LAW6001 Taxation Law Assessment 2 Sample
Task
Summary In response to the issues raised in the case study provided, research and develop a 2000-word tax advice that addresses (a) assessable income (b) allowable deductions (c) calculations of income/deductions and (d) your conclusions and recommendations. Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this business law case study help.
Context This assessment assesses your research skills, your ability to synthesise an original piece of work to specific content requirements and your ability to produce a comprehensible piece of advice which addressing the client’s needs. It also assesses your written communication skills. The ability to deliver to a brief is an essential skill in the workplace. Clients may well approach advisors seeking a combination of specific information needs and advice on the tax implications of a particular arrangement in the Australian tax jurisdiction. It is therefore important to be able to identify all the issues presented by an arrangement and to think about the potential consequences of different approaches to addressing the client’s needs.
Task Instructions
• Your case study needs to identify and discuss the tax implications of the various issues raised.
• A report (word document, approx. 2,000 words) must be submitted for the calculations of the assessable income; allowable deductions and taxable income of the taxpayer including identifying and discussing them. E.g., how the amounts of income & deductions have been derived. If any receipts and payments are not assessable or deductible, the reasoning for non-inclusion of these in assessable income or deductions as per relevant legislation or cases.
• Critically analyse the following case study. With respect to each task:
• Review relevant case law and legislation (ITAA1936, ITAA1997)
• Apply the law to the facts of the case study
• Reach a conclusion/ give practical advice to your client.
• You will be assessed in accordance with the Assessment Rubric.
• This case study must be presented as an individual effort. The case study requires individual research. It is expected the student will survey the relevant literature, including decided cases, and select appropriate additional resources.
• Your case study assignment help is not just a list of answers. Your reasons for your conclusions and recommendations must be based on your research into the relevant cases and legislation.
• The format of the report should be a business report and using APA referencing style
Case Study:
Comprehensive Individual Tax Return Advice Question 1 On 17 July 2020, Ken Fong acquired a restaurant as a going concern, paying $850,000 for the land and buildings, plant and equipment and goodwill. Upon taking possession Ken realised that the plumbing and electrical systems required repairing. In August 2020 he spent $27,000 for the repairs so that the restaurant could open for business. Shortly after opening, the tiles in the kitchen cracked and fell off the walls. Ken had them replaced, restoring them to their original condition, costing $6,400. In November 2020 Ken decided to replace all the kitchen cooking equipment in order to reduce the likelihood of having to replace it in the future. The cost was $30,000. At the same time Ken entered into a contract to have the equipment regularly inspected and serviced. The contract fee was $1,500 per year. At that time, he also decided to pay a pest control company $2,000 a year to rid the restaurant of pests and ensure health and safety standards were maintained. In January 2021 a violent summer hail storm caused damage to the roof of the restaurant. Instead of making repairs, Ken decided to replace the entire roof along with the roofing insulation and ducted air conditioning. The roof replacement cost $32,000 and the insulation and air conditioning added another cost of $7,400. At that time Ken contracted builders to construct an additional room to cater for increased patronage. The cost of the addition was $26,800. Required With reference to relevant legislation and cases, advise Ken on the deductibility of the expenditure incurred on repairs and improvements to his restaurant in August 2020, November 2020 and January 2021.
Question 2
Maurice is an individual tax resident of Australia for tax purposes. He has the following assets:
• His home was acquired on 20 February 1989 for $140 000. The home was never used for any income producing purpose. The estimated market value of the house on 1 March 2018 is $310,000
• Shares in FUL Pty Ltd acquired on 10 April 1984 at a cost of $15 000.
• Furniture acquired on 20 May 2010 for $10,500.
• Yacht acquired on 9 July 2020 for $25,000
• Block of vacant land acquired on 20 June 1997 at a cost of $100 000. The estimated market value of the vacant block on 15 May 2021 is $475,000. Maurice subsequently sold the following assets during 2020-2021 (arm’s length transactions):
• His home was sold on 1 March 2021 for $325,000
• The FUL Shares were sold on 15 March 2021 for $19,000
• The furniture was sold on 1 May 2021 for $5,000
• The yacht was sold on 29 June 2021 for $37,000
• The block of vacant land was sold on 30 May 2021 for $465,000. Maurice also has a carry forward capital loss of $12,500 from the sale of an antique drumkit and a carry forward capital loss $5,000 from the sale of underperforming shares in an earlier income year. Maurice is not a share trader. Maurice has also incurred interest expenses on the vacant block of land of $110,000 over the time he owned the vacant block. He never used the vacant block for any income producing purpose. Required With reference to relevant legislation and cases calculate the net capital gain or loss as applicable for Maurice for the 2020/21 income year. You must show all possible methods to calculate capital gains (you must reference each step in the process to the relevant legislation. The numbers in the calculation will not be sufficient) and identify reasons why inclusion/exclusion of all capital gains tax assets
Solution
Question: 1:
Facts and Issues of The Case:
In the current case, the taxpayer has made various repairs and maintenance from time to time to the business organization, the taxpayer has spent some money on pre-starting of the business, during the course of the business, and after the business. Therefore the question in this context arises that whether the expense of the repairs is deductible against the income of the taxpayer or the expense of the repairs is not a deductible expense (Razak, 2020).
Legislation:
In the income tax assessment act, 1997 there are different provisions are there that allow the business expenditure as a general deduction or a special deduction. Any expense that is incurred by a taxpayer for the purpose to meet their repair expense is deductible from the gross income of the taxpayer to get the assessable income of the taxpayer. Tax ruling 97/23 (Mcgregor Lowndes & Crittall) it is clearly established that the tax deduction in case of repairs expense is not admissible if the expense of the repairs is of a capital nature. The assessable income of any person means the income on which the tax is calculated the gross income is income earned by the person (Weltman, & J.K. Lasser Institute 2018).
The different Para of the same ruling provides an explanation and difference between the repairs and improvements. According to the tax, the ruling repair is the expense that incurs by the business for the purpose of restoring the functional efficiency of the organization and on the other side, the improvement in the asset refers to those expenses that incur for the purpose of increasing the functional efficiency of the asset. The expense related to the improvement of the asset is the capital expense and therefore the expenses are called the capital expense and therefore those expenses are not allowed to deduct while calculating the assessable income from the gross income (Property investors benefit from 'repair' year-end deduction. 2017).
If any amount is expenses or incurred as initial repairs of the asset, that is the repair that incurs before bringing such asset into use then such repairs have a nature of the capital repairs and therefore such expense of capital repairs incur as an initial expense is not allowed as a deduction. If any damage, the defect has an existence at the time of acquisition of the asset than in such case the repairs incur for removal of such defect, the damage is considered as the capital nature repairs and therefore such expense is not allowable as a deduction. Any expense on repairs of the organization if incurred for the purpose of complying with the government bodies and government regulations than in such case the expense of repairs is of revenue nature and deduction with respect of such repairs expense is allowable to the organization.
Applicability:
Expenditure for the month of august
During the month of August, the taxpayer incurs two major expenses for the asset as repairs the description and allowability of such expenses are as follows-
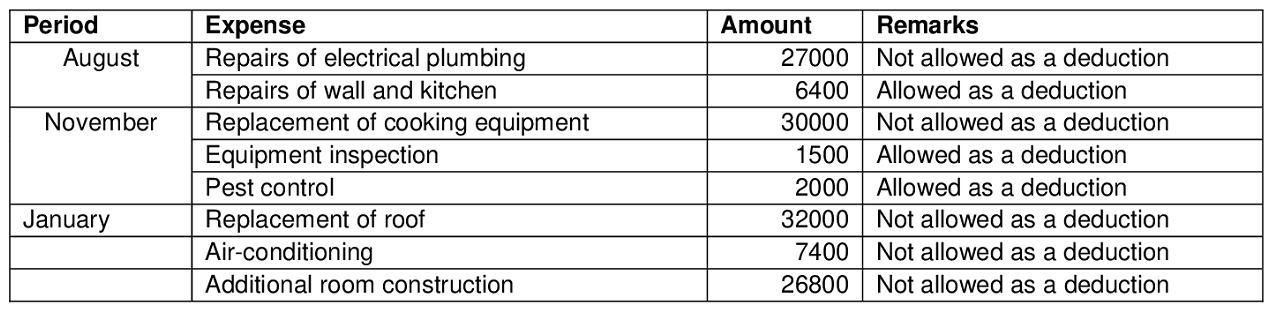
(i) The taxpayer incurred $ 27000 On the political and plumbing expense of the asset such damages and defects of the property were in existence when the asset was acquired and also the damages result from the previous owner and not with the actions of the Taxpayer. Since the expense of $ 27000 is an initial repair expense therefore according to the applicable laws such expense should be capitalized as a part of the cost of the asset and depreciation is allowable thereof (Anonymous. 2020).
(ii) Expense of $ 6400 Incurred for wall and kitchen – such expense is a revenue expense because they are damaged with the act of taxpayer and this is a revenue expense and revenue repairs that are associated with the building and therefore such expense is not considered a capital expense and deduction with respect of the same is allowable.
Expenditure incurred for November 2020
During the month of November, the taxpayer has incurred three types of repairs expense those are as follows-
(i) In the current month the taxpayer has incurred the expense of $ 30000 for the replacement of the cooking equipment that will increase the efficiency of the operations of the organization, therefore such expense is not repaired they are called as improvement and therefore such expense is capitalized in the books of accounts and depreciation is allowed on the same.
(ii) $ 1500 has been paid for the equipment inspection, equipment inspection is a revenue nature expense and therefore it can be considered as the revenue expense and charged against the income of the business organization, and deduction si allowed of the same expense.
(iii) For a compilation of health and safety standards the restaurant must conduct a pest control for every year, therefore such expense is a type of revenue expense and deduction in respect of the pest control expense is allowable for the business (Batter, &Biscopink, 2019).
Expenditure in the month of January
In the month of January, two major expenses is incurred, $ 32000 is incurred for the purpose of replacement of the roof, replacement of the roof is a major expense of the organization. The expense is treated as an improvement and such expense is allowed to be added to the cost of the asset and proper depreciation has been charged on such asset.
Expenditure incurred for the purpose of construction of additional rooms are a type of improvement of the building. and therefore such expenses incurred for the purpose of construction of additional rooms are of a capital nature and deduction is not allowed for the same expense incurred for the purpose of construction of additional rooms.
Conclusion:
From the above discussion, it can be concluded that the following amount is considered as an allowable deduction or the following amount is not allowed as the allowable deduction
Question: 2:
Legislation related to the case:
Definition of capital Gains – Capital gains and capital losses are gains and losses that are arrived in the capital gain tax event of the capital gain assets, if during the capital gains event if consideration price of the capital asset is higher than the cost of the capital gain asset or the indexed price of the cost of the capital asset, on the other side of the cost of the asset or the index price of the cost of asset if higher than the consideration of the capital asset, than there will be a capital loss of the assets (Healy, 2017).
Any capital asset that is acquired before 20 September 1985 or specified under the exempted assets is not liable to be any Capital gains tax.
Steps to calculate the capital gain or loss- For the purpose of calculation of the capital gains tax, the capital gain or loss should be first calculated, there are different steps that must be followed for the purpose of calculation of the capital gain or loss from the capital asset-
Step 1: the identification of the fair value of consideration is the first step for calculation of the capital gains, in the case of sale the exchange amount is the FVOC, or in the case of an exchange, the fair value is considered as the fair value of the consideration.
Step 2: After identification of the consideration price of the asset, the second step for the purpose of calculation of the capital gain is to calculate the cost base of the asset. The cost base of the asset is derived by including the acquisition cost of the asset along with any indexation if required. For the assets acquired before 20 September 1999 the indexation method is applied for the purpose of increasing the cost base (Pattison-Gordon, 2017).
Step 3: After identifying the proceeds of the capital assets and identification of the cost base of the asset. The cost base of the asset is being deducted from the proceeds of the capital gain event the difference comes positive then it is considered as the capital gains and if in any other case of the difference comes to negative then it will be considered as the capital loss.
Step 4: For every capital gain event, the same process till step 3 is being followed.
Step 5: Combine the capital gains and capital losses of each capital gain asset sold during the tax period.
Step 6: Adjust the previous year's cumulative carried forward losses.
Step 7: The net capital gain is taxable at the applicable rate and if the net capital loss is there then it is forwarded to the future tax period for the purpose of adjustment in the future years.
Calculation:
In the current tax period, the taxpayer has sold various capital gains assets the treatment of the capital gain and the capital loss from the capital gains asset is as follows-
Capital gains / Loss from sale of the home - Home is covered under the exempted list of the assets to be sold therefore in case there is a sale of the home to the other person such sale is not liable for the capital gains tax.
Capital gains / Loss on sale of FUL shares – The taxpayer acquire the shares of the FUL shares before 20 September 1985, therefore such sale of shares are not covered in the capital gains and capital loss, and the capital gains and loss are not liable for such sale of FUL shares.
Capital gain / Loss on the furniture sale – The furniture in the current case is acquired in 2010 at a cost of $ 10500, the said furniture is being sold at $ 5000. As the asset is being used for private purposes and there is no depreciation on such asset, therefore, the capital loss in the current case is $ 10500 - $ 5000 = $ 5500.
Capital gain / Loss on Yacht – In the current case, the taxpayer held the Yacht, for less than 12 months therefore the indexation and 50 % deduction is not allowed, therefore the capital gain on the sale of yatch is as follows-
Proceeds from the Yacht = 37000
Cost base of the assets = 25000
Tax on sale of yacht = 12000
Capital gain/loss on sale of land –
The taxpayer sold the block of land at a proceed of $ 465000, the cost price of the asset is $ 100000 and during the holding period of the asset, the taxpayer has incurred a cost of $ 110000. The capital gain on sale of a plot of land is as follows-
Capital gain as per indexation method
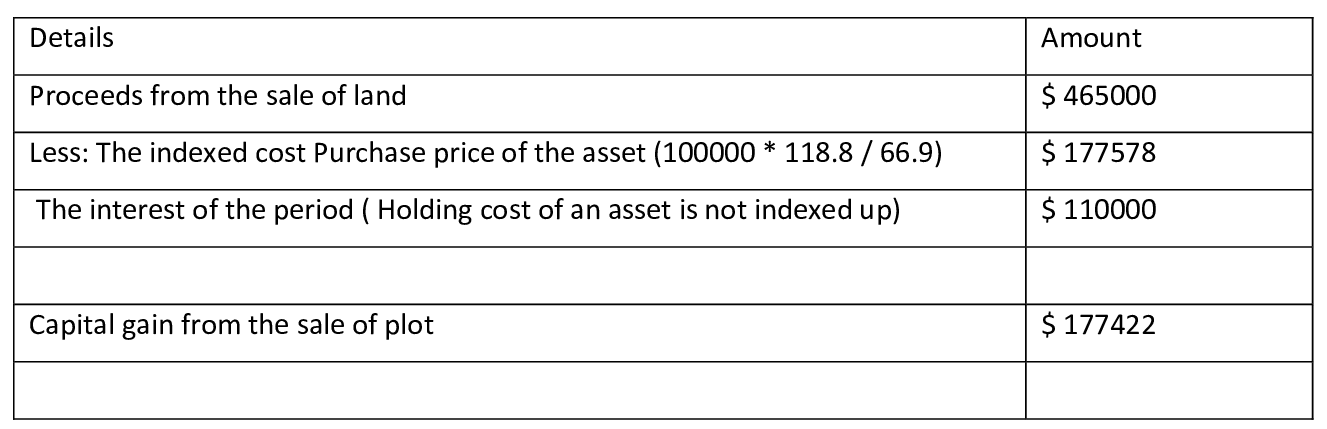
Capital gain as per 50 % CGT discount method
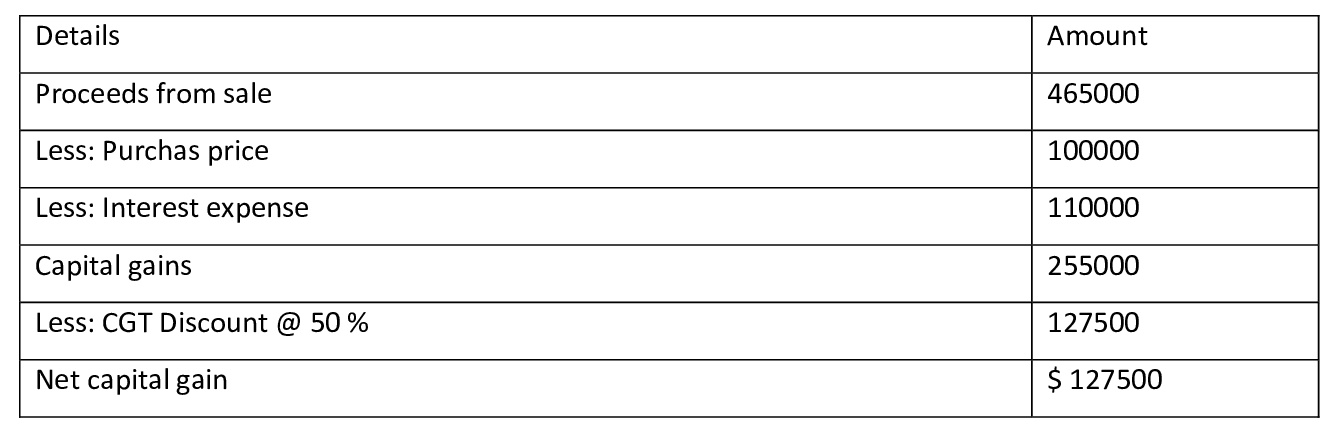

In the current case since the capital gain is less in the 50 % CGT discount scheme, therefore, taxpayer should adopt this scheme (Anonymous. 2019, pg 12(3)).
Capital gain / Loss from collectibles –
Loss of collectible will forward for future years and cannot be adjusted with other capital gains.
Previous year's capital loss of shares will be adjusted in a capital gain of the current year.
Net Taxable capital gains / Loss-
The net taxable capital gains / Loss is as follows- (5500) + 12000 + 127500 + (5000 )
= 129000
References
Anonymous. (2019). Arkansas: income tax: casualty loss deduction denied for failure to establish the pre-casualty fair market value of the real property. State Tax Review, 80(5), 2–3.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/7985344152
Anonymous. (2020). A renewed chance to revisit old assets for repairs and maintenance expenses. The Tax Adviser, 51(4), 236–237. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/8672699797
Batter, A., &Biscopink, E. (2019). Notice 2018-99 and the deduction disallowance for employer parking: the straw that broke the camel's back. Corporate Taxation, 46(3), 23–26.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/8181362429
Healy, B. (2017). Tax incentives for business owners. Businesses, 34(16), 37–57.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/7245418371
Pattison-Gordon, J. (2017). Millionaires' tax clears the legislature. The Boston Banner, 52(47), 1–7.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/8932426426
Property investors benefit from 'repair' year-end deduction. (2017). Spokesman-Review, E.2, 2.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/7250793193
Razak, S. H. A. (2020). Zakat and waqf as instrument of islamic wealth in poverty alleviation and redistribution. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy, 40(3-4), 249–266. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSSP-11-2018-0208
Weltman, B., & J.K. Lasser Institute. (2018). J.k. lasser's small business taxes 2018 : your complete guide to a better bottom line. John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved October 20, 2021.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/v2/oclc/1012132648
LAW6000 Business and Corporate Law Assignment 2 Sample
Assignment Brief
Length: 2000 words +/- 10%
Learning Outcomes
This assessment addresses the following subject learning outcomes:
a) Demonstrate a sound comprehension of the essential elements required to create, manage and discharge a contract and assess the remedies available for breach of a contract;
b) Examine legal principles related to the creation and operation of various forms of business organizations and critically evaluate their effectiveness across a range of business scenarios.
c) Explain the processes for incorporating, managing, and winding up a company, including key director duties, the importance of the Corporations Act 2001, and the role of regulatory bodies.
d) Evaluate the role of agency in contract formation for different business vehicles and identify the associatecd risks such as vicarious liability for negligent acts.
e) Employ legal skills (statute law and case law), critical reasoning, and make informed judgments as to likely legal outcomes of a range of business scenarios.
By 11:55 pm AEST/AEDT Sunday of Week 9 (Module 5.2)
Weighting: 25%
Total Marks: 100 marks
Context:
This assessment allows students to solve practical problems that arise from a fact scenario and to give appropriate advice to clients.
Instructions:
There are five case studies for case study assignment help you are required to critically analyse. With respect to each case study:
? Identify the legal issue(s) arising from the facts of the casestudy
? Identify the appropriate legal rules that requires discussion in the case study
? Apply the law to the facts of the case study
? Reach a conclusion/ give practical advice to your client.
