Order Now
- Home
- About Us
-
Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research
-
Assignment Writing
-
Resources
- Referencing Guidelines
-
Universities
-
Australia
- Asia Pacific International College Assignment Help
- Macquarie University Assignment Help
- Rhodes College Assignment Help
- APIC University Assignment Help
- Torrens University Assignment Help
- Kaplan University Assignment Help
- Holmes University Assignment Help
- Griffith University Assignment Help
- VIT University Assignment Help
- CQ University Assignment Help
-
Australia
- Experts
- Free Sample
- Testimonial
MITS5501 Software Quality, Change Management and Testing Assignment Sample
IT - Research Report Assignment 2
Assignment Brief
Objective(s)
This assessment item relates to the unit learning outcomes as in the unit descriptor. This assessment is designed to improve student presentation skills and to give students experience in researching a topic relevant to the Unit of Study subject matter.
INSTRUCTIONS
For assignment help, in assignment 1 you were required to do a 10-13 minutes’ presentation on a recent academic paper on on Software Quality, Software Change Management or Software Testing.
Assignment 2 requires writing a report or critique on the paper that you chose in Assignment 1 to Presentation and Participation component above.
Your report should be limited to approx. 1500 words (not including references). Use 1.5 spacing with a 12-point Times New Roman font. Though your paper will largely be based on the chosen article, you should use other sources to support your discussion or the chosen papers premises.
Citation of sources is mandatory and must be in the IEEE style.
Your report or critique must include:
Title Page: The title of the assessment, the name of the paper you are reporting on and its authors, and your name and student ID.
Introduction: Identification of the paper you are critiquing/ reviewing, a statement of the purpose for your report and a brief outline of how you will discuss the selected article (one or two paragraphs).
Body of Report: Describe the intention and content of the article. If it is a research report, discuss the research method (survey, case study, observation, experiment, or other method) and findings. Comment on problems or issues highlighted by the authors. Report on results discussed and discuss the conclusions of the article and how they are relevant to the topics of this Unit of Study.
Conclusion: A summary of the points you have made in the body of the paper. The conclusion should not introduce any ‘new’ material that was not discussed in the body of the paper. (One or two paragraphs)
References: A list of sources used in your text. They should be listed alphabetically by (first) author’s family name. Follow the IEEE style.
The footer must include your name, student ID, and page number.
Note: Reports submitted on papers that are not approved or not the approved paper registered for the student will not be graded and attract a zero (0) grades.
What to Submit
Submit your report to the Moodle drop-box for Assignment 2. Note that this will be a turn- it-in drop box and as such you will be provided with a similarity score. This will be taken into account when grading the assignment. Note that incidents of plagiarism will be penalized. If your similarity score is high you can re-submit your report, but resubmissions are only allowed up to the due date. If you submit your assignment after the due date
and time re-submissions will not be allowed.
Note: All work is due by the end of session 9. Late submissions will be penalized at the rate of 10% per day including weekends.
On Time Days Late _______Turn-it-in Similarity % _______
Solution
Introduction
The purpose of this report is to critically review the academic article identified in assessment-1. The chosen academic paper is on “AZ-model of software requirements and change management in global software development” which belongs to the course unit: “Software quality and Change Management”.
It has been possible for an individual researcher to discuss the selected article in following sections: Reviewing the Literature Survey; Critically reviewing the Proposed AZ-model; Undertaking a research method to collect data, information relevant to the topic; Discussion based upon the results and finally find the outcomes of the research report.
Literature Survey
This section is one of the major parts of this research report. Here, the researcher critically reviews the chosen academic paper and compares it with other similar papers.
Review of the Chosen Academic Paper
This paper indicates information about Requirements Change Management (RCM) and Global Software Development (GSD). Due to the lack of information communication, changes of customers’ demands, changes in management strategies might be required. With a centralised software development system, an organisation can improve its poor requirements management [7]. This literature is a proposed study of the AZ-model which has been explored through RCM & data collection process. Use of tools, technologies have been preferred here with various methods and tactics.
Comparison Literature I: Empirical investigation of barriers improvement in GSD
According to ([7]), this paper supports the chosen academic article and provides information for critical review. Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) has been represented here with Initiating (I), Diagnosing (D), Establishing (E), Acting (A), and Learning (L)- IDEAL approach. During the research and review, Software Process Improvement Capability Determination (SPICE) has been recommended.
This research is a key context of supply chain management (SCM) which is a process improvement activity for GSD context. Planning, Conducting, and Reporting are the three phases of this research paper that added value to the software development model [7].
