Reports
HN06008 Effective Care Plan for a Person Experiencing Mental Health Issues or Illness Report 2 Sample
Overview
Length: 2500 words (+/- 10%)
Weight: 50%
Due date: End of Week 4 (11.59pm Sunday)
Thorough assessment of the impacts on individuals with mental health issues is critical to formulate an evidenced-based and client-informed care plan. This assessment requires you to undertake a comprehensive assessment on one client you have encountered in your nursing work. You will present their case coherently, undertaking a full assessment in order to generate an evidenced based plan of care. Care planning in mental health must also be undertaken in full collaboration with the client and you will have an opportunity to consider this in your particular case.
Note: if you have not encountered a client that you can use for this assessment you will be provided a link to a video where a young man is being interviewed by a psychiatrist. There is adequate detail in the following video for you to complete this task and develop a plan of care. Psychiatric interviews for teaching: psychosis (University of Nottingham, 2012). Please note that this video has been made by the University of Nottingham for teaching purposes. The psychiatrist is a real psychiatrist but the patient is played by an actor. This assessment supports unit learning outcomes 1, 2 and 3.
Your assessment submission should include a cover page. Download the Cover page template.
Task
1. Introduce one client-focused complex case where the client is experiencing major impacts on their mental health and wellbeing. Ensure that you include the following: (700 words)
a. relevant demographical, and contemporary cultural and biopsychosocial detail;
b. relevant detailed data using an established and coherent framework for assessment; and
c. ensure full anonymity is maintained.
2. Critique the role of trauma in the development of this mental health issue. (300 words)
3. Investigating the key holistic health needs from both practical and theoretical perspective, rationalise and formulate a plan of care using an evidenced-based care framework. Consider: (1000 words)
a. cognitive, behavioural environmental/social and pharmacological strategies; and
b. ensure your strategies take into account the theory around trauma-informed care. Provide evidence for your proposed interventions and include how the plan will be evaluated.
4. Conclude with an analysis on negotiating collaborative care planning for clients in mental health to ensure the promotion of recovery and person-centred care. (500 words)
Supporting resources
APA 7th referencing: Overview (Victoria University Library, 2024)
Solution
Introduction to the client-focused complex case where the client is experiencing major impacts on their mental health and wellbeing
a. Relevant Demographical and Contemporary Bio-psychosocial Detail
The client who is being considered here is a 52 year old man who once worked as a police person. However, due to an accident, he has been paralyzed. Now, the matter is that as he was an active person, such an accident and the bed-ridden condition caused the person to become depressed and this kind of depression causes the person to get violent sometimes and at the time when the person becomes angry or out of control, he becomes less willing to take any medicine and can harm anyone wants or forces to him to take medicine or food at that time. In this kind of situation, he becomes unwilling to live actually and that’s the reason why he gets violent and denies taking any medicine or food at that time. The person is belonging to the Christian culture and has spiritual thoughts. When he was an active person, he went to church in a regular manner and still now, when he is calm and composed, he is found having spiritual discussions with others. The physical condition of the person is being recovered and some physiotherapy is going on. His left portion of the body got paralyzed. But now, he has found himself regaining mobility slowly. However, the mental health of the person is deteriorating in a regular manner. Previously, he was found to be violent once a week. However, now, every day, he is getting violent and at that time one can manage the person and if the person would do something harmful to one at this time, then it would really be an unfortunate event and that’s why it’s important to ensure the recovery of the person in an immediate manner and the mental healing treatment should be designed properly and immediately (Spytska., 2023).
b. Relevant Detailed Data Using an Established and Coherent Framework for Assessment
The bio-psychological model can be regarded as a comprehensive framework that is effective in evaluating depression from a holistic perspective and it helps in finding out the interaction between the biological and the psychological factors in the development of depression (Joorbonyaan et al., 2021). Hence, this model or framework can be used. By using the framework, it's possible to assess the biological condition of the patient along with the psychological and social condition of the patient and their internal relationships. In the following section, the assessment data is going to be provided.
Biological Assessment
As per the collected data, there is no family history of depression of the person and it means that the depression is not genetic. The physical health of the person is improving. His blood pressure is normal 82 / 120 and his pulse rate is 75 – 78 which is also almost normal. The SPO2 level of the person is 96. The person does not have any kind of addiction. The only issue that the person is facing biologically is related to the mobility of his left side due to the car accident as the accident caused neurological issues to the left part of the body and there were some fractures also. However, the fractures have been managed with operations and the physiotherapy is going on and he is regaining the mobility in a slow way. It means that the biological condition is fine though the paralyzed life of almost 5 years and an early retirement from such an active job like police service has caused mental issues among the person (Glazener et al., 2021).
Psychological Assessment
The person is facing mood swings as sometimes he is found being calm and sometimes he is getting completely negative towards life and starts being violent it’s found that the person has negative thought patterns with respect to the cognitive patterns, Depressive patients, sometimes, are found with cognitive distortions such as black and white thinking and self criticism that caused the person to become unwilling in living the life and getting the treatment (Bonfa Araujo et al., 2022). He is found facing some common symptoms of depression like loss of interest or pleasure in activities and fatigue.
Social Assessment
Social assessment for the Assignment Help is needed to understand the level of depression as people suffering from depression are generally socially inactive (Elmer & Stadtfeld, 2020). He has a strong relationship with family and sometimes he is found being involved in some discussions with his daughter when he is calm. However, their involvement with family members has been reduced as most of the time he prefers sitting alone.
c. Ensure Full Autonomy is Maintained
As the person is in the state of giving consent, he is involved in decision making and his consent is being taken before making any considerable change in the treatment. The consent is being taken when he is in a calm and natural state. The healthcare professionals are communicating with the patient very effectively while respecting his dignity. They are trying to empower the patient as far as possible and setting goals by considering the fastest recovery of the patient (Dutra et al., 2022).
1. Role of trauma in the development of the mental health issue
By considering the viewpoint of Coventry et al., (2022), it can be stated that trauma plays a significant and complex role in the development of mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and others. In this case, the person is facing post-traumatic depression from the stress of being unable to live a normal and active life that he has habituated with. By considering the thing that happened to the person, it can be stated that the person is suffering from chronic trauma. Chronic trauma is a situation where a person is in long-term exposure to a traumatic event and in this regard, the trauma has been created by the accident that the person has faced and till now the person has been facing the impact of the accident as his body’s left side is in a paralysis state. Post-traumatic depression can be related to emotional, physical, or sexual trauma. However, in this case, the physical trauma is relevant. The person is always thinking of his life before witnessing the trauma when he was associated with a highly active profession. However, now, he is dependent on others in regard to the process of mobility, and such a thought is haunting the person and causing him to become restless sometimes and develop negative thoughts among the person where he is showing less willingness to take any medicine. It means that the whole mental issue that the patient is currently facing is due to the trauma he has witnessed only.
3. Key holistic health needs and care plan
a. Cognitive, behavioral, social and pharmacological strategies
Cognitive strategy
In this case, the healthcare professional is required to consider using the cognitive behavioral therapy framework as it helps the individual to find out and challenge negative thoughts such as he is worthless or his life will not be better anytime (Nakao et al., 2021). By assessing the mental state of the concerned person, it can be stated that he is thinking the same and that’s why his interest in living is being affected. He is thinking that he will be unable to get a life like before and that’s why he is losing interest in living. With cognitive behavioral therapy, it's important to make the person avoid and challenge such negative thoughts and be positive. If he can think of the positive parts related to his recovery and the life he is going to get after recovery, his mental issue will be resolved.
Behavioral Strategy
In this case, the behavioral activation strategy or behavioral activation framework will be used. It requires a depressed person to be involved in different activities for their mental health (Malik et al., 2021). By assessing the person, it has been found that most of the time he prefers sitting alone and thinking of something and it has also been seen that the person is suffering from fatigue and has less interest in being associated with any activity. This is a sign of depression and that’s why it's important to make the person engaged in some activities through proper counseling. First of all, the avoidance of isolation needs to be implemented. It has to be ensured that someone is with him until he is sleeping or getting physically tired. As he is a spiritual person, someone who is associated with him can be involved in a spiritual discussion with the person. The counseling process should be done through communication where the mental health expert would be involved with him in the discussion related to anything that he prefers and in this way he needs to be kept active throughout the day. The physiotherapist who is taking care of his mobility can help him to indulge in some physical activity that he will be able to do and appreciate the activities as it will help the person regain the confidence that he has lost.
Social Strategy
In this case, social support needs to be strengthened and it's needed to improve the situation related to social isolation. The person prefers being alone and it would take the person to a more depressing situation and that’s why it's immediately needed to retrieve him from the state. It is important to indulge the person in social activity that he prefers. For instance, if he prefers being associated with a discussion regarding politics, then someone who knows about politics should be indulged with him in a discussion. Sometimes, he is communicating with his daughter which means that there is a preference for communicating with this family member and that’s why it can be stated that the daughter should spend more time with the person while indulging in a conversation that the person prefers like spiritual discussion, political discussion, discussion regarding any book or story or anything else that the person prefers discussing. It can work as family therapy and it is definitely needed for the person as the family members can be the best ones to make him understand how important he is to them so that his interest in living and responding positively to the treatment can be increased. The person can be involved in any social gathering where his friends and family members will gather. These strategies will help him to be active and less likely to think of negative factors (Van Orden et al., 2021).
Pharmacological Strategy
As the person is getting violent as an outcome of depression, it’s important to provide him with antidepressant medications in a regular manner as being violent will affect his mental as well as physical condition and there will be chances of harming others as well. Some medicines that can increase the availability of serotonin in the brain can be used in order to make the person calm and less depressant. The power of the medicine is required to be changed by considering the situation of the patient. If the situation of the patient gets better and healthcare experts find that there is a low or no chance of being violent, the power of the medicine can be decreased. However, for now, it should be consumed regularly by the patient.
b. The strategies taken into account the theory and evidence for the propose intervention including the evaluation plan
Theory
The trauma-informed care theory has been used here. By considering the theory, it can be stated that healthcare and mental health professional recognizes the impact of trauma and design the overall treatment process by considering the impact (Leotti et al., 2024). In this case, at every step of the care process, the traumatized incident has been considered and that’s why it has been suggested to be involved in positive discussion with a person regarding politics, books, movies, spiritual thoughts, or anything else that can help him to forget the incident of trauma for sometimes and by consider8ing the traumatized incident and its impact, treatment for helping him to regain the mobility has been designed.
Evidence for the proposed intervention
By considering the viewpoint of Ozturk(2021), family support can be regarded as an effective counseling strategy in the case of trauma-based depression, It can be regarded as an evidence-based on which family therapy has been suggested here. On the other hand, Stanton et al., (2020) have stated that being involved in activities can help a depressed person to eradicate negative thoughts and that’s why regular activities have been suggested here. It means that the strategies have been designed with proper evidence which means an evidence-based care approach is being used here.
Evaluation plan
The effectiveness of the proposed strategy will be evaluated based on the recovery of the [patient. If it's found that the frequency of being violent is being reduced, it can be stated that the patient is being recovered. If it is found that the patient is being engaged in any positive conversation on his own, it can be stated that he is being recovered. His regular activities are needed to be assessed for the evaluation of the effectiveness of the strategy.
4. Analysis on Negotiating Collaborative Planning for Clients to Ensure the Promotion of Recovery
According to various national mental health-care policies In this case, the person who is getting the service is not a passive recipient (Santos & Cutcliffe, 2018). Hence, collaboration with the person is highly needed. It is definite that collaborative care planning is needed for the promotion of recovery. If collaborative care planning is adopted and the patient with mental health issues is involved in decision-making related to the next step of the treatment, Then he will be able to think that he is being provided with importance in the care process and that it needs to help him in gaining the confidence.
At the time, when he finds that he is an important part of the care planning process, his interest in implementing the plan and responding to the care plan effectively will be increased and it will ensure the promotion of recovery.
Thirdly, the involvement of the person in care planning will ensure the development of a better plan as he has an awareness of the mental situations he is going through and if he is involved in the planning, he is expected to help the mental and physical health professionals to understand what his actual issues are and why he is getting violent sometimes. Adequate information regarding these factors will help them to develop the best care plan that will suit their requirement.
Fourthly, if the person would be involved in the care plan, then he is not expected to show violence in availing the treatment as he will be aware of the goal of the treatment. In this case, the healthcare experts will get the chance to develop short and long-term goals of the care process while discussing with the patient that will help him to understand that he has a high chance of recovery and when he will be focused on the goal of recovery, his negative thoughts will be eradicated as he will know that all healthcare professionals are trying to help him to get the previous life that he was living before the trauma and the achievement of short term goals like increasing mobility or overcoming fatigue will help the person to become highly interested in being involved in the treatment for the achievement of the next goal that will surely ensure the fastest recovery process (Hoyvik et al., 2024).
The last thing is that there is an ethical framework related to autonomy and the consent-taking process in regard to the treatment process of any patient. Based on the ethical framework, it can be stated that healthcare professionals should always show respect for the dignity of the patient. Taking consent from the patient and involving him in the treatment planning is a way to show respect and as the person has the ability to give consent (obviously when he is not in the violent stage), taking consent of him will ensure the development of a better recovery plan.
References
.png)
.png)
Essay
SPS201 Alcohol and Other Drugs Essay 1 Sample
Assignment Brief
a) Description
This assessment requires analysis on three foundational areas of learning –
1. Understanding of addiction
2. The Cycle of Addiction
3. Evidence based models (choose one evidence-based model only)
b) Format
To be successful in this assessment you must address all three areas. You are required to clearly demonstrate your understanding of what addiction is, in terms of your what you have learnt, how the cycle of addiction impacts as well as giving a very clear understanding of one evidence-based model.
This assessment serves as a preparatory guide to the learning that students are expected to acquire and develops the research and analysis skills required to complete subsequent assessments. Your assessment must be submitted through Turnitin and must adhere to the College’s academic integrity and authorship requirements. The questions and instructions contained in the file will be available three weeks before the due date.
Note Research literature
Your essay must be based on a review of the literature and should include at least five primary academic references, ie peer-reviewed (scholarly) journal articles or book chapters. Do not rely upon non-academic and other web-based secondary references as these do not constitute academic references for the purpose of your assignment, which if relied upon for theoretical support, may mean you have NOT met the requirements of the assessment.
Referencing
You must use APA 7 referencing.
Table of references: You must include a Table of references section in your essay and acknowledge any sources that you use, including all web-based sources.
Structure of essay
As the assignment conveniently provides the three foundational areas to be addressed, there is a lot of sense to use them as headings, as they form the basis of assessment criteria. If there are identifiable questions or sub-issues within each heading, then it may be a good strategy to also include these as sub-headings under each heading.
Solution
Introduction
The nature of addiction is examined in this essay within the context of neurobiological disease and a learned behaviour due to sociocognitive factors. Therefore, using the existing social learning model this study aims to uncover the different dimensions of addiction such as compulsive use, loss of control as well as continued use despite negative consequences. Further, the essay evaluates downstream and upstream processes of the substance dependence that involves questions like withdrawal, relapse, and detoxification to demonstrate the problems that people encounter in their recovery. Thus, this work aims at presenting information concerning effective strategies in the treatment of addiction with regard to the psychological and social spheres.
Understanding of Addiction
Figure 1: Addiction as a brain disease
Source: (Surgeon General, 2016)
The diagram shows that there are identified changes in areas that are unidentifiable in the brain, and these areas are generally related to different stages of addiction. Giving examples it can be added that there is a concept of three stages, preoccupation or anticipation, binge or intoxication and withdrawal or negative affect and associated specific parts of the brain are described (Surgeon General, 2016). Addiction is widely accepted and defined as a neuropsychological disorder with genetically determined behavioral deregulation, impaired control over drug and other addictive behaviors, and negative life consequences (Siomek-Gorecka et al., 2021). This disease conception of addiction is rooted in knowledge that continued use of substances or participation in addictive activities can alter the brain structure especially in areas like, reward, motivation, and memory. The brain circuits which seem to become involved when a person has an impulse to stop participating in an addictive activity, get affected and results to the inability of individuals to cease indulging themselves in the addictive process even when they want to.
The simplest definition of addiction is a psychological and physical reliance on an object or an activity. It therefore leads to craving and reward cycle which in one way or the other has negative effects on the user, the surrounding society and physical wellbeing (Wiers, and Verschure, 2021). Addiction can be explained through certain feature: Compulsive use, the need to perform the addictive behavior despite the adverse effects. On the other hand there is an impulsivity issue when persons lose control over their actions or decisions, despite being able to comprehend the consequences of their actions. The last stage is continued use, where the person continues with the behaviour despite adverse consequences, and often tend to minimize them in their lives for the assignment helpline.
The Cycle of Addiction
The addiction cycle is a cycle of dependency which include phases such as withdrawal, relapse and detoxification all of which cause dependency. Detoxification is characterized by the outward withdrawal from the addictive behavior and one notices adverse emotions or physical sensations, which are normally associated with the addictive substance. Different substances or behaviors will cause different kinds of withdrawal symptoms, but they all prompt the person to engage in the behavior again in order to escape the physical or emotional discomfort associated with withdrawal (American addiction centers, 2019).
Relapse as the crucial stage in the cycle of addiction implies returning once again to the process of using a substance as well as coming back to those situations when controlling impulses is impossible because of the urge’s extremity. Hence it can be added that it is a common and challenging aspect of recovery that mainly reflects on the chronic nature of addiction (Guenzel and McChargue, 2023). Detoxification, on the other hand, entails clearing the body of substances that one is addicted to and most often patients undergo it under the close supervision of the doctor because withdrawal can come with its side effects. Detox is used, as a rule, at the early stage of therapy; its goal is to eliminate physical dependence on the substance and finalization of withdrawal symptoms before starting counselling and therapy.
Evidence Based Models: The Social Learning Model
The social learning model is an empirically supported theoretical orientation for understanding substance dependence in which learned behaviours, environmental stimuli and interpretations and meditational processes are central. This model propounds that dependence behaviour including alcoholism results from observational learning and reinforcement. The social learning model does not consider addiction a singular, stable, and singular state of affairs, but certainly provides a dimensional form encompassing a constellation of behaviors and implications that can affect individuals’ different sides with different degrees of addiction dependent on their social environment, choice, and perception (Smith, 2021).
The social learning theory revolves around the fact that addiction is learned through the late recoils which are usually picked from other people in the society, peers or even family members, media personalities. The external environment hence involves what people see around them in form of behaviors over substance use or other forms of addictions where they may be tempted to perceive these actions as ways of handling stress or some pressures. These behaviours remain learned because when behaviour is associated with perceived rewards such as relief from anxious states, social acceptance or pleasure. Because of this reinforcement, addiction-related behavior becomes strengthened and will most likely lead to habitual actions (Brady et al., 2021).
Cognitive processes also have a role in social learning model since people’s perception about the substance or behaviors can either lead them to engage in addiction. For example, if the learners think that alcohol will help them to overcome social phobia, they will be most likely to take alcohol in social events. Additionally perceiving the negative consequences downplaying the risks or overestimating control over usage, can maintain addiction behaviours. These cognitive processes, along with those learned behavioral responses, form the cycle that then perpetuates addiction.
Therefore, the social learning model supports the forms of treatment that tackle the behavioral as well as the cognitive parts; they may use treatments such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Offering guidance on identifying and directly confronting addictive beliefs, replacing negative behaviors with helpful ones, the model offers a clear structure for establishing long-term recovery, in a way expressing the conclusion that addiction is not exclusively the result of a person’s inherited traits and tendencies, but also a stably developed response to learned stimuli (Smith, 2021).
