PBHL20010 Working and Learning in Cross Cultural Communities Assignment Sample
Question
The first assessment help task is a case study of about 2000 words that you will complete on an individual basis. The case study will require you to choose one of the eight stakeholders and discuss their role in a public health emergency; the nature and direction of their interest based on their position in the community and their function in society; and their actions. You must also choose a specific emergency situation from which you will draw examples to illustrate your discussion. This may be an epidemic of disease (for example- a natural disaster (flood, bushfire, earthquake, etc); or an anthropogenic event (chemical spill, industrial explosion, etc). You must specify the emergency and stakeholder group in the case study. You will also need to use appropriate academic references to support your understanding of stakeholder participation, communication needs, and responsibility.
The stakeholders you may choose from are:
1. Local government
2. Science/health experts
3. Local business interests
4. The media
5. Representatives of the long-term community (people who have lived in a given location for 10 years or more)
6. Representatives of new groups (people who have recently arrived in or moved to a given location)
7. Local health care personnel
8. State (or higher level) government
Your case study must have the following sections: 1) Introduction – identifies the chosen stakeholder, the emergency and gives a general indication of who they are or where is the Public health Event – for the stakeholder group you have chosen, describe their role in a public health emergency; make sure to consider whether their role is official or personally at risk of health impacts and it he other kinds of risk they experience; 3) Risks and Responsibilities – for the group you have chosen, describe the nature of the section; make sure to consider whether the risk is direct or indirect, whether it is a risk to health or another kind of risk, what the specific health or non-health risk involves responsibilities are in relation to the public health emergency and its own and the risks of other stakeholders; 4) Role in Public health Decision-Making – for the group you chose, they contribute to decision-making in the context of a public health emergency; be sure to discuss whether their contribution is official or unofficial, the channel through which decision-making process, and the degree to which their impact is informed by evidence-based and non-evidence-based knowledge; and 5) Conclusion – discuss the position you have chosen in a public health emergency; you may want to consider whether they are actors or bystanders, for example, or use some other classification, but be sure stakeholder group is likely to be affected significantly, the nature of the impact, and why you believe this would occur.
This essay writing help must be written in a formal, academic style (not first person) and must be fully referenced. Harvard referencing is preferred for this unit. If you need help the referencing guides available online and through the Library as soon as possible.
Answer
1.0 Introduction
Public Health professionals are aimed towards protecting the health of the populations. Within a particular Public Health field, they also work to prevent the disease and make sure that the injury of the person does not spread (Harper et al. 2020). When an infectious disease is spreading such as that of coronavirus Public Health professionals work to track and stop the same while making sure that they can keep communities as healthy as possible.
The current reflection is based on my learning and experience of the scenario. It is focused on reflecting the specific experiences and other instances of the learner. The job experience is based in the larger context of community engagement. It highlights my experience of what I have learnt about public health and my job as a public health professional in the public health emergency of a covid-19 pandemic.
2.0 Learning during Scenario
The learning processes within the course of the scenario were extensive. This is so because I participated in scenarios every week and in a group of 5 members. It helped me understand the perspectives of other individuals and gain an idea about how they would view the same situation differently from me.
The process of learning is firstly involved in studying the scenarios and understanding the variables which revolve around the same. We then discussed the scenarios and the complications it presents which enabled us to gain a deeper insight about information that is presented. In this way we got to know how the other person would view the same situation. In this way we were able to understand the scenario completely which made solving answers easier (Rosa et al. 2020).
After the discussion we each picked up a question for answering. I learnt a lot from the information presented in this scenario as well as the perspectives shared by my group members. As an individual, I found it hard to work in a group and participate in group discussions. Due to these scenarios, I was able to develop team working skills along with the ability to participate in a discussion while presenting personal viewpoints and also learning about that of others. I got to know that there are a couple of underlying gaps in my knowledge because the perspective presented by my group members were highly differing and I got to know that a need for future learning exists as I need to strengthen my course knowledge and perform better.
3.0 Reflection on Scenario Experience
The self-analysis highlights that I need to revise the contents of my course and link them with the scenario so that I am able to understand the case is shared within them and answer the questions in a better way. I also need to undertake future learning about how to understand and reflect upon case studies so that I would be able to perform better in real life situations.
In the PBHL20007 unit, I got to know about the persistence of cultural shock within Public Health with specific reference to language and food. Reflected how the students who come from their country to Australia experience cultural shock as it acts as a barrier while adopting food and culture which is highly different from whether they have experienced all their life. Students also feel lonely when they leave their country because they leave behind their family and friends and also take time to make new friends with people who belong to different cultures and have different viewpoints and identities (Banerjee & Firtell 2017).
In this way they find themselves alone whenever they have a problem to encounter with specific reference to academic or personal life. I found this to be resulting in heavy stress which makes it difficult for international students to perform well in university. Differences in study pattern and the required level of academic writing skills also act as a bird in which need to be managed along with handling emotional and psychological health.
In PBHL20008, I got to know how to engage with cross-cultural communities. I research the information before the placement so that I would know my roles and responsibilities. I focused on the Australian indigenous community in the second assignment of this unit which was based on a case study of rural and remote areas. I reflected upon the mental health and physical status of the community members.
I gained an insight that they have poor accessibility to health services and quality food which further possesses a negative impact on their physical and mental health (Takeda & Melby 2017). I also found the patterns of heavy alcohol consumption due to problems such as lack of knowledge and stress. I give solutions so as to make sure that these communities are able to fulfil their cultural needs by increasing their knowledge regarding food and education and engaging with other community members.
4.0 Descriptive Elements of the Scenario
From the scenario, I learnt a lot of important things that improved my existing knowledge base and also allowed me to explore a lot of unexplored ideas and viewpoints. As highlighted earlier, me and my other group members participated in the scenarios every week where we performed various activities. It is vital to note that me and my group members were not able to meet and interact physically so as to fulfil this scenario activities and hence, we created a group over WhatsApp so that we could discuss the contents of the scenario and also reflect upon or learn from the same. My group members were highly considered rated because whenever one individual did not understand something the entire group would remain online and discuss the same way until it was clear to everyone which highlighted interpersonal participation.
In addition to this, I also got to know about its stakeholders within a public health scenario along with the members of the community and the public health professional. The most important insight I gained about the stakeholders was in reference to the responsibilities and roles performed by them in large Public Health events such as with situations of epidemic or pandemic.
These scenarios also help me to understand how to treat people and members of the community who are infected from the infection or illnesses. I gained an insight that I do not need to provide just the medical care for medicines and rather I need to provide them with adequate emotional support so that they do not feel that they are alone in this and rather have emotional support as and when required.
The major consideration here was that I firstly need to determine all the variables present in the condition so that I have all the required information for solving the issue. This is capable of helping me as a public health professional when I would be dealing with people who are affected from a public health event as well as individuals who were not affected. This is so because people who are affected are dealing with illness as well as emotional issues which makes it hard for them to concentrate on the positive aspects and have confidence that they will get better.
On the other hand, people who are not affected live in the constant state of fear and panic because they feel that they would catch the viruses and will not be able to protect themselves within the public health epidemic (Edmonds et al. 2020). This situation was common in the times of covid-19 pandemic because the people who had not contracted the coronavirus lived in a state of panic and hysteria where they were highly protective of themselves and found it hard to live a normal life while taking the required precautions.
It has been identified that the stakeholders of the public health infection control were management, program staff, funding agencies, Public Health professionals, and community members (Glenn et al. 2021).
I (as a public health professional) and other stakeholders were interested in making sure that infection control is being done properly where everyone is performing their jobs in the desired manner while focusing on the interests of the community. The outcome of the situation was collecting swabs for testing people for covid-19 and injecting what scenes to others.
The role of these stakeholders was directed towards making sure that the infection control happened in the desired manner and that each person performing the job was doing it correctly. It is vital to note that operations in public health can be tedious because there is a perfect set of instructions that need to be followed to take a single swab for a test or to inject a vaccine (Calisher et al. 2020).
The group of stakeholders who is the most at risk include public health professionals and community members. The key reason behind the same is that they are in close contact with the virus. The group which is at risk for non-health loss includes funding agencies. Their monetary resources are at stake while managing the public health event.
5.0 Job Experience in Public Health
I have been performing the role of Public Health professional as infection control in the public health emergency of the covid-19 pandemic. My role involved covid swapping and vaccination, PPE spotter. These were focused on controlling the spread of infection in the community and making sure that the stakeholders of Public Health are satisfied. My job did not only have a medical front but also reflected critical importance as me along with other practitioners was working closely with the virus.
During the situation, I felt fearful of contracting the virus myself. This is so because I was closely working while the people were submitting their samples for a test which might or might not be positive but I always felt at risk by performing my job as a public health professional in a public health emergency. Before the situation, I felt that I should do something to contribute to the diversification of the community of Australia and help them make it easier to manage the covid-19 pandemic.
After the situation, I felt that I have done good and worked for the benefit of society in order to promote Public Health. I felt that other people who were present at the scene also had similar feelings about the situation to myself. It can be further evaluated that the things that did not go so well involved me not being able to handle my emotional challenges and feelings of fear while making sure that I am doing my job in the desired manner. I was also not able to manage my academic and personal life while I was engaged in professional activities as a public health practitioner.
Apart from this, I signed up for the job without actually thinking about how I am going to protect myself which led to feelings of anxiety and fear while I was working. It can be analysed that I did not have paid the required attention to the demands of my academic life and emotional health because of which I was not able to handle the stress of the things going around me and they might have experienced Burnout at work. The sense which I can make of the situation now revolves around how if I could have undertaken better time management and stress management the situation would have been better.
Along with this, I think that if I would have developed these skills the situation of Burnout wouldn't have taken place which put me at risk of a public health emergency. I feel that even though I performed my job properly I did not pay the required attention to other aspects of my life which caused emotional distress. I feel that the learning and knowledge which I gained from this experience can be implemented in future situations so that I can handle them in a better way.
6.0 Conclusion
From the reflection, it can be concluded that learning during the scenario enabled me to develop team working skills and ability to participate within group discussions. I also got to know about gaps in my current knowledge and the ways in which I can undertake future learning. The units PBHL20007 and PBHL20008 further contributed to my learnings of cross culture public health. The public health stakeholders were discussed along with their relationships with specific reference to the public health event of covid-19 pandemic.