Your analysis should refer to appropriate cases and statutes and be referenced using the APA
Reference system.
Submission is through SafeAssign by 11.55 AEST Sunday of Week 9 of the relevant trimester
Question 1 (20 marks)
James has recently decided to open up a consultancy business near the city. He has identified appropriate premises and immediately gets into negotiation with Bradley, the landlord. He wishes to lease the commercial property for a period of five years. James proposes to demolish some of the interior walls to allow for better lighting and to then fit out the space to suit the modern image that he desires for his business. James and Bradley agree that the work would be completed in one month. It is agreed that once a lease agreement is signed James can commence the work in preparation to move into the premises.
James signs his part of the agreement and sends it to the offices of Bradley’s solicitors. He then commences the work to demolish the walls and fit out the premises. Three weeks later as James was about to complete the fit out of the premises, he learns that Bradley has yet to sign the agreement and has in fact entered into negotiations with Simon with a view to leasing the premises to Simon.
James has completed a substantial amount of work and is preparing to move in. He has in fact printed all his stationery. He approaches Bradley who says that there was in fact no contract and that he is likely to lease the premises to Simon. James is distraught and seeks your advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles, use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise James on whether he is able to enforce the agreement with Bradley and the remedies that may be available to him.
Use appropriate case law in support of your answer.
(20 marks)
Question 2 (20 marks)
Elizabeth is a major shareholder in Millennial-Relics Pty Ltd. Elizabeth and has noted that the company maintains the old-fashioned ‘memorandum of association’ which has been prepared for Millennial Relics Pty Ltd.
The objects clause as drafted, limits the objects of the company to the development, manufacture and sale of motor vehicle batteries. Elizabeth believes that the research work that Rahim is doing (and future technology which may be developed as the full implications of Rahim’s work are realized) may have spin- offs into a number of related areas including dynamos for driver-less electric cars.
Elizabeth has spotted an opportunity that may allow the company to enter into a contract with like-minded companies for the development of state of the art dynamos that will be compatible with all types of electric cars. She is however concerned that the narrowness of the ‘memorandum’ may hamper the company’s ability to move into the emerging lucrative area and also the development and commercial exploitation of the dynamos which the company’s ongoing research may uncover may not be pursued lawfully.
Elizabeth has read that there is no legal reason to have a memorandum or articles, even if they are now called a corporate constitution. The company’s research may also expose potentially exploitable products or secret processes in other areas related to artificial intelligence. When Elizabeth raised these concerns with the company’s other shareholders, they told her that they had been advised by the lawyers that this was the standard form for their companies, and that there was no cause for concern. Elizabeth is not convinced.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Elizabeth of the company’s position regarding any new contracts that it may enter in connection with the development of dynamos for driver-less electric cars and also explain how the replaceable rules may be of use to the company in the future. (20 marks)
Question 3 (20 marks)
In December 2020 Greg Napole was driving along a busy street with his spouse and two children in the car.
As they approached a busier section of the road Greg had to slow down significantly and as he was driving past a nearby park, a southern blue gum tree fell onto the car that he was driving killing wife Marsha and seriously injuring his two children and himself. Greg and his two children were hospitalised for two months with several broken bones. Upon recovery, Greg learnt that the tree had fallen because its root system had been destroyed by underground water leaking from a water channel that had been constructed by the local council, City of Small-town Council, in the year 1998. Greg is keen to have the council compensate him for the injuries he and his children have suffered and for the loss of his wife.
The local council has denied liability. They claim not to have a duty of care to Greg and his family. Greg wishes to pursue his claim and has now come to you for advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Greg as to
whether he would be successful in negligence against City of Small-town Council. Please explain fully, using relevant case law. (20 marks)
Question 4 (20 marks)
Jaswant and his two friends, Davinder and Lachlan have been in a partnership for the last three years. Their business has grown and they now wish to expand into other states and territories. Their other friend Nicholas is a solicitor and he advises them to incorporate their business under the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) to take advantage of the principle of separate legal entity and to allow them to trade in any state without having to comply with local partnership legislation. Jaswant, Davinder and Lachlan have brought in some of their own assets into the business and their partnership agreement specifically states that the assets will remain their individual property. They are concerned that they may not be able to do this after incorporation. They are also concerned about whether they will be able to contract with the company for the provision of some of the services the national business will be delivering. They each have specialist skills and are hoping to be remunerated by the business for their skills.
The three friends have also agreed to appoint Nicholas as the company solicitor and would be the only solicitor used by the company. This would be set out in the constitution that Nicholas would draw for the company. Lachlan is however concerned that if their relationship with Nicholas becomes strained, it may be difficult to use another solicitor if he chooses to enforce the constitution. Lachlan now approaches you for advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant sections of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) and appropriate case law, use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Lachlan of the effect and consequences of converting their partnership into a company and further whether Lachlan would be able to enforce the envisaged constitution if they wanted to use a different solicitor. (20 Marks)
Question 5 (20 marks)
Rahab is an executive working for a large pharmaceutical company which has recently transferred her to an overseas branch to manage the roll out of a global vaccine. She decides to leave the apartment Where she lives and to put her household goods in storage. She contacts a company known as KingStore Pty Ltd, Which specialises in the storage of goods. The company agrees to store Rahab’s goods for the period she will be away.
Before signing the contract of storage, Rahab asks about the condition of the building in which her goods will be stored. She has heard about recent floods in the state and just wants to be sure that her be safe. The company manager replies: “Our building is in excellent condition. We built it only two years ago and we used the best building materials. Your goods are safe with us.”
Rahab decides to enter into a written contract with the company and stores her goods with them. The contract which she signs does not, however, say anything about the condition of the building, nor does it make any reference to the other statements made to Rahab by the company manager concerning the quality of the building materials.
Some months later, the company telephones Rahab at her new place of work and advises her that her goods have been badly damaged due to recent heavy rainfall which caused water to enter the building in which Rahab’s goods have been stored, and to damage them. The reason for the entry of the water into the building is that the building was badly built and poor building materials were used. As a result, the building’s foundations sank when the heavy rainfall fell, thereby causing a large gap between the bottom of the doors to the building and the floor of the building where the goods were stored.
Rahab now wants to sue the KingStore Pty Ltd for the loss she has incurred as a result of the damage to her goods.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Rahab
Of her legal position at common law against the storage company and discuss what remedies would
flow from them. Give full reasons and use any relevant case law. Do not consider any statutory rights.
Solution
Question 1
Issue
Whether James can enforce the agreement entered with Bradley. If yes, then what are the remedies that can be availed by the James?
Rule
In Australia, in order to formulate a legal binding contract there must be presence of all the contract essentials which includes an offer, an acceptance, a consideration, the legal intention of the parties and the legal capacity of the parties. When there is a valid contract, then, the parties must comply with the contractual terms (Wong, 2017).
Now, at times an agreement is established between the parties which is subject to the formation of some formal contract. At times one party to the contract signs the agreement but the other party did not do so and decides to finalise the contract at some future time or date. In Masters v Cameron (1954) it was held that if the intention of the parties portrays that they wish to abide by the terms of the agreement, then, it makes no difference whether a formal contract is prepared or to be prepared at some future date or that the agreement would be signed at some later event. As per Baulkham Hills Private Hospital Pty Ltd v GR Securities Pty Ltd (1986) in such situations, there is a valid contract amid the parties irrespective of the fact whether a final draft is executed by the parties or not. If there is lack of intention, then there is no contract amid the parties. (Tolhurst, 2011)
Application
James wants to take on lease the premises of Bradley for five years. James and Bradley agreed that once the lease is signed amid the two then James is permitted to carry out the repair work within the premises which would take a month to complete and then move into the premises. James signs his part of the agreement and sends the same to the solicitors of Bradley, however, the same was not signed by Bradley. James commences the work and after three weeks he learns that Bradley is not willing to sign the agreement with him, rather, he is in negotiations with Simon.
It is submitted that by applying Masters v Cameron, the intention of both James and Bradley depicts that they intend to enter into a contract immediately as James was permitted to carry out the work at the premises and can then enter the vicinity. Also, James has signed the document and had completed his part of the obligation of the contract. Thus, the head of the agreement is intended to be abide by both the parties and thus Bradley cannot deny the enforceability of the contract amid James and Bradley.
Conclusion
It is thus concluded that there is a binding contract that exists amid James and Bradley and if Bradley did not abide by the agreement, then, it is considered as a breach of contract and James is liable to seek the expenses incurred by him for the repairs and compensation and damages for the stationery.
Question 2
Issue
Whether Elizabeth can enter into contracts which are beyond the object clause of the constitution of the company? How replaceable rules can be used in future?
Rule
Salomon v A Salomon & Co Ltd [1896] when any company is incorporated, then, the same acquires the status of a separate legal entity, that is the acts of the company are considered its own acts and the officers are not held liable for the same. In common law, as per Ashbury Railway Carriage & Iron Co v Riche (1875) the acts which are beyond the objects or powers of the company are held to be ultra-virus and thus not enforceable. However, as per section 125 of the Corporation Act 2001, no act by the company can be termed as ultra-virus even when the same is beyond the powers (object) of the company.Further, if there is no constitution, then, as per section 135 of the Act, the company can be run by the replaceable rules set under section 141 of the Act.
Application
As per the facts, Millennial-Relics Pty Ltd is a company in which Elizabeth is the major shareholder. The company follows its Memorandum of association. The object clause of the company only permits the company to the ‘development, manufacture and sale of motor vehicle batteries’. Elizabeth wants to expand the operations of the business to dynamos of driver less electric cars upon which Rahim is doing research but is restrained by the object clause.
It is submitted that if Elizabeth enters into contracts that are beyond the object clause, then, such contracts are not invalid as per section 125 of the Act 2001 and the company must honour the same.
Elizabeth can rely on the replaceable rules made part of section 141 of the Act to run the company in future.
Conclusion
It is concluded that even if Elizabeth enters into the contract that is beyond the object clause, still such contracts will held to be valid in the eyes of law.
Question 3
Issue
Whether the local council can be held negligent for the losses caused to Greg and his family?
Rule
When any defendant undertakes any acts or omission, then, he must make sure that no loss is caused to the plaintiff provided the plaintiff is his neighbour. To make any defendant negligent the main elements are:
i. The defendant is under duty to provide care to every plaintiff with whom he is sharing proximate relationship and who is reasonably foreseeable. The defendant must make sure that no harm of any kind should be caused to the plaintiff because of his acts and omissions;
ii. That if the duty of care is not comply with by the defendant, then the duty is held to be breached (Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad Co);
iii. It is necessary that because of the breach, there should be some harm caused to the plaintiff which is not remote and which is caused because of the acts of the defendant (Home Office v Dorset Yacht Co Ltd [1970].
Application
Greg Napole was driving along a busy street along with his spouse and 2 children in December 2020. While he was driving one tree fell on the car killing his wife and causing injuries to him and his children. They took medical aid for 2 months.It is submitted that the local council can be held negligent because:
i. It is the duty of the local council to ensure that any acts that are undertaken by them should not cause any kind of harm to any person who are their neighbours.
It is submitted that Greg was a person who was using the road like any other travellers and the local council is aware of the same. Thus, Greg and local council are neighbours of each other and Greg is reasonably foreseeable. Thus, Local council owns the duty of care towards Greg and any person who was travelling with him;
ii. The duty of care was not complied with by the council as the tree that was fallen on the car of Greg was because of root system of the tree was destroyed because of the water leaking from the Channel that was constructed by the local council. Thus, the level of care that must be taken by the council was met while making the Channel. There was breach of duty of care.
iii. The loss that is caused to Greg was because of the breach on the part of council and the loss is not remote in nature.
It is thus stated that the local council is negligent towards Greg and his family and the council must compensate Greg for the losses so caused to him.
Conclusion
The council is negligent towards Greg and his family and thus must compensate for the losses so caused to him.
Question 4
Issue
Advice Lachlan of the effect and consequences of converting the partnership into a company?Whether Lachlan would be enforcing the constitution if they wish to use a different solicitor?
Rule
As per section 124 of the Corporation Act 2001, upon incorporation, a company has all the powers that of an individual including the power to make contracts.
Application
Jaswant and his friends, Davinder and Lachlan are sharing partnership relationship from past 3 years. If a company is established then:
The main effects of a company
i. The main effect is that the company will become a separate legal entity, that is, the acts of the company will be considered to be its sole acts and no officer will be held personally liable for the same (Shum, 1991).
So, if the three friends operates a company, then the actions taken by them will be on behalf of the company and they will not be held personally liable for the same.
ii. Since the company will be a separate legal entity thus it has the potential to enter into contractual relationships and thus itscan contract for the services of the national business.
iii. Since all the three have special skills, thus, they can be employed by the company and will be reimbursed by way of salary by the company.
iv. Nicholas can be appointed as the solicitor of the company by entering into a contract of employment.
The main consequences of a company
i. If the three friends establish a company, then, the assets that are brought by them in the business will become the property of the company and will be used to settle the liabilities at the time of winding up. Thus, they cannot treat the property as their own.
ii. The company has to pay taxes which will be ultimately borne by the officers;
iii. There are lots of paper work and time consuming in the formation of the company.
Conclusion
It is thus concluded that establishing a company will benefit the friends as the company will be a separate legal entity and has perpetual succession. The company can make contract but it will be lots of money and time that will be invested in its formation. Also, if Nicholas is appointed as lawyer then he will be an employee and he can be removed by terminating the contract of employment.
Question 5
Issue
Whether Rahab will be able to sue the King Store Pty Ltd for the losses so caused to him because of the damage of the goods by rainfall?
Rule
In common law, if any one party to the contract makes a false statement with the intention that the other party enters into a contract with him, then, the contract suffers from misrepresentation and is not enforceable by law. Any aggrieved party has the right to terminate the contract and sue the other party for damages as the contract was based on misrepresentation (Beever, 2007).
Application
Rahab was transferred to an overseas branch to deal with the roll out of a global vaccine. She left her house and put the goods in storage of a company King store Pty Ltd. The company specializes in storage and assured Rahab that their building is excellent and was built 2 years ago and is made with the best building material. That the goods will be safe with them.
Rahab decided to store the goods, however, nothing regarding the promises made by the company was mentioned in the contract. After few months, the company informed Rahab that the goods so stored were damages because of the heavy rain. The reason for the damage was that the building was badly built with poor quality material.
It is submitted that when the contract was made then the company knowingly made a representation that the building wasw made with a good quality material which in fact was not true. The false statement was made with the intention that Rahab enters into a contract with them and thus there was a misrepresentation made on the part of the company towards Rahab (Ciro et al., 2019).
So, Rahab can terminate the contract and seek damages.
Conclusion
It is thus concluded that Rahab can sue the company and seek damages for the losses so caused as the contract that was made amid them was based on misrepresentation.
Bibliography
Books/Articles/Journals
Beever, A. (2007). Rediscovering the law of negligence. Hart. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/496273579
Ciro, T., Goldwasser, V., & Verma, R. (2019). Law and business ebook (5th ed.). Oxford University Press Australia. https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.torrens.idm.oclc.org/lib/think/reader.action?docID=5979408&ppg=1
Shum, C. (1991). Business associations : an introduction to agency, partnership and company law (2nd ed., Ser. Hku press law series). Hong Kong University Press. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/650877514
Tolhurst, G. J., Carter, J. W., &Peden, E. (2011). 'masters v cameron' - again! Victoria University of Wellington Law Review, 42(1), 49–64.https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/4822652359
Wong, A. (2017). Company law. (E. Chapple, Ed.) (First). Wiley. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/1040039461
Case laws
Ashbury Railway Carriage & Iron Co v Riche (1875) L.R. 7 H.L. 635
Baulkham Hills Private Hospital Pty Ltd v GR Securities Pty Ltd (1986) 40 NSWLR 622 (SC).
Donoghue v Stevenson [1932] UKHL 100;
Home Office v Dorset Yacht Co Ltd [1970] UKHL 2, [1970] AC 1004
Masters v Cameron (1954) 91 CLR 353.
Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad Co., 248 N.Y. 339, 162 N.E. 99
Salomon v A Salomon & Co Ltd [1896] UKHL 1.
BUS1006 Business Law Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Due date: Week 7
Group/individual: Individual
Word count/Time provided: 2500 words
Weighting: 30%
Unit Learning Outcomes: ULO4 & ULO5
Assessment 2
Students must search Australian legal databases and find a court decision that has been decided over the past few years. The court decision must be on legal issues that arise on contract law. Once you have chosen a relevant court decision, you must critically review the decision. In critically reviewing the decisions, you must address the following points:
- Summarise the facts of the case for assignment help
- Identify the legal issues
- Analyse the applicable laws and discuss the relevant aspects of contract law which are applied on the case.
- Critically review the decisions
Apart from critically reviewing the court decisions, students are required to do a literature review on the relevant contract law principles or rules. In that, an in-depth discussion must be included on the meaning, scope, and application of the relevant aspects of contract law.
Solution
Introduction
The criteria of Contract Law are mainly defined as the agreement between two individuals, people and businesses. If someone doesn't follow the agreement, then it is definitely termed as a breach of contract in the negotiation of legal terms legislations. The criteria of contract law also help to exchange major promises between two people in order to manage the affordability of obligations recognised by the enforced laws in a very optimised manner. In this study, a specific Australian court decision will be selected based on the legal issues of contract law. The selected court decision for this study is the High Court of Australia Bulletin [2021] HCAB 5 and it is significantly related to the execution of contract law based on the decision of anti-tendency direction.
Literature review on relevant contract law
Concept and scope of contract law
The idea of contract law is significantly referred to as the passing of unique promises between two or more individuals by following the rules and norms of legal entities in a very reliable and viable manner. The implication of contractual legal entities can easily follow the agreement between new sponsored business partners in a very reliable and viable manner. The major laws used in this specific case study mainly include constitutional law, criminal law and industrial law based on the implication of the High Court of Australia Bulletin (Amigud and Dawson, 2019). The accommodation of industrial law is mainly based on the agreement of enterprises that can be very useful to viably detect serious misconduct of code through the help of certain disciplinary actions in a more meaningful and viable manner. In industrial law, the breach code can be easily identified with the validity of breach of conduct through the help of new business knowledge based on cases of contravened EA in early intervals of time (Awdry and Newton, 2019). In the context of industrial contract law, the respondents are significantly required to append for the proceedings of federal circuits that mainly deals with the valid implication of sources based on the proper conduction of legal codes and authorities in a very suitable manner. According to the actions of Industrial Law in the given case study, almost 56% of casual employees are required to be resituated based on the satisfaction of leave entitlements with the valid negotiations of Fair Work Regulations At of 2009.
Principles of Contract Law
In the country of Australia, the optimum intention for the development of legal relations can be easily confined with the help of valid contract law. Meanwhile, the four major principles of contract law in Australia are Acceptance, Legal Obligation, Meaning and Elements (Bretag, 2019). In contract law, the criteria of acceptance deliberately occur when one party mainly attends the quality of the other party based on the implication of a new research plan and tactics on a reliable basis. The overall optimisation of compliance also helps to generate new amounts of money with the integration of authentic business systems that can be functionally categorised through the growth of new business management systems on a daily basis. The acceptance of a reliable contractual agreement will be done based on the negotiation of agreement papers by following the implications of rules and legal items for future prospects.
The major principle of contract law can also be used to measure the reliability of the concept of return on benefits. On the other hand, the criteria of legal obligations are mainly defined as those duties in which each party is legally contracted with the agreement of sources based on the money of products and exchanges for future activities. On both sides, the implication of legal obligations is required to be disputed through the exchange of productive tools and agreements by following the laws of the Australian government (Crosweller and Tschakert, 2021). The connections of major exchanges can also be easily deliberated by following the mandatory legal actions based on the implications of a lawful basis.
On the contrary, the meaning in contract law is mainly defined as the simplest definition of planning that can be used to functionally result in the requirements of legal access to a person based on the valid execution of mutual assent of disputes in a very predominant and reliable manner. Furthermore, the elements in contract law of Australia are mainly known to be mutual assent and consideration that can be used to viably implicate the authorisation of resources in a very reliable and viable manner with the implication of new business resources and tactics on a formal basis in the future (de Rochefort-Reynolds, 2020). According to this given case study, the major case laws used in terms of the negotiation between two parties in terms of contract mainly include Palmer v the State of Western Australia, Edwards v The Queen, Deputy commissioner of taxation v Shi and Hamilton v The Queen (Draper and Newton, 2017). In this given case study, the implication of industrial law is suitably based on the limited validation of enterprise agreement through which the prosperity of the legal code of conduct can be easily determined in the future. The reliability of new business tools and deliberations can also be judged based on the valid stability of business respondents in order to manage the special working holiday tax rate whose value is up to $3986 AUD.