Conclusion
Hence it can be concluded that addiction includes biological, psychological and social determinants. The essay researched that addiction is not a simple issue but is witnessed through the cycle of dependency and learning that supports it. The social learning model offers an insight into the broaden scope of behavior and cognition influencing addiction and adding to its maintenance. In addition to that it can be added that implementing effective interventions is essential as it targets both behavioral and cognitive aspects fostering long term recovery through different strategies such as cognitive therapy. Hence addressing such addiction from implementing multidimensional perspective can help in developing better and efficient comprehensive and impactful support systems for those affected by drug addictions.
References
.png)
Reports
NUR133 Professional Nursing Practices Report 3 Sample
This task will introduce you to develop your reflective skills necessary to develop foundations of critical thinking and clinical reasoning. Reflection is about questioning and learning through experiences regardless of if they are positive or negative. This Reflective Journal is a good resource to refer to as the Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) National competency standards for the registered nurse highlight that nurses reflect on their practice. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health is a unique area of health care and this unit will help to establish the building blocks for you as a nursing student to provide culturally safe care.
Learning Outcomes:
1. Explain the impact of historical, social and political processes on the health of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders and demonstrate understanding of the social justice implications and impact on health outcomes.
2. Demonstrate and compare a strengths-based versus a deficit model of nursing practice in relation to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health care.
3. Identify the diversity of health-related knowledge and practices within Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities and the impact of these on health-related choices, including traditional medicine.
4. Explain the principles and concepts of cultural safety in clinical practice and outline the impact of power dynamics between health care professional and client on nursing care delivery within Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
Solution
Refection using the Gibbs reflective Cycle
Introduction
This reflective journal will be developed in accordance with the key concept of Gibbs’ reflective model.
.png)
Figure 1: Key components of Gibbs reflective cycle.
(Source: Cooke, Greenway & Schutz, 2021.p.104857).
In addition, each on the learning outcomes will be attained referring to the key components of Gibbs’ reflective theory for better understanding (Cooke, Greenway & Schutz, 2021.p. 104857).
1. Impact of Historical, Social, and Political Processes on Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health
Answer:
Description
In my course, I understood how the historical, social and political factors influenced the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health status. Colonisation affected the health of Indigenous people (Yashadhana et al. 2021. 114230). The social inequalities had affected health. Displacement and exclusion have had long term effects.
Feelings
On perceiving these factors, I felt a kind of shock and a kind of sorrow that hit me for the first time. I had not realized just how deep-rooted historical prejudice is that affects Indigenous people to this day. I always wondered why colonial policies continued to echo current disparities in healthcare.
Evaluation
I was privileged to learn a lot on the connection between “social justice” and “health” as a result of the learning experience. One good feature was the detailed analysis of how some policies have led to exclusion in the provision of health care service due to absence of culturally sensitive services.
Analysis
It is imperative to demonstrate that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health outcomes can be influenced by historical, social and political processes. The colonization process dislocated indigenous people. It is suggested that Indigenous Australians have higher prevalence of chronic diseases and mental health disorders and shorter life expectancy.
Conclusion
This reflection for the assignment helpline has helped me learn better how history and politics affect health. I have gained knowledge about the social justice and the colonization of Indigenous peoples. Knowledge on such aspects will enable me to be more emphatic, culturally-responsive to such unique history.
Action Plan
In future, I will practice the importance of finding out the history and social backgrounds of this community. This will contribute to the enhancement of the cultural safety in healthcare settings.
2. Strengths-Based vs Deficit Model of Nursing Practice
Answer:
Description
I learned about the comparison between the strengths and weakness paradigms of a nursing model for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. The first one is the Deficit Model that concerns with the missing or the damaged part in the patients’ health. The second one is Strengths-based model that highlights patient’s potential, capabilities and assets (Lavoie-Tremblay et al. 2024.p.100190).
Feelings
I was more in favour of the “strength-based paradigm”. It can be considered as more encouraging. It made many patients feel like they can control their treatment processes. On the other hand, the deficit model seems more disempowering because it labelled the patients as lacking in some way.
Evaluation
The strengths-based model was much more efficient and less oppressive method in comparison with traditional healthcare system. It promotes empowering relationship rather than discouraging them. In my opinion, both models can be employed based on the clinical scenario.
Analysis
The strengths-based model is less likely to produce negative health outcomes, especially among culturally vulnerable populations. In terms of healing what deficit model does is bring forth constructs that essentially pathologize the “Indigenous patients”. The strengths-based approach embraces the Indigenous cultural practice.
Conclusion
As a future professional, I will embrace a “strengths perspective” every time in order to deal with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander patients. This model promotes a working partnership based on trust, acknowledgement and recognition.
Action Plan
I will endeavour to gain further training and information on culturally safe care. Even, I will consider the heath of each patient from a strength based perspective effectively.
3. Diversity of Health Knowledge and Traditional Medicine
Answer:
Description
I have come across different views on the health knowledge and practices among the aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders local people. These communities have started to rely on modern conventional medicine with the traditional belief (Brodie et al. 2023.p.100096).
Feelings
I got interested in terms and topics stemmed from traditional knowledge. Initially, I had not realized how much Indigenous people actually rely on traditional medicine.
Evaluation
The way how several societies performed health has enriched me to some extent. The same has altered my view of how healthcare must look. It had made me call into question some of the assumptions that I used to have about initially.
Analysis
Modern medical practices are a vital aspect of many Indigenous societies around the world. The same can improve the health of those societies when combined with Indigenous programs (Gall et al. 2021.p.670).
Conclusion
Such reflection further emphasized on the requirements of cultural competency in the health sector. Cultural competence is a valued “care delivery model” needed by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander population.
Action Plan
I would like to spend more time with Indigenous health practitioners. The same will enable me to understand how some Indigenous health principles can be safely and efficiently integrated to the practice of nursing.
4. Cultural Safety and Power Dynamics in Clinical Practice
Answer:
Description
Cultural safety was explained to me as policy and procedure model that eliminates racism from healthcare settings (Mitchell et al. 2022.p.590).
Feelings
As initially indicated, I was especially inspired by one of the most critical ideas of the Aboriginal culture known as ‘cultural safety.’ It offered a practical guide concerning the problem solving aspect Indigenous patients experience in clinical settings.
Evaluation
Cultural safety of a population is a vital approach in the management and treatment of their (i.e. indigenous people) health needs. It assists to build a satisfaction among the patients.
Analysis
Cultural safety leads to improve the health standard of the Indigenous patients. It is important to understand that the quality of healthcare is shaped by the relations of the healthcare provider and the patient.
Conclusion
As per my understanding, cultural safety is very important aspect of nursing care. I must gain better understanding about it in order to enhance my expertise over the period.
Action Plan
I will actively continue to expand my knowledge in cultural safety. These will include listening to the patients, honoring patient self-determination and maintaining patient confidentiality.
Conclusion
Using the Gibbs Reflective Cycle to the following learning outcomes have helped me to understand the challenges associated with caring for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. In addition, this reflection has provided me with ways to enhance my practice.
Reference list
.png)
Reports
EDEC360 Professional Identities in Early childhood Report 1 Sample
Childcare – Report Ass 1
Assessment Description
There are three parts to this assignment. You are required to:
- a) develop a centre philosophy statement - (no references in this section. This should be written for everyone who comes into the centre to read and understand)
- b) a supporting statement of reflective practice that takes into account key elements of this unit (this is where you write your justifications and decision making for your centre philosophy. Include all references used to write it including data, literature, theories etc.)
- c) include an appendix of your Module Book One, Two and Three Topic Activities (A screen shot of your contribution of the labelled Topic Activities underneath the green Module Books eg. Whiteboard, quiz, forum etc.)
a) You are required to develop a centre based philosophy statement. You will undertake drafting, review and peer feedback throughout the modules with those in your collaborative leadership group to refine your centre philosophy statement. Undertake the ACECQA self assessment tool to determine appropriate NQS to follow up for inclusion in your statement.
Give consideration to the impact of learning outcomes for children in relation to the complexity of their social and cultural world, families and learning environments. Include a range of stakeholder perspectives and ways communication strategies foster interaction and collaboration for a broad range of learning communities within an early education and care centre (e.g. leadership, teaching staff, children, parents, community members, legislative
authority, and transdisciplinary professionals). It is important to keep in mind that this is not the teachers’ or the staff’s philosophy but the centre’s philosophy. This means that all parties need to have a ‘voice’ in the document.
The statement must be reflective of the nature and importance of professional advocacy, leadership roles, responsibilities, legislative requirements, and practices early childhood teachers play in the development an maintenance of a well-managed learning environment in which educators work in collaboration with others.
Give consideration to the following key issues as located in the NQS when developing the philosophy statement:
• Ways children, families and teachers and their complex social and culturalcommunities learn in their complex learning environments;
• discourses of professional identity for early childhood teachers
• professional advocacy, leadership, roles and responsibilities of early childhood teachers in maintaining learning communities and learning environments.
• how do teachers, young children, their families and broader community members communicate together with transdisciplinary workers.
The philosophy statement must be reflective of key theories and literature of early childhood education and care
but would not actually refer to these theories and literature.
b) The supporting statement of reflective practice must demonstrate understanding of the above mentioned key theories and key elements of this unit through the use of early childhood literature drawn from the required text, set readings and other materials presented throughout the semester and referenced in the reference list.
c) Include evidence of your completion of Module Book One, Two and Three Topic Activities as an appendix at the back of your assignment
Word count - 2000 words total. This is entirely up to you to make a professional decision about how you will use the word count. You can choose to do 1000 each, or
a) 800 words centre philosophy
b) 1200 words supporting statement
Other people might like to complete Part A 500 and Part B 1500.
Either way, the total will be 2000 words.
References - expected at least 20 from a variety of sources as suggested throughout this book in Part b regardless of how you choose to break up the word count in Part A and Part B. All ideas from Part A and B must be referenced in Part B.
Solution
Part A- Centre Philosophy
Our keen respect is for Australian community children who belong to Aboriginal groups. Those people are considered the root of the community and we value their growth through our community school philosophy. We value a collaborative partnership among the community and families so that we can make the best environment for children. The vision we chose to work is that every child is our responsibility so we are committed to promoting diversity and inclusion in every sphere of organization. Looking at our mission statement we value the environment in which children are growing so it needs to be family value-oriented. The reason for our philosophy statement is developed on the issue potential that people face the gap of family in child learning. So, to keep the learning less disruptive we are planning to engage the community and family so that growing partnerships at the organization can spread the support for society. The plan we developed for the Australian child directly encourages the social value by which they can receive a fair chance of living. The benefits of empowering community children and sharing support for identity creation are possible.
A commitment to Children
Every child in society belongs to a unique nature which makes them different from each other. As we value every child, that child-centered program needs to be built based on strength, unique culture, and capabilities. At the time the program makes them learn social skills, the ability to use scope, and other chances of becoming active citizens is possible. The central thing of our philosophy of working is to make children capable of learning and using every skill we share through activity. As we planned to promote a connection for which the initial journey can begin with a simple friendship with children. The key principles we need to follow while we arrange a safer place of learning for children include-
- Prepare a bias-free culture for children's growth as we respect diversity in each step we make for learning program development.
- Always worked with influences of collaboration so that people can easily connect with the program arranged.
- The learning environment as always creates the push for their skill adoption so it needs to be mindful for the assignment helpline.
A Commitment for Educators
In the stand of applying the framework of ACECQA then the commitment of educators is needed. We aim for collaboration in which the role of the educator comes as a bridge to the connection for learning influences. One key value we considered for the educator role is intentional teaching so that children can view their interests and learn in an active form. Only bookish knowledge is not our type of education we always valued responsive teaching so that a sense of priority can be formed among the community. We planned to use the play learning method so that a scope of interaction is easily formed.
Commitment to Family and Community
As we planned for collaboration, children's first connection with their family comes. So, when we can make the connection with them by our responsible attitude, the outcome for better participation is generated. On the other hand, community is the key responsibility of our philosophy which we consider in each commitment. At the beginning of learning when the children are at the stage of brain architecture development, the relationship with the community shapes the adoption. We need to keep the regularity for community engagement so that a growth of professional values and support for child growth is generated automatically.
Commitment for Pedagogy
Every perspective we include in sharing the role and associated commitment to the philosophy of development makes sense for children's development support. Looking at the priority for the pedagogy involvement then social values, and beliefs all are managed for sharing with children. The actual importance this shareholder plays is to create positive influences for the children's learning that ensure an effective development plan. We planned to focus on cultural competence so that the values of being and belonging are shared by the organization. Only this sense of cultural values only makes the connection for the community by pedagogy communicator.
Environmental Commitment
Before concentrating on the quality of the environment needed for children's growth then its stimulation needs to be understood. The key aspects that a learning environment can promote for the children must be problem-solving, analytical thinking, and social value-oriented. A whole cycle of community is not except for the environment so children need to learn their responsibility from childhood. We planned the philosophy of collaboration. We also include children's knowledge which is planned by project-based activity. We value sustainability and respect for every single associate we face during the learning environment. The philosophy plan is developed by valuing the contribution that supports the future world from a community perspective.
Part B- Reflection
The stimulation we used for making our philosophy plan supportive as well as engaged application of quality areas of the National standard is used. As per the National Standard during children's learning stage skills and experience come from the community, and home (ACECQA, 2024). My knowledge of quality education I have applied to keep the standard high as Australian Child education demands for. From the perspective of the action area has been chosen by Australian Child Education then our philosophy matches with well-being. Furthermore, the importance of high-skill professional guidance notes for children's quality education priority of the early childhood education workforce is understood (Australian Government, 2024). As per Phillips and Boyd (2023), the early childhood environment always encourages the growth and well-being nature of children. I chose to work on quality so that our organization can earn the value of community.
Children
We realized that children are the most valuable as well as vulnerable part of society. Due to this, we need to keep safety as a priority while planning for service delivery in aspects of their development and learning. I choose to use Education and Care Services National Law 2010 to ensure the safety of every child's participation within our organization. The justified reason for the legislation is to make the education service effective (ACECQA, 2024). I am always concerned that the activity planned for the children should meet with quality as it makes the value of authenticity. As per Harrison et al. (2024), the Australian Quality Framework always monitored the service standards so that types, and efficiency all can be measured easily. The perception of valuing children always impacts the learning habits and adopted skills by the organization that provides services. As per the National Quality Framework, we choose collaboration so we ensure every sphere of collaboration can promote the value of safety as well. The location we have chosen to sustain our services causes the demand for fair treatment as legislation demands. The Convention on the Child Rights Act claims their rights to get fair treatment, healthy living, and others (Australian Human Rights Commission, 2024). In this way, we have planned for a safer environment that easily matches the collaboration in terms of the philosophy plan. The approach we chose for our organization ensures safety, well-being, and prosperity in the same way. However, the design of the National Quality Framework comes into practice to promote an equal chance of education for Australian children and families (Cross et al. 2022). We also used this in our philosophy so that we can support the positive growth from the learning plan.
Educator
As the role of educator is always linked with quality education offered in early life some quality determination is essential. We choose to work on that so that every connection we make through our services can extract benefits. In the sense of educational qualification, they need to be 50% in a diploma or higher category (ACECQA, 2024). As well as we choose to expand this qualification with responsive teaching and a sensible response approach. French and Watt (2023), stated that early childhood educators' efficiency comes with the intrinsic motivation they hold or receive from their surroundings that even impacts policy progression. Applying leadership theory Trait a leader's quality is assumed to be inherited nature which makes the preferable as per situation needed (Cherry, 2024). We linked that with early childhood educators as they always work with social value, update knowledge, and responsibility both come from their sense of belonging. As we choose to focus on collaboration, we need a supportive and situational leadership style that influences the educator role. The child rights approach is used to support Child safety within the organization Act of the Australian Human Rights Commissions 2018 (ACECQA, 2022). We also include the practices of safety by planning a safer environment that meets with the National Quality Standard of Australia. The most effective resources used by educators in their operation include child-centered programs and learning opportunity-based (Australia, 2024). Both of the nature helps to arrange qualified programs that match with educational excellence for educators.
Families
The social connection we considered under the approach and strategy of early childhood learning comes from family first. As per the Early Years Learning Framework children access the best development with the educator's assistance (ACECQA, 2022). It has been found that as much as the diversity they faced, the sense of belonging developed automatically. In our organization, we keep the program foundation based on family, culture, and other aspects. We always value safety, well being, and responsibility which is initiated by family. The principles we used for making the family part of children's development include being non judgmental about children's families. Always being understanding of family perception and keeping the environment welcoming (Veyldframework, 2022). The value we promoted for the family directly enhances the connected surroundings which we also valued in philosophy development. As per Phillips et al. (2020), children's early age learning always creates the nature of being a responsive senior citizen who lives with values. The sense of identity, playing an active learner role, and the ability to be an effective communicator all are generated through the Early Years Learning Framework (Only About Children, 2024). However, our organization also used this sense of belonging for which we considered family as a part of child learning.
Community
At the time we focused on collaboration and community relationships were the values that shaped children's growth outcomes (ACECQA, 2024). The quality of the promotion community offers a sense of belonging, identity as well as learning continuity. In our plan, we promote a community-based program where children feel a sense of belonging. As per Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological System Theory, the ecological environment and its relations with children make an impact on the capacity to discover, grow, and sustain (Crawford, 2020). Though the types are multiple for social position as microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem and others (El Zaatari & Maalouf, 2022). The focus of our philosophical aspect is to make children connected with social belonging with a safety of secured development.
Pedagogy
In the aspect of Early Childhood Learning Framework educator role for critical thinking always makes the simplicity of learning programs efficient (ACECQA, 2024). We choose to motivate the program with intentional teaching so that children can revive the purpose of learning. The ability pedagogy can hold for shaping surroundings to children thinking it crosses a wider dimension. For example, nature pedagogy always bridges the connection of children with nature like it makes the value for connection (ACECQA, 2024). Additionally, the sense of managing the commitment for the children and learning role of pedagogy need to be justified with a prepared learning environment.
Environment
At the point we discussed children learning from surrounding environment influences comes into consideration. The nature of sustainability makes them learn to being and belong to sourcing where they can socialize. It is not limited with dynamics of theoretical perspective; it leads the children to learn from influences. We planned to execute this connection by activity-based program when children are forced to face the need of learning. Additionally, we promote them with humanity which is required to make them responsible citizens of the society. However, this philosophical mindset and working flow helps us to engage with child supported learning promotion.
References
.png)
.png)
Reports
EDET461 Effective Teaching 6 Professional Engagement and Reflection Report Sample
Assignment Details
Description and Structure of AT1 ePortfolio and Professional Learning Plan
Self audit of professional practice to evidence and reflect on attainment of the Professional Standards. Identify professional learning needs and construct a plan for professional learning including rationale for continued learning and use of appropriate sources/resources.
Structure
The assignment is broken into 4 sections: identify, select, apply learning & evaluate.
1. Identify
Professional learning plan, which includes goals to improve practice drawn from data from reflective practices. Types of reflective practices and further planned practices noted and evaluated as appropriate to develop learning against Professional Teacher Standards.
2. Select
Types of professional learning related to professional learning goals sourced and linked to Professional Teacher Standards.