References
Banerjee, S & Firtell, J 2017, ‘Pedagogical models for enhancing the cross-cultural online public health learning environment’, Health Education Journal, vol.76, no.5, pp.622-631, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Srikanta-Banerjee/publication/317387894_Pedagogical_models_for_enhancing_the_cross-cultural_online_public_health_learning_environment/links/60be3017458515218f9ee08b/Pedagogical-models-for-enhancing-the-cross-cultural-online-public-health-learning-environment.pdf
Calisher, C, Carroll, D, Colwell, R, Corley, R B, Daszak, P, Drosten, C, Enjuanes, L, Farrar, J, Field, H, Golding, J & Gorbalenya, A 2020, ‘Statement in support of the scientists, public health professionals, and medical professionals of China combatting COVID-19’, The Lancet, vol. 395, no. 10226, pp. 42-43, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://escholarship.org/content/qt05h3r4qr/qt05h3r4qr.pdf
Edmonds, J K, Kneipp, S M & Campbell, L 2020, A call to action for public health nurses during the COVID?19 pandemic, ‘Public Health Nursing (Boston, Mass.’), vol.37, no.3, p.323, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7262140/
Glenn, J., Chaumont, C. & Villalobos Dintrans, P 2021, ‘Public health leadership in the times of COVID-19: a comparative case study of three countries’, International Journal of Public Leadership, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 81-94, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJPL-08-2020-0082/full/html
Harper, C A, Satchell, L P, Fido, D & Latzman, R D 2020, ‘Functional fear predicts public health compliance in the COVID-19 pandemic’, International journal of mental health and addiction, pp.1-14, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11469-020-00281-5
Rosa, W E, Gray, T F, Chow, K, Davidson, P M, Dionne-Odom, J N, Karanja, V, Khanyola, J, Kpoeh, J D, Lusaka, J, Matula, S T & Mazanec, P 2020, ‘Recommendations to leverage the palliative nursing role during COVID-19 and future public health crises’, Journal of hospice and palliative nursing: JHPN: the official journal of the Hospice and Palliative Nurses Association, vol.22, no.4, p.260, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc8018720/
Takeda, W &Melby, M K 2017, ‘Spatial, temporal, and health associations of eating alone: A cross-cultural analysis of young adults in urban Australia and Japan’, Appetite, vol.118, pp.149-160, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wakako-Takeda/publication/319113899_Spatial_temporal_and_health_associations_of_eating_alone_A_cross-cultural_analysis_of_young_adults_in_urban_Australia_and_Japan/links/59d6d7700f7e9b42a6aa0a78/Spatial-temporal-and-health-associations-of-eating-alone-A-cross-cultural-analysis-of-young-adults-in-urban-Australia-and-Japan.pdf
AC7026 - Master of Public Health (Nutrition) Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Module Title: Nutrition related diseases
Distributed on: 26.01.2021 / Teaching week 27
Submission Time and Date: To be submitted by 9:00 am GMT on Tuesday 4th May 2021
Word Limit: 3000 words (+/-10%)
Weighting -This coursework will be mark out of 100 and accounts for 70% of the total mark for this module
Submission of Assessment
Electronic Management of Assessment (EMA): Please note if your assignment is submitted electronically it will be submitted online via either Blackboard or Turnitin by the given deadline. You will find a Blackboard/Turnitin link on the module’s eLP site. It is your responsibility to ensure that your assignment arrives before the submission deadline stated above. See the University policy on late submission of work.
Assessment Instructions:
Funding for nutrition research comes through research councils (MRC, BBSRC, innovate UK), industrial sponsors or charitable organizations. In almost all cases funding is awarded competitively based on written grant applications. Here we will mimic that process, you are asked to create a three-year research grant project to address a pressing issue in the area of diet and disease.
Your project needs to be conducted by one person, working with limited support (i.e. technical help) and within three years. Strong projects will have the capacity to make meaningful improvements to health and will build upon topical issues covered in the module. (These improvements may be direct or indirect, i.e. your project might directly stimulate behavior change, or it might better inform those who set nutrition policy). You are encouraged to talk to the module leader about the suitability of your project ideas at an early stage.
Typically, a grant application is structured as:
Lay summary (500 words max) This is a plain language overview of your project, written for a non-expert audience.
Background and significance (850 words max) A concise literature review showing that you have something new to add, you need to be selective with your literature here, identify the most important work, show what questions are not yet answered.
Hypothesis and Aims (250 words max) be very implicit, what is your question and what do you hope to achieve?
Deliverables (400 words max) What will you determine and by when (include time points)? Structure as bullet points, GANTT charts are also useful.
Study design (650 words max). What work will you do? can it be done within 3 years? Please provide details of the study.
Impact (350 words max) This can be the hardest section to write. Why is this work important? Who will benefit and how? What steps will you take to make sure that the maximum benefit is realized?
Costings. (A page showing that you have planned how much money you will need, this includes yearly costs for staff, equipment, travel expenses, etc. Please be realistic, the project needs to deliver value for money but without costs affecting the quality of the work.
Module Learning Outcomes for assignment help
Learning outcomes assessed by the assignment:
1. Understand priorities in public health nutrition
2. Critically evaluate the scientific basis of current public health nutrition concerns
3. Independently develop plans to interrogate the nutrition evidence base.
Word Limit Guidance: For assessments where a word limit is indicated, a student’s ability to write within the word limit is part of the assessment concerned. Where a word limit is indicated students should provide a final word count by highlighting all text included in the main body of the assessment (the main body of the assessment does not include the reference list) and simply stating that word count.
The main body of the assessment includes:
-the title (if applicable)
-an abstract (if applicable) -the main body of text (including any sub-titles)
-in text citations e.g. (Smith, 2018) -direct quotations, case studies etc.
-tables, figures (including any table/ figure titles), illustrations and footnotes
Referencing Guidance.
Referencing is a key aspect of the academic assessment process, as it allows students to:
• acknowledge the contribution that other authors have made to the development of their work (and
therefore, help avoid plagiarism)
• evidence students independent research and depth and breadth of reading i.e. student ‘scholarship ‘
• demonstrate understanding of concepts proposed by other writers while developing their own ideas
• inform their readers of the sources of theories, datasets, quotes etc. that have been referred to, and enable readers to find the sources quickly and easily themselves.
Solution
Beriberi
A nutrition deficiency disease
Overview
The purpose of this project is to ensure better solution to a nutrition deficiency disease, beriberi, which causes fatal illness. The disease was first discovered in the year 1593 in England and is still an issue in most of the underdeveloped countries such as Bangladesh, Thailand and Kiribati. The purpose of the project is to eradicate beriberi by spreading awareness among people who are affected, providing medical aid to those people with the help of the local government and presenting schemes and policies to the government including financial aid. Many poor, underdeveloped and developing countries such as Kenya, Uganda, Kiribati, Bangladesh etc. are still facing these issues due to lack of public healthcare facilities, nutritional policies and lack of medical supplies to the people suffering from these nutrition deficiency diseases. Poverty is one of the major reason to cause beriberi as a person in unable to consume nutritional diets due to lack of capital. Proper nutrition and diet plans will help prevent this disease (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). Through this project, I would like to address such a problem with a solution to how we can eradicate this kind of disease from spreading. Arranging proper nutrients foods will also help people with thymine deficiency to gain thymine in their body. The awareness campaign should be done in different parts of the world where the problem regarding this issue is very widespread.
A sever thymine deficiency or vitamin B1 deficiency causes Beriberi. Wet and Dry beriberi are the two of its kind which causes due to low intake of Vitamin B1 or thymine rich food. Wet beriberi affects cardiovascular system resulting, in extreme case, blockage of heart and increase in heartrate affecting the circulatory system of a human body. Whereas, on the other hand, dry beriberi cases sever nervous breakdown and affects the nervous system causing paralysis, in extreme case. Consuming alcohol in a large amount and in a disorderly manner may also be the cause of thymine deficiency resulting to cardiovascular issues. Enlargement of heart, nausea, swollen legs, loss of appetite and lactic acidosis can be observed in infants affected with chronic or acute beriberi (Buttriss, 2015). Due to lack of thymine, cardiovascular and nervous system do no respond and function well as lack of thymine prevents doing so. 80 Percent of the people, due to abuse alcohol, which prevents their body to absorb thymine which in turn causes deficiency of thymine inside the body. These diseases are mostly found in third world countries rather than the developed countries. Low standard of living and ignorance towards healthcare plans lead to these kind of deficiency and causes many other nutrition deficiency diseases.
Background and significance
A forgotten disease that is still a clinical issue in many countries in southeast Asia including Bangladesh (Smith, H. A. 2017). Thymine was the first vitamin B that was discovered. In July 2009 an unknown illness caused death to a large number of African Union soldiers in Mogadishu which was later identified as wet beriberi. Laboratory investigations did not show any metabolic, infectious or toxic abnormalities which is why it was difficult to understand the nature of the disease (Emukule G, et al. 2011). After examining the blood sample of 16 soldiers it was identified that the levels of erythrocyte transketolase activation coefficient was high which caused thymine deficiency. This is considered to be an ancient disease but it is still existing in many parts of the world. The question is why is this disease still exist and how nutrition research will help control these diseases? Nutrition research will help understand the deficiencies and the food supply chain which will help people lead a healthy life and providing better outcomes for the economy. The main issue is to understand that a high number of diseases are caused due to deficiency or excess of nutrients consumptions (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). A proper nutrition and diet research will help understand the food consumption cycle which will be the stepping stone to eradicating diseases caused due to improper consumption of nutrition. Though cases of beriberi can be still seen with the introduction of advance technology and scientific methods deficiencies diseases like beriberi can be controlled.
Individual response to diet and food
Due to different metabolic rates, diet cannot be same for all people rather it should be according to the genetics, epigenetics and ethnics differences. The discovery of variability in diet will help in personalizing the diet for different people resulting in a better inform policy. The first thing is to understand the variability of metabolic responses in different people to different diet and food which can be done with the help of the following:
Omics:
Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics are the two omics research that helps identify how nutrients reacts to different genes, proteins and metabolites that will help identify the individual health and its issues (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). It will help understand how nutrients are digested, metabolized and absorbed in different human bodies. This will help create new biomarkers which will help identify health deficiency of an individual.
Microbiome:
Different microbes such as bacteria and virus that are present inside a human body contributes to microbiomes. Microbes varies from person to person and each has a unique microbe that makes microbiomes identical and different from each other though the subpopulation may consist same microbiomes. The microbiota that changes due to change in age, diet and physiological rates should be determined accordingly to adjust the diet of an individual. Research is needed to determine different microbiota that reacts differently to different nutrients. It is also important to understand its role in disease prevention and progression.
Genome:
The role of DNA and RNA and its determination is important so as to understand the proper diet that an individual need. Genome gives a complete information about an organism as it provides all the information which is required for an individual to function (Gropper, & Smith 2013). By identifying this it will be easier to analyze what deficiencies an individual has which will help in overcoming the deficiencies diseases like beriberi.
Impact of nutrients in healthy growth and development
The research will help improve the health and well-being of an individual. Early determination of the nutrients (Buttriss, 2015) will help resist the diseases later to affect individual’s livelihood and development progression.
Early nutrients:
The role of diets is essential for the parents while preconception and during pregnancy which will help respond to early nutritional events. The introduction of an infant to solid food is a major decision as this may lead to obesity in future. The assessment of the nutrition in the early life is essential as this may cause a lot of diseases if not taken care of at an early stage.
Nutrition and reproduction:
Nutrition greatly impacts on maternal and paternal fertility. So this is an area that needs to be researched as it affects in preconception as well as post conception. Impact of nutrients are huge and it plays a key role in preventing diseases relating to reproductive organs such as prostate and ovarian cancer. The determination of the factors and mechanism is important for change in health of an individual.