Applications of Contract Law
The application of contract law is that it viably helps to exchange the authorisation of economic goods and services in the country of Australia. This law also helps to deal with the negotiation of sponsored partners that helps to mitigate the breach of the contract throughout the authorised meetings of minds by elongating the terms of the contract in the future. Meanwhile, the validity of legal documents is another application of contract law that deals with the implication of source based on the capacity as well as the viable legality of systems in a very suitable manner (Feinerman, 2019). According to the given case study, the main application for the perseverance of contract law is Immigration.
The criteria of immigration mainly help to implement the criteria of non-refoulment obligations in which granted refugee and humanitarian can also be negotiated through the execution of Global Special Humanitarian based on the implication of 12 months of imprisonment for the breach of contract in Australian subcontinents. As per the given case study, the other application of Australian contract law is the delegation of plaintiff procedural fairness under the valid assumption of the Mitigation Act (Harpur, 2018). This law is only applied after the decisions made by the constitution of the ministry for the optimum integration of large business resources in the future. Moreover, the valid applications of authorised contractual agreements can be negotiated through the help of non-revocation decisions made with the validity of pursuant to s 501CA (4).
Summarise the facts of the case
The case study named High Court of Australia Bulletins is mainly focussing on the implication of Australian contractual cases that are being decided and reserved for the purpose of judgement. This particular case study also provides valid information about the Court’s Original Jurisdiction by mainly granting a special and predominant leave to appeal based on proceedings and vacated in a very reliable and viable manner (Hemming and Daniel, 2018). In this case study, major laws that are being discussed mainly include constitutional law, immigration law, criminal law and industrial laws of Australia. In the study, the description of hand down cases by the High Court of Australia in June 2021 based on the association of legal terms and laws has also been provided. Moreover, this particular case also summarises the facts of aliens, deportation, duty to remove, vesting of judicial power and false imprisonment. In this case study, the idea of breach of contract in Australian legislation has also been provided that mainly helps to grant visas limited by implications in the future.
This study also provides a brief description of the case law named Commonwealth of Australia v AJL20. This particular case study also summarizes the facts of constitutional laws that are being implied by the freedom of communications on the behalf of foreign principal activities on the provision of a legitimate purpose in order to determine the breach of contract in the future (Hile, 2021). According to Migration Act 1958, the removal of the concerns of non-citizens in Australian residents can be widely deliberated through the removal in accordance with the Act in order to maintain the mortgage that is being extinguished due to the breach of contract.
Identification of legal issues
In this case study of the High Court of Australia Bulletins, the issues related to the Corporations Act of 2001 has been noticed by this limited assurance of leased engines and leaving engines and authentic engine leases for the major implications of third party activities. Meanwhile, the legal issues related to the effective consolidation of new breach of contract can be viably utilised that can be implicated by the formation of the Court of Appeal. This mainly results in the emergence of issues related to the implication of contested credibility within the business. The overall implantation of inadmissible and prejudicial evidence can be viably determined through the substantial miscarriage of justice in the future (Matulionyte, 2019). The implication of justice mainly helps to maintain the overall delegation of resources based on the authentic stability of criminal law and justice.
Moreover, the other legal issue systematically related to this specific case study is the 5 years’ minimum penalty of jurisdiction that is being implied by the magistrate of the district court in suitable intervals of time. On the other hand, the issue of unconscionable conduct of respondent lenders can easily cause the manual implication of breach of contract to appeal the findings of the primary judge within the navigation of future prospects (Schmulow and O’Hara, 2018). The other issue is the major apprehension of biases all around the courts that can be easily justified with the help of a hypothetical observer on a formula basis. On the other hand, the other legal issues of this case study mainly include the trial of the judge made through the implication of the interlocutory interpretation decision that is being punctually exhausted after the judgment made by the Australian Court in the future. Moreover, the issue of jurisdiction under the power of the primary judge can help to measure the affordability of legal contractual exercise between the two parties in the future.
Applicable laws and discuss aspects of contract law
In the case study of the High Court of Australia Bulletins, the major laws used are criminal law, industrial law, constitutional law, tax law and industrial law. In this study, the major implication of constitutional law is mainly to define a certain case law of the Australian Court named Commonwealth of Australia v AJL20 (Sherborne, 2017). In this case, the main judgement was delivered on 23 June 2021 through the execution of false imprisonment of people with the tactical execution of new business growth and technique in a very reliable and viable manner. The execution of new business formats can also be used to maintain the optimum integration of the latest business style and techniques based on the optimum configuration of Chapter III of the constitution in several business concerns with the attribution of contracted features in the future.
The constitutional law can be used to mainly impose the conflicts within the registration obligations that can be used to measure the holding of Conservative Political Action Conference with the negotiation of breach of contract in the future. On the other hand, the implication of constitutional law can be utilised through the methods of state legislative powers based on the implication of alternative sources with the prospects of Federalism (Sherman and Bosse, 2018). According to the Criminal Law of Australia, the foresight of profitability of consequence can be easily measured with the case-law of Aubrey v The Queen (2017) 260 CLR 305. This case law significantly helps to measure recklessness with the indication for the breach of agreement in the future (Steel, 2017). On the other hand, the tax law has also played a significant role in this case study by mainly pursuing the case law named Deputy Commissioner of Taxation v Huang. Moreover, the optimum practice of freeing order helps to determine the persuasion of Australian Foreign Assets that helps to seek judgement among well-renowned respondents for the attribution of Federal Court Rules in 2011.
Furthermore, the relevant aspects of contract law applied in this case study mainly include casual employees, privity of contract, declaratory relief and judicial power of the commonwealth. The implication of contractual matters can help to maintain the delegation of new business resources that results in the practical enforcement of new terms and agreements in the future. The authorisation of privity terms can also be used to respect in the negotiation of third party contracts with the doctrine of enforceable rights and desirable controversies of liability in the future. In this case of contact, the case law used to replicate the breach of contract mainly include the optimum mechanisms of judgements with the implication of Hobart International Airport Pty Ltd v Pacific Airports (Ullah and Al-Turjman, 2021). The attribution of payable amount can also be negotiated between valid appellants that helps to configure the cases of strong contractual business sources in the future. On the other hand, the corporations of insolvency will help to mandate the optimum benefits of contributors that can be obtained with the ASIC authorises of the person in the future. The suitable implications of NSW courts can be easily appealed through the raising of paying purpose among individuals during the effective time frame of the contractual agreement in the future.
Critically review the decisions
In this particular case study, some accurate and some falsified decisions have been made on the basis of behaviour concerns of non-citizens in the country of Australia. In the case-law of Migrant Services v Moorcroft, the huge had made wrong decisions related to the integration of contracts and based on the agreement of Migration Act of 1958. This decision is false as the agreement between two major parties has been cancelled and the third party cannot remove the implication of hard consequences in the future. On the other hand, the case of Chetcuti v commonwealth of Australia has also provided a valid limitation of action based on the exclusion of agreements between users (Whincop et al. 2018). Moreover, the decision of the judge in this case law is accurate due to the implication of the naturalisation of aliens in the country of Australia. The breach of contract was done with the navigation of British Subjects in the major colonies of 1949. Moreover, the formal and authentic justification of this court decision can be effectively managed through the constitution of power management in the future. In the end, the case law of Mineralogy Pty Ltd v The State of Western Australia, the court judge has decided the defendant of agreement relations between two business sources based on the optimisation of Amendment Act of 2020.
Conclusion
Hence, it is concluded that implication of Australian databases has been used to select the case study of High Court of Australia Bulletins that has mainly made the decisions of anti-tendency direction with the specifications of case laws. In the end, valid decisions have been made related to the original jurisdiction of the court based on the implication of constitutional laws and immigration acts from this case study.
References
Amigud, A. and Dawson, P., 2019. The law and the outlaw: is legal prohibition a viable solution to the contract cheating problem?. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education.
Awdry, R. and Newton, P.M., 2019. Staff views on commercial contract cheating in higher education: a survey study in Australia and the UK. Higher Education, 78(4), pp.593-610.
Bretag, T., 2019. Contract cheating will erode trust in science. Nature, 574(7780), pp.599-600.
Crosweller, M. and Tschakert, P., 2021. Disaster management and the need for a reinstated social contract of shared responsibility. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, p.102440.
De Rochefort-Reynolds, A.J., 2020. Confused Seas: Identifying the Proper Law of Arbitration Agreements in Maritime Contracts-England, Singapore and Australia. Austl. & NZ Mar. LJ, 34, p.1.
Draper, M.J. and Newton, P.M., 2017. A legal approach to tackling contract cheating?. International Journal for Educational Integrity, 13(1), pp.1-16.
Feinerman, J.V., 2019. Legal institution, administrative device, or foreign import: The roles of contract in the People's Republic of China. In Domestic law reforms in post-Mao China (pp. 225-244). Routledge.
Harpur, P., 2018. Australia-The Licensing of Temporary Agency Work Arrangements: Australian Labour Hire Licensing Acts and the Regulation of On-Hire and Gig Work. American Bar Association, Section of Labor and Employment Law, International Committee Newsletter.
Hemming, A. and Daniel, M., 2018. Halsbury's laws of Australia: contract GC I_II_V. Update of contract GC I, II, and V.
Hile, J., 2021. Dude, Where’s My Data? The Effectiveness of Laws Governing Data Breaches in Australia. Journal of Telecommunications and the Digital Economy, 9(2), pp.47-68.
Matulionyte, R., 2019. Empowering authors via fairer copyright contract law. University of New South Wales Law Journal, The, 42(2), pp.681-718.
Schmulow, A.D. and O’Hara, J., 2018. Protection of Financial Consumers in Australia. In An International Comparison of Financial Consumer Protection (pp. 13-49). Springer, Singapore.
Sherborne, A.K.E., 2017. Restitution in the conflict of laws: characterization and choice-of-law in Australia. Journal of Private International Law, 13(1), pp.1-34.
Sherman, B. and Bosse, J., 2018. Regulating access and benefit-sharing in Australia. International Workshopon Access and Benefit-sharing for Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, p.89.
Steel, A., 2017. Contract cheating: Will students pay for serious criminal consequences?. Alternative Law Journal, 42(2), pp.123-129.
Ullah, F. and Al-Turjman, F., 2021. A conceptual framework for blockchain smart contract adoption to manage real estate deals in smart cities. Neural Computing and Applications, pp.1-22.
Whincop, M.J., Keyes, M. and Posner, R., 2018. Policy and Pragmatism in the Conflict of Laws. Routledge.
CLWM4000 Business and Corporations Law Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Word Count - 2000 Words (+/- 10%)
Weighting: 30 %
Total Marks: 30
Submission: Via Turnitin
Due Date: Week 9
Your Task
Using the Case Study provided, you will need to undertake an analysis of the various legal issues that are identified, cite relevant rules applicable to the issues, explain the application of the rules to the facts/situation in the case scenario using the IRAC method.
Assessment Description
You are required to answer the following three (3) questions, based on the Case Scenario below
Assessment Instructions
• Your assessment is to be submitted via Turnitin in WORD format. “PDF submissions will not be accepted”
• You must follow the KBS presentation guidelines for assignment help
• Please refer to the assessment marking guide to assist you in completing all the assessment criteria and for information on the use of references and legal citations
CASE SCENARIO
Julia Brennan is an Australian Super Model who had started on an intensive fitness program to prepare for her new TV Commercial that will advertise a new type of gym equipment. She knows that she needs to be super fit. In addition to her fitness program, she decided to consultant dietician about what sort of food she should eat to accelerate her program. The dietician suggested that she have at least one protein smoothie every day. She had done a bit of research to find out what might be the best type of blender for her to buy. When she went to the local electrical store, she found that the only blenders that they had for sale did not meet her needs as they were no powerful enough for smoothies.
So, she decided that she needed to go to a larger store. She had heard good things about, the “Super Big Brand Store” so decided to go there to purchase a blender that met her needs. She was very happy to find that the blender was on sale at the “Super Big Brand Store” The Sale Sign stated “Buy it today and you will get 50% off” it is high quality, superb, safe and durable. You won’t regret it”.
When she went to the counter to pay for it, she was informed by the Sales Assistant that the blender was not on sale for 50% off as the Sale Sign had stated. The Sales Assistant told her “sorry that was yesterday, and I cannot give you 50% discount!
Julia was in a hurry and she just wanted to get started as soon as possible with her protein shakes, so she bought it and kept her receipt. She went back home, she plugged it in and as soon as the blender started the upper lid came straight off as did the sharp blender blades.
Unfortunately, the blades injured her right hand and she needed to go straight to the Hospital Emergency Department. The Doctor told her that she would need stitches in her hand, and she would be unable to use her hand for four weeks unless the cut had healed, and the stitches could be removed. Julia was very upset when she realized that she would not be able to participate in the planned TV Commercial and that another Super Model would have to take the job. She would also lose the $12,000 that was the agreed payment for the commercial.
Three weeks after the accident, Julia went back to the “Super Big Brand Store” to complain about the blender and about the injury to her hand finger! While she was waiting for the Store Manager, she noticed that the same Sales Sign was displayed “Buy it today and you will get 50% off” it is high quality, superb, safe and durable. You won’t regret it”.
She asked the Sales Assistant whether the blender was 50% off as the Sales Sign had stated. The Sales Assistant responded, “Sorry that was Yesterday”. She realized that the displayed Sales Sign did not mentioned the date, so it was difficult to figure out why the Sales Assistants kept saying “Sorry that was Yesterday”. She started to suspect that there was something wrong with the way that the store was operating. Instead of waiting for the Store Manager,
She decided to call a Solicitor from the firm “Injuries at Law” for legal advice.
QUESTION 1 – Contract Law (10 Marks)
• Please advise Julia, if she entered in a contract with the “Super Big Brand Store.”
o In your answer explain the meaning of Contract and which elements need to be satisfied to be in a simple contract and how to identify if this contract can be invalided.
o You will need to address all the “essential elements of a simple contract” including (Offer and acceptance, intention and consideration) as well as “elements of a valid contract” (Capacity, Legality, Genuine Consent, Mistake, Misrepresentation, Durres, Undue Influence and Unconscionability and explain if Julia can invalidate the contract.
o You will also need to address and explain what sort of remedies she will be entitled if she decides to void the contract under the Contract Law in Australia.
QUESTION 2 - TORT LAW (NEGLIGENCE) (10 Marks)
• Please advise Julia, if she has a claim under the tort of negligence.
o You need to address all the “essential elements under the tort of negligence”.
o You also need to address if the “Super Big Brand Store” has any defences under the tort of negligence.
o Explain what sort of remedies she will be entitled to claim under the tort of negligence in Australia.
QUESTION 3 – Australian Consumer Law (10 Marks)
• Please advise Julia, if “Super Big Brand Store” breached her Australian Consumer Law Guarantees under the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 (Cth) Schedule 2.
o You need to justify your view as to whether these guarantees are available. Don’t forget to explain if Julia will be entitled to claim the remedies and
o You also need to explain if the “Super Big Brand Store” will have to pay
SOLUTION
QUESTION 1
Issues in the prevailing case scenario
Present case scenario contained issue related with contract law. It is required to ascertain whether or not Julia has formed contract with the “Super Big Brand Store”?
Rules and regulations
A contract is a set of promises that are legally enforceable. Australian contract law is primarily governed by the ‘common law’. Some of the essential elements need to be satisfied for formations of valid contract are -
1. Offer and acceptance: When one party accepts the offer of another party it leads to the formation of a contract. Offer can be given to any single person or group of person, which can be observed in the case of Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co.
2. Legal relations: Contract is not just formed by acceptance of offer but there should be intention of parties for creation of legal relations (Tadros 2020).
3. Consideration: It is the price paid by one party to another; price is not just in terms of money but can also be in terms of risk, interest, rights.
4. Legally capable: Not everyone can enter into a valid contract, persons with issues related to legal consent like bankrupt, prisoners, mental issues cannot enter into a valid legal contract (Werbach & Cornell 2017).
5. Consent: These are the elements under the contract on which both the parties agree mutually it must avoid any miscommunication, misinterpretation, mistakes etc.
Apart from above aspects, a contract is invalid if these conditions are there:
1. Fraud has been committed.
2. Consent in the agreements is not understandable or not possible to be fulfilled.
3. Consent has been obtained through undue influence, duress, mistake, unconscionable conduct, and misrepresentation. In the case of Derry v Peek, contract is considered as void because consent is obtained through fraudulent misrepresentation (Clarke 2010).
One must have to convince the second party to agree on the contract if there is misrepresentation under the contract. Misrepresentation is an inaccurate statement which tries to persuade a person or a group to enter in the contract. It has no such effect until and unless the second party was aware of its existence. Further, duress takes place, when individual enter in a contract because of some force or violence their entry is not voluntary (Lamont, Stewart, & Chiarella, 2019). Undue influence occurs when an innocent party is threatened or misbehaved by the other party or even if someone is forced by their elders or any other ascend person for their own benefits is an act of influencing. In fact, a ‘mistake’ is something which exits but it shouldn’t have.
Remedies
Liquidated and damages Claims: Liquidating damages means providing a sum of money under a clause in contract for the breach to other party, further the sum mentioned above is not included in penalty. Damages could be viewed as replacement of the performance from the breached contract, which means a plaintiff is placed in a situation where he would have if the contract was performed correctly (Clarke, 2010).
Equitable Remedies: There are two main equitable remedies for breach of contract.
Specific performance – Under this the breaching party is ordered to perform in the way it was supposed to according to the laws. This order is laid only if the compensation could not be provided.
Injunctions – These are the order or you can say warning by court to not perform such breaches in contract.
Application
By application of above rules, it can be said that, there is valid contract has been formed between Julia and Store as all essential elements such as offer and acceptance, consideration, intention, and legal capacity has been satisfied. It should be noted that, there is violation of terms and conditions of the contract by Store as blender was not as per Sale Sign that states about its quality, safe, durable, and excellence. Based on this, Julia would entitle to claim remedies such as 50% discount on blender, medical expenses, and loss of income as damages under contract law designed in a manner to place plaintiff in a situation if the contract has been executed appropriately.
Overall, it has been concluded that, valid contract has been formed between Julia and Store. However, due to breach of terms and conditions by store, Julia can entitle to claim remedies from store.
QUESTION 2
Issues in the prevailing case scenario
Present case scenario contained issue related with tort law (negligence). In this, it is required to give advice whether or not Julia has a claim by application of tort of negligence?
Rules and regulations
Essential elements as per the tort of negligence are as follows -
Duty of care: It’s a legal responsibility to take reasonable care generally the scope of care not much it depends upon the relationship of the two parties. The duty of care involves the care which is not to harm intentionally or unintentionally to other party. In the legal case of Donoghue v Stevenson, it was held that, even if there is not any contractual relationship, an individual should be capable to sue another who assisted losses to them (Taylor 2020).
Breach: Under this the ‘duty of care ‘is breached that whether the occurred situation is reasonable or not, which means the plaintiff is not entitled to all the risks but if there is an obvious risk involved the plaintiff has to cover (Stoyanova 2020).
Causation: Under this the plaintiff has to prove that the injury which is occurred or the sufferings is the part of breach of duty of care. In the legal case, Amaca Pty Ltd v Ellis, there was inadequate causation to provide negligence.
Damages: The final element of the negligence is the damages. After the plaintiff proves the duty of care, breaching and causation they can receive the compensation for the loss.
The compensation is made on the basis of how the impact of lossinjury is on the plaintiff, like severity of injury, loss in financial terms or the impact of injury on the future of the plaintiff.
Defences
There are two defences a defendant can use where they are found liable for negligence:
Volenti non fit injuria: It means that the claimant has agreed that he had accepted the involvement of risk. Under this if the party successfully proved the acceptance he would not be liable for the loss (Armstrong 2019).
Contributory negligence: Under this the partial liability is taken away if the defendant can prove that there was the contribution of the claimant too in their losses.
Remedies for Negligence Claims
First remedy for negligence claims is the compensation. The claimant will be provided with the sum of compensation he had to suffer from the damages. Damages could be provided for both financial and non-financial losses (Gibbs Wright Litigation Lawyers 2020).
In case of personal injury, the claimant will be provided with additional damages like the loss of his income due to the injury or medical expenses (Eldar 2020).
Application
By application of above rules and regulations in the prevailing case scenario, it can be said that, Julia is eligible to claim as per tort of negligence as sales assistance owned duty of care towards Julia and due to violation of such duty of care, she has suffered from losses, and such losses was also not too remote. Further, there is not any defenses available to store as there is not any voluntary acceptance of risk by defendant and concept of contributory negligence would also not applied. Therefore, Julia would entitle to claim monetary compensation for the losses suffered by her along with loss of $12000 that was agreed payment for commercial performance.
