Order Now
- Home
- About Us
-
Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research
-
Assignment Writing
-
Resources
- Referencing Guidelines
-
Universities
-
Australia
- Asia Pacific International College Assignment Help
- Macquarie University Assignment Help
- Rhodes College Assignment Help
- APIC University Assignment Help
- Torrens University Assignment Help
- Kaplan University Assignment Help
- Holmes University Assignment Help
- Griffith University Assignment Help
- VIT University Assignment Help
- CQ University Assignment Help
-
Australia
- Experts
- Free Sample
- Testimonial
ECON6001 Economic Principles Assignment Sample
Case Study Assessment 3
Assignment Brief
Individual/Group - Group
Length - (2000 words +/- 10%)
Learning Outcomes:
(a) Analyze, individually and in teams the role of fundamental microeconomic and macroeconomic principles in business decision-making.
(b) Critically evaluate the applicability of various theories to economic policies and business decision making related problems.
(c) Critically evaluate the role and impact of various forms of government intervention in the economy including business implications.
(d) Communicate complex economic concepts to business professionals.
Submission - by 11:55pm AEST/AEDT Sunday of Module 5.2 (week 10)
Weighting - 25%
Total Marks - 100 Marks
Context:
COVID-19 continues to adversely affect economies and is burdening the fiscus of many economies globally. It has implications not only on national budgets but on macroeconomic management.
This assessment aims at:
• Assessing the students’ ability to critically analyse the impact of COVID-19 on key sectors of the pair of countries given, one from the ASEAN nations and another from Asia Pacific nations.
• Testing the students’ ability to perform a comparative analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on the forecast macroeconomic performance in 2021 and 2022
• Testing students’ evaluation of the efficacy of fiscal policy in dealing with the COVID-19 induced recessions
• Evaluating the students’ understanding of the concept of quantitative easing and how it has been used, if any, to assist in combating the COVID-19 induced recessions.
Instructions:
In a group of three (3) students, for case study assignment help you are required to complete this assessment task considering the following:
(a) Your facilitator is going to allocate to your group, a pair of countries from the following table of countries:
Selected ASEAN countries Selected Asia Pacific Countries
Malaysia Japan
Philippines India
Singapore Indonesia
Thailand Hong Kong
Cambodia South Korea
Myanmar Bangladesh
New Zealand
Vietnam Australia
Brunei Singapore
Indonesia Philippines
Vietnam Malaysia
Thailand Hong Kong
Singapore New Zealand
Singapore Hong Kong
Focusing on the five main sectors of the allocated pair of countries, perform a critical comparative discussion of how they have been affected by COVID-19. (15 marks)
(b) On the basis of that information and other sources of data, compare the countries’ projected macroeconomic performance in 2021 and 2022, your discussion should focus on real GDP, unemployment and inflation. Sources of useful data could be government websites, think tanks, IMF, OECD, Asian Development Bank and the World Bank. (10 marks)
(c) Discuss how these two countries have used fiscal policy in combating the COVID-19 recession. (10marks)
(d) Critically evaluate the following statement, “Fiscal policy should lead and monetary policy follows in dealing with the recession as a result of COVID-19”. Discuss this in the context of the two allocated countries and any third country from the table of countries given above. (10 marks)
(e) Quantitative easing (QE) is one of the untraditional monetary policy approaches that can be used by central banks. Discuss how it can be used to deal with severe economic crises such as the recession caused by COVID-19. To what extent have these countries (the three in part (d)) used this unconventional monetary policy tool to contain the recession emanating from the advent of COVID-19? (10 marks)
Consider the following:
• Use reliable data sources such of those of international organizations such as country government websites, IMF, World Bank, OECD, Asia Development Bank, journal articles by economists and academics
• Remember to cite inside the report the sources of information used and include the reference list at the end.
• You are expected to take a critical approach when writing the report.
• A peer review is expected. This is where you tell the audience how you organized yourself as group to work on the project. Challenges, difficulties and success stories must be told. It is important to be truthful about the group dynamics and perhaps even tell us what you learnt about working in a team. The peer review is worth 5 marks.
Students usually ignore this part and as a result throw away 5 marks unnecessarily.
Submission Instructions:
Submit this task via the Assessment link in the main navigation menu in the ECON6001 Principles of Economics folder. The Learning Facilitator will provide feedback via the Grade Centre in the LMS portal. Feedback can be viewed in My Grades.
