Order Now
- Home
- About Us
-
Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research
-
Assignment Writing
-
Resources
- Referencing Guidelines
-
Universities
-
Australia
- Asia Pacific International College Assignment Help
- Macquarie University Assignment Help
- Rhodes College Assignment Help
- APIC University Assignment Help
- Torrens University Assignment Help
- Kaplan University Assignment Help
- Holmes University Assignment Help
- Griffith University Assignment Help
- VIT University Assignment Help
- CQ University Assignment Help
-
Australia
- Experts
- Free Sample
- Testimonial
ECON6000 Economics Assessment Sample
Question
JobKeeper payments have been extended until 28th March 2021. This purpose of this grant is to ensure that all the businesses and non-profit organisations significantly affected by COVID-19 remain adequately supported. This said, not all the Australian residents are eligible. Eligibility criteria says that you have to be either an Australian citizen or a permanent resident or hold a Protected Special Visa.
You are a Business Economics Analyst working in ABC Company. The senior management of this organisation wants you to prepare a report to help the management understand how this JobKeeper payment can affect their employees. Your reasoning should indicate whether JobKeeper grant would help improve income elasticity of demand. Finally, as the company employs many temporary visa holders and student visa holders on a part-time and full-time basis, the senior management also want your recommendation surrounding the grant of JobKeeper payment to all categories of employment irrespective of their visa status.
Your report should cover the following:
1) What is your understanding of JobKeeper payment and the eligibility criteria for JobKeeper grant? Should JobKeeper be given to those working full-time or part-time irrespective of their visa status? If so, will this affect overall market demand or not? Do JobKeeper grants have an impact on individual demand, supply and price? If so, are there likely to be significant changes or will the impact be minimal? Provide examples to support your answer. Use appropriate supply and demand diagrams to explain your views. Do not cut and paste diagrams from external sources. Ensure that your diagrams are professional.
2) What is the impact of JobKeeper on income elasticity and price elasticity? Is demand elastic or inelastic? Provide examples to support your answer. Will people use the substitution effect to manage affordability or will there be no impact on buying capacity? Provide reasons to support your answer. Use diagrams to explain your
views. As in the previous case, please do not cut and paste diagrams from different sources.
Answer
Executive Summary
The Covid-19 pandemic affected the business and life of every individual. Based on this scenario, the Australian Government focused on the JobKeeper Payment scheme with reference to the demand and supply scenario into consideration. This report is based on giving guidance to ABC Company with regard to the means by which the respective senior management can distribute its grant of JobKeeping payment and continue its operations within the Australian market at large.
Introduction
The JobKeeper program designed by the Australian Government mainly entails businesses claim a fortnightly payment of a total of around $1,500 per eligible employee. This is mainly an attempt on part of the Government concerned to enable the residents to cope up effectively with such an economic crisis as a result of the outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic in no time thereby attempting to keep the productivity level intact. This particular report work focuses on giving guidance to ABC Company with regard to the means by which the respective senior management can distribute its grant of JobKeeping payment.
Question 1
Relate a brief understanding about JobKeeper payment and specify eligibility criteria for it. Coronavirus pandemic affected the business organisation where the motivation to be stable in the business jobs has become tough in Australia. Focusing on this context, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) is focusing to develop a JobKeeper Payment Scheme that can focus primarily on providing a subsidy for the business organisations. The prime purpose behind such a grant is to ensure that all businesses and non-profit organisations that are significantly affected by Covid-19 manage to remain adequately supported as well as help the concerned workers that are attached with such organisations during such crisis periods (Petrov & Petrova, 2020, p.7644).
In addition to this, the behavioural responses are a major factor for the creation of incentives for the firms to force down the turnover rate that can provide access to the payments.It is mainly the residents of Australia who are eligible for JobKeeper payments. For enjoying the associated benefits of this particular scheme, besides the need of the person concerned to be a certified citizen of Australia, the other applicable options include the fact that the person concerned either should be a permanent resident or needs to have a Protected Special Visa.
Discuss effectiveness of JobKeeper payment on overall market demand and to whom it must concern
From the point of view of a Business Economics Analyst, it can be stated that the provision of JobKeeper payments to part-time or full-time employees irrespective of their visa status is deemed to be a necessary one. This is because such a scheme has eventually been initiated by the Australian Government to ensure that almost all organisations operating within the very economy are adequately supported. Now, employees, irrespective of their country of origin are undoubtedly considered to be building blocks of any organisation. For instance, the ABC Company can be seen to be run by several temporary as well as student visa holders on a full-time and part-time basis.
