BMG872 Global Strategy, Development & Implementation Assignment Sample
RATIONALE
The strategic management process helps organisations identify what they intend to achieve and how they will accomplish valued outcomes. The magnitude of this challenge is greater today than ever before. A new competitive landscape is developing as a result of the increasing globalisation. When students take this module, they will already have considered the global environment in which organisations have to operate and survive. This module focuses on how firms’ sizes can become or remain international in scope. It analyses how organisations can use the strategic management process to understand those international competitive forces and develop competitive advantage systematically and consistently. This module links the internationalisation process examined in Semester one to focusing on multinational management of the firm.
AIMS
The primary aim of this module is to develop an understanding of the strategic management of an enterprise engaged in international business. This includes understanding how the competitive position of a firm is devised based on analysing structure, country-based sources of advantage and their distinctive competencies. Further, translating strategy into organisation action requires understanding the advantages and disadvantages of the many organisational forms and processes that may be used to attain the desired competitive position. The secondary aims are to (1) develop an understanding of the international business that integrates specific functional activities comprising the firm and (2) provide the opportunity to further develop analytical skills and decision-making in situations characterised by uncertainty and complexity.
OBJECTIVES
On successful completion of this module students will be able to:
• Understand the catalysts for international expansion, including country, industry, and firm influences;
• Understand unique management issues that confront international business units;
• Analyse different competitive strategies in globalising industries;
• Understand the process of international expansion generically;
• Examine how changes in strategy create organisational tension, especially in headquarter-subsidiary relations;
• Analyse historical globalisation patterns in strategic industries;
• Assess strategies needed to compete internationally.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Successful Students Will Be Able To:
1 Demonstrate knowledge and thorough understanding of the fundamental concepts, principles, theories, practices and legislative frameworks underlying international business as an academic discipline and as a tool for improved management of international businesses.
2 Apply critical evaluation to complex arguments and evidence in the field of international business.
3 Formulate strategies to support successful international operations in diverse contexts.
4 Assess the implications, risks, security, integrity and confidentiality aspects of applying innovative solutions across multi-national and trans-national companies.
Solutions
The main concern of performing the present study is to develop an understanding of the strategic management of an enterprise engaged in international business. For developing such understandings the Volkswagen is selected as a brand, which belongs to the automobile industry. Company is presently running business activities in 153 nations, which wants to expand its business in international market of Indonesia. The turnover of company for the year 2020 was €222.884 billion, and it employed a total of 662575 (Volkswagen, 2021).
This study contains several models such as PEST, Porter’s five forces, diamond model, for analyzing the country of expansion. Additionally, potential managerial issues and their solutions also provided.
Main Analysis
Reasons behind international expansion-
In 1937 Volkswagen was established by Deutsche Arbeitsfront in Berlin (Volkswagen, 2021). Additionally it was reported that Volkswagen has faced highest increase in its market share between 2019-2020 as the % jumped from 24.3% to 26.2 % and with the revised strategy of the company, it aims at increasing such share to 5% by 2025 (Volkswagen, 2021). Thereby after such an amazing performance in around 153 countries the Volkswagen is planning to expand further its business in Indonesia. The company noticed potential growth in term of economy in Indonesia. Further, such international expansion would help them to achieve their target of attaining market share by +5% by 2025 (VW plans to build car factory in Indonesia, 2018).
Possible strategic choices available to the company
Also the economy of the country is growing vastly along with the need for the automobile companies (Global Strategic Choices, 2020). As per few reports it is estimated that around 80 vehicles per 1000 individuals in Indonesia which is even higher than in US. Further the reason behind Indonesia as a strategic choice is given through-
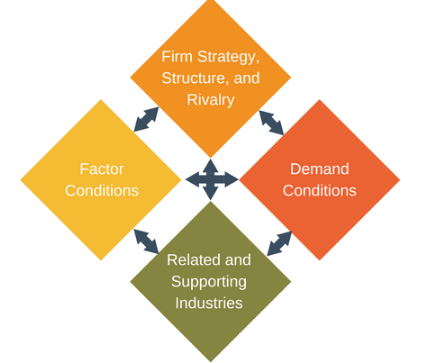
Figure 1 Porter's diamond model
(Source: Porter’s diamond model, 2018).