I declare that except where I have referenced, the work I am submitting for this assessment task is my own work. I have read and am aware of Torrens University Australia Academic Integrity Policy and Procedure viewable online at https://www.torrens.edu.au/policies-and-forms
Solution
Executive Summary
The report emphasizes on the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic situation on the economy and industries of India and Philippines, with the purpose of discussing the policy frameworks of the concerned nations and their implications in this aspect. The primary industries and sectors of both the countries can be seen to have been adversely affected by the ongoing pandemic crisis. Both the concerned countries can be seen to have used fiscal policies extensively to boost their economies out of the recessionary situation caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic crisis. However, unlike that of India, Philippines could not incorporate a huge relief package under its fiscal policy frameworks for the COVID-19 pandemic situation and this is mostly due to the lack of such resources for the small and developing nation like Philippines. Fiscal policies can be seen to have been prioritized and there has also been incorporation of different extents of quantitative easing, not only in India and Philippines but also in the developed countries like that of Australia in the present period.
Introduction
Overview of the Report
Every country across the world can be seen to have different growth patterns and trends in economic development and much of the same can be seen to be related to the primary industries and their contribution to the growth of the concerned economies as well as on the economic policies that are taken by the governments of the concerned countries. However, the growth and performance of the economies and the industries operating in the same, can be seen to be considerably affected by different internal as well as external fluctuations taking place across the globe and in the country itself (Deb et al., 2020). One such fluctuation or phenomenon of immense importance is that of the ongoing crisis of the COVID-19 pandemic across the globe, that has not only led to deaths of millions of people, but can also be seen to be causing immensely negative implications on the businesses, industries and economies of almost all the nations across the globe.
Purpose of the Report
Keeping this into consideration, the concerned document emphasizes on the impacts of this pandemic on the economy and industries of India and Philippines, with the purpose of discussing the policy frameworks of the concerned nations and their implications in this aspect.
Comparison of five main sectors and their performance in COVID-19
India has been performing impressively in the global economic framework over the years and is considered to be one of the most prominent developing nations across the globe. The primary industries or sectors of the concerned country, that can be seen to be contributing impressively in the GDP of the concerned country, can be shown with the help of the following figure:
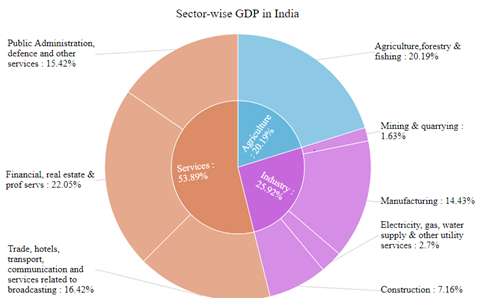
Figure 1: Primary sectors and their contribution to the GDP of India
(Source: Statisticstimes.com, 2021)
The textile sector, the real estate sector, the agricultural sector, the manufacturing sector and the tourism sector can be seen to be the top five and prominent sectors in India, contributing substantially to the growth and the GDP of the concerned country over the years. However, the ongoing crisis of the COVID-19 pandemic situation can be seen to have affected these major industries and their profitability and revenue generation, much of which can be attributed to the lockdowns and the restrictive measures that are being taken by the government of India to contain the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic situation (Mckinsey.com, 2021). The effects of the concerned pandemic situation on these industries can be shown with the help of the following figure:
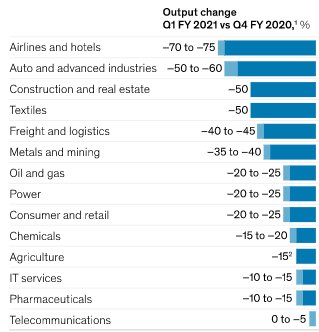
Figure 2: Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic situation on the outputs of the different sectors
(Source: Mckinsey.com, 2021)
The construction sector, tourism sector and the textile sector can be seen to have been majorly affected and the effects can also be seen to be severe in the different manufacturing operations and in the agricultural sector (Pib.gov.in, 2021).