3. Apply Learning
Plan for professional learning to be applied to practice.
4. Evaluate
Indicate how success will be measured, impact on learning (children and teachers), sharing of new learning with colleagues. The requirement for each of the 4 sections of the assignment will be described in the following page.
Identify
- Include a professional learning plan.
- Ensure the professional learning plan has clear, concise and relevant goals for your professional learning that you can work on and with, to improve your practice.
- The development of your plan should come from a range of data from your reflective practices.
- There should be a discussion of and evidence of the reflective practices that you have undertaken to develop your professional learning goals.
- Note and evaluate further planned practices that you will do in the future that are linked to your goals.
- The evaluation of the practices that you are planning to undertake in the future should include a discussion of the significance and appropriateness of the activities planned to help you develop your learning against specific and targeted Graduate Professional Teacher Standards.
Select
- Once you have developed your goals you now need to source professional learning options to help you achieve your stated goals.
- Include a description of the learning options you have sourced.
- Include an evaluation of the learning options you have sourced, and how well they will help you achieve your stated goals.
- Match the learning options to your professional learning goals.
- Link the professional learning options to the Graduate Professional Teaching Standards.
Apply Learning
- This section involves you planning for the professional learning to be applied to practice.
- You will have a detailed plan for professional learning from multiple sources.
- The plan will include a detailed explanation of how your plan for learning will be applied to practice.
- You will also need to highlight how your continued ongoing learning will be maintained in relation to your stated goals and linking this to the Graduate Teacher Standards.
Evaluate
- In this section you need to explain how you ill measure the success of your stated goals and intended professional learning you will undertake to achieve your goals.
- You will need to ensure that your goals that you have included in the first section are achievable and have some way to be measured.
- The plan in this section should be detailed to indicate how success will be measured. This success measurement will include the impact on learning for both yourself, children and other teachers/educators.
- You will also need to discuss how you will share your new knowledge with your colleagues.
Academic Writing
The marking rubric for this assignment allocates 10 marks to academic writing.
Please ensure the following points are addressed in your assignment submission:
- Clear level of writing
- Critical evaluation of issues
- Cohesion
- Within the word limit
- Good academic English expression
- Free from errors
- Correct use of APA referencing
Solution
1. Identify
1.1 Professional Learning Plan
Goal 1: Professional learning engagement for better classroom practice
In the route of expecting a successful learner this goal of engaged professional learning is selected. Based on AITSL report the goal of being a engaged classroom provider that reflects connectivity is developed. As the flow of information becomes engaging for teachers it reflects over the students' adoption of it. This goal refers to engaging in educational sharing within collaboration of colleagues, and experts. Fairman et al. (2022), always a need for keeping professional learning relevant and suitable for the teachers so that constructive feedback accesses the benefits of improved capability. It needs to be wise while dealing with children's development as this goal educates teachers the same way. Understanding the early childhood curriculum and planning it with updated information makes the outcome productive.
Goal 2: Collaborative relationship to make efficient environment
The second goal for a professional learning plan is to help to keep the education challenges overcoming patterns. As peer recommendation and feedback session encourages the sense for problem solving analytical skill is route for safer environment preparation. This leads to choose this second goal for professional learning plan. This works as stimulation when children feel the urge to pay attention and work over boundaries with the goal of achieving a target. It needs simple tasks like when teaching children societal values and it needs to be arranged in a problem-solving manner. For example, after giving them information about any social value and testing it by students' ability to become an active citizen. A scope of challenges setting through makes children face the situation and always develops the scope for continuous learning flow (Loyola et al., 2020).
1.2 Significance and Appropriateness Against Graduate Professional Teacher Standard
The first chosen goal is linked with the graduate professional teaching standard, which promotes professional engagement (AITSL, 2022). As students need the connection that stretches better learning from an engaged classroom this standard is aligned. This enhance professional with continuous improvement and practices so that student learning improvement can be planned. Key focus under elected standard 6 is mainly allied with 6.2 that encourages learning practices and 6.3 engage with colleagues that is collaboration. The nature of working over personal growth through collaboration always encourages me to learn new things. A scope of supporting colleagues and discussion over constructive feedback always guide individuals to work on skill adoption. Linking with students' growth then this feedback also guides them to know about the strategy that supports education flow. The quality of informed feedback is the result of engagement which is planned through goal 1. As per Howell (2021), instead of using bring-down feedback the use of constructive feedback always encourages the flow of sustainable education development. It makes the chances of keeping learning assessed through every lesson plan. The capability of the teacher comes as a determinant that makes the environment engaging for children and personal growth. On the other hand, the 2nd goal is based on standard of the teacher standards which encourages the flow of making student participation a priority (AITSL, 2022). A goal of towards safer environment promotion always keep students attach with development learning this standard is chosen for professional learning plan. As standard 4 is selected under which 4.1 and 4.3 that is support student participation is considered. By using this ability of produced a safer environment become easier for a teacher. Without teacher ability and proper planning; these benefits can never come in favor. It needs teacher skills and ways of planning an environment where along with education and the flow of participative activities are also performed. It is considered as the goal as only class knowledge cannot make the engagement for all environment stimuli work for that influence. Always engagement is needed to make the education flow useful for students' development and as a graduate teacher professional success comes in favor. With the application of suitable knowledge and information, a clear flow can be generated for the educational settings for the assignment helpline.
2. Select
2.1 Professional learning options to achieve the goal
2.2 Linking with Graduate Professional Teaching Standard
The scope and potential generated through this professional learning plan come with the productivity of quality confirmed education growth. In linking with the national quality framework this personal goal promotes the value of development ability for Graduate professional teacher standards. The highly accomplished standard of Australian professional teacher is chosen that also mentioned about using professional standard of Australia even that supports in engagement. Additionally, Goal 1 is always valued engagement for which framework promotes the achievable standard. As in 6.2 right approach implementation is mentioned for which as action digital platform is consider this makes the chances of improvement. Additionally, engross with colleagues that is 6.3 is also considered for which constructive feedback is use in practices.
As a teaching aspect students' safety, connection, and their values adoption from the environment all are the responsibility of the teacher (Darling-Hammond & De Paoli, 2020). Additionally, in the previous discussion, the chosen standard of Graduate Teacher professional standard link is mentioned. Now, in detail, the first goal is linked with NQS's 5th value so that this promotional growth comes with the consideration of quality action plan recognition. In this aspect of promoting quality education proper plan of classroom activity and behavior handling is come. As 4.2 refer about classroom activities for which ICT tools are adopted that transform classroom as safer environment of learning. On the other hand, 4.3 is also used for handling behavior that is plan by digital setup encourage the adoption that creates an imaginary world for the children. Along with that supportive approach and use of a quality framework, this planning encourages growth that promotes sustainable education patterns.
On the other hand, as per the professional standard, every value needs a proper plan and executive strategy that encourages a productive outcome. In this Australian professional Teacher standard lead is chosen which inform about better classroom activity and behaviour handling. In previous discussion challenge handling skill importance for supports children even personal skill this correlation makes the benefits for developed Goal 2. Painstaking teacher-student relationship and working with value sharing approach make teaching important as well as possible for achieving the goal set for professional teaching (Hagenauer et al. 2023). Furthermore, quality and action are planned for each goal-oriented indicating the potential it holds for well managed classroom education. Once the legislation and framework are aligned with strategy, reliability grows for workplace safety as well as possible growth outcomes.
3. Apply Learning
From the perspective of Goal 1, suitable ways to apply in practice are discussed below-
- The application of an active learning approach for teachers and students encourages the flow of personal as well as professional growth. Additionally, the style used for this learning design helps to keep the flow of learning productive.
- Application of engagement theory and its type of focus is given for cognitive learning. It proceeds through hands-on activities which keep the motivation of self-growing by problem-solving attitude (Barkley & Major, 2020).
- In the extent of aiming for engagement rather than group tasks, group presentation always works as the best fit for a teacher. On the other hand, having the nature of being connected with colleagues always improves learning efficiency.
- Considering the influencing role of digital tools for student's emotional and behavioral engagement, the learning is in the shape of experience-based (Heliporn et al., 2021). The benefits of the construction of a healthy relationship always come for the teacher.
- Further, it needs evaluation so that students' growth in learning can be measured. Any new strategy and tools that are used for engagement learning need to be measured so that investing in resources comes in favour that supports sustainable learning.
On the other hand, Goal 2 used the following practices to achieve the discussed following -
- In Australian education innovation and efficiency work hand in hand which need consideration for quality, safety, governance, and teaching. The collaboration for the environment is planned which refers to safety learning (Nutbrown, 2021). It is planned to start with setting safety standards of AQF (Australian Qualification Framework) for all students included in education.
- Equity in education is prioritized for which student participation can be encouraged through formative action planning. More on that, education needs to be performed in a diverse background where children feel safe and comfortable for new learning.
- The planning of including ICT tools is also considered to transform education flow that supports the educational interest for all socio economic classes of the society (Bogossian & Crave, 2021). Furthermore, social mobility and value for all students make for higher chances of achieving Goal 2. A change to think wisely and adopt advancement makes the productive flow which supports significant improvement.
- From the perspective of education as a fundamental right teacher's role comes to encourage the students to participate and value their limitations. Every assistance planned for Goal 2 promotes the new vision of teaching as the standard always demands improvement.
In the selected and discussed ways for applying learning a sense of positive improvement is generated. It has been found that a goal specific journey always comes with efficiency as a teacher and as a student's guide. The approach and resources planned to use for education all show the chances for outcome for future scope.
4. Evaluate
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
New learning shared with colleagues
First, goal-oriented learning can help to know the strategy for engaging in learning. Additionally, the experience of strategy making by including tools, students' specific approach, and others directly helps colleagues to know the ways. As this goal is aligned with the safety framework a reliability and positive outcome is expected. This sense can be shared with colleagues so that they also remain aware of quality framework practices within the Australian context (Monteiro et al. 2021). It is essential to keep the learning professional so that the value of personal growth comes as value-oriented knowledge. A teaching or teacher's success always comes through approval, strategy is planned to include in practices. Working with personal values and promoting the value for children always expands the acceptance that leads to wider success optimization. It has been found that working with specific skills and values always encourages the rapid transformation that guides quality education planning.
The second goal-oriented experience values the information for making an environment collaborative yet safer. As children, safety and comfort always motivate them to keep learning continuously (Monteiro et al. 2021). Additionally, safety with informed quality encourages the environment's acceptance by all students. Maybe they are from diverse backgrounds yet keeping the environment socially mobile helps to spread the interest of participation. This experience sharing guides colleagues to keep this in mind for preparing an environment that enhances safety as a priority for all. The knowledge and capability come through these experiences and develops the potential environment formation which encourages safety learning aspects.
References
.png)
.png)
Reports
ECE305 Designing Early Childhood Learning Spaces Report Sample
Task description
Write a paper discussing your personal philosophy on the design of environmental spaces for children, drawing on your previously held philosophies that were developed in previous subjects, and incorporating content and theorists covered in this subject. In this paper you are also required to connect your philosophy with the relevant Early Years Learning Frameworks.
Your philosophy should include a justification for all statements made, that link to relevant literature, theorists and early childhood frameworks. You can choose the format of your statement. For example:
• You could provide the statements first and then write a complete essay as the justification for all the statements.
• You could provide one statement at a time with the justification immediately after it or you could include the statements in an essay overall (the statements must be bolded though, to make them clear).
• You could develop another way of presenting this that meets the criteria.
In developing your philosophy, you MUST include statements and justification for the following areas:
• Your beliefs about the meaning of environment in early childhood education
• The role of the environment in early childhood education
• Your beliefs about the design of the environment
• Your beliefs about the links between the environment and children’s wellbeing, relationships, and social-emotional development. You must also include:
• A general introduction and a short more general conclusion
• Adequate referencing and a correctly formatted reference list.
Solution
Introduction
A philosophy in early childhood education acts as the guiding framework for educators, influencing actions and decisions concerning learning environments made for children. I believe a variety of factors appear to shape philosophies: personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, theoretical perspectives, professional learning. My personal philosophy on the design of children's environmental spaces takes me all the way back to the view that the environment is most supportive, hence very strategic in influencing children towards all-rounded development, wellbeing, and social-emotional growth. This philosophy has been developed from my engagement with early childhood theories developed by Vygotsky and Bronfenbrenner. The practices that come out of this are lined up with principles outlined in the EYLF.
Philosophy Statement
Belief 1: Environment is the 'Third Teacher' in ECCE.
Essentially, this refers to that understanding by which, in the developed early childhood settings, the environment goes beyond the physical space and acts as an active participant in the process of learning. In this regard, this perception for The Assignment Helpline is strongly attributed to the philosophy underlying the Reggio Emilia approach, whereby the setting is considered a 'third teacher' after teachers and other peers. An environment enriched with a diversity of materials and flexible spaces will allow for exploration, creativity, and autonomous learning that will foster a child's curiosity toward the world around them. The EYLF mentioned that dynamic environments which are responsive to the needs of children support the accomplishment of this particular outcome, known as Outcome 4: Children are confident and involved learners (EYLF 2022).
Belief 2: The environment should be designed to reflect and respect children's identities, cultures, and interests.
An environment that respects and expands children's cultural backgrounds and individual interests helps to foster children's sense of belonging and identity. It satisfies the very essence of Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory framework with an emphasis on considering all the various layers within a child's environment—from immediate settings, like family structures, to broader cultural contexts (Nolan & Owen, 2024). It also refers to the theory of designing spaces that allow educators to acknowledge children's lives and communities, creating an inclusive environment for positive self-esteem and cultural competence. EYLF Outcome 1 also deals with the issue of environments setting up a connected feel of the child with the world around it.
Belief 3: The environment has to be such that it would foster social interaction and collaborative learning.
At the very core of how children learn and develop is social interaction. According to Vygotsky's sociocultural theory, environments that foster cooperation, communication, and shared experiences let children learn from one another, sharpen their social skills, and build strong bonding. This can be achieved in group areas, open spaces, and flexible seating (Sarmiento-Campos et al., 2022). It is, therefore, a philosophy that is aligned with the outcome 5 of the EYLF: Children are effective communicators.
Belief 4: The environment should help children feel safe and promote their emotional well-being and positive mental health.
The quality of the environment in which children spend time is strongly related to their emotional well-being. Feelings of security, comfort, and stability are very basic to the mental health of a child and can be provided by a well-designed environment. This is possible through the provision of calm, orderly, and predictable space alongside quiet areas where the child may retreat and self-regulate. Maslow's hierarchy of needs says that basic needs for safety and love, according to him, need to be met first in children in order for higher-order learning and development to take place (Griffin et al., 2023). In the EYLF, it is underlined that high-quality settings promote children's social and emotional well-being; hence, it aligns with Outcome 3: Children have a strong sense of well-being, as presented in DEEWR, 2009.
Belief 5: The environment should invoke a sense of connection to nature and to care for the environment.
Such environments include natural elements and outdoor spaces, which enhance the children's affinities for nature and a sense of environmental responsibility. Research on biophilia argues that humans have an innate love of nature; therefore, exposure to natural environments improves well-being and cognitive functioning. By incorporating natural materials, gardens, and outdoor play areas into early childhood settings, educators open the possibility of nurturing children to not only appreciate the natural world but also to engage in sustainable practice. Outcome 2 in the EYLF emphasizes this by seeking environments that help children learn social responsibility and respect for the environment.
Justification
The aforementioned beliefs are choice-based on theoretical perspectives and practical considerations. The emphasis on social interaction by Vygotsky and the ecological systems theory by Bronfenbrenner offers a great platform to start understanding the role of the environment in children's learning and development. Further, the approach of Reggio Emilia strengthens that one which believes the environment to be an active factor as well as an educational process within itself. It is, nonetheless, through Maslow that such interaction of the environment with wellbeing is revealed and examined under the prism of the biophilia hypothesis in a way that puts emphasis on the need to create spaces capable of being not only functional but also nurturing and inspiring.
I have distilled these notions into my practice by attending to the provisions of environments that are not biased, flexible, and reflective of the wide range of needs and backgrounds from which children come. Aligning my philosophy with that of the EYLF guarantees that the created environments are developmentally appropriate and support not only the goals for early childhood education but also wider purposes such as belonging, social, and emotional well-being, and lifelong learning.
Conclusion
That is to say, my personal philosophy of the design of environmental spaces for children revolves around a belief in the environment as one of the major elements in conditioning diverse experiences for children's learning, well-being, and socio-emotional development. Guided by theoretical perspectives and taking its cue from the EYLF in setting out to create an enabling environment, I strive towards creating one that is inclusive, engaging, and equal for all Children. This philosophy will help further mould my practice in giving only the best learning experiences for children in my care.
References
Camacho, J. S., & Villegas, L. (2024). Foundations and Implications of the Integral Ecology and Sustainable Development Goals in Catholic University Education. Religions, 15(4), 480–480. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel15040480
EYLF. (2022). Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia (V2.0). https://www.acecqa.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-01/EYLF-2022-V2.0.pdf
Griffin, K. E., Arndt, S. S., & Vinke, C. M. (2023). The Adaptation of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to the Hierarchy of Dogs’ Needs Using a Consensus Building Approach. Animals, 13(16), 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162620
Nolan, H., & Owen, K. (2024). Medical student experiences of equality, diversity, and inclusion: content analysis of student feedback using Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems theory. BMC Medical Education, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04986-8
Sarmiento-Campos, N.-V., Lázaro-Guillermo, J. C., Silvera-Alarcón, E.-N., Cuellar-Quispe, S., Huamán-Romaní, Y.-L., Apaza, O. A., & Sorkheh, A. (2022). A Look at Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory (SCT): The Effectiveness of Scaffolding Method on EFL Learners’ Speaking Achievement. Education Research International, 2022(20904002), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3514892
Reports
96331 Planning and Evaluating Health Services Report Sample
Length: 2000 words (+/- 10%)
Formatting Requirements
In your submission, apply 12-point font size and double-spaced paragraphs. Ensure the document you upload is easily legible and has been spell checked and proofread before submission. Please ensure your reference list is accurate and complete.
Referencing
A reference list should be submitted at the end of the document with APA 7th formatting applied. A minimum of five (5) quality references should be included. Do use normal in-text referencing and quote articles or reports in the usual manner.
Facility Characteristics
- The facility is based on the Mid-North Coast of New South Wales (or a similar rural location in your State). The facility is inland from the coast and has high-care residents with dementia(s) in addition to lower care residents with mobility and related health issues.
- There is only one road in and out to the facility. It has nearby forest and bush as well as high rainfall at certain times of the year.
- Due to climate change, the seasonal pattern of weather events is not as predictable as it used to be.
Consider the following elements in your plan:
- preventive measures (e.g. landscape management, burn-offs etc.)
- continuity measures (e.g. power, water, food, medications)
- emergency response measures (e.g. evacuation – when, how, to where?)
- resident and workforce safety
- partners in the plan (e.g. local SES and Ambulance Service)
- responsibilities (who makes what decisions?)