The sudden outbreak of Covid-19 has adversely affected almost every such individual. Thereby, in order to keep workings of the Australian economy in order through production of adequate amounts of goods or services within the geographic boundary of Australia, initiation of JobKeeper payment upon employees irrespective of their visa status is likely to prove effective with regard to maintaining the level of productivity throughout (Bekkers& Koopman, 2020, p.97).
Analysis of associated impact on market demand
The associated impact on overall market demand level is illustrated with the help of a diagram as follows:
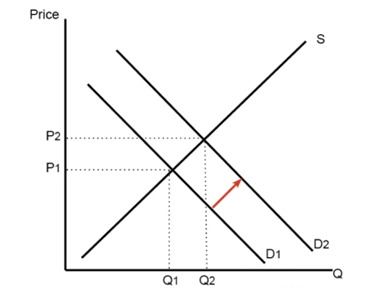
Figure 1: Impact on Overall Market Demand
(Source: Created by Learner)
With reference to the above figure, it can be seen that a provision of JobKeeper payment is most likely to indicate an increase in quantity demanded from Q1 to Q2 thereby shifting the demand curve rightwards from D1 to D2. Such an increase in quantity demanded bears high probability to impose a relatively high pressure upon the suppliers concerned owing to emergence of supply constraints backed by imposition of rules or regulations to avoid further spread of Covid-19 pandemic in this regard. This automatically seemed to have contributed to rise in corresponding market price of the products concerned from P1 to P2 guided by the sole motive of maintaining an equilibrium position within the existing market scenario. Besides this, such increment in price level accompanied by arousal greater demand from individuals getting insured by JobKeeper grants might also have been a result of costlier production process as a result of need for maintenance of certain safety norms while manufacturing the products.
With examples, analyse impact of JobKeeper grants on individual supply, demand, and price
Demand and supply rate is dependent on the ratio of business and production, where elasticity in the Australian economy rolled up to a new extent. In this portion, the sudden outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic affected the Australian economy with the result in the unemployment generation that led to the prevalence of a situation where excess supply condition grew in the initial terms driving the decrease in the supply ratio (Hodder, 2020, p.268).
Due to this fact that employees in Australia are losing their jobs, it led to the generation of acute contraction where the economic scenario can get a chance of loss in the supply ratio and demand graph. Moreover, the introductions of JobKeeper payments are based on boosting the demand level of the individuals to some extent. In addition to this, the gradient increment undoubtedly shows an impact on the supply level of the products where the dependency on the sales in the market is broadly based on the services in the market and demand. To understand the extent of the impact of the change in demand from the supply level, it is important to focus on the following explanation:
Impact on individual demand, supply, and Price:
The JobKeeper grant is likely to enhance the level of purchasing power available in hands of the individuals at large. Such increment bears a high probability to show the corresponding impact upon goods of varied types. However, the associated impact upon supply level is unlikely to be high owing to the prevalence of supply constraints thereby contributing to enhancement of associated price level in order to maintain an equilibrium position.
Some of the scenarios are illustrated as follows:
Normal Goods: These goods are referred to as the kind of goods that experience an increment in their demand level due to the hike in the income of customers. The supply of normal goods is based on the factor of income elasticity where the hike in the income leads to the increase in the demand for the goods. The supply of these goods is most likely not affected by the exposure of the JobKeeper payment option in the business organisation of Australia (Mohner&Wolik, 2020, p.641).
Necessary Goods: These goods relate to the services or products based on which the customers need to purchase irrespective of the change in the income level. These goods are not affected by the change in income and remain constant during the changing business scenario as well as income stability. Thus, the changes in the demand are constant.
Inferior Goods: These goods refer according to the demand change and hence show a slight change in the income level. Moreover, there is an inverse relationship with the income level and decreasing income level leads to the increase in the supply of these products. Thus, the automatic shift in the business and income affects the supply curve towards the left leading to the increase in the supplied link.
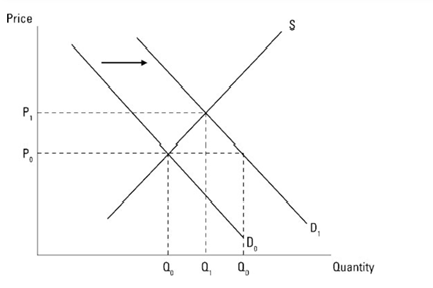
Figure 2: Impact on Individual Demand, Supply, and Price Level
(Source: Created by Learner)
From the above figure, it can be deduced that exposure to JobKeeper payment kind of initiated to individuals demands a greater number of products Q1 than before which was Q0. The supply level, to cope up with this excess amount (Q1-Q0), contributed to raising the price level from P0 to P1. For instance, it can be seen that Covid-19 was a lesson for the government of Australia where they need to focus on undertaking an initiative to boost the manufacturing sector of Australia, and in addition to this, it is estimated that $107 million is required to strengthen the supply in the required commodity.