On the other hand, the contributions of different sectors to the GDP of Philippines, over the years, can be shown as below:
Figure 3: Contributions of different sectors to the GDP of Philippines
(Source: Statista.com, 2021)
The tourism sector, the agricultural sector, the real estate sector, outsourcing, retailing and the construction sector can be seen to be the top five industries or sectors contributing massively to the economic growth of the concerned country (Unido.org, 2021). There has been nearly 80% decline in the tourism demand in the concerned country due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic situation, while there has also been considerable reduction in the production volumes of the general manufacturing sector of Philippines as shown below:
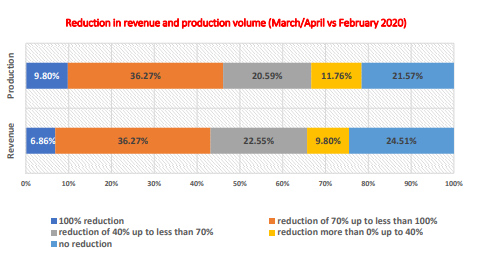
Figure 4: Reduction in production volumes of the manufacturing industries in Philippines due to the COVID-19 pandemic situation
(Source: Unido.org, 2021)
The agricultural sector has been comparatively less affected while there have been substantial implications of the pandemic situation on the retail and the outsources sectors of the concerned country, much of which can be attributed to the changing demands and preference patterns for the products and services of the concerned sectors of Philippines.
Comparison of the projected macroeconomic performance of India and Philippines in 2021-2022
The two countries considered in this report are expected to have differences in their projected macroeconomic performances, based on the ways in which they are trying to mitigate the adverse impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic crisis situation on their economies. India, is expected to have an increase in the GDP in 2021, with the expected GDP being 2850 billion USD in 2021 and the same is expected to grow further to around 3000 billion USD in 2022. However, the growth of Philippines is expected to be slower in the coming years, with the expected GDP to be 373.00 USD billion in 2021 and 379.00 USD billion in 2022 and this may be due to the slower recovery of the concerned nation from the impacts of the ongoing pandemic crisis (Data.worldbank.org, 2021). The unemployment in Philippines is expected to have the following trends with the slow recovery of the economy:
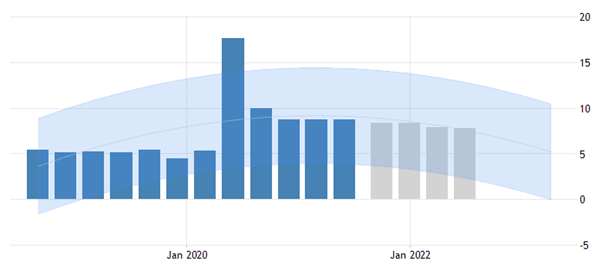
Figure 5: Predicted unemployment in Philippines in 2021-2022
(Source: Tradingeconomics.com, 2021)
However, although India also experienced a considerable spike in the unemployment due to the pandemic situation and the consequent lockdowns and restrictive measures, it is expected to experience a more impressive fall in the unemployment rate in both 2021 and 2022:
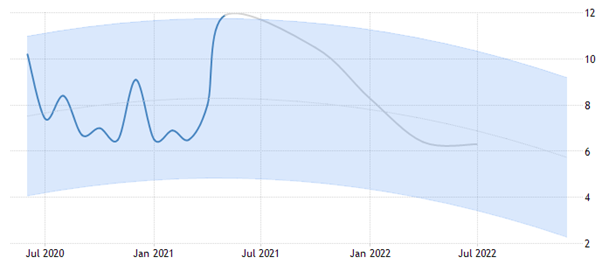
Figure 6: Projected unemployment rate in India in 2021-2022
(Source: Tradingeconomics.com, 2021)
The projected evidences highlight that while Philippines will be having a stagnated fall in unemployment in 2021 without much changes in 2022, India is expected to experience a continuous fall in unemployment in both 2021 and 2022 with the recovery of the concerned economy (Statisticstimes.com, 2021).
There will also be a fall in the inflation, as expected for India, and this may be due to the fall in prices of products and services for boosting the demand in the concerned economy in the COVID-19 aftermaths, as shown below:
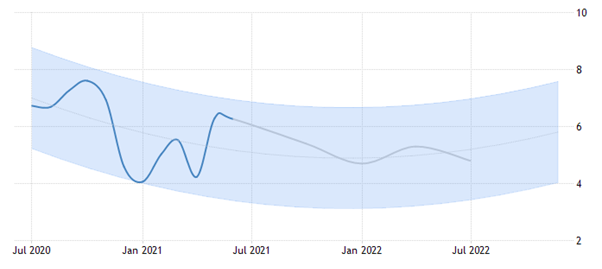
Figure 7: Expected inflation rate in India in 2021-2022
(Source: Tradingeconomics.com, 2021)
However, the inflation rate for Philippines is expected to experience a constant decline in 2021 and 2022 and this can be shown as below:
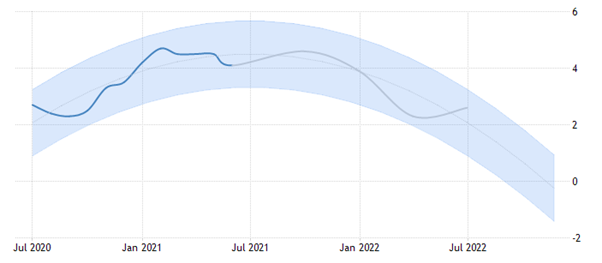
Figure 8: Expected inflation rate of Philippines in 2021-2022
(Source: Tradingeconomics.com, 2021)
This can be due to the fact that due to the slow recovery of the economy of Philippines from the pandemic situation, the recessionary phase is expected to be prolonged in case of Philippines as compared to India.
