PPMP2008 Initiating and Planning Projects Assignment Sample
Word limit: 2500 words +- 10%
Due date: Week 9 Friday (13 May 2022) 11:45 pm AEST
Weighting: 30%
Overview
The objective of this assessment is to help students learn about a range of trending topics in project management, especially throughout initiating and planning stages of projects - through conducting research. You are required to analyse two cases such as a failed project, and distil lessons learnt through answering a range of questions. The lessons learnt will inform the development process of the project plan for a new project of a similar nature (e.g. Assessment 3). Several questions will be asked in relation to the topics discussed in the unit. The questions address different knowledge areas covered in the unit (e.g. scope management, cost management, stakeholder management and risk management) in relation to project initiation and planning. Therefore, for students, it is essential to acquire a good understanding of the topics covered during the unit.
Assessment Details
Two case studies are considered for this assessment. The case descriptions are provided as an attachment to this document. You must carefully read the cases and questions and answer to each question logically by using quality references from academic journals, books, PM standards (e.g. PMBOK and other authenticated sources (such as PMI and APM websites). You must clearly link theory to the case throughout your discussions.
This assignment must be delivered in a report format containing:
• Executive summary – overview of the purpose of report, findings and lessons learned,
• Table of content,
• Introduction - purpose of the report, cases summaries, and the structure of the report,
• Body – Answer to the questions by referring to relevant project management knowledge
and use of techniques. Cite high quality and relevant references,
• Conclusion – concluding each case finding and lessons learned,
• Reference list – Harvard style,
• Appendices (if any).
Case Study for Assignment Help
Case 1: Transurban’s West Gate Tunnel pushed back to 2024!
The Victorian government has signalled a breakthrough in its long-running dispute with Transurban over the $6.7 billion West Gate Tunnel project, with a potential site selected to move toxic soil and tunnel boring expected later this year for a new deadline of late 2024.The dispute over toxic soil disposal has meant tunnelling on the project has stopped for more than a year. Transurban and its builders said last month they would not meet the revised delivery date of 2023 for the Melbourne tunnel, which was originally expected in 2022. The blowout in timelines and budget is expected to flow onto other major projects including the $15.8 billion North East Link, the $11 billion Melbourne Metro Tunnel (already blown out by nearly $3 billion), the $10 billion Melbourne Airport Rail (designs for which were released on Monday) and the suburban rail loop, which is expected to cost at least $100 billion. Opposition spokesman for transport infrastructure David Davis said that because the government failed to provide a breakdown of the projects in last year’s budget, taxpayers remained in the dark. The opposition estimated that costs for major projects had already blown out by more than $25 billion, ahead of the May state budget. The government has urged a national strategy to co-ordinate a pipeline of more than $400 billion in state-based infrastructure projects, amid fears a shortage of bidders, skills and raw materials will lead to further cost blowouts and delays. Infrastructure Australia is working on a dashboard for national cabinet by mid-year to help co-ordinate the national supply-side constraints. “Infrastructure Australia is undertaking research to provide comprehensive demand and supply-side analysis of market capacity and capability, with a focus on increasing transparency of key risks for infrastructure delivery,” the body’s chief of policy, Peter Colacino, said on Tuesday. Corey Hannett, director-general of Victoria’s Major Transport Infrastructure Authority, told a media briefing on Tuesday that the approval of a site at Bulla, which received planning and environmental approval on Monday, would help kick-start the troubled West Gate Tunnel. He said the project should be completed within three years of starting later this year, leaving a deadline for late 2024. Transurban declined to comment. “We are hoping a site will be chosen shortly [for the toxic soil],” Mr Hannett said. “We are in daily conversation with Transurban and their builders John Holland CPB. We need the joint venture and Transurban to choose a site, the site needs to be constructed ... if it takes about six months ... we are anticipating to see tunnel boring starting later this year, then it’s about a three year process from there. “Originally, the tunnel boring was starting in 2019, it’s now a couple of years later ... Transurban said a couple of weeks ago they can’t make 2023, so we’ll provide further advice once they provide a date for tunnel boring.” Please carefully explore the following material before attempting to answer the questions:
? West Gate Tunnel: Another Case of Tunnel Vision?