Conclusion
Overall, conclusion can be drawn from above analysis that, Julia would be entitled to claim under tort of negligence and consequently remedies can be claimed by her, which includes loss of income as well as medical expenses.
QUESTION 3
Issues in the prevailing case scenario
Issue in the given case scenario is based on Australian Consumer Law. It is required to provide advice to Julia whether or not provisions of consumer guarantee as given in the schedule 2 of the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 has been violated by the “Super Big Brand Store”. In addition to this, suggestions should also be provided with respect to remedies of Julia and what is required to be paid by “Super Big Brand Store”.
Rules and regulations
Australian Consumer Law is explained in the schedule 2 of the Competition and Consumer Act 2010. As per the cited law, it is required by organizations to offer consumer guarantee for most of the products and services sold by them. It is essential that, organizations that are engaged in selling of goods must provide guarantee as explained in section 51 to 59 of the cited Act that such goods are –
• Goods must be as per the acceptable quality. It suggests that, products should be secure, has no mistake, seems acceptable, and performs all aspects that are expected generally.
• Goods should be appropriate for the purpose that customer made recognized to the company prior to purchasing.
• Goods should be described reliably (Bianchi 2018).
• Goods should be match as per demonstration.
• It should comply with any express warranty.
• They should have a clear title.
• There should not be any hidden charges.
• It should have repairing facility for a rational period of time except the advised is provided to customer otherwise.
If an organization sells goods to consumer that fails to fulfill above prescribed guarantee, then in such case, consumers are entitled for the remedies, such as repair, refund, replacement of goods, and monetary compensation for any significant losses, based on the situations (Pearson 2018). If the issue is significant or it could not be fixed, then in such case, customer can select to reject the product and gain a refund of whole amount or replacement of goods, or retain the product and avail compensation for the decrement in the value of product. In the legal case ACCC v Valve Corporation (2016), it was held that, Australian Consumer Law would also implement on the foreign companies. Therefore, company has liability for misleading customers through demonstrating that refund was not entitled to them and not including any guarantee connected to the quality of services.
Section 259 offers the right of Consumers to seek compensation for the losses sustained by them because of the issues in goods and services, consisting of repair, replacement, and refund of defective goods. Section 259(4) provides remedy for the consequential losses caused to the customer as a consequence of the issue in goods and services as decision is given in case of Barton v Transmissions and Diesels Ltd (Consumer rights obligation 2020). Normally; it is financial like expenses of repairing, transportation, inspection. Additionally, lost time and productivity could also be included in the damages.
Application
By application of above rules, it is advisable to Julia that Australia Consumer Law Guarantees has been violated by the store. It is because, there is implied guarantee given under cited Act, that goods must be as per reliable quality, however as soon as blender started by Julia, she has suffered from injury because store’s failure to comply with guarantee stated under the Act. It is mainly because of bad quality of blender. Since, problem in goods is major in nature, therefore Julia has right to reject the goods and obtain the refund of whole amount or replace the goods. She may also retain the goods and claim compensation for reduction in amount of goods. In addition to this, $12000 can also be claimed as it is consequential losses taken place from violation of consumer guarantee.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, store has breached the guarantee provided under schedule 2 of the cited Act, and therefore Julia is entitled to claim remedies, which may be either replacement of goods or refund the amount. Additionally, she also claims loss of income of $12000. Therefore, store is required to replace or refund the amount of blender along with losses of income suffered by Julia.
REFERENCES
Armstrong, A 2019,’Negligence and prescribing’, Journal of Prescribing Practice, vol 1, no. 10, pp.512-516, https://doi.org/10.12968/jprp.2019.1.10.512
Bianchi, L 2018, ‘Consumer law: Changes to Australian consumer law: Key benefits for vulnerable consumers’, LSJ: Law Society of NSW Journal, vol. 50, no. 3, pp.71-73, https://search.informit.org/doi/abs/10.3316/agispt.20181108003624
Clarke, J 2010, ‘Australian contact law’, Available through<https://www.australiancontractlaw.com/law.html> .[ Accessed on 27th August 2021].
Consumer rights obligation 2020, Available through < https://www.accc.gov.au/business/treating-customers-fairly/consumers-rights-obligations> . [Accessed on 27th August 2021].
Eldar, S 2020, ‘Cross-Victim Defences’, Criminal Law and Philosophy, pp.1-17. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11572-020-09552-7
Gibbs Wright Litigation Lawyers 2020, ‘Remedies for negligence claim’ ,Available through <https://gibbswrightlawyers.com.au/publications/negligence-disputes-australia> . [Accessed on 27th August 2021]
Lamont, S, Stewart, C, & Chiarella, M 2019, ‘Capacity and consent: knowledge and practice of legal and healthcare standards’, Nursing Ethics, vol 26, no. 1, pp.71-83, https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733016687162
Pearson, G 2018, ‘Enforcement and Effectiveness of Consumer Law in Australia’, In Enforcement and Effectiveness of Consumer Law (pp. 75-97), Springer, Cham, https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-78431-1_3
Stoyanova, V 2020, ‘Common law tort of negligence as a tool for deconstructing positive obligations under the European convention on human rights’, The International Journal of Human Rights, vol 24, no. 5, pp.632-655. https://doi.org/10.1080/13642987.2019.1663342
Tadros, E 2020, ‘Elements of a contract’, Available through <https://fls.org.au/law-handbook/consumers-contracts-the-internet-and-copyright/how-contract-law-works/elements-of-a-contract/>. [Accessed on 27th August].
Taylor, 2020, ‘Elements of negligence’, Available through <https://www.taylorandscott.com.au/compensation-lawyers/four-elements-make-negligence-claim/>. [Accessed on 27th August 2021].
Werbach, K. & Cornell, N 2017, ‘Contracts ex machine’, Duke LJ, 67, p.313, https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/duklr67&div=11&id=&page
LAW5398 Construction Law Assignment Sample
You have been approached by Mrs Jacintha Mernda who is aware of your recent enrolment in the Construction Law Unit at Swinburne University of Technology. Mrs Mernda asks you for advice on a planned construction project. Her intention is to build a four storey apartment building in one of the suburbs in Melbourne. The apartment would have private residences, ready to rent or purchase on the second, third and fourth floors; a restaurant, coffee shop, and other shops on the ground floor; and a carpark in the basement. The carpark will be for only the residents or workers in the building. Visitors will park along the road.
Mrs Mernda needs advice with the following:
What is the building classification for her project and why is he building classified that way (See National Construction Code)?
What is the best type or types of contracts she needs for the project?
Will she need to employ an engineer? If so, what will be the Engineer’s role?
Will she need a liquidated damages clause and if so, can you provide her with a sample of a good clause she can use?
Will she be able to request a variation to the project once the construction has commenced? If so, what are her rights and obligations in case of a variation?
How can she ensure that her construction project is Covid-19 safe?
NB: Although the project is in Victoria, Mrs Mernda is happy for you to use examples and even laws from overseas or interstate, if you want to. She does not require you to entirely rely on Victorian Law, but you may do so, if you’re able to.
Solution
Introduction
Construction project is determined as the activities through which different projects are made such as buildings, apartments, house and many other things in which people can easily live or conduct their business activities. The following case study is also based on the construction law and it aims to determine the construction of a four storey building that is located in Melbourne. The following case study for assignment help will provide an analysis of the classification of the project and the best type of contract that is suitable for the project. On the other hand, the role of engineer and safety of project from the COVID-19 impact will also be analysed in the following .
Main body
What is the building classification for her project and why is he building classified that way
As per the national construction code, following are the building classification that is based on the building made or approached by Mrs Jacintha Mernda:
• Residential building
One or more family residences, boarding or shacking up houses, seminaries, residences, apartment houses, and individual garages of such structures are all examples of a "residential building" that provides sleeping accommodations for regular residential purposes. One or more rooms in a structure used as a residence, with the required amenities and utilities to meet the needs of an individual or family (Ahmed, 2019).
• Business building
Offices, banks, professional businesses, and courthouses are all considered to be business buildings since their primary purpose is the conduct of business or the maintenance of books and records. The term "business building" refers to any structure used for commercial, retail, or wholesale operations, as well as service agencies. This list is not intended to be exhaustive; rather, any structure or location used for commercial, retail, or wholesale operations, as well as service agencies, should be considered a business building.
• Multi storey building
The phrase "multi-story building" is used to describe a structure with numerous stories above ground. The term "multi-story" refers to a building with more than four levels. Living in such a building has both benefits and downsides. A multi-story building is a three-dimensional or light-weight steel structure with numerous levels and vertical circulation (Ingle and Mahesh, 2020).
What is the best type or types of contracts she needs for the project?
There are different types of project contract that can be implemented for the current project of four storey building. Following are certain similar contracts for the project:
Contract with a Cost-Plus Subscription
Contractors get compensated for all of their construction-related expenditures when they enter into a cost-plus contract. That's the component of the name that refers to the price. Direct expenditures such as labour, materials, and supplies, among other things, might be included in the total cost. These expenses also include overhead charges, which might include things like insurance, travel, and a percentage of their office rent. In addition, they earn a certain amount of profit on the sale of the product. That is the "advantage." Contractors tend to see this form of building contract as being very favourable in general (Owusu et al., 2019).
Material expenses are unlikely to go above budget, at least for the time being. Furthermore, they are confident in their ability to make a profit. When the scope of the project is unclear or there isn't enough material to produce an accurate estimate, this kind of arrangement is ideal. Quality is also important to them.
Contract for the design and construction of a building
Traditionally, finished drawings are sent to the owners before construction bids are solicited. This results in two different contracts as well as a lengthier overall procedure. When it comes to the design-build contract, things work a little differently. In accordance with its name, a design-build contract tackles both the design and building expenses at the same time. According to this sort of contract, the building process really starts before the final design has been finalised and approved. To save both time and cash, the owner benefits from this method since the civil and structural projects are delivered under the same contract. It also assists in the simplification of contacts and the establishment of repeatable processes (Kim et al., 2020).
With the design-build contract, architects and contractors are able to work together more quickly and prevent disputes. Companies who want to expedite project delivery, take advantage of the advantages of collaboration, and simplify procedures are embracing it in increasing numbers. As a result, designers have more involvement into the building drawing process, which reduces the need for revisions (Oswald et al., 2019).
Will she need to employ an engineer? If so, what will be the Engineer’s role?
Yes, she will need to employ an engineer for the construction project of four storey building. Among civil engineers' most important responsibilities is their work on architectural projects as well as the improvement of building infrastructure. They assist in the development of systems surrounding the facility in order to address site problems related to utilities and guarantee that the project is viable. Because of the wide range of skills and knowledge they possess, they are able to create building designs from the ground up and supervise their implementation as they see proper. In such cases, they assume responsibility and work in collaboration with physical labour and other engineers who are in charge of the technical procedures associated with the project (Heigermoser et al., 2019).
It is expected by the customers who employ contractors for tasks that they would include environmentally friendly and energy-efficient elements into their freshly built structures. It is at this point that energy engineers come into the open and offer other techniques of generating electricity for buildings to those now in use. In order to satisfy these needs, they include alternative energy sources, such as solar energy, into their designs.
This not only makes the structure more energy efficient, but it also helps to reduce the rising cost of utilities. Because of this, the construction becomes more valuable, making it a highly sought-after project. Additionally, the cooling and circulation of buildings are two other utility difficulties that have arisen throughout these development projects (Karimi et al., 2018). Mechanical engineers are responsible for installing these HVAC systems as early in the design process as possible to guarantee the safety of the building's occupants. They also, as previously said, help to enhance the quality of the money spent on its energy requirements.
Residents are at danger of inhaling toxic chemicals and contracting serious diseases or mutations if they do not have access to these services. In addition, if a building does not have a functional ventilation system, the State Board of Health may impose a punishment on the owner. As a result, it is no longer a question of choice, but rather a requirement for contractors to take into consideration (Wei et al., 2019).
Will she need a liquidated damages clause and if so, can you provide her with a sample of a good clause she can use?
Arbitration clauses contain a provision for liquidated damages in the event that a party breaches the contract. Liquidated damages are often based on the company's inability to fulfill identified objectives if the project does not meet the completion date stated in the agreement (i.e. handing over the site to the customer). It is common to utilise daily or weekly rates in their calculation. It's important to note that liquidated damages are not fines; rather, they're a pre-determined amount of money due to the customer if the contractor misses the completion date. Temporary housing fees, moving expenses, and the like are all examples. Fixed daily or weekly sums, however more complex equations may be used if the job is phased, where there is partial ownership, and so on. It is critical that the calculating process be described in detail and in a formal manner (Sun et al., 2019).
Clients may sue for unliquidated (reality) damages if their actual losses vary significantly from those anticipated at the moment of the agreement's signing, unless the provisions of the contract specifically specify otherwise. These damages are not pre-agreed upon, and are normally assessed by the courts in the event of a lawsuit since liquidated damages are not a punishment, they must have been established based on an accurate assessment of losses. They may be seen as a punishment by the courts and so unlawful, although this is rare since courts are very hesitant to meddle in financial agreements made freely by two business parties of comparable standing (Martinez et al., 2020).
Will she be able to request a variation to the project once the construction has commenced? If so, what are her rights and obligations in case of a variation?
As soon as building has begun, she might seek a change in scope. Due to the fact that her rights and responsibilities in the event of a variance are significant, she will be in a better position to handle it. On the other hand, the construction will be acknowledged as a part of the project and thus, it will be easy for the development of the construction. Once the project is started it will become easier for the project manager to focus on the successful execution of the business objectives in order to complete a project on time and achieve all the goals (Mohandes and Zhang, 2021).
On the other hand, the rights and obligations in the case of variation will also be focused towards the completion of the project through which the activities of the development of the four-storey building can be easily made and it can be made as per the construction law. Moreover, the laws will also be focus in order to determine the execution of the construction activities and it will be commenced as a part of the variation to the project (Owusu et al., 2019).
How can she ensure that her construction project is Covid-19 safe?
It was addressed at a recent RICS webinar entitled COVID-19: influence on the building sector, which brought together specialists in the construction industry as well as company owners, managers, and legal representatives. Personal protective clothing, cabins spaced wider apart than normal, delayed start times, additional washing sites, and the establishment of a social distancing coordinator post were all recommended as possible practical solutions.
While dealing with the COVID-19 situation, it has become clear that trust is one of the most critical factors of success. Creating a professional atmosphere that encourages unity and trust allows for the development of reaction plans and procedures that safeguard staff and customers. However, the process of creating that culture begins at the very top (Townsend and Gershon, 2020). In order to be effective, executives must include the whole firm and provide help to people working on the ground. All participants must listen attentively and clearly explain their goals, their openness, and their expectations for the scenario, as well as what they think will or won't work. When everyone is on the same page, it is easy to create a consistent culture and a site response plan that reduces the risk of COVID-19 contamination for company employees, trade partners, customers, and the general public. For safety and compliance reasons, it's a good beginning step.
Communication is essential for every construction firm, and this is truer more than ever. It is essential to maintain open lines of communication between company project management team, trade partners, and customers. Even when staff are present on-site, meetings may be conducted by video or teleconferencing. If meetings must be done in person, make sure they are held in a space large enough to allow for six feet of distance, or consider conducting them outdoors if the weather permits (Lotfi et al., 2022).
Conclusion
From the analysis of the above report, it is concluded that contract with a cost plus subscription is the best type of contract for the current project and designing all construction activities implemented photo development of the apartment. On the other hand, it is concluded that role of engineer is very important in the construction project and it must be focus on the basis of liquidated damages clause.
References
.png)
.png)
LML6003 Migration Law Assignment Sample
SCENARIO
You are a registered migration agent and operate a busy and popular practice. You rely heavily on your client co-ordinator, Anna, to organise your consultations every day and to obtain some brief information about the clients you are scheduled to see. Anna has a very good way of eliciting information from the clients, ensuring they proceed with the booking, but she is careful to never provide any immigration assistance in the process. You look at your calendar and you only have one appointment for today. You look at an email from Anna and it states the following:
Cheryl Lim from Singapore is coming into the office at 1pm today (please remember you have a CPD seminar from 12 noon to 1pm).
You may recall Cheryl as you helped her with obtaining a Student Class TU subclass 500 visa last year to complete a Bachelor of Laws at Victoria University. She has completed 6 months of this course. Cheryl completed the Graduate Diploma in Migration Law at Victoria University and decided at the time she wanted to pursue a law career.
Cheryl is coming into the office today and she wants to know whether she can change her course to a Certificate IV in Cookery instead at Swinburne University in light of her recent passion for cooking which she developed during the lockdown. I have attached her visa grant notice from her file.
You open up the visa grant notice and note that conditions 8105, 8202, 8501, 8516, 8517, 8532, 8533 and 8534 are attached to her visa. Her visa is valid until September 2023.
QUESTION
Prepare a checklist of issues, including visa options, that you would consider in advance of your meeting with Cheryl, based on the limited facts. You must support your answers by reference to the specific legislative provisions.
SCENARIO
You are a registered migration agent. You receive an email from a client, Stan, who wants to meet you for advice about his migration matter. You recall Stan’s name as you met him and his wife very briefly once at a party you attended, and they were very friendly and seemed to be completely smitten with each other. Your receptionist books an appointment for him to meet you at your office at 11am. You decide to review his matter and prepare a memo before you meet with him. An extract of the client’s email is below. “I hope you remember me, I met you at Susan’s birthday party. Susan recommended that I contact you. I think you may have met my wife, Cindy too. It is probably best I give you some background information about Cindy and my relationship. I know many people commented that our relationship was picture perfect, but sadly it is not. I met Cindy in my hometown of Sicily and yes I instantly fell in love with her. I arrived in Australia on a temporary Prospective Marriage Class TO subclass 300 visa about one year ago having been sponsored by Cindy, an Australian citizen. We had a beautiful wedding with a small number of family and friends. Cindy’s brother never liked me, and he heavily influences Cindy’s actions. One evening during a family dinner, we had a disagreement over the results of a soccer game. As you may assume, being Sicilian, I am a passionate supporter of my team. Things escalated and he punched me for no reason other than expressing my views about the referee’s decision which resulted in my team winning. After this, Cindy appeared to take her brother’s side and her temper worsened each day and I was subjected to constant verbal abuse and sometimes physical abuse. Cindy would lose control of her temper over things as minor as leaving the milk out of the fridge for more than 5 minutes whilst I made my coffee. A few weeks ago, she smashed a bottle over my head screaming at me that she hoped that would knock some sense into me. I started bleeding and went to the local doctor/general practitioner (GP), who told me I needed to go to the hospital to get stitches. When the nurse asked me what happened for the medical report, I said that I had accidently tripped over. I did not want to get Cindy into trouble, and I was also fearful of what she and her brother would do if I told anyone what had actually happened. There was a very kind nurse who insisted I call a friend of her’s named Steve. I called Steve not really knowing why, and he was a great support to me as a friend as he had been through a similar situation in his homelife. I found out last week he is also a social worker. Steve encouraged me to let other people know what was going on, so I told Susan who told me to inform you. Cindy’s behaviour is escalating, and yesterday I decided to leave her forever. I am still awaiting a decision on my Partner Class UK/BS subclass 820/801 visa and am unsure what my current visa status is as Cindy has all my immigration papers. I really want to stay here as I feel like there are some wonderful people in this country and after COVID, there are more opportunities here than Italy. If possible, I would like to visit my family in Sicily for a week just to recoup.”
QUESTION
Prepare a memo in advance of your meeting, outlining the following:
(a) What is Stan’s current visa status and can he travel and why?
(b) Is there is anything Stan can do to seek permanent residence and explain the steps required and what additional information you would require to support the application? You decide to do some additional research and come across the following case: Thaworn v Minister for Immigration, Citizenship, Migrant Services and Multicultural Affairs [2021] FCCA 2133 (27 August 2021).
(c) What are the implications of this case, if any? You must support your answers for assignment help by reference to the specific legislative provisions.
Solution
Several issues may occur in case of the meeting that will occur with Cheryl as a Registered Migration Agent. As per the “Visa Grant Notice”, several conditions have been attached to the visa of Cheryl. The checklist of issues that have been made in accordance with the issues for the visa of Cheryl is below:
.png)
As per the issues that have been briefly explained in the checklist, Cheryl will have to acknowledge the issues with respect to the c conditions that have been attached to the visa that she acquired. Condition 8105 has been applied when there has been an absence of any individual in Student 500 visa. The demand of Condition 8105 is that the holders of student visa can work only less than 40 hours each half month at the time in of their course which is within session. This is the principal condition that has been known by several students.