Comparison Literature II: Use of RE Tools in Global Software Engineering
As per the ideas of ([8]), this paper indicates requirements engineering (RE) tools for GSD. To support the literature survey of the chosen paper, this paper has been valued. In this study, the concept of Global Software Engineering (GSE) was also introduced. The objective of the paper is to support the chosen academic article with the concepts addressed in a different perspective. In the global software development market, the demand for changing the environment is high. Thus, evolving RE tools in GSD is an important aspect [2].
On the other hand, as per the International standard of software development, to achieve the effectiveness in requirements management, following steps to be followed which are: Change proposal, Review, Approval, Change notification. To change the market requirements as per the customers’ demand is a necessary and standard guideline for GSE [8].
Research Methodology
To continue with the research paper review, research methodology has been determined as a major section/part of the assessment [1]. In order to achieve the research problem and project objectives, it has been possible for the researcher to set research questions (RQs) and try to solve this by the end of this section.
? RQ1: How to propose the AZ-model of software requirements?
? RQ2: What is change management in GSD?
? RQ3: Which types of research methods seem suitable for this paper?
? RQ4: How to address the literature concept and analyse the data based on results?
To solve these RQs and propose the AZ-model of RCM in GSD, secondary data has been collected. The data are relevant to the research topic phase and sufficient to implement the AZ-model [2].
Collection of Data
Data collected in the form of questionnaire & survey [3]. Use of lightweight software development methodology in favour of heavyweight software development methodology has been proposed here. With the help of a project management research method, the AZ-model of RCM can be implemented. Moreover, Project manager is engaged to carry out development activities of the proposed AZ-model. Considering the Project management factor, it has been possible to set survey questions and answer accordingly.
Based on the perspective of ([7]), Software Development Methodology (SDM) refers to this AZ-model and is applied to collect data from survey respondents.
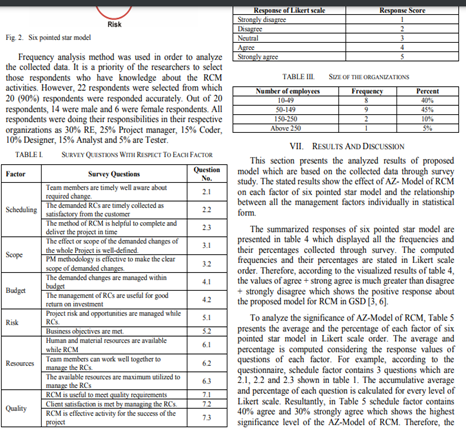
Figure 1: Sample Collected Data
Proposed Model
In this section, researchers are going to propose a model based on the empirical study and questionnaire survey [4]. Delay of one site effects in the proposed model implemented in six different areas of project management. Moreover, a six-pointed star model has been introduced here based on the guideline of Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBoK).
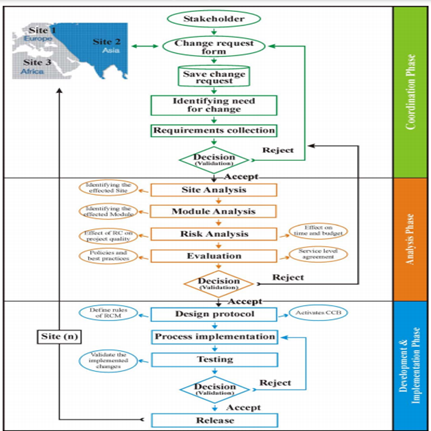
Figure 2: Proposed AZ-model of RCM
(Source: [7])
Findings and Analysis
From the collected database, it has been observed that, AZ-model can be implemented successfully if the GSD and PMBoK requirements have been fulfilled. The major findings of this academic paper are as follows:
? Workflow and Change Management
It is an important category that has been featured for global software development. In the case of GSD, high-awareness among the team is required for effective communication and model implementation [5]. However, multiple user access and collaborative life cycle management are the key approaches of software development and meeting change requirements. Regarding this, collaborative life cycle management and global stakeholder collaboration has been prioritised.
? System and Data Integration
In this case, the AZ-model framework can be implemented considering data import, data export and tool integration. System and data integration category focuses on the data collection & resources, RE and proposed AZ model [6].
? Shared Knowledge Management
The selected academic paper is useful for supporting stakeholders’ decisions, multiple user access and collaborative life cycle management. On the other end, for GSD it is necessary to introduce global stakeholders’ collaboration.
? Traceability
This is an important category featured by the GSD [1]. Flexible tracing, bi-directional tracing and traceability analysis are the key aspects of the AZ-model implementation and software development. Throughout the implemented software development lifecycle traceability seems to be a vital resource factor.