- decision-making timeframes (e.g. alert levels, critical events and times)
- Assessment 3: Health and social care in emergencies and disasters
Solution
Introduction:
The aged care facility for which the disaster preparation plan is developed is situated in a rural location on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales. The facility is known to provide care and assistance to dementia patients who are considered to be high care residents as well as an elderly population with mobility and other health complications as low care residents. It has three floors where each floor has 11 rooms and 4 elderly individual lives in each room. The total strength of the facility is 43 out of which 31 are residents and the remaining are the staff. It has 4 ambulances and 2 cars for 24 hrs assistance. The aged care facility is surrounded by forest and bushes which also has high rainfall throughout the year which increases the risk of fire and flood disasters within the facility. It is also found that the facility is connected to part of the city through one road which serves as the in and out pathway for the facility (Cvetkovic et al., 2022). Focusing on the environment the locality of the aged care facility along with the climatic condition, the following fire disaster preparedness plan has been developed in order to provide safety and precautious assistance to the residents.
Plan:
Scope and application:
The aged care facility demands an increased need for a property fire disaster preparation plan due to the increased risk of complications associated with living residential patients. It is because patients living within the aged care facility are either suffering from life threatening conditions or are vulnerable to mobility. It has been found that cooking is one of the leading causes of fire within care facilities which accounts for 60% of the cases of fire disasters. The aged care facility is situated in NSW which has high bush fire risk due to climatic change. It has also been found that the elderly population sustains an increased risk of mortality associated with fire disasters when compared to the general population. Also, resident aged above 85 years sustains further risk than other patients within an aged care facility. Thus it is necessary that a well structured preparedness plan is developed and implemented based on prevention, continuity emergency response as well as other safety measures.
Preventive Measures:
Preventive measures account for one of the significant strategies to minimize the risk of fire and associated disasters and thus it is important to analyze the factors as well as eliminate them at a very early stage. In conditions where the risks cannot be minimized or eliminated at an early phase it is necessary to maintain proper precautions measures in order to maintain the safety as well as security of the patients (Shokouhi et al., 2019).
.png)
.png)
Continuity Measures:
Continuity measures for the assignment helpline focus on the efforts and strategies that are performed in order to maintain the continuous supply of resources and facilities associated with the setting. The continuity measures that need to be maintained in the aged care facility during a fire disaster include power supply medication and treatment facility, food and nutrient supply, clean water delivery as well as health associated risk management (Shokouhi et al., 2019).
It will be necessary that proper backup needs to be maintained in order to ensure that food and water appropriately supply it to the residents in case of fire or associated disasters. Medical and treatment facilities need to be arranged and stored in order to ensure stable delivery to the patient in need during the time of disaster and associated crises (Indriani, Prasanti & Permana, 2020).
Emergency Response Measures:
Emergency response measure in aged care facility highly includes evacuation which necessarily highlights the need to evacuate deep patient or resident toward a safe location.
.png)
.png)
.png)
Resident And Workforce Safety:
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
Partners In the Plan:
There is a wide range of stakeholders who need to be accounted as equal partners in the plan in order to develop a well structured fire disaster preparedness plan as well as conduct safe evacuation of the resident as well as the workforce.
The Local State Emergency Service: the SES functions by helping the general population and communities in order to prepare, respond as well as recover from any kind of natural disaster which can be a flood cyclone fire or earthquake. They conduct active suggest search and rescue operations and emergency service delivery, ensuring preparedness and delivery of safety regulations (Kankanamge, Yigitcanlar & Goonetilleke, 2020).
Fire Brigade: Another chief stakeholder to be an active partner in the plan includes the fire brigade service which will be assisting in case of any disaster they will ensure technical assistance during the disaster in order to avoid any emergency associated with life, property, or the associated hazards. They will ensure humanitarian services to the aged care facility in order to avoid any complications such as uncontrolled fire, collapsed buildings, or emergency rescue (The State of Queensland, 2022).
Ambulance Service: It will be necessary that the preparedness plan includes the involvement of ambulance services as an active partners as they will provide immediate actions and rescue in terms of the health and safety of the disaster victims. The ambulance services deliver pre-hospital care and medical assistance in cases of emergencies which also includes disasters. As the aged care facility is located in a rural setting and is connected by a single road, it will be necessary that immediate rescue assistance and treatment operations are conducted prior to reaching any healthcare facility (Hidayati & Nisak, 2019).
Responsibilities:
Local State Emergency Service: Decides on the strategies and procedures that need to be followed in case of emergency in order to contain safe evacuation of the residents as well as workers (Kankanamge, Yigitcanlar & Goonetilleke, 2020).
Head of the facility: In case of an emergency situation due to a fire disaster it will be necessary that decisions based on safety and evacuation are carried out by the head of the aged care facility in relation to the aged care facility and involved workforce and residents.
Workforce: Further decisions will be made by the workforce based on the health and well being of the patient as patients with mobility issues must be addressed respectively to health needs whereas dementia patients must be assisted based on their high care demand (The State of Queensland, 2022).
Decision Making Timeframes:
During a fire disaster, it will be necessary that three chief alert levels need to be followed in order to maintain safe evacuation and minimize life threatening consequences.
Advice: During the initial alert level it will be necessary to analyze the indication of disaster. It focuses on the that a fire has started in a nearby locality which thus develops no immediate state of danger. In such situations, it will be necessary to remain up to date on the condition and start and start preparing for emergency conditions (NSW Rural Fire Service, 2023). It will be necessary that the workforce working within the aged care facility keeps regular track of the fire and the increased risk.
Watch And Act: Further in the stage of the watch and act it will be necessary to acknowledge that the level of threat or danger has increased to an extent where conditions are changing and the preparedness actions need to be implemented in order to protect the workforce as well as the aged care residents (NSW Rural Fire Service, 2023). In the such condition when the watch and act level has reached, It will be necessary to start preparing for immediate evacuation and assisting patients in preparing themselves for emergency situations.
Emergency Warning: The emergency warning phase highlights the stage of fire where the level of risk is at its peak. In such conditions life-threatening conditions often take place and danger increases with time. Thus in such conditions, it is necessary that immediate precautious actions and evacuation strategies are implemented in order to reach the area of gathering and further and further seek professional help (NSW Rural Fire Service, 2023). In such conditions, any delay in misconduct may lead to a risk to life. As soon as an emergency warning develops it will be necessary that the workforce as well as residents within the setting continue clearing the area based on the provided evacuation strategies in order in order to reach the nearby safe locations.
Emergency contact:
Conclusion:
The fire disaster preparedness plan focuses on the procedures that need to be followed in order to maintain the safety of the workers as well as the residents in terms of their health and well-being as well as conduct a safe evacuation. The plan instructs and guides the workforce as well as the residents regarding the activities, actions, as well as strategies that need to be maintained in case of fire emergency, emerge and the situation demands immediate evacuation without any casualty.
References:
.png)
.png)
Reports
HEALTH6002 Nursing Report Sample
How Covid has directly affected the mental health of the people?
Research Question
• What is the effect of covid on people?
• What is the effect of covid on the mental health of people?
• What are the causes and protections for people to stable their mental health?
• How can it affect the mental health of people?
With the help of those questions, the researcher can get the correct information about the covid and its impact on people. During this pandemic, people are stressed and feel unwell every day because they have nothing to do for work.
Why this topic is significant
It is important to analyse “how covid affects people's mental health”. With the help of this, people get the idea of how to recover from that effectively and purposefully. Mental health includes emotional and social well-being. It virtually affects people's think, feelings and actions. It can effectively help determine how to handle stress, relate to others and make healthy choices (Hossain, Tasnim, et al., (2020). It is very important at every stage of life from childhood. It is also important for health professionals because, with this, they have some knowledge and information about the covid and its impact on mental health. This research will help health professionals solve problems, get ideas for solving issues, and help people get out from the mental stress which occurs from the covid. Most of the time, information is overloaded, preventing people and making issues for them to get stressed (Kumar & Nayar, (2021). So, people must avoid those kinds of news and information, which create stress and mental issues. To make people aware of mental health issues, take and share free health screenings and educate people about the topic.
How will the research contribute to solving this issue and the problem?
This research used both primary and secondary research methods to gather information about the topic. People need to get aware about the covid and its impact. This research is helpful to people and health professionals to overcome and solve issues that are increased by the covid on people's mental health (Vindegaard & Benros, (2020). This research includes ways to prevent such as getting enough sleep, avoiding unnecessary jargon and information, keeping away from the screen, eating healthy and many more tips. The research includes other ways to solve a problem, like people needing mental exercise to keep better treatment for avoiding stress and emotions. Here researchers do deep research on the process of affecting people and how it affects people. So, the whole research helps solve issues and problems generated by the covid Huang & Zhao, (2021). When people and the health profession read this paper and study, they have several ideas and options for moving with great work and happiness. This is very important for people to get the correct and creative ideas for solving issues. Those are the reason why research helps to solve issues and problems.
References
Hossain, M. M., Tasnim, S., Sultana, A., Faizah, F., Mazumder, H., Zou, L., ... & Ma, P. (2020). Epidemiology of mental health problems in COVID-19: a review. F1000Research, 9.
Kumar, A., & Nayar, K. R. (2021). COVID 19 and its mental health consequences. Journal of Mental Health, 30(1), 1-2.
Vindegaard, N., & Benros, M. E. (2020). COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: Systematic review of the current evidence. Brain, behavior, and immunity, 89, 531-542.
Huang, Y., & Zhao, N. (2021). Mental health burden for the public affected by the COVID-19 outbreak in China: Who will be the high-risk group? Psychology, health & medicine, 26(1), 23-34.
Case Study
NURBN2024 Mental Health Recovery Plan Case Study Sample
Scenario: Mental Health Recovery Plan
Note: This is information is a continuation of Bens story from Task 1, all previous information and video still applies Ben, a 25-year-old qualified builder, was brought into the Emergency Department by the Police three days ago following an aggressive episode involving his girlfriend outside their house. Ben behaviour raised concerns, leading the Police to believe that he was mentally unwell and posed a risk to himself and/or others. As a result, Ben was detained and taken to the local health service. Ben has a history of depression and borderline personality disorder, with known suicide attempts. His depression has been ongoing since he was 21 years old. Additionally, he has been using substances since the age of 14. His girlfriend informed the police that his substance use had become much worse & in recent months and that he had started acting strangely Upon admission to the Emergency Department, Ben was found to have a mixture of alcohol, ice (methamphetamine), and cannabis in his system. He was also experiencing a psychotic episode. The healthcare professionals managed his acute symptoms and determined that he is now stable enough to be discharged from the inpatient unit to a community setting. However, given his complex history and current mental state, a comprehensive recovery plan is necessary to support his transition and rehabilitation. Your previous MSE and risk assessment contributed to his care and after 4 days, he is to be discharged in the community.
You have just started in the community and have requested to continue working with Ben at the Community Mental Health Service. Ben has agreed to this as he is comfortable with you, having previously met you in the Inpatient Unit. He has also been taken off the mental health act and is now a voluntary patient Ben’s Current presentation and information: Ben’s symptoms of psychosis seem to be resolved currently prescribed Olanzapine 10mg BD is also prescribed Diazepam 5mg TDS. These medications were also used as part of Ben’s withdrawal from his methamphetamine and cannabis whilst he was in hospital. Ben previously was on Diazepam 10mg TDS. The psychiatrist would like this to be reduced and will review these medications with a view to discontinuing when appropriate.
When in hospital, Ben also started a SSRI called Escitalopram 10mg Daily. The psychiatrist would like this to be monitored [AC1] with an increase to 20 mg if tolerated, Ben was [AC2] previously on other antidepressants before admission and stated, “they did nothing for him”. He has not had Escitalopram before.
Ben still presents as low in mood; he still states his girlfriend will leave him and will lose his job and is embarrassed about how he was brought into hospital. These statements appear to be related to his mood and do not fit delusional content. He has stated that he has no plans to take own his life, but he does on occasion think about if he could just go to sleep and not wakeup as his thoughts “don’t stop” sometimes and he just wants to get away.
Overall, Ben still has till has some mild symptoms of withdrawal, and this has generally been managed well in hospital with an Amphetamine Withdrawal Scale and his regular medication. He currently feels he cannot miss any doses of the Olanzapine and Diazepam, otherwise he may will “lose it”. Ben has discharged, back to his home with his girlfriend. She has been very supportive during his inpatient stay. His girlfriend is worried about future relapse. His mother Cathy has also been supportive to Ben during this time and has volunteered to help where she can. Ben’s workplace has organised him some sick leave. Ben’s girlfriend has discussed with you that his boss is very supportive around mental health issues and wants him back at work when he is ready.
INSTRUCTIONS:
Instructions for Students
Task is focused on creating a recovery plan for Ben mental health, considering his transition from inpatient care to a community setting. This assignment will help you demonstrate your understanding of recovery planning, mental health interventions, monitoring and collaboration. Please carefully read and follow the instructions provided below.
Task Overview: You are required to create a recovery plan for Ben, a 25-year-old individual who was discharged from an inpatient unit to a community setting after a recent aggressive episode and psychotic episode. Your recovery plan should address mental health history, substance use, and recovery goals, considering evidence- based interventions and a include collaborative approach involving Ben, healthcare providers, family, and support network. Recovery plan can follow structured headings of Recovery plan template (provided in assessment resources) Rubric and Scoring: Your submission will be evaluated based on the rubric provided. Each criterion carries a specific point value, and your total score will be calculated out of 60 points and weighted to 50% of total grade.
Solution
Introduction
Ben is dealing with bipolar disorder and he has history of engaging in self-harming behaviour. After improvement in his condition of psychosis, he has been transferred to community care setting. For Assignment Help, this study includes a detailed interpretation of mental health recovery plan to be considered for Ben. Detailed analysis of recovery objectives, intervention risk assessment, and relapse prevention plan has been given here.
Mental health
Recovery goals
As per MSE, Ben has poor personal hygiene and he has anxiety and stress-related issues. He is dealing with emotional instability and issues while communicating about problems faced currently thus goal for Ben is to consider current distress associated with symptoms of substance withdrawal and overthinking are mentioned below.
- To improve emotional resilience and limit anxiety within 6 months through emotional wellbeing activities to ensure a positive mindset.
- Reducing habit of overthinking and managing outbursts of emotion within 6 months for managing family, occupational personal lifestyle through improving emotional resilience.
Nursing interventions
Emotional resilience-enhancing activities during treatment of mental health disorders provide scope to improve positive emotions and ensure a sense of self-satisfaction (Prakash et al., 2020). Similarly, in context of Ben, focus needs to be placed on improving emotional resilience. Under community care setting a personal wellbeing project is applicable for Ben as it helps to limit symptoms of anxiety and stress by improving resilience. Mental wellbeing training is associated with idea of ensuring positive mental health indications such as well-being and resilience in case of depressive symptoms associated with interpersonal reasons and other causes (Riepenhausen et al., 2022). Key resources to be considered in case of well-being training include community setting and social support. In this context, resilience skills are developed through cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT). Benefits of CBT include better adaptability to adverse situations, positive coping skills, and self-regulation as well as better socialisation ability (Polizzi & Lynn, 2021). In context of case of Ben, application of CBT under wellbeing training can provide opportunities to improve positive thought processes and avoid situations of poor anger management and better self-regulation. Through application of CBT there is also possibility of avoiding issues of poor personal hygiene maintenance and better socialisation can also help improve issues in communication and language. Here community health service provider has the role of assisting Ben to improve self-awareness regarding recovery and deterioration symptoms for self-monitoring. Ben needs to be assisted with using mood chart and other self-monitoring techniques.
Family relationship and occupation
Recovery goals
Based on an assessment of mental health condition and current progress made it can be identified that Ben is dealing with issues to communicate emotions and issues with others and he has manager management issues. Currently Ben is on leave from his workplace as his employer arranged leave for his mental condition and treatment. Poor emotional management and poor hygiene management can impact family and professional life in terms of poor living arrangements and finance management. Due to poor communication and mention management Ben deals with poor relationships with family members such as his mother and girlfriend. Thus based on current situation Ben's goals for improvement are mentioned below.
- Improving positive relationships with family members and colleagues in workplace through enhancing socialisation ability within 6 months.
- Improving living arrangements and personal hygiene through enhancing self-management ability within 7 months.
Nursing interventions
Ben works as a qualified builder and due to substance misuse issues; he becomes unable to manage mention which can significantly impact his professional life. Due to a poor professional lifestyle, there can be poor financial management issues and employment opportunities can become limited. In this context, area to focus on is socialisation for better family relationships and emotional and self-management for better professional life. In this context, mild exercise such as swimming yoga, or meditation can be beneficial. Further engagement with community activities can help to improve socialisation. Meditation is beneficial for dealing with anger management issues in terms of enhancing sense of peace and calm as well as limiting anxiety and agitation due to depressive thoughts (Malakoutikhah et al., 2022). In this context supporting Ben to engage in mediation and other emotional wellbeing activities can help to improve his concentration and anger management ability to avoid negative impact of poor mention management of occupation and family life. Engaging in community activities and socialisation provide scope to avoid long-term mental health issues including Alzheimer's (Morton et al., 2021). As Ben already has a history of substance misuse and depression as well as suicide long-term effects of such conditions cannot be avoided. In this concrete, ensuring socialisation through engaging with community-based activities provides scope to retain emotional wellbeing. Thus guiding Ben to engage in socialisation activities and emotional resilience-enhancing activities as well as monitoring improvement can provide long-term outcomes.
Physical health and medication management
Recovery goals
Ben is currently under medication of Escitalopram 10 mg daily and he has a fear of developing old symptoms thus he thinks that he cannot avoid any dosage of Olanzapine and Diazepam. He is dealing with fear of engaging with substances again as he often overthinks and hallucinates about the situations. Considering physical health, poor personal hygiene is a major concern, and signs of withdrawal which include excessive thrust and weakness. Thus along with medication management, there is a need to focus on limiting signs of withdrawal and a healthy diet as there are also side effects of psychotic drugs. Considering area of physical health and medication management below-mentioned goals are applicable.
- To increase confidence and limit anxiety along with improving personal hygiene within 6 months through counselling and guided assistance.
- Engaging with family-centred activities for limiting anxiety and poor medication management along with following a healthy diet during time of withdrawal.
Nursing interventions
Ben has a history of substance abuse due to withdrawal signs his physical health can be impacted. Thus family centred interventions are beneficial for him. Involvement of family and communication about issues with family help to limit potential recurrence of substance misuse. Smiley in case of Ben communication with family members, specifically his mother, needs to be improved. Thus under supervision of community health service family-centred activities and changes in moods and wellbeing of Ben can be monitored. As he is currently under withdrawal and psychotic medication monitoring of vitals along with symptoms of withdrawal is needed. Ensuring a proper and healthy diet along with mild exercise can help to poop with symptoms of withdrawal. CBT can help Ben to overcome withdrawal stage and return to his old lifestyle. Thus as a community services provider has role to support Ben to access necessary resources and facilities.
Substance abuse
Recovery goals
Ben has overcome habit of substance misuse however signs of symptoms play a significant role in recurrence of habit. Thus signs of withdrawals need to be managed along with popper lifestyle management. Thus ensuring a scheduled lifestyle with mild exercise and socialisation can help Ben to overcome challenges of relapse. Ben has mentioned that he has no intention to harm himself but he is disturbed due to contour thoughts which cannot control. Thus to ensure concentration and lesser anxiety mindfulness training is beneficial in this case. Thus goals for substance misuse are mentioned below.
- Improving emotional resilience through mindfulness training and enhancing daily lifestyle routine of Ben within 6 months.
- Enhancing awareness regarding substance misuse and long-term effects within 2 months.