Role of nutrition in health maintenance
Health maintenance requires continuous research to understand the role of nutrients and novel ingredients and its contribution in health (Chern, & Rickertsen, 2003). To rely on researches that help to dietary guidance including DRI is essential for health policy. At an early stage it is recommended to better understand the nutrient needs which will help in maintaining health in all population and subpopulations.
Optimal body functions:
It is better to determine the role of nutrition and fitness, together and individually to maintain the functions of the body that includes muscular, skeletal and nerves system.
Energy balance:
Researches require to identify system wide changes that important to reach optimum energy of a body. Experimental approach has not proven to be much effective in the past as it was unable to reach the population whereas system wise approach will help to reach wide scale of population to understand the energy balance.
Role of nutrition in medical management
Nutrition researches play an important role in connecting the diseases with their treatments. Researches that are evidence based results in more effective policy making that ensures proper patient care
Disease Progression:
To understand the medical management of the diseases, research plays and important role. It helps understand how a body response to different disease when nutritional factors influence both disease initiation and its progression. Research will also help us understand the role nutrition plays in prevention of the diseases.
Nutrition Support:
Nutritional researches are required to determine to understand the best support that is needed to for survival and growth of an individual and subpopulation (Eilender, 2016). It will help understand how nutrients helps with chronic disease among infants and the elderly people.
Understanding nutritional related behaviors
Drivers of food choices:
The drivers that influences food choices are:
• Government policies
• Cultural differences
• Environment
• Food marketing and social media
Nutrition and brain function:
The marketing of healthy food behaviors will greatly help the population to consume healthy diets. The diets will influence hormonal changes which in turn will help in metabolism (Gropper, & Smith, 2013). of an individual. Factors such as consumption of the different diets, variety, eating frequency etc. will help researchers to understand the pattern of the intake of the nutrients. It is important to understand how eating influences neural biochemistry and brain functions.
Food supply
• Collaboration between nutrition and agricultural production
• Identifying the quality factors that influences the consumption of food
• Introduction of biotechnology and nanotechnology to influence food production and providing novel nutrients to individuals
• Enhancing the knowledge of food to understand its availability.
The above factors will help identify and control nutrition deficiency diseases. In many countries there are people who still follows culture ignoring the biological harm they bring to themselves. Awareness campaigns with the help of the local leader may convince them to take precaution and understand the essentiality of consuming medicines.
Hypothesis and Aims
As beriberi is one of the many diseases that is caused by deficiency of vitamin, thymine, it is necessary to understand how food environment affects the dietary patterns and what is needed these to solve the problem.
Below is a few question that needs to addressed:
• What kind of dietary change is needed and is the current dietary change significant?
• How does assistance program helps reach and promote proper dietary patterns?
• What are consequences of negative dietary responses?
• How is marketing playing an important role in influencing dietary choice of food and how are its impacts?
• How do we monitor, assess and evaluate the dietary change changes?
• How does inclusion of quality of food influences its consumption?
• How does promoting local production of food and its supply influence dietary patterns?
The above questions are very important to address as the dietary patterns of an individual is directly related to its health care. Proper nutrition intake is far less costly then taking medicines at the stage where the disease will be chronic. The rise in number of beriberi cases in southeast Asia including Japan helps us understand that this is not only a concern in the underdeveloped countries but also in the developed countries.
As this is a disease that is caused due to deficiency of nutrition the aim and objective should be to make policies that will provide proper nutritional diets to every individual. With the help of the local government the following schemes and policies can be implemented:
National food policy plans:
Making Desirable Dietary Plans, which will formulate the requirements of energy such as needs of micronutrients and macronutrients are essential. It can influence the future of agriculture and food policies of the country. Desirable dietary plans are adaptive and improving in nature as it changes according to the growing needs of the people (Shi, 2019). A plan that will help change the idea of food nutrients and its intake not only for the urban people but also for the rural people, poor people, people living in hilly areas and people under poverty. The USP of this plan is that it is not static in nature and it will vary according to the nature of the requirement.
School feeding programs:
This is a step that can be taken very actively as it will nourish the children from a very basic level. This is a part of right to food to everyone. Introducing feeding programs in schools will not only feed them but also will encourage them to come to school every day. The countries that have a high level of poverty such as Bangladesh and Pakistan (Shi, 2019) should introduce feeding programs in the government schools so that the children are exposed to multi nutrients. In this way government can also observe the intake of the food at a large scale and plan the production and availability of the food accordingly.
Anti-poverty programs:
In this program the idea is to pay an amount to the poor section of the society directly so that they can consume adequate amount food to feed their family. This can be given according to the number of members of family members present in the family. In 2003 Mexico came up with such a plan to provide direct money to the needed class of the people. This will help the government to understand the food consumption of the country according to which policies can be made.
Deliverables
It is better to find ways to identify these diseases at a very early state so that it can be addressed accordingly. The following things should be done at an early stage to avoid these deficiencies:
• Medical checkup for every individual once in a year funded by the government
• People who are affected with these diseases should be able to access free medicine
• Involving the funded organisations to conduct medical camps in the areas with large number of cases of beriberi are high
• Making locally produced food more feasible to the people through government subsidized markets where people can afford local vegetables and food at low cost
Inadequate thymine consumption, less absorption of thymine and abnormal metabolism will result in a loss of thymine through urinary track. Transketolase is an important factor that reduces thymine in the body, when it functions improperly (Carpenter, K. J. 2000). Irritability, insomnia, loss of appetite are also the symptoms that effects the psychological stages. Factors that are influencing the thymine requirement are as follows:
• Composition of the diet: The dietary requirements of carbohydrates and fats are to be maintained in proportion. Increase in fat containing diets though does not effect at large but the consumption of carbohydrate in a large quantity happens to increase the requirements of thymine
• Climate: This influences the requirement of thymine as climate is directly proportional to energy consumption.
• Age: For the individuals those who are actively involved in work will have to increase the intake of minimum thymine.
• Body weight: The requirement of thymine will differ according to the body weight. More is the weight more is the consumption of energy and more is the requirement of thymine.
• Physical activity: More workout and activity will lead to more loss of energy resulting in more requirement of thymine.
• Pathological condition: Pathological condition influences the consumption of thymine. Patients having gastronomical disorder, alcohol issues, thyroid disorder etc. will require to consume their thymine accordingly that’s will not affect their health further.
The GANTT chart below shows the planning and duration that is needed to initiate the project. As most of the cases are observed to occur in the backward areas like Bangladesh, Pakistan, Kenya etc. choosing one of these places is important. In this project we will work in the areas of Bangladesh and try to eradicate this disease with the help of the government by making policies and schemes. Below is the time frame shown in GANTT chart to initiate the plan.
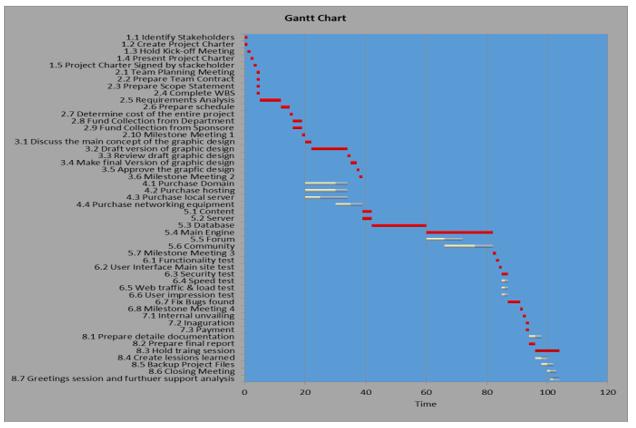
GANTT Chart
Study design
Availability of the food ingredients should not be the reason for inadequate food intake or dietary composition. Cultural diversity and changes in food habits according (Eilender, E. 2016). to that must also be the key points while making dietary plans and policies. Integration of human rights education in school level is an important policy (Battle-Fisher, M. 2014) that should not be ignored as it will help people would realize of the right to food. To identify food insecurity in the vulnerable groups and the reason for their inadequate supply of food (National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). 2013). Measures should be taken according to the results found about why is their insecurity of food among these groups.
With the help of the local government of Bangladesh the following work is to be done to address the issue:
• Collaborating with the human rights groups and nutrition community which can be a stepping stone towards success in overcoming nutrition deficiency diseases
• Conduct education and awareness programs that are essential as this will help people to understand their right to food and why is it important to all
• Educating the people about nutrition sensitive food with the help of local volunteers which will not only help them understand the importance of food nutrients but also will help them choose from the diverse food options which they can afford and will be available to them easily
• Collaborate with the NGO’s to organise camps and programs for free medical checkup to the people holding below poverty level cards.
• It has been estimated that about 40% of the population is have inadequate thymine intake which needs to addressed by appointing free volunteers in different areas where the poverty level is spiking (Shi, L. (2019).
The project will take more or less two and a half years to conclude where we can set up people andorganisation who will carry on with the work. Research is one of the most important part which will take first two quarters after the grant approval. The reason why it should be done is because this is a kind of disease that can be eradicated with the help of a little awareness. The only reason this disease is existing is because of poor food and nutritional policy of the government in the country and that is the target of this project which is to make policies and programs, collaborate with the human rights groups, ask for help from the funded organisations and collaborate with the pharmaceutical companies providing vitamin B1 medicines at a subsidized rate.
Impact
One of the overriding challenges is to identify the group of people that requires right to food which will help in further studying about how and what to plan. Next comes the identification of the food insecurity and finding the root cause of this inadequacy of food (Chern, W. S., &Rickertsen, K. 2003) should be the ultimate priority. The fundamental approach should be taken to identify these problems and when the plans are in action to monitor its implementation to venerable groups. Socio-economics factors will highly influence these plans and it may happen that sometime the plan may not works as expected but the basic idea and the plan should not be altered. Human rights principal make human right framework more effective (Ho, L.-sang. 2013) as it will involve multiple stakeholders to get involved that will help in proper implementation of the plan and its smooth running. Right to food involves nutrition benefits as well and if these two are constantly been involved together the outcome will be sustainable development (Ho, L.-sang. 2013). Education and information on human rights and right to food will also play a vital part. This will help people of different vulnerable groups and ethnic groups to follow their culture without suffering from nutrition deficiency diseases.
Costing
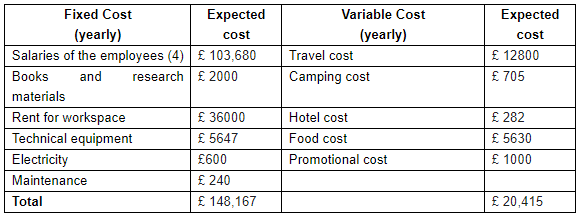
Grand total: £168,582 per annum
References
Battle-Fisher, M. (2014). Application of systems thinking to health policy & public health ethics public health and private illness
Buttriss, J. L. (2015). Public health nutrition (2nd ed., Ser. The nutrition society textbook ser) John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Carpenter, K. J. (2000). Beriberi, white rice, and vitamin b: a disease, a cause, and a cure
Chern, W. S., &Rickertsen, K. (2003). Health, nutrition and food demand.