However, several titbits are still present that are essential for every student to know. A permission has not been provided to the student who is the holder of visa to work till the course that has been done by them has commenced and has been within session. The student who is the holder of a visa cannot have the permission for working un limitedly when there has been an absence of their course within the session. The student who is the holder of a visa by whom master has been commenced by research or by whom there has been a persuasion of doctorate course, can be capable of working for unlimitedly after the commencement of research course which is postgraduate.
Therefore, it can be said that Cheryl Lim will not be able to complete any other course that she has chosen for as she has to complete the course of “Bachelor of Laws at Victoria University” as per the titbits of Condition 8105. This comes under the” Migration Act 1958”. The restrictions that come under this Condition will not allow Cheryl to do any sort of work in Australia before the completion of “Graduate Diploma in Migration Law at Victoria University.” While considering the second condition that is Condition 8202 on the student visa, any breach of this specific condition makes it vulnerable in the case of student who possesses the visa to its cancellation.
If there has been an occurrence of cancellation of visa, it will be quite difficult in case of that particular student who possesses the visa and has done breach of Condition 8202. This condition is important in the case of an entire student visa as per the” “Migration Act 1958”. There should be an enrolment of the student within any sort of registered course there should be an enrolment of the student in any sort of registered course which possesses same or higher level as compared to registered course in the case of which visa has been granted to the student.
There should be the maintenance of satisfactory attendance by the student in the course that has been pursued. In addition to that, progress of course in the case of each period of study should be maintained as per the requirement of the education provider of the student. There may be a difficulty while applying for Student Visa 500 as there has been an absence of enrolment in registered courses by Cheryl. Condition 8501 specifically states that there has been a requirement of health insurance in case of the student who has to apply for a visa.
Exact wording that this condition possesses is that there should be a maintenance of adequate arrangements by the holder in the case of health insurance while holder resides in Australia. The association of visas with those visas that are working are “The Temporary Work (Skilled) subclass 457 visa, “The Temporary Graduate Subclass 485 visa and “Most temporary working visas where the primary purpose is to work”. In the case of Cherlyn, the second working visa has been important. This is due to the matter that there has been a desire of change in the course by Cherlyn.
This is against the rules of acquiring a visa in the case of the student who wants to pursue higher studies in Australia by switching from one course to another. In the matter of Condition 8516, there has been a requirement of satisfaction of either the primary, or the secondary criteria as per the requirement of the case so that the visa can be granted. In the case of Cherlyn, she has to meet the requirements that are essential for the switching of one course to another and from one University to another in Australia.
In this case, the requirement is that Cherlyn should possess Student Visa 500. With the help of this, she is able to change her course, however, after completion of the first year of that course that has been pursued by her. Especially, if there has been an initial satisfaction of criteria by any student in the grant of Student Visa 500, then criteria cannot be met on time. However, when there has been a satisfaction of criteria later, there has been a continuation by the student in the satisfaction of criteria. The satisfaction of criteria has been associated with the issues that may be encountered at the time of issuance of visa.
Condition 8517 has been imposed on the visa holders who are students on the student visa that they possess. In the case of Cherlyn, there has been an applicability of Student Visa 500. There must be a maintenance of adequate arrangements by the holder in the case of education of the School Age-dependent of that holder who lives in Australia above 3 months. In this case, adequate arrangement refers to proof of financial stability. As per the Condition 8532, if the age of the holder of student visa is not 18 years, then, the holder has to reside with parents whose age is 21 years and have a good character.
Arrangement of accommodation, general wellbeing, as well as, support of holder should have to be approved by education provider possessed by the holder. There should not be any entrance by the student in Australia before nominated date given with the help of education provider. Hence, age of Cherlyn has to be checked otherwise there may be an issue in entering Australia as per this condition. As per the Condition 8534., only Subclass 485, 590 and Protection Visaswill be granted. In the case of Condition 8533, no issue will be there for Cherlyn.
Question A
To Immigration council
From XYZ
Date: 05/09/2022
Sub: Memo for requesting permanent residency in Australia
Respected sir/ madam
I would like to inform you that I am very happy to submit this reference letter that I am able to immigrate to Australia. I met Cindy in my hometown of Sicily and yes I instantly fell in love with her. One evening during a family dinner, we had a disagreement over the results of a soccer game. r. I am still awaiting a decision on my Partner Class UK/BS subclass 820/801 visa and am unsure what my current visa status is as Cindy has all my immigration papers. I hope that will you feel free to contact me with any additional questions or concerns.
Yours sincerely
XYZ
In this case, Stan cannot be able to travel as the current visa status has been dependent upon the “Form-I 765 “. In this case, the person who wants to travel to any other country from Australia to any country has to carry the immigration papers with him or her. However, in the case of Stan, there has been a difficulty in carrying those papers as they are in the hands of his wife. It will be quite difficult for him to be in another country as there has been a continuation of conflict in the middle of his wife and him. In addition to that, as per case scenario, it has been understood that the brother-in-law of his wife, Cindy will not allow her sister to give the papers to her husband. This may occur as he may want to harass Stan in case of visiting Sicily with his family. If Stan is able to visit his family in Sicily, then, the matter of conflict in the middle of both his wife and him may get sorted out. However, the brother of Cindy has not no intention to sort out the conflicts that have already existed in the middle of them.
In addition to that, there may be a possibility of filing a case against Cindy and her brother by their family members of Stan. This may happen as Stan has been tortured both mentally and physically by his wife and his brother-in-law regularly. Moreover, in order to get the immigration papers back from his wife, Stan has to file a case against her under the “Australian Visa Classes''. However, Stan does not want to do that and hence, it will be troublesome for him to travel to Sicily and to meet his family for recouping.
Stan cannot be able to travel as the visa about which he has given the description allows both the partners to travel together. Hence, in the case of Stan, it is mandatory to take Cindy to the palace where he wants to and has to travel. In addition to that, another condition in the case of this visa is that there has been a requirement of the permission of the partner for traveling to any other part of the world as the partner has equal rights as the holder has. In the case of Stan, Cindy will definitely not provide any sport of permission to meet to family who reside in Sicily. Moreover, there has been an issue in the case of Stan if he has a thought of asking permission for travel from Cindy. The issue is that Cindy will get to know the fact that there will be a matter of recouping in the mind of Stan with his family which is the only reason for him to meet his family. After knowing the fact, Cindy will not give permission to Stan which will become problematic for Stan to meet his family members in future.
Question B
There are three ways to get a permanent residency: the provincial nominee program, the express entry system and family sponsorship, which is the simplest way to get permanent residence in Australia. Stan can do any of them to get a permanent residency which is registered by an individual migration agent. The express entry system has initiated in the year 2015 which also required job offers. During the same time, migration agents are checking the eligibility which leads to permanent residency. According to section 318 of the migration act, individual applicants are lawfully admitted to the country when their residence status is more than 5 years. Apart from that, the eligibility criteria are checked by the migration agent and after completing the criteria they are eligible for the visa confirmation. During the same time, designated authorities are trying to evaluate several PR processes in the processing time.
Required Steps:
In order to, get permanent residency in Australia migration programs and some other rules are necessary which have to be fulfilled by the individual applicants. Applicants have to be more than 45 years and the work streamand applicant have to pass the English language test to get a proficiency certificate.There are five crucial steps to getting a permanent residence which is listed below:
.png)
Figure 1: Process of migration law
(Source: Stevens, 2019)
Skills assessment
In order to, ensure the work experience and educational skills of the applicants' a skill assessment is mandatory. Each occupation has different skills such as trade occupation, engineering occupation and migration agent can check the criteria as per requirement . Educational and work experience are required which have to pass by the applicants. Apart from that, employment skill assessment is a crucial stage that has to be passed for permanent residency. An individual applicant can apply for lawful admission to the country if their residence has been in the country for over five years, according to section 318 of the migration act.
Visa requirements
A specific test is crucial for individual applicants who are nominated by the regional nominated visa. The territory government is choosing the nominee for a visa holder and who has to be filled these roles. There are some important steps of visa requirements such as occupation lists, family stream, and work stream or other options which have been considered by the Australian employer sponsorship. A skills assessment report has been tested during the application and government-certified authorities are examining the health and character of the applicants. In order to, pas the key requirements are mandatory to get permanent residency in a specific country.
Occupation
Occupation is the important and first step which is required for permanent residency which is educational and work experience. All positive skills are required, which are checked by the government authority. The general skilled migration visa is eligible after identifying which occupation matches at a certain time. The legal residence status is five years for permanent residence which is not applicable not all citizens. LPR (Lawful permanent residence) isAlso known as who is lawfully authorized to permanently live within the country.
Lodge visa application
After receiving the state nomination actual visa application through the immigration account government are trying to checking the current status of applicant. All the personal documentation such as work experience, and educational documents are the main evidence that is needed to provide to lodge a visa application which is considered the final application.
Additional information
Besides the application history, some additional information is also required to support individual applications such as relocating to the city, and company-based information. Educational criteria are required for a personal reason which is additionally supporting the individual documents. Sometimes professional certificate references from colleagues as well as technical and language skills are also important. Apart from that, it is the important conditions that are considered by the holistic approach that sometimes secure a position which is represented by accurate professional certificates. In 2015, the express entry system was launched, and job offers were also required. Client testimonials are positively supported by the individual who is considered a formal recommendation for full-time employees. Sometimes formal details of the individual clients are used as legitimacy proof which is important to develop the professional careers of the applicants.
During the same time, employment duration is mandatory as an additional information system which is effectively leading to a successful work permit. The minister for immigration, citizenship, migrant services and multicultural affairs first respondent administrative appeals tribunal is the second respondent which is evaluated by the Migration act 1958. The ministry for implications and multicultural affairs is trying to identify the same reason such as good character, which comes under the refugee review tribunal of 1998. In order to, seek permanent residency this additional information is required for individual applicants and there are explain some crucial steps to identify the progress of the permanent residency.
Question C
Eligibility to apply for citizenship
The major benefits of being a permanent resident such as there are no boundaries to keep renewing a residency permit, and continuously checking the legal status. Apart from getting confirmation applicants easily access the job market, full-time location in the country as well as the right to return to Australia. Three are some major benefits of social security such as employment benefits, and an advantage during sickness, which is comes under the social security act of Australia. Unemployment is considered a major difficulty for the individual residents as well as visa category overseas individual skilled workers. The industrial laws are equal for the permanent resident, compensation benefits are easily got for the same reason and more job opportunities in the future. During sickness, entitlement to Medicare is considered a crucial facility for permanent residents.
Access to the “primary and secondary government scheduling” is not applicable for the temporary resident however that might be depending on the government or the other migration authorities. The implementation strategy has been considered by the government of the country after confirming the permanent resident. This implementation strategy has been considered by the government or migration authority to identify or improve the major benefits. Skilled workers are trying to identify the major benefits which are engaged by employer sponsorship. As a permanent residency, there are some pathways that have to be followed by the individual resident that can able to maximize the future scope. Under the refugee review tribunal of 1998, the ministry for implications and multicultural affairs is trying to identify the same reasons under the category of good character.
Eligibility to receive future scope
There are some legal pathways that have to be followed by the applicants to get a permanent president. Skilled workers are required to identify the benefits which areneeded to be followed by the resident such as the legal pathway which is mandatory to receive future scope from the government. The major benefits are required to involve the implication strategy and that need to be followed to improve the relationship among the legislative committee. Apart from that, the eligibility criteria have been explained for permanent residents and that is able lead to get economical opportunities over the country. The future scope is received from the government is to improve public service skills during the same time. The final implications are considered when a resident is permanent or involved in the multicultural society which is contributed to a wonderful living experience.
For the permanent resident, several legal pathways have to be followed by the individual and that can able to identify how to maximize the major benefits and government has complete the specific process after issuance of the permanent visa. A skilful person is trying to identify all the opportunities which have been provided by the government and that are needed to improve the business benefits of the country in the future. There is some time needed some time to identify how to maximize future opportunities after getting permanent residence. Individual testimonials are considered formal recommendations for full-time employees when they are positively supported by the client. Some mandatory registrations are defined by the state authorities and that can able positively lead to future benefits. In order to, get permanent residency some internal authorities find out the major benefits which are usually required for future opportunities.
Improved multicultural environment
A multicultural environment is able to be identified by the permanent resident and that can be involved by the individual governments. A multicultural environment is required to entertain individual residents which are provided by the government after completing the migration process. During the same time, higher education loans have been guaranteed for the permanent resident which is including basic benefits to encourage individuals.
Reference list
.png)
.png)
LAW301 Business and Corporation Law Assignment Sample
Assessment Task
Read the following case scenario and answer the question -
You are an intern in the corporate office of MicRonalds Pty Ltd which runs fast food outlets in different cities around Australia. You have received instructions from Kylie Eagle, the company’s corporate counsel to write a Memorandum of Advice in relation to potential claim by Lizzy Grant, a customer who was recently injured in their MicRonalds’ 24-hour city restaurant.
In the early hours of the morning on 4th January 2022, Lizzy Grant was on her way home from a long and tiring night shift. She decided to stop at the MicRonalds’ 24-hour outlet at 5:30 a.m. to purchase some breakfast. While at the restaurant she ordered her food and as she was waiting, she decided to use the toilets at the far end of the outlet. They were usually very clean. As she approached the toilets, she saw a sign that had been placed at the entrance and which read “Caution: Wet Floor. Cleaning in progress”.
She did not wish to wait for the cleaning to be completed and she went into the toilets. When she was leaving the toilets, she slipped on the wet floor and fell. She suffered a broken wrist and a bruised head. She was not able to return to work for eight weeks. Kylie has informed you that the cleaning of the restaurant toilets on that morning was being done by one of the employees, Lance, who had stepped away to get a dry mop to complete the cleaning. He was also in charge of spot cleaning throughout the day. Lizzy has now threatened to commence proceedings against both MicRonalds Pty Ltd and Lance.
Kylie would like you to write a memorandum of advice on whether there are grounds to hold
MicRonalds Pty Ltd liable. Required With reference to relevant legal principles, use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to draft a suitable Memorandum of Advice that addresses the nature of the claim that Lizzy Grant may make against MicRonalds Pty Ltd and whether in fact they can be held liable in any way.
Ensure you incorporate relevant case law principles and case law support in your brief?
Solution
1. Legal Issue
Lizzy Grant is a customer of MicRonalds. After a long night shift, Lizza Grant decides to stop at the MicRonalds for breakfast. When Lizzy Grant was in the restaurant decided to use the toilet; however, there was a caution sign that the floor was wet and cleaning was in progress. However, Lizza Grant neglected the warning sign and slipped on the wet floor. The issue is whether Lizzy Grant can claim damages from MicRonalds Pty Ltd and Lance.
2. Relevant Law
In the case of Arabi v Glad Cleaning Service Pty Limited (2010), the plaintiff fell and slipped on a pedestrian ramp in the shopping centre at Bankstown. The plaintiff's right knee was injured after the accident occurred. The plaintiff's evidence is that they were talking on the phone while walking up the ramp. It is an occupier's duty to take reasonable care in the commercial premises to avoid a foreseeable risk of injury for both the lawful entrant and their own safety. In this case, a proper system of cleaning and inspection should be considered as per section 5B(1)(B) and Section 5B(2) of the Civil Liability Act 2002, with other relevant things. The court held that if the plaintiff proves the defendant's liability in case of maintenance of insufficient duty of care, then this case will be remitted to the district court for reassessment.
In the case of Vairy v Wyong Shire Council (2005), the High Court dismissed the plaintiff's appeal as the possibility of a man being hurt while jumping from the cliff was not beyond the realm of possibility (foreseeable risk). It would be unreasonable to expect the Council to post warning signs at every location within its jurisdiction from where such an accident may occur. Because of its potential for confusion, the idea of "obvious risk" is not to be utilised to adjudicate concerns of breach of duty. Injury predictability must be determined prospectively, considering the state of affairs prior to or during the damage.
In the case of Sleiman v Franklin Food Stores Pty Ltd (1989), the plaintiff went shopping with family in the local shopping centre. The plaintiff found a special product while moving along to the shopping centre. When the plaintiff reached the refrigerator slipped and fell on the floor due to water spillage. The plaintiff's feet were badly injured because the accident occurred. The court held that the occupier breached the duty of care. This incident occurred at a shopping mall, and the plaintiff was a customer. It was the defendant's duty to prevent harm on the commercial premises.
3. Application of the relevant law
Based on the case law mentioned above, MicRonalds Pty Ltd. is not liable for the damages as no negligence was determined under section 5B subsection (1) (a) and (c) of the Civil Liability Act 2002 No 22. The caution sign was placed by Lance, responsible for cleaning the toilet, taking the necessary precaution against the risk of harm under section 5B subsection (2) (a). Moreover, section 5C subsection (a), (b), and (c) further substantiates that the burden of taking precaution, doing an act and taking action to avoid the risk of harm was present in the case. It can be further stated that Lizzy contributed to negligence under section 5R subsection (1) by ignoring Lance's warning sign at the toilet's entrance. Hence, Lizzy was aware yet failed to take precautions against obvious risk under section 5F subsection (2) and section 5G subsection (1).
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, Lizzy cannot claim damages as the incident occurred due to her negligence.
References
Legislation
Civil Liability Act 2002 No 22
Cases
Arabi v Glad Cleaning Service Pty Limited [2010] NSWCA 208
Sleiman v Franklin Food Stores Pty Ltd [1989] Aust Torts Reports 80-266
Vairy v Wyong Shire Council [2005] 223 CLR 422
LAW1081 The Individual and the State Formative Assignment Sample
John is a playwright and political activist living in the state of Triland, a state party to the European Convention on Human Rights. Terence is the director of a local theatre club in Triland’s capital city, Stereopolis, and has asked John to write a play about contemporary life and society in Triland. John’s script portrays various national politicians and religious figures as lascivious, immoral, and corrupt. The play includes a very lurid satirical depiction of Mathilda, the mayor of Stereopolis. Mathilda, who is a deeply religious, married mother of four, is portrayed in the play as an adulterer who regularly receives sexual favours in return for preferential treatment in tenders for local contracts.
After several months of rehearsal in Terence’s home, the theatre club is ready to put the play on for the public. They hire a large room in the local town hall and invite their friends and family to watch a private preview of the play, as well as Tina, who is a journalist for the newspaper ‘The Triland Daily’ and a few local dignitaries, including the mayor of Stereopolis and her family. Terence has already sold a number of tickets for the play, which is due to be performed to the paying public two weeks after the preview has taken place.
Mathilda is deeply offended by the play. She complains to the Triland Police Force and John and Terence are arrested under the Triland Police Force’s common law powers of arrest. They are subsequently prosecuted under the ‘Protection of the People from Public Immorality Act’ for the offence of ‘offending public morality’ and they are both sentenced to a 500 Trilandese dollar fine and a 6-month suspended prison sentence for this offence. Mathilda also informs Terence that the play is cancelled and that the Triland Police Force will break up any gathering at which the play is to be performed to the public.
Tina publishes an article about the play, including the controversy surrounding its cancellation by the Mayor of Stereopolis, in the ‘Arts and Society’ inside pages of the Triland Daily. The article contains a detailed account of the dispute, alongside photos of the actors dressed in costume and a reproduction of the most offensive quotations, including those that concern Mathilda. Mathilda sues John and Tina in defamation and succeeds before domestic courts, obtaining sizeable compensation for injury to her feelings and reputation and an injunction against the further publication of the offensive material. Please advise John, Terence, and Tina on the likelihood of making a successful application to the European Court of Human Rights under Article 10 ECHR. Please assume that all the applicants have exhausted domestic remedies and that their claims are admissible.
Solution
In the present case scenario for assignment help , it has been noticed that, Mathilda has been significantly offended because of the play and therefore she sued John and Teena in defamation and obtains success prior to domestic court, availing significant amount of compensation in relation to the damages to her feelings and reputation. Further, she also availed injunction order in contrary to the further publication of the violent material. Therefore, in the prevailing case scenario, it is required to provide advice to John, Terence, and Tina on the probability of filing application in successful manner as per Article 10 of ECHR (European Court of Human rights).
The European Court of Human Rights has taken into account the freedom of expression and right of information, which is part of Article 10 of European Convention of Human Rights, a significant basis for advancement of democratic community and every individual. The European Court of Human Rights is applicable on wider definition of the idea of ‘information’ specifically that could play vital role in advancement of democratic community .