Usage of fiscal policies for combating the COVID-19 recession
Both the concerned countries can be seen to have used fiscal policies extensively to boost their economies out of the recessionary situation caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic crisis. In case of India, the government had launched a fiscal package of 22 billion USD for supporting the businesses, investments and also to strengthen the “Make in India” program, thereby supporting the small and medium industries in the concerned country. There are also different employee support programs and unemployment support as well as health care packages that have been incorporated under the fiscal policies of the concerned country to combat the COVID-19 recession (Home.kpmg, 2021). There have also been tax cuts incorporated by the government of India and similar fiscal policies can also be seen to have been implemented by Philippines to combat the recessionary effects of the ongoing pandemic crisis. However, unlike that of India, Philippines could not incorporate a huge relief package under its fiscal policy frameworks for the COVID-19 pandemic situation and this is mostly due to the lack of such resources for the small and developing nation like Philippines. However, there has been special risk allowances for health workers that have been launched by the concerned country, which is similar to the health insurances that have been implemented for the health workers of India, by the government of the concerned country.
Evaluation of the statement in terms of India, Philippines and Australia
There is a notion that in case of a recessionary situation, the fiscal policies are more effective and should be prioritized and the monetary policies should accompany the same. This has been the case for both India and Philippines as well as for the developed nations like that of Australia in combatting the recessionary effects caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic situation. In case of India as well as Philippines, extensive tax cuts and exemptions are evident. On the other hand, Australia can be seen to have launched an elaborate fiscal relief package as well as programs like that of the Job-Keeper program to support the businesses to retain their workforces during the pandemic situation. These can be seen to be similar to that of India, which has also prioritized in providing direct support to the businesses and the general population of the concerned country (Imf.org, 2021). However, the policies taken by India can be seen to be a mixture of the fiscal as well as the monetary policies, and the monetary policies include more relaxed borrowing and lower interests which can also be seen to be similar in case of Australia. Philippines, on the other hand, can be seen to have mostly emphasized on fiscal policies than that of the monetary policies although there have been changes in the rate of interests in the concerned country, which has been done to boost the borrowing and the investment operations in the country to mitigate the recessionary situation caused by the ongoing pandemic crisis (Home.kpmg, 2021). Thus, it can be asserted that in case of the concerned three countries, fiscal policies have been prioritized and monetary policies have been supportive policies to combat the negative impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic situation on the respective economies of the concerned three countries.
Quantitative Easing and its usage to contain the COVID-19 recession by the three countries
The quantitative easing is an unconventional monetary policy, which is taken to increase the money supply, investment and lending activities in an economy and this is done by the central bank of an economy, by purchasing longer-term securities in the open market and is especially incorporated in recessionary situations. India, in the present period, can be seen to be incorporating this quantitative easing policy, to combat the stagnant economic situation created by the COVID-19 pandemic situation. To stimulate the economy, in 2020-2021, the Reserve Bank of India has bought bonds worth more than 14 billion USD to increase the money supply in the economy, which in turn is expected to help in boosting the investments and the lending activities in the economy, thereby contributing potentially in the expansion of businesses and the production activities in the concerned country (Bloomberg.com, 2021).
The Reserve Bank of Australia, can also be seen to have started with the quantitative easing policy, with an amount of more than 80 billion dollars being spend on the QE program, where Australian government bonds are being purchased and 20 billion dollars is being spent on purchasing the state and territory government bonds by the concerned nation. This has been helping the government to stimulate the economy by increasing the money supply and it is working as evident from the impressive recovery of the Australian economy, the business activities and the investments in the business operations in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic situation (Imf.org, 2021). Like that of Australia and India, Philippines can also be seen to be taking the quantitative easing measures by buying up the government securities and this is being done directly to avoid the deflationary situation created by the COVID-19 pandemic situation. However, in case of Philippines the level of bond buying and quantitative easing can be seen to be lower than expected. Nevertheless, all the nations considered in this case, can be seen to be incorporating the unorthodox monetary policy of quantitative easing at different extents to mitigate the recessionary impacts of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic situation (Pib.gov.in, 2021).