? West Gate Tunnel - Ministers Assessment Final
? 'A fundamental betrayal': City council attacks plan to pump more cars into CBD
There are more resources to explore – Do your own research.
1. What are the potential risk events which could impact the project ? (Some risk events may have happened)?. Make your argument based on risk management theory and provide examples from the case (at least three risk events should be identified and linked to the case).
2. How does the West Gate Tunnel project authority handle the project's risks? Were they the appropriate approaches to handling risks?
3. Suggest the appropriate risk response strategy for each risk event identified and discuss your rationale.
Case 2:
Myki was poorly planned and overly ambitious: Auditor-general In 2005, the Victorian government invested almost AU$1 billion into the state's Myki smart card ticketing system, which was introduced to replace the ageing Metcard system. A report published on Wednesday by the Victorian auditor-general's office, titled Operational Effectiveness of the Myki Ticketing System, has examined Myki to determine whether the expected benefits and outcomes are being achieved. In his report, Victorian Auditor-General John Doyle pointed the finger at Myki's "poor initial planning in its original scope" as one of the underlying reasons behind its lack of success. "The time taken to develop and implement Myki more than quadrupled from the initial expectation of two years, to in excess of nine years," Doyle said in his report. The auditor-general said that the original contract was "vaguely specified and overly ambitious", and that the state has incurred "significant, additional, unanticipated costs", as Myki's budget blew out by 55 percent -- AU$550 million more than its initial AU$1 billion commitment. In December 2012, Public Transport Victoria (PTV) assumed responsibility for Myki once the rollout had been completed and Metcard switched off; according to the report, PTV expected that Myki would deliver around AU$6.3 million to AU$10.8 million per year in economic benefits to Victoria and Victorians when they took on the responsibility. Doyle said he is concerned that PTV does not yet possess a complete and reliable picture of Myki's operational performance, due to shortcomings in performance monitoring. "PTV needs to urgently address these issues and assess the residual benefits achievable from Myki going forward, to optimise value from the state's significant and ongoing expenditure," he said. With PTV planning to re-tender the contract once its 2016 expiry date is reached, the auditor-general suggested that the transport authority needs to urgently address current issues to avoid perpetuating past mistakes. The report also found that between July 2010 and June 2014, the Public Transport Ombudsman received more than 5,450 complaints about Myki. Additionally, as of December 2014, more than 13.4 million Myki cards had been issued, with the system processing around 7.8 million "touch on" transactions per week from 9.9 million active cards. In FY2013-14, the total fares collected by Myki across all transport modes was around AU$800 million.
Please carefully explore the following material before attempting to answer the questions:
• Operational Effectiveness of the myki Ticketing System
? Major eGovernment Projects in Health, Education and Transport in Victoria
There are more resources to explore – Do your own research.
Questions
1. Why did the Victorian Auditor-General point to “poor initial planning in its original scope” as one of the main reasons for the Myki project’s failure? Make your argument based on project management theory and provide examples from the case (a minimum of 2 pieces of evidence should be identified and linked to the case).
2. Provide at least 2 recommendations that could help avoid poor project scope planning of the project. Support your arguments with evidence and reference linked to the project.
3. Identify at least 4 stakeholders of the project. Perform stakeholder analysis and develop a stakeholder engagement strategy to engages these stateholders. Discuss your rationale based on stakeholder management theory.
Solution
Introduction
In this report, the project management system of two case studies is briefly discussed. In the case study 1, it includes the potential risks, impacts, and risk management theory, appropriate approaches in risk handling and risk response strategies to overview the risk mitigation and business management processes of West Gate Tunnel Project in Melbourne, Australia. An alternative in the business model is implementation.
In terms case study 2, it demonstrates the reasons of Myki’s project failure, recommendation, stakeholders’ identification, stakeholders’ analysis and stakeholders’ management theory to provide efficient project management procedure and planning. In this case study, it analyzes the areas the organization requires to make improvement in terms of MYki’s Project. Overall, the report suggests an efficient project management system to improve the implementation procedure.