European Court of Human Rights Rules as per Article 10 is considered as primary aspect of the Convention. It explains about the right to freedom of expression, however it could be observed from Para two, it is not regarded as absolute right. As per explanation in the cited Article –
1. Every person possesses the right of freedom of expression. This right should consists of freedom to embrace opinions and to obtain and communicate information and plans without any interfere by the public authorities and notwithstanding of frontier. The Article must not restrict States from needing the license for broadcast, cinema enterprises, and TV.
2. The application of such freedoms, as it runs with rights and duties, might be dependent on conditions, rules, limitations or drawbacks as are explained under laws and regulations and are essentially in a democratic community, in the advantage of safety of nation, territorial disorder or offence, for the security of ethics or health, for the safeguarding of rights or image of others, for security of the information obtained in confidential manner, or for keeping the authority and fairness of judiciary .
The range of application of above Article 10 has been taken into account by European Court of Human Rights in the latest case of Zarubin and Others v. Lithuania. In the cited case, expulsion of Lithuania and restriction on re-entry of Russian Journalist in order to engage in work of broadcasting in state-owned Rossia-24 subsequent to their activities at meeting in Vilnius. In this, it has been decided by European Court through majority that applications were not admissible. It was the ultimate decision. The court was ready to admit the measures implemented alongside candidates has considered as an intervention with the right of expression as given in Article 10. Although, further it has been held and reflected by authorities that measures taken by court had been essential in the benefit of security of country and has been equivalent . Specifically, the behavior of applicant at the meeting, demonstrated by authorities as stimulating and hostile, has not been as per the tenets of dutiable journalist.
On the basis of above aspects, it can be said that, freedom of rights of expression has been given in the Article 10 of European Court of Human Rights, but it was subject to several exceptions that should be construed in narrow way. In some case, rights under ECHR also compete with each other in a provided case. For instance, it could occur with Article 10 and Article 8. As per Article 8 of ECHR, every person possesses rights with respect to their privacy and family life, their home, and their correspondence. In a condition in which balancing exercise is considered between Article 10 and Article 8, significant emphasis is applied by the court in relation to the proportional position of the particular rights being requested in the case. Reasoning for intervention with or restriction on every right should be considered. There should be application of equivalent principle as applied in the legal case of Zarubin and Others v. Lithuania.
Elements and benchmark of the reasoning of court particular to defamation case (Safeguarding of reputation)
In establishment of factors of defamation, it is required by court that there must be objective connection between the impugned statement and the individual suing in defamation. In the legal case of Reznik v Russia judgment, it was held by the court that only subjective opinion of the publication as defamatory is not considered as sufficient element for establishment of the aspect that individual directly or indirectly affected through the publication . Further, it is considered by court that protection of reputation must be restricted to that of living individual and not to be based upon the reputations or image of deceased person except in some particular conditions. Further, the main factor of defamation is the harm on reputation. For Article 8 to come into play, harm on image of person should capture particular extent of significance and in a way assisting unfair to the personal satisfaction of the right to respect for personal life . In the legal case, Karako v Hungary, the extent of seriousness of the intervention needed for Article 8 of the ECHR to be implemented in the context of safeguarding of reputation is explained as such a significant intervention in the personal life that personal integrity of person is compromised . It has been noticed that, in the several cases in relation to defamation, it has been found by court in explicit manner or implicit manner, that the extent of seriousness has been grabbed and there would be application of Article 8 that reflects about right to privacy of person. In the legal case of Fuchsmann v Germany, decision related to claim of defamation brought by the applicant for offensive comments against him on internet portal, court held that article 8 was applicable .
In some cases, small group of individuals like board of directors of the company could also take defamation actions in which the target is the group, where the members could be identified as a reasonable person. This condition was occur in the legal case of Ruokanen and Others v Finland, which is related with allegation of rape in the course of party for team of basketball players .
It can be said that, court understands right of protection of every person with respect to their image, focusing that image of individual consists of one of the main element of their personality. The reason behind the same is that, it shows unique elements of person and differentiates the individual from their partners. Therefore, the right to protect image of person is one of the main element of personal advancement and primarily assumes the right to control of individual with respect to use their image, consisting of right to refuse publication thereof . The right with respect to private life, consisting the right to secure reputation as an important aspect of private life. It has been held by the court that reputation of person is supposed to be an independent right usually when realistic assertions were significantly in violent nature that their publication would create unavoidable impact on the life of plaintiff.
By going through the given case scenario, it has been observed that, John is required to write play with respect to contemporary life and community in Triland. Script written by John reflects several local politicians and religious pictures as non-ethical, lascivious, and dishonest. This play also includes significant lurid satirical portray of Mathilda, who was mayor of city. She has been noticed that, Mathilda was very religious, and had four children, is depicted as an adulterer who continuously obtains sexual favors in profit for favorable treatment in tenders for national contract. This depiction actually defames reputation of Mathilda. Although, as per Article of 10 of European Convention of Human Rights, individuals possess right to freedom of expression, and according to this, any person can express their opinions and expressions in free manner, but it is not considered as absolute right and subject to some terms and conditions only. Since, as per Article 8, it has been seen that, person has right to respect privacy, and defamation is considered as main element of personal life. This article contains detailed account of the conflicts, along with the images of actors in costumes and production of major violent lines, consisting of those related to Mathilda. It is considered as attack on reputation of Mathilda, which is considered as central element of defamation and it also includes significant level of seriousness. Therefore, it can be said that, by application of Article 10 with addition to Article 8, John, Terence, and Tina would not probably get success in filing application to the Article 10 of European Convention of Human Rights.
References
.png)
LAW6001 Taxation Law Case Study Sample
Task Summary
In response to the issues raised in the case study provided, research and develop a 3000-word tax advice that addresses (a) assessable income (b) allowable deductions (c) tax calculations and (d) your conclusions and recommendations that arise from a fact scenario and to give appropriate advice to clients. Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Context
This assessment allows students to solve practical problems that arise from various scenarios and to give appropriate advice to clients. This assessment assesses your research skills, your ability to synthesize an original piece of work to specific content requirements and your ability to produce a comprehensible piece of advice which addressing the client’s needs. It also assesses your written communication skills. The ability to deliver to a brief is an essential skill in the workplace. Clients may well approach advisors seeking a combination of specific information needs and advice on the tax implications of a particular arrangement in the Australian tax jurisdiction. It is therefore important to be able to identify all the issues presented by an arrangement and to think about the potential consequences of different approaches to addressing the client’s needs.
Task Instructions
- This case study must be presented as a group effort. The case study requires collaboration of effective team work. It is expected students will take parts and survey the relevant literature, including decided cases, and select appropriate additional resources.
- Your case study is not just a list of answers. Your reasons for your conclusions and recommendations must be based on your research into the relevant cases and legislation.
- With respect to each case study:
- Advise the best investment option for clients from the facts of the case study
- Identify the appropriate legal principles that requires discussion in the case study
- Apply the law to the facts of the case study
- After reaching a relevant conclusion, provide practical advice to your client(s).
- Your case study needs to identify and discuss the tax implications of the various issues raised.
- A report (word document, approx. 3,000 words) must be submitted for the calculations of the assessable income; allowable deductions and taxable income of the taxpayer including identifying and discussing them. E.g., how the amounts of income & deductions have been derived. If any receipts and payments are not assessable or deductible, the reasoning for non-inclusion of these in assessable income or deductions as per relevant legislation or cases. After all analysis, you must provide the best solution to save income tax payable.
- Your case study is not just a list of answers. Your reasons for your conclusions and recommendations must be based on your research into the relevant cases and legislation.
Solution
Question 2
In the given case scenario, it is required to determine net tax payable by the beneficiaries of trust for the tax year 2020-2021.
The taxable profit of the trust is referred as assessable income generated during the year after getting deduction of allowable expenses, which is worked out of the notion that the beneficiary are resident of the country. Since, the profit of the trust is ascertained as per the trust deed and its net profit is ascertained as per the taxation laws and therefore both amounts are not same. Usually, tax is charged on the net profit of the trust in the hands of the beneficiaries on the basis of their share in the net profit of trust notwithstanding of the fact that whether or not the profit is actually paid to them (Australian Taxation Office, 2021). For Assignment help For instance, if share of the beneficiary was 50% in the net profit of trust, then they would be assessed for 50% share in the net profit of trust, which is considered as proportionate mechanism. It is required by trustee to give details about every beneficiary of their proportion in the net profit by which they could include such amount in the taxation return.
Rules for franked distributions:
Unless not restricted through the trust deed, franked distribution is particularly entitled by the beneficiary, assisting in taxed is charged on the beneficiary with respect to the franked distribution (Mather, 2017). In such manner, franked distribution could be allocated to the particular beneficiary for the purpose of tax. if not any beneficiary is particularly entitled for the franked distribution, then in such case, tax is charged on proportionate manner for entire beneficiaries on the basis of their entitlement to the profit of trust, which suggests that in the same manner as of other net profit of the trust. Moreover, if any beneficiary has right to off-set of franking credit then in such case, they are also required to include this amount in the assessable profit (Millar, 2017).
Apart from the above aspects, a loss occurred by trust in the financial year could not be divided among beneficiaries. Although, it could be carried forward and implemented for deduction of the net profit in the subsequent year.
Rules for capital gains:
Unless not restricted through the trust deed, capital profit of the trust could be streamed to beneficiaries for the purpose of tax by creating them particularly entitled to the profit. This would allow permission to beneficiary to balance the capital profit with their capital losses, application of applicable discount and subject to the condition of integrity rules, obtain the advantage of any franking credit connected to a franked distribution (Slott, 2020).
Capital profit and franked distribution to which not any particular beneficiary is specifically permitted are allocated in the proportionate manner on the basis of their current share to the net income of trust as per Division 6 Part III of ITAA 1936.
Rules of taxation:
Individuals aged more than 18 years and company beneficiary are required to make payment of tax on their portion on net profit of trust at the rates of tax applicable to them. Further, beneficiaries are required to pay tax on behalf of minors on the basis of their share in net profit of trust. Some special norms are applicable of income generated by minor less than age of 18 years. Under such norms, they are required to pay higher amount of tax rates on particular types of profit like distribution from a family trust.
Rates of income tax for individual less than age of 18 years:
If an individual is less than 18 years, some of the profit may be changed to higher tax rates as compared to an adult. Although, they are required to make payment for the same rates as an adult for –
- All profit they receive if they are an excepted individual, this might be applicable if they have completed full-time study and engaged in work in full time or they have disabilities. Or they are permitted to a double orphan pension (Boadway, Brooks, & Macnaughton, 2019).
- Profit they receive as excepted profit, it consists business profit or employment profit, centrelink payment, and profit from estate of deceased person.
If there is any element of net profit of the trust for which there is not any beneficiary is exist, then in such case, tax is charged on the trustee on the corresponding share of the net profit. Further, if there is not any existence of net profit then tax is charged on trustee on any net profit. It should be noted that, trustee is usually levied tax on the net profit of trust at the greatest marginal rates applicable on the individual apart from some types of trusts that are charged to tax at altered individual rates (Australian Taxation Office, 2021).
Computation of Net Profit of Trust
.png)
Table 1 Computation of net income of trust
It has been noticed that, total capital gain from sale of shares 20000 and 7000 respectively and capital loss from prior years of $50000. By setting off capital loss from capital gain on sale of shares, in this year, not any capital gain is generated by trust. Further, remaining capital loss is 23000 (50000-27000), which would be carried forward in the subsequent year.
Shares of beneficiary –
.png)
Table 2 Computation of share of beneficiary in net income of trust
In the above case, it has been noticed that, share of the beneficiary was 95%, and therefore tax on the 5% net income would be charged in the hands of trustees.
.png)
Table 3 Computation of tax payable by beneficiaries
References
.png)
HI6027 Business and Corporate Law Case Study Sample
Purpose of the assessment (with ULO Mapping)
The purpose of the Group Assignment is to provide students with an opportunity to work in a collaborative environment in solving three case problems by citing the relevant legal rules and cases and applying these to the facts of the case.
In this Group Assignments, students are required to:
- Critically analyse the main features of the Australian Legal System and the foundations of company law. (ULO 1)
- Critically analyse the basic principles of Contract, Tort, and privacy law and apply them in resolving legal issues arising in commercial transactions. (ULO 2)
- Research and advocate the appropriateness of the different types of business structures and the legal environment in which they operate and their advantages and disadvantages in various commercial contexts. (ULO 4).
Purpose:
The Group Assignment aims to provide students with an opportunity to work in a collaborative environment in solving three case problems by citing the relevant legal rules and cases and applying these to the facts of the case. Students are to form groups, with a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 students per group. The assignment consists of a 2,000-word written report.
Instructions: Please read and re-read carefully to avoid mistakes.
Group Report
1. This group assignment consists of 3 parts. Part A is a question on Contract Law, Part B is a question on Negligence and Part C is a question involving Corporations Law. All questions must be answered.
2. Question A is worth 20 marks, while Question B and Question C are worth 10 marks each.
3. The total word limit for the group report is 2,000 words (+/- 10% allowed)
- Word limit for Question A – 1,000 words
- Word limit for Question B – 600 words
- Word limit for Question C – 400 words
Word count limits are strictly enforced. A deduction of two (2) marks will be imposed for every 50 words over the word count for either part of the report. Anything over the word count will not be read by your lecturer.
4. The total word count for the report as well as each part must be clearly written on the cover
sheet of the assignment. A paper will not be marked if the word counts are not written on the cover sheet.
Solution
Part A
Issue
Issue in the given case scenario is based on contract law. In this case, it is required to give advice to Sierra Foxtrot Airport with respect to its contractual position in connection with three tenders, such as Green Grow, Sow This, and Grassy Plains.
Legal rules and regulations
A contract is referred as binding agreement in a legal manner. Formation of the valid contract is based on the following elements –
Agreement: For creation of valid contract, first requirement is the agreement that usually includes the element of offer and acceptance and consists ‘meeting of minds’ between more than one people (Ridoan and Sifat 2018, p. 70(2)). In order to create offer, not any particular form is needed, and it could made to a single person or public at large, which is explained in case of Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. Further, offer must be distinct from invitation to deal. For Assignment help In the legal case, Backpool & FLyde, it was stated by court that, invitation to tender are also normally regarded as invitation to deal, with the tenders themselves creating offers that may be rejected or accepted (Australian Contract Law, 2019). Although, invitation to tender may run with it distinct offer to take into account all tender submitted. Further, acceptance is refereed as unequivocal statement through the offeree assenting to the offer.
Consideration: It is the amount asked by one party from another party for exchange of their promises (Valcke 2019, p. 292(3)). It could be anything that is stipulated by the promisor except it should not be illegal. In the case of Dunton v Dunton, giving up freedom is also considered as adequate consideration.
Intention of parties for creating legal connection: In order to building valid contract, parties to an agreement should have intention to create legal relationship. At the time of assessing every case, usually court implements some presumptions to distinct types of contracts. Therefore, in the domestic and social type of contract, it is presumed that, contract has not been formed with the intention to enter into any legal relationships (Bagheri, Kamal and Mansour 2017, p. 512(2)). On the other side, in the commercial type of contract, it is presumed that intention of parties is to make legal connection, and the same aspect has been observed in the case of Rose & Frank.
Capacity: There are some people or class of individuals that do not possess adequate capacity to formation of contract, and as a result thereof contract would not be enforceable against them(Zottola et al, 2018, p. 12(1)). For example, person of unsound mind is not have capacity of contract and therefore any contract made with them is considered as valid contract and therefore contract will not be enforceable against them.
It has been noted that, communication between two parties plays significant role in order to form valid agreement (Hart, 2020, p. 22(3)). As a general rule, communication would be effective only when it is send by one party and received by another party. However, by application of the postal rule of communication, it has been observed that, communication would be effective from the date when a valid post is posted, and not from the date when post is received by offeree. However, a contract cannot be creates until the post has been examined that their offer has been accepted by this act and it cannot be made by complying with the postal rule of acceptance (Korolev et al, 2018, p. 1008 (3)).
Application
In the prevailing case scenario, Sierra Foxtrot Airport has called for tenders for supply for green seeds with a closing date of 1 June. In this, there are three companies, namely Green Grow, Sow this, and Grassy Plains, has been applied. By above rules and regulations, it has been noted that, calling of tender is invitation to offer, and therefore there is not any obligation on the Sierra Foxtrot Airport to accept the minimum tender.
By considering the tender of Green Glow, it has been noted that, company has submitted this application in timely manner; therefore it is eligible tender application. Although, Foxtrot Airport do not want to give this contract to the cited organization because of unreliability of goods and services provided by Green Glow. Therefore, there is not any contract has been formed between Green Glow and Foxtrot Airport. The reason behind the same is that, in order to create valid contract, there must be valid agreement between two parties, and the same aspect is not exist in the given case.
Along with this, by considering the tender of Sow This, it has been seen that, company has submitted tender application within prescribed time, and application has been also received by Foxtrot Airport. However, such application is not considered by Foxtrot Airport at the time of discussion about giving contract to anyone company. Therefore, it can be said that, there is not any valid contract has been formed between them.
Lastly, by considering the tender application of Grassy Plains, tender application has been filed by company before the closing date but it was received by Foxtrot Airport on 2nd June and is spite of this, it was considered by company. Further, Foxtrot Airport has granted its acceptance on this tender, but this acceptance has not been received by the Grassy Plains. It is because, postal worker has destroyed the application, and without any actual communication, it is not possible to form the contract. The above analysis reflects that, communication may be performed by verbal or written manner, but it must be effective. In the absence of any effective communication, formation of the valid contract would not be possible.
Conclusion
To sum-up, it can be ascertain that, Sierra Foxtrot Airport has not formed any legal and valid contract with any of three companies. Due to this, it is advisable to the Airport Company that there is not any contractual liability occur with other companies.
Part B
Issues
In the prevailing case analysis, issue is concerned with the claiming of damages for the negligence. It is required to provide advice to Darcie on whether or not her case against Madeleine would be successful in the context of negligence aspect.
Legal rules and regulations
Negligence is referred as failure to exercise reasonable care. There are certain elements that should be proved by plaintiff in order to make claim against negligence. Such elements are duty of care, violation of duty of care, and causation ( Fhloinn, 2017, p. 180 (3). If all three elements have been proved by plaintiff successfully, then an ultimate part of a negligence claim consists of damages. Analysis of such three elements is as follows –
Duty of care: It is the first element that should be proved by plaintiff that, duty of care present between the plaintiff and the negligent individual. It usually consists of care not to assist injury to other people through actions or inactions (Dutescu, 2017, p. 218(1). There is not any single factor to explain about whether or not there is existence of duty of care. Although, mostly cited test for ascertainment of duty of care present is the neighbor principle, which was also explained in legal case of Donoghue v Stevenson. In the cited case, it was stated that, person should take reasonable care for avoidance of act or omission that could reasonably foresee will be probably to injure their neighbor (Legal Service Commission of South Australia, 2020).
Breach: Whether or not breach of duty has been occurred would be based on what is regarded as ‘reasonable’. In this aspect, it is required by plaintiff to demonstrate-
- There was a major risk of harm.
- Such risk was foreseeable.
- A normal person would have taken safeties against the risk in the similar situations(Miller and Antonucci 2016, p. 145(2)).
It should be noted that, in case of obvious risk, there will be not any liability arise on defendant as the risk was quite obvious to a normal individual and therefore the plaintiff has obligation for their own actions (Civil Liability Act 2002 NSW, 2020).
Causation: It should be required to prove that, as a result of violation of duty of care, damages have been suffered by plaintiff. In the absence of this, negligence claim could not be established as given in case of Amaca Pty Ltd v Ellis (Taylor & Scott Lawyers, 2021).
Damages: If all above three elements has been proved by plaintiff in successful way, then they would be eligible to get compensation for their harm that has been caused.
Application
In the given case scenario, property of Madeline at which garage sale has been conducted included a concrete driveway comprised sections of joined in an expansion joint that extended across its length. It is expected by Madeline that significant number of purchaser will attend the sale and she reasonably knew about the variation in the extent of adjoining concrete slabs in the forecourt of her home. When Darcie (buyer) has entered into premises, she does not have any idea regarding such disparity in slabs and due to this she fell towards the grounds.
The relationship between seller and purchaser give rise to a duty of care. Such care has been breached by Madeline as she knew about the disparity in the level of adjoining concrete slabs, and which may create injury to other person. Darcie has suffered from injury because of such breach of duty of care as if Madeline has taken adequate steps to remove disparity in the concrete slabs then it is probable that she may not suffered from injury.
Conclusion
To sum-up, it is advisable to Darcie that her case against Madeline would be successful as there is existence of all elements of establishment of negligence claim.