Issues addressed
While conducting systematic literature review (SLR) of the chosen article, several issues/barriers have been addressed [2]. Due to lack of organisational support and lower level of management, sometimes software development and change management has not been possible. Moreover, during the AZ-model implementation, non-availability of sufficient resources could be a major issue. Lack of client management support, lack of awareness towards the change management environment badly impacted on the GSD attributes.
Due to communication difficulties with the stakeholders the software requirements and change management may lead to misinterpretation [3]. Vital issues with the AZ-model implementation are popularly known as cross-cultural barriers among GSD organisations. Furthermore, an individual researcher faces lack of resources while reviewing this academic paper which is also a barrier. PMs were hesitant to allocate proper budget, financial support in terms of implementing the AZ-model.
Results and Discussions
This section shows the results of the proposed model and collected data in statistical form. Summarizing the data and relevant results of the six-pointed star model is the main objective of this part [4]. Researchers are prioritising the literature survey responses and evaluating the responses. To analyse the significance of the AZ-model, it is necessary to value the average, higher, and low percentage of the results from survey responses. Moreover, the evaluation criteria with the RE tool shows the performance features of the AZ-model. To analyse the results and discuss the relevant factors, a shared knowledge management and investigation method has been applied [7].
It has been possible for an individual researcher to identify and evaluate the outstanding score (CFI) from the collected database. However, in order to address the RQs, issues to be resolved on an immediate basis. On the other hand, while executing the GSD and change requirements for AZ-model, the survey data (positive/ negative/ neutral responses) are valued [5]. Significant differences observed during analysis of the results from the collected database. Categorizing the issues in a robust framework has also been valued for software process improvements. Demonstrating the Likert-scale value from the SLR exhibits in the form of results. Last, but not the least, from the proposed AZ-model and analysing the critical barriers researchers are able to modify the framework as per requirement [7].
Conclusion
After critically reviewing this academic article, how most of the software development organisations get facilities of AZ-model can be observed. Moreover, how this model can be useful in future work has also been understood from this academic paper. This paper demonstrates the key issues of AZ-model implementation and recommended for client & vendor management. How the RE tools become an advantage of GSD and AZ-model implementation has been analysed from this study [8].
In the future, global software management seems to be relevant for AZ-model implementation and featuring the gaps identified during the process improvement. Supporting features of GSD may be unsoundly obtained for the system integration part. Finally, not yet importantly, this paper provides ideas of traceability, software development, collaboration with the stakeholders and communicating with them for the next stage of change management in software industries.
References
[1] A.A. Khan, J. Keung, M. Niazi, S. Hussain and A. Ahmad, “Systematic literature review and empirical investigation of barriers to process improvement in global software development: Client–vendor perspective”, Information and Software Technology, vol. 87, pp.180-205, 2017. Accessed on: July 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Arif-Khan23/publication/315382990_Systematic_Literature_Review_and_Empirical_Investigation_of_Barriers_to_Process_Improvement_in_Global_Software_Development_Client-_Vendor_Perspective/links/5b4d651ea6fdcc8dae246cc7/Systematic-Literature-Review-and-Empirical-Investigation-of-Barriers-to-Process-Improvement-in-Global-Software-Development-Client-Vendor-Perspective.pdf
[2] C. Djoweini, “The driven parameters of Software Development Projects”, 2019. Accessed on: July 31, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1371926/FULLTEXT01.pdf
[3] E. Serna, O. Bachiller and A. Serna, “Knowledge meaning and management in requirements engineering” International Journal of Information Management, vol. 37, no. 3, pp.155-161, 2017. Accessed on: July 31, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401216306582
[4] J. Band and M. Katoh, Interfaces on trial: Intellectual property and interoperability in the global software industry, Routledge, 2019. Accessed on: July 31, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9780429046841/interfaces-trial-jonathan-band-masanobu-katoh
[5] K. Curcio, T. Navarro, A. Malucelli and S. Reineh, “Requirements engineering: A systematic mapping study in agile software development”, Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 139, pp.32-50, 2018, Accessed on: July 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121218300141
[6] M. El Bajta and A. Idri, “Identifying Software Cost Attributes of Software Project Management in Global Software Development: An Integrative Framework”, In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent Systems: Theories and Applications, pp. 1-5, 2020, September. Accessed on: July 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3419604.3419780
[7] M.A. Akbar, M. Shafiq, J. Ahmad, M. Mateen and M.T. Riaz, “AZ-Model of software requirements change management in global software development”, In 2018 International Conference on Computing, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (ICE Cube) (pp. 1-6), IEEE. 2018, November. Accessed on: July 28, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhammad-Tanveer-Riaz/publication/330387529_AZ-Model_of_software_requirements_change_management_in_global_software_development/links/5cf4a8aa92851c4dd024128d/AZ-Model-of-software-requirements-change-management-in-global-software-development.pdf