Factor Conditions:
The factor condition includes resources, climate, demographics and geographical locations. The Automotive industrial sector in Indonesia holds 10.16% of share in the market. As per 2020 reports the automotive sector had around 532 thousand of sales of motor vehicles in Indonesia. It could be said that the country is the primarily location for the manufacturing of innovative and luxury cars. Also the country is best performing care seller for brands like Toyota, Honda, and Brio etc. Further the flow of workforce within the country is also impressive as it provides with the more skilled, talented employees (Butt, Katuse, and Namada, 2019).
Demand Conditions:
These demand conditions states about the nature of the home market for demand for the particular industry’s goods and services. The demand for automotive sector is Indonesia is notably rising. It holds around 10% of share in the market and the sale of motor vehicle is seemed to be increasing year by year (Waluya, Iqbal, and Indradewa, 2019). Therefore it would be any fair and reasonable decision of Volkswagen to invest in Indonesia as this market would definitely provide them with lucrative returns on such investments.
Firm’s Strategy, Structure and Rivals:
This section reveal about the nature of rivalry created operational, management structure of companies, there vision and mission for success etc. The Volkswagen faces high competition in the market such as through its competitors BMW, Audi, Mercedes etc. The Indonesian market has the competence to adapt itself as per new technologies, new environmental conditions and protect its existing companies from new entrants.
Related and Supporting Industries:
This section includes the availability of the suppliers or supporting industries in the nation. Volkswagen is a high quality automotive brand and has a wide network of its suppliers around all over the globe (Wu, and Ang, 2020). Indonesia has also wide availability of supporting industries which could support the growth of Volkswagen in the region.
Strategies for Internationalization
Internationalization strategy is referred as strategies by which company sells its products and services exterior to its domestic market. Some of the internationalization strategies could be adopted by the cited organization is as follows –
Transnational: In this strategy, company is operating from its headquarter in its nation of origin, although, it also permit the organization to increase with full-scale operations in overseas market. Transnational organizations sell their goods and services in several nations in all over globe. The difference lies in the manner in which goods is marketed in every nation. Some of the main feature of the cited strategy consists of companies have distinct marketing, research and development department to address the local consumers, similar goods and services sold in distinct market, and some others (Bretos, Diaz-Foncea, and Marcuello, 2020).
Multi-domestic: The cited strategy makes investment in establishment of existence in overseas nation and tailoring its goods to the local market. This strategy can be adopted their goods and offering and reposition their marketing planning to participate in foreign audience. It considers foreign tradition, custom, and culture norms. In this strategy, usually headquarter is operated in the country of origin. However, company could set up localized headquarter in foreign nation from which they could manage the connection with foreign consumers (Kresnawan, et al. 2021). Some of the main features of the cited strategy consist of emphasis on establishment of existence and tailoring goods to suit in the new market, competitive benefits ascertained distinctively in every nation, and others.
Global: When the organization adopts global business strategies, the entire world is treated as one market and leverage economies of scale to increase revenue and reach. In this strategy, company has minimum local variations, like products and services are homogenized for reduction of cost while reaching as several individuals as possible. Usually, headquarter is established in the country of origin, while also setting up operations in the foreign market. Some of the main features of this strategy include integrated mechanism in all over distinct nations, homogenized goods for minimization costs, and fewer adjustments required to break into globalized market.
International: It is considered as one of the most common strategy, which emphasizes on exporting goods and services to overseas nations while keeping manufacturing headquarter at home. This suggests that, organizations avoid the requirement to invest in employees and facilities in foreign nation. Business goals are primarily in the direction of the home nation, but with some connecting to the international market.
Based on above strategies, translation strategy would be appropriate for the Volkswagen as it has combine factors of global and multi-domestic strategies. By adoption of the same, Volkswagen could increase full-scale operations in Indonesia. In this strategy, company’s international business activities are coordinated by cooperation and interdependence between its head office, operational department, and globalized situated subsidiaries. Volkswagen can gain several benefits due to transnational strategy inclusive of better market penetration, lower cost, better understanding of culture, and more efficiency.