Part C
Issues
The prevailing case scenario is concerned with analysis and discussion of the director’s duties as per common law and corporation Act. It is required to ascertain whether the directors of Bluff Solutions Pty Ltd have breached their duty of care.
Legal rules and regulations
According to section 180 of the Corporation Act, director of company possesses to carry activities with an extent of care and diligence that a normal person will be predicted to demonstrate in that role (Roles and Responsibilities of directors, 2020). At the time of taking any decision, directors are required to be applying an enquiring mind, and take into account the overall position of company (Australian Securities and Investment Commission, 2021). In practice, this duty require every director to –
- Become familiar with the basics of business organization.
- Observation of policies and affairs of company (Chaffee, Davis-Nozemack 2017, p. 1428(2)).
- Stay informed and makes suitable enquiries with respect to activities of company.
- Possess an informed opinion regarding financial capacity and solvency of company (General duties of directors, 2020).
Further, section 180(2) of the cited Act states that a director who make business judgment is taken to satisfy the duty of care requirement for judgment, if they –
- Judgment has been taken in good faith and proper reason.
- Not having any material interest in subject matter (Ponta, 2018, p. 645(2)).
- Inform themselves up to the extent they believe to be suitable in reasonable manner (Corporation Act 2001).
- Rationally believe that it is in the interest of company (Yoshikawa and Hu 2017, p. 100(1)).
Application
In the given case scenario, director Jerry has directly provided his opinion about the report that it is correct even if some of the information has not been examined and supported by up to date data, which shows that duty of care has been breached by Jerry definitely. Further, it can be said that, remaining directors of the company also rely on the report and invested the money of company in the new software application, which creates foreseeable risk of harm to the company. But, by application of business judgment rule, it has been taken in good faith by the remaining directors and they rationally believe that it was in the interest of company.
Conclusion
Based on above analysis, it can be concluded that, Jerry Robinson, directors of Bluff Limited has breached duty of care as stated in Corporation Act 2001 and common law.
References
.png)
.png)
LAW6000 Business and Corporate Law Case Study Sample
Context:
This assessment allows students to solve practical problems that arise from a fact scenario and to give appropriate advice to clients.
Instructions:
There are five case studies you are required to critically analyse.
With respect to each case study:
- Identify the legal issue(s) arising from the facts of the casestudy
- Identify the appropriate legal rules that requires discussion in the case study
- Apply the law to the facts of the case study
- Reach a conclusion/ give practical advice to your client.
Your analysis should refer to appropriate cases and statutes and be referenced using the APA
Reference system.
Question 1
James has recently decided to open up a consultancy business near the city. He has identified appropriate premises and immediately gets into negotiation with Bradley, the landlord. He wishes to lease the commercial property for a period of five years. James proposes to demolish some of the interior walls to allow for better lighting and to then fit out the space to suit the modern image that he desires for his business. James and Bradley agree that the work would be completed in one month. It is agreed that once a lease agreement is signed James can commence the work in preparation to move into the premises. James signs his part of the agreement and sends it to the offices of Bradley’s solicitors. He then commences the work to demolish the walls and fit out the premises. Three weeks later as James was about to complete the fit out of the premises, he learns that Bradley has yet to sign the agreement and has in fact entered into negotiations with Simon with a view to leasing the premises to Simon.
James has completed a substantial amount of work and is preparing to move in. He has in fact printed all his stationery. He approaches Bradley who says that there was in fact no contract and that he is likely to lease the premises to Simon. James is distraught and seeks your advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles, use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise James on whether he is able to enforce the agreement with Bradley and the remedies that may be available to him. Use appropriate case law in support of your answer.
Question 2
Elizabeth is a major shareholder in Millennial-Relics Pty Ltd. Elizabeth and has noted that the company maintains the old-fashioned ‘memorandum of association’ which has been prepared for Millennial-Relics Pty Ltd.
The objects clause as drafted, limits the objects of the company to the development, manufacture and sale of motor vehicle batteries. Elizabeth believes that the research work that Rahim is doing (and future technology which may be developed as the full implications of Rahim’s work are realised) may have spin- offs into a number of related areas including dynamos for driver-less electric cars.
Elizabeth has spotted an opportunity that may allow the company to enter into a contract with like-minded companies for the development of state of the art dynamos that will be compatible with all types of electric cars. She is however concerned that the narrowness of the ‘memorandum’ may hamper the company’s ability to move into the emerging lucrative area and also the development and commercial exploitation of the dynamos which the company’s ongoing research may uncover may not be pursued lawfully. Elizabeth has read that there is no legal reason to have a memorandum or articles, even if they are now called a corporate constitution. The company’s research may also expose potentially exploitable products or secret processes in other areas related to artificial intelligence. When Elizabeth raised these concerns with the company’s other shareholders, they told her that they had been advised by the lawyers that this was the standard form for their companies, and that there was no cause for concern. Elizabeth is not convinced.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Elizabeth of the company’s position regarding any new contracts that it may enter in connection with the development of dynamos for driver-less electric cars and also explain how the replaceable rules may be of use to the company in the future.
Question 3
In December 2020 Greg Napole was driving along a busy street with his spouse and two children in the car. As they approached a busier section of the road Greg had to slow down significantly and as he was driving past a nearby park, a southern blue gum tree fell onto the car that he was driving killing wife Marsha and seriously injuring his two children and himself. Greg and his two children were hospitalised for two months with several broken bones. Upon recovery, Greg learnt that the tree had fallen because its root system had been destroyed by underground water leaking from a water channel that had been constructed by the local council, City of Small-town Council, in the year 1998. Greg is keen to have the council compensate him for the injuries he and his children have suffered and for the loss of his wife.
The local council has denied liability. They claim not to have a duty of care to Greg and his family. Greg wishes to pursue his claim and has now come to you for advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Greg as to whether he would be successful in negligence against City of Smalltown Council. Please explain fully, using relevant case law.
Question 4
Jaswant and his two friends, Davinder and Lachlan have been in a partnership for the last three years. Their business has grown and they now wish to expand into other states and territories. Their other friend Nicholas is a solicitor and he advises them to incorporate their business under the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) to take advantage of the principle of separate legal entity and to allow them to trade in any state without having to comply with local partnership legislation. Jaswant, Davinder and Lachlan have brought in some of their own assets into the business and their partnership agreement specifically states that the assets will remain their individual property. They are concerned that they may not be able to do this after incorporation. They are also concerned about whether they will be able to contract with the company for the provision of some of the services the national business will be delivering. They each have specialist skills and are hoping to be remunerated by the business for their skills. The three friends have also agreed to appoint Nicholas as the company solicitor and would be the only solicitor used by the company. This would be set out in the constitution that Nicholas would draw for the company. Lachlan is however concerned that if their relationship with Nicholas becomes strained, it may be difficult to use another solicitor if he chooses to enforce the constitution. Lachlan now approaches you for advice.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant sections of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) and appropriate case law, use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Lachlan of the effect and consequences of converting their partnership into a company and further whether Lachlan would be able to enforce the envisaged constitution if they wanted to use a different solicitor.
Question 5
Rahab is an executive working for a large pharmaceutical company which has recently transferred her to an overseas branch to manage the roll out of a global vaccine. She decides to leave the apartment where she lives and to put her household goods in storage. She contacts a company known as KingStore Pty Ltd, which specialises in the storage of goods. The company agrees to store Rahab’s goods for the period she will be away.
Before signing the contract of storage, Rahab asks about the condition of the building in which her goods will be stored. She has heard about recent floods in the state and just wants to be sure that her goods will be safe. The company manager replies: “Our building is in excellent condition. We built it only two years ago and we used the best building materials. Your goods are safe with us.”
Rahab decides to enter into a written contract with the company and stores her goods with them. The contract which she signs does not, however, say anything about the condition of the building, nor does it make any reference to the other statements made to Rahab by the company manager concerning the quality of the building materials.
Some months later, the company telephones Rahab at her new place of work and advises her that her goods have been badly damaged due to recent heavy rainfall which caused water to enter the building in which Rahab’s goods have been stored, and to damage them. The reason for the entry of the water into the building is that the building was badly built and poor building materials were used. As a result, the building’s foundations sank when the heavy rainfall fell, thereby causing a large gap between the bottom of the doors to the building and the floor of the building where the goods were stored. Rahab now wants to sue the KingStore Pty Ltd for the loss she has incurred as a result of the damage to her goods.
REQUIRED:
With reference to relevant legal principles use the IRAC legal problem-solving approach to advise Rahab of her legal position at common law against the storage company and discuss what remedies would flow from them. Give full reasons and use any relevant case law. Do not consider any statutory rights.
Solution
Question 1
Issue
The main issue is to assess enforceability of contract in case terms and conditions have been agreed by both the parties but not signed by one of the party.
Rule
Enforceability of contract
The elements necessary for enforcing agreement between two parties in accordance with provision of Australian contract law is as follows:
• It is necessary to have clear offer from one party and another party must have provided acceptance against same.
• It is necessary that consideration must have been provided against promise.
• The evidence of mutual intention of legally enforcing contract should exist.
• The terms of contract should be certain (Australian contract law, 2019).
• The parties of contract should be capable to enter into contract or agreement.
Remedies for breach of contract
The two remedies available for breach of contract is as follows:
Common law remedies: This refers to damages and liquidation claims provided as ‘substitute’ for performance. For Assignment help Further, liquidation damages can be claimed in can specified sum has been provided in contract in context with breach of contract (Australian contract law. 2019).
Equitable remedies: The two equitable remedies are specific performance i.e. making order to perform contract and second is injunction i.e. giving order to not to do contract.
Applicability
The decision provided in case of Australian Woollen Mills v The Commonwealth (1954) 92 CLR 424 could be considered for clarifying existence of offer as it asserts same as expression of a party for being bound to stated terms i.e. it is something more than declaration of person stating his or will to negotiation (Australian Woollen Mills v The Commonwealth (1954) 92 CLR 424). In others actual terms should be accepted by the party. In present case both the parties have accepted to the terms of contract and do have mutual intentions to be enforcing the contract legally. As it has been clearly provided that both the parties accepted the terms and agreed that work would complete in one month. Further, only formality of signing is left and no objection has been made after receipt of agreement signed by Bradley till three week where on the other has substantial amount of work has been completed. Further case of Empirnall Holdings v MachonPaull (1988) could be applied in present case which asserts that no specific form of acceptance is required for enforceability of contract.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that above specified remedies i.e. common law remedies and equitable remedies can be claim as contract has been breached by Bradely.
QUESTION 2
Issue
In present case existing position of company in context with making new contract is to be accessed along with explanation relating to replacing rules which may be use to company in future.
Rule
Memorandum of Association (MOA)
As per section 125 of Corporation Act 2001 MOA refers to document which regulates company’s external affairs such as form, structure and objects. Further it has been provided that company can choose to include objects clause in its constitution (Corporations Act 2001).
Section 141 of Corporations Act 2001
It asserts that company registered before 1st July 1998 would require memorandum of association and article of association. However, companies registered after 1st July 1998 may be governed by replaceable rules as per section 141 of Corporation Act 2001. Replaceable rules refer to set of minimum rules in context with management of company and its employees (Graw, 2017). These rules are replaceable in case an organization makes decision to adopt a constitution i.e. it can either incorporate or replace provision with its own.
Applicability
In present case as existing object clause is limited to manufacture and sale of motor vehicle batteries and does not include electric cars; thus before making any contract relating to same it is necessary to amend memorandum of association in order to continue business operations in smooth manner. Further regarding replaceable rules, in case company is registered after 1st July 1998 than it does not require MOA and AOA and it can govern its operations in accordance with ‘Replaceable Rules’ as per section 141 of Corporation Act 2001 (Memorandum of Article of Association, 2020).
Conclusion
It can be concluded that decision of use of replaceable rules depends on date of registration of company and contract which are not covered in existing object clause can be made after making appropriate amendment in object clause of memorandum of association.
QUESTION 3
Issue
To assess where claim can be made in context with negligence against City of Smalltown Council as heavy loss has been suffered by Greg due to same.
Rule
Provision for ‘Tort of Negligence’
Negligence occurs in case one party fails to take reasonable care in order to avoid causing damage to another person. Thus, the four factors necessarily to be proven for claiming loss due to negligence is availability of duty of care, breach of duty, damage and causation (Stevens, 2017, p 17).
Damages for Negligence
Damages are considered as prime remedy for tort action of negligence i.e. nominal damages, aggravated damages, punitive damages and compensatory damages. These can be claimed on the basis of nature of negligence (Tort of Negligence, 2020). Nominal damages are provided in case plaintiff does not succeed in proving any injury or damage and compensatory damages are provided in case of serious invasions. Punitive damages are awarded in case of breach of confidence or tort relating to misuse of personal information as in case of Weller v Associated Newspapers Ltd [2014] EWHC 1163 (QB).
Applicability
In present case loss has been suffered by Greg due to accident as the tree fell while he was driving. The main reason behind accident was felling of tree; the incident occurred as the root system of tree was destroyed due to underground water leaking channel which has been constructed by local council, City of Small town council. Thus, it would be appropriate to state that it was their duty to ensure that it is maintained appropriately and no loss has been occurred to general public due to same. The recent decision provided in case of Libra Collaroy Pty Ltd v Bhide [2017] NSWCA 196 could be considered where decision was provided that landlord is responsible for collapsed balcony as it was his responsibility to provide appropriate structural integrity of the balcony (Libra Collaroy Pty Ltd v Bhide [2017] NSWCA 196). Further, the decision provided in case of Thistle Co of Australia Pty Ltd v Bretz (2018) asserts that it is responsibility of innocent person to prove negligence in order to claim damages as remedy, thus Breg would require proving that he has suffered heavy loss due to negligence of City of small town council.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that in present case all the four variants for proving negligence are available i.e. of duty of care, breach of duty, damage and causation. As City of small town council was responsible for management of water channel and due to its leakage the tree fell down which eventually resulted in accident. Further, breach has been made by not maintain water channel appropriately and damage has been borne by Greg in form of accident due to the accident. Thus, Greg would succeed in claiming damages in context with accident against City of small town council for its negligence.
QUESTION 4
Issue
In present case Lachlan is dealing with issue regarding effect and consequences of converting their partnership into company. Another issue to be considered is to assess whether Lachlan would succeed in enforcing envisaged constitution in case they wanted to use different solicitor.
Rule
Consequence and effect of converting partnership into company
• As per Australian provisions, in order to convert partnership into company, it is necessary to dissolve partnership as it cannot be transferred into company. Even it is necessary to cancel Australian Business Number (ABN) relating to partnership.
• It is necessary to ensure whether it would be proprietary or public company and it is to be registered with ASIC (Lopes et al, 2020).
• Further, existing assets should represented as owed to company; as it will have separate legal entity assets owned by same would only be part of business.
• The key principle required to be considered is that in case directors of company does not accomplish their responsibility appropriately than they would be responsible personally for debt incurred by company.
• Directors are liable for remuneration in accordance with their skills and experience i.e. their contribution to the business operation (Ndzi, 2017, p1).
Applicability
In present case the three partners are Davinder, Jaswant and Lachlan wanted to convert their partnership into company. Thus, initially they would require dissolving their partnership in order. Further, as the business structure would be of company; thus they would be able to operate in overseas market or change product function in order to accommodate this growth as advantage of corporate structure. It can be accessed from above analysis that as company does have separate entity; thus the assets which would be in name of company would be considered as business asset only. In present case as all the three partners have bought some of their assets in partnership and now they wanted same to remain their individual property; hence they would not be able to claim expenses relating to same as it is no more part of business. In context with remuneration it would be appropriate to state that they would be able to claim remuneration only if they are appointed as director of the company (Ndzi, 2017, p 1). Lastly, main perception to be considered in case of corporation business structure is they require accomplishing their obligation with business perception rather than personal else they would be responsible for debt or damages relating to specific transaction.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that above specified effects and consequences are to be considered by all the three partners regarding transforming partnership into company. Further, Lachlan would not be able to enforce envisaged constitution in case they distinct to different solicitor as in corporate business structure decision are taken by majority of shareholders by passing appropriate resolution.
QUESTION 5
Issue
Assessment of remedies in present case loss has been occurred by Rahab as damage to her goods as the building in which goods were kept was damaged.
Rule
Provision relating to misrepresentation
Misrepresentation refers to providing wrong information to one party by another between which contracts has been made (Australian contract law, 2019). Further, it has been provided that in case one of the parties of contract relies on misrepresentation and suffers loss then they can claim damages or cancel the contract.
Remedies for misrepresentation
Rescinding the contract: The claimant can rescind the contact in case the party who has suffered opt for same.
Damages: It is alternative of rescission i.e. to claim for loss due to relying on misrepresentation. However, the person could not succeed in claim in case they fail in proving that they do have reasonable grounds for believing that they do have reasonable grounds to believe that misrepresentation statement was true (Stevens, 2017).
Applicability
The decision provided in case of Google Inc V ACCC [2013] asserts that in case it has been appropriately stated that the party of contract is not responsible for facts or statements provided in advertisement than they cannot be held responsible for same. Thus, it is necessary that decision has been made on the basis of statement provided by one of the party and claimant is not aware that these are untrue (Google Inc V ACCC [2013]). In present case as Rahab made contract after ensuring that goods were kept in storage which was having good condition and was not aware that another party was providing false statement knowingly. Hence, he would claim damages in context with goods provided to another party.
Conclusion
In accordance with above provisions as King Store Pty Ltd. has provided misrepresentation and contract has been dependent on same; thus Rahab would succeed in claiming loss in context with damage relating to goods.
REFERENCES
.png)
LAW6001 Taxation Law Case Study Sample
Task Summary
In response to the issues raised in the case study provided, research and develop a 3000-word tax advice that addresses (a) assessable income (b) allowable deductions (c) tax calculations and (d) your conclusions and recommendations that arise from a fact scenario and to give appropriate advice to clients. Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Context
This assessment allows students to solve practical problems that arise from various scenarios and to give appropriate advice to clients. This assessment assesses your research skills, your ability to synthesise an original piece of work to specific content requirements and your ability to produce a comprehensible piece of advice which addressing the client’s needs.
It also assesses your written communication skills. The ability to deliver to a brief is an essential skill in the workplace. Clients may well approach advisors seeking a combination of specific information needs and advice on the tax implications of a particular arrangement in the Australian tax jurisdiction. It is therefore important to be able to identify all the issues presented by an arrangement and to think about the potential consequences of different approaches to addressing the client’s needs.
Task Instructions
• This case study must be presented as a group effort. The case study requires collaboration of effective team work. It is expected students will take parts and survey the relevant literature, including decided cases, and select appropriate additional resources.
• Your case study is not just a list of answers. Your reasons for your conclusions and recommendations must be based on your research into the relevant cases and legislation.
• With respect to each case study:
• Advise the best investment option for clients from the facts of the case study
• Identify the appropriate legal principles that requires discussion in the case study
• Apply the law to the facts of the case study
• After reaching a relevant conclusion, provide practical advice to your client(s).
• Your case study needs to identify and discuss the tax implications of the various issues raised.
• A report (word document, approx. 3,000 words) must be submitted for the calculations of the assessable income; allowable deductions and taxable income of the taxpayer including identifying and discussing them. E.g., how the amounts of income & deductions have been derived. If any receipts and payments are not assessable or deductible, the reasoning for non-inclusion of these in assessable income or deductions as per relevant legislation or cases. After all analysis, you must provide the best solution to save income tax payable.
• Your case study is not just a list of answers. Your reasons for your conclusions and recommendations must be based on your research into the relevant cases and legislation.
Solution
Case 1
Working Notes
Notes 1 Total sale
In case any item of business trading stock is used for private purpose then in accordance with assertions provided by Australian taxation office; it is considered to be sold and its value is accounted in business assessable income. For Assignment Help, In present case as coffee machine has been taken to home for personal use it would be recognized as part of business income (Using trading stock for private purposes, 2020).
Note 2: Total purchases
In accordance with Para 9 of AASB 102, inventories are required to be measured at lower of cost or net realisable value. In present case the cost of inventory in 2000 and net realisable value of same is 1800; thus it would be recognized at 1800 i.e. lower of net realisable value or cost (AASB 102 Inventories, 2020).
Note: 4 PAYG withholding
As per ATO provisions, employers does have responsibility to assist payee in accomplishing their tax liability and same is done through withholding payments from the amount paid to employees; thus it is part of salary or wage and deductible expense as well (Creighton, 2017).
Note 5: PAYG for personal tax commitments
When income or business receipts a certain amount as per taxable provisions; one is required to make payment of income tax instalment which could be quarterly or monthly. PAYG instalment assist in avoiding large bill; thus it is not a business expense hence no deduction would be available regarding same (Wollner, Barkoczy & Murphy, 2020).