Nursing interventions
Ben is currently under signs of withdrawal and in this stage, lack of mindfulness can result in a relapse of previous situation. In this context supporting mindfulness activities and patient education regarding long-term and negative impacts of engaging with substances on health can be beneficial. In this context, a collaborative approach by engaging Ben's mother and girlfriend in a discussion regarding substance misuse and ways to consider better lifestyle management can be beneficial. Mindfulness training activities can help to ensure better self-control and enhance adaptability along with improving emotional intelligence and mental clarity (Drigas & Mitsea, 2020). In this context assisting in engaging with mindfulness training in activities can enhance Ben's self-control and ability to adapt to a new and healthy lifestyle pattern. Assisting Ben and his family to understand measures to consider for avoiding substance misuse in case of any type of psychological distress can help to ensure long-term possibility of limiting consumption of substances. Thus a family-centric approach and continuous monitoring of emotional resilience associated with mindfulness training is needed here.
Risk assessment
Ben is needed to be monitored in terms of his behaviour with family members, friends such as his girlfriend, and in his occupational life. Through proper counselling and continuous assessment of behaviour and lifestyle management activities, risk assessment can be done. A timely assessment of lifestyle behaviour and emotional resilience can provide scope to assess risk associated with potentiality of developing bipolar disorders and other psychological issues (Singh et al., 2022). In this context of behavioural assessment, there is the possibility of understanding current mental state and by interpreting interrelationship between family members and occupational performance there is possibility of determining effects of ongoing medication and treatment practises. Similarly in case of Ben through monitoring and assistance of his family members, there is possibility of determining potentiality of any risky behaviour and taking strict action in case of any potentiality of self-harming or anger management issues.
Discharge planning
During discharge, there are certain areas to be considered for avoiding mismanagement of medication, and relapse of situation including patient education and detailed assessment (Gledhill et al., 2023). In this case, while discharging Ben a patient education session follow-up check-up schedule as well as a diet plan and other physical activity and mindfulness training plan needed to be provided. Benefits of patient education during discharge include health empowerment, better health outcomes, and ensuring a better quality of life for patients (Ådnanes et al., 2020). It also reduces rate of readmission and in case of Ben due to symptoms of withdrawal through proper patient education and awareness along with collaboration of family members and his girlfriend; there is a possibility of avoiding situation of relapse. In case of Ben communicating with family members, arranging patient education sessions is beneficial. During discharge, proper details regarding physical exercises and ongoing medication along with therapies to be considered for him need to be communicated properly with family members to ensure collaboration and family centred treatment plan. In case of occupational lifestyle stress factors to be avoided in occupation also need to be communicated with Ben and his family members to reduce recurrence of substance misuse and psychotic condition.
Relapse prevention plan
Developing a relapse prevention plan requires recognising stages of relapse which are mainly three stages emotional, mental, and physical (Ociskova et al., 2022). It also becomes necessary to understand factors resulting from psychological turbulence to cause relapse of any type of psychotic symptoms. In context of Ben, there is a possibility of relapse of substance misuse habit and development of bipolar disorder along with anxiety and stress. In this context, major focus is to monitor triggers which are anxiety and depression as well as losing control over maintaining emotion. In case of any changes in behaviour such as lack of control over emotion and emotional distress, there is a need for further appointments with a psychiatrist and assistance of a community service provider to limit relapse of situation. In this context collaboration and monitoring through family members and friends is necessary as well as continuous socialisation and maintaining a lifestyle with a healthy diet and exercise can be beneficial to avoid relapse of such a situation.
Conclusion
Based on overall analysis it can be identified that in case of Ben, there is need to focus on applying CBT, physical exercises, and mindfulness training to enhance concentration and self-confidence. Engaging in mindfulness activities can help to overcome challenges of poor lifestyle and poor occupational performance. Patient and family-centric approach is considered for discharge planning and relapse prevention step-by-step monitoring of triggers is recommended.
References
.png)
Case Study
LMED28001 Chemical Pathology Case Study 1 Sample
The total word count for this case study report is between 2,000 to 2,500 words (excluding references). Reports should be typed in Word and adhere to the format of the given template (Arial, 12pt, Single spacing).
The report must be your own work and your name, student ID and page numbers should be included in the footer of all pages of the report.
Abstract: 10 marks (200 words max)
Criteria for High Distinction in this section:
The abstract should provide a clear and concise overview of your report and the findings of your biochemical tests. A clear but brief outline the case history is provided, along with the tests performed, rationale of the tests and how they can be used to diagnose the specific disease to reach a final conclusion in this case.
No references are included in the abstract.
Introduction: 15 marks (400 words max)
Criteria for High Distinction in this section:
The introduction should clearly outline the necessary background information, including signs or symptoms, underlying pathophysiology, clinical and the laboratory information of relevance.
A clear and concise explanation of aims and objectives of the tests are provided, with a brief conclusion to the section specifying the conclusion/diagnosis with no discussion.
Materials and Methods: 10 marks (no word limit)
Criteria for High Distinction in this section:
The methods that you have used or intend to use (further tests) to arrive at the provisional diagnosis are clearly and concisely summarised.
The sources to these methods need to be clearly referenced, even if it is simply the prescribed text/lecture material/laboratory manual. Reference is made to specific instrumentation that could be used to conduct these biochemical tests (e.g. biochemistry analyser) and the manual is sufficiently referenced. The written work is an original and brief summary of the method used and not a reproduction of text from these references.
Results: 20 marks (no word limit)
Criteria for High Distinction in this section:
The results section provides a clear summary of all data/results with reference ranges.
The layout is clear, legible and uncluttered. All figures or tables are labelled clearly with legends where appropriate. Units have been properly included.
Interpretation of results is limited to a description of how they compare to the normal reference ranges. The results are presented, however not discussed in this section. Further tests (if required) with expected results are outlined.
Discussion: 30 marks (No word limit)
Criteria for High Distinction in this section:
Provisional and differential diagnoses (if any) should be clearly stated and discussed with reasons provided in relation to the clinical and laboratory results.
Expected results of further tests must be included to support your provisional diagnosis and/or align with your differential diagnosis(es). Your conclusions reached and the evidence required to reach these conclusions is compared with existing literature on similar case studies.
The full text of the published articles forms the basis for this discussion (don’t draw comparisons from other abstracts without reviewing the full text of the articles). The pathophysiology of the diagnosis and possible treatment options (if any) are also discussed. Finish your discussion with a final concluding statement.
Solution
Abstract:
The report has been carried out focusing on the case study of an 80-year-old man who was admitted to the ER due to certain signs and symptoms which included chest pain, shortness of breath, and severe cough. After admission to the er the patient was provided with blood tests or serum biochemistry assessment where certain proteins and enzymes were evaluated in order to assess any underlying abnormality It was found that the patient sustained abnormality in anion gap, urea level as well as creatinine level. For Assignment Help, Based on these abnormalities the patient was provided with three diagnostic tests which included UEC tests, troponin test as well as CK-MB test. Each test was carried out based on their respective field of assessment as the UEC test was provided to evaluate urea level electrolyte level as well as creatinine level in the Serum. Further CK-MB test was carried out to evaluate any suspected risk of heart attack and a troponin test to analyze any threat of renal failure or cardiac muscle damage. After completion of the assessment of the selected three biochemical tests, it was found that the UEC test along with the anion gap test provided better insight into the underlying health condition. The biochemical test assessment highlighted the risk of renal failure in the patient which led to the state of shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough.
Introduction:
The report focuses on analyzing and evaluating the case study of a patient named Mr. David Gilmour who is 80 years old and was admitted to the ER Department of a local hospital. The patient was admitted with a major complaint of chest pain Cough as well as difficulty in breathing. After admission to the er blood Cup squad was conducted in order to analyze the vitals of the patient after 24 hours of the blood test a second work was initiated in order to sustain detailed information post admission to the ER and provided healthcare assistance. It has often been found that heart failure often leads the heart muscle towards deprived pumping of blood. In such conditions, fluid built up occurs within the lungs which causes shortness of breath in the suffering patient. Similarly in the case of renal failure, often flute retention in the lungs leads to chest pain and shortness of breath which were two of the main symptoms identified in the patient. It has also been found that often chronic kidney disease or anal failure leads to a heart attack as the heart withstands increased pumping of blood to deliver it to the kidney.
On analysis of the serum biochemistry of the patient, it was found that on Day One the anion gap counts 5 which was the same on the day to result. It was also found that the urea and creatinine levels also increased from their normal reference ranges. The urea level in the serum was 18.9 on day 1 and 17.5 on day 2 at the same time creatinine level was 0.18 and 0.16 on the respective day results. After evaluation of the blood test on Day 1 and Day 2, three tests were requested for the patient in order to identify and evaluate the underlying causeway of the signs due to which the patient was admitted to the ER. The tests include blood UEC, CK – MB, and proponent test which are used in order to suspect myocardial infarction for heart attack sustained by the patient. These tests are used in order to evaluate the risk of heart attack and kidney function in relation to abnormal Creatinine, Troponin as well as Urea levels in the Serum. The report does will focus on analyzing and evaluating the two chief suspected underlying health conditions; heart attack and renal failure with the use of 3 referred biochemical tests.
Materials and Methods:
Blood – UEC
UEC test is also known as the kidney function test but just carried out using the assessment of urea, electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, and chloride as well as creatinine. Electrolytes and urea are accounted to be the most frequently used biochemistry test which helps in the assessment of Renault failure or associated kidney health (Dhanani et al., 2018). Urea and electrolyte tests provide significant information in terms of hemostasis and excretion and the inclusion of a creatinine test supports the result with glomerular filtration rate within a patient (Bamanikar, Bamanikar & Arora, 2016). In order to conduct advanced electrolyte tests, often Anion Gap Blood Test is carried out in order to evaluate the acid-base balance or PH balance of a patient’s blood. This test indicates whether the blood is acidic or non-acidic in nature based on the electrically charged minerals present in the body which includes bicarbonate sodium and potassium (Yang et al., 2017).
CK-MB Test
The CK-MB test is a standard blood test that is used to analyze and measure certain enzymes released in the blood first of these enzymes includes the creatine kinase-myocardial band. This enzyme is generally released from the heart when the heart or muscle from other parts of the body sustains severe damage. Generally, creatine kinase is present in the heart but it releases creatine kinase-myocardial band after muscle damage (Kim & Hashim, 2016). It has also been found that in the case of renal failure, the creatine kinase-myocardial band is falsely elevated due to muscle damage in the kidney. ichroma™ CK-MB is known to be a fluorescent immune assay or FIA which is used as a diagnostic procedure for Creatine Kinase Isoenzyme-MB in the blood or serum of the human body (Lab Industries, 2016).
Cardiac Troponin Test
Cardiac troponin tests are used in order to measure the troponin T or troponin I protein level in the blood. It is used in order to assess heart attack or suspected renal failure as Troponin proteins are released in conditions where the heart muscle sustains damage. The test indicates the amount of damage that occurred within the heart as the greater the amount of released troponin proteins in the blood, the greater the damage cardiac-specific troponin biomarkers are generally used in relation to different symptoms along with abnormal ECG as well as suspected myocardial infarction in case of patients suffering from chronic kidney disorder (Mair et al., 2018). Cardiac Troponin assessment is carried out with the help of standard blood tests where blood samples are used in order to measure the amount of troponin raised in the blood.
Results:
In the case of a creatinine urine test, urine samples are corrected over a period of 24 hours in order to assess the creatinine released out of the body. The normal range of Serum creatinine is 0.04 – 0.12 mmol/L which when exceeds indicates an abnormality in kidney function or renal health (Delanaye, Cavalier & Pottel, 2017). The electrolyte test examines the sodium, manganese, and potassium level in the blood which actively maintains the acidic and nonacidic nature of the blood. It is also used in anion gap blood tests which helps in evaluating the pH of the blood. An increase or decrease in anion level or electrolyte level in blood leads to shortness of breath and heart attack. The condition was similar in the case of the patient as the anion gap was 5 which was below the normal range of 10 – 20 mmol/L. The urea test indicates the normal ability of the kidney to break down urea, of the level of urea in the blood is high then it indicates kidney failure or renal disease. The normal range of urea in serum is 2.5 – 8.6 mmol/L, but in the case of the patient, the range was 18.9 and 17.5 within a period of 24 hours indicating abnormality (Laville et al., 2023).
The CK MB test provides an inside regarding the serum level of the creatine kinase-myocardial band which generally remains under 4% in normal test results. It is due to the fact that a minimal amount of the enzyme often enters the bloodstream from the salty tissues. In conditions where the CK-MB level exceeds more than 4% of the total CK in serum, it indicates the condition of muscle damage in the heart. The test is known to lag the ability to differentiate between heart attack-associated muscle damage or another source of damage within the body (Chen et al., 2022). In such conditions, other diagnostic methods are generally used in order to identify the condition of an underlying heart attack. The normal range of the enzyme in the Serum is 0 – 3.8 ng/mL, and exceedingly more than the designated range indicates muscle damage.
The normal troponin level found in the body is 0.0 – 0.4 ng/mL but a slight increase in the level of Troponin often indicates heart muscle damage associated with myocardial infarction or heart attack. The blood troponin test helps in analyzing the troponin level within the blood as well as any indicated risk of a heart attack. In case of kidney failure, decreased glomerular filtration rate leads to elevated cardiac trouble in T level which is also identified with the help of cardiac troponin blood test.
Discussion:
A differential diagnosis often takes place when the signs and symptoms indicate more than one underlying health condition and thus demands additional examination and testing to provide an appropriate diagnosis. With the help of differential diagnosis, the test to evaluate the underlying health condition narrows down and précised health assessment is carried out (Webster et al., 2017). Focusing on the case study of the patient, the serum biochemistry as well as identified biochemical test. It has been found that a state of differential diagnosis develops due to the indicated science and symptoms. The signs and symptoms as well as the serum biochemistry of the patient indicate the chance of renal failure, as well as a heart attack as both health condition, indicates similar clinical indications. After collection of the biochemical tests, it has been found that the anion gap blood test, as well as the UEC test, was found as a differential diagnostic assessment as both the tests highlight the risk of renal failure as well as underline the threat of heart attack. A low anion gap in Serum Test indicates the state of alkalosis where the blood is considered to be less acidic than the normal range. It has been found that a low level of albumin in the blood often leads to a state of low anion gap and it serves as a major indication of underlying health conditions such as kidney disease or cardiac complications (Asahina et al., 2022). It was found from the case study that the patient sustained shortness of breath as well as chain which both indicate renal failure as well as a heart attack. After the connection of the anion test, it has been found that the patient had a low anion level in the blood which thus develops a state of differential diagnosis between heart attack and renal failure.
The UEC test includes three different assessments of electrolytes and creatinine with altogether indicate the function of the kidney or any state of renal failure. It has also been found that after the conduction of electrolyte and creatinine tests, a state of differential diagnosis developed as these three examinations often indicate the risk of acute heart failure as well as renal failure. Urea nitrogen is considered a waste product that is removed from the blood by the kidney (Peng et al., 2021). When the blood contains an increased level of urea it indicates that the kidney is not functioning appropriately and at the same time increases the risk of certain cardiovascular events which includes heart failure (Jujo et al., 2017). Also after evaluation, it has been found that abnormal level of an electrolyte such as sodium potassium or manganese in blood indicates the risk of mural health conditions which mainly includes renal disease, irregular heart rhythm as well as high blood pressure. Manganese is considered to have a major influence on cardiovascular events along with potassium and calcium it plays a necessary role in managing intracellular potassium concentration. The creatinine test is carried out using a standard blood test where the creatinine level in the blood or the serum creatinine is measured. Though it has been found that serum creatinine is considered in the case of patients with renal failure but increased creatine along with worsening of the renal condition is highly common in patients with heart failure which increases during any acute heart attack episode (Vassalotti et al., 2016). Thus based on the evidence it is necessary that further a well-calculated diagnostic test is recommended to the patient in order to evaluate the underlying cause of the health condition. Based on the above discussion it has been found that the patient is suspected to suffer from major chronic kidney disease which is associated with the occurrence of cardiac complications. Thus it will be necessary to provide the patient with an appropriate chronic kidney disorder diagnosis in order to evaluate the underlying renal condition and associated complications.
Conclusion:
After evaluating and analyzing the above evidence and the biomedical test results it has been found that the patient is suspected to suffer from venal failure which is the underlying cause of cardiac complications, abnormal serum level, and shortness of breath thus it will be necessary that the patient is provided with an appropriate diagnosis which identifies the cost and provides better treatment approach. The biochemical tests provided the patients with a state of differential diagnosis as the test indicated both the condition of renal failure as well as a heart attack.
References:
Asahina, Y., Sakaguchi, Y., Kajimoto, S., Hattori, K., Doi, Y., Oka, T., ... & Isaka, Y. (2022). Time-updated anion gap and cardiovascular events in advanced chronic kidney disease: a cohort study. Clinical Kidney Journal, 15(5), 929-936. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfab277
Bamanikar, S. A., Bamanikar, A. A., & Arora, A. (2016). Study of Serum urea and Creatinine in Diabetic and nondiabetic patients in a tertiary teaching hospital. The Journal of Medical Research, 2(1), 12-15. Retrieved from: https://www.medicinearticle.com/JMR_201621_04.pdf
Chen, M., Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Zhang, J., Peng, Y., Bai, J., ... & Gao, Z. (2022). Target-responsive DNA hydrogel with microfluidic chip smart readout for quantitative point-of-care testing of creatine kinase MB. Talanta, 243, 123338. Retrieved from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123338
Delanaye, P., Cavalier, E., & Pottel, H. (2017). Serum creatinine: not so simple!. Nephron, 136(4), 302-308. https://doi.org/10.1159/000469669
Dhanani, J. A., Barnett, A. G., Lipman, J., & Reade, M. C. (2018). Strategies to reduce inappropriate laboratory blood test orders in intensive care are effective and safe: a before-and-after quality improvement study. Anaesthesia and intensive care, 46(3), 313-320. Retrieved from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0310057X1804600309
Jujo, K., Minami, Y., Haruki, S., Matsue, Y., Shimazaki, K., Kadowaki, H., ... & Hagiwara, N. (2017). Persistent high blood urea nitrogen level is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events in patients with acute heart failure. ESC heart failure, 4(4), 545-553. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5695177/pdf/EHF2-4-545.pdf
Kim, J., & Hashim, I. A. (2016). The clinical utility of CK-MB measurement in patients suspected of acute coronary syndrome. Clinica Chimica Acta, 456, 89-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2016.02.030
Lab Industries (2016), Ichroma CK-MB. Retrieved on 13 April, 2023 from: http://www.labindustrias.com/web/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/INS-CK-EN-CK-MB_Rev.07_161216-1.pdf#:~:text=ichroma%E2%84%A2%20CK%2DMB%20is,acute%20coronary%20syndrome%20%28ACS%29
Laville, S. M., Couturier, A., Lambert, O., Metzger, M., Mansencal, N., Jacquelinet, C., ... & Massy, Z. A. (2023). Urea levels and cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 38(1), 184-192. Retrieved from: https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfac045
Mair, J., Lindahl, B., Hammarsten, O., Müller, C., Giannitsis, E., Huber, K., ... & Jaffe, A. S. (2018). How is cardiac troponin released from injured myocardium?. European heart journal: acute cardiovascular care, 7(6), 553-560. https://doi.org/10.1177/2048872617748553
Peng, R., Liu, K., Li, W., Yuan, Y., Niu, R., Zhou, L., ... & Wu, T. (2021). Blood urea nitrogen, blood urea nitrogen to creatinine ratio and incident stroke: the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. Atherosclerosis, 333, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.08.011
Vassalotti, J. A., Centor, R., Turner, B. J., Greer, R. C., Choi, M., Sequist, T. D., & National Kidney Foundation Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. (2016). Practical approach to detection and management of chronic kidney disease for the primary care clinician. The American journal of medicine, 129(2), 153-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.08.025
Webster, A. C., Nagler, E. V., Morton, R. L., & Masson, P. (2017). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 389(10075), 1238-1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32064-5
Yang, S. W., Zhou, Y. J., Zhao, Y. X., Liu, Y. Y., Tian, X. F., Wang, Z. J., ... & Hu, D. Y. (2017). The serum anion gap is associated with disease severity and all-cause mortality in coronary artery disease. Journal of geriatric cardiology: JGC, 14(6), 392. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5540871/pdf/jgc-14-06-392.pdf
Reports
MBA621 Healthcare Systems Report 3 Sample
Your Task
Individually, develop a 1500-word report on how the use of digital health care technologies can help address some of the challenges with providing health care to rural and remote Australians.