Country analysis
Reasons behind choosing Indonesia as subsidiary company’s location
PEST analysis
.jpg)
Porter five forces
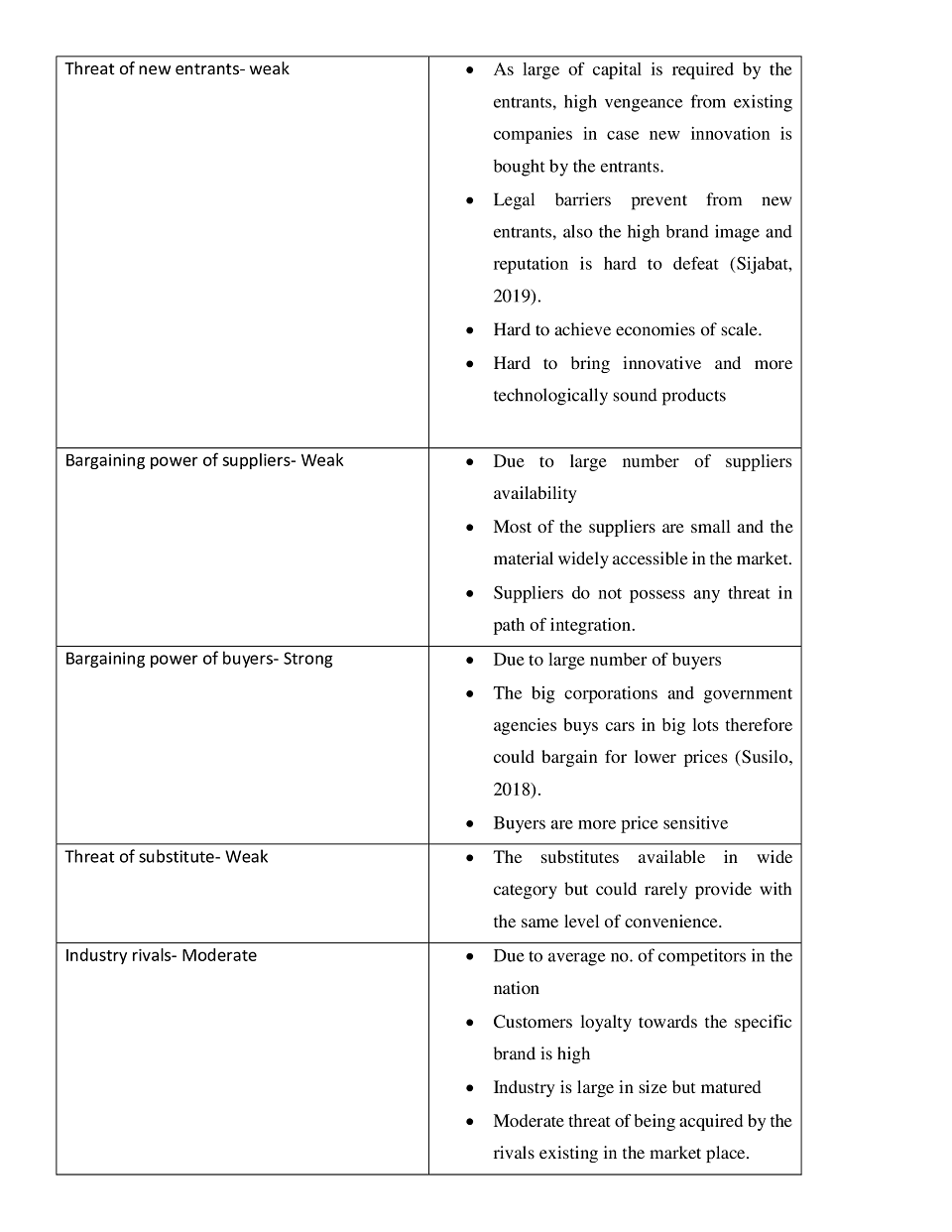
Table 2- Porter five forces model
The market is seemed to be safe and the Volkswagen already have and existing brand image which would help it to grow even more lucratively (Oh, Kim, and Shin, 2019).
Strategic methods of entry and possible consequences
Licensing
It is a type of business arrangement under which the one company provides permission to other company for the purpose of manufacturing its products against specific payments. The international licensing allow the firms to manufacture in the region for the specific period of time either exclusively or non- exclusively (Micek, et al, 2021). This way the firms could also take the advantage of the existing firm’s pipeline and generate revenue. This mode of entry comes with various benefit such as opportunity for passive income, new business creation opportunities in international markets, involvement of risk is very much less from both the sides.