Purpose of the Report
The purpose of the report is to promote an efficient project management system and suggest a development process of the project plan. On the other hand, to implement basic knowledge in terms of project management techniques and processes. It visualizes the uses of stakeholders’ in the business project management system, their responsibilities and impacts. It provides knowledge of choosing the business management procedures and stakeholders’ required for the particular field. The report also considered a description on the needs and requirement for better project management system and implementation procedures.
Case Summaries
• In case study 1, it includes the stoppage of business project implementation process due to soil toxicity. It can lead to human health disposal and environmental impacts.
• In case study 2, it includes the project failure of Myki’s ticketing system. It is due to poor project planning procedure and project management system.
Case Study 1
Potential Risks
The potential risk analyzed in terms of West Gate Tunnel is toxic soil, time and cost efficiency. In this report, it is analysed it impacts a major effectiveness in the project. Due to the purpose the toxic soil disposal may cause disrupt and stop the implementation practices as well. The discovery of toxic soil may disrupt the human inhabitant as it consists of chemical such as pollutants, and contaminants in soil. The concentration of the chemicals may present in a high concentration that result in leading risk in human health and stability (Prenger-Berninghoff et al., 2014). Before the initiation of the project, the project manager, risk management team and other stakeholders’ must have a discussion regarding the effective outcome of the project.
Before the initiation of the project, Transurban must focus on the project planning procedures and strategies. The stoppage of the West Gate Tunnel project has led the organization to face wastage of time and cost effectiveness. Due to toxic soil disposal, the organization has to stop working on West Gate Tunnel Project that leads Transurban to face gradual loss in business management system. Along with, the project was also linked with the other major project as well such as North East Link, Melbourne Metro Tunnel, Melbourne Airport Rail and Suburban Rail Loop. Due to the purpose of disrupt, it is time-wasting and influences the cost system effectively. For this, the organization has to implement an appropriate plan to manage disrupts analyzed in the project implementation process. The project leaders must focuses on the supply chain management system , human resources management system, project management system and implementation procedures. It requires stakeholders’ engagement and effective communication between the stakeholders to control the situation and improve the project management procedures.
Impacts of the Project
For effective impact on the project outcome, Transurban requires to focus on the few key elements, implementation processes, inquiry, scope management and requirement, stakeholders’ communication and engagement plan, environmental impacts and project outline.
Key Elements
Table 1: Key Elements and Explanation on the impact of the project
(Source: Developed by the author)
Implementation process
Planning Scheme Amendment
The implementation of the project requires amendment documentations and the planning scheme amendment must be approved by the minister (Maclennan, 2017). It requires approval on the planning and environmental impacts visualizes the effectiveness on the West Gate Tunnel Project.
Planning Assessment
It includes the processes of the project implementation and the approval decisions such as planning scheme amendment and EPA approval. The assessment includes the process of reducing the environment effects. Moreover, the planning assessment improves the waste project management system as well.
Inquiry
The organization has to pass through an inquiry regarding the environmental effects.
Scopes management and requirement
The organization focuses on scopes on managing the project implementation. The organization must provide a documentation and research material for project management and approval.
Stakeholders’ engagement and communication
For appropriate planning of the West Gate Tunnel Project, it requires stakeholders’ engagement during the implementation of the project. It results in better analysis, innovations and outcomes of the project. Moreover, it requires better communication with the stakeholders as well.
Table 2: Implementation Process and Impacts
(Source: Developed by Author)
Risk Management Theory
The West Gate Tunnel Project disposal is caused due to soil toxicity. The toxicity is made by per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances. The risk management team should focus on the environmental impacts for better project outcome. The team must implement an alternative change in the business management system and implementation procedure (Maamir, & Derghoum, 2021). It requires an appropriate communication between the stakeholders’ and the risk management team. It results in finding the scopes to improve the implementation procedure. For the implementation of West Gate Tunnel project requires approvals such as planning, scopes, and environmental effects. It leads to better project initiation and implementation.
Appropriate approaches in Risk Handling
Due to the stoppage of the project, the organization is facing a gradual fall in the market in terms of cost efficiency. To implement new ideas from the beginning of the project may leads in wastage of time, delays and high cost. The risk management team should focus on the cost effectiveness as well in terms of implementing the business planning (Yazdi, & Zarei, 2018). The stakeholders’, the finance management team, and the risk management team must have an effective engagement and communication regarding the implementation of the project. It results in short-term solution, no delaying of the project and less cost.