Conclusion
The above discussion makes it evident that the COVID-19 pandemic situation has been affecting the economies of different nations adversely and this is evident in case of both India and Philippines, as can be seen from the effects of the same on the top five industries of both the concerned countries. There is different fiscal as well as monetary policies that can be seen to be incorporated by the governments of these two countries as well as by the government of developed nation like that of Australia to mitigate the adverse effects of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic situation and there are also evidences those fiscal policies are gaining more emphasis and prioritization in case of these countries to take their respective economies out of the recessionary situations. However, different extents of quantitative easing can also be seen to be taking place in these countries and these are being done to increase money supply, lending and investments and to decrease the recessionary situations in the economies of these concerned countries in the COVID-19 pandemic situation.
References
Bloomberg.com. (2021). Bloomberg - Are you a robot? Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-04-07/india-s-central-bank-holds-rate-as-virus-surge-risks-recovery.
Data.worldbank.org. (2021). GDP growth (annual %) | Data. Data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG.
Deb, P., Furceri, D., Ostry, J. D., & Tawk, N. (2020). The economic effects of Covid-19 containment measures. https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/journals/001/2020/158/article-A001-en.xml
Home.kpmg. (2021). Philippines: Tax developments in response to COVID-19. KPMG. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://home.kpmg/xx/en/home/insights/2020/04/philippines-tax-developments-in-response-to-covid-19.html.
Imf.org. (2021). Policy Responses to COVID-19. imf.org. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://www.imf.org/en/Topics/imf-and-covid19/Policy-Responses-to-COVID-19.
Mckinsey.com. (2021). Getting ahead of coronavirus: Saving lives and livelihoods in India. mckinsey.com. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/india/getting-ahead-of-coronavirus-saving-lives-and-livelihoods-in-india.
Pib.gov.in. (2021). Fiscal and monetary policies to deal with slowdown due to COVID-19. Pib.gov.in. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1656925.
Statista.com. (2021). Philippines - share of economic sectors in the gross domestic product 2020 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/578787/share-of-economic-sectors-in-the-gdp-in-philippines/.
Statisticstimes.com. (2021). India GDP sector-wise 2020 - StatisticsTimes.com. Statisticstimes.com. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://statisticstimes.com/economy/country/india-gdp-sectorwise.php.
Tradingeconomics.com. (2021). Philippines Inflation Rate | 1958-2021 Data | 2022-2023 Forecast | Calendar. Tradingeconomics.com. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://tradingeconomics.com/philippines/inflation-cpi.
Tradingeconomics.com. (2021). Philippines Unemployment Rate | 1994-2021 Data | 2022-2023 Forecast | Calendar. Tradingeconomics.com. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://tradingeconomics.com/philippines/unemployment-rate.
Unido.org. (2021). IMPACT ASSESSMENT OF COVID-19 ON THE PHILIPPINE’S MANUFACTURING FIRMS. Unido.org. Retrieved 2 August 2021, from https://www.unido.org/sites/default/files/files/2021-03/UNIDO%20COVID19%20Assessment_Philippines_final pdf

Download Samples PDF
Related Sample
- DASE201 Data Security Assignment
- HLTINF001 Comply With Infection Prevention and Control Assignment
- MBA5005 Managing Human Capital Assignment
- BMG704 International Finance
- PHCA9521 Global Health and Development Assignment
- SIT763 Cyber Security Management Report
- ACCT6007 Financial Accounting Theory and Practice
- MBA622 Comprehensive Healthcare Strategies Reports
- PUBH6013 Qualitative Research Methods 3A Report
- PUBH6013 Qualitative Research Methods Report
- FPH201 First Peoples Culture, History and Healthcare Report 3
- PUBH6005 Epidemiology Report
- AURTTA017 Carryout Vehicle Safety Inspection Assignment
- BEC4008 Business Economics Assignment
- BRH606 Business Research for Hoteliers
- BUMGT5920 Management in a Global Business Environment Assignment
- Stock Based Compensation Plans Assignment
- COIT20262 Advanced Network Security Assignment
- MBA505 Business Psychology Coaching and Mentoring Report 3
- THH2112 Digital Marketing for Tourism and Hospitality Assignment

Assignment Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research


.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






