dimensions (the 4+1 model)
An important model for understanding cultural differences and their influence on marketing is the Cultural Dimensions model formulated by Geert Hofstede, which formulates four specific dimensions important for understanding cultural values. These dimensions include individualism-collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, power distance and masculinity-femininity, which determine the specific orientation of different cultures across the world. According to Guzman et al. (2018), these separate dimensions would influence the kind of values and principles that people within these societies would adhere to for maintaining balance. There is, for instance, greater importance attached to group values like belongingness and harmony in collectivistic rather than individual societies. As stated by Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) these values, in turn, would determine the kind of marketing strategies that are adopted by MNCs and their unique cultural preferences.
Hofstede’s model provides an analysis of the areas that every company need to improve on so that success can be reached in the market. According to Reddy et al. (2017), this again is applicable during the expansion mainly because it can help in bringing about a combat and mitigation for the external environment that exists. In this way, one of the important lessons that is to be brought about in this case is the ways with which the Hofstede’s dimension can help in the understanding of the level of success that can be gained even before entering the market. However, as pointed out by Katsikeas et al. (2019) it is also to be noted that achieving all the dimensions might not bring about success for any organisation, as the model cannot be comprehended in adjusting any one variable of the culture. Hence, although the application is convenient for understanding the potential success that can be gained in the market, it can also bring about doubts about the application.
2.5 Types of Marketing Strategies Used in MNCs
The multinational firms are usually those, which have their operational bases across geographical and cultural regions, which enables them to implement different marketing strategies to compete with a large international market. As observed by Dadzie et al. (2017), the 4Ps of the marketing mix, which includes place, product, price and promotion, influences the marketing approach adopted by firms. This often results in organisations adopting marketing practices like demand differentiation, segmentation, positioning and targeting, which are used to target different markets. This approach is suitable for these firms in understanding the cultural and social demographics of consumers and their impact on consumer choices.
Another important type of marketing that is used in the MNCs is that of the standardisation. According to Song et al. (2018), the reason for this is that the standardisation of the products, approach as well as distribution channels are made which can bring about global and domestic transactions. In this way, the effectiveness of the market can be determined in bringing about an identified aspect of the cultures. As identified by Felipe et al. (2017) the fact that local needs are to be met is also one of the areas in which the marketers and the companies can bring about successful transition into the market. For this reason, it is necessary that an overview of the market be maintained so that the marketing strategies used can bring about effective coordination between the employees and the customers. In this way, such an aspect is important for the marketing strategies, which in turn can be related to the MNCs.
According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), many firms have increasingly adopted international marketing strategies in which the element of standardization plays a crucial role. They suggest that for multinational organisations, maintaining a definite brand image is essential, which is reflected in their uniform logo, slogan or name, and motivates them to standardize their products across cultural regions. It has also been stated by Tan and Sousa (2018) that business relatedness is an important aspect that affects the decisions of MNCs to sustain themselves in the global market. This relatedness can be achieved by adopting a marketing approach that is built on uniform distribution channels and products across markets.
Multinational organisations are also known for adopting marketing strategies that are specific to a particular region or locale and take account of cultural differences. As illustrated by Luo and Shenkar (2017), localization is a significant marketing approach that is adopted by MNCs, which allows them to adapt to a competitive marketplace by being more responsive to the local cultural needs of consumers. They suggest that this approach is also crucial for integrating a cost-effective marketing approach by employing an indigenous workforce and formulating a culturally specific language of communication. According to Hennart (2019), these firms are now increasingly engaged in cross-border transactions, which emphasize the role of technology adoption and digitized services in marketing.
2.6 Elements of Culture
The various elements of culture, which have a considerable influence on the marketing strategies of firms, include language systems, values, customs, religious beliefs and business norms. According to Payne et al. (2018), different elements of a workplace culture, which includes the values, vision, engagement and leadership support, have an impact on the internal and external communication strategies adopted by firms. These values would, for instance, determine the level of transparency and openness that multinational organisations would display while communicating their marketing strategies to consumers.
In the opinion of Gherasim and Gherasim (2018), the different cultural elements that influence international marketing include material culture and spiritual culture. Material culture includes the total material achievements, including crafts, weapons, clothing, dwellings and jewellery, which reflect on a society’s collective benefits and production skills. The spiritual culture includes aspects like symbols and language, which would impact the communication styles and language skills that these organisations would adopt. Steenkamp (2019) has also suggested that as against the arguments of the popularity of global consumer culture through increasing globalisation; a local consumer culture is also becoming increasingly important, which motivates organisations to adopt localized marketing strategies.
The elements discussed above are different elements of national and regional culture that determines the market strategy and orientation of multinational corporations. In the view of Paurova et al. (2019), a corporate culture within an organisation is an important determinant of the marketing strategies that it would adopt and includes elements like harmony and leadership skills. This implies that marketing in MNCS is affected by the internal as well as an external culture of these firms.
In the view of Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017), the level of acceptance of marketing and advertising through audio and visual mediums is dependent on the specific cultural characteristics of the consumers to whom they are being directed. According to Elsbach and Stigliani (2018), organisational culture influences the problem-solving activities adopted by a firm, which influences their marketing and commercialization of products and services. This implies that elements like creativity and innovation within a corporate culture are important determinants of the communication strategies of firms.
Other elements also exist which can be considered to bring about an analysis of the existing culture so that the global marketing strategy can have a perfect application in the market. In the words of Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) elements in the form of language, symbols, values and norms are some of the areas that are to be considered so that the cultural elements in the market can take place. As stated by Tan and Sousa (2018) it is necessary that an active account of the areas be undertaken so that the marketing probability along with that of the social securities can have a significant impact in bringing about cultural understanding of the factors associated with the market. In this regard, it can be stated that one of the areas that is considered in terms of the cultural aspects had been the ways with which commitment to the ethical form of work is undertaken to bring about marketing success. Thus, as pointed out by Steenkamp (2019) for this reason, the elements associated with the cultural aspects and benefits are regarded to have a significant impact in the overall commencement of the work as well as the attitude that takes place among the marketers. This is an important element of success associated with the cultural and marketing management implication.
2.7 Cultural Differences and Global Marketing Strategies
The marketing operations of multinationals involve a substantial amount of cross-cultural transactions and acquisitions, which make them susceptible to multiple cultural differences across organisational divisions. According to Kotler (2019), the global marketing approach adopted by many firms has become more responsive to the needs and values of consumers across the world. Consumers, in this sense, are more participative and empowered as their marketing choices are shown to have a considerable impact on firms and their branding methods.
This implies that cultural differences across their consumer bases have enabled MNCs to adopt global marketing strategies that are responsive and inclusive of these differences. These differences are also reflective of the managerial strategies that are adopted by these firms, which determine the level of communication that can be reached with consumers. These firms have their bases across different geographical regions and consist of employees that belong to different cultural backgrounds. This implies that a company culture that is adept and managing cultural differences is an important step forward in formulating effective global marketing strategies that would be beneficial for consumers (Groysberg et al., 2018).
Effective management of cultural differences would further be beneficial in gaining varied opinions and perspectives of employees from different cultural backgrounds, resulting in more inclusive and creative international marketing methods. According to Watson et al. (2018), cultural differences play a crucial role in influencing the international market entry strategies, which are adopted by firms, including their specific relational approaches, which impacts their business success. Consumer preferences and tastes have an influence on economic integration across borders and result in the adoption of relational, hybrid and digital global marketing models.
2.8 Impact of Culture on Marketing Strategies in the MNCs
As discussed in previous sections, the different elements of culture, including its symbols, values and language systems, have a critical impact on the marketing strategies that are adopted by different organisations. In the opinion of Song et al. (2018), the reactions of consumers to different marketing methods and product offerings of MNCs depend on their specific national cultures. It has been assessed that products that match the tastes and cultural preferences of consumers would have a higher level of acceptance across different consumer categories. This would, in turn, result in an increase in consumer loyalty for these products and create a suitable brand image for these multinational firms.
Another important aspect that can be regarded in this case from the point of view of the marketing is that cultural differences can have a significant impact in bringing about major development in the business. According to Groysberg et al.(2018), the fact that one of the important elements of the marketing is based on the language that is spoken among the different nations brings about a considerable understanding of the associates of the products. In the words of Elsbach and Stigliani (2018), every marketing element is stated to be considered based on the creativity displayed in reaching to the audience.
The overall impacts that can be associated in this manner include one of the important aspects for bringing about trust among the existing audience. This can be brought about severely of loyal customers and any organisation that is looking to expand in a market that does not speak English can use the knowledge to improve the level of sales. For this reason, as stated by Watson et al. (2018) language becomes one of the most important elements among the marketing strategies, which is necessary for bridging cultural indifference as well as maintaining the required applications in coping up with the challenges that exist in the market. In the words of Yun et al. (2020) such an impact is deemed to be of utmost importance in ensuring that every organisation remains aware of the marketing strategies associated with the business.
According to Yun et al. (2020), culture is an important determinant of innovation within an organisation and determines its capacity to manage its external and internal resources. This implies that organisations that support cultural differences can formulate greater innovation and creativity within their marketing strategies. In the view of Felipe et al. (2017), cultural values also have a considerable influence on the level of agility that is inbuilt within different firms. This implies that support for dynamic cultural differences results in the adoption of marketing practices that are flexible and inclusive of consumer preferences across global markets. In recent decades, diversity marketing has emerged as an important marketing method for firms, which is based on formulating advertisement strategies that look into the certain definite aspects that would appeal to consumers of a particular culture (Petrescu & Krishen, 2019).
Further, these strategies look at the cultural needs of subsections within national culture and the marketing strategies that would appeal to them. There has been, for instance, a considerable amount of attention paid to the cultural preferences of women by global fashion brands, which have multiple bases in different parts of the world. This implies that marketing strategies that are inclusive of cultural differences have a significant role in popularizing the brand name and image of multinational organisations.
2.9 Challenges of Marketing
The process of integrating cultural differences within the marketing strategies of firms also creates a number of challenges, which have been understood from different perspectives by scholars. According to Katsikeas et al. (2019), the international marketing methods used by these firms often integrate a specific tone and language that could be regarded as offensive by people of certain cultures. The messaging format and language used by these organisations can also not be properly understood by consumers belonging to different countries, resulting in a huge problem of miscommunication or misinterpretation of advertisement messaging.
Further, it has been opined by Leonidou and Hultman (2019) relationship marketing has emerged as a critical challenge for many of these firms which look towards formulating joint ventures and partnerships with businesses across cultural boundaries. This implies that effective management of cultural diversity is important for the collateral business ventures, as well as the consumer-centric marketing approaches adopted by MNCs.
As already stated, the language plays an important role in bringing about prolific venture in the business. According to Payne et al. (2018), it is also necessary that the organisations understand the local language before expansion so that more customers can be attracted. The limitation or challenge that the language brings about to the marketing perspective is that of the ability to gain the trust of the audience. The local companies are preferred more irrespective of the way; the foreign companies display the language. Hence, as stated by Paurova et al. (2019) this remains as one of the areas in the marketing departments that can have a negative impact in bringing about cultural integrity.
For this reason, possible recommendations in this aspect can be brought about in providing the companies with an associated tour of maintaining the marketing competence. As pointed out by Elsbach and Stigliani (2018) another challenge that can be brought about is that of the beliefs. The beliefs are aligned with the culture and hence any form of unethical approach taken by the marketers can be regarded to bring about challenging impact in maintaining the success. For this reason, this can be regarded as having a huge impact in bringing about marketing propositions.
2.10 Strategies Adopted By MNCs To Deal With Cultural Differences in Marketing
An effective strategy of dealing with cultural differences for MNCs is by adopting an internal managerial approach that supports and sustains cultural differences. According to Reddy et al. (2017), support for cultural diversity within an organisation is dependent on the ability to sustain a dynamic workforce that has distinct intellectual capabilities. They suggest that this aspect is crucial for organisations in reaching out to a larger base of consumers and influences employer branding. Authors like Ali and Konrad (2017) have stated that the presence of a workforce which is racially diverse allows firms to connect to a consumer base that is racially diverse. This would be effective in enhancing the level of engagement that firms would have with their consumers by being inclusive of their cultural demographics.
This further underlines the importance of diverse leadership and inclusive recruitment practices for fostering a diverse employee culture within firms. Several MNCs across the world have implemented customer relationship management strategies as an important factor for driving performance. These strategies, which include networking through social media, play an important role in enabling firms to connect better with consumers and understand their cultural preferences.
2.11 Literature Gap
The scholarly writings reviewed in this section have not addressed critical questions related to cultural differences, which includes the variations in cultural orientations of consumers within a specific geographic region. These writings have not integrated market research or knowledge of varied consumer choices to determine consumer approaches towards standardized and localized marketing strategies. Further, industry reports from different MNCs have not been evaluated to measure the success of distinct marketing strategies with respect to profits earned in business.
2.12 Summary
The literature review provides the necessary approach with which concepts and theories of the dissertation topic along with its variables can be understood. The overall assumptions of the topic along with that of the strategies that are to be understood by the MNCs are well highlighted in the literature review. The chapter helps in gaining clear idea of the areas that exist in bringing about the effectiveness of the cultural differences and at the same time help in the contribution of changes in the market. The next chapter provides an analysis of the data that is to be collected and the mode of analysis that are to take place.
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Introduction
The chapter is directed at identifying those methods that can help in bringing about successful completion of the research. The data that can be suitable for the completion of the research is to be identified and the mode of analysis that is to take place is to be taken into consideration. In this case, one of the important applications of the chapter is that it can help in bringing about an understanding of the ethical considerations that are required for bringing about the full collection of the data. The limitations that have been encountered by the research are also stated in the chapter.
3.2 Research Philosophy
The research philosophy provides the ways with which data about a phenomenon is to be gathered and analysed. The research philosophy is important in bringing about insights into problems that can be used for the development of hypothesis and quantitative research. According to Abutabenjeh and Jaradat (2018), the research philosophy consists of three types, which include positivism philosophy, interpretivism philosophy as well as the realism philosophy. The application of the interpretivism philosophy is undertaken in this dissertation mainly because it can help in bringing about understanding the subject that is being studied. The study is conducted based on the principles so that specific roles can be performed for ensuing and inciting the social world.
For this reason, the application is important as the cultural phenomenon associated with the marketing principles and the social cultural differences be taken into consideration. With the application of the interpretivism philosophy, new perspective on the topic can be found which is useful for bringing about reliability as well as the validity of the study. Thus, the application is important in bringing about understanding of the crucial subject matter and uses it for attaining the objectives set for the dissertation.
3.3 Research Approach
The research approach formulates the plan and procedure that exists in bringing about broad assumptions of the data collected and its methods. The application is based on the research problem that has been addressed in bringing together the existing hypothesis as well as that of the research objectives. One of the important applications of the research approach it helps the research align any information with the hypothesis developed for the research. The research approach consists of either the inductive or the deductive approach. The application of the deductive approach is considered in this case mainly because the research undertaken is based on the development of hypothesis due to the already existing theories.
As stated by Skarbek (2020) research strategy is to be conducted so that the hypothesis developed can be tested. In this way, deductive reasoning can be made so that the existing theories can be tested in a way that can help in the analysis of the topic. For this reason, the application of the deductive approach is considered as effective for this research as it can help in bringing about reasoning of the topic along with the generalisation of the important theories.
3.4 Research Design
The research design helps in deciding the framework that is to be adopted for maintaining the research methods and techniques. The application of the research design helps in the utilisation of methods, which are important and suitable for conducting the study in a successful manner. The research design comprises of three types that include the descriptive design, explanatory design and the exploratory design. For this dissertation, the application of the descriptive research is undertaken. The reason for this is that the topic can be systematically, effectively and accurately described.
In this way, the topic can have in-depth discussion, which can be considered to have flexibility in the study that has been conducted. At the same time, with the application of the descriptive design, more than one variable can investigated. This can make the study more flexible. Along with this as pointed out by Busetto, Wick and Gumbinger (2020), the descriptive design can also help in bringing about validity and reliability of the data that has been collected. For this reason, the use of the descriptive design in this case is justified in bringing about successful completion of the research. It can help in providing in-depth analysis of the topic as well as the concepts.
3.5 Data Collection Method
The data collection method brings about an analysis of the ways with which required information for the completion of the research can be gathered. According to Ruggiano and Perry (2019), the data collection method is usually of two types that include the primary data collection method and the secondary data collection method. In this case, the application of the primary data collection method is undertaken. The reason for this is that it can help the researcher direct knowledge of the existing work and bring about theories that can be aligned with the literature. Moreover, the researcher can also target those people that can provide authentic information for the dissertation to be successful. In this way, the researcher had selected the interview method.
The reason for this is that with an interview method, the research can set up open-ended questions, which is important for gaining valuable insights in the topic. The interview is conducted on 6 managers of different MNCs selected via random sampling method. This can help in understanding the scenario associated with the cultural differences of global strategy that are formulated across the MNCs. For this reason, the selection of this data collection method is justified.
3.6 Data Analysis Method
The data analysis method sets up the ways with which the collected data can be interpreted and presented so that it can justify the objectives and hypothesis that has been set up. The data analysis method consists of either the qualitative method, quantitative method or the mixed method. As stated by Guest, Namey and Chen (2020) although the use of quantitative method is used for, analysing the data collected from primary sources, in this case, the application of the qualitative method is made. The reason for this is that better understanding and insight of the topic can be made by this application.