Alteration in Designing Process
• Information and reviewing in terms of scopes lowering the extension components and modification of the project (Zhang, 2016).
• Information and assessment in terms of environmental impacts focuses on lowering the components and modification of the project.
Case Study 2
Reasons for Myki Project Failure
The Victorian Auditor General predicted that Myki is ‘poor initial planning in its original scope’. The project failure is caused due to the appropriate project planning, contractual arrangements, and deficiency in governance. Moreover, it is cost efficient and causes delays in the implementation procedure.
The organization requires an appropriate planning for better project implementation. The boards of directors, stakeholders and the team members require having a proper communication for better project implementation. It strengthens the project management system within the organization. The discussion between the stakeholders’ and team member results in new innovations and further implementation procedure.
In this case, the organization must focus on improving the project planning, structure, and analysis process. For effective project planning and implementation procedure, it must follow agile project management system for efficient project planning, analysis and implementation. Following the agile project management techniques provides effective market strategies. Moreover, it analyzes the demands of the consumers in terms of Myki’s ticketing system project. In this system of project management, the organization provides a feedback analysis team to collect feedback from the consumer after releasing few features in the market. On the basis of the demand and feedback analysis the project implementation procedure takes place. It requires efficient stakeholders’ engagement and communication with the scope management team, finance management team, and risk management team. Moreover, it results in better project implementation and planning strategies.
Recommendation
• The organization must follow agile project management system for better project planning, analysis and implementation procedure. On the other hand, the organization should provide several teams working on different categories such as scope management team, project management team, finance management team, risk management team, system developing team, etc.
During the implementation process, the organization must release few features in the market for analysis and testing purpose. It should provide a separate feedback analysis team for collecting feedbacks from the consumers to analyze the market demands and the areas to make improvement in the project implementation.
• The stakeholders’ within the organization are required to implement an appropriate project planning and arrangements. The organization should be associated with the efficient stakeholders’ engagement. It includes the boards of directors, supervisors, project manager, and finance manager. A proper engagement between the stakeholders’ analyzes the areas of improvements and implements new innovations for better outcome. On the other hand, a efficient communication with the team members requires better understanding and requirements of the project. Overall, it increases the productivity of the organization and results in appropriate planning and implementation procedure.
Stakeholders’ Identification
The stakeholders’ essential for Myki’s project management system are,
• Project manager
• Finance Manager
• Resource Manager
• Supervisor
The stakeholder contributes a major significance in the project management system. They plan the business model, structure, and make arrangement on it. They lead the different teams in terms of project management system. The entire project planning relies on the following stakeholders. They analyze the outcome and further productivity of the company through business model (Balmer, 2017). It leads different teams such as project management team, finance management team, feedback analysis team, risk management team, scope management team and waste management team for the better implementation of the project. The project manager, finance manager, resource manager, and supervisor are required to have an efficient communication with the stakeholder (Wood et al., 2021). It requires better project management and understanding of the project implementation procedure to the team.
Stakeholders’ Analysis
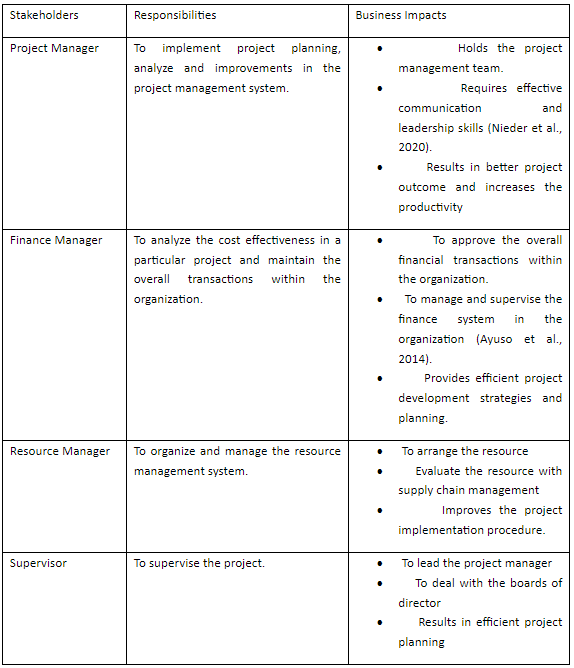
Table 3: Stakeholders’ Analysis
(Source: Developed by Author)
Stakeholders’ management theory
The stakeholders contribute an effective significance in terms of project management system. The stakeholders’ within the organization has an interconnected relationship (Eskerod et al., 2015). It connects the stakes of the organization such as between the business and suppliers, consumers, employees, investors and others. Moreover, these are the key elements of the stakeholders’ analysis.