Eilender, E. (2016). Public health and community nutrition (First, Ser. Nutrition and
dietetics practice collection). Momentum Press.
Gropper, S. A. S., & Smith, J. L. (2013). Advanced nutrition and human metabolism (6th ed.)
Wadsworth/Cengage Learning
Ho, L.-sang. (2013). Health policy and the public interest. Routledge
National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). (2013). National health and nutrition
examination survey (Vol., estimation procedures, 2007-2010, Ser.
Shi, L. (2019). Introduction to health policy (Second, Ser. Gateway to healthcare management)
Health Administration Press
Smith, H. A. (2017). Forgotten disease: illnesses transformed in chinese medicine
Watson JT, El Bushra H, Lebo EJ, Bwire G, Kiyengo J, Emukule G, et al. (2011) Outbreak of Beriberi among African Union Troops in Mogadishu, Somalia. PLoS ONE 6(12): e28345. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028345
7140SOH Health Policy in Organisations and Systems Assignment Sample
Module Learning Outcomes
There are four learning outcomes for the module and by the time you have completed it, it is envisaged that you will be able to:
1. Critically analyse the global stakeholders to determine the key policy actors and organisations and analyse the roles they play in the development and implementation of national, transnational, and global health policy
2. Critically analyse the policy drivers and the factors associated with the development and implementation of health policies in high-, middle- and low-income countries
3. Apply economic evaluation to critically analyse the impact of health policy in high-, middle- and low-income countries
4. Critically review the leadership challenges and skills in implementing policy changes at an international, national, and local level
Coursework 2 (2500 words)
Smoking tobacco is a significant risk factor in developing lung cancer. Policies to reduce the impact of smoking are designed to reduce lung cancer and other smoking related diseases. Critically analyse how the United Kingdom and South Africa have implemented anti-smoking policies and discuss their effectiveness. Discuss 2 or 3 policies in total.
You should include the following for assignment help
• Data demonstrating incidence and prevalence of smoking in each country
• Policy drivers in UK and South Africa and resource allocation
• An analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the policies to reduce tobacco use
• Whether there are any conflicts of interest in national government
• Leadership challenges and skills in implementing policy changes at an international, national, and local level
• Comparison of two countries and the effectiveness of the policies
• Headings to make your work clearer to the reader
Submission Guidance
It is important to you and the tutors that your project is written and presented in a professional manner. The following requirements must be adhered to in the format of assignments
1. Your limit does allow for +/- 10% words in length. The limit includes words used in tables, graphs, charts and diagrams, but excludes the front cover, the table of contents, references list and appendices. If you exceed the +/- 10% word limit you may receive a 10% penalty on your coursework mark
2. The front cover page - see appendix 1 for the template.
3. The type font should be Arial and the font size for the body of the text 12 point.
4. One and a half (1.5) line spacing must be used.
5. All pages should be numbered consecutively, in the footer on the right.
6. Your student number should be in the footer on the left.
7. References, citations and quotations should be in Coventry University APA 7th Edition only (https://libguides.coventry.ac.uk/apa)
8. Any diagrams, tables, photographic images etc. should be appropriately labelled and referenced.
All coursework must be submitted through the assignment links via the AULA page.
Referencing
Coventry University have adopted the CU APA 7th edition Referencing System as the standard format for citations and references. There is a Centre for Academic Writing which can provide detailed support on the APA style of referencing. There is also a useful reference guide on the CU Harvard Style that I advise you to download and keep.
This can be found at:
https://libguides.coventry.ac.uk/apa
Solution
Introduction
Overview of smoking prevalence globally
As per the viewpoint of West (2017), there are about 1 billion tobacco smokers globally, which accounts for 7% of women and 30% of men. Although, the prevalence rate of smoking tobacco varies according to the determinant factors of different countries.
From the above-illustrated figure, it has been found that the overall prevalence of tobacco smoking is 23% globally, whereas it is approximately 32% for men and only 7% for women. Although, the prevalence of tobacco smoking has been decreasing considerably over the years due to anti-smoking advertisements and the implementation of anti-smoking policies.
Introduction to the UK, including the prevalence of smoking
The UK, the abbreviated form of the United Kingdom, is a sovereign nation within the northwest part of Europe, which is one of the most developing industrial countries across the entire world.
From the above-depicted figure, it has been understood that the prevalence or occurrence of smoking cigarettes amongst both women and men has declined substantially since 1974. In the year 2019, only 12.5% of all women and approximately 15.9% of all males smoked cigarettes, which is nearly one third compared to the rate, which was reported in 1974 (Statista, 2022).
Introduction to South Africa, including the prevalence of smoking
South Africa is the northernmost nation within the African continent, which is well-known for its cultural diversity, natural beauty and varied topography.
The above-demonstrated figure shows that approximately 35% of all respondents, participated in the “Statista Global Consumer Survey” smoke cigarettes as one of the most popular tobacco products (Statista, 2021). On the other hand, other tobacco products are Hookah, cigars, pipe tobacco, e-cigarettes, chewing tobacco, oral nicotine pouches and others.
Policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK
As per the report of GOV.UK (2018), the main policy drivers for the reduction or minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption or uptake of tobacco products. Additionally, one of the main policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco is to increase awareness of the citizens of the UK regarding the side effects of consuming tobacco by giving examples of the number of deaths or cancer patients due to this.
Policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa
One of the key policy drivers, which play a major role in the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa, is to increase tax rates on purchasing tobacco (Lau et al., 2018). Another key policy driver is to increase the prices of cigarettes, as it has been helping to minimize the intensity of consuming tobacco amongst the poor of South Africa (Boachie & Ross, 2020). Although, the effects of increasing prices of tobacco products vary based on the gender, race and age groups of the individuals in South Africa.
Main Body
Policy drivers in the UK, including resource allocation
The primary policy, which is involved with the minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK is the "Health Act (2006)”, which was implemented in the year 2007. The primary focus of this policy is to ban tobacco smoking in enclosed workplaces and public spaces for controlling the number of deaths causing due to passive smoking. In this context, this policy has become more effective while making England smoke-free by the implementation of the "Tobacco Control Plan for England” in 2017 (Hackshaw et al., 2010). In this context, the two most important policy drivers are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption of tobacco (Opie-Martin et al., 2020). Additionally, the two important resources while reducing tobacco smoking are initiation by increasing the tax rate and prices of cigarettes and cessation control by increasing the awareness of the citizens (Sun & Mendez, 2019).
Policy drivers in South Africa, including resource allocation
“Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” is the main policy, which drives the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa, whose key drivers are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption for restricting or prohibiting smoking within public spaces (South African Government, 2022).
The above-depicted figure demonstrated the phases of reducing tobacco smoking after the implementation of “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” and other “Tobacco Products Control Amendment Acts” periodically (Reddy et al., 2013). The figure also shows that the number of purchasing cigarettes has been decreased after the execution of anti-smoking policies. The resource allocation for this policy is government initiatives, awareness programs, and strict government regulations against tobacco smoking.
Leadership challenges in the UK during policy implementation
While implementing the policy for reducing the consumption of tobacco, the economic impact is one of the most vital leadership challenges, which the government and other regulatory bodies of the UK have been facing. In this context, Ekpu & Brown (2015) stated that the economic effects of tobacco smoking are based on two leadership challenges, such as the expenses of minimizing the prevalence of smoking amongst smokers and expenses of tobacco utilization itself. On the other hand, the government of the UK has also faced challenges regarding the imposing of tax on tobacco purchasing by its citizens (Till, McKimm & Swanwick, 2020). Lastly, it can be said that the lack of penalties for the individuals who violate the laws, rules and regulations of anti-smoking is another significant leadership challenge, due to which the numbers of deaths caused by passive smoking have been increasing considerably.
Leadership challenges in South Africa during policy implementation
The report of the World Health Organization (2022) depicts that strengthening the execution of the agreement of tobacco control is one of the most vital leadership challenges within the African Regions, including South Africa. Due to this particular leadership challenge, the usage and consumption of tobacco by the citizens of South Africa and other African regions have been increasing rapidly (Tukuru et al., 2021). An increase in purchasing power of the consumers related to tobacco is one of the leading leadership challenges, due to which the markets of South Africa have been growing more accessibly. Increasing awareness of the citizens of South Africa is another most crucial challenge, which the government of the country has been facing while implementing the policy (Warner, Tam & Koltun, 2014). In this context, comprehensive monitoring is required to be followed for informing the civil society and government about the purchasing of tobacco products.
Weaknesses and strengths of the policy in the UK
One of the most vital strengths of tobacco smoking control policies in the UK is its execution of a smoking cessation campaign named "No Smoking Day” in the mid-1990s (Owen & Youdan, 2006). The strength of this policy or campaign is its effectiveness in lowering the prevalence of smoking within the country. Due to this policy, the rate of tobacco smoking decreased to 25% amongst adults in 2003 from 33% since its implementation. On the other hand, the most vital weakness of the anti-smoking policy in the UK is the inability of the government to successfully comply and enforce “Tobacco Advertising and Promotion Act 2002” effectively (CPI, 2019). Another weakness is the incapability of the government to invest additional money in this policy.
Weaknesses and strengths of the policy in South Africa
One of the most vital strengths of “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” is its strict implementation in South Africa for considering tobacco smoking as the second considerable health concern after AIDS/ HIV (Plagerson, et al., 2019). Strength of this policy in South Africa is to become the first country to ban the smoking of cigarettes within enclosed workplaces and public spaces. Another important strength of this policy is to increase the minimum age of the citizens of South Africa to legally access tobacco (Bonnie, Stratton & Kwan, 2015). One of the most vital weaknesses of this policy is the incapability of the South African Government to impose this policy while selling and advertising tobacco products compared to the advertising of anti-smoking products in the country.
Impact of the UK’s economic condition on the implementation and development of the policy
According to the data of the World Bank (2022), the UK is a high-income country whose average income is $12,696 and above. The economy of this country has an impact on the implementation and development of tobacco control policies under the "Health Act (2006)”. In this context, Ekpu & Brown (2015) stated that the government of high-income economies like the UK acquire a huge amount of tax revenues from the consumption and production of tobacco. Additionally, more employment opportunities within the tobacco industry create. The economic condition of the UK helps the government to invest in anti-smoking policies and procedures more effectively so that tobacco smoking amongst adult smokers can be controlled effectively. Sometimes, the government does not focus on the strict rules and regulations of this policy for its own economic gain or interest.