Various perspectives on the subject can be taken into consideration, which can well be described to bring about a positive impact in meeting the objectives set for the research. For this reason, the application of the qualitative research approach is quite effective in this study. The data analysis method of the qualitative nature can help in describing the nature of the study as well as formulate steady approach for the overall application of the research.
3.7 Ethical Considerations
For the research to be completed in an ethical manner, it is necessary that an understanding of the rules and regulations associated with the research be undertaken. One of the ethical considerations that had been taken in this case is the fact that none of the respondents was force to participate in the research. The participants were provided with the free will to reject the questions at any time. Consent of all the 6 managers were taken in terms of interviewing as well as bringing about recording of the data collected. The data collected had not been manipulated in any way to suit the researcher.
The exact data that had been collected from the participants were considered and applied for bringing about meeting the objectives. Along with this, each of the data collected had been stored in safe places such as the cloud and portable devices that are accessible only to the researcher. After the completion of the research and results, the data collected are deleted so that it cannot be used for any other research that is intended to take place on the same topic.
3.8 Research Limitations
The research conducted had been undertaken successfully by aligning every method with the justified account of the method. However, there had been certain limitations that existed in bringing about successful collection of data and its application in the research. One of the major limitations that can be pointed out in this case is the fact that gaining the confidence of the participants had been difficult. The initial target participants had been difficult to gain as in most cases there had been negativity about the desire to participate. Some of the participants were reluctant to provide positive answers and hence the limitation of biasness existed. Collection of the secondary data had also been difficult mainly because the topic selected is unique. With these setbacks, the researcher also found it difficult to commence with the completion of the research within the time set. Hence, this is regarded as another research limitation associated with the research.
3.9 Summary
The chapter is important in helping to understand the data collection method that is to be used. In this way, one of the important applications that are to be made is that of the justification of the methods that have been used. For this reason, the chapter is important in bringing about the widespread understanding of the areas that can be utilised for the analysis as well as the collection of the data required for bringing about success. The next chapter provides an interpretation of the data that has been collected so that alignment with the collected literature review can be made.
CHAPTER 4: DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
4.1 Introduction
The chapter provides an overview of the interpretation of the data that has been collected. It is to be noted that the interview analysis is undertaken based on the responses provided by the managers. The importance of the chapter is that it allows the researcher with an opportunity to maintain a considerable impact in bringing about meeting the objectives in a stable manner. The chapter also allows direct quotations from the respondents to be used, which is aligned with the literature so that validity of the data collected is made. This is in accordance with the data management process that is undertaken by the respondents.
4.2 Interview Analysis
Question 1: How do you maintain the cultural impact on the company?
The cultural diversity has a lot of impact on the ways with which each company are to maintain its existence. In this regard, it can be stated that the overall understanding of the methods that are slated for the companies to succeed can help in the management of the MNCs in the market. The interview questions provide an idea of the ways with which such cultural impact on the companies can be maintained keeping in mind its advantages and disadvantages.
One of the interesting points that had been raised from the interview responses had been the fact that decisions that are made are related to the contribution that is made by the employees. In the words of the first manager, it has been stated that the decisions are taken based on the benefit that is provided for the organisation. The first manager had quoted that “Cultural impact is maintained by including decisions of every employee within an organisation for the benefit of growth”. As observed by Ottman (2017) this strongly suggests that the effectiveness of the cultural impact is strong and is regarded to have a significant factor for the employees in the organisations.
Similarly, the cultural barriers that exist are also encouraged to overcome mainly because it can help in bringing about perfect decisions for the employees. For this reason, according to Feng et al. (2019), the overall cultural barrier along with that of the organisational support are deemed to have a considerable impact on the MNCs. The response provided by the third manager has a significant contribution in bringing about an understanding of the possibilities of success that can be gained from the proper support of the entire cultural phenomenon.
The third manager has been quoted to say, “The impact is directed at having a considerable approach while maintaining the cultural phenomenon of business”. This provides evidence that the overall application associated with the cultural phenomenon can well be respected in bringing about the approach in business that in relation to the strategic business process. According to Guzman et al. (2018), it is also regarded to have an exquisite impact on the ways with which the difference in the cultural upbringing can help in gaining success in the international stage. For this reason, such an aspect is regarded to have a considerable impact in bringing about a phenomenon change in the organisational set-up.
The impact of the culture is strongly supported by the fourth manager mainly because the overall the cultural barriers tend to provide hindrance for the MNCs. In this way, in the words of Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) each of the MNCs can be assured that the undertaking of the cultural phenomenon associated with the barriers along with that of the responsibility of the managers are regarded to have similar impact in bringing about a considerable difference in the cultural benefit. As such the response provided by the fourth manager is, “Every individual belonging in different cultures are tended to overcome any cultural barrier and participate in the cultural practises”.
This also proves the fact that overcoming the cultural barriers is the main source of attraction that is to be imposed in the MNCs. As stated by Gherasim and Gherasim (2018) with this, the cultural differences and its impact cannot be deemed to have a special coordination while trying to maintain the effective phenomenon in the business market. This is in relation to the fact that each of the considerations that are undertaken by the companies is deemed to have different approach while trying to formulate a sensible marketing strategy for success.
Question 2: What type of cultural differences exists in the MNCs?
The interview tries to identify the differences that exist in the MNCs while trying to understand the level of success that are encountered with the different cultural phenomenon. According to Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017), it is to be considered that each of the cultural differences play a huge role in bringing about a considerable approach that can help the MNCs identify the areas in which progress is to be made. As stated by Cropanzano et al. (2017) this is in accordance with the level of satisfaction that are to be expected from each organisation and the intention that the MNCs have in bringing about cultural competence in the market.
The interview suggests that the cultural difference that exists is one way of predicting the overall success that is to be encountered in the organisations. In the words of Kotler (2019), the MNCs have people that belong to different cultures and hence can be considered to have a significant impact in realising the varied aspects in the world. It is also necessary that meeting the objectives of the company are done to maintain the organisational culture within the market. The response from the third manager provides an overview of the thoughts and process that exist while trying to understand the cultural differences in the MNCs. It is responded that, “The management is done on different cultured people with the same aim of meeting the objectives of the company”.
This is in relation to the fact that every culture is different and that the aim of the organisations is to ensure that the mission as well as the vision statement remains the same. In the words of Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) aligning the work with the goals is the common factor that is required to be maintained by the MNCs so that the level of success can be required to build about a considerable approach to the market. The response of the fifth manager in which the different countries and its impact on the organisations are highlighted also supports the level of differences that exists. The response provided includes the quote, “The cultural differences that exist belong to different areas of the country as well as the world. This is in relation to the varied aspects between the people”.
For this reason, it can be stated that every marketer is to understand the various methods that are needed for training the people in the different cultural areas. According to Feng et al. (2019), the fact that such diversity is present in the world can also be considered to play a major role in bringing about level of success with which each of the satisfaction level of success are amassed by the MNCs. In the words of Guzman et al. (2018), this can be considered as a relative measure for bringing about balance between the people of varied culture as well as that of the existing cultural market. For this reason, the response provided is crucial for attaining the level of success required for the organisations.
The response provided by the sixth manager also helps in the identification of the benefits that are brought about by the differences in the culture. It has been quoted by the manager that “The cultural differences helps in bringing about a type of urgent phenomenon for the managers to comprehend the business practises”. This is in addition to the fact that the overall cultural phenomenon along with that of the cultural aspects for the business practises is necessary to overcome the marketing challenges that are present in the MNCs.
Question 3: What challenges are faced while maintaining cultural differences in the MNCs?
With the existence of the cultural differences, the organisations gain benefit in terms of the globalisation of its business. However, as stated by Katsikeas et al. (2019) there are also certain challenges that exist in bringing about considerable approach that may hinder the overall progress. The cultural differences can hinder working together which in turn can be regarded as a process associated with the overall maintenance of the cultural areas within the organisation. As pointed out by Dadzie et al. (2017) this is in relation to the fact that each of the culturally diverse people can have a significant impact in the overall business set-up.
From the interview, it is clear that the differences play an important role in bringing about challenges for the organisations. Song et al. (2018) is of the opinion that one of the major points of challenge as stated by the managers includes the fact that language seem to be the problem between most of the people. Despite English being the communicative language, most of the people around the world prefer to speak in the native tongue. For this reason, MNCs need to impose the understanding of the commonality of the languages and ensure that the success is dependent on the language spoken by the employees.
The first manager is quoted as saying, “The cultural differences bring about challenges in the form of language and the alignment of the cultural phenomenon in the markets”. This implies that irrespective of the ways with which the cultural phenomenon is distributed among the organisations, it is necessary that an overall attitude towards the development of the phenomenon be brought about so that an overwhelming attitude is maintained by the organisations. In this way, one of the extensive applications of the language barrier is to be brought about so that the challenging impact can be faced with ease. In the words of Felipe et al. (2017) the cultural impact have a huge prophecy that is required to be fulfilled by the MNCs in terms of gaining the required actions for success.
The response provided by the third manager can be considered as interesting in every aspect; the reason for this is that the response tends to provide an identified aspect on bringing together the differences in the work culture. As respondent by the third manager, “The cultural differences tend to have a significant impact in bringing about challenges in the form of language as well as work culture”. This provides justification of the fact that it is necessary for each of the global management issues to be associated with the change in the times of the applications related to the cultural barrier of work. As stated by Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) it is necessary that such criteria be developed keeping in mind the different cultural approach that countries have in bringing about devotion for the organisations.
Another interesting point that is brought about by the fifth manager is the beliefs that people have in the organisations. In the response to the question, the fifth manager had responded that “The challenges that exist is aligned with the culture, beliefs as well as the ethical considerations that exist in the different cultures”. This clearly suggests that the MNCs need to be ethical correct and composed while trying to build a steady approach to the market. According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), it also brings about the fact that each of the marketing ideas is associated in maintaining the organised approach related to the beliefs of the people. For this reason, such a phenomenon is regarded as a way to ensure that the success in the organisational expansion remains.
Question 4: What is the role of cultural differences while formulating global marketing strategies?
The global marketing strategies play an important role in bringing about a considerable approach to business and the way the marketing phenomenon can assist an MNC to have a severe impact on the business profile. According to Luo and Shenkar (2017), this is in accordance to the fact that the business undertaken is to be associated with the formulation of the global marketing strategies that can help in bringing success while expansion of the market. In this way, the interview pays an important as well as understandable approach in bringing together the roles that are assigned to the culturally diverse group in maintaining the different marketing strategies within the organisations.
The interview provide a wide range of the view involved in bringing about culturally managed global strategies that can be associated with the marketing phenomenon. One of the responses from the managers is the fact that the marketing principles are engaged in bringing about a considerable positive outcome for the business. As stated by Hennart (2019) this is in relation to the fact that each of the global phenomenon can well be accounted for bringing about a cultural aspect associated with the global marketing phenomenon. In this way, the application is capable of maintaining the identified scenario wherein an aspect of marketing management along with the cultural change can be developed.
The response provided by the third manager highlight this point, stating that, “The global strategies are used to formulate the existing roles associated with engaging the marketing principles and change the phenomenon of cultural dimensions”. This is in clear relation to the fact that every marketing principle is to be associated for bringing about a cultural competence in the existing MNCs. Along with this, the application of the existing cultural phenomenon along with that of the cultural competence are to be regarded as ways to bring about differences in the cultural dimension within the organisations. For this reason, the interview provides a significant impact in maintaining the applied cultural phenomenon in the business organisations.
The response provided by the second manager is also insightful in bringing about an identification of the globalisation and its impact. It is stated by the manager “The cultural differences play a role in understanding the globalisation that exists in the business for maintaining the overall objective of the organisation”. This is in relation to the fact that every aspect of the global phenomenon is important for maintaining the cultural aptitude, which in turn is associated with the global rising of the administrative set-up of the organisations. For this reason, in the words of Felipe et al. (2017) the globalisation phenomenon brings about a compatible capability in maintaining the required scale associated with the existing global phenomenon in the market.
This is relation to the fact that globalisation is the current advantage that is provided in the world which is associated in bringing about a different perspective for the organisations. Every cultural competence along with that of the strategic management aspect are related to the important cultural phenomenon that are associated with the way cultural dominance is brought about in the organisations. In this way, the overall attitude that is in existence with the marketing phenomenon is regarded to have a positive impact in the application of the cultural competence of the markets. Thus, the interview response is quite responsive for bringing about application for global marketing phenomenon.
Question 5: What are the types of marketing strategies that are used in the MNCs?
The marketing strategies that are used in the MNCs are regarded to have an important application in the growth of the organisations. According to Elsbach and Stigliani (2018), each of the marketing strategies that are used is related to bring about a type of advocacy that deals with the overall understanding of the cultural heritage that exists in the organisations. In the words of Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) one of the important lessons that can be gained from this case is the fact that it is necessary to understand the cultural importance that is in accordance with the MNCs for bringing about growth in the overall domestic domain of the organisational set-up.
It is important to note that each of the managers in the interview had high regards in trying to maintain the superlatives associated with the MNCs. The fact that the sixth manager tried to promote the language and the beliefs are the major differences in the marketing setting brings about an additional support for the organisation. It has been stated by the sixth manager in the interview that “Marketing strategies are also in accordance with the cultural differences that exist within the organisations. The language and beliefs are the differences”. As stated by Tan and Sousa (2018) this is in accordance to the fact that every organisation phenomenon is related to the overwhelming aptitude that is associated with the cultural phenomenon. Keeping this in mind it can be considered to have a helpful account of the overall existing competence in the market.
It can be stated that one of the existing knowledge associated with the organisational success is that it can be related to the overwhelming prospective of identifying the cultural competence in the business market. The fourth manager has provided this thought as a form of assessment by in which it has been stated that the marketing principles along with that of the cultural differences are the major areas that are in accordance for the organisational success. In the response provided by the fourth manager, the cultural competence is related to the significant contribution in bringing about identified phenomenon associated with the marketing principles.
The response from the manager is that “The marketing strategies that are used for differentiating the cultural phenomenon are associated with the types of work that is undertaken in the marketing principles. This is in accordance to the cultural implications in the business”. This can be considered as a way to bring about a sense of cultural competence and at the same time can be associated in bringing about an overall account of the significant impact that exists in the MNCs. According to Steenkamp (2019), the elements that are associated with the cultural competence are related to have a competing factor that can well be regarded to have a significant impact in the overall justification of the cultural process.
In this regard, it can be stated that the response of the second manager is also enlightening mainly because the overall marketing factor can be associated in maintaining the cultural competence in the activities. This can bring about the fact that an overall analysis of the existing cultural phenomenon can well be brought about by identifying the business activities. The response provide of the manager is that “The marketing strategies used are in favour of bringing about cultural differences and as such can be associated in maintaining the cultural phenomenon of business activities”.
Question 6: What type of management is done to mitigate the challenges?
The cultural challenges brought about for the organisations have certain impacts that can be regarded as negative and can lead to problems in the ways with which the organisational setting is maintained. Keeping this in mind, the researcher had opted to identify those areas that could be used for mitigation purpose and with the help of the respondents, these areas had been highlighted. As understood by Yun et al. (2020) each of the MNC managers were inclined to the fact that the cultural diversity, although is very unique can provide huge differentiation in the market bringing about global challenge in terms of its maintenance.
The response provided by the third manager in this case can be analysed to understand the mitigation techniques better. It has been responded that “It is necessary that an identified account of the challenges be understood in accordance with the managerial perspectives associated with the organisations”. This is an indication that a planned action is a requirement mainly because it can help in the development of the organisational setting associated with the overall and overwhelming attitude of the organisational cultural success. In the words of Petrescu & Krishen (2019), the fact that this organisational success is related to the adversities in the business is considered as a way of maintaining the organisational set-up and brings about an effective coordination between the employees. This is necessary for the overall application of the activities involved with the organisational set-up.
At the same time, the response provided by the first manager point to exact problems that in existence for the MNCs. The manager has been quoted saying, “The management of the cultural phenomenon is done based on the cultural barriers that exist along with that of the organisational objectives”. This indicates that the overall success of the MNCs is related to the communication and understanding of the employees in bringing about a cultural competence in the market. According to Leonidou and Hultman (2019), this is also in relation to the fact that each of the employees has a tendency to undertake a proper application of the marketing strategies that provide a significant outcome in maintaining the success of the business. For this reason, such an objective is crucial for the identification of the challenges involved in the marketing aspects.
Another interesting point in this case can be brought about is the fact that not only is the cultural differences a challenging factor but also the methods of marketing that is involved. This is in relation to the fact that every market need to be understand based on every factor that can help in the growth as well as the overall attribute of the organisational culture. In the words of Katsikeas et al. (2019), such an application can well be directed at bringing about cultural application in the market and likewise change the necessary credentials associated with the marketing opportunities. Such a thought is displayed in the response provided by the sixth manager.
The quote provided from the sixth manager is thus, “The mitigation of culture is based on the marketing strategies in bringing about successful expansion in the target market”. This is an indication that the overall marketing prowess along with the cultural diversity can well be connected together. This can also help in bringing about an applied application of the methods used to communicate with the local people and help the MNCs gain the necessary success upon the expansion in the market. For this reason, this is regarded as a useful thought for aligning the marketing strategies along with that of the cultural competence.
4.3 Interview interpretation
The interviews have provided an overview of the thoughts and ideas that are to be presented for the completion of the dissertation. The data collected are genuine and help in the identification of those factors that can be related to the cultural phenomenon and importance of an organisation. Each of the managers related to the MNCs have a strong view of the organisational set-up and the ways with which each of the cultural phenomenon can bring about success. In this way, the interview provides an overview of the impact and the barriers that the cultural phenomenon tend to bring about for the MNCs.