Consequences
The chances of getting IP theft increasing generally in licensing type of mode of entry, the misuse of intellectually properties, exposure, privacy theft and other issues comes with it.
Joint Venture
This is the most preferred mode of entry as it creates the company with another partner especially in the emerging markets. Under this the company could take advantage of the partner company’s infrastructure, reputation and local knowledge. This also comes with the opportunity to get new capacity and expertise (Guzik, Doma?ski, and Gwosdz, 2020). The risk is also shared equally among the partners and enables the company to work comfortably in the new environment as well.
Consequences
The imbalance is created in the level of investment, expertise, assets and liabilities bought by both the parties in the venture.
Mergers and acquisitions
This mode of entry is solely based on the fundamental decisions made by the firms in order to enter in a new market. The merger and acquisition strategy wishes to expand the business of brand in term of geographical areas as well as the area of capabilities. This way the brand could also achieve the economies of scale. This mode of entry provides with the power and control over the market (Bretos, Diaz-Foncea, and Marcuello, 2020). Further the biggest and foremost advantage of such entry is that it benefits in tax.
Consequences
As a result of such merging and acquisition entry the workforce of small firms might get exhaustive re- skilling. Also the risk of getting over employed department could also be raised under such entry type. Due to the acquisition or merger process the loss of business understanding and loss of experienced workers could also be seen.
Based on above three modes of entry, it can be said that, joint venture would be appropriate mode of entry for the Volkswagen. The reason behind the same is that, it assists towards reduction of political risk that is reflected in the PEST analysis. Along with, it also enables transfer of technologies, knowledge of overseas market among the partnering firm. Since, Porter’s diamond model reflected that, in Indonesia, there is several related and supporting companies, and therefore by entering into joint venture with local firm, company can access success in that market.
The Potential Organizational and Managerial Problems in New International Environment
Organizational co-ordination
One of the major problems the company would face in the new international environment is the coordination in the organization. An inadequate coordination in the company could assists towards reduction in productivity, complicated procedures and significant time for completion of activities. One of the main reasons behind this issue is duplication and unclear departmental priorities (Dwijendra, 2020). In this aspect, planning of new projects would require to take into account content of information that distinct divisions would need by keeping their activities proper, along with the time when the information is needed. Therefore, if the Volkswagen’s management does not do proper planning and strategies for the international expansion, then they will suffer from issue of organizational co-ordination.
Culture Issue (Hofstede)
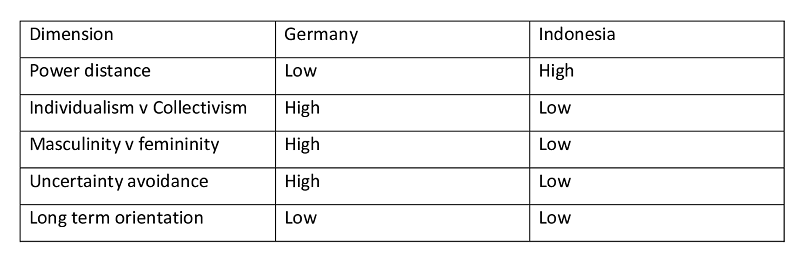
In this aspect, Hofstede proposed six culture dimension that reflects the cultural differences among distinct nations, and same is explained as follows –
Power distance: The greater power distance in Indonesia in comparison to Germany suggests a more acceptance of unequal power distribution, differences in hierarchy, and significant differences in pay.
Individualism v collectivism: The lesser individualism in Indonesia in comparison to Germany reflects that measures tending to emphasis or reward individual like performance related payment, individual appraisal system, does not observe fertile basis, or at least might be less successful as compared in Germany.
Masculinity v femininity: The lower masculinity in Indonesia in comparison to Germany suggests that the tendency of the Germans to desire to get the job done, notwithstanding of the emotional or relationship expenses that might be included, creates the Germans observe rude, while more femininity mechanism of Asian partners looks to the Germans like neglecting the issue (Stehle, and Erwee, 2007).