Assessment Description
The purpose of this individual assessment is to holistically consider the key learnings throughout the subject and evaluate how current and emerging trends in digital health care technologies are being used and can be used to assist with many of the challenges facing the Australian health care sector.
Assessment Instructions
Australia is the 6th largest country by land mass in the world, yet has only a population of just over 25 million people, most of whom are located in urban environments. Despite Australia’s policy of providing universal and equal access to health care to its people, it continues to struggle with equity when it comes to rural and remote regions, many of which are populated by Indigenous Australians. This assessment requires you to evaluate the role digital health care technologies have helped and can help address some of these gaps to the benefit of all stakeholders.
Areas covered in your report should include:
• A Cover page
• An Executive summary
• A Table of Contents
• An overview of the current health care challenges facing rural and remote Australians.
• A concise discussion of the current digital health care technologies available for these communities, including an examination if they provide quality care and service provision.
• An examination of the ethical considerations related to the use of digital health care technologies for rural and remote regions, including those who identify as Indigenous Australians.
• An evaluation of the key stakeholders involved and the benefits they receive through the use of digital health care technologies for rural and remote regions, many of which are populated by Indigenous Australians.
• A conclusion
You are required to use at least 10 sources of information and reference these in accordance with the Kaplan Harvard Referencing Style. These may include websites, government publications, industry reports, census data, journal articles, and newspaper articles.
The cover page, Executive Summary, Table of Contents, Reference List, tables, issues, and graphs are excluded from the word count.
Solution
Overview of the current health care challenges facing rural and remote Australians
Australia is 6th largest country in world functioning with 2% or 500,000 people living in the remote areas of the country (health.gov.au, 2023). Health care facilities are services are equal right for all individuals living in any location of the country. For Assignment Help, However, it can be analysed that unequal distribution of resources within the nation govern unequal healthcare facilities to the patients in remote areas. The major principle of Australian healthcare system is to govern equal and optimised healthcare facility to all of the citizens with universal access. The country is unable to govern the effective functioning of respective principle in health care sector as the health outcomes in respective remote and rural locations in comparison to urban health care are very low (Batterham et al., 2022).
.png)
Figure 1 overall death rates and major reasons
(source: aihw.gov.au, 2023)
The differences can be more chronic diseases-based suffering, issues in GP specialisation, higher rates of hospitalisation, poor access to quality of care which is major due to lower availability and less choice of resources within the area (Shaddock and Smith, 2022). The health care issues like diseases, viral fever, mental health instability, heart issues, lung diseases, higher fatigue etc. can be seen in people. The current health care system in rural areas with an overview picture might be fulfilling all types of government-based promises but for quality care the resources governance is not up to the mark.
.png)
Figure 2 experiences by patients in remote areas of Australia
(source: aihw.gov.au, 2023)
Majorly four types of issues are responsible for such scenarios in Australia which incur barrier to quality services. Geographical remoteness which is lesser infrastructure or accessibility to any prime for good health care. Social economic factors which is low income and lower attainment in education and work availability which is lesser demands of labours. Additionally, the climatic scenarios and risk to injury and exposures to people in urban areas are very high. Overall, the rural health care system with social and geographical derivatives which do not function in favour of citizens (Pawaskar et al., 2022).
Digital health care technologies and its governance in Australia
Digital technologies, such as eHealth Records, could play an important role in the evolution of health care. However, the adoption of this principle is being led by advanced countries such as Australia. A dangerous enthusiasm for technological solutions to complex social problems could be attributed to the challenges that policymakers in many countries have found themselves facing as they try their best. (Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2023)
The experience of Australians with digital health has improved since January 2019, when the number of records containing data on my healthcare record increased from 5.39 million to 22.31 million in December 2021, where more than 537 million documents have been uploaded. From March 2019 to February 2020, monthly viewings of content on the platform increased by 476 percent compared to the pre-pandemic period from July to December 2021. Public hospitals shall be able to use documents uploaded by other providers for the provision of appropriate services. Views of most needed documents that shed light on a patient's medical history and treatments have more than doubled since December 2020: medicines from 250,000 to 520,000per month and diagnostic imaging from 70,000 to 190,000 per month. (Ridley, 2022)
Offering services in 179 number of remote areas, 70% of Queensland area is rural and 6% out of which have first nation people. Government invests about 107.2 million dollars in year 2022 which includes 72 million dollars in transformational of health payment and services and governs 32.2 million dollars in management of National Digital Health (digitalhealth.gov.au, 2023). In terms of rural section, the digital technologies are used to understand the number of patients in one day, type of diseases, issues with current services, lines and waiting time, frequency of revisiting patients for respective sector of diseases etc. The main function is to identify the diseases and manner in which patients are frequently visiting the hospitals. The data in further section govern research and development strategies to better healthcare systems in Australia (Healey et al., 2022).
.png)
Figure 4 better connectivity required in remote areas of Australia
(source: ama.com.au, 2023)
User friendly mobile devices, good testing machines, personalisation in quality of care using technology, governance of virtual treatment at home etc. types of modern solution in terms of rural digital technologies is governed by Australian government under 10 yearlong plan for rural areas. However, in current section of working issues in accessibility and correct tech-based use in diagnosis and treatment is required which is not governed by the care takers (ama.com.au, 2023). Many times, the hospital professionals are not trained enough to govern solution towards IT domain. Communication quality with first nation people in Australia is governed by digital tech but often the patients and visitors do not understand technology in prominent manner. Hence, it can be understood that government is governing major efforts in drafting digital tech with health care systems but channelizing the change can be majorly adverse due to lack of understanding (Toll et al., 2022).
Ethical considerations related to the use of digital health care technologies for rural and remote regions.
Ethics play a vital role in governing effective support to all types of stakeholders. In terms of healthcare systems in Australia ethical considerations are majorly not only trained to employees but also monitored in their working (Morris et al., 2022). The change governed through digital technology in rural areas also majorly have many types of ethical considerations which are kept in mind so that no patient is deprived from their respective rights. In accordance with NDIS, seven types if rights are governed in healthcare system which are respect individual, respect self-determination, respect privacy, act with integrity, honest and transparency, deliver services, ensure quality and safety and respond to violence (ndiscommission.gov.au, 2023).
.png)
Figure 5 NDIS Code of ethics
(source: ndiscommission.gov.au, 2023)
The digital technology for example in recording the data of patient through scanner is first informed to the patient and then the device is used. The consent-based function has been regulated in current digital tech systems in rural areas (Banbury et al., 2023). However, the phases of ethics on the other hand like right to know and delivering of services with quality of care are not governed in the system which is because of lesser resources and higher patient load. Government’s efforts towards improvement in healthcare systems in Australia have been furnishing the facilities in remote areas as well.
.png)
Figure 6 creating camera vision for such remote regions in Australia
(source: digitalhealth.gov.au, 2023)
For Aboriginal community of Tjuntjuntjara in western Australian region which is 650 km many people have been governing the use of digital technology. The government-based helpline number in detection of patient’s health issues is mainly used by Aboriginal community of Tjuntjuntjara in which it is considered as better way of communication by people as they know how to use that particular tech. 78% of patients had their treatments by using calling and tele calling digital tech during covid 19 for Aboriginal community of Tjuntjuntjara. Australian government has made partnership with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities in order to govern verbal support of digital technology to govern acceptance of change in productive manner (Coombs et al., 2022).
Stakeholder evaluation
35% of indigenous people in Australia live in rural and remote areas and require optimised healthcare services in order to withstand the epidemics and changes in climatic functions. many times, the data collection governed by digital tech allocated by the government aids the regions to have qualified number of resources in an effective manner. The digital technology in rural regions supports connection of urban areas and government. Any healthcare professional sitting in any remote region can have a connection with national level professional who can govern effective resources allocation and manage the services in remote areas as well (Chandra et al., 2022).
The digital technology like mobile service vans, my health record, electronic prescriptions, telly calling to doctors, virtual home assistance, communication with doctors in urban areas etc. aids creating sense of confidence in better of health of any individual (Yao et al., 2022). The connection through services makes people fulfilled and never undercut by government. Good quality, good care, better facilities which no such large mobility is accessed to people satisfying them cure at home. Hence, efforts by Australian government in rural and remote technology for all types of Aboriginal and first nation people is productive but needs to amplify same as that in urban areas.
Conclusion
The above report concludes that health care systems also need upgradation and the connection to all major health care centres. The respective rural and remote area-based analysis for the Australian rural population is presented in the above report. Lack of resources, utility factors and issues in mobilisation is governing major healthcare issues to the first nation people in Australia. However, with pace of time and efforts of government better connectivity based digital tech are used so that clustering on entire system govern better facilities to individual irrespective of the region where they are.
References
.png)
.png)
Reports
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Report 1 Sample
Assessment Task
This assessment task requires you to watch four case study videos, available in the assessment folder in Blackboard and select one (1) to be your case study patient. Then you will identify health services that meet the needs of your chosen patient and determine if these services are available to your patient in a rural town of your choice.
Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Instructions
The table below lists the four case study patients from the videos and relevant discharge information.
.png)
Your patient is preparing for discharge from hospital. So, the focus of your chosen services will be Primary Care services in the community. For this assessment your case study lives in a rural town.
You will need to identify and research any rural town of your choice and the health services available in that town. Follow the task instructions below.
To complete this assessment task, you should:
1. Identify which case study you have chosen and list all of your patient’s discharge needs based on the information provided in the case study video and the discharge information in the table above.
2. Identify four (4) healthcare professionals and the services they provide relevant to your case study. Your references will need to be from Australian sources. NOTE: At least one (1) service must be a nursing service.
3. Rural town – Select and research a rural town in Australia. Name your chosen town, where it is located and the demographics such as population size, numbers of males and females, number of adults vs children. You will use this town to answer the questions below.
4. Determine if the health professionals and services you identified for your character (in point 2 above) are available in your town, and if so, what are the typical hours of operation for this type of service in the rural town?
5. When comparing the identified discharge needs of your patient with the services available in your town, are there any gaps in the services available? Briefly explain your answer. (Gaps may be due to, but not limited to, a lack of service in the town, a lack of ability to access the services due to cost or opening hours).
Structure
Include a cover page with relevant information.
Use suitable headings and subheadings for the information presented, page numbers should appear on each page of the document ideally in either the header or footer.
All work must be word processed, spell checked, grammatically acceptable, and professional in appearance. This assessment should not be written from a first person, but from a third person perspective. That is, “I, we, my, our” are not acceptable.
All claims are to be supported by suitable and relevant academic references.
Solution
1. Identification of the case study and the discharge needs
The case study of Frank has been chosen, highlighting the efficacy of Australian healthcare services in providing timely and need-based service. As the patient has insulin based diabetes, the discharge information requires the patient's background information to be checked in detail (Australian Commission on SQH, 2020). For Assignment Help, It is to be ensured at first that the follow up care at home must be significant in delivering value-based care for the patient. The family needs to share the diet chart and other essentials that are a must-have for Frank. The case is complicated as he also has a foot ulcer that needs serious intervention from the nurses, therapist and doctors. The doctors will consult with the family members and assess the situation to determine if the home has safety for a speedy recovery and if the situation is risk-free.
What is of the utmost necessity to Frank is the provision of easy and convenient transportation that affects the discharge service. The timely and safe discharge entails proactive measures to plan for the diabetic patient. The well protected discharge also carries the exact documentation procedure before the planning and execution (Australian Commission on SQH, 2020). Social and empathetic support must be given to the patient who needs that assistance more than anything else. Community support is collected before discharging the patient to self-care. Equipment’s, medication and management devices for diabetes management are made available in front of the patient before discharge. The foot-care requirements of Frank are attended to and there is an MDT special foot team in the hospital to save the patient from another degenerating crisis.
2. Identification of the healthcare professionals
Medical Doctors: Medical practitioners and specialists in Australia are registered with the national board and follow the enforced guidelines (Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care, 2022). In the case of Frank, Medical doctors can diagnose the disease with proactive treatment. Injuries, disorders and many other ailments related to diabetes are treated with care with a mission to achieve healthy outcomes. The curative measures are applied to get the treatment done effectively. Significant training is given to the medical practitioners to enable them to be perfect in dealing with a challenging situation.
Pharmacists: These professionals in Australia have a considerable role (PSA, 2021). Frank might be facilitated with a suitable prescription and the pharmacist also supervises dispensing of medication, anti diabetic insulin products and other essential products. They can share the appropriate guidelines and tips for overcoming the dangerous consequences of ulcer induced traits. They might conduct clinical trials for Frank, who might be given ambulatory service.
Nursing professionals service: Value based nursing services will be offered to Frank, who will also get help from the nursing professionals. The nurses are responsible for extending cordial support to the patient in crisis. Disease prevention could be done by the interference of the nurses taking care of Frank and ensuring he gets the exact kind of treatment for his mental and physical needs.
Professional counsellors: The presence of professional counsellors in the Australian Territory of health takes care of the patients' minds. The therapeutic effect might be exerted on Frank in getting holistic care from the counsellors. Ethical practice will enhance the professionals' ability to determine the professional output and the success of the therapy. ACA is in contract with many hospitals supplied with psychotherapists and counsellors. The individual developing diabetes might be prone to psychological downturns and a fragile psyche. At that moment, the help of the counsellors might save the situation.
3. The description of the Australian rural town
The identified rural town is Birdsville in the province of Queensland, full of cultural diversity and indigenous costumes. The number of males present in the regions is 12,545,154 (49.3%) and 12,877,635 (50.7 %) (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2021).
.png)
Figure 1: The demographic information
Source: (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2021).
Population enhancement in the region accounts for the fact that this area is full of natural resources, social amenities and other geographic convenience. According to the 2021 census, the Population size is 110, with a median age of 40. The indigenous status in Australia is 812,728 (3.2 %), and the non-indigenous variety is 1,234,112 (4.9 %) (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2021). Anglican, Catholic and Christian people reside in this small Australian town.
4. The types and hours of operation
In 2021-22, 50% of the patients were visited by doctors in less than 20 minutes. Elective surgeries in Australia are affected by the restriction imposed on the guidelines. The patient must often wait over 365 days to complete the surgery (AIHW, 2023). In Queensland. 85 % of people are seen to have treatment within the clinical time. Waiting time denotes the time measured for the patient from admission until he is ready for surgery. The surge can be done between 7 Am to 7 P.M.
5. Gaps in the Discharge Service
Frank will get all the required care at discharge, yet there might be a few gaps that can affect the healthcare system the communication gaps between the organisational procedures and patient satisfaction. Sometimes, doctors do not disclose the necessary information to the patient's families. The lack of immediate services during the discharge time of the patients upholds the gaps in the services. The lengthy operating hours might hinder the patient from accessing the service. The discharge fees get excessive, letting the patients not be readmitted to the same hospital.
Reference List
.png)
Reports
FPH201 First Peoples Culture, History and Healthcare Report 3 Sample
Assessment Task
Based on the health issue selected in Assessment 2 report, create a digital poster on cultural safety and respectful practice that is directed towards an audience of health professionals in the health promotion and/or health care disciplines.
Please refer to the Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Context
Improving the health status of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples in Australia is a longstanding challenge for health services and governments in Australia. While there have been improvements on some measures of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health status, they have not matched the rapid health gains made in the general population in Australia. The inequality in health status experienced by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples is linked to systemic discrimination. This has been identified as a human rights concern by United Nations committees and acknowledged as such by Australian governments.
This assessment will advance your evidence evaluation, critical analysis and visual presentation skills which may be transferable to poster development and delivery in the professional context. Designing and delivering posters also develop competency in advocacy for health problems.
Instructions
1. Create a digital poster on the health issue selected for the Assessment 2 report, directed towards an audience of health professionals in the health promotion and/or health care disciplines.
2. You are required to clearly define who is the chosen health professional audience in your poster. This could be a health promoter, public health professional, nurse, clinical health practitioner or similar.
3. The focus of this poster is to inform the chosen health professional’s decision making, actions, and best practice when promoting health and/or delivering health care for their community members that relates to a specific health condition
4. The digital poster needs to address the following points:
• Identify and discuss the implications for your chosen health professional’s decision- making and actions for their community members who are at risk of or have the specific health issue.
• Make recommendations for best practice to respond to their community members’ needs as they relate to the specific health issue.
• Promote cultural awareness and respectful practice in day to day health provision and outcomes.
5. Please refer to the attached FPH201_Assessment 3_Poster Guidelines.pdf for more information about how to create a poster.
6. You are strongly advised to read the rubric which is an evaluation guide with criteria for grading your assignment – this will give you a clear picture of what a successful digital poster looks like.
Solution
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the main cause of death and disability in Australia, and “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” groups have a higher CVD risk than non-Indigenous Australians. For assignment help, This digital graphic aims to promote cultural awareness, highlight the value of respect in daily health care delivery, and increase awareness of the consequences of CVD on healthcare professionals who work with these communities.
Implications for Health Professionals
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a serious health issue that disproportionately affects “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians” compared to non-Indigenous Australians. Indigenous Australians have a higher incidence of CVD risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. This is partially attributable to colonization's disruption of traditional lifestyles as well as the continuing consequences of institutional racism and social deprivation. Chronic stress is a major risk factor for CVD and is exacerbated by the historical trauma and ongoing discrimination experienced by Indigenous Australians (Bohren et al. 2020).
Indigenous Australians' CVD risk factors are already increased by their difficulty accessing and receiving adequate healthcare. Delays in diagnosis, inadequate management of chronic illnesses, and greater rates of hospitalisation and CVD mortality can be brought on by problems including geographical separation, barriers to culture, and a lack of care that is culturally safe. The social, cultural, and historical aspects of Indigenous Australians' health must be taken into account by healthcare providers in order to address these inequities. In order to address social determinants of health and increase access to healthcare services, health professionals must also collaborate with Indigenous communities.
Best Practice Recommendations
To care for “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” populations effectively and respectfully, health practitioners must complete cultural safety training. It entails being aware of these communities' distinctive requirements as well as their history, culture, and way of life. With the use of this training, healthcare professionals may identify and address health issues with the help of “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” people (Curtis et al. 2019).
Additionally important to promoting health and preventing CVD is community involvement. To create culturally appropriate health programmes that reflect the values, priorities, and beliefs of “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” communities, health professionals should work in partnership with these groups. Through community ownership and involvement in health programmes, this collaboration may significantly increase those programmes' efficacy.