As stated in the literature reviews, the cultural differences are regarded to have a significant impact in the business. In the words of Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), the choices made by the organisations are regarded to have a significant impact on the decision making process. As stated by Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017) it is also evidenced from the interview that the decision making process are related to the overall cultural impact and the way barriers of the culture had been restricted. In this way, formulation of the process associated with the cultural differences can well be considered as important in the business set-up.
Another important phenomenon that can be considered from the interview is the fact that with the presence of the cultural barriers it can be difficult for most of the employees to be involved in direct working of the cultural practises. As stated by Cropanzano et al. (2017) it can also bring about an identifying knowledge based on the phenomenon that exists in maintaining the cultural importance. For this reason, the overall cultural phenomenon along with that of the differences that exist tend to have a significant impact in identifying the positive impact that might be associated with the cultural importance. Thus, for this reason, it can be stated that the cultural phenomenon is related to the diversity of the organisational set up.
In this way, the overall differences that exist in the organisations are considered to have an interpretation of the existing process. In this way, as stated by Kotler (2019) one of the important discussions that can be regarded is the fact that cultural differences are in existence for overcoming the cultural process associated with the organisational set-up. For this reason, one of the important aspects that can be associated with the cultural phenomenon includes the planning to overcome the barriers. However, before that an analysis of the barriers that exist which may have a negative impact on the marketing phenomenon is considered.
One of the strong areas of the interview is that it helps in the identification of the cultural differences that exists in the MNCs and the way each of the differences are the results of the success that can be predicted for the organisations. As stated by Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017) it is necessary that one of the cultural impacts that can be considered in this case is the fact that despite the differences in the cultural areas every MNC need to ensure that the organisational objectives are met. In this way, as pointed out by Kotler (2019) the overall success that are in existence are directed for bringing about success via the differences in the culture and the way globalisation can bring about considerable approach for the MNCs in different markets.
The marketing strategies and the cultural differences are the varied results that allow an MNC to maintain a proper application in the business market from which different scales are to be analysed. According to Feng et al. (2019), the fact that each of these scales is associated with the marketing techniques is one way of introducing the overall marketing schemes that are in relation to the existing phenomenon in the business. In the words of Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017) every MNC need to analyse the need of the market by the varied cultural diversity that exists so that the strategies are formulated and directed at bringing about success within the organisational aspects.
Every MNC need to be associated with the idea that the overall success with which the organisational expansion and built is met need to be directed at the cultural competence. According to Guzman et al. (2018), with the barriers playing a key role as a hindrance process, the cultural phenomenon is to bring about an analysis of the key areas in which such aspects can be regarded to have a significant impact on the market. For this reason, in the words of Reddy et al. (2017) every associated application for the cultural diversity along with the consenting form of change that exists are to be brought about by the management of the cultural needs of the organisations. For this reason, it can be stated that the marketing principles and strategies are required to be fulfilled keeping in mind the cultural phenomenon.
The interview also suggests that it is important for the MNCs to respect the cultures that exist in bringing about change in the organisations. In the words of Katsikeas et al. (2019), the fact that ethical considerations are part of the organisational set up is one of the challenging aspects that are in existence for the companies. According to Cropanzano et al (2017), the application of Hofstede’s model in this case can well be considered keeping in mind that the cultural phenomenon along with that of the ethical issues are regarded to have a suitable approach in building a case for organisational management. The training of the employees about the needs is to be maintained in the current market.
In this way, one of the essential understandings that can be considered in this case is the fact that the overall markets along with the cultural benefits are to play an important role for success. However, as suggested from the interview as well as the literature, the language might play a huge role in diminishing the cultural importance, which in turn can bring about possible hindering scenario. As pointed out by Guzman et al. (2018) it is also to be notified that the cultural phenomenon is regarded to have an extensive benefit in maintaining the applications of the MNCs and its quest for expansion in the market.
The application of the Hofstede’s model is required to be kept in mind while trying to understand the cultural differences. The fact that the beliefs as well as the competence of the organisational aspect are some of the areas of benefit is regarded to have a significant impact in building a case of identified aspects. As stated by Katsikeas et al. (2019) it is also to be regarded as ways of bringing about an assessment towards the mentality of the people, which in turn can well be considered to have a seeming application in the market. Keeping this in mind the barriers of the cultural phenomenon along with that of the necessities that exist in the organisational set up are some of the ways with which every organisation can maintain success in business.
The fact that the beliefs and attitudes of the people are related to bring about a challenging aspect is required to be maintained keeping in mind the cultural differences that exist. In this way, it can be stated that the MNCs along with that of the applications of the cultural impact need to be associated with the type of work and difference that is expected within the organisations. According to Gherasim and Gherasim (2018), the success that exists in the organisational setting is directed at bringing about a considerable approach in the organisational setting for maintaining the necessary success level. As such, roles of the culturally diverse people are kept in mind for the success of the MNCs in the market.
One of the important understandings that can be developed in this case is the fact that the globalisation plays an important role in bringing about advocacy within the organisations. According to Payne et al. (2018), it can also be stated that the global affect the business along with that of the cultural competence together bring about a significant understanding of the overall cultural phenomenon. In the words of Gherasim and Gherasim (2018), this is in relation to the fact that every MNC need to be associated with the existing global competence in maintaining the employees that are culturally diverse and hence can be associated in bringing about a competing factor associated with the identification and success of the cultural importance.
The globalisation is also associated in bringing about a cultural knowledge of the prowess associated with the cultural application within the organisations. According to Steenkamp (2019), it is necessary to understand the effectiveness of the cultural competence as it can help in maintaining the growth of the MNCs. In this way, as stated by Paurova et al. (2019) every cultural factor that is associated in bringing about a competing factor within the market is regarded to have a significant impact in maintaining the cultural phenomenon associated with the organisational development. This is in relation to the effective applications as well as the cultural diversity that exists in the MNCs.
It is to be considered as one of the most anticipated form of cultural competence in which the overall existence of the cultural impact can bring about a sense of competitive advantage for the organisations. In the words of Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017) this is in accordance with the fact that one of the effective considerations in this case is due to the fact that the organisational structure along with the globalisation of the efforts are required to be kept under practise for considering the impact associated with the cultural competence.
The fact that the marketing strategies are associated with the use of the MNCs in bringing about a complete analysis of the market is required to be based on the ways with which the overall effectiveness of the cultural differences can be identified. As stated by Cañas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017) it is in relation to this that every manager that has been targeted provided an unaccountable understanding of the strategic aspect associated with the marketing principles. Hence, as stated by Elsbach and Stigliani (2018) for this reason, the overall accountable factor that is in existence for the cultural understanding and competence is required to be kept in mind so that the working hypothesis can be understood.
The cultural differences that are in existence are related to bring about a considerable account of the existing phenomenon of the market. According to Kotler (2019), the overall application of the cultural assessment along with that of the existing organisational positions are some of the ways with which marketing strategies can well be accounted for in the market. As stated by Groysberg et al. (2018) this is in regards to the fact that marketing competencies along with those cultural differences are soon to be regarded as ways of bringing about marketing expansion. For this reason, one of the most important applications in the business is related to the cultural impact along with those of the coordinated effort of managers.
Another important element that has been considered in this case is the fact that the marketing principles are related to the MNC success by identifying the efforts undertaken by the cultural implementation. According to Watson et al. (2018), this is in accordance with the fact that each of the cultural phenomenon that is related to the marketing strategies are required to bring about a wide aspect of understandable process that is associated with the languages and beliefs of the employees. For this reason, in the words of Song et al. (2018) it can safely be assumed that the overall assumption that is made in the organisational success along with that of the beliefs made be related to the overall cultural phenomenon associated with the marketing strategies.
In this way, one of the important phenomenon that is to be undertaken in this case is the fact that mitigation of the challenges are to be done so that the necessary applications along with the cultural differences are set to be maintained by the strategic cultural aspects. As stated by Groysberg et al (2018) this can well be regarded to have a considerable approach in maintaining the organisational objectives. For this reason, such a competence is necessary for the cultural dominance of the organisations. The mitigation strategies are to be associated with the overwhelming possibilities of success that can be gained from the organisational success.
The mitigation strategies tend to have a possible positive outcome only if it is maintained properly. From the literature review it is suggested that the overall maintenance associated with the cultural diversity along with the marketing management are some of the areas that are in relation to the company. In the words of Payne et al. (2018) it can well be deemed to have a considerable income in determining the ways with which each of the MNCs can bring about the required light for progressing with the methods in the market. Paurova et al. (2019) is of the opinion that the overall expansion technique is stated to be in the limelight and hence elements of the factors that bring about cultural hindrance is considered while engaging in the cultural expansion.
Another important issue that can be discussed in this case is the fact that each of the cultural mitigation factors can be associated with the existence of the marketing factors. According to Elsbach and Stigliani (2018), the fact that during expansion, every business is inclined to maintain the required level of marketing assessment are some of the areas that are looked after. From the interview, it is clearly suggested that each of the marketing phenomenon are associated with the challenges that exist in the language as well as the beliefs that the people have. This is in accordance to those areas that can be deemed as identified approach for bringing about massive change in the cultural importance.
Thus, for this reason, it can be stated that the overall activity associated with the cultural phenomenon as well as those of the existing marketing ventures are some of the areas in which every cultural differentiation can be put in practise. It can also be used to define the roles played by the MNCs to set up the marketing competence so that the overall phenomenon associated with the cultural competence is associated.
4.4 Summary
From the interpretation as well as the overall analysis of the interview, it can be stated that the cultural impact is quite high in the MNCs. Every manager tries to incorporate a culturally diverse group so that assistance with the globalisation can be undertaken. In this way, the overall management along with the effectiveness of the scenario that is related to the cultural impact are considered as important elements of success within the organisations. The chapter provides valid points that can be used for meeting change strategies related to cultural importance. The next chapter helps in meeting these changes and forms a stable conclusion for the dissertation.
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
5.1 Conclusion
The dissertation focuses on the role of cultural differences in influencing different marketing strategies in MNCs. The fact that it is necessary for the cultural diversity to have massive importance in the organisations is one of the important strategic importance in the world. It is important for every organisational set up to maintain a basic culturally diverse team so that the success in the markets can be maintained. The focus is on the MNCs and the way such cultural diversity can bring about a technically challenging aspect for every organisation to have a sensible approach to the marketing strategies keeping in mind the marketing objectives.
The literature review as well as the interview both suggests that it is necessary for the MNCs to identify the challenges that exist in the market and prevail in the management of the cultural competence. In this way, the overall objectivity of the marketing promotions along with that of the culturally diverse workforce are some of the areas that are to be regarded as a mode of consequence upbringing for the organisations. The fact that each of the factors associated with the cultural predicaments are considered as successful marketing phenomenon in the organisations.
For this reason, the dissertation tends to provide an analysis of the cultural importance that exists in the market, which in turn can be associated with the ways aligned with the principles of marketing. The challenges that are faced by the MNCs are regarded as being effective for bringing about a schedule associated with the cultural phenomenon. The dissertation tries to focus on the organisational set-up, which can well be considered to have a proper marketing strategic management. In this way, the dissertation helps in maintaining the overall predictability of the cultural importance.
In this way, the overall dissertation helps in bringing about a considerable attitude for the MNCs to have a significant impact in bringing about strategic management in the cultural importance of the organisations. The overall challenges that are associated with the MNCs are required to build about considerable importance for the marketing aspects. In this way, it is necessary that the marketing as well as the cultural diversity be related to one another in helping with the success of the organisations and its effectiveness in the business market. In this way, the business provides an overall application of the business market within the organisations.
5.2 Linking with objectives
Objective 1: To understand the importance of culture for MNCs
The objective tries to analyse the ways with which the culture followed in the MNCs are important for its success. The overall application of the success for the MNCs is related to the ways with which the importance of the cultural phenomenon is dedicated to have competence in the market. In this way, one of the applications of the cultural elements is the fact that it can bring about diversity keeping in mind the globalisation aspect. The literature review as well as the interview both provides evidences of the ways with which the cultural applications can bring about a foundation for the MNCs to expand its base and operate without having the fear of failure.
The marketing strategies associated with the MNCs are usually directed at bringing about an identified factor associated with the culturally developed employability. In this way, the overall applications of the market along with that of the cultural aspect associated with the MNCs are some of the areas that is required to be kept in mind. For this reason, it can be stated that the objective has been met and can be associated with the overall conclusion of the dissertation.
Objective 2: To understand what is meant by cultural differences at MNCs
The objective tries to understand the meaning of the cultural differences and the way each of the MNCs can be brought about for bringing the overall competence in the market by following the cultural differences that exists in the organisations. It is important to note that the cultural differences that are in existence also tend to have a significant impact in bringing about marketing strategies that can occur within the organisations. For this reason, it is safe to assume that the cultural differences in existence are associated with the foundations that are related to the marketing departments of the MNCs.
The interview suggests that each of the managers are well aware of the benefits and challenges that the cultural differences can bring about in the organisations and hence are related to have a lengthy application in bringing about considerable approach for the overall business marketing. The literature review also supports the fact that the businesses are well occupied in bringing about a considerable approach in maintaining a lengthy analysis of the cultural impact and the way globalisation can take place keeping in mind the overall objectivity of the cultural differences in the market. Thus, it can be said that the objective has been met.
Objective 3: To examine the cultural differences that occur in MNCs and how they are managed
The objective tries to identify the cultural differences that occur in the MNCs and the way it is managed to bring about effective marketing strategies. The fact that each of the marketing principles is associated in bringing about a considerable approach to the business is also to be kept in mind. It is for this reason, that the overall marketing strategies that are associated with the cultural differences be identified in a way that can help in bringing about cultural differences along with the application in the market.
In this way, the MNCs can be considered to have a significant impact in raising the standard associated with the globalisation of the market and can be associated in bringing about a considerable approach for the overall marketing phenomenon. The MNCs are to analyse the challenges that are faced so that it can maintain a considerable interest in bringing about a marketing formula for the overall application of the resources. This is regarded to have an important analysis of the structure associated with the cultural impediments of the MNCs. Thus, it can be stated that the objective has been met.
Objective 4: To evaluate the role of cultural difference as an important factor in the formulation of Global Marketing Strategies
The objective tries to understand the role that the cultural differences play and the factor of formulation that are brought about by the global marketing strategies. The fact that the globalisation is important in bringing about unity among the MNCs in various cultures is some of the areas that are explored. The interview provides an overall view of the effectiveness that is associated with the cultural differences in the globalised market and the way each market can be made to thrive under the cultural differences that exists. For this reason, the global marketing strategies are associated with the development of the cultural phenomenon that is available in the market. Thus, the overall marketing strategies along with the cultural differences are regarded to have a significant impact in bringing about a considerable approach towards the expansion of the MNCs. This is in relation to the fact that each of the MNCs can well be regarded to have a significant impact in analysing the market. For this reason, it can be stated that the objective has been met.
5.3 Recommendations
The literature review as well as the interview had provided with various mitigation strategies for the challenges that can exist in the application of the cultural diversity. The recommendations that can be provided via the understanding of the two concepts are that of identifying the market before making an investment. In this way, one of the important aspects that can be regarded for the organisations is the fact that it can be used for the beneficiary applications associated with the change in demand of the customers. The cultural competence along with that of the cultural innovativeness are some of the areas that can be regarded to have a significant attitude in bringing about the competency in the market.
For this reason, understanding the marketing phenomenon as well as bringing about extensive change to the cultural differences is a requirement to be fulfilled. MNCs need to be able to promote a product or service using the universal language as well as the global language so that a customer centric marketing approach can be maintained. In this way, one of the ways with which the cultural diversity can be brought about is the ways with which each marketing competency along with that of the employees working are aligned with the expanded market strategy. This can well be regarded as a mode of understanding the cultural competence that exists among the business.
At the same time, another point of understanding that can be maintained is the fact that each of the MNCs is to be aligned with the market by considering the opportunities. This is relation to the fact that while the language may be deemed as barriers, other aspects such as political as well as economic factors can be used to gain the support of the Government. In this way, the support of the Government can help in bringing about the required level of competence that can be deemed as interesting for bringing about a cultural formulation within the MNCs.
Keeping this in mind, it can be pointed out that the beliefs of the people are to be aligned with that of the organisation. The application of the dimensions of the Hofstede model is required to be associated with the cultural application of the business associates. In this way, the overcoming of the situation associated with the marketing syndromes can be explained in bringing about the required competency in the market. Such recommendations can well be deemed to have an important impact for the MNCs to succeed with the culturally diverse employees.
5.4 Future scope of the study
The current study focuses on the ways with which cultural differences can influence the different marketing strategies of the MNCs. For this, several interviews of different managers are undertaken, which can be regarded to have a prolific impact on the overall success of the researcher. In the future, the topic can be directed at bringing about a considerable approach in understanding the ways with which different cultural phenomenon can allow each of the managers to maintain a timely application of the cultural enhancement so that during the time of expansion this cultural knowledge can be used extensively. For this reason, in the future, the effectiveness of the cultural phenomenon associated with the expansion of the MNCs is considered.
Bibliography
Abutabenjeh, S. & Jaradat, R., (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36(3), 237-258.
Ali, M., &Konrad, A. M. (2017). Antecedents and consequences of diversity and equality management systems: The importance of gender diversity in the TMT and lower to middle management. European Management Journal, 35(4), 440-453.https://eprints.qut.edu.au/104824/3/104824.pdf
ama.org, (2020), Creating a Culture of Brand Love [Online],Retrieved from: https://www.ama.org/marketing-news/creating-a-culture-of-brand-love/ [Retrieved on 16th March]
Busetto, L., Wick, W. & Gumbinger, C., (2020). How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurological Research and practice, 2(1), 1-10.