Uncertainty avoidance: In this aspect, uncertainty avoidance is high in Germany and low in Indonesia, which reflects that Germans have advanced wide formal system of rules, standards, or quality to control their environment purposely.
Long term orientation: Both Indonesia and Germany has low long term orientation, which reflects about culture of saving and planning for the future.
Table 1 Hofstede’s cultural dimension
Organizational Structure (Centralization v Decentralization)
Organizational structure reflects the number of layers for management and the manner of interaction with one another. In case of centralized organizational structure, business decisions are taken at the top of business and commands are given to subordinates (Nindito, et al, 2020). However, centralized management system usually is slow in responding to changes in business environment or domestic changes near their branches. Further, in case of decentralized organizational structure, authorities of decisions are shifted from senior management to the lower level employees, by which employees possess more decision making responsibilities (Witiastuti, et al, 2017). Therefore, management of Volkswagen at the time of international expansion may face the issue for ascertainment of which type of organizational structure should be implemented.
Recommendations to overcome potential problems
In order to overcomes the above confronted issues the management of Volkswagen is recommended to-
Harness local market expertise-
The local knowledge of the market is must when setting up business internationally (Braun, and Van Erp, 2021). With help of these local experts the business could easily operate and even expand its operation in the new international environment. These experts would help in providing the valuable insights to management which would help them to hire the talent as per the market required and would also help in reducing the burden of HR team. The local experts further would help the management to create their reputation in new location by demonstrating their commitment in regards of the local culture and community.
Navigating New Legislation
There are number of legislations and jurisdictions at the new global market which are to be fulfilled by the management (Bai, 2021). Understanding of these laws and regulations and applying them in the daily operational practices would help the business to achieve success in the new international market. This could be done by hiring a local lawyer for the firm which would advise regarding the local legislations and provide the best possible guidance to the company (Nindito, et al, 2020).
Cross Border Knowledge
Sharing of knowledge could also help the business to overcome the international business related problems as this would help the business to establish regional structure cross the market. Regular share of insights and best operational tips who help to motivate the employees as well as would increase the productivity and efficiency of the business by providing best possible services to the international market (Witiastuti, et al 2017).
Democratic Management Style
It is recommended that, company should implement democratic management style that encourage more collaborative manner of working. The reason behind selection of this management style by Volkswagen is that, in motivates creativity and involvement in decision taking procedure. Such involvement also assists towards commitment of teams for achieving outcomes, assisting towards greater productivity level. Some of the factors of successful management include planning, effective communication, integration, motivation, management of workload, and evaluation.
Conclusion
From the above analysis made for the purpose of international expansion of Volkswagen in Indonesia, it could be said that the new location selected by the company is worth to invest in. The rising demand for automotive sector in Indonesia makes it an appropriate choice by the Volkswagen brand to invest in such region as this would provide it with lucrative returns. Lastly some of the potential problems like cultural issue and organizational structure identified in the process of internationalization. In order to address such issues the recommendation of hiring local expert, democratic management style and cross border knowledge is provided to company.
References
Bai, Y., (2021).Analysis of Overseas Management Strategy of the Volkswagen Group. In 6th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development (ICFIED 2021) (pp. 229-234). Available from: https://www.atlantis-press.com/article/125954257.pdf [Accessed on 20th November].
Braun, C. and Van Erp, J., (2021). International regime complexes and corporate crime: a research agenda based on the Volkswagen diesel fraud case. Crime, Law and Social Change, pp.1-22.Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10611-021-09980-z[Accessed on 20th November].
Bretos, I., Diaz-Foncea, M. and Marcuello, C., (2020). International expansion of social enterprises as a catalyst for scaling up social impact across borders. Sustainability, 12(8), p.3262.Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/693348[Accessed on 20th November].
Butt, M.A., Katuse, P. and Namada, J., (2019). Government’s role as moderator in relationship of porter’s diamond factor conditions and firm’s performance. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478), 8(6), pp.40-48.Available from: http://www.ssbfnet.com/ojs/index.php/ijrbs/article/view/510[Accessed on 20th November].
Dwijendra, N.K.A., (2020). Identity Struggle Perspective in Car-Shaped Shrine in Paluang Temple, Nusa Penida Bali, Indonesia. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(4).Available from: https://www.academia.edu/download/62926501/PR201653_copy20200412-45691-e6r5cy.pdf[Accessed on 20th November].