[8] S. Yos and C. Chua, “Requirements engineering tools for global software engineering”, In Proc. 13th Int. Conf. Eval. Novel Approaches Softw. Eng.(ENASE), vol. 1, pp. 291-298, 2018, March. Accessed on: July 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.scitepress.org/Papers/2018/67601/67601.pdf

Download Samples PDF
Related Sample
- MCR006 Financial Management Assignment
- CSM80011 Systems Processes and Technologies for Construction Poster 1
- UMH207 Understanding Mental Health Assignment
- Data Science and Analytics Assignment
- BAS121A Fundamentals of Marketing Assignment
- ICT5356 Principles of Artificial Intelligence Report
- 5011SP5 Accounting for Management M Report
- ACC601 Introduction To Financial Accounting Assignment
- The Role of Physics in our Daily Life Essay Assignment
- LAW1081 The Individual and The State Formative Assignment
- MBA641 Strategic Project Management Assignment
- TACC602 Accounting for Business Assignment
- MBA642 Project Management Plan Report 3
- ITECH7407 Real Time Analytics Assignment
- PROJ6004 Contracts and Procurement Report 1
- PRJM6010 Project and People Assignment 2
- BMG872 Global Strategy Development Implementation Assignment
- COIT20248 Information System Analysis and Design Assignment
- MBA631 Digital Marketing and Communication Assignment
- PROJ6004 Contracts and Procurement Case Study

Assignment Services
-
Assignment Writing
-
Academic Writing Services
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- College Assignment Help
- Writing Assignment for University
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Architecture Assignment Help
- Total Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- My Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Global Assignment Help
- Write My Assignment
- Do My Assignment
- Solve My Assignment
- Make My Assignment
- Pay for Assignment Help
-
Management
- Management Assignment Help
- Business Management Assignment Help
- Financial Management Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Risk Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Logistics Management Assignment Help
- Global Business Strategy Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Portfolio Management Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Hospitality Management Assignment Help
- Healthcare Management Assignment Help
- Investment Management Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- CRM Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Nursing
-
Finance
- Finance Assignment Help
- Do My Finance Assignment For Me
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Financial Reporting Assignment Help
- International Finance Assignment Help
- Business Finance Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help
-
Accounting
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Accounting Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Tax Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Theory Assignment Help
-
Computer Science and IT
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data mining Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Network Topology Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
-
Law
- Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Tort Law Assignment Help
- Social Media Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Human Rights Law Assignment Help
- Evidence Law Assignment Help
- Administrative Law Assignment Help
- Enterprise Law Assignment Help
- Migration Law Assignment Help
- Communication Law Assignment Help
- Law and Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Science
- Biology
- Engineering
-
Humanities
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- Auditing
- Mathematics
-
Economics
- Economics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Business Economics Assignment Help
- Marketing Plan Assignment Help
- Demand Supply Assignment Help
- Comparative Analysis Assignment Help
- Health Economics Assignment Help
- Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Political Economics Assignment Help
- International Economics Assignments Help
-
Academic Writing Services
-
Essay Writing
- Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Essay Help Online
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- Help With MBA Essays
- Essay Writing Service
- Essay Writer For Australia
- Essay Outline Help
- illustration Essay Help
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Professional Essay Writers
- Custom Essay Help
- English Essay Writing Help
- Essay Homework Help
- Literature Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- MBA Essay Help
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Writing Essay Papers
- Write My Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Help Writing Scholarship Essay
- Help Writing a Narrative Essay
- Best Essay Writing Service Canada
-
Dissertation
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Statistics Dissertation Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Programming
-
Case Study
- Write Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study Help
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- Case Study Writing Services
- History Case Study help
- Amazon Case Study Help
- Apple Case Study Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- ZARA Case Study Assignment Help
- IKEA Case Study Assignment Help
- Zappos Case Study Assignment Help
- Tesla Case Study Assignment Help
- Flipkart Case Study Assignment Help
- Contract Law Case Study Assignments Help
- Business Ethics Case Study Assignment Help
- Nike SWOT Analysis Case Study Assignment Help
- Coursework
- Thesis Writing
- CDR
- Research


.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