Cañas-Bajo, J., &Silvennoinen, J. M. (2017). Cross-Cultural Factors in Experiencing Online Video Contents in Product Marketing. International Journal of Art, Culture and Design Technologies (IJACDT), 6(1), 40-56.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jose-Canas-Bajo/publication/317171061_Cross-Cultural_Factors_in_Experiencing_Online_Video_Contents_in_Product_Marketing/links/5fb159e792851cf24cd304a1/Cross-Cultural-Factors-in-Experiencing-Online-Video-Contents-in-Product-Marketing.pdf
Cropanzano, R., Anthony, E. L., Daniels, S. R., & Hall, A. V. (2017). Social exchange theory: A critical review with theoretical remedies. Academy of management annals, 11(1), 479-516.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Russell-
Cropanzano/publication/311427396_Social_Exchange_Theory_A_Critical_Review_with_Theoretical_Remedies/links/59e13579aca2724cbfdb73cb/Social-Exchange-Theory-A-Critical-Review-with-Theoretical-Remedies.pdf
Dadzie, K. Q., Amponsah, D. K., Dadzie, C. A., & Winston, E. M. (2017). How firms implement marketing strategies in emerging markets: An empirical assessment of the 4A marketing mix framework. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 25(3), 234-256.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kofi-
Dadzie/publication/318383155_How_Firms_Implement_Marketing_Strategies_in_Emerging_Markets_An_Empirical_Assessment_of_The_4A_Marketing_Mix_Framework/links/5a1cc1930f7e9b2a5316b850/How-Firms-Implement-Marketing-Strategies-in-Emerging-Markets-An-Empirical-Assessment-of-The-4A-Marketing-Mix-Framework.pdf
Elsbach, K. D., &Stigliani, I. (2018). Design thinking and organisational culture: A review and framework for future research. Journal of Management, 44(6), 2274-2306.https://escholarship.org/content/qt5qh451j5/qt5qh451j5.pdf
Felipe, C. M., Roldán, J. L., & Leal-Rodríguez, A. L. (2017). Impact of organisational culture values on organisational agility. Sustainability, 9(12), 2354.https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/9/12/2354/pdf
Feng, Y., & Mueller, B. (2019). The state of augmented reality advertising around the globe: A multi-cultural content analysis. Journal of Promotion Management, 25(4), 453-475. [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yang-Feng-36/publication/323946109_The_State_of_Augmented_Reality_Advertising_Around_The_Globe_A_Multi-Cultural_Content_Analysis/links/619fbf09f8565a76fdf47bab/The-State-of-Augmented-Reality-Advertising-Around-The-Globe-A-Multi-Cultural-Content-Analysis.pdf [Retrieved on 16th March]
fm-magazine.com, (2019), 5 factors that make international business complex [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.fm-magazine.com/news/2019/oct/international-business-complexity-201921740.htm [Retrieved on 16th March]
Gherasim, A., &Gherasim, D. (2018). Cultural Environment in International Marketing. Economy Transdisciplinarity Cognition, 21(1).https://www.ugb.ro/Downloads/Info%20Studenti/20172018/etc2018no1/18_Adrian_Gherasim,_Daniel_Gherasim.pdf
Groysberg, B., Lee, J., Price, J., & Cheng, J. (2018). The leader’s guide to corporate culture. Harvard business review, 96(1), 44-52.https://egn.com/dk/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2020/01/HBR-The-Leaders-guide-to-Corporate-Culture.pdf
Guest, G., Namey, E. & Chen, M., (2020). A simple method to assess and report thematic saturation in qualitative research. PloS one, 15(5), e0232076.
Guzman, E., Oliveira, L., Steiner, Y., Wagner, L. C., &Glinz, M. (2018, May). User feedback in the app store: a cross-cultural study. In 2018 IEEE/ACM 40th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Society (ICSE-SEIS) (pp. 13-22). [Online], Retrieved from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3183428.3183436 [Retrieved on 16th March]
Hennart, J. F. (2019). Digitalized service multinationals and international business theory. Journal of International Business Studies, 50(8), 1388-1400.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41267-019-00256-2
Katsikeas, C., Leonidou, L., &Zeriti, A. (2019). Revisiting international marketing strategy in a digital era: Opportunities, challenges, and research directions. International Marketing Review, 37(3).https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/147784/1/IMR-Leonidou.PDF
Kotler, P., Kartajaya, H., &Setiawan, I. (2019). Marketing 3.0: From products to customers to the human spirit. In Marketing wisdom (pp. 139-156). Springer, Singapore.https://www.academia.edu/download/59472062/Management_for_Professionals_Kartikeya_Kompella_-_Marketing_Wisdom-Springer_Singapore_201920190531-30412-1tnhibf.pdf#page=147
Leonidou, C. N., &Hultman, M. (2019). Global marketing in business-to-business contexts: Challenges, developments, and opportunities. Industrial Marketing Management, 78, 102-107.https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/130645/3/Leonidou%20and%20Hultman%202018%20-%20Special%20Issue%20IMM%20-%20Editorial%20Final.pdf
Luo, Y., &Shenkar, O. (2017). The multinational corporation as a multilingual community: Language and organisation in a global context. In Language in international business (pp. 59-92). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Oded-
Shenkar/publication/5223197_The_multinational_corporation_as_a_multilingual_community_Language_and_organisation_in_a_global_context/links/55a3fea708ae81aec912df8b/The-multinational-corporation-as-a-multilingual-community-Language-and-organisation-in-a-global-context.pdf
Ottman, J. A. (2017). The new rules of green marketing: Strategies, tools, and inspiration for sustainable branding. Abingdon: Routledge.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41267-019-00256-2
Paurova, V., Gajanova, L., &Kliestikova, J. (2019). THE ROLE OF CORPORATE CULTURE IN THE CONTEXT OF CORPORATE MARKETING STRATEGY. Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, 367-374.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Anita-Sindar/publication/337914952_DOES_DIGITAL_OPPORTUNITY_AFFECT_FINANCIAL_INCLUSION/links/5df2a6bd92851c836478cde7/DOES-DIGITAL-OPPORTUNITY-AFFECT-FINANCIAL-INCLUSION.pdf#page=374
Payne, J., Cluff, L., Lang, J., Matson-Koffman, D., & Morgan-Lopez, A. (2018). Elements of a workplace culture of health, perceived organisational support for health, and lifestyle risk. American Journal of Health Promotion, 32(7), 1555-1567.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6106858/
Petrescu, M., &Krishen, A. S. (2019). Strength in diversity: methods and analytics. Journal of Marketing Analytics, 7(4), 203-204.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41270-019-00064-5
Rao-Nicholson, R., & Khan, Z. (2017). Standardization versus adaptation of global marketing strategies in emerging market cross-border acquisitions. International Marketing Review.https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/101141/1/Global%20StrategiesEMFsIMR%20Post%20Peer%20Reviewversion.pdf
Reddy, C. N., Adhikari, J., &Chitranshi, J. (2017). Understanding and managing gender diversity challenges at leadership positions: A review. Journal of Strategic Human Resource Management, 6(2), 40.https://www.academia.edu/download/60685416/Understanding_and_Managing_Gender_Diversity_Challenges_at_Leadership_Positions20190923-48010-c56lj7.pdf
Ruggiano, N. & Perry, T.E., (2019). Conducting secondary analysis of qualitative data: Should we, can we, and how?. Qualitative Social Work, 18(1), 81-97.
Skarbek, D., (2020). Qualitative research methods for institutional analysis. Journal of Institutional Economics, 16(4), 409-422.
Song, R., Moon, S., Chen, H. A., & Houston, M. B. (2018). When marketing strategy meets culture: The role of culture in product evaluations. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46(3), 384-402.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Reo-
Song/publication/314347217_When_Marketing_Strategy_Meets_Culture_The_Role_of_Culture_in_Product_Evaluations/links/5be5b1f192851c6b27b29334/When-Marketing-Strategy-Meets-Culture-The-Role-of-Culture-in-Product-Evaluations.pdf
statista.com, (2021), Marketing services spending in the U.S. 2017-2021, by category [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/987009/marketing-spending-us-category/ [Retrieved on 16th March]
statista.com, (2021, Estimated number of companies worldwide from 2000 to 2020, by region [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1260719/global-companies-by-region/ [Retrieved on: 16th March, 2022]
Steenkamp, J. B. E. (2019). Global versus local consumer culture: Theory, measurement, and future research directions. Journal of International Marketing, 27(1), 1-19.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1069031X18811289
Tan, Q., & Sousa, C. M. (2018). Performance and business relatedness as drivers of exit decision: A study of MNCs from an emerging country. Global Strategy Journal, 8(4), 612-634.https://dro.dur.ac.uk/22100/1/22100.pdf
tradewindfinance.com, (2022), How Can Technology Impact International Trade Finance Companies? [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.tradewindfinance.com/news-resources/how-can-technology-impact-international-trade-finance-companies [Retrieved on 16th March]
Watson IV, G. F., Weaven, S., Perkins, H., Sardana, D., &Palmatier, R. W. (2018). International market entry strategies: Relational, digital, and hybrid approaches. Journal of International Marketing, 26(1), 30-60.https://asset-pdf.scinapse.io/prod/2774569787/2774569787.pdf
worldbank.org, (2018), Regional Trade Agreements [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/regional-integration/brief/regional-trade-agreements [Retrieved on 16th March]
Yun, J. J., Zhao, X., Jung, K., &Yigitcanlar, T. (2020). The culture for open innovation dynamics. Sustainability, 12(12), 5076.https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/12/5076/pdf
The Role of Cultural Differences in Influencing Different Marketing Strategies in MNCs
This is a vital part of your Programme and will contribute substantially to your personal development. Your MSc Dissertation is worth 40 Credits (two times as much as a taught Module). For academic dissertation help, you will be expected to demonstrate where appropriate your skills in providing:
(a) A synthesis of the literature.
(b) An analysis of quantitative and/or qualitative information.
(c) A summary of empirical results whether found by experimentation, observation, survey or interview.
(d) The implications of the findings.
Dissertation Objectives
There is a set of generic learning outcomes that are expected to be demonstrated. These are that students should, on completion of the Dissertation, have demonstrated:
(a) An ability to organise and plan their own research activity within the context of their original Dissertation specification and time limit.
(b) The production of a logical, coherent and well-structured analysis of both existing knowledge of their Dissertation field and their own contribution to that field.
(c) The applicability of concepts learned in the taught Programme to their specific field of applied research and the critical ability to evaluate the limitations of these as applied to that field.
(d) Where applicable, the relevance of their work to their organisation generally and to specific issues within the organisation with which they are involved.
These generic learning outcomes are reflected in the Assessment Criteria for all MSc Programmes in The Business School. This is detailed below:
The overall pass mark for the Dissertation is 50% (P1)
Nature of the Work
The main purpose of the Dissertation is to enable you to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the examiners that you can undertake an independent piece of research in a specialist area of your choice at Masters Level.
This will involve you in showing that you can design, implement and defend a research project in terms of the research problem identified; the research method(s) used and the conclusions arrived at.
Word Limit
The word limit, excluding abstract, acknowledgements, table of contents, reference list and appendices is set at 15,000 words (+/- 10%) for all MSc Dissertations in The Business School.
Submission of Dissertation
A number of ‘rules’ apply to the submission format for the MSc. Dissertation. These are presented in detail in a later Section of this guide. However it should be noted that these ‘rules’ are to be strictly adhered to in the interests of consistency, comparability, readability and quality of presentation.
Writing the Dissertation can seem like a major obstacle as it is likely to be the biggest single piece of academic work you will have undertaken. However, if you have a clear idea of the structure and nature of the research you have done or are doing then it makes it much easier to have a clear plan for the structure of the Dissertation.
Structure
The structure of the final Dissertation is to be presented as follows:
First inside page - Title, your name and year (2021, 2022, etc.)
(See Appendix III for an example of the FRONT page and the FIRST inside page)
• Declaration
• Abstract
• Acknowledgements
• Contents page
• List of Tables & Figures
• First Chapter - Introduction (research purpose and objectives)
• Chapters 2, 3, 4 etc.
• Final Chapter – Conclusions and Recommandations
• References
• Appendices
References
A single list in alphabetical order by author or organisation of all of the works cited in your text. There must be a 1-1 relationship here; if you have cited a source in your text then there must be an associated reference. Similarly if you have referenced a source then there must be an associated citation in your text. The Reference list must not be in bullet- or numbered-list format and (unlike the rest of the Dissertation) should be formatted at single-line spacing.
Appendices
Additional supporting material such as a copy of the questionnaire, interview schedule, letter of introduction, tables of statistics etc. This material is seen as essential to the Dissertation but would otherwise interrupt the flow of text and is therefore placed in an appendix.
Solution
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
People from many different cultural backgrounds collaborate to achieve a shared objective in this age of globalisation. In this manner, one of the essential elements to be established is how each group of individuals may be brought together to create the ultimate success story with which the organisations can prosper. This is one of the crucial aspects that are to be developed. The marketing tactics that multinational corporations implement (MNCs) ensure that different cultural groups cooperate by becoming dependent on one another and continue to implement successful strategies that may contribute to the advancement of the situation. The primary objective of this dissertation is to determine which marketing strategies are necessary for the success of multinational corporations (MNCs). This will be accomplished by determining which marketing strategies are essential for influencing cultural differences and identifying those strategies that are essential for bringing about the success of MNCs. In this chapter, the researcher is given the study's historical context and the research's purposes, objectives, and questions, which might assist the researcher in maintaining an appropriate research guide.
1.2 Background
The cultural habits of the global market have a significant impact on the marketing mix approach. Because of the technological revolution, contemporary businesses may more effectively extend their operations to worldwide markets. As a result, awareness of cultural variations in an international context is critical to a company's foreign business strategy. The economic parts of commercial organisations have developed more rapidly due to globalisation. Technological advancements have impacted international corporate organisations' financial models, and innovative elements may be seen in their present marketing methods (tradewindfinance.com, 2022). The ability of technology to analyse cultural characteristics before moving on with the creation of marketing plans has transformed the marketing strategies of worldwide organisations.
Several multinational organisations have emphasised their business techniques to serve many worldwide clients' needs better. On the other hand, regional economic accords have a significant influence on corporate strategy. For foreign organisations, adopting a marketing plan has become more difficult due to the proliferation of cultural regulations (worldbank.org, 2018). For an international organisation's marketing plan to be more effective, the management of international organisations must analyse the economic characteristics of a specific culture.
Economic agreements significantly influence the pricing strategy of services and goods. Thus it is important for management to analyse the economic agreement. Knowledge of local customs and traditions enhances the success of a company's an advertising and marketing campaigns. Marketing techniques of an organisation's management are heavily influenced by local language and culture (FM-magazine.com, 2019). Before launching a marketing plan, management must thoroughly understand the local language to boost the efficiency and efficacy of marketing services and goods in developing new markets.
McDonald's management has been ineffectual in its approach to overseas markets due to the detrimental influence on the company's financial health at a higher level. Failing in international markets has diminished the brand value of its goods, making it unable to improve its position even on its turf (Feng et al., 2019). The management of this company has decided to empower local officials to start creating efficient advertising campaigns in their respective regions, even though authorities can assess all cultural elements that have a greater chance of influencing the promotion of its goods and services.
Because of cultural variances and activities conducted by various cultural groupings, customers' requirements vary (ama.org, 2020). ThusCultural customs shape consumer behaviour. It is critical for businesses looking to expand into new areas to grasp their cultural identity.
1.3 Research Aim
This study aims to determine the influence that cultural variations have on multinational corporations' various marketing methods. Dissertation findings may be used to show how MNCs have been successful because of the contributions of people from different cultures.
1.4 Research Objectives
? To evaluate the significance of culture for MNCs
? To analysethe meaning of cultural differences at MNCs
? To evaluate the cultural differences in MNCs and how they manage those
? To identify the role of cultural difference in Global Marketing Strategies
1.5 Research Questions
? What is the significance of culture for MNCs?
? What is the meaning of cultural differences at MNCs?
? What are the cultural differences in MNCs and how they manage those?
? What is the role of cultural difference in Global Marketing Strategies?
1.6 Research Hypothesis
H1: Cultural variations have a significant impact on the myriad of marketing approaches used by multinational corporations (MNCs).
H0: There is no effect of cultural variations on the various marketing methods used by multinational corporations (MNCs).
1.7 Research Rationale
Figure 1: Differences in the cultural aspects in the different countries
(Source: Guzman et al., 2018)
Various nations have different cultural features. Community members of various ethnic backgrounds choose separate lives, and the things they use to sustain these lifestyles vary. Thus the management of an organisation needs to be aware of these differences to develop an efficient marketing plan. Organisational managers may use the distinctions in power politics to differentiate between the many marketing tactics that can help them better advertise their goods and services to their clients. For successful globalisation, organisation management must continue their active engagement by implementing a more effective marketing plan.
Figure 2: Marketing spending is increasing dramatically
(Source: statista.com, 2021)
Organisational management must spend more money to reach overseas markets and promote goods and services. The marketing system used by organisations, such as directories, telemarketing, public relations, and sales promotions, receives significant funding from upper management. Telemarketing accounted for 61.4 billion dollars in U.S. spending in the 2020 fiscal year. However, overall marketing expenditure has risen to 244.7 billion dollars (statista.com, 2021). To cover the costs of its increased promotional spending, the company has had to raise the prices of its goods and services.