Impact of South Africa’s economic condition on the implementation and development of the policy
As per the data of the World Bank (2022), South Africa is an upper-middle-income country according to its economic condition. Although its economic condition is lower than that of the UK, it is the first upper-middle-income country, which imposed continuous increases in terms of excise tax for reducing the consumption and production of tobacco smoking. In this context, the government of South Africa has been shedding light on the improvement of the health conditions of its citizens by increasing the prices of cigarettes. Additionally, the average price of cigarettes within the retail sector of South Africa has been hiked by 110%, due to which its poor citizens are incapable of purchasing cigarettes due to which, consumption of tobacco smoking has been lowered considerably (Chelwa, van Walbeek & Blecher, 2017).
Conflicts of interest within national government in the UK
For controlling the consumption of tobacco, the government of the UK has been making efforts in terms of conflicts of interest amongst the policymakers. In the year 2017, the government of the UK has recently launched the “Tobacco Control Plan for England” so that awareness of the citizens regarding the side effects of tobacco smoking can be increased effectively. The government has been focusing on the strict implementation of its public health policies under the "Health Act (2006)” so that the health conditions of the citizens can be protected and secured significantly. No economic profits should be considered while imposing the strict regulations of tobacco control policies in the UK.
Conflicts of interest within national government in South Africa
While describing conflicts of interests within national government in South Africa, the role of interest groups can be illustrated as they are the associations within the political system of the nation, which influence public policy based on any social issue (Asare, 2009). Here, tobacco smoking is one of the greatest social issues, due to which the number of deaths has been increasing. In this context, the government has totally banned the advertising of tobacco products along with the increasing advertising of anti-smoking products.
Comparison between the UK and South Africa regarding the effectiveness of smoking reduction
While comparing between the UK and South Africa about the effectiveness of smoking reduction, it has been observed that South Africa is most effective in reducing tobacco smoking compared to the UK as the government of the UK acquire economic gain and advantages of tobacco consumption and production (Nation Master, 2022). While imposing the policy, the government of the UK face challenges regarding economic loss as the tobacco sector of the country contributes a large amount of money to the economy. For dealing with this challenge, the government of the UK started to increase awareness of the public through “No Smoking Day” besides ceasing the production of tobacco. On the other hand, the government of South Africa faced a challenge while imposing an increased tax on tobacco products. Although, the government executed many tobacco control policies for securing the health conditions of its citizens.
Theoretical interventions regarding control of tobacco smoking
While supporting the above-described evidence regarding tobacco control, it has been observed that the theories or models of behavior change are relevant. In this context, some theoretical interventions related to tobacco cessation or control are “Transtheoretical model”, “Health Belief Model”, and “Social Cognitive/Learning theory” (Roberts, Kerr & Smith, 2013). The core aim of these theoretical interventions is to cease the consumption of tobacco by helping the smokers to change their behaviours towards tobacco smoking. In this context, the government of the UK has launched “No Smoking Day” for encouraging the smokers not to smoke to that particular day so that their behaviour can be changed for at least one day. Additionally, the government of South Africa has shed light on the health concerns of its citizens through the application of “Health Belief Model” so that the awareness of the individuals regarding the side effects of tobacco smoking can be understood.
Conclusion
In the above discussion, an overview regarding smoking prevalence has been provided by considering the statistics from across the globe. The research has showcased Africa is having the highest prevalence of smokers in which 7% of smokers can be accounted as female and 30% are male individuals. The above analysis has also provided some statistical information from different sources. From the analysis, it can be noted that the rate of smoking among the citizens of the United Kingdom is being declined since the year 1974. However, during the last few years, the statics have mentioned that more than one-third of the rates identified in 1974 have been recognised in the nation. Following the statistics showcased in the discussion majority of the individuals have responded that they do not smoke or consume any tobacco items, whereas, 35% of individuals in the nation smokes cigarettes daily. In the above discussion, a statistical overview has been presented from the results of “Statista's global survey” where cigarettes have been recognised as one of the highly accepted and consumed tobacco materials in South Africa.
It can be also be concluded that, in the United Kingdom, the government have taken several measures and policies for reducing the tobacco and cigarettes consumptions rates by establishing several healthcare protocols and regulations. One of the major and most effective policy drivers that are used by the UK government is transcending a major awareness regarding the negative impacts of smoking among the citizens of the nation. The government and other healthcare communities are trying to showcase the negative effects of smoking and consuming tobacco by giving examples of an increasing number of deaths and an emerging number of cancer patients as well. On the other hand, the South African Government have also intended to take several actions, such as; increasing the tax rates on tobacco products or taking actions against the uncontrollable supply chain of the substances. Here, the primary motive of the government is to minimise the intensity of smoking among the youth population of the country and increase a major awareness regarding healthy lifestyles as well.
In the above discussion graphical representations have been used for showing the changes in tobacco consumption rates in South Africa from the year 1690 to 2009. The research has also provided the references of several acts, such as; the “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 and 93” along with the “Tobacco products control amendments acts”. At the same time, it is evident that over the decades due to the leadership issues within the nation several challenges have been faced by the UK government for setting the amendments and rephrasing the regulatory systems within the nation. The same account has also been presented in terms of South African governance procedures. It seems that the changes in leadership options and style mainly harmed the civil society and their lifestyle. Also at some point unlike the UK due to the slow speed of development at some parts of South Africa dealing with the consumption rate of tobacco seems to stay less effective even after the establishment of government protocols.
References
Asare, B. E. (2009). Tobacco regulation in South Africa: Interest groups and public policy. African Journal of Political Science and International Relations, 3(3), 099-106. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJPSIR/article-full-text-pdf/FCFC4587529
Boachie, M. K., & Ross, H. (2020). Determinants of smoking intensity in South Africa: Evidence from township communities. Preventive Medicine Reports, 19, 101099. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211335520300590
Bonnie, R. J., Stratton, K., & Kwan, L. Y. (Eds.). (2015). Public health implications of raising the minimum age of legal access to tobacco products. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://tobacco.cleartheair.org.hk/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/18997-2.pdf
Chelwa, G., van Walbeek, C., & Blecher, E. (2017). Evaluating South Africa's tobacco control policy using a synthetic control method. Tobacco Control, 26(5), 509-517. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://scholar.google.com/scholar?output=instlink&q=info:toqmvfMf6Q8J:scholar.google.com/&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5&as_ylo=2010&scillfp=2313872938218841645&oi=lle
CPI. (2019). Smoking ban in the United Kingdom. Centre For Public Impact (CPI). Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.centreforpublicimpact.org/case-study/smoking-ban-united-kingdom/.
Ekpu, V. U., & Brown, A. K. (2015). The economic impact of smoking and of reducing smoking prevalence: review of evidence. Tobacco use insights, 8, TUI-S15628. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.4137/TUI.S15628
GOV.UK. (2018). Tobacco commissioning support: principles and indicators. GOV.UK. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/alcohol-drugs-and-tobacco-commissioning-support-pack/tobacco-commissioning-support-pack-2019-to-2020-principles-and-indicators.
Hackshaw, L., McEwen, A., West, R., & Bauld, L. (2010). Quit attempts in response to smoke-free legislation in England. Tobacco control, 19(2), 160-164. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://tobaccocontrol.bmj.com/content/tobaccocontrol/19/2/160.full.pdf
Lau, Y.K., Tam, J., Fleischer, N.L. & Meza, R., (2018). Neighbourhood deprivation, smoking, and race in South Africa: a cross-sectional analysis. Preventive medicine reports, 11, pp.202-208. From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211335518301141
Nation Master. (2022). South Africa vs United Kingdom: Facts and Stats. Nationmaster.com. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.nationmaster.com/country-info/compare/South-Africa/United-Kingdom.
Opie-Martin, S., Jones, A., Iacoangeli, A., Al-Khleifat, A., Oumar, M., Shaw, P.J., Shaw, C.E., Morrison, K.E., Wootton, R.E., Davey-Smith, G. & Pearce, N., (2020). UK case control study of smoking and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration, 21(3-4), pp.222-227. From: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/21678421.2019.1706580
Owen, L., & Youdan, B. (2006). 22 years on: the impact and relevance of the UK No Smoking Day. Tobacco control, 15(1), 19-25. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2563638/
Plagerson, S., Patel, L., Hochfeld, T. & Ulriksen, M.S., (2019). Social policy in South Africa: Navigating the route to social development. World Development, 113, pp.1-9. From: https://findresearcher.sdu.dk:8443/ws/portalfiles/portal/151844724/Revised_Manuscript._15.8.2018.pdf
Reddy, P., Sewpaul, R., Sifunda, S., James, S., Yach, D., Resnicow, K., ... & Mbewu, A. (2013). A decade of tobacco control: The South African case of politics, health policy, health promotion and behaviour change. South African Medical Journal, 103(11), 835-840. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://journals.co.za/doi/pdf/10.7196/SAMJ.6910
Roberts, N. J., Kerr, S. M., & Smith, S. M. (2013). Behavioral interventions associated with smoking cessation in the treatment of tobacco use. Health Services Insights, 6, HSI-S11092. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.4137/HSI.S11092
South African Government. (2022). Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993 | South African Government. Gov.za. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.gov.za/documents/tobacco-products-control-act.
Statista. (2021). Tobacco product usage in South Africa 2021 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.statista.com/forecasts/856757/tobacco-product-usage-in-south-africa.
Statista. (2022). Cigarette smoking in the UK by gender 1974-2019 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/423001/cigarette-smoking-in-great-britain-by-gender/.
Sun, R., & Mendez, D. (2019). Initiation versus Cessation Control Policies: Deriving Optimal Resource Allocation Strategies to Decrease Smoking Prevalence Under a Fixed Budget. MDM policy & practice, 4(1), 2381468319832036. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2381468319832036
The FINANCIAL. (2020). Efforts to control tobacco undermined by conflict-of-interest among policymakers, new research reveals ? FINCHANNEL. FINCHANNEL ? News Making Money. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://finchannel.com/efforts-to-control-tobacco-undermined-by-conflict-of-interest-among-policymakers-new-research-reveals/.
Till, A., McKimm, J. & Swanwick, T., (2020). The importance of leadership development in medical curricula: a UK perspective (stars are aligning). Journal of healthcare leadership, 12, p.19. From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7079548/
Tukuru, M.O., Snyman, L., Postma, T.C. & van der Berg-Cloete, S.E., (2021). Dentistry in South Africa and the need for management and leadership training. South African Dental Journal, 76(9), pp.532-536. From: http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?pid=S0011-85162021000900009&script=sci_arttext&tlng=es
Warner, K. E., Tam, J., & Koltun, S. M. (2014). Growth in tobacco control publications by authors from low-and middle-income countries. Tobacco Control, 23(3), 231-237. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://scholar.google.com/scholar?output=instlink&q=info:DeIJWTzNih4J:scholar.google.com/&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5&as_ylo=2010&scillfp=1682438322522218787&oi=lle
West, R. (2017). Tobacco smoking: Health impact, prevalence, correlates and interventions. Psychology & health, 32(8), 1018-1036. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5490618/
World Bank. (2022). World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk. Datahelpdesk.worldbank.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519.
World Health Organization. (2022). Tobacco Control. WHO | Regional Office for Africa. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/tobacco-control.