For instance, the lump sum amount of investment is deemed to be ofgreat help onpart of businesses to prioritise the concept of both medical products and medicines thereby playing a vital role in boosting the needs of individuals. This is becausecritical supplies are based on boosting the stages of demand. Co-investment is based on the financial resources of the finished products where these concepts enable to fix the six-priority area of the government.
These include the following:
• Products that enable health such as medical products
• Critical and limited resources as well as resource technology
• Food and beverages
• Clean energy and recycling
• Space
• Defense
From the above six priorities of the critical assessment, the manufactures in Australia have risen to address the challenges that can deliver manufactured products during the Covid-19 and even in the long-term scenario. In addition to this, presently the businesses are focusing on presenting the unlocked potential of delivering the essential materials for the future. Moreover, the delivery of each material is based on playing an important role in the development of strengths as well as strategically investing in boosting the role of technology or science in the industry (Rapacciniet al., 2020, p.231). In every aspect of the supply growth, it is important to focus on the change in the quality of the products. This can be supported by referring to the fact that clear supply effects owing to incidences such as closed factories, quarantines, impaired mobility, and disruptions witnessed in the supply chain have undoubtedly affected the level of production. Irrespective of the non-availability of consumer price index information for a number of months as a result of economic lags, the breakeven inflation expectations following the hit by Covid-19 shock has enabled obtain somewhat a brief idea about the actual workings of JobKeeper grants at large.
Question 2
With examples, point out the impact of JobKeeper upon price elasticity and income elasticity
Taking the case of Covid-19 into consideration, it can be reviewed that the individual needs to focus on the assessment of buying products in normal life. However, the current scenario of the business and income is continuously changing with the impact on the income as well as on the price elasticity. The current on-going scenario of the Covid-19 crisis impacts the daily wage with the exposure to the risk scenario and loss in the work in Australia. The incorporation of the JobKeeper payment scheme is hence based on accessing the greater amount of financial resources.
Price Elasticity: It is referred to as the primary key of the economic measure that states the degree of responsiveness and the change in the quantity of the product purchased by the people and change in the demand price level.
Elastic Demand: It is a type of price elasticity where the quantity changes in the product or service are more than the change in the price level. The exposure to the Covid-19 crisis led to several issues that were balanced with the access to the JobKeeper Payment scheme that acted as a relief in controlling the economy of Australia. It is also observed that there is a decrease in the demand of an individual by households resulted instabilisation of the taxation and prices for better ranges (Rapacciniet al., 2020, p.227). For example, exposure to such an economic downturn made individuals reduce the demand level of luxury items such as branded apparel, luxurious home appliances, expensive branded watches, and cars from Ford Motor or Daimler thus making the people focus more on saving and limit the expectations.
Inelastic Demand: This particular kind of price elasticity focuses on the factors regardless of the increase or decrease in the price level of the products and service, the purchasing process remains the same irrespective of the nature of the small amounts.
The JobKeeper Scheme focuses on the exposure of all these uncertain economic scenarios leading to a minimal fall in quantity demanded. These changes are not discouraged by the customers in order to reduce the consumption of limited resources such as oil irrespective of the rise in the market price.However, irrespective of such an attempt on part of consumers to limit their expenses level, demand for medicines have shown a sharp rise irrespective of their market price level thereby indicating prevalence of the inelastic nature of demand for necessary or life-saving commodities even in such pandemic situation.
Income Elasticity: This income elasticity is related to the economic measure by giving an idea of the responsibility to exchange the goods and services based on the income level of each individual. The assessment of the JobKeeper payments plays an important role in the management of the individual part where the low-income background and other options of engaging the individuals in consumption and inferior products lead to the economic crisis at the initial phase of the lockdown. Thus, negative influence of the income elasticity focused on the economic crisis during the growth of lockdown.
With proper evidence and diagram, discuss whether people use substitution effect to manage affordability
The individuals, guided by the sole motive to afford the necessary products within the number of financial resources available in their hands, are likely to opt for the substitution effect. This is most likely to be guided by an initiative on their end to switch to alternative items that are as cheap as possible to cope up with such an economic crisis.
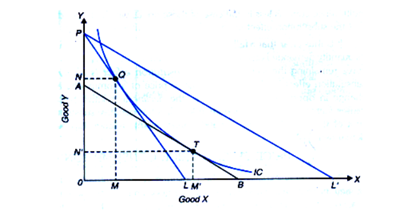
Figure 3: Substitution Effect to manage affordability
(Source: Created by Learner)
By referring to the figure above, the income effect shows an impact on quantity purchase as a result of a change in associated income level. This results in a movement to a different indifference curve (IC) backed by such change in the ability to purchase a given quantity of Good X against a new quantity of Good Y, which is a substitute of Good X. Besides this, prevalence of supply constraints in this regard has also been another major factor behind the emergence of such substitution effects as a result of partial curb down of various sectors.