This study will provide insight into how multinational corporations' marketing strategies interact with regional cultural norms. Organisational management may benefit from this study's focus on the impact of cultural characteristics on marketing strategy in foreign nations. It will help them better grasp the cultural influences that affect marketing strategy in foreign countries. This paper's main goal is to shed light on cultural behaviours that have a greater potential to affect MNCs' marketing strategies. For other organisations, this report might be a useful starting point in their efforts to keep up with the growing trend of globalisation. Using this specific study article, managers of organisations may better understand crucial facets of culture in other nations, increasing their company's chances of international growth success.
1.8 Research Significance
An important aspect of this study is that it examines social and cultural trends' role in shaping marketing strategy. There has never been a more critical time to examine how cultural differences affect a company's marketing strategy than now, thanks to the proliferation of multinational corporations and their capacity to expand across international marketplaces. Nearly 213 million organisations, according to the latest statistics, will be in existence throughout the globe in 2020. (statista.com, 2021). In other words, if this is the case, it suggests that these companies are driven to consider the cultural preferences of the customers they serve worldwide.
1.9 Structure of the Dissertation
The dissertation's five chapters are devoted to achieving the stated goals. The first chapter introduces the research, providing context for the rest of the book. It lays forth the goals, objectives, and issues that must be addressed to apply the ideas and concepts discussed in the dissertation effectively. In the second chapter, the factors linked with the issue are critically explained together with the current notions and theories. Various academic papers and arguments are discussed in this section. Data collection and analysis methods are discussed in the third chapter, devoted to accomplishing the study's goals. The fourth chapter aids in evaluating the data acquired and aligning it with the literature review evidence. The conclusion of the study is developed in the last chapter.
1.10 Summary
For this study, it is necessary to examine the influence of culture and comprehend cultural differences in marketing. This study's goals include a look at how various cultural facets affect multinational corporations' marketing strategies. Additionally, it has explored issues such as the problems of cultural differences in marketing and the techniques used by companies to overcome these obstacles.
CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
The literature review analyses key ideas and theories to conduct an in-depth study on the subject. An overarching strategy can only be devised if a thorough understanding of the current research literature is obtained first. In this scenario, one of the most significant aspects is that both the issue and the variables are argued and counterargued. Scholars' differing viewpoints are emphasised in this chapter to maintain an exhaustive investigation that can identify the issue.
2.2 Concept of cultural differences
When identifying the ideas and values necessary to make a system work, cultural variations influence how an integrated system of socially learned values is put together. It is possible to discern the general application of cultural differences amongst the many social groupings in the market. A key benefit of cultural differences is that they provide a broader range of options for employees inside an organisation, according to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017). Cultural variations are seen as having a long-term impact on an organisation's business strategy when it comes to making decisions and establishing plans. Because of this, the notion is critical in bringing together individuals from all backgrounds and fostering globalisation that allows each company and its workers to have an enormously beneficial influence on the current market, as stated by Gherasim&Gherasim (2018).
2.3 Theory
Social Exchange Theory (SET)
Marketing and cultural differences are examined using ideas such as the social exchange theory to understand the link between the two. This is a key paradigm for explaining cross-cultural communication. Social behaviour is generally seen as a direct outcome of the interchange and interaction between various groups. These social connections are evaluated for their efficacy by evaluating the benefits and drawbacks they provide.
Social interaction
It is claimed in the idea that a person would consider the costs and benefits of social contact while deciding whether or not to engage in it. As stated by Caas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017), the theory may be used to comprehend better and sustain the level of communication between individuals influenced by diverse cultural trends, which is one of its most important uses. For this reason, the behaviour of society's members may be predicted by looking at the dangers and advantages of various scenarios.
Communication
This suggests that individuals often anticipate other people's contact with them to result in reciprocal behaviour as part of the communication process. This shows that incentives and costs are essential in evaluating social relationships within groups (Cropanzano et al., 2017). Applying this theory to marketing is feasible by focusing on the potential benefits customers will get from implementing various marketing strategies. Because cultural differences affect the relative value consumers place on a marketing message, cultural differences are important criteria for understanding marketing tactics.
Culture
Without an examination of the culture, it is impossible to identify the areas that need development. To fully comprehend the behaviour of each group, the total application of growth methods must be linked to cultural phenomena, according to Kotler, Kartajaya, and Setiawan (2019). Feng et al. (2019) claim that applying the social exchange theory to organisations is an effective and efficient approach to analysing the market and applying the effects that may be present in today's market condition. This notion may be used by businesses looking to expand internationally.
2.4 Model for cultural differences
Cultural dimensions by Hofstede (the 4+1 model)
The Cultural Aspects model developed by Geert Hofstede is a helpful framework for comprehending the influence different cultures have on marketing. It elucidates four key aspects that are essential to knowing cultural values, and it does so in a comprehensive manner. These four factors—individualism against collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, power distance, and masculinity versus femininity—impact the myriad of cultures that can be found worldwide. According to Guzman et al. (2018), the many features listed above impact the norms, values, and beliefs that people in these cultures uphold to maintain a sense of equilibrium. Collectivistic groups, for instance, place a higher premium on qualities such as acceptance, belonging, and harmony than individual societies. According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), these values impact the different cultural preferences of MNCs. These preferences, in turn, impact the marketing strategies used by MNCs.
The methodology developed by Hofstede examines the domains in which every company has room for growth to attain greater success in the market. According to Reddy, Adhikari, and Chitranshi (2017), this is also important throughout the development process because it may help combat and mitigate the current external environment. This was significant since it was relevant throughout the growth process. It is essential to remember that in this particular setting, Hofstede's dimension may be a helpful instrument in assessing how successful a firm maybe even before it hits the market. This is something that you should keep in mind at all times. To be sure, attaining all of the model's dimensions may not be enough to guarantee success for any business. This is because Katsikeas et al. found that the model cannot be completely comprehended by altering only one culture-related factor at a time (2019). As a consequence, the app, although helpful for determining the extent to which a market has the potential to be successful, may also cause users to have concerns over the app itself.
2.5 Marketing techniques adopted by MNCs
When striving to compete in a global market that is so large and diverse, multinational corporations often use a wide range of marketing strategies. This is partly due to their customer base's geographical and cultural diversity. The 4Ps of the marketing mix, location, product, price, and promotion, all impact the marketing tactics companies use. Dadzie and his colleagues made this discovery (2017). As a direct result of this approach, many businesses use various marketing strategies, such as demand differentiation, segmentation, positioning, and targeting, to better target certain audiences. This methodology is appropriate for these kinds of businesses when it comes to researching their clientele's cultural and social backgrounds.
Another important marketing tactic used by MNCs is the uniformity of marketing. According to Song et al. (2018), the standardisation of products, strategies, and distribution channels, which may lead to global and domestic transactions, explains this phenomenon. This is one way a market initiative's effectiveness in bringing about a certain aspect of cultures may be evaluated. Felipe et al. (2017), point out that marketers and companies have the potential to benefit from the change in the market by catering to the requirements of the local community. It is essential to maintain a watchful eye on the industry to ensure that the marketing methods being used can successfully coordinate the interactions between staff and clients. The prominence of multinational firms may be connected to the significance of this aspect for marketing strategies.
Global enterprises need to maintain a consistent image of their brand. Doing so pushes them to standardise their products across different cultural zones and compels them to utilise the same logo, slogan, or name. According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017), standardisation has become an increasingly significant component of many organisations' attempts to advertise their products or services around the globe. According to Tan and Sousa, a multinational corporation's degree of business relatedness is a significant factor in determining whether or not it will continue operating in the global market (2018). Establishing a feeling of connectivity may be accomplished in several ways, one of which is by adopting a marketing strategy built on maintaining similar distribution techniques and commodities throughout markets.
In the same vein, it is normal practice for multinational firms to adopt marketing strategies that are distinctive to an area's culture and location. According to Luo and Shenkar (2017), localisation is an integrated marketing approach that multinational businesses (MNCs) employ to adapt to a competitive market by better matching the cultural expectations of their consumers. This allows MNCs to satisfy the needs of their customers better. They suggest that the use of a native labour force and the development of a language of communication that is culturally suitable are prerequisites to successfully incorporating a strategy for cost-effective marketing. According to Hennart (2019), international business transactions highlight the significance of digital services and the application of new technologies in marketing.
2.6 Elements of culture
Language systems, values, traditions, religious perspectives, and corporate standards are some of the cultural aspects that may significantly affect a company's approach to selling products and services. According to Payne et al. (2018), a company's workplace culture, which includes the company's values, vision, participation, and leadership support, directly influences the firm's internal and external communication strategy. This influence can be positive or negative, depending on the situation. These ideas, for instance, may affect the degree to which multinational corporations are transparent and open with their clientele.
According to Gherasim and Gherasim (2018), the multiple aspects of culture, including material and spiritual, drive worldwide marketing. Material culture comprises everything from clothing and homes to jewellery and weapons, which is the best indicator of a civilisation's overall strengths and manufacturing capabilities. Material culture can be found in almost every aspect of society. Consequently, the spiritual culture will affect the communication tactics and language talents used by these groups. In addition, Steenkamp (2019) asserts that local consumer culture is becoming more important, which pushes businesses to use localised marketing strategies. This is the case despite declarations that global consumer culture is growing more popular due to rising globalisation.
Multiple facets of national and regional culture impact multinational corporations' market strategies and directions. According to Paurova et al. (2019), the culture of a business is comprised of elements like harmony and the capacity to exercise leadership, which affects the marketing strategies the firm uses. This shows that marketing in multinational firms is impacted not just by the internal cultures of these organisations but also by the cultures of the outside environments in which they operate.
According to Caas-Bajo and Silvennoinen (2017), the level of contextualisation determining a consumer's propensity to accept marketing and promotional messages conveyed via audio and visual media is quite high. A firm's approach to problem-solving is impacted by its organisational culture, which in turn has repercussions on how the company markets and sells its products and services (Elsbach and Stigliani, 2018). This indicates that how a corporation communicates is impacted by elements such as the focus on creativity and innovation within the organisation's corporate culture.
To successfully implement the global marketing strategy on the market and carry out cultural research, other considerations may be necessary to take into account. According to Rao-Nicholson and Khan, some of the aspects of the market that need to be investigated for the presence of cultural components include linguistics, symbols, values, and customs (2017). According to Tan and Sousa (2018), an active account of the locations is essential so that marketing potential and social security may significantly impact cultural awareness of the market variables. This was shown to be the case for these factors to have an effect. To put it another way, one of the cultural aspects that have been taken into consideration to achieve commercial success is how an organisation's commitment to the moral behaviour of its employees in the workplace has been carried out. Because of this, Steenkamp (2019) contends that cultural traits and advantages significantly impact the beginning of the work as a whole and the mindset that prevails among marketers. This significant component has important repercussions for both the cultural and managerial aspects of marketing.
2.7 Cultural Differences and Global Marketing Strategies
Because multinational corporations engage in such a high volume of cross-cultural transactions and acquisitions, the marketing operations of these corporations are susceptible to the cultural differences that exist across their target markets. According to Kotler, Kartajaya, and Setiawan's research, many businesses have recently adopted a global marketing approach that is more attuned to the needs and priorities of consumers in various countries and cultures (2019). The marketing choices made by customers have been shown to have a considerable impact on the branding strategies used by businesses; as a result, customers now have more agency and are more actively engaged in the decision-making process.
This would imply that multinational corporations have been able to modify their global marketing strategies to capitalise on the cultural variety within their client bases. The management strategies these organisations put into practice also play a part in deciding how much interaction they have with their consumers. These corporations have locations worldwide and hire employees from a diverse spectrum of cultural, racial, and ethnic backgrounds. As a consequence of this, a company culture that is capable of dealing with cultural differences represents a huge step forward in the process of establishing effective international marketing strategies that are beneficial to consumers (Groysberg et al., 2018).
When they are handled well, employees who come from a variety of cultural backgrounds have a variety of perspectives and points of view, which may lead to marketing tactics that are more inventive and inclusive. According to Watson et al. (2018), cultural differences substantially affect the foreign market entry techniques that firms employ. These tactics include the specific relational approaches that affect an organisation's economic success. The preferences and tastes of consumers have an impact, in turn, on economic integration across borders, which influences the adoption of relational, hybrid, and global digital marketing approaches.
2.8 Impact of culture on marketing strategies in the MNCs
As discussed in earlier chapters, a wide variety of cultural aspects, including symbols, value systems, and language structures, significantly impact the marketing strategies used by a variety of firms. Song et al. (2018) state that the national cultures of the countries where multinational corporations operate affect the marketing strategies and product offerings that these corporations use. It is more probable that a diverse group of consumers would embrace a product if it is crafted considering its target audience's gastronomic and cultural preferences. Customers are more likely to remain loyal to these products, which will assist these multinational firms in developing a favourable perception of their brand.
When considering marketing strategies, it is essential to keep in mind that cultural differences have the potential to have a significant amount of effect on the development of significant business. According to Elsbach and Stigliani (2018), every part of marketing should be examined in light of the uniqueness employed to connect with the target audience. To put it another way, Groysberg et al. (2018) assert that one of the most important components of marketing a product is relying on a universal language that individuals from various nations can understand.
As a direct consequence, one of the essential components of establishing trust with the audience you already have is improved. This may have a catastrophic impact on long-term customers. Any business attempting to expand into a new region where English is not the predominant language may benefit from being aware of this knowledge. According to Watson et al. (2018), language is one of the most critical parts of a marketing strategy. This is because language is key for bridging the gap between cultural differences and maintaining the required applications while dealing with market difficulties. According to Yun and colleagues (2020) research, an impact of this kind is of the utmost relevance in ensuring that every organisation comprehends its marketing plan.
According to Yun et al. (2020), a company's culture is one of the most important factors in determining how well it can innovate and successfully manage its internal and external resources. According to this, companies that promote racial and cultural diversity may want to consider developing marketing strategies that are more original and inventive. According to Felipe et al. (2017), cultural values play a crucial part in influencing the degree of adaptability implemented in various businesses. This is what we mean when we say that marketing strategies are adaptable because supporting dynamic cultural variations leads to adaptable marketing strategies that consider consumer preferences across worldwide marketplaces. This is what we mean when we say that marketing techniques are flexible. Companies are increasingly resorting to diversity marketing, crafting advertising campaigns that emphasise the distinctive traits of various cultures to attract a larger spectrum of prospective clients. This marketing is becoming more popular (Petrescu&Krishen, 2019).
Multinational fashion companies in various countries have been paying particular attention to the cultural preferences of women in different parts of the world. Accordingly, the promotion of multinational firms' brand names and images is significantly aided by using multicultural marketing strategies. Consequently, these approaches focus more intently on the best ways to market one's wares to certain cultural subsets that exist inside the larger national culture.
2.9 Challenges of Marketing
According to a large number of academics' findings, there are various challenges associated with integrating cultural diversity into a company's marketing strategy. According to Katsikeas and colleagues' research, these firms' global marketing tactics often use a tone and terminology that some cultures can consider offensive (2019). Because these companies are based in various countries and employ languages and communication styles native to those countries, there is a significant problem with the advertising message being misunderstood or misinterpreted.
According to Leonidou and Hultman, relationship marketing has become a significant challenge for many of these companies as they pursue the development of cross-cultural joint ventures and partnerships. Many of these businesses are interested in forming joint ventures and partnerships with businesses located in other cultural regions (2019). As a result, effective management of multinational corporations' subsidiary firms' cultural diversity is essential to the success of customer-focused marketing strategies.
As was said before, the language used in a business endeavour greatly affects the level of success it has. According to Payne and colleagues, among other things, businesses must understand the native tongue before extending their operations to increase the number of customers they serve (2018). The failure of the language to win the audience's trust is a barrier or obstacle from the marketing standpoint. Local businesses are favoured above their foreign counterparts, irrespective of how the foreign companies display their language. According to Paurova et al. (2019), this continues to be one of the areas in marketing departments that has the potential to have a negative impact on the organisation's cultural authenticity.
Elsbach and Stigliani (2018) note that another issue that may arise is a person's conviction in their ability to solve the situation. This suggests that every unethical practice used by marketers has the potential to significantly impact their capacity to sustain their current level of accomplishment. Consequently, this may be seen as having a substantial impact on the formulation of marketing plans. As a result, one of the ideas that may be considered for this sector is the provision of businesses with an accompanying tour of maintaining their marketing ability.
2.10 Ways Developed By MNCs To Market Among Cultural Differences
It is possible to get around cultural differences by implementing an internal management strategy that recognises, appreciates, and preserves such distinctions in global organisations (MNCs). According to Reddy, Adhikari, and Chitranshi (2017), for a company to foster cultural diversity, it must have a dynamic workforce comprised of individuals with a wide variety of intellectual skills. They contend that this is essential to a company's ability to appeal to a more diverse group of customers and prospective employees. According to the research of writers such as Ali and Konrad (2017), it is much simpler for companies to appeal to a wide range of consumers if they have a diverse workforce. Considering the diverse cultural backgrounds of the people who use a company's goods or services would enable firms to forge stronger connections with the consumers who buy their goods and services.
To successfully create an inclusive working environment, it is essential to have a diverse board of directors and to hire practices that include people from various backgrounds. The management of a company's relationships with its customers, often known as customer relationship management (CRM), is an essential performance driver for many multinational companies (MNCs) worldwide. By using these tactics, which include networking on social media, businesses may improve their connections with consumers and get a deeper understanding of the cultural preferences of their clients.