7069SOH Managing & Planning resources in Healthcare Organisation Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
1. Critically apply financial performance management, budgeting, and cost-benefit analysis to healthcare organizations
2. Critically evaluate the legal, ethical, educational, and professional factors which impact the management of the healthcare workforce
3. Critique the skills and knowledge required by healthcare leaders which impacts upon finance and workforce.
Coursework 2
3000-word individual coursework addressing Learning Outcomes 2 -4
This assessment component counts for 15 credits
In 3000 words, addressing learning outcomes 2-4, complete the following assessment task:
Critically evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of resource planning and management in a health system you are familiar with, focusing on the following key areas for assignment help:
1. Priority setting and decision-making processes
2. Workforce planning and development
3. Human resource and talent management
Prepare a business case for improvement in one of the key areas that maximizes the strengths and addresses the areas of weakness you have identified.
Your individual coursework report will be assessed using the HLS Faculty Postgraduate Assessment Marking Rubric and the coursework 2 assessment guidelines, which you will find in the appendices in the module guide.
It is important to you and the tutors that your project is written and presented in a professional manner. The following requirements must be adhered to in the format of assignments:
1. Your limit does allow for +/- 10% words in length. The limit includes words used in tables, graphs, charts and diagrams, but excludes the front cover, references list and appendices. If you exceed the word limit you will be penalised 10% from your mark
2. The front cover page - see appendix 4 for the template in the module guide.
3. The font type should be Arial and the font size for the body of the text 12 point.
4. One and a half (1.5) line spacing must be used.
5. All pages should be numbered consecutively, in the footer on the right.
6. Your student number should be in the footer on the left.
7. References, citations, and quotations should be in Coventry University APA Referencing only. Ensure that all statements and arguments are supported with reference to the evidence in the relevant literature.
8. Any diagrams, tables, photographic images etc. should be appropriately labelled and referenced.
Solution
Introduction and context
In this particular study, the Midland Healthcare system is being focussed majorly in association with their initiative to provide acute treatment to the mentally ill patients. In order to attain such objectives, this study will look into a specific healthcare system for the purposes of resource planning and management, among other things. The investigation will also look at topics such as decision-making and prioritization, workforce development, and human resource management, to name a few. Midland Healthcare will offer inpatient treatment for a range of acute mental health illnesses and needs, according to the findings of the research (Midland Healthcare, 2021). In order to aid in the rehabilitation of its 40 patients in the acute care center, the organization supplies more than only medicine to them (Mesfin et al., 2020). In addition, the organization provides counseling, support, and therapy to those who are recovering from diseases.
Discussions
The business case for improvement
The high number of readmissions for mental health concerns that Midland Healthcare has witnessed has prompted the organization to focus its efforts on improving patient outcomes after they have been discharged from its facilities. The organization hopes to use this money to extend its services to the general public as well as to aid patients who have been discharged from the hospital in improving their overall health status.
Table 1: Smart objectives
(Source: Self-developed)
In order to be able to provide adequate care to the patient even after the discharge with not only medicine but also therapeutic, counselling, and supporting process the management of Midland healthcare needs to fund a lot in this particular proposal. Besides, preliminary investigations of Midland Healthcare's resource planning and management practices, according to the organization, must be completed before any substantial adjustments can be introduced (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). The activities of identifying, analysing, and obtaining the resources that are required for the project's success are all included in the definition of resource management in project management. What is certain is that, no matter what the nature of the project is, it will always need human and physical resources, including the necessary workers and labor, as well as construction materials and equipment, as well as facilities, information technology, and other resources.
Option appraisal
The health-related obstacles faced by patients, service users, and members of the community are the main focus of resource planning and management in healthcare systems, with the bulk of attention being focused on these difficulties at any one time (Mesfin et al., 2020). The availability of sufficient resources to address the needs of patients is critical to providing them with a decent quality of care. This is particularly true in the case of Midland.
Identifying unmet patient requirements and matching them with available resources within an organization is the purpose of resource planning and management in the healthcare industry. Creating prior goals that are both acceptable and attainable in order to enhance patient outcomes is a priority for the organization, which also acknowledges and analyses the mental health requirements of individuals who are treated by them. The Midland Health System provides patients with access to an array of additional equipment and gear that may be of assistance with their mental health care needs, in addition to medical equipment and drugs. There is also an enormous number of staff that are there to serve customers at any time they want it.
Benefit analysis
The costs and benefits of several different methods must be weighed and compared to achieve a decision on resource allocation before any conclusions can be reached. Other public-sector healthcare organizations are also under the control of the federal government, in addition to Midland Hospital (Midland Healthcare, 2021). All choices, from financial decisions to input and labour decisions to capital decisions, are imposed by the United States federal government (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). The government's use of this budgeting information, on the other hand, is what enables them to categorize expenditures and calculate the amount of money that will be required to complete the project to its completion.
The Midland Institute for Mental Health also has responsibility for human resources and talent management, which is important given that the quality of therapy provided to patients is highly dependent on the growth of current staff members. When it comes to achieving long-term success, companies such as Midland Corporation understand the need of investing in human capital. For example, the company recognizes the importance of recruiting and maintaining highly trained and motivated personnel over the long term. Counselors, social workers, and therapists are examples of professional staff members who are offered opportunities for professional development because they have direct patient contact. Given how critical it is for these professionals to keep up with their education and training, it is critical that resources be given and budgetary choices are made with a strong focus on their continued education and training in mind.
Midland will conduct a review of the present personnel and material levels, as well as how they may be expanded or repurposed, as part of its attempts to close the gap between the actual and expected states of things in the industry. A sufficient number of staff members must be maintained to ensure that both inpatients and outpatients continue to get support and treatment without jeopardizing the organization's goals and objectives. This is especially important in emergencies (Midland Healthcare, 2021). This gives us an idea of the identification and execution of measures to reduce the gap between demand and supply for employees inside the organization as a direct result of this strategy.
It is also feasible to evaluate whether or not more supplies or equipment will be necessary for therapeutic operations by comparing the existing condition to the planned state. In order to make a choice, it is important to first recognize a problem and then communicate with others in order to discover a solution to that problem. A healthcare system's additional responsibilities include the provision of high-quality services that are tailored to the specific needs of each individual patient. As a result of the organization's legal and ethical obligations to treat each patient as an individual, Midland's staffs is ready and willing to treat each patient as if they were a separate and distinct individual.
Cost analysis
Midland organizes its resources in order to maximize efficiency, and it does it via the use of a cost-benefit analysis approach, as well as planning and forecasting procedures. Midland's approach to resource planning places a strong emphasis on incremental budgeting as well as activity-based budgeting, with the kind of budgeting chosen depending on the particular components of a project as well as the demands placed on the workforce. When it becomes essential to increase the percentage of the previous year's budget that is being utilized in the current year's budget, incremental budgeting must be employed to accomplish this. To put it another way, this method is simple and easy to comprehend (Rangachari & L Woods, 2020). As a result of this, the budget may be overstated or underestimated, which may result in inefficiencies in the budgeting process as a result of the budgeting process as a whole over a longer period of time. As a consequence, management is likely to exaggerate the severity of the crisis, resulting in the waste of financial resources as a
Result of their decisions.
Table 2: Budget template of Activity-based budgeting
(Source: Developed by the researcher)
It is used as an example to illustrate how activity-based budgeting techniques may be used to real-world problems in order to obtain successful outcomes. The project described in the introduction is utilized to demonstrate this. The use of budgets to account for cost drivers and activities that vary from those that occur in the usual course of business is critical when these changes arise. Budgets must be used to account for the differences in costs and activities that have occurred. Identification of the specific amount of money that will be required to achieve the project's objectives, on the other hand, may prove to be a challenging task.
Table 3: Operating budget structure
(Source: Self-developed)
In Healthcare facilities, the operating budget is generally done to forecast expenditures as well as revenues for the upcoming years (Wang & Jobarah, 2021). In this case of Midland Healthcare, the operating expenditures for a new project and expansion of their care to the general public as well, therefore, has been done. A simple operating budgetary structure has been provided for a better understanding of all the possible expenses for Midland healthcare during the course of the project. By the differentiation between expected and actual operating expenses, Midland healthcare can successfully able to generate its operating budget for the project and based upon that can significantly fund better.
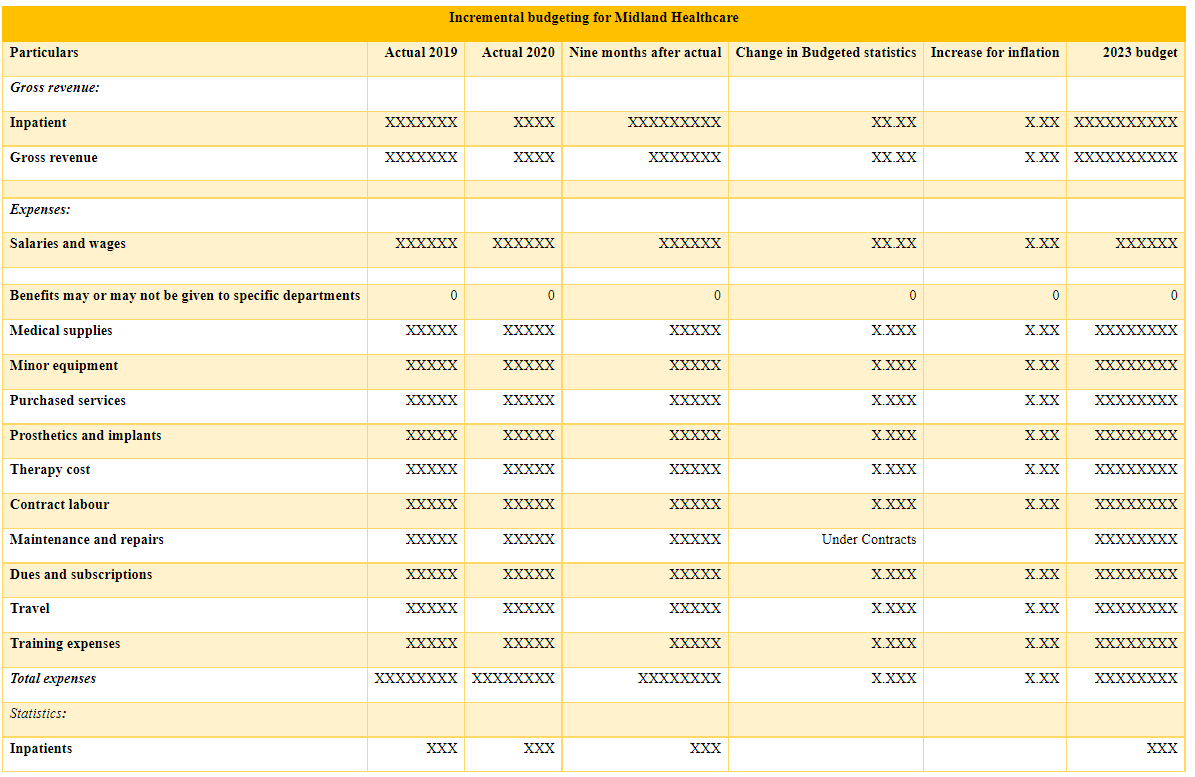
Table 4: Incremental budgeting structure
(Source: Self-developed)
Incremental budgeting on the other side can help the Healthcare financial experts to make small and significant changes to the pre-existing budget for creating a whole new budget (White, 2020). For the case of Midland Healthcare combining the previous budget needs to only add the incremental amounts in this particular budget for getting a clear identification of the new budget numbers. Incremental budgeting is easy to implement as well as a calculator and it can help Midland healthcare in the continuity of the funding. However, this particular process leads to extra spending as well as doesn't consider all the charges.