Global Strategic Choices, (2020), (online), Available through <https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_international-business/s12-01-global-strategic-choices.html> [Accessed on 18th November].
Guzik, R., Doma?ski, B. and Gwosdz, K., (2020). Automotive industry dynamics in Central Europe. In New Frontiers of the Automobile Industry (pp. 377-397). Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-18881-8_15[Accessed on 20th November].
Kresnawan, M.R., Yurnaidi, Z., Bilqis, A., Natasha, T. and Wijaya, B.S., (2021). Electric Vehicle Readiness in Southeast Asia: A PEST Policy Review. Perceptions of Energy Resources Efficiency for Sustainable Development in the Developing Context of Nigeria: Implications for Enterprise Development in the Energy Sector, p.105.Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lukman[Accessed on 20th November].
Micek, G., Guzik, R., Gwosdz, K. and Doma?ski, B., (2021). Newcomers from the Periphery: The International Expansion of Polish Automotive Companies. Energies, 14(9), p.2617.https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/14/9/2617[Accessed on 20th November].
Nindito, H., Soeparno, H., Santoso, C.B. and Napitupulu, T.A., (2020). November. Technology Adoption of Smart Tourism in Indonesia: Systematic Literature Review. In 2020 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS) (pp. 13-17).Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9354280/[Accessed on 20th November].
Nurhadi, H.Q.A., Nurcahyo, R. and Gabriel, D.S., (2021). Strategic Development for A Filter Automotive Component Company in Facing the Electric Vehicles Era in Indonesia. In 11th Annual International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, IEOM 2021 (pp. 758-766). Available from: http://www.ieomsociety.org/singapore2021/papers/144.pdf[Accessed on 20th November].
Oh, C.H., Kim, M. and Shin, J.,( 2019). Paths and geographic scope of international expansion across industries. International Business Review, 28(3), pp.560-574.Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969593117306340[Accessed on 20th November].
Porter’s diamond model (2018). (Online). Available through<https://expertprogrammanagement.com/2018/04/porter-diamond-model/>[Accessed on 20th November]
Sijabat, R., (2019). Macro-environment analysis of the tourism industry in Indonesia: findings from the PEST analysis. Innovative issues and approaches in social sciences, 12(3), pp.96-118.Available from: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/e06f/97c91de33529ccce4a4a07344e647e7b0e80.pdf#page=96[Accessed on 20th November].
Susilo, D., (2018). Macro environment analysis of automotive industry in Indonesia. BISE: Jurnal Pendidikan Bisnis dan Ekonomi, 4(2), pp.65-73.Available from: https://jurnal.uns.ac.id/bise/article/view/25342[Accessed on 20th November].
Volkswagen, 2021, (online), Available through <https://www.volkswagenag.com/> [Accessed on 18th November].
VW plans to build car factory in Indonesia, (2018), (online), Available through <https://en.antaranews.com/news/121433/vw-plans-to-build-car-factory-in-indonesia> [Accessed on 18th November].
Waluya, A.I., Iqbal, M.A. and Indradewa, R., (2019). How product quality, brand image, and customer satisfaction affect the purchase decisions of Indonesian automotive customers. International Journal of Services, Economics and Management, 10(2), pp.177-193.Available from: https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJSEM.2019.100944[Accessed on 20th November].
Witiastuti, R.S., Putri, V.W., Wijayanto, A. and Sudarma, K., (2017). Improvement Efforts in Marketing Value Drivers through E-Marketing for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Superior Processed Products in Semarang Regency, Indonesia. International Journal of the Computer, the Internet and Management, 25(1), pp.21-24.Available from: http://www.ijcim.th.org/past_editions/2017V25N1/25n1Page21.pdf[Accessed on 20th November].
Wu, J. and Ang, S.H., (2020). Network complementaries in the international expansion of emerging market firms. Journal of World Business, 55(2), p.101045.Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1090951618302979[Accessed on 20th November].
Stehle, W. and Erwee, R., (2007). Cultural differences influencing German HR policies in Asia. Journal of Asia Business Studies.




.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