In order to reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors in “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” communities, access to healthcare services must be improved. Health practitioners should endeavour to remove the obstacles that prevent people from receiving healthcare, such as lengthy wait times, a shortage of staff, and a lack of transportation. They should also take into account the social aspects of health, which include CVD risk factors like poverty, education, and subpar housing. Health practitioners can assist in preventing and managing CVD risk factors in these populations by addressing these variables (Schill & Caxaj, 2019).
Cultural Awareness and Respectful Practice
Particularly when it comes to delivering treatment to “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” people, cultural safety and knowledge are vital in the healthcare industry. The system of healthcare may not always be able to accommodate the patients' specific cultural demands, which health professionals must be aware of. Since cultural, social, and historical factors have a bearing on their patient's health and well-being, it is crucial to provide socially safe and appropriate care. To do this, health professionals must be aware of these influences (Fernando & Bennett, 2019).
Recognising the past oppression of “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” people by the healthcare system and trying to create a more equal and respectful environment is key to addressing imbalances of power in healthcare systems. This entails paying close attention to patients and their families input, appreciating it, and involving them in decisions regarding the patient's care.
This involves being aware of how Australians of “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” descent may differ from non-Indigenous Australians in their cultural practices and beliefs. “The National Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health Worker Association (NATSIHWA)” has produced cultural safety standards that health workers should be aware of in order to guarantee that their practices adhere to cultural safety principles (Oosman et al. 2019).
Conclusion
Health professionals have a critical role to play in tackling the enormous problem of cardiovascular disease in “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” communities. Health professionals can lessen the burden of CVD on this group by putting in place culturally appropriate practices, integrating community members in the prevention and promotion of health programmes, and enhancing access to healthcare services. They can also foster trust among “Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander” peoples and enhance their health outcomes by increasing cultural awareness and respectful behaviour.
Reference
.png)
Case Study
CAP203 Care of The Person with an Acute Illness Case Study Sample
Assessment Task
This assessment is designed to further assess your knowledge of pre-operative nursing care. This assessment follows on from Assessment 1. From your analysis of the case study you will answer a series of questions. Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Context
The Registered Nurse plays an important role in the preparation of a person for surgery. This assessment provides you with the opportunity to apply theory to a clinical scenario. To complete this assessment you will need to apply clinical reasoning processes as you continue to examine the case study from Assessment 1.
You will be required to integrate the information from analysis of the data provided together with your knowledge of pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and legal and ethical principles to the holistic nursing care of a person during the pre-operative period of an acute surgical admission.
You will need to use the following processes from the clinical reasoning cycle to complete the assessment:
- Establish Goals
- Take action
Instructions
To complete this assessment, you will need to examine and analyse the case study presented below and provide responses to the questions asked.
This assessment continues on from Assessment 1 and now requires you to identify the appropriate nursing interventions and specific goals required for the patient problems identified in Assessment 1.
The case study is provided below for your further analysis.
Case study
Maria Romano is a 76 year old woman admitted to the Emergency Department via ambulance. Maria fell when watering her garden and was unable to get up. She was lying in her garden for 3 hours until her daughter came home from work and found her. Maria's medical history includes osteoporosis, glaucoma and she has recently been diagnosed with early dementia. She has no significant surgical history. Maria lives with her daughter Paulina and Paulina's husband, Sam. Maria's current medications include Aspirin 75mgs daily, Alendronate Sodium 10mg orally daily & Latanoprost eye drops to both eyes nocte. She was administered Intravenous Morphine and inhaled Methoxyflurane by the paramedics.
Assessment data:
Airway: patent
Respiratory rate: 18 breaths/min Oxygen saturation: 97% on room air Heart rate: 90 beats/min Blood pressure: 110/70 mmHg Capillary refill: 2 seconds
Right leg shortened and externally rotated Right hip bruised and oedematous
Right foot pink, cool to touch, no paraesthesia or abnormal sensation, pedal pulse present
Alert: orientated to time and place Pain score: 5/10 on rest, 7/10 on movement
Temperature: 35 C
Small laceration to lower left leg
Blood glucose: 9 mmol/L
Intravenous cannula inserted Cephalic vein Left arm
X-rays reveal an Intertrochanteric fracture of the Right femur. Maria is seen by the Orthopaedic surgeon and is scheduled for an Open Reduction and Internal fixation (ORIF) of the fracture. She has been placed on the Emergency Operating List. The Registered Nurse has just administered Intravenous Morphine 2mg and the anaesthetist has been contacted to perform a femoral nerve block. The orthopaedic registrar will visit Maria in the next 10 minutes to gain consent for the surgery. Maria is accompanied by Paulina, who is clearly upset about her mother's hospitalisation. Paulina informs you that she is so worried about how thin Maria is.
She is also concerned that Maria has been falling frequently over the past few months, she purchased a walking frame for Maria but she rarely uses it. You note that Maria is upset that she is going to require surgery. She is worried about her garden and who will water it while she is in hospital.
Questions
- Discuss the Registered Nurse's role regarding the issues related to informed surgical consent, confidentiality and privacy that were identified in Assessment 1 (120 words)
- Develop four short term goals to be achieved in the pre-operative period. These goals should relate to the problems identified in Assessment 1. Discuss who must be involved in the development of these goals (80 words)*
- Discuss the nursing interventions required to meet the identified goals and pre-operative patient problems (from Assessment 1). Ensure that rationales are provided for these interventions (400 words)*
- Answers to Questions 2 & 3 can be presented in a table (see a suggested format below)
.png)
Solution
Registered nurses’ role
In the case of Maria, consent issues arise in terms of accompanying her immediate family, her daughter Paulina, in the surgical process and recovery from her current cognitive condition. For Assignment Help, Maria's current cognitive condition interim of dementia has made informed consent difficult, and her daughter Paulina is also upset about the hospitalisation; thus, there is needed to manage the situation for informed consent. As per Australian healthcare guidelines, informed consent is taken only after giving accurate and relevant information regarding intervention and outcome, as well as ensuring privacy and confidentiality to the individual (Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in healthcare, 2022). The role of the RN here is to delegate and provision the informed consent process and ensure that the patient and immediate family has enough knowledge of the process to give informed consent (Queensland Government, 2022). Also, maintaining privacy and confidentiality related to patient’s problem help in the healing of the problem quickly. Similarly, in the case of Maria, the RN has to follow the same.
Short term goals
- Providing energy to the body
- Increasing haemoglobin in the body before surgery
- Managing pain associated with fracture
- Assuring Maria to avoid preoperative distress
While developing the goals, surgeons, orthopaedics, nutritionists, general physician as well as registered nurses are needed to be involved.
Nursing intervention
.png)
.png)
.png)
References
.png)
Reports
MBA622 Comprehensive Healthcare Strategies Report Sample
Your task
Students are to write a 1500-word report that analyses an industry segment of the Australian Healthcare sector based on the below selection of sectors.
Assessment Description
This assessment provides students with an opportunity to research and analyse a particular healthcare segment to gain an initial insight into the opportunities and challenges that currently exist for organisations that deliver healthcare services in Australia in that segment. Students will present that research and analysis in the form of a formal report which requires students to adhere to a report structure.
Assessment Instructions
Students are to investigate an industry segment of the Australian healthcare sector and examine and evaluate its model of operations and growth over the last ten years. Recommended industry segments include:
- General public hospitals
- General practices
- Private hospitals
- Specialist medical services
- Pathology or diagnostic imaging services
- Dentistry or other related services
- Oncology services
- Mental health services
- Allied healthcare services
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Aged care
However, students are encouraged to determine the scope of their analysis in consultation with their lecturer. Assessments 2 and 3 will build on the initial analysis undertaken in Assessment 1.
Solution
Introduction
The segment selected is aged care services. The objective is to provide an analysis of the segment and provide the ethical issues. Aged care offers help to elderly inhabitants to facilitate them with daily livelihood and other requirements. For Assignment help, The aged care business offers older Australians a variety of diverse services, permitting them to access suitable stages of care when and where they need it as they grow old (Henderson et al., 2017). In conveying aged care facilities to the Australian society, the subdivision is both a fundamental sponsor of the comfort and self-respect of older Australians and a significant supplier to the Australian market. It can comprise aid with daily living, health care, lodging and apparatus such as walking structures or slopes.
Health Industry Segment
The Main Activities of aged care services comprise offering housing room for older people in standard housing care services and offering to house for aged citizens in a retirement community (health.gov.au, 2021).
Government-funded aged care facilities are accessible to qualified citizens. Government-funded aged care facilities comprise in-home help (care in residence), housing care in aged care (nursing) homes, and temporary care for instance respite care. In-house aged care offers support to help the elderly stay free for as long as achievable. It can assist with things such as personal care, transportation, foodstuff, shopping, housework, physio, communal actions, and adjustments to the care home. Housing care in aged care is for elderly citizens who can no longer reside at residence and require continuing aid with daily errands or health care. Temporary care can assist to develop comfort and autonomy or retrieving on their feet after an infirmary stay. It can moreover give the elderly or their carer a break. Aged people can get temporary facilities in their house, an aged care residence or in society (health.gov.au, 2021).
The Australian Government finances:
After-hospital or changeover care – help for up to twelve weeks to assist them to get well after a wait in the infirmary
Temporary curative care – support till eight weeks to assist them to enhance their health and sovereignty
Respite care – help for some hours, days or more to give the elderly or their carer a break (health.gov.au, 2021).
The corporations having the major market share in the Aged Care facilities in Australia comprise Allity Aged Care, Arcare Aged Care, BlueCross and many more.
Ality
Allity is a net of forty-four homes situated throughout Queensland, NSW, Victoria and South Australia with a communal familiarity of their administration that makes it one of the mainly appreciated and reputable suppliers in the Australian aged care business.
Arcare
Arcare is currently one of the mainly pioneering aged care sources in Australia. Their initial aged care home was constructed in 1997 and since then they have developed to thirty-six all through Victoria, Queensland as well as New South Wales. Each house is completely credited by the Australian Aged Care superiority group with facilities counting 24-hour treatment, getting old in place, enduring care, responsive (dementia) care and relief care (healthcare channel. co, 2021).
BlueCross
A foremost private aged care source, BlueCross has been offering a broad variety of supple and receptive aged care facilities throughout the city and local Victoria since 1993. From residential care to in-house support and reprieve care, they are dedicated to serving elderly people subsist the best life likely daily. At present, the company runs thirty-four aged care homes in Victoria, sustaining over twenty-six hundred residents and more than a thousand patrons residing in their homes (Healthcare channel. co, 2021).
Bupa
Bupa is a health and care business dedicated to serving the clientele to survive longer, better, better-off lives. It presents a wide variety of services, counting aged care and retreat, dental, visual, health indemnity, and social safety plans, to progress the wellbeing of all Australians.
Bupa Australia and New Zealand is a division of the Bupa Group. It is a global healthcare corporation. It invests earnings into offering further and improved healthcare for the advantage of present and upcoming clientele around the globe (healthcare channel. co, 2021).
Analytical Tools Application
Porter’s five forces
Threat of entry
New entrants in aged care services brings novelty, new ways of doing things and put force on aged care by lower cost strategy. Increased threat demands for barrier in business for safeguarding the competitive edge of business.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
All most all the corporations in aged care services purchase their raw material like medicine, mask and other supply from several suppliers. Suppliers in central position can reduce the margins of aged care (health.gov.au, 2021).
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Buyers are frequently a demanding group. They want to pay money for the best contributions accessible by paying the least amount price as achievable. This put pressure on aged care services in the long run (Walker and Paliadelis, 2016).
Threat of substitute
When a new invention or service meets a comparable purchaser needs in dissimilar ways, industry abundance suffers. This is the case with aged care companies and it increases the need of understanding customer demands (Hugo et al., 2018). .
Rivalry
If the opposition among the present players in a business is strong then it will coerce down prices and reduce the general profitability of the business. Aged care services function in a very competitive sector. Increased rivalry can decrease the profitability and hamper the business sustainability in the long run.
Industry factors influencing operating conditions
Political
Political factors have an important function in determining the issues that can impact aged care services’ long term productivity in a country. An aged care service operates in Health Care Equipment & Services in many countries and pictures itself to diverse kinds of political environment and political system risks. Government spending can impact the tax policies of aged care and consumers can get advantage of the subsidies.
Economic
The Macro environment factors like – inflation rate, savings rate, interest rate, foreign exchange rate and economic cycle decide the collective insist and collective investment in an market. Economic factor regulate the spending of consumers, for instance high inflation rate or unemployment will reduce the purchasing power of consumer.
Social
Society’s traditions and way of doing things impact the traditions of a business in an environment. Social understanding assists the healthcare professional in understanding the root cause and the expected behaviour towards certain group. For instance, people are shifting towards natural cures and understanding the societal demands can assist in the treatment.
Technological
Technology is fast disrupting various industries across the board. Over the last 5 years the industry has been transforming really fast, adopting digital technology for improving the services to the elderly. Digital tools assist in tracking the health and taking appointments from home which makes the process faster. Technology has also created different devices like hearing aid which increases the performance of aged care services.
Environmental
Aged care services in Australia must check for the climate, waste management and laws regarding the environmental damage. Environmental standards must be complied for operating otherwise heavy penalty can be faced by business. It will lead to loss and defamation of aged care name.
Legal
Copyrights, discrimination law, consumer protection and other laws must be applied as not abiding the rules can damage the reputation and profitability of the firm.
External Industry Challenges, Internal Weakness, and New Trends
The initial main trend experiencing the Australian aged care segment revisits to demographics again, and that is the irrefutable mass of the five million well-built baby boomer group who are currently incoming their retreat years in large figures (Dyer et al., 2020). Actually with approximately one-third of Australia's baby boomers by now past the authorized withdrawal age of sixty-five and about eight per cent of all Australians of sixty-five years and over existing in housing aged care, insist for novel aged care beds will increase by an expected seventy-six thousand places in the subsequent five years (japara.com.au, 2021).
Aged care in Australia is at present a hybrid arrangement, with the federal government partially casing the expenses of residential care lodging for aged and immobilized people who go by a string of eligibility experiments through what is identified as the Aged Care Funding Instrument (ACFI). Since 2016 entire federal government expenditure on aged care and correlated facilities was seventeen billion dollars for about 270,000 citizens (Harrison et al., 2019). With the figure of people in aged care likely to develop exponentially in impending years, the federal administration will locate it ever more hard to support the present stage of care it offers, meaning additional market-based advances will be required. Prosperous Australians with important resources like extremely-valued homes will be likely to shell out the superior out-of-pocket bill for aged care lodging, to finance those who have slight or no resources and thus little means to finance their treatment (Henderson et al., 2016).
Ethical issues
Care for the aged looks like healthcare in some way so that the recognizable values of medicinal ethics – admiration for autonomy, beneficence, and nonmaleficence - would moreover relate to principles in aged care.
There is though some major dissimilarity. The values of medical ethics have appeared mainly in the situation of the healthcare action of patients. For instance, the concentration of admiration for autonomy is on the capability and the liberty of patients to make choices regarding their health care. There are instances when cohorts or family associates might be concerned about those choices; however, the moral focus has been on the patient.
One difference to the conservative centre on autonomy is the additional acknowledgement of respect for self-respect. Related outlines of individual stress can be observed in the growth of planned nationwide codes of ethics for housing aged care.
Conclusion
Australia’s residents are getting older, because of longer life suspense and low fertility rates. The impact of aged population is a boost in the number of Australians wanting help in aged care. In answer, more private company providers are incoming the market, in rivalry with the government-funded as well as not-for-profit providers that have traditionally conquered.
Reference List
.png)
Reports
PUBH6013 Qualitative Research Methods 3A Report Sample
Context:
This assessment involves preparing a report with data analysis/discussion of interviews and a brief presentation. Assessment 3A advances skills in analysing and reporting qualitative data, and reflexivity of practice. Key understanding includes how to generate meaning from qualitative data, how to report the results of qualitative analysis, and how to reflect on one’s own performance to identify strengths and opportunities for growth. The assessment prepares students for an important task common to the public health practitioner role.
Instructions:
Analysis: Use the resources in module six to:
1. Code the data that you collect from your interviewees.
2. Develop themes based on your coding.
3. Report on the themes that you’ve identified, supported by relevant quotes from your interviewees. Report this part in the same style as the results section of a qualitative journal article.
Reflection: reflect on your experience of interviewing and analysing the data. What did you do well, and what did you struggle with? What could you learn to do better?
What did you learn through this experience?
Transcripts: All students MUST submit their interview transcripts as Appendices at the end of their report.
Reports submitted without interview transcripts will not be graded.
Solution
Introduction
Studies shown that risk of experiencing poor mental health issue among international student due to number of factors which contribute for the same, it includes, isolation from the culture and families, financial stress, academic pressures and language barriers (Kim & Kim, 2021). During this Covid-19 period, this impact has increased as people were restrained in the place and is unable to return to their loved ones. For Assignment Help, Considering the severity of the topic, it has been selected for the research. The aim of the research is to evaluate the impact of Covid-19 on the Mental Health of International College Students. To achieve the aim, interview has been conducted and the collected data are analyzed.
Data Analysis
The data collected has been collected through a semi-conducted interview with 4 students. Interview forms to all the four colleagues will be done by Video chat, as during covid 19, travelling is restricted. The students were asked 7 questions (attached in appendix 1) and their answers (attached in appendix 2) are being recorded for the thematic analysis, which helped to analyse the themes that are being made which provide necessary information regarding the study (Song, Zhao and Zhu, 2021). The results of the data collected include Codes that depict various themes with specified quotes to describe the situation of international students during Covid 19.
Results
After going through the interview answers the following Codes have been evaluated.
.png)
.png)
Depression and anxiety
After examining the answers of the interviewers, it has been made out that many of them are having signs of depression and anxiety. Going through all the answers it is sure that the pandemic had brought up severe mental trauma to the students, especially the ones who cannot even meet up with their families (Oswalt et al., 2020). One of the students quoted “I really had depression as being locked in a room alone is very bad, I was unable to make the simple decisions in life and things were getting really hard for me”.
- Students feel like they are being trapped: From the interview answers, it can be made that the students do not feel like they have any kind of freedom. They are always inside a room and cannot go out to do anything they need to be in their rooms and do everything for themselves (Oswalt et al., 2020). Constantly being in the same place for days and days has been making the students feel hopeless and they cannot think rationally.
- Students cannot describe their mental state to their families: It can be said that till now many parents do not understand mental health and which is making it more difficult for the students to deal with their mental health. Many of them even cannot talk about it with their peers due to the fear of being judged (Forbes-Mewett & Sawyer, 2019).
- There is a fear and feeling of anxiety among students: Many students are having anxiety, where they cannot think rationally and start blaming themselves as highlighted in imposter syndrome (Usher, Durkin & Bhullar, 2020). Many students could not even study properly as things were online and they are unable to cope with the change in the study system.
Lack of Mental health Assistance:
As the students are suffering there is a need of letting them go through counselling or get medical help. But as told before students are not comfortable sharing their mental state with their parents and peers due to the taboo that they will be considered as psycho or will be judged (Khan et al., 2020). Many students seek mental health assistance but do not know what to do or where to get it. The interview answers reveal that it is less likely that they are getting the required medical attention. One of the students quoted that “No, my family didn’t hear me out and that was a bit stressful as they were the last people to share what I was going through”.