Risks
Midland has a policy of doing a cost-benefit analysis in order to determine the training and development needs of its personnel. Following that, the technique is used to evaluate the costs of such training to the benefits that may be gained as a result of such training. Despite the fact that this is a simple strategy, it does not offer a comprehensive picture of the desires and objectives that exist inside the labor market (Limbu, Piryani & Sunny, 2020). Along with benchmarking, the organization uses key performance indicators to measure the success of each individual person inside the organization as a complement to benchmarking, and this is in addition to benchmarking (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). Managers set objectives for the level of the workforce and put a heavy focus on it throughout the workforce and talent planning cycle in order to guarantee that demand and supply are kept in balance. However, the training and maintenance cost is too high. In that case, it is more likely to put adverse effects on the budgetary aspects and planning of the initiative as well. Comparatively speaking, benchmark-based testing delivers a more accurate representation of a product's overall performance than other testing approaches.
Table 5: The risk matrix
(Source: Self-developed)
The development of a business case for enhancing the management of human resources and talent in healthcare organizations was crucial to achieving the aim of enhanced performance in this sector (Berberoglu, 2018). People are a very significant resource in healthcare organizations since they are accountable for providing patient-centred services.
Evaluation
It can certainly be considered, the Midland healthcare in order to take action for all the considered strategic lookout to help the mentally unstable individuals get better health outcomes even after discharging need to follow the "logic model" for monitoring, measuring as well as ensuring the success of the proposed impacts. As per the views of Howarth et al., (2020), the Healthcare facility first and foremost needs to look for adequate resources or inputs according to the logic model. Assessment of adequate resources or inputs or labour can help in understanding the ability of the facility to successfully implement the changes.
Figure 1: The Logic Model
(Source: Howarth et al., 2020)
The second necessity of the logic model represents all the activities of the change implementation. Midland Healthcare, therefore, needs to access all the activities such as upgrading the training process, hiring more experts, restructuring group points of the organization, and more can be utilized for accomplishing the proposed planning for better success. On the other side, as per the opinions of Mills et al., (2020), the logic model also requires the planner to extensively focus on the output as well. After accomplishing the planned initiatives this particular model can help the Midland Healthcare facility to drive the service for acute facility care patients in providing treatments regarding the aftercare of discharge. Last but not least, the "logic model" as for the last movement included help the service providers in analyzing the level of accomplishment to the intention. The Midland Healthcare facility therefore can successfully address whether the service they were willing to provide is accurately meeting their intention of what is actually needed to be.
Conclusion
It can finally be summarised that Midland Healthcare has been quite affected by the alarming rate of increment in the readmission rate in the mental health facilities due to lack of aftercare. After the discharge, there are very few patients that get accurate aftercare, support, adequate therapy, and more to recover. This particular scope is very narrow to the general public as a service in the Healthcare sector. Henceforth, Midland Healthcare has taken the initiative to provide more than medicinal care including counselling, support as well as therapy to the patients for recovering from the disease as aftercare. Initially, this particular organization is willing to guide 40 rehabilitation patients combating mental illness in their own acute care center. Therefore, the resources and finances of this particular business have been evaluated for understanding the scope of running this initiative. Through SMART objectives, various perspectives of the proposal have been analysed. Strategic priorities such as "preliminary investigation of resources and management practices", "analysing the scope of resource management", "provide adequate training" and more have been taken under consideration. Finally, it can be concluded that there are certain skills that are required by the Healthcare leaders to impact the finances and workforce such as "operation knowledge beyond country-specific level", "managers need to have global perspective", "practicing unity" and "mentoring others".
References
Midland Healthcare. (2021). Best Multispeciality Hospital in Lucknow | Midland Healthcare. Midland Healthcare. Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://midlandhealthcare.org/
Rangachari, P., & L Woods, J. (2020). Preserving organizational resilience, patient safety, and staff retention during COVID-19 requires a holistic consideration of the psychological safety of healthcare workers. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(12), 4267. https://www.mdpi.com/743378
Limbu, D. K., Piryani, R. M., & Sunny, A. K. (2020). Healthcare workers’ knowledge, attitude and practices during the COVID-19 pandemic response in a tertiary care hospital of Nepal. PloS one, 15(11), e0242126. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0242126
Berberoglu, A. (2018). Impact of organizational climate on organizational commitment and perceived organizational performance: empirical evidence from public hospitals. BMC health services research, 18(1), 1-9. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12913-018-3149-z
Al-Haroon, H. I., & Al-Qahtani, M. F. (2020). Assessment of organizational commitment among nurses in a major public hospital in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 13, 519. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7320227/
Mesfin, D., Woldie, M., Adamu, A., & Bekele, F. (2020). Perceived organizational culture and its relationship with job satisfaction in primary hospitals of Jimma zone and Jimma town administration, correlational study. BMC health services research, 20(1), 1-9. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-020-05319-x
Wang, Z., & Jobarah, H. (2021, December). Predictive Analytics Method Underpin Planning and Budgeting Evolution. In Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference. OnePetro. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://onepetro.org/SPEADIP/proceedings-abstract/21ADIP/3-21ADIP/D031S088R003/474128
White, J. (2020). (Almost) Nothing New Under the Sun: Why the Work of Budgeting Remains Incremental. In Budgeting, Policy, Politics (pp. 111-132). Routledge. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780429336232-8/almost-nothing-new-sun-work-budgeting-remains-incremental-joseph-white
Howarth, M., Brettle, A., Hardman, M., & Maden, M. (2020). What is the evidence for the impact of gardens and gardening on health and well-being: a scoping review and evidence-based logic model to guide healthcare strategy decision making on the use of gardening approaches as a social prescription. BMJ open, 10(7), e036923. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/7/e036923.abstract
Mills, T., Shannon, R., O’Hara, J., Lawton, R., & Sheard, L. (2022). Development of a ‘real-world’logic model through testing the feasibility of a complex healthcare intervention: the challenge of reconciling scalability and context-sensitivity. Evaluation, 13563890211068869. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/13563890211068869
7138SOH Global Healthcare Challenges Assignment Sample
Description of the coursework
You are required to write an essay addressing either TYPE-2 diabetes or Tuberculosis. For either option, your essay will be provided with a case-study to inform or use as knowledge- base to write your essay exploring and analysing factors in globalisation and global change that influence aspects of the disease that you chose to write on.
OPTION 1: A Global Health Perspective in Fighting Diabetes – The China Case-study
Type-2 diabetes, a consequence of malnutrition, is now one of the commonest non- communicable diseases whose emergence, control and management are influenced by globalization process and global change.
Critically analyse how factors within globalisation process and global change contribute to the increased global burden of type-2 diabetes, and set out the challenges facing global and public health agents in their fight against the disease.
Guiding Instructions for doing the essay
Through analysing and interpreting globalisation issues beyond those identified in the case- study on fighting type 2 diabetes in China, use guidance 1-4 below to structure a 2,500 word essay in response to the task described in Option 1.
Students will be required to analyse a case-study of a global healthcare issue and use it as knowledge base to do the essay coursework.
Word count: 2,500 words (± 10%), Credit worth: 20 credits
1. Identify and describe FOUR globalization factors and explore to clarify how EACH factor influences global emergence and prevalence of type-2 diabetes [1000 words].
2. Identify and describe the role of FOUR categories of agents involved in activities for the prevention, control and management of type-2 diabetes [375 words].
3. For each of the FOUR categories, identify and examine the challenges facing specific Organisations or initiatives in performing their role to reduce the global burden of type-2 diabetes [1,000 words].
4. Draw your conclusions about (i) globalization and type-2 diabetes emergence, and (ii) challenges facing global efforts to reduce impact of type-2 diabetes [125 words].
An effective essay should demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the connections between complex globalisation processes and malnutrition leading to type-2 diabetes. The essay should therefore critically analyse the meaning of globalisation and clarify how its processes influence malnutrition, health inequalities and emergence of type-2 diabetes. An effective essay also shows evidence of thinking about global and public health systems’ response to type-2 diabetes crisis by discussing the challenges facing global agents and partnerships in fighting the disease.
For further advice on writing the essay see module guide subsection 6.3.3 General essay guidelines Assessment
OPTION 2 – Fighting Tuberculosis: A Global Health Perspective
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the commonest communicable diseases whose emergence, and effectiveness of the control and treatment strategies are influenced by globalization process and global change.
Critically analyse how factors within globalisation process and global change contribute to increased emergence, spread and global burden of tuberculosis, and set out the challenges facing global and public health agents in their fight against the disease
Guidance for doing the coursework
(i) Guidance for doing the coursework will be provided in synchronous sessions in Week 5 or Week 11.
(ii) The weekly student-led seminars are also designed to help students develop the skills to critically analyse and interpret ideas about globalisation and health that are highlighted in case-studies. We expect students to actively participate in seminar discussions to familiarise themselves with the approaches to critical analysis of the concepts that feed into their coursework because they will be expected to use the approaches to do their coursework.
(iii) As the module progresses students will complete a Proforma Essay Plan (use template provided) for weekly review with the tutors to show how they plan to logically respond to the coursework task in order to achieve the module learning outcomes.
Structure of the essay
(i) The work should have a concise and informative essay title that shows full interpretation of the coursework task. Title of the case-study being used as the knowledge base for the essay is therefore NOT appropriate.
(ii) The case-study will be accompanied with FOUR clearly numbered instructions to follow in structuring your essay responding to the coursework task.
(iii) Introduction - The essay should have a helpful introduction that interpret the assessment task, clarify about its aim, and an outline of the argument to be presented in response to the coursework task.
(iv) Main Body - The essay should be structured as A FLOWING RESPONSE to the coursework task and must logically follow the order of the guiding instructions provided with the case-study.
• No subheadings
• No bullet points or listing of ideas, and
• No graphs, maps and / or tables.
The task requires students to instead verbally interpret, describe and explain the information presented relevant to the topic being discussed.
(v) Conclusion – In line with instruction 4 on the guidance for doing the coursework, the essay should summarise the discussion so that the reader gets a clear overview of what you have argued in response to what the coursework required you to do.