2.11 Literature Gap
Academic papers evaluated in this area have not addressed crucial topics about cultural distinctions, such as the disparities in cultural orientations among consumers in a certain geographic location. These texts show no evidence of customer preferences for standardised and localised marketing methods. There has also been no evaluation of the profitability of different marketing tactics based on industry reports from various multinational corporations (MNCs).
2.12 Summary
A thorough literature study may understand the dissertation subject and its variables. According to the literature study, the MNCs need to understand the underlying concepts and tactics of the issue to succeed. Through this chapter, readers will better understand how cultural variations impact business performance while contributing to market shifts. The next chapter offers an overview of the data that will be gathered and the methods of analysis used.
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Introduction
This chapter will focus on determining the methodologies that may contribute to the effective conclusion of the research project. It is necessary to determine the data that will be appropriate for the conclusion of the study, and it is also necessary to take into account the method of analysis that will be used. One of the most significant applications of this chapter is that it may assist bring about a grasp of the ethical concerns that are essential for bringing about the complete collection of the data. This is one of the major applications of the chapter. The restrictions that have been imposed on the study as a result of its findings are also discussed in the chapter.
3.2 Research Philosophy
The research philosophy outlines the procedures for collecting and analysing data about a phenomenon and offers the rationale for doing so. The research philosophy needs to play a role in generating new insights into challenges, which can then be included in creating hypotheses and quantitative research. According to Abutabenjeh and Jaradat (2018), research philosophy has three distinct schools of thought. These schools of thought include realism philosophy, positivism philosophy, and interpretivism philosophy. In this dissertation, the philosophy of interpretivism is put to use primarily due to the fact that it has the potential to assist in the process of bringing about knowledge of the topic that is being researched. The research is carried out in accordance with the principles so that certain functions may be carried out for the purpose of ensuring and motivating the social world.
Justification
Interpretivism was the research philosophy that was used for this research. The school of thought known as interpretivism maintains that people are complex, multifaceted entities that are capable of seeing the same world in a variety of different ways (Snyder, 2019). For the purposes of this study, it was necessary to make use of primary data, which was gathered by conducting interviews with the respondents. These participants included the administrators of an elderly care facility. In addition to this, the study needed the collecting of secondary data from academic publications and other scholarly works, as well as an analysis of this data based on rational considerations.
In both instances, it was required to interpret the received data in a subjective way. The researcher used qualitative methodologies in order to perform the analysis of the data that was obtained (Newman and Gough, 2020). As a result, interpretivism became the research philosophy of choice. The primary objective of the study was to gain an in-depth understanding of the thoughts, emotions, experiences, and lives of people who were a part of the population that was the focus of the investigation, as well as to develop an empathic comprehension of the motivations that lie behind the actions and behaviours that they engage in on a daily basis (Rinjit, 2020).
3.3 Research approach
The research approach is the strategy and technique that exists in bringing about broad assumptions of the data gathered and its procedures. It is formed by the research approach. The application is based on the research issue that has been solved by bringing together the current hypothesis and the research objectives. This has been done in order to accomplish the research goals. One of the essential uses of the research technique is that it provides assistance to the research in aligning any material with the hypothesis produced for the study. Either the inductive or the deductive method may be used as the research strategy. In this particular scenario, the application of the deductive method is something that is being taken into consideration, mostly owing to the fact that the investigation being carried out is predicated on the formation of a hypothesis as a result of the theories that are already in place.
Justification
The deductive research technique was used for this research. When the researcher set out to do deductive research, he or she began with an existing hypothesis that was connected to the subject of the investigation (this theory was obtained as a result of previous research conducted through an inductive approach). On the basis of this previously established theory, the researcher proceeded to develop a hypothesis that may be shown to be incorrect (Dwigo and Dwigo-Barosz, 2018). Following that, the researcher went out to gather information pertinent to the subject of the investigation. The main and secondary methods of data collecting were used in conjunction with one another to compile these results. The researcher's hypothesised explanation was put to the test via the data collecting process, which was the primary objective.
Following the collection of data, a qualitative analysis was performed on it in order to acquire a deeper understanding of the subject of the study (Zangirolami-Raimundo et al. 2019). Following an examination of the data, the researcher was able to reach a conclusion on whether or not the hypothesis should be accepted. One of the benefits that accrued to the researcher as a result of their use of the deductive method was that the conclusion was guaranteed to be accurate. This was due to the fact that all of the premises that were initially taken into consideration were accurate in every circumstance, and the researcher's line of reasoning was logical and appropriate (Nayak and Singh, 2021).
3.4 Research design
The research design contributes to the process of determining the framework that will be used in order to keep the research methodologies and procedures intact. The use of the research design aids in the utilisation of techniques that are essential and appropriate for performing the study in an effective way. This is made possible via the application of the research design. The research design may be broken down into three distinct categories which are descriptive design, explanatory design, and exploratory design.
Justification
The researcher has used an explanatory research design. Explanatory research can manifest in many ways, such as experiments conducted in which the researcher assesses a hypothesis by attempting to manipulate variables or interviews and surveys that are used to gather insights from participants about their experiences (Snyder, 2019). Both of these types of studies are examples of explanatory research. Research with an explanatory focus attempts not to add to existing knowledge or to provide a solution to a particular issue; rather, its objective is to comprehend why something takes place. The researcher got a greater understanding of a topic via an explanation study, but this kind of research does not assist them in predicting what could occur in the future.
Research that seeks to explain anything sometimes goes by other titles, such as ex post facto research and causal research. The primary objective of research that seeks to explain anything is to improve participants' comprehension of the topic at hand. Either fundamental or applied research may accomplish this goal. When the researcher wishes to explain the link between two variables that the researcher cannot alter, then they will utilise this technique. In light of this fact, the researcher has little choice but to depend on secondary data in order to comprehend the variables (Snyder, 2019). When doing explanatory research, the data are often gathered prior to the start of the study, and they are also typically gathered by a person or organisation that is not the same as the one conducting the research. The practices of random sampling and random allocation are not used in explanatory research.
3.5 Data collection method
An investigation of the many approaches that may be used to amass the essential data for the successful conclusion of the study is produced by the data collecting technique. According to Ruggiano and Perry (2019), there are often two distinct kinds of data gathering methods, which are referred to as the main data collection technique and the secondary data collection method. In this instance, the principal data collection mechanism is put into action to acquire the necessary information. The rationale for this is that it may assist the researcher in directing their knowledge of the previous work and in developing hypotheses that can be linked with the previous study. In addition, the researcher may focus their attention on the individuals who are able to provide genuine information that will contribute to the achievement of the dissertation.
Justification
The secondary method was used by the researcher. The secondary data collection was carried out via the use of secondary research, in which the researcher looked through previously published material that was accessible in academic publications and papers (Rinjit, 2020). The gathering of data from secondary sources was carried out with the expectation that the information collected from secondary sources, which are known to be accurate and trustworthy, would be of assistance in completing the picture painted by the primary sources' contributions. This would help prove the validity of the results and conclusions drawn from the current study in a significant manner (Mishra and Alok, 2022). The PRISMA method was used.
Figure 2: PRISMA Table
(Source: Author)
A check of a database revealed that the researcher discovered 309 documents that were connected to the research topic. In addition to this, the researcher located ten more documents coming from various other sources. As a result, there were a total of 319 recordings chosen. All instances of duplicate records included within these records were eradicated. There were 200 records that were identical to one another. Because of this, the researcher was only able to access 119 entries. Following this, these 119 data were reviewed, and it was discovered that 100 of these records did not include the full-text articles but instead contained just the abstracts. After removing these 100 records, the study was reduced to include just 19 publications. From these 19 articles, we eliminated the ones that were published years before 2018. In the end, the researcher was only left with five publications to base the study on while collecting secondary data and carrying out the investigation.
3.6 Data Analysis Method
The process of analysing the data determines the means by which the gathered information may be evaluated and presented in such a manner that it can validate the aims and hypotheses that have been established. The qualitative method, the quantitative method or the hybrid technique will make up the data analysis method. In this research, the researcher has utilised the thematic analysis where the objectives have been broken down into themes and then analysis has been made on the gained literature.
3.7 Ethical Considerations
In order to do research in an ethical way, one must first acquire a grasp of the laws and regulations that are related to the study. This must be done in order to finish the research. When doing the secondary research, it was imperative that all of the information gathered come from trustworthy sources. The authors of each of the sources that were used to obtain information were appropriately credited in this work. Additionally, it was assured that the study article that was published was the researcher's own original work, which was free of any instances of plagiarism (Newman and Gough, 2020). The findings from the primary study were mostly utilised, together with the information gathered from secondary sources, to either validate those findings or to highlight any discrepancies that were found between the two sets of findings. As a result, the data gathered from secondary sources were used only for the goal of providing inspiration, and there was absolutely no kind of plagiarism involved (Rinjit, 2020).
3.8 Reliability
The dependability of the findings was taken into consideration throughout the course of the research's execution. The term "research reliability" refers to the degree to which the procedures that were followed in the course of the study were able to provide the same findings each and every time (Andrade, 2018). It is possible to say that the research methods are trustworthy and are not influenced or affected by external factors because they are consistent and can produce the same results when employed multiple times. This is because the research methods used in the present study produced the same results when they were employed multiple times (Phillips et al. 2021). One of the ways that the dependability of the study techniques was assured was by continually applying the same procedures to various groups of individuals over the course of a certain amount of time. This was done over a period of time. According to Sürücü and MASLAKI (2020), this method of determining dependability is known as the test-retest evaluation.
3.9 Validity
When people speak of the validity of research, we are referring to the amount to which the research methodologies are able to measure what it is that they are intended to measure. To put it another way, it is an evaluation of how accurately the study procedures and tools assess the appropriate things (Unsworth et al. 2021). Internal validity and external validity are the two categories that may be used to classify different kinds of research validity. The term "internal validity" refers to the degree to which the conclusions of the study are congruent with the actual conditions that exist in the real world (Andrade, 2018). On the other hand, the term "external validity" refers to the degree to which the findings of the study are relevant to a variety of settings or are capable of being duplicated in those settings (Phillips et al. 2021).
3.10 Research limitations
The study that had been done had been carried out effectively since every approach had been aligned with the description of how the method was justified. Despite this, there were a few obstacles that needed to be overcome before the study could successfully gather data and use it in its findings. Collecting the secondary data was also a challenge for us, particularly due to the fact that we chose a novel subject to investigate. Because of these obstacles, the researcher had a tough time getting started on the task of completing the investigation within the allotted amount of time. As a consequence, this is considered to be another weakness of the research related to the study.
3.11 Gantt Chart
3.12 Summary
This chapter is essential in assisting with the comprehension of the data gathering technique that is going to be used. In this manner, one of the significant applications that are to be made is the justification of the procedures that have been carried out. This is one of the key applications that are to be made. As a result of this, it is essential that the chapter contributes to the development of a broad comprehension of the domains that may be used for the analysis as well as the collecting of the data that is necessary for the achievement of success. In the next chapter, an interpretation of the data that has been gathered will be presented in order to facilitate alignment with the literature review that has been gathered.
CHAPTER 4: DATA ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
4.1 Thematic Analysis
4.2 Discussion
4.2.1 Significance of culture for MNCs
People's reactions to business and how they feel about being on time are examples of how people's attitudes regarding time might be described. Communication, the speed with which they responded to deadlines, and the length of time they waited around for appointments were all issues (Gabel-Shemueli et al. 2019). For example, Americans have a reputation for being prompt, and the expression "time is money" well encapsulates their mentality in this regard throughout the course of time. People who live in other nations, on the other hand, could have a more relaxed attitude about time.
Analogically, Multinational corporations that have operations in a number of countries should take into account the diverse cultural attitudes towards time. People have varying attitudes about their jobs and their free time for a variety of reasons. People in certain nations put in far more hours of labour than is required to fulfil their most fundamental needs to do with living (Duan et al. 2020). This mindset is illustrative of their perspectives on money and material advantages. The presence of cultural differences in people's overall attitudes about their jobs is connected to the fact that people's drive to accomplish their goals. Multinational corporations should be prepared for various attitudes about change transition between many distinct nations.
They need to take into account a number of significant aspects of cultural norms, such as what characteristics of a culture are resistant to change, the ways in which the process of change unfolds in various foreign nations, the ways in which the areas of resistance that each of them faces are unique, as is the amount of time required to accomplish the same change (Swoboda & Batton, 2019). The weight that a nation places on a certain line of work is a crucial factor in determining both the quantity and the quality of individuals who are interested in entering that profession. Multinational corporations will have available to them individuals holding jobs that, in certain nations, are regarded as among the most honourable professions greater number of local experts and professionals.
The impact of a country's culture on the daily operations of a multinational corporation is both substantial and pervasive. Companies that operate on a global scale are simultaneously influenced by more than one culture. This means their subsidiaries are based in the travel to many places, and as a result, they experience many diverse national cultures (Yoo & Lee, 2019). Because of this, one particular global corporation creates its corporate culture by taking into account the various cultural norms that prevail in the countries in which it does business. As a result, it is of the utmost importance for multinational corporations to adjust their methods of manufacturing, marketing, and sales activities that are determined by the culture of the nation in question.
Many difficulties are brought about for us as a result of the wide variety of languages spoken in different nations outside the United States international corporations. In spite of the fact that there is a growing trend toward embracing English as the worldwide business language, businesses are conscious that it also incites opposition from the natives in many of the nations in which they operate (Masovic, 2018). The nonverbal aspects of language add another layer of difficulty to the already challenging task of business communication. Nonverbal Communication presents challenges for global corporations as a result of the many interpretations accorded to its constituent parts throughout the world.
Nonvocal components of speech, such as eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, and so on, and vocal components of speech, such as words timbre, loudness, and speaking pace, among other aspects. When looking at things from the point of view of a global corporation, it is very important to have a solid understanding of the local language (Gabel-Shemueli et al. 2019). The lack of familiarity with the local language has a negative impact on the performance of the company's overseas subsidiaries' management of their company. Appointing expatriates to key executive positions is one strategy for minimising the impact of language barriers. Nationals who have a strong command of the parent company's language and are qualified for employment in the local subsidiary business culture.
The most typical issue is that a significant section of the parent company's workforce has either restricted or nonexistent possessing knowledge of the local language, which helps to cut down the amount of time spent on parent-subsidiary communication (Duan et al. 2020). Staff members of the subsidiary who are fluent in the language of the parent company or translators. As a consequence of this, the amount of information that the workforce of the parent firm gets and processes has been greatly reduced. This issue increases to a large degree if those working in the area are fluent in more than one language.
The existence of more than one of anything. The variety of people who live in a nation may often be gleaned from its linguistic landscape. There are various nations in Europe, such as German, which employs a high number of migrant workers, which increases the likelihood of encountering linguistic challenges due to the country's linguistic diversity (Swoboda & Batton, 2019). For example, a significant number of businesses in Germany make use of guest workers hailing from Spain and Turkey. Consequently, German, Turkish, and Spanish are the languages spoken during regular meetings with the workforce.
4.2.2 Meaning of Cultural Differences in MNCs
Multinational organisations are the outcome of economic structures that adapt to the global economy. In addition to this, the cost of labour is significantly reduced, and the quality of services and products that are produced is superior. Multinational corporations are structures that are multicultural, which on the other hand, necessitates a distinct management philosophy due to the difficulties that might and often do come from cultural differences (Vaara et al. 2021). Keeping this in mind, being multicultural involves having a good attitude and being open to the beneficial impacts of interacting with people of various cultures, which results in the development of major new ways of interacting with one another.
The most significant component of being multicultural is having a favourable impression of the cultural variation that may bring good revenue to the company. This can be accomplished by exposing oneself to as many other cultures as possible (Cheng et al. 2022). Multinational corporations are present in practically every industry, and because of this, they demand management and personnel that come from a variety of cultural backgrounds organisations (Abugre & Debrah, 2019). Because they employ individuals who come from a variety of cultural backgrounds and religious perspectives, these firms need not just to manage production in the conventional sense, but they also need to really manage the disparities amongst their employees.
However, investment partnerships with other nations enable multinational corporations to function either independently or in cooperation with foreign countries. This, in turn, unavoidably brings about the manifestation of the cultural differences that exist between the countries. The actions of multinational corporations are distinct from those of local corporations due to the fact that multinational corporations employ workers and managers from a diverse range of countries, each of which comes from a unique cultural background (Karjalainen, 2020). As a result of globalisation, a significant number of corporations now have commercial interests in more than one nation. Both outsourcing and offshoring are now standard business practices, and as a result, managers are required to establish processes and procedures that may be suitably used in a variety of locations.
In any case, effectively transplanting management approaches utilised in one nation to another country poses obstacles due to variations in the business processes, communication styles, and cultural values that are prevalent in the two countries. Cletus et al. (2018) highlight the need to understand the cultural environment in which management activity is evaluated as either successful or inefficient. Cletus et al. (2018)present a set of intercultural competencies that are applicable to all managers functioning in a global setting. Companies that operate on a global scale are required to recognise and accept the fact that their managers must at all times take into consideration the impact of cultural variations on the techniques they use.
In a multinational company where cultural differences are not taken seriously or managed effectively, this can result in a toxic organisational climate and culture. On the other hand, in multinational companies where cultural differences are recognised as important and managed effectively, this can result in a culture that values synergy (Vaara et al. 2021). To put it another way, cultural synergy refers to the process of bringing together all of a group's distinctive characteristics with the intention of producing an efficient system.