The organization should follow descriptive approach in terms stakeholders’ management theory. During the process, it requires to develop more accurate model, structure and planning of the project (Hörisch et al., 2014). The theory must provide the organization an effective, practical and ethical way. In this way, it provides the organization a highly complex and turbulent practices.
Table 4: Stakeholders’ Theories and Impacts
(Source: Developed by Author)
Conclusion
In this report, it includes the overall improvements required for project planning procedures. For better project outcome, it is essential to implement an appropriate project planning. For business project implement, it is requires to follow a particular project management system for productive outcome and implementation of the project. The organization must follow a particular project management system in terms of project type. On the other hand, stakeholders’ engagement provides an effective change in the project model and arrangements whereas efficient communication with the leading team such as finance management team, risk management team, etc. results in better understanding and implementation of the project management system.
References
Prenger-Berninghoff, K. et al., 2014. The connection between long-term and short-term risk management strategies for flood and landslide hazards: examples from land-use planning and emergency management in four European case studies. Natural hazards and earth system sciences, 14(12), pp.3261–3278. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_doaj_primary_oai_doaj_org_article_637ac9473ab24c2b9c88b64125838d70
Maclennan, A., 2017. Information Governance and Assurance, London: Facet Publishing. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_miscellaneous_2133333566
Maamir, S. & Derghoum, M., 2021. Toward Preventive Management of Risks Theory: Foundation of Process Structuring the Theory. Management dynamics in the knowledge economy, 9(2), pp.185–203. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_doaj_primary_oai_doaj_org_article_346a0c8dbd8a493f9209fa39c7f227ca
Yazdi, M. & Zarei, E., 2018. Uncertainty Handling in the Safety Risk Analysis: An Integrated Approach Based on Fuzzy Fault Tree Analysis. Journal of failure analysis and prevention, 18(2), pp.392–404. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_journals_2002116049
Zhang, Y., 2016. Selecting risk response strategies considering project risk interdependence. International journal of project management, 34(5), pp.819–830. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_miscellaneous_1815987532
Balmer, J.M.T., 2017. The corporate identity, total corporate communications, stakeholders’ attributed identities, identifications and behaviours continuum. European journal of marketing, 51(9/10), pp.1472–1502. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_emerald_primary_10_1108_EJM-07-2017-0448
Ayuso, S. et al., 2014. Maximizing Stakeholders’ Interests. Business & society, 53(3), pp.414–439. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_miscellaneous_1531003569
Hörisch, J., Freeman, R.E. & Schaltegger, S., 2014. Applying Stakeholder Theory in Sustainability Management. Organization & environment, 27(4), pp.328–346. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_miscellaneous_1687666180
Perez, A. & del Bosque, I.R., 2016. The stakeholder management theory of CSR. International journal of bank marketing, 34(5), pp.731–751. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_journals_1795937542
Nieder, T.O. et al., 2020. Mapping key stakeholders’ position towards interdisciplinary transgender healthcare: A stakeholder analysis. Health & social care in the community, 28(2), pp.385–395. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_miscellaneous_2299773832
Wood, D.J. et al., 2021. Stakeholder Identification and Salience After 20 Years: Progress, Problems, and Prospects. Business & society, 60(1), pp.196–245. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_crossref_primary_10_1177_0007650318816522
Eskerod, P., Huemann, M. & Ringhofer, C., 2015. Stakeholder Inclusiveness: Enriching Project Management with General Stakeholder Theory. Project management journal, 46(6), pp.42–53. https://cqu-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1rb43gr/TN_cdi_proquest_journals_1758455031




.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