Referencing
Arguments in the essay should be referenced using APA style of referencing. As a guide, every 1,000 words used in the essay should have at least 10 references to show evidence of wide reading
Solution
OPTION 2 – Fighting Tuberculosis: A Global Health Perspective
Introduction
Tuberculosis could be referred to as a potentially serious infectious disease that to measure only impacts the lungs (Churchyard et al., 2017). The bacteria which causes this disease tends to spread from person to person through tiny droplets that are released into the air through sizes and cops. Most people that have been infected with the bacteria do not have any symptoms. However, the common symptoms of tuberculosis include coughs that are blood tinged, night sweats, weight loss, and heavy fever. Treatment isn't always required for those individuals who do not report any symptoms. Patients with active symptoms require a long course of treatment which involves multiple antibiotics. It is a highly common disease in the world right now which is easily transmissible (Pescarini et al., 2017). It could be partially preventable by vaccine and is treated by a medical professional. In order to do so the individual needs to gain a medical diagnosis.
Main body
The globalisation factors that contributed in to spread and prevalence of tuberculosis on a global level are discussed as follows:
Migration: it has been identified that up to 2% of the world's population is living outside the country of their birth. It has led to an impact on the population mobility on use of health services and the entire health paradigm (Oppong, 2020). They have now become a burden on the host Nations and the importance of this particular aspect is regularly increasing. The drivers of mobility which includes the process of international movement along with back and forth transition between different risk environments have been major factors in the management of infectious disease in the areas which receive heavy influx of migrants. It is vital to note that the issues of Management and high level and broad which have also been cross-cutting in the past (Lönnroth et al., 2016). These include policies and managing the migration process for skilled labour requirements. It is upon the host country to make sure that people and the territory for fulfilling their purposes are not acting as the agent of diseases and imposing a burden on the Healthcare system. They also need to take into account biometric characteristics and population demographics for assessing the labour coming into the country and the ways in which they could impact others around them. Family reunification has also become a considerable factor with in the migration paradigm as it dictates the behaviour of the person entering another country and the ways in which the individual would contribute to these issues are also encompass Health Care professional. Training and maintenance of competence as the need to cater to the migrant population as well as the citizens while dealing with the communicable diseases such as tuberculosis (Lee, 2018). It is essential on behalf of the host country to monitor the health service use and health outcomes in both local and migrant populations in order to make sure that communicable diseases such as tuberculosis are not studied at white scale due to the influx of people in the country.
Global travel and tourism: it is vital to note that movement is associated with the spread of disease in many ways. One of the major ways in which travel helps infectious diseases to spread is by introducing new microorganisms into a new Geographic area. When a novel pathogen enters a population that did not have an experience of this microbe it is likely to cause disease outbreak. Microbes that mostly cause symptomatic and mild infections intended to spread widely and still manage to cause disaster outbreaks (Allen & Feigl, 2017). Microorganisms that survive in the human host completely such as the tuberculosis bacteria readily spread in a new area. However, if one or more intermediate vectors or hosts are involved or the microbe has a complicated life cycle the introductions of bacteria and to a new Geographic area really lead to outbreaks because the requirement of a catalyst can act as a barrier. It is necessary to understand that a permissive condition can exist in a new location that introduces the pathogen to infect and spread (Laranjo et al., 2018). For instance, in that location where people do not cover their mouth and face while sneezing and coughing can lead to a severe spread of Tuberculosis. However, in a particular location where people are educated about the disease and unaware that the need to cover their faces with masks when visiting in public for controlling the spread of diseases are likely to restrict the spread of tuberculosis on their own behalf (Abdisamdov & Tursunov, 2020). Introduction of a new micro oven use of graphical areas has been considerably facilitated by global travel and tourism because the countries now do not have many restrictions while welcoming people into their territory and are highly flexible which makes it easy for people to go to another region and infect the population for best assignment help.
Lack of monitoring measures: it is necessary to note that tuberculosis almost feels like a coughing and sneezing which is highly common. When an individual travel through a global border and reports coughing and sneezing it is highly unlikely on behalf of the airport authorities or other individuals to stop the individual and check the symptoms (Zumla & Abubakar, 2018). Due to this, most of the patients suffering from tuberculosis are able to enter another country without too many restrictions and monitoring measures which expose the people of a foreign Nation towards the development of the disease. However, it is vital to understand that people who themselves are suffering from tuberculosis do not have the slightest idea that they are suffering from this particular disease and hence act as an agent of spreading the same without the required information (Wirth, 2018). This is also because of lack of monetary measures where the first people tend to view fever and sizes as a response to the weather and not as something that could be life threatening diseases.
Lack of education and awareness: there are some nations that do not have the required education and awareness for detecting the diseases and end up acting as agents for spreading them in other developed countries. The World Health Organisation reported that eight countries accounted for around two third of the total disease count which was led by India. It was then followed by China, Philippines, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, South Africa, and Bangladesh (von Delft et al., 2016). All of these countries are developing countries and due to lack of awareness and education within the citizens contributed to the Global spread of Tuberculosis. Lack of education and awareness is a globalisation factor because now people have taken diseases and their spread very lightly as compared to the times when they were living their secluded borders (Schaller et al., 2019). For instance, there are still some countries in the world which have no idea about the existence of tuberculosis in the first place and feel that fever and sneezes are just a common response of the body and nothing they should be looking out for while screening people coming into their country or checking them.
Agents are of paramount importance as the preparation of documents by the health agencies requires specific knowledge of these agents (Verma et al., 2019). It is necessary to note that the role of four categories of agents which are involved in the activities of the prevention control and treatment of tuberculosis are discussed as follows:
International Healthcare Institutions: it is necessary to note that as tuberculosis processes a serious threat to people on a worldwide basis, Health Care Institutions are among the first agents who are responsible for treating and preventing tuberculosis in the region. International Institutions include Public Health Care facilities, World Health Organisation, CDC, NHS, etc. It was the World Health Organisation which declared the will clauses to be an international emergency 1993. It has helped the world to recognise the presence of tuberculosis and then develop ways for fighting the same. Presence of international Healthcare Institutions enables the entities to develop and implement a strategy on a global level for controlling tuberculosis and preventing the disease. It also streamlines the treatment because when a drug is developed in one country it could be given to the other regions as well so that they could minimise the impact of the bacteria (Mason et al., 2017).
Primary Health Care providers: when an individual suffers from basic symptoms of cough and sneezing the person is likely to visit the nearby hospital or clinic. The doctors there uh are known as Primary Health Care providers if they are in near to people and perform the early diagnosis of the situation (Camacho et al., 2020). They play an important role in detecting tuberculosis because the Primary Health Care provider needs to look out for all the symptoms and not classify TB as a common cold due to cough, sneezing, and fever (Armocida & Martini, 2020). It is essential that they take the required measures otherwise the cases can go undetected that can lead to a global epidemic of the bacteria. If the cases are not identified then it is highly unlikely that they could be prevented because the world would not have the information about an eruption of tuberculosis in a particular region.
Scientists and researchers: they are one of the most important agents because they work in order to develop vaccines and other Diagnostic procedures that could be used for identifying the prevalence of tuberculosis in the first place and then we used the antigenic method for developing the required vaccines (Rohde & McNamara, 2018). However, it is necessary to note that researchers also closely work with advanced and improved drugs which are effective for controlling the strains that are sensitive and resistant to existing medicines. Advancements in Global Medical Science have led to the duration of several drugs that have helped in controlling as well as curing tuberculosis such as MDR-TB (Balogun et al.., 2021). It is because of the efforts of researchers and scientists that it has been possible.
Non-governmental organisations: there are also vital agents in the treatment and prevention of tuberculosis on a global level. This is so because these organisations work in favour of underprivileged and economically backward people who might not even have the required awareness and education of identifying the tuberculosis in the first place. Non-governmental organisations work in order to spread awareness and educate people about how to distinguish TB from common cold (Kaplan et al., 2018). In many parts of the world it has been because of NGO that people have been given the required vaccination and drugs which are very costly if procured on a private level.
It is necessary to note that the agents also face challenges while performing their role to reduce global impact of tuberculosis. The challenges are as follows:
International Healthcare Institutions: One of the major challenges faced by the international Healthcare institutions in reference to control, prevention, and treatment of tuberculosis is the early detection of bacteria. This is so because it is highly difficult to distinguish tuberculosis from common cold and in order to do so speciality centres have been developed that have the required equipment (Lanza et al., 2020). International Healthcare Institutions tend to monitor these activities because they need to allot emergencies and provide the required material for global management of diseases.
Primary Health Care providers: The major challenge faced by Primary Health Care providers is the lack of resources (Burzynski & Keshavjee, 2020). This could be both physical as well as human resources. This is so because Primary Health Care providers are unlikely to have all the machinery and equipment that is needed to test every particular disease including tuberculosis. In some cases, they also fall short of nurses and other Health Care staff which makes it difficult on their behalf to manage the patients.
Scientists and researchers: Researchers and scientists tend to face the challenge of time (Rizzo et al., 2016). This is so because after a disease has been declared as a global emergency or a local epidemic that they need to collect the samples of antigens and test it along with the performing experiments in order to identify the ways in which particular bacteria reacts to different vaccines and chemical compositions (Denecke et al., 2019) . It takes a couple of months or an entire year depending on the complexity of the disease. It is a challenge because until the researchers and scientists develop vaccines through extensive R&D procedures the patients continue to develop adverse symptoms without an effective drug or medicine to help them deal with the same.
Non-governmental organisations: However, it is necessary to understand that Non-governmental organisations also face tough challenges while dealing with Global diseases because of lack of proper funding and the strategic direction (Demetriades, 2017). On some occasions they tend to collaborate with the government or private business Institutions for making the vaccine or drug easily accessible to people. It is necessary to understand that funding can play a major role because if an NGO would not have the required money it is highly unlikely that they would be able to procure vaccines or other resources for helping underprivileged people (Brown & Savulescu, 2019). However, the money is not only used in procuring vaccine supporters for also spreading awareness and educating people against tuberculosis and the ways in which they could minimise the impact on their own behalf. It is because of these and those that if people in remote areas are aware about the existence of TB and able to distinguish the same from the common cold so that they could seek for advanced treatment and not contribute to spreading on a community level.
Conclusion
From the essay, it can be concluded that globalisation has facilitated the spread of tuberculosis. This is so because globalisation has made it easy for people to travel around the world along with the flow of goods and ideas. This has not only contributed to the emergence of opportunity there but it has also made it easy for diseases to travel across borders and become an epidemic.
The major factors include migration, travel, lack of education, and lack of monitoring measures. Lack of education and monitoring measures are globalisation induced factors because the countries around the world have eased the restrictions of entering into territory and do not test people against common cold or other aspects which exposes them towards the risk of welcoming tuberculosis as an epidemic. The four categories of agents that are involved in the activities of prevention control and treatment of tuberculosis include International Healthcare organisations, Primary Health Care providers, scientists and researchers, and non-governmental organisations. It is necessary to understand that these agents deal with their own challenges in order to handle the epidemic of tuberculosis. Have a comma the common challenges include lack of resources and funding.
List of References
.png)
.png)
.png)




.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