In order to arrange the impacts of all of these cultural differences to generate synergy, it is vital to first develop cultural synergy. This will allow you to create synergy by combining the effects of different cultures. Knowledge of a culture entails not only comprehension and awareness of the cultural makeup of each person but also an appreciation of the cultural makeup of a certain group (Cheng et al. 2022). In addition to this, it is a very significant component of interaction across different cultures and helps individuals to function well in environments characterised by several cultures. Intercultural competence is primarily concerned with the ability to negotiate cultural differences by means of successful communication, effective awareness, and interaction.
The capacity to negotiate cultural views, meanings, attitudes, and values in order to have successful communication behaviours is what we mean when we talk about intercultural competence. This skill may belong to either a person or a community. Additionally, it facilitates efficient functioning despite cultural differences, which is when people comprehend their numerous identities in a multicultural setting (Abugre & Debrah, 2019). This is made possible by cultural competency. Persons who are able to communicate in an intercultural way are able to manage their interactions with people who reflect divergent or distinct emotional, cognitive, and behavioural orientations.
4.2.3 Cultural differences in MNCs and how they manage
Multinational corporations have the additional responsibility of striking a balance between respecting all of the world's cultures and ensuring that their staff in every office are working together toward a single goal (Rodríguez-Rivero et al. 2022). Developing a sense of community throughout all of the offices is one strategy for accomplishing this goal. A daily email or a blog that is company-wide might be used to highlight achievements and deliver news from all of the offices. Tools for online cooperation or groups on social media sites may help bring personnel of different cultural backgrounds to a single goal.
To be agile enough to compete across cultural boundaries, small multinational enterprises with headquarters in the United States need to alter the culture of their own organisation. Taking up a culture of constant learning is one approach (Noyan, 2018). The training might consist of lectures on the cultural differences across nations, as well as incentives to encourage staff to go to the countries in which the company has operations. The use of a multinational staff at the headquarters helps everyone become more aware of the existence of cultural differences.
Consumers' views and behaviours are significantly impacted by culture to a large degree. When a company expands into a new market, the business models that it uses should be modified so that they take into consideration the norms, customs, and preferences of the new market. For example, modifications need to be made to the product and service offerings, as well as to the pricing methods and marketing approaches (Hart et al. 2019). If the local culture does not drive the notions of business, then there is a larger risk of failure for international companies. If your business attempts to break into a new market and is unsuccessful, the associated costs might be quite high. It takes international merchants, on average, seven years of operating at a loss before they either give up or sell their company to a competitor operating in the local market.
When doing business on a global scale, using the philosophy that "one size fits all" is an ineffective strategy. It is impossible to achieve success on the world stage without adopting a global mindset. The interface that occurs between "globalisation" and "localization" is referred to as "glocalization," and the word was coined to characterise this interaction. Globalization, on the other hand, puts a focus on standardising international practises, products, and services, whereas localization places an emphasis on adjusting processes and item offerings to fulfil the individual requirements of local industries (Gutiérrez et al. 2021). Localization, on the other hand, comprises procedures and product offerings that are adjusted to satisfy the individual needs of local markets. The term "glocalization" refers to a hybrid approach that brings together the ideas of standardisation and adaptability. The term "glocalization" refers to the process of combining aspects of a local culture with aspects of a global culture, such as ideas, products, or procedures. The concept of glocalization is based on the recognition that the potential for economic synergy is hindered by deeply ingrained cultural institutions that are difficult to change.
There is a chance that cultural divides inside a country are just as substantial as those that exist between countries. There is substantial geographical heterogeneity within developing markets, both in terms of the tastes of consumers and the circumstances of the market. On the other hand, distinctions seen inside a nation are typically ignored (Lim, 2020). According to the findings of four-fifths of the world's largest multinational corporations, decisions about their offshore operations are made at the country level rather than the city level. There are many different elements that might lead to the development of a subculture; location and ethnic origin are only two of them. Consider, for example, the different consumer profiles that men and women in the United States have in relation to one another in terms of the products and services they purchase.
Even though women are responsible for 88% of all retail sales, marketing activities often neglect the ways wherein male and female consumers behave and consider differently. This is despite the fact that women are responsible for 88% of all retail transactions. In addition, the buying behaviours and preferences of female customers vary depending on factors such as generation, ethnicity, and professional sector (Rodrguez-Rivero et al. 2022). Companies run the risk of alienating a sizeable percentage of their clientele if they fail to recognise the cultural diversity that exists within the marketplaces in which they operate. According to the findings of certain studies on mergers and acquisitions, the social integration process is far more difficult in domestic settings than in international ones. This is due to the widespread misconception that cultural barriers are of little significance within the context of a country, which in turn serves to amplify the impact of such barriers.
4.2.4 Role of cultural differences in Global Marketing Strategies
When one is engaged in the business of selling goods or services across international boundaries, one must pay primary attention to the cultural differences that are present in marketing. This is due to the fact that the cultural atmosphere in each nation is quite different from that of the others. This suggests that in order to exhibit an awareness of the culture of a given state, multinational firms first need to display an understanding of the culture of the state in which they want to market their products (Paul, 2019). Before a corporation begins on a push to compete on a global scale, careful consideration need to be paid to the major cultural characteristics that are outlined in the following sentence. Before beginning to promote their products and services in a foreign country, companies need to be aware of the substantial cultural differences that exist in the industry of marketing. The language barrier is one of the major of these differences.
In the past, translation projects have been marred by catastrophic errors, which have had far-reaching repercussions (Fan et al. 2018). One of the most memorable and embarrassing mistakes that occurred in international marketing occurred when General Motors was marketing its cars under the brand name "Nova," which, when translated into the local languages of South America, meant it wouldn't go (Fan et al. 2018). This was one of the most memorable and embarrassing mistakes that occurred in international marketing. It should come as no surprise that these errors do not assist the corporation in selling its goods. Therefore, in order to prevent the risk of their company failing, organisations need to pay attention to language and translations. Pricing tactics may seem to be economic considerations; nevertheless, they really reflect significant cultural variations that are relevant to marketing (Yousaf & Xiucheng, 2018).
Age and other demographic factors have a big role in the cultural distinctions that exist inside marketing, just as they do within domestic marketing. For instance, in underdeveloped nations, the percentage of older individuals who can read and write, particularly those over the age of 60, is quite low (Paley, 2021). As a result, you could make the decision to steer your marketing message in a direction that is not directly targeting this demographic group, particularly when you are selling digital gadgets. In addition, before you can adjust your marketing messaging, you need to have a solid understanding of the demographic groupings that predominate in the nation in question (De Mooij, 2021). Instead of appealing and communicating to the minority, this will assist your nation appeal and communicating to the majority.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
One of the most significant changes in the business world over the last several decades has been the proliferation of multinational corporations. It is common knowledge that these companies are enormous, with both the people and sufficient financial resources to compete with the Gross National Products of some of the less developed nations with a sophisticated economies. Rao-Nicholson and Khan (2017)found that transnational corporations in the consumer products industry businesses in every sector do exist that concentrate a disproportionate amount of their resources on marketing and other more persuading marketing techniques than non-international businesses.
In most cases, the marketing of consumer products is the primary focus of the businesses that are physically present in any given location. Consumers and governments, in equal measure, are accountable for the product regardless of the circumstances, with reference to the firm being connected with the brand and everything connected to or relating to it. It is believed that a global company is culturally tied if it focuses on the needs of its customers (Caas-Bajo and Silvennoinen, 2017). This is true to a large measure due to the fact that customers of such things are members of certain cultural groups and tendencies regardless of the phases of life in which they find themselves. This elucidates why in recent years, marketers have begun to pay more attention to the role that cultural factors play in their actions.
Although the satisfaction of groups of people is the driving force behind the development of any civilisation, they indicate a very varied and broad range of expectations that society has of its individual members. They are intended to fulfil not just bodily needs but also those of esteem and camaraderie needs. It seems to reason, given the diversity of requirements and possibilities for marketing (Cropanzano et al., 2017). Researchers in marketing agree that having a good grasp of the culture of a population is essential for both academics and working professionals. They must have an understanding of culture since it is the source of everything acceptable target goals that are particular for any universal human demand.
According to the companies' reports, cultural differences have a wide range of effects on marketing methods that are used by multinational corporations, which require the utilisation of various strategies in accordance with certain circumstances and impacts (Feng et al. 2019). The companies also claimed that marketing tactics were used in order to purposefully beat the competition in order to get greater market shares and increased sales, as well as to withstand the test of time regarding the ever-shifting patterns and how they impacted the demand and the supply.
Some of the many approaches involved the utilisation of high-quality items, regular advertising in regional media outlets, the development of optimal price structures, incentive sales promotions, and the development of brand-new products. In the end, every company implemented some effective countermeasures to offset the cultural effects that were impacting its operations. Companies that do business in two or more countries simultaneously and derive at least part of their earnings from those operations are considered multinational corporations operations overseas, as well as ownership of certain assets located in other nations (Guzman et al. 2018).
These are considered to be supranational economic and technological entities that were formed out of the free movement of capital, products, and services in tandem with the advancements in those areas in terms of means of communication and transportation infrastructure (Rao-Nicholson and Khan, 2017). These are also businesses that call for management in addition to the management of producing sources in the conventional sense, but also, owing to the employment of individuals from a variety of cultural backgrounds and beliefs, as well as the navigating of these distinctions.
Companies are able to, because of the common investment relationships they have with several nations, work both alone and in collaboration with other nations, making the management of cultural differences more complicated and inevitable (Song et al. 2018). The type of ownership has a different role in the operations of global corporations compared to that of local businesses regarding the ethnicities of those in managerial positions.
In addition to having employees that come from a variety of cultural backgrounds, the multicultural workforce profile at international companies necessitates the harmonisation of the expectations of these workers and the company as a whole criterion set by the firm, which inevitably results in the need to handle cultural variances (Felipe et al. 2017). The difference may be thought of as any other attribute that a person employs in order to differentiate themselves from other people. People may be distinguished from one another based on a number of factors, including their race, culture, gender, age, sexual orientation physical adequacies'. Some definitions of difference take into account additional factors, such as a person's ethnicity, nationality, or social status, religion, modes of education and communication, location of birth, and occupational choice are some examples.
The management of cultural diversity requires an understanding that each culture's ideas, attitudes, behaviours, and modes of expression are unique. Understanding how to navigate these disparities would be essential management ability for CEOs working at international companies. One of the most pressing concerns facing managers in the management of workers from multinational corporations that are now present in practically all areas of the economy is consequently referred to as globalisation.
5.2 Linking with Objectives
Objective 1: to evaluate the significance of culture for MNCs
This objective of the researcher has been linked with the second chapter of the research, which is the literature review. The globalisation of today's economic systems has given rise to a new kind of business organisation: the multinational corporation adjusting to the conditions of the global economy. Multinational corporations, in order to maintain their position as market leaders in the world economy, prefer to create goods and services in other nations rather than exporting their products to such countries, rather than doing the opposite. This is the foundation for it the reality of transnational corporations.
Objective 2: to analyse the meaning of cultural differences in MNCs
This objective of the researcher has been linked with the fourth chapter of the research, which is data analysis. The concept of cultural difference refers to a framework that occurs when individuals belonging to several group identities coexist inside the same social structure (Tereza and Fleury, 1999). The first step in managing cultural differences is to develop an atmosphere that is accommodating to personnel from a variety of backgrounds to make the most of their capabilities while also directing and managing these disparities in a way that is consistent with the organisation's aims. In other words, it refers to the practice of guiding and controlling the attitudes and behaviours of workers from a variety of different organisations' cultures that are congruent with the objectives of the organisation.
Objective 3: To evaluate the cultural differences in MNCs and how they manage those
This objective of the researcher has been linked with the second chapter of the research, which is the literature review. Multinational corporations are distinct from other types of businesses due to the fact that they are present in practically all economic activity areas in the sense that they need the management of workers from a variety of cultural backgrounds. The responsibility for personnel, including managers, specialists, and employees, who are accountable for the administration of a multinational corporation's offshore assets to several nations on the one hand, with various cultural, legal, and political systems; and on the other, with their ties with the personnel working in the host nation on the other, making it vital for these organisations to handle the cultural disparities that exist among its members (Dereli, 2005).
Objective 4: to identify the role of cultural differences in Global Marketing Strategies
This objective of the researcher has been linked with the fourth chapter of the research, which is data analysis. It refers to the practice of capitalising on cultural differences in order to gain competitive advantage rather than destroying them via organisational processes. They should be supporting them through the management and organisational settings. This encompasses all of the organisational and management tasks that are associated with having a feeling of leadership in a global setting. The construction of multicultural teams, as well as a multicultural structure that is reflective of all of these teams, should be accomplished.
5.3 Limitations of the study
There are various issues that were faced by the researcher while doing this research. Firstly, the researcher had to face issues in gathering data for the research. Since most secondary sources had to be paid for access, it became an issue for them. Being a student, it was not possible to pay for the data. The researcher also had time issues since he was given a specific period within which the dissertation had to be completed. The researcher had to maintain the authenticity of the research. The researcher had to ensure that the data were safe so that they were not revealed before publication.
5.4 Future scope of the study
This research can be used by other researchers in the future. The data that had been analysed in the data analysis chapter can be used by other researchers so that they can use it as a secondary source. This will help them in doing their research effectively based on the same topic. This research can also be used by different MNCs as well as SMEs so that they can opt for an effective marketing strategy so that customers from different cultures can be attracted and retained within the organisation. Through this, the sales of the company would increase, along with gaining loyal and satisfied customers.
5.5 Recommendations
? When selling products or services in international markets, it is essential to take into account significant cultural variations, including religious views. They have an impact on how people in a specific culture think about a variety of goods and services. It is necessary for organisations to get an understanding of the influence of religion and the part it plays in society (Luo and Shenkar, 2017). For example, in Muslim nations, promoting secular women’s clothing can be prohibited since the religion in these countries mandates women to wear in a modest fashion, which is heavily controlled. In addition, some marketing campaigns have been at odds with religious organisations since it was believed that the messages were insulting to a certain faith. This has led to a conflict between the two. Before beginning to sell their wares on a global scale, businesses must first acquire an understanding of religion, which is a highly important but often overlooked facet of global business.
? Eating habits are additional crucial cultural distinctions in marketing that international organisations need to grasp. Before promoting its menu, a firm that sells food should make it a priority to have an understanding of the eating customs of the area in which it operates (Hennart, 2019). In India, for instance, McDonald's and other fast-food chains were forced to switch from selling meat goods to selling veggie products because of local regulations. In a similar vein, these businesses have begun to progressively cater to the preferences of people from other countries, such as rice meals for the Asian market.
? Companies are already aware, as a marketer, that the personalities and cultures of people in a given nation or area combine to form the purchasing habits of those individuals in that nation or region. They need to find out if people in a certain nation make individualistic or communal purchasing choices before they can promote their items there (Payne et al. 2018). They will be able to use this information to build a marketing plan that draws in the whole society or a strategy that appeals to certain personalities. They are also expected to have a solid understanding of the psychological and cultural forces that play a role in consumers' purchasing choices.
? Not only are there distinctions in terms of ethnic and national identities, but there are also variances in terms of values, heritage, and cultural standards amongst the various socioeconomic and generational groups (Gherasim and Gherasim, 2018). This is an example of cultural diversity. In order to account for variances in the provision of values depending on the services and goods, which might be lost in translation, marketers need to modify their message.
? Companies in this day and age are truly investigating the cultural differences and taking serious consideration of these diversities in order to target the demographic and geographic groups that are different. The actual essence of comprehending the groups is having solid information about them and continuing to build on that knowledge (Steenkamp, 2019). As a result, it assists in the development of marketing plans and ensures their smooth execution inside businesses, resulting in skyrocketing profits and widespread approval. In order to sell their wares outside of conventions, the organisations need to make demographic and cultural assumptions about the customers they are targeting.
? Distinctions in ideas and cultures have an effect on consumers all over the world; as a result, marketers need to comprehend these differences in order to formulate more effective strategies (Paurova et al. 2019). Understanding culture requires having a solid grasp of a variety of topics, one of which is familiarity with the target demographic of cultural productions. When developing marketing campaigns, a concentration and emphasis on the particulars of the process are equally vital; as a result, this aspect is given consideration for improved management.
? In addition to that, it consists of branding, slogans, and labelling that are tailored to the requirements of certain audiences. In addition, the perspective of the consumer is also an essential component that plays a significant role in the organisation and places emphasis on the subtle shifts brought about by the diversity of its demographics (Caas-Bajo and Silvennoinen, 2017). Communication is yet another essential aspect that has to be taken into consideration so that businesses may provide better services to their clients.
? Customers' tastes and requirements may be comprehended when there is clear communication between the parties. It contributes to the process of culturally bridging the gap between different communities and organisations. It also helps serve certain demographic persons' throughout the nations and it helps provide consumers with goods and services that are tailored to their needs in accordance with their preferences. (Elsbach and Stigliani, 2018) When marketers comprehend and have an understanding of a wide variety of cultures, it is much simpler for them to design and sketch out tactics in accordance with the requirements.
? The marketing tactics of the company are determined by the values of the society, and the people are required to exercise a great deal of consideration while making judgments of this kind. When developing marketing strategies, it is important to tailor advertising to a wide variety of demographic groups in order to accurately represent cultural distinctions in the target audience (Tan and Sousa, 2018). When formulating strategies to meet the specific requirements of individuals, marketers need to have a solid comprehension of the cultural distinctions that exist, in addition to having individualistic thoughts and perspectives. Branding, advertising, and campaigning need to be done in a way that is congruent with the local culture in order to achieve greater market penetration.