Taking the Covid-19 pandemic scenario into consideration, it can be seen that such an outbreak affected the global business scenario with the influence on the global health of individuals. Based on this ratio, the manufacturing industry suffered from the changes in the lifestyle pattern and demand demographics. In addition to this, the complete scenario of the manufacturing business emerged as history and required a path to enable the business growth with the focus on availability of the stocks. In this ratio, the Australian Manufacturing sector focused on the concept of a modernised view of the workforce as the work criteria in the Chinese business manufacturing industry can be seen (Norouzi et al., 2020, p.101654).
Moreover, the initial analysis of the hit should focus on the results of Covid-19, where the Australian supply chain analysis provides a report of the major disruption of the demand structure. This can be due to the result of the limited supplies that the Australians are facing due to the huge crisis. Given this, domestic manufacturing is the major purpose for which the limited supplies and demand limitation can be an important factor. However, these results are limited to a point of supplies only. Thus, the period of crisis led due to the outbreak of Covid-19 emerged as a forced scenario with the decrease in the large percentage of manufacturing reduced. In addition to this, rapid adaptability is growing where the companies are associated to enlarge their particular industry so that they can ramp up the capability of the sector.
Based on the above analysis, the Australian Government adopted some strategies to initiate the growth of the individual industries. On this note, the Australian Government in order to refuel the economy based on taking the initiative so that it can move away from the short-term solutions that are cheap or indicate the overseas labour that focuses on the investment of the local system. Every bit of the business economic growth is based on the high profitability as well as on the solution that can particularly move the manufacturing sector on the local premises.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that the JobKeeper scheme is of great help to bring real benefits in the business organisations by involvement of the utilisation of the existing teams, brand new services or products, and many more. Moreover, it is important in the scenario of economic recession where harsh conditions can lead to destruction in casual employment.
Reference List
Petrov, A., & Petrova, D. (2020). Sustainability of transport system of large Russian city in the period of COVID-19: Methods and results of assessment. Sustainability, 12(18), 7644. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/18/7644
Bekkers, E., & Koopman, R. B. (2020). Simulating the trade effects of the COVID?19 pandemic: Scenario analysis based on quantitative trade modelling. The World Economy.30(2), 56-178. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/twec.13063
Norouzi, N., de Rubens, G. Z., Choubanpishehzafar, S., & Enevoldsen, P. (2020). When pandemics impact economies and climate change: exploring the impacts of COVID-19 on oil and electricity demand in China. Energy Research & Social Science, 68, 101654.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214629620302292
Hodder, A. (2020). New Technology, Work and Employment in the era of COVID?19: reflecting on legacies of research. New Technology, Work and Employment, 35(3), 262-275.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/ntwe.12173
Mohner, M., & Wolik, A. (2020). Differences in COVID-19 risk between occupational groups and employment sectors in Germany. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 117(38), 641.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7817783/
Rapaccini, M., Saccani, N., Kowalkowski, C., Paiola, M., & Adrodegari, F. (2020). Navigating disruptive crises through service-led growth: The impact of COVID-19 on Italian manufacturing firms. Industrial Marketing Management, 88, 225-237.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0019850120304247

Download Samples PDF
Related Sample
- SITXMPR007 Develop and Implement Marketing Strategies Assignment
- INFS5023 Information Systems for Business Assignment 2
- Building Wellbeing and Resilience Assignment
- FPH201 First Peoples Culture, History and Healthcare Report 3
- MBA506 Thinking Styles Negotiation and Conflict Management Report
- Finance Broking in Practice Assignment
- MOD005778 Dynamics and Fluid Mechanics Assignment
- ACCT6007 Financial Accounting Theory and Practice Report
- HI6025 Accounting Theory and Current Issues Assignment
- PUBH6006 Community Health and Disease Prevention
- MBA402 Governance Ethics and Sustainability Case Study 2
- Cultural Differences Role in Marketing Strategies for MNCs
- HN06008 Effective Care Plan for a Person Experiencing Mental Health Issues or Illness Report 2
- SITXFSA002 Participate in Safe Food Handling Practice Instruction Assignment
- MBA631 Digital Marketing and Communication Report
- MIS603 Microservices Architecture Report
- MANU2123 External Project Proposal Assignment
- MIS606 Professional Practice Assignment
- LC3002 English For Academic Purpose Resit Information
- CVE80010 Principles of Sustainability Report 3

Assignment Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research


.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