Note 6: Other deductible expense
Other deductible expenses include decline in value of assets. It is assumed company complies with policy of accounting assets at market value, thus decline in values is being written off year. Hence same is deductible expenditure (Mather, 2018).
Note 7: Depreciation
Depreciation of coffee machine on straight line basis for each year
62000/10 =6200
For year 2020/21; it would be charged for 11 months i.e. 6200/12*11 =$5683
Depreciation of BMW motor vehicle on straight line basis for each year
89000/8 i.e. 11125
As vehicle is purchase on 1st May 2021, depreciation would be charged for 2 months and 40% only as it is used for business to specified extent only.
11125/12*2*40%
= 742
Total depreciation = 5683+742 =6425
Other notes and assumption
• It has been provided that cash receipts have been received as contribution by Michael to expand the business; thus it is a capital receipt and not considered as part of business income.
• Further cash drawings of $3000; are personal drawing thus same would be reduced from capital and not considered while calculating business profits.
• Payment of penalty for breach of Australian Customer regulation of $900 is not allowable as business expenditure; thus same would not be considered while evaluating business income.
• It has been assumed that company complies with straight line method of depreciation on its assets; thus same has been applied for calculating depreciation for motor vehicle and machine.
STATEMENT PRESENTING CALCULATION OF OTHER INCOME
Notes: In accordance with Australian taxation office provisions, insurance payout in context with personal items is not taxable. It includes insurance recovery received for family home or personal injury is not taxable. Thus, in present case recovery for medical relating to injury of Michael would not be taxable. However, other recovery i.e. receipts regarding business or income producing assets is to be taxed. Thus, compensation for loss of income as well as recovery against recovery of shop would be considered in assessable income as it is relating to personal.
STATEMENT PRESENTING CALCULATION OF CAPITAL GAIN ON SALE OF MOTOR VEHICLE
Note: An assumption has been made that motor vehicle has been used for more than one year and adjustable amount represents amount after making adjustment in context with depreciation and other deductions. In accordance with taxation provision of Australian taxation provision, gains on assets which are held by individuals for minimum period of twelve months would be considered as long term capital gains and they are subject to 50% exclusion.
STATEMENT PRESENTING NET TAX LIABILITY OF MICHAEL PAYABLE FOR YEAR 2020/2021
.png)
.png)
Working Note:
Tax liability on ordinary income
Tax on capital gain
References
SAP103 Welfare Law Case Study 1 Sample
There are three case studies to complete for this assessment:
Case Study A
Case Study B
Case Study C
Tabitha has been re-admitted to the local public hospital for psychiatric treatment. She has a Mental Health Tribunal hearing coming up to decide whether she can leave the psychiatric ward and receive her treatment in the community. Tabitha wants to leave the hospital and go home. Tabitha is a long-term client of a community mental health support service. She has been receiving support from Peter (a community service worker) at the support service for five years. She trusts Peter and has asked him to attend the Mental Health Tribunal hearing with her.
Before the Tribunal hearing the medical treatment teams must write a report on Tabitha’s medical treatment and her progress in recovering from her mental illness. In the report, the treatment team have requested that Tabitha remain in the hospital for treatment for a further three months.
The treatment team must also advise Tabitha of the time and date of the Tribunal hearing and provide her with a copy of the report that they have prepared as evidence for the tribunal. The hospital has complied with this protocol. Peter attends the Tribunal hearing with Tabitha. With Tabitha’s consent Peter presents a written report that he has prepared with provides detail of Tabitha’s past attendances at the support service. The report includes dates and times of attendance and records the successful completion by Tabitha of activities organized by the support service. During the hearing, the Chair of the Tribunal asks Peter to talk to the tribunal members about Tabitha’s family support and her personal relationships, including where Tabitha will go to live if she is discharged from hospital. Upon hearing this request from the Chair, Tabitha tells Peter that she would like legal advice before she says anything further to the Tribunal.
Question 1:
Identify the principle of administrative law that was applied by the hospital when they advised Tabitha of the Tribunal hearing and give her a copy of their report? (2 marks)
Question 2:
Is Peter able to advise Tabitha on mental health law and how the law will apply in Tabitha’s circumstances? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
Case study B
Susan is a community services worker with expertise in family violence. She is part of a team of professionals that visits the local aged facility service fortnightly. Bert has recently moved to the aged care facility and staff have been concerned about injuries that are evident when they help him to shower and dress in the morning. During discussions with Bert, he disclosed that a family member who has been taking care of him has been violent towards him and takes his pension money. With Bert’s consent the staff refer him to Susan and her colleague Jed who is a lawyer.
The staff have arranged for Bert to speak with Jed and Susan immediately about applying for a court order to protect Bert from further violence, and to discuss safety planning with them.
In your answer to questions below refer to the readings.
Question 5:
Identify three benefits to Susan of working in an integrated team with Jed? (3 marks)
Refer to Forell and Nagy (2021) Health justice insights: health justice partnership as a response to domestic and family violence. Sydney, Health Justice Australia Inc, for the common features of a family violence partnership. (Week 2 in Moodle)
Question 6:
What are the benefits to Bert of being able to speak with an integrated support team at his aged care facility? (2 marks)
Question 7:
What are the inter-professional tensions that Susan might experience working together with Jed to support Bert? (3 marks)
Case study C
Beatrice is 12 years old, and she has been having trouble at school. On the weekend Beatrice attends a netball match organised by Matthew who is a youth worker employed by a local government run agency. After the game, Beatrice tells Matthew that she is having trouble at school, and she wants to change schools because she is frightened of her teacher. Beatrice also tells Matthew that she has been hiding at the local shopping mall during the day to avoid going to class. Beatrice gives Matthew a piece of paper with her personal information written down including her address, her phone number, and the name of the teacher she is frightened of.
Question 8:
Discuss whether Matthew is mandated to report his concerns about Beatrice’s safety under local legislation in your jurisdiction, in which you are presently living. (2 marks)
Question 9:
Can Matthew ask Beatrice further questions about her experience with the teacher? Refer to the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner for the text of the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), a Schedule to the Privacy Act 1988 (Cth) (PA), to identify and discuss limits that apply for the collection and retention of private information by organisations and APP entities. (3 marks)
Question 10:
What is Matthew’s ethical obligation in relation to keeping Beatrice’s personal information private?
Solution
A
Question 1:
When the hospital was either informing Tabitha about the Tribunal hearing or providing her with a copy of its report for the Assignment Help and the hospital was operating under a principle of administrative law known as the right to be heard, and in line with the principle of natural justice. This principle enables persons who are on the receiving end of administrative decisions to air their issues and be told the basis on which the decision was made. The hospital has respected Tabitha’s right to be informed of the hearing so she can prepare to oppose the report. This practice has been done in compliance with the “Mental Health Act 2016 (QLD)”, which recognizes the rights of the patient and procedural fairness, especially in dealing with mental health tribunals.
Question 2:
Peter cannot help Tabitha with information on mental health law or how the law is going to affect her case. This is so because Peter is a “community service worker” and not a “legally trained person”. In Queensland the “Legal Profession Act 2007” regulates who can give legal advice, only legally qualified persons are permitted to do so. Consulting without legal education and training may essentially constitute the unauthorized practice of law. Tabitha is a client, and Peter works for her cause and helps her to get information about community services in her situation but he should advise her to consult a legal attorney who specializes in mental health law to address this matter.
Question 3:
Regarding Peter, who wants to assist Tabitha and grant her request for legal assistance, some procedures can be suggested.
- Report to the Tribunal Chair that Tabitha wants an attorney to represent her, and request the brief recess.
- Call Legal Aid Queensland or a community legal advice centre of mental health law to seek emergency help.
- Support Tabitha to find that the Mental Health Review Tribunal of Queensland has provided free legal aid services for all mentally ill patients under the Mental Health Act 2016.
- Give Tabitha the phone and address of the Queensland Law Society to help her find a private solicitor of mental health law.
- Propose to assist Tabitha to speak to the selected legal lawyer to explain the advice, given to her.
Peter should write down these actions and refrain from interfering with Tabitha’s right to consult a legal attorney.
Question 4:
The following procedures would have to be followed by Peter to be able to receive Tabitha’s informed consent for him to talk to the Tribunal members concerning her relationship status.
- It is clear and simple to tell Tabitha face-to-face what the Tribunal wants to know about relationships and where she has been living.
- Elaborate on the consequences of submitting the information which would be likely occur due to this action and how it is going influence the Tribunal’s decision.
- Make sure that Tabitha knows she has the right to say no.
- Mention other solutions, for example, giving only basic facts about Tabitha or letting her defend herself.
- Give her enough time to think through without making her feel that she is under immense pressure to decide.
- If Tabitha agrees then get written consent from her and keep it in writing.
- Discuss and agree on the particulars about which she is okay to share.
- Provide comfort to Tabitha informing her that she can withdraw consent at any one time throughout the hearing.
This process accords with Queensland’s guardianship principles and mental health act that champions patient, voluntary and informed participation.
B
Question 5:
Three advantages for Susan to be the integrated work team with Jed:
- Enhanced capability to address complex needs: No doubt, Susan, who specialises in family violence, would be able to offer a full range of support together with legal advice from Jed if needed because she comprehends all the potential safety issues connected with the situation around Bert.
- Improved service coordination: This enables general communication and passing around of Bert’s details between Susan and Jed, there is no disjointed care.
- Increased professional knowledge and skills: By working together with other professionals, Susan can learn more about the legal procedures dealing with care for the elderly and thus help other clients like Bert in the future.
These and other benefits are also in line with what Forell and Nagy (2021) found regarding health justice partnerships where there is enhanced service capability, simplified access to legal assistance, and enhanced capacity to recognize and prevent domestic violence (FORELL and NAGY, 2021).
Question 6:
Advantages of Bert to be able to address an integrated support team at his aged care facility:
- Accessibility and convenience: Bert can get social support and legal aid in a familiar and comfortable environment instead of moving between locations and services.
- Holistic and coordinated care: This allows the members of the integrated team to approach Bert’s needs holistically and, therefore, tackle his safety, legal, and welfare issues concurrently.
These benefits correspond with Kennedy et al.’s (2016) discussion of the pros of integrated services, as these enhance outcomes for clients by fostering coordination and also update ‘the four-dimensional model’, which entails client concerns on social, psychological, and legal levels.
Question 7:
Potential interprofessional conflicts which Susan may face while working with Jed in supporting Bert:
- Differing professional values: Susan’s perception of work as involving mediation and solving conflict may pose a conflict with Jed’s more aggressive approach to seeking legal redress.
- Confidentiality constraints: It is argued that while Susan has some mandatory reporting responsibilities, these will clash with Jed and his duty to keep his client confidentiality as well as privileged information.
- Role boundaries: The relationships could be characterised by a lack of clarity or ambiguity as to who does what, which may confuse as to who is doing what or when, and hence a lack of clear provision and delivery.
Kennedy et al. (2016) outline these endeavours in integrated services identifying that there exists tensions between legal and human service professionals in areas such as knowledge, method and ethical practices. These tensions may cause misunderstandings in the process, therefore, it is a premise that should be managed for interdisciplinary teams to collaborate in the best way possible in developing and implementing interventions for clients like Bert.
C
Question 8:
In Queensland, Matthew is required by the “Child Protection Act 1999” to report his suspicions of Beatrice’s safety. Matthew is surely a ‘relevant person’ under the Act, given that he is a youth worker working for a local government organization. The Act set down a principle that a person must report any suspicion of a child who has been abused, is being abused, or is likely to be abused; and may not have a parent capable of preventing the abuse. It was relatively easy to see that Elements such as Beatrice’s statement about being scared of her teacher and skipping school only to hide at the mall could cause Matthew to suspect harm toward the child, thus demanding he report to the Department of Child Safety.
Question 9:
Matthew can further interrogate Beatrice with some more questions regarding her experience with the teacher, but he needs to observe some elements of the “Privacy Act 1988 (Cth)” of Australia referred to as the APPs. From APP 3, we learn that Matthew must not collect personal data he does not reasonably require to perform his tasks or undertake the activities for which he was established. He should capture information from Beatrice (APP 3.6) and explain to her the reason for collecting the information, and how the information will be used (APP 5). Matthew must confirm that the information is timely, accurate and comprehensive (APP 10). He should ensure that the information is certainly protected (APP 11) and can only be used or disclosed for the sole purpose for which it was collected unless the following exceptions apply where the use of “disclosure is necessary to prevent harm (APP 6)”.
Question 10:
Given the Australian Association of Social Workers Code of Ethics 2020, Matthew has two responsibilities concerning the “privacy of Beatrice’s personal information”. “According to Section 5.4.1”, Social workers should respect the rights of clients to “privacy and confidentiality”, and provide information only where consent has been freely given or where mandated by law. However, Section 5.4.2 stipulates that the client has a right to be informed of the restrictions of confidentiality and where, and when the social worker is legally required to disclose information with or without the client’s consent. In Beatrice’s case, Matthew should discuss with her that while her information will be kept confidential, there may be a need to disclose information to other authorities in the interest of safety should he find out that she poses a danger to herself or others due to the nature of her disorder.
Readings
Australian Association of Social Workers Code of Ethics 2020, Sections 5.4.1 and 5.4.2.
Kennedy et al., (2016). Relationship between Human Service Practice, Law and Ethics
Office of the Australian Information Commissioner for the text of the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), a Schedule to the Privacy Act 1988 (Cth) (PA)
S FORELL & MT NAGY, 2021. Health justice partnership as a response to domestic and family violence
LML6001 Practitioner Legal Skills for Australian Migration Law Case Study Sample
SCENARIO
You are a registered migration agent and have been practicing for over 5 years. You have thoroughly enjoyed practicing in this industry. You have witnessed some unfair outcomes in terms of delegates making decisions where they have misapplied the legislation.
It has been particularly disheartening in these situations, where your clients who are in Australia, did not have the funds or the will to lodge a review application to the Administrative Review Tribunal, despite you offering to assist them at a reduced fee at the review application stage.
You have always thought that it is unrealistic and unfair that after clients having waited for a long time, sometimes for over two years, for a decision on a visa application and once it has been refused, they only having 35 days to remain in Australia to sort out their affairs whilst on a bridging visa.
You are also of the view that it is unfair to the Australian community, as usually your clients who are subject to refusal are employed and in most cases the employer reaches out to you to see if there is anything they can do to help your clients remain in Australia as they are so valuable to their business and would impact the business and the clients.
Over the years, to help alleviate the pressure on your clients that have been refused a visa, you have advised them to apply for a Protection (Class XA, Subclass 866) visa, which would generally provide them with an additional few years, due to the processing time, to remain in Australia on a bridging visa to sort out their affairs before having to depart the country.
When advising clients of the Protection visa option, you generally assist in the background, you do not issue a service agreement and provide the advice pro-bono as a fairer approach in these circumstances. Generally, you say that it is up to the client to decide if they would like to pay you anything, but you do not expect it. Your community has awarded you many certificates of appreciation for assisting your community in this way. In 2024, the Government released the following media release “What are you doing to safeguard Australia’s protection visa system?”
Question
In light of these facts, have you breached any obligations under the Migration (Migration Agents Code of Conduct) Regulations 2021 and what steps would you implement to meet your obligations? You must support your answers by reference to the specific legislative provisions.
Solution
Introduction
The Migration (Migration Agents Code of Conduct) Regulations 2021 (the Code) requires registered migration agents to meet the statutory obligations under the Migration Act 1958 (Cth) and the Migration Regulations 1994 (Cth) by adhering to the professional conduct contained in the Code . The recent government reforms for the Assignment Help regarding the integrity of the Protection Visa system require an evaluation of whether migration advice complies with the legal and ethical standards. This analysis discusses possible obligations breach and the measures to take to assure compliance.
Potential Breach of Obligations
1. Provision of Advice on Protection Visas Without a Service Agreement
According to Regulation 8 of the Code, migration agents are required to act in accordance with the law and maintain comprehensive records of all services provided to clients . It may be a breach of this requirement if the failure to issue a formal service agreement is combined with advice on Protection Visas. Transparency and accountability in migration advice services depend on such agreements. The service agreement is a legal agreement between the migration agent and the client that sets the expectations between them, so that disputes are unlikely to occur, and professional obligations are met.
2. Facilitation of Non-Genuine Protection Visa Applications
The Australian Government has clearly said that registered migration agents should not help people who do not genuinely fulfil Australia’s protection obligations when applying for Protection Visas. Section 9 of the Code requires migration agents to act with honesty and good faith . The giving of advice in such a way that produces applications that are not of substantial merit may constitute facilitating misuse of the Protection Visa system and therefore contravene professional and legal obligations. This is especially important considering the government’s recent reforms to prevent exploitation of the Protection Visa system.
3. Potential Breach of Regulation 23: Duty to Act in the Best Interests of the Client
While the purpose of advising clients on Protection Visas may have been to give them more time to make their arrangements before they leave, such advice must be judged in terms of the duty to act in the best interests of clients. Migration agents are required by regulation 23 of the Code to avoid misleading clients as to their prospects of success . The failure to act in the best interests of the clients may be constituted by the advice to lodge Protection Visa applications as a strategic measure rather than as a result of a genuine claim for asylum. In addition, particularly if giving misleading advice, there are potential legal and financial consequences for clients.
4. Failure to Maintain Professional Integrity
The Code of Conduct requires migration agents to adhere to integrity in their professional dealings, pursuant to Regulation 31 of the Code . A lack of clear documentation, service agreements and potential facilitation of applications that are not meritorious could be indicative of conduct that falls below the standards of integrity expected of migration agents. Additionally, failure to keep adequate records could expose a compliance risk under the Migration Regulations 1994 . Maintaining public trust in the migration system is dependent on professional integrity and therefore any failure to live up to these standards will result in disciplinary action and damage to your reputation.
Measures to Ensure Compliance and meet obligations
The following measures will be taken to rectify any potential breaches and adhere to regulatory obligations.
Issuance of Service Agreements for All Clients
In the future, when dealing with clients, there will be a formal service agreement that will include the scope of services, fees, and legal obligations. This is in line with Regulation 19 of the Code which requires clear terms of engagements to improve transparency and accountability . Service agreements are one of the most important tools that ensure that the client and the migration agent are both aware of their rights and responsibilities.
Provision of Transparent and Legally Sound Advice
Advice on Protection Visas will be given based on a client’s genuine engagement with Australia’s protection obligations. Every case will be rigorously scrutinized to ensure compliance with the Migration Act 1958 and related regulations . It is crucial to give clear and true advice to clients so that they are aware of their situation and can make an informed decision on their visa applications.
Adherence to Ethical Conduct and Reporting Mechanisms
Professional integrity will be maintained by strict adherence to ethical guidelines under the Code. It includes not engaging in practices that may assist with unmeritorious applications and reporting any unethical conduct by other migration agents to the Office of the Migration Agents Registration Authority (OMARA) . Reporting mechanisms are important instruments for the profession’s integrity preservation and for timely and appropriate handling of misconduct.
Enhanced Record-Keeping and Documentation
The following will be adopted as a structured approach to record keeping:
• Keeping records of consultation or legal advice given.
• Making sure that all clients receive signed service agreements.
• Assessing eligibility for Protection Visits in order to support transparency and accountability. It is important to ensure that agent keeps proper records in order to prove compliance with professional and legal obligations. It also acts as a safeguard in case of some disputes or a regulatory audit.
Participation in Continuing Professional Development (CPD)
Professional development activities will continue to be done to make sure that migration advice remains compliant with recent legislative changes. CPD activities will enable participation in updated knowledge on ethical obligations and regulatory requirements. Migration law is an ever-changing field, and continuous learning is vital to ensure that migration agents are always well informed and able to give accurate legal advice.
Client Education and Informed Decision-Making
The following will be implemented as a structured approach to client education:
• Writing out the Protection Visa process and providing written materials.
• The risks and consequences of lodging non genuine Protection Visa applications are clearly explained.
• Encouraging clients to seek independent legal advice should be necessary. By empowering clients with the right information, clients are left to make informed decisions on their migration options. It also prevents vulnerable people from being tricked by operators who are not trustworthy.
Conclusion
An evaluation of past practices suggests some actions may have inadvertently breached provisions of the Migration Agents Code of Conduct 2021. A structured, transparent way of dealing with these concerns will be adopted. By sticking to statutory and professional obligations, migration agents ensure that they can keep on providing clients with effective and lawful assistance and maintain the integrity of the migration system. The implementation of these measures will not only guarantee the compliance with the Code but will also reassert the ethical obligations the profession by itself prescribes.
Bibliography
.png)

.png)



.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