Bibliography
Abugre, J. B., & Debrah, Y. A. (2019). Assessing the impact of cross-cultural communication competence on expatriate business operations in multinational corporations of a Sub-Saharan African context. International Journal of Cross-Cultural Management, 19(1), 85-104. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1470595819839739
Abutabenjeh, S. & Jaradat, R., (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36(3), 237-258.
Ali, M., &Konrad, A. M. (2017). Antecedents and consequences of diversity and equality management systems: The importance of gender diversity in the TMT and lower to middle management. European Management Journal, 35(4), 440-453.https://eprints.qut.edu.au/104824/3/104824.pdf
Ama.org, (2020), Creating a Culture of Brand Love [Online],Retrieved from: https://www.ama.org/marketing-news/creating-a-culture-of-brand-love/ [Retrieved on 16th March]
Andrade, C., 2018. Internal, external, and ecological validity in research design, conduct, and evaluation. Indian journal of psychological medicine, 40(5), pp.498-499. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_334_18
Busetto, L., Wick, W. & Gumbinger, C., (2020). How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurological Research and practice, 2(1), 1-10.
Cañas-Bajo, J., &Silvennoinen, J. M. (2017). Cross-Cultural Factors in Experiencing Online Video Contents in Product Marketing. International Journal of Art, Culture and Design Technologies (IJACDT), 6(1), 40-56.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jose-Canas-Bajo/publication/317171061_Cross-Cultural_Factors_in_Experiencing_Online_Video_Contents_in_Product_Marketing/links/5fb159e792851cf24cd304a1/Cross-Cultural-Factors-in-Experiencing-Online-Video-Contents-in-Product-Marketing.pdf
Cheng, H., Agbanyo, G. K., Zhu, T., & Pan, H. (2022). Internationalisation of multinational companies and cognitive differences across cultures: a neuroeconomic perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8928576/
Cletus, H. E., Mahmood, N. A., Umar, A., & Ibrahim, A. D. (2018). Prospects and challenges of workplace diversity in modern day organisations: A critical review. HOLISTIC–Journal of Business and Public Administration, 9(2), 35-52. https://sciendo.com/downloadpdf/journals/hjbpa/9/2/article-p35 .pdf
Cropanzano, R., Anthony, E. L., Daniels, S. R., & Hall, A. V. (2017). Social exchange theory: A critical review with theoretical remedies. Academy of management annals, 11(1), 479-516.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Russell-Cropanzano/publication/311427396_Social_Exchange_Theory_A_Critical_Review_with_Theoretical_Remedies/links/59e13579aca2724cbfdb73cb/Social-Exchange-Theory-A-Critical-Review-with-Theoretical-Remedies.pdf
Dadzie, K. Q., Amponsah, D. K., Dadzie, C. A., & Winston, E. M. (2017). How firms implement marketing strategies in emerging markets: An empirical assessment of the 4A marketing mix framework. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 25(3), 234-256.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kofi-Dadzie/publication/318383155_How_Firms_Implement_Marketing_Strategies_in_Emerging_Markets_An_Empirical_Assessment_of_The_4A_Marketing_Mix_Framework/links/5a1cc1930f7e9b2a5316b850/How-Firms-Implement-Marketing-Strategies-in-Emerging-Markets-An-Empirical-Assessment-of-The-4A-Marketing-Mix-Framework.pdf
De Mooij, M. (2021). Global marketing and advertising: Understanding cultural paradoxes. Sage. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=lyIxEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT16&dq=cultural+differences+in+Global+Marketing+Strategies&ots=CntK6Nuqpe&sig=BYNGY3GKO22teChVnBjn0dcZkNQ
Duan, Y., Huang, L., Cheng, H., Yang, L., & Ren, T. (2020). The moderating effect of cultural distance on the cross-border knowledge management and innovation quality of multinational corporations. Journal of Knowledge Management, 25(1), 85-116. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JKM-11-2019-0656/full/html
Elsbach, K. D., &Stigliani, I. (2018). Design thinking and organisational culture: A review and framework for future research. Journal of Management, 44(6), 2274-2306.https://escholarship.org/content/qt5qh451j5/qt5qh451j5.pdf
Fan, A., Shen, H., Wu, L., Mattila, A. S., & Bilgihan, A. (2018). Whom do we trust? Cultural differences in consumer responses to online recommendations. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJCHM-01-2017-0050/full/html
Felipe, C. M., Roldán, J. L., & Leal-Rodríguez, A. L. (2017). Impact of organisational culture values on organisational agility. Sustainability, 9(12), 2354.https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/9/12/2354/pdf
Feng, Y., & Mueller, B. (2019). The state of augmented reality advertising around the globe: A multicultural content analysis. Journal of Promotion Management, 25(4), 453-475. [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yang-Feng-36/publication/323946109_The_State_of_Augmented_Reality_Advertising_Around_The_Globe_A_Multi-Cultural_Content_Analysis/links/619fbf09f8565a76fdf47bab/The-State-of-Augmented-Reality-Advertising-Around-The-Globe-A-Multi-Cultural-Content-Analysis.pdf [Retrieved on 16th March]
FM-magazine.com, (2019), 5 factors that make international business complex [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.fm-magazine.com/news/2019/oct/international-business-complexity-201921740.htm [Retrieved on 16th March]
Gabel-Shemueli, R., Westman, M., Chen, S., & Bahamonde, D. (2019). Does cultural intelligence increase work engagement? The role of idiocentrism-allocentrism and organisational culture in MNCs. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management, 26(1), 46-66. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CCSM-10-2017-0126/full/html
Gherasim, A., &Gherasim, D. (2018). Cultural Environment in International Marketing. Economy Transdisciplinarity Cognition, 21(1).https://www.ugb.ro/Downloads/Info%20Studenti/20172018/etc2018no1/18_Adrian_Gherasim,_Daniel_Gherasim.pdf
Groysberg, B., Lee, J., Price, J., & Cheng, J. (2018). The leader’s guide to corporate culture. Harvard business review, 96(1), 44-52.https://egn.com/dk/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2020/01/HBR-The-Leaders-guide-to-Corporate-Culture.pdf
Guest, G., Namey, E. & Chen, M., (2020). A simple method to assess and report thematic saturation in qualitative research. PloS one, 15(5), e0232076.
Gutiérrez, G., Barbarin, O., Klicperová-Baker, M., Padakannaya, P., Thompson, A., Crowe, S., & Khoury, B. (2021). A global perspective on psychologists' and their organisation's response to a world crisis. Revista Interamericana de Psicología/Interamerican Journal of Psychology, 55(2), e1713-e1713. https://journal.sipsych.org/index.php/IJP/article/view/1713
Guzman, E., Oliveira, L., Steiner, Y., Wagner, L. C., &Glinz, M. (2018, May). User feedback in the app store: a cross-cultural study. In 2018 IEEE/ACM 40th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Society (ICSE-SEIS) (pp. 13-22). [Online], Retrieved from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3183428.3183436 [Retrieved on 16th March]
Hart, A., Toma, M., Issa, F., & Ciottone, G. R. (2019). Absence of cultural awareness training in international non-governmental organisations. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine, 34(5), 486-488. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/prehospital-and-disaster-medicine/article/absence-of-cultural-awareness-training-in-international-nongovernmental-organizations/DF03A7A3105C46F14AB0F630748E4285
Hennart, J. F. (2019). Digitalised service multinationals and international business theory. Journal of International Business Studies, 50(8), 1388-1400.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41267-019-00256-2
Karjalainen, H. (2020). Cultural identity and its impact on today's multicultural organisations. International Journal of Cross-Cultural Management, 20(2), 249-262. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1470595820944207
Katsikeas, C., Leonidou, L., &Zeriti, A. (2019). Revisiting international marketing strategy in a digital era: Opportunities, challenges, and research directions. International Marketing Review, 37(3).https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/147784/1/IMR-Leonidou.PDF
Kotler, P., Kartajaya, H., &Setiawan, I. (2019). Marketing 3.0: From products to customers to the human spirit. In Marketing wisdom (pp. 139-156). Springer, Singapore.https://www.academia.edu/download/59472062/Management_for_Professionals_Kartikeya_Kompella_-_Marketing_Wisdom-Springer_Singapore_201920190531-30412-1tnhibf.pdf#page=147
Leonidou, C. N., &Hultman, M. (2019). Global marketing in business-to-business contexts: Challenges, developments, and opportunities. Industrial Marketing Management, 78, 102-107.https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/130645/3/Leonidou%20and%20Hultman%202018%20-%20Special%20Issue%20IMM%20-%20Editorial%20Final.pdf
Lim, J. R. (2020). How organisations in different cultures respond to crises: Content analysis of crisis responses between the United States and South Korea. International Journal of Strategic Communication, 14(4), 294-316. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1553118X.2020.1812613
Luo, Y., &Shenkar, O. (2017). The multinational corporation as a multilingual community: Language and organisation in a global context. In language in international business (pp. 59-92). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Oded-Shenkar/publication/5223197_The_multinational_corporation_as_a_multilingual_community_Language_and_organisation_in_a_global_context/links/55a3fea708ae81aec912df8b/The-multinational-corporation-as-a-multilingual-community-Language-and-organisation-in-a-global-context.pdf
Masovic, A. (2018). Socio-cultural factors and their impact on the performance of multinational companies. Eco forum Journal, 7(1). http://www.ecoforumjournal.ro/index.php/eco/article/view/729
Mishra, S.B. and Alok, S., 2022. Handbook of research methodology. http://74.208.36.141:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/1319/1/BookResearchMethodology.pdf
Nayak, J.K. and Singh, P., 2021. Fundamentals of research methodology problems and prospects. SSDN Publishers & Distributors. http://dspace.vnbrims.org:13000/jspui/bitstream/123456789/4653/1/Fundamentals%20of%20Research%20Methodology_Nayak.pdf
Newman, M. and Gough, D., 2020. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application. Systematic reviews in educational research, pp.3-22. https://library.oapen.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/23142/1007012.pdf?sequence=1#page=22
Noyan, A. G. (2018). Study on the association of the management of differences in multicultural organisations and employee performance: An example from the textile sector. Lectio Socialis, 2(1), 38-48. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/lectio/issue/34436/363430
Ottman, J. A. (2017). The new rules of green marketing: Strategies, tools, and inspiration for sustainable branding. Abingdon: Routledge.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41267-019-00256-2
Paley, N. (2021). The manager's guide to competitive marketing strategies. Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780203736463/manager-guide-competitive-marketing-strategies-norton-paley
Pandey, P. and Pandey, M.M., 2021. Research methodology tools and techniques. Bridge Center. http://dspace.vnbrims.org:13000/jspui/bitstream/123456789/4666/1/RESEARCH%20METHODOLOGY%20TOOLS%20AND%20TECHNIQUES.pdf
Paul, J. (2019). Marketing in emerging markets: a review, theoretical synthesis and extension. International Journal of Emerging Markets. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJOEM-04-2017-0130/full/
Paurova, V., Gajanova, L., &Kliestikova, J. (2019). THE ROLE OF CORPORATE CULTURE IN THE CONTEXT OF CORPORATE MARKETING STRATEGY. Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, 367-374.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Anita-Sindar/publication/337914952_DOES_DIGITAL_OPPORTUNITY_AFFECT_FINANCIAL_INCLUSION/links/5df2a6bd92851c836478cde7/DOES-DIGITAL-OPPORTUNITY-AFFECT-FINANCIAL-INCLUSION.pdf#page=374
Payne, J., Cluff, L., Lang, J., Matson-Koffman, D., & Morgan-Lopez, A. (2018). Elements of a workplace culture of health, perceived organisational support for health, and lifestyle risk. American Journal of Health Promotion, 32(7), 1555-1567.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6106858/
Petrescu, M., &Krishen, A. S. (2019). Strength in diversity: methods and analytics. Journal of Marketing Analytics, 7(4), 203-204.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41270-019-00064-5
Phillips, S.M., Summerbell, C., Hobbs, M., Hesketh, K.R., Saxena, S., Muir, C. and Hillier-Brown, F.C., 2021. A systematic review of the validity, reliability, and feasibility of measurement tools used to assess the physical activity and sedentary behaviour of pre-school-aged children. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 18(1), pp.1-28. https://ijbnpa.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12966-021-01132-9
Ranjit, K., 2020. Research methodology. http://14.99.188.242:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/11658/1/Research%20Methodology%20A%20Step-by-Step%20Guide%20for%20Beginners%20by%20Ranjit%20Kumar%20%28z-lib.org%29.pdf
Rao-Nicholson, R., & Khan, Z. (2017). Standardisation versus adaptation of global marketing strategies in emerging market cross-border acquisitions. International Marketing Review.https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/101141/1/Global%20StrategiesEMFsIMR%20Post%20Peer%20Reviewversion.pdf
Reddy, C. N., Adhikari, J., &Chitranshi, J. (2017). Understanding and managing gender diversity challenges at leadership positions: A review. Journal of Strategic Human Resource Management, 6(2), 40.https://www.academia.edu/download/60685416/Understanding_and_Managing_Gender_Diversity_Challenges_at_Leadership_Positions20190923-48010-c56lj7.pdf
Rodríguez-Rivero, R., Ortiz-Marcos, I., & Patiño-Arenas, V. E. (2022). Exploring the Influence of Culture in the Present and Future of Multicultural Organisations: Comparing the Case of Spain and Latin America. Sustainability, 14(4), 2327. https://www.mdpi.com/1504782
Ruggiano, N. & Perry, T.E., (2019). Conducting secondary analysis of qualitative data: Should we, can we, and how?. Qualitative Social Work, 18(1), 81-97.
Skarbek, D., (2020). Qualitative research methods for institutional analysis. Journal of Institutional Economics, 16(4),409-422.
Snyder, H., 2019. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, pp.333-339. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296319304564
Song, R., Moon, S., Chen, H. A., & Houston, M. B. (2018). When marketing strategy meets culture: The role of culture in product evaluations. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46(3), 384-402.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Reo-Song/publication/314347217_When_Marketing_Strategy_Meets_Culture_The_Role_of_Culture_in_Product_Evaluations/links/5be5b1f192851c6b27b29334/When-Marketing-Strategy-Meets-Culture-The-Role-of-Culture-in-Product-Evaluations.pdf
Statista.com, (2021), Marketing services spending in the U.S. 2017-2021, by category [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/987009/marketing-spending-us-category/ [Retrieved on 16th March]
statista.com, (2021, Estimated number of companies worldwide from 2000 to 2020, by region [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1260719/global-companies-by-region/ [Retrieved on: 16th March, 2022]
Steenkamp, J. B. E. (2019). Global versus local consumer culture: Theory, measurement, and future research directions. Journal of International Marketing, 27(1), 1-19.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1069031X18811289
Sürücü, L. and MASLAKÇI, A., 2020. Validity and reliability in quantitative research. Business & Management Studies: An International Journal, 8(3), pp.2694-2726. https://www.bmij.org/index.php/1/article/download/1540/1365
Swoboda, B., & Batton, N. (2019). National cultural value models and reputation of MNCs. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CCSM-05-2018-0061/full/html
Tan, Q., & Sousa, C. M. (2018). Performance and business relatedness as drivers of exit decision: A study of MNCs from an emerging country. Global Strategy Journal, 8(4), 612-634.https://dro.dur.ac.uk/22100/1/22100.pdf
tradewindfinance.com, (2022), How Can Technology Impact International Trade Finance Companies? [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.tradewindfinance.com/news-resources/how-can-technology-impact-international-trade-finance-companies [Retrieved on 16th March]
Unsworth, J., Melling, A. and Porteous, D., 2021. Development and Evaluation of the Validity and Reliability of the Leading and Managing Care Pre-Registration Nursing Student Assessment Tool. SAGE Open Nursing, 7, p.23779608211000259. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/23779608211000259
Vaara, E., Tienari, J., & Koveshnikov, A. (2021). From cultural differences to identity politics: A critical discursive approach to national identity in multinational corporations. Journal of Management Studies, 58(8), 2052-2081. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/joms.12517
Watson IV, G. F., Weaven, S., Perkins, H., Sardana, D., &Palmatier, R. W. (2018). International market entry strategies: Relational, digital, and hybrid approaches. Journal of International Marketing, 26(1), 30-60.https://asset-pdf.scinapse.io/prod/2774569787/2774569787.pdf
worldbank.org, (2018), Regional Trade Agreements [Online], Retrieved from: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/regional-integration/brief/regional-trade-agreements [Retrieved on 16th March]
Yoo, J. S., & Lee, Y. J. (2019). National culture and tax avoidance of multinational corporations. Sustainability, 11(24), 6946. https://www.mdpi.com/589390
Yousaf, S., & Xiucheng, F. (2018). Halal culinary and tourism marketing strategies on government websites: A preliminary analysis. Tourism Management, 68, 423-443. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261517718300827
Yun, J. J., Zhao, X., Jung, K., &Yigitcanlar, T. (2020). The culture for open innovation dynamics. Sustainability, 12(12), 5076.https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/12/5076/pdf
Zangirolami-Raimundo, J., Echeimberg, J.D.O. and Leone, C., 2018. Research methodology topics: Cross-sectional studies. Journal of Human Growth and Development, 28(3), pp.356-360. http://pepsic.bvsalud.org/pdf/rbcdh/v28n3/pt_17.pdf




.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