- Not enough programs to guide the students: The students must get proper counselling or therapy which would help them. However, there are not many programs online or other modes from where they can get the proper information for these. It becomes very important for educational institutions to hold counselling and other informative programs which would guide the students properly (Wang, Hujjaree & Wang, 2020).
- Families do not assist with mental health: It is hard to believe, but still many families do indeed understand mental health or the problems related to it. It is not their fault though as most of them are not very informative about this situation. But mostly even if the students open up to the parents the parents do not provide them with the proper financial or physical assistance which further increases the mental strain (Wu et al., 2020).
Poor or no Coping Mechanisms
As time passes on and people cannot deal with the problem, they are facing they start finding alternatives to deal with it. Many students do stuff that is not good for their health and still uses it as a coping mechanism. While interviewing one student quoted that “I got engrossed in pornographic sites” which is sign of a toxic coping mechanism. They are trying to worry less about how they feel by sticking to things that are not all healthy and are indeed doing more harm to them (Zhai & Du 2020). The students don’t realize that and this impacts their mental health even more.
- Students are trying to overcome their mental issues with a toxic alternative: No one wants to hold onto something painful and people try to avoid that with something which might be harmful. Most of them are found to do illegal kinds of stuff like smoking, drinking, and being at home alone so that they can overcome the trauma (Chirikov et al., 2020).
- They have formed habits that would affect their health in the long run: As discussed above the students have formed toxic habits and these toxic habits would start affecting their health even more. No matter how much they try to overlook their mental stress on the other hand they are degrading their health even more by getting addicted to habits that are not appropriate.
Physical Restrictions and Its Mental Impact:
Students are locked inside homes and have nowhere to go and even many students have been stuck outside their homes as they cannot go back to their parents due to the restrictions forged outside (Talevi et al., 2020). Many students want to get access to open spaces where they can relax but people are only allowed to go for emergency. During the interview one quoted “I really wanted to meet my friends have fun with them” and mostly others also answered something related to meeting friends and families
- Students are not allowed to go outside and that makes their mental state stressful: students want to meet their friends in real life and want to talk to them and that is natural when they are distanced from others it becomes difficult for them to resist themselves from meeting each other (Chen et al., 2020). The more they are stuck inside the more they feel lonely and which increases their stress in them.
- There is no one to talk with or spend time with: Many students have been stuck outside their native home which makes them alone and away from their parents. This creates a huge impact on their mental state as they cannot even go and talk to their parents even if they want. No matter how much connectivity is there a physical presence of people matters to every student (Talevi et al., 2020).
- They want to go out and meet others: It is natural as after all student life is mostly about enjoying the youth. Students need to focus on academics but having friends around helps them to share their thoughts in person have fun and go to different places to hang out. Due to the restrictions, the students cannot meet each other anymore which makes it difficult for them to open up, and hence it seriously affects everyone mentally.
Reflection
While I was performing this study there were a lot of things that I went through and it was a bit stressful on my part as well. No matter what I have been through the same and after going through the answers I may not completely but was relating to them and was able to understand what they might have gone through. I made the interview questions as straight forward I could and was able to get the information I needed from the students I interviewed. I would have preferred a structured interview to a semi-structured one as no matter how much you try to say there is no bias there is a huge chance that the participant didn’t share everything they wanted. I guess next time I would try to make a good bond with the interviewee and make them feel comfortable. I would also try to make sure that the questions should be set in a way that it becomes easier for the interviewee to answer them. Even after all this, I learned a lot from this study. I was cleared that many students like me have gone through the same and there is nothing wrong with feeling low in life. I would always suggest that mental health must be given priority and taken care of.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that the covid-19 has impacted the mental health of many students and especially those who were locked outside their homes away from their families. Mental health should be taken care of properly. Educational institutions should look into it must educate both the parents and the students so that they lead a healthy life.
Reference
.png)
Case Study
MBA623 Healthcare Management Case Study Sample
Your task
Individually, you are required to write a 2000-word analysis based on the annual report provided in MyKBS, under the assessments tab.
Assessment Description
In this assessment, students will be given an opportunity to analyse the environment of healthcare management in Australia and the increasing need to deliver better value to all stakeholders by applying the principles of best practice leadership, team-building and organisational design in a healthcare setting. You will need to demonstrate an understanding of the policy framework and the system dynamics driving change in the healthcare sector and an ability to evaluate the importance of sound financial management for healthcare organisations.
Assessment Instructions
An important skill that a healthcare manager must develop is the ability to analyse a health service or organisation in terms of how well it is meeting its stated mission and objectives. Using the information from the Annual Report that will be provided to you in electronic format, you are to write a formal report that investigates the central organisation in terms of its:
1. Political and policy environment
2. Organisational design and coordination
3. Leadership and teamwork
4. Financial resource utilisation
5. Attitude to, and utilisation of, technology
From your analysis of these elements, you will attempt to identify areas where improvements may be sought. You will justify your arguments for why these improvements should be introduced and present them in the form of detailed recommendations to the Chief Executive and the Board. You will undertake whatever additional research is required to give you a better understanding of the organisation and its activities and any research that is needed for you to formulate your recommendations. This research will form the basis of the Reference List of your report. The primary sources for research should be relevant published academic journals and texts but other sources of information such as newspapers, magazines and reports may also be of value. As stated earlier, the format for this assessment is a formal report. If you have not undertaken a task like this before, your research would also include how to structure and present information in a report format. An Executive Summary is considered to be a key component of a formal report and in this instance is included in the word count for this assessment.
Solution
Political and Policy Environment
The political stability in Australia is quite good, as the organisations operating in different industries including the healthcare sector are provided with proper support and resources to establish the overall healthcare segment in the country. For Assignment Help, The legal acts imposed by the political organisations emphasise on the healthcare development all across the country, and on the grounds of this organisations such as Calvary set up their internal policies integrating them in their SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures). Calvary Health Care Bethlehem continues to adhere with the policies imposed by the government on the basis on competitive neutrality. The organisation revised its healthcare policy of being culturally responsive towards the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Community by leading on to a new direction acknowledging the policies of government (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021). Since 2019 August, an important body of work has been initiated and carried out in order to screen for the cognition alterations alongside the delirium on the ward. The execution was directed by a new policy alongside a program of education and learning. The ongoing screening education for the new medical workers has been integrated in their orientation program and the results concerning the same are presented regularly during the meeting with medical staffs (Dixit and Sambasivan, 2018). Apart from this, the significant accounting policies of the organisation comprise of taxation policy, goods and services tax, income recognition, and revenue recognition policy. All these policies are accounted when preparing the financial report. Out of these, the key changes in company’s accounting policy relates to the timing of the revenue recognition from applying the AASB 15 under different streams of revenue. The auditing group evaluate the appropriateness of the all these policies used by the organisation alongside its reasonableness comprising of the accounting projections, as well as related disclosures made the board of directors (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021). However, there are certain policies concerning the welfare of the public that are not adopted as of now, but might turn out to be an essential policy in the future.
Organisational Design and Coordination
In an organisation such a Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, it is of paramount importance to have a proper strategy in place concerning organisational design and coordination. The efficient functioning of a health service is influenced by the organisational structures alongside the coordination. The organisation structure of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem comprises of arrangements including responsibilities, authority, information and knowledge sharing, and result. The organisational design of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem is a formal and directed process used for incorporating people, technologies, and information (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021). This serves as a key structural component, which makes it feasible for the organisation in maximising the value through aligning their hierarchical design with the overall vision and mission of the company. In a healthcare setup such as Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, the importance of coordination among the different departments needs to be quite high and effective, as it is directly related to the outcome of a patient. It is of utmost importance for the healthcare managers to ensure smooth and hassle-free coordination in order to reap fruitful results by providing a thorough treatment to their patients.
At the micro-level of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, medical professionals are grouped together in order to work in units having a mutual supervisor. The structure of any organisation is quite complex by nature, and there is a high possibility of problems taking place every now and then accompanying the company benefits indirectly (Sandhu, 2019). Every company design has certain dysfunctional as well as functional characteristics. As per the structural contingency theory, it is of importance to consider the complex trade-offs within the design of organisation. Integration and differentiation are two vital components in this case. Integration includes the coordination of activities between the healthcare units, comprising of conflict management resulting in better patient outcomes (Heath et al., 2017). On the other hand, in differentiation every part of the company is managed in order to meet a specific need of speciality work in the healthcare setup. From the application of this theory in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, it can be stated that the organisation somewhat adopts and follows a hybrid approach to carry out their operations. Although it is of extreme importance for Calvary Health Care Bethlehem to have their total focus on better patient outcomes, which they do, but in certain instances, the organisation also needs to use the differentiation approach in order to meet a specific need of a specific group of patients (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021).
At the macro-level of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, there is a significant interdependence accounting for interconnectedness of work, task uncertainty, size, sharing of resources, and so on. Thus, the organisation needs to have a structural approach in place for ensuring a smooth coordination concerning the hierarchy, procedures and rules, planning and objective setting, lateral relations, and vertical information system. In this context, the organisation makes use of a program organisation design. In this design, the organisation standardises the work processes by using rules, regulations, plans, schedules, policies, procedures, and protocols. This design also allows the organisation in standardisation of skills with specification of skills or training needed to carry out the work, as well as standardisation of output by specifying the form of intermediate outcomes of work (Ali et al., 2017).
Leadership and Teamwork
Leadership is a vital aspect for any organisation operating in any industry. In this context, leaders entail the frontline managers directly supervising the care providers, middle managers accountable for their respective departments, and the top managers such as CEO for managing the entire organisation (Fletcher et al., 2019). The leaders of Calvary Health Care Bethlehemfocus of strategic way of solving issues by incorporating strategic function in their leadership constituting of objectives with subsequent action for achieving the same. As known, the internal system of any healthcare organisation involves numerous complexities giving rise of problems. The 8-step strategic problem-solving process can be used, as it provides an integrated perspective towards a problem resolution, and can provide fruitful results. Besides this, the leaders of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem adopt a transformational leadership skill, as for implementing a certain change needs clinical and administrative leadership (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021). Alongside this, sustaining the leadership in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem is also quite effective, as they have a proper strategy in place for succession planning and self-care. The members of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem are highly motivated for the upcoming initiatives being brought to the table for development of better care for the patients. Furthermore, the members with managerial roles in the organisation are clinical with communication, as for making a team to get a job done efficiently it is imperative. It is often seen that due to lack of communication between the speciality groups led to unfortunate outcomes for the patient.
Moreover, teamwork is another essential component in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem led by leaders will excellent leadership skills. The teams and units working with each other provided with a defined purpose, composition, structure, and specific processes. The teams work as a formal group within the organisation, which is task-oriented with a specific purpose. The teams operate staying in the organisational context and interact with organisational sub units to ensure proper medication of the patients. The work teams of the organisation collaborate for providing a specific service, the support teams provide support for the primary functions, the parallel teams include individuals serving within the work teams also play a vital role in assisting, the project teams produce one-time outputs, and management teams provide the overall direction having a purpose (Sfantou et al., 2017). All these departments conducting a set of activities hold a value for the stakeholders including themselves, as well as the patients, their family, other associated medical firms, and so on.
Financial Resource Utilisation
The Australian government spent an amount of 185 AUD on the health services and goods during 2017-2018 (Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, 2021). However, the real financial problem existing is that the mix of funding alongside the responsibility of the service delivery amid the state or territory governments and the commonwealth. This discrepancy has led to shifting of costs and gross inefficiencies, alongside poor service integration. As per the financial reports of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem, it can be said that the organisation has a well-managed flow of financial resources with apt use for treating their patients with utmost care and medication (Edney et al., 2018). The rise of globalisation has influenced the overall healthcare sector due to which the organisation was required to make use of their financial resources not only for people of Australia, but also tying up with healthcare institutions in other countries to create a positive relation, which can pay off during the need of the moment. Besides, it has been identified that some of the medical expenses this company receives from funding from the Victorian department of health due to its name in the denominational hospital list. It is a great help in managing both time and financial resources.
Attitude To and Utilisation of Technology
Calvary Health Care Bethlehem each year works on interdisciplinary teams for collaborating them for developing the assistive technology resources for improving patient quality of life. Current important updates involve developing modified eye gazing systems, interaction processes as well as environmental management teams for patients’ wheelchairs. New planning devices have additionally brought to enable patients for driving wheelchairs along with management of other devices through a single change during hand movements are impaired. Change management options have developed patients’ skills for using mainstream technologies like iPADS, mobile phones, and tables. Permission to these devices on wheelchairs permitted effective selections and management over how they interact, move and work relaxingly (Poojitha, 2018).
The Vitro application has been applied in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem in 6 months end-to-end offering the healthcare company with an entirely paperless process in which all medical information was being stored electronically. This project unit that involved all medical employees from both the Calvary Health Care Bethlehem team and Vitro group have worked collaboratively for identifying as well as reviewing the present paper forms of that total 197. At the time of reviewing procedure this became evident that streamlining as well as effectiveness can be made, the opportunities was taken to evaluate the needs of Calvary Health Care Bethlehem that outcomes in the minimization to 67 forms that would be converted in Vitro applications.
Recommendations for Improvements
Focus on better technologies should be one of the current solutions for Calvary Health Care Bethlehem as well as overall healthcare industry in 2021. Applying the online data as well as modern interaction tools efficiently will be needed for the future of the care unit in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem. Technology will act as a role in around each area of health, involving health record keeping. It can be said that developing an online health recording process in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem similar to My Heath Record. Having this type of portal and record keeping app will help the company in providing and accessing major health data of all the patients (both old and new) involving any past allergies, health conditions as well as treatments, medicine history along with scanning reports can be evaluated by one system in the entire Calvary Health Care Bethlehem. On the other hand, it can be said that this type of change in the company will also help the medical practitioners, doctors, health care workers in this company working in remote, regional areas. Online technology will ensure this probable for the medical care workers and doctors in Calvary Health Care Bethlehem to have video appointments with all the patients who cannot visit to the centres or Calvary Health Care Bethlehem hospital for appointment with experts. This type of solution is particularly relevant and impact in the current COVID-19 pandemic.
Reference List
.png)
Research
PUBH6007 Program Design, Implementation and Evaluation Report Sample
Context:
This assignment help is on Needs Assessment in public health, and you have 2 options (choose one) for submission (it is an individual assignment in report structure).
Instructions:
Option 1: Choose a setting such as a community, health service (e.g. hospital, primary health care service) or neighbourhood you know well in Australia ( Examples (not limited to) are:
(1) a particular community (for example, indigenous population, women etc)
(2) a health service (such as hospital, primary health care service, GP practices etc)
(3) a neighbourhood that you know well (where you currently live in)
How to proceed with Option 1:
STEP 1: A discussion of how you would assess different types of needs (normative, expressed, comparative, felt, etc.) and how you would prioritise the findings, justifying your choices. For this purpose, you would either know of/be in the situation in reality first. Then, you would have to undertake rigorous literature review to understand different types of needs assessment and consider alternative views to justify the choices for this context.
STEP 2: Any potential challenges for your needs assessment and how you would address them. This could be relating to policy, contextual issues or others.
STEP 3: A SWOT analysis, where you identify the Strengths, Weaknesses Opportunities and Threats of your organisation or program.
STEP 4: A determination of program priorities, based upon your needs assessment
In your needs assessment, you may determine multiple programs priorities – justify why you would choose the priorities you have identified. Are there any population groups that would benefit best from your program? Mention these, justify.
AN EXAMPLE
Let us take a GP practice in a specific growing suburb in Melbourne as a context. The waiting list seem to be increasing as many patients are approaching the GP and there are no other practices close by. It could also be that much of the population is working, and they need after hours service. If you are part of this situation ( working in the practice or living in the suburb) – you would have an idea as to what type of need had risen. From that point, think about what type of needs assessment is required (via comparing few types of needs assessment from literature review), and justify your choice. Then, we are looking at potential challenges to really confirm this need, through the needs assessment. Subsequently, look at the SWOT analysis. There may be many GPs in the practice (Strength), but, the hours may not suit the working population in the suburb (weakness). The threat may be that due to non suitable opening hours or waiting list, the population may begin to move to another closer suburb (where there are more GPs open late) which then (threatens) the practice. And the (opportunity) is there for this GP practice to open for more hours or have shift based GPs for different hours, keeping the practice open later. This is a simple SWOT and there may be many more.
In this situation, you would be looking at a program design that allows the GPs to open later hours or shifts, which cater to the mainly working population, young families in the new suburb/neighbourhood. You may prioritise working women, kids or mainly working men as population groups that would best benefit.
Solution
Introduction
Primary healthcare service is the selected community for undertaking the present report into consideration. In order to create a detailed understanding about the needs of principals and community analysis, the priorities placed by primary healthcare service in particular emphasis upon aboriginal population and indigenous groups within Australia needs to be revealed. The present discussion primarily explores around the different norms, expressions and comparisons are needed to be prioritised and applied upon aboriginal population of Australian primary healthcare service community. The reality oriented understanding helps to critically evaluate the possible challenges Faced in the operations performed by GP, nurses and professional health workers to govern their role across the primary healthcare services (Mistry, Harris & Harris, 2021). The SWOT analysis enables the internal potentials, areas of shortcomings, possibilities of new scope and limitations can be understood. As the organizations perform forming a community within the primary healthcare services, the prioritization of multiple service areas acting upon the large population interest benefits catering to health requirements of Australian people get justified.
Different normative needs and findings justifying the choice of primary healthcare in indigenous group aboriginal population community Australia
Primary healthcare within Australia create the initial point of contact with the people of Australia to attend care, comfort and health treatment. In case of both chronic as well as acute conditions proper management is taken up as a responsibility with the quality of professional intervention are indicated towards multiple healthcare domains. President under the National Safety and quality primary healthcare NSQPH creates the standard as a committee of primary care within Australia to determine highly developed effectiveness to treat patients (Kim et al. 2021). Under the national general practice hack reduction scheme, Australian indigenous groups and aboriginal community tried to be creating a feasible Raj Kumar optimistic normative layout for any incident reported by patients.
The conduct taken up by NSQPH develops a standard during October 2020 to a span of January 2021. All the issues faced by aboriginal population community Australia on a health hazard level hard constructively handled to create safe environment and proper cure through the preliminary consolidation program. There are multiple face to face workshops established to cater to patient requirements on a subjective level. The online free counselling, Internet based survey and consumer oriented service approach helped feedback retriever loop to analyze and enhance their quality in terms of primary healthcare provision (Measham & Turnbull, 2021). With a total capacity of 211 Primary Health care providers more than 105 feedbacks were received from the care users. Search consultations carried out through online interface facilitate during ongoing pandemic situation and lockdown related stress factors to be addressed for clients in indigenous groups of Australia.
Challenges addressed by the primary healthcare services among indigenous groups aboriginal community in Australia
The health department of Australian government takes specific focus upon the challenges faced by primary healthcare services Australia. Taking the policy regulations into consideration, the fragmentation taking place in case of Commonwealth as well as state fund services tend to lead to adverse challenges. The complexities get even more critical when policy levied by the government create restriction upon funding and arrangements of reported cases. There are increasing feedbacks received regarding poor coordination across the primary healthcare service planning and improper execution and delivery of welfare and social care services. It is directing towards misdistribution effects which hinder the workforce with shortages and inadequacy in optimum resources to handle increasing demand for health care requirement (Day et al. 2021). As the life expectancy across the aboriginal population segment is quite low especially for the females, tremendous challenges are faced by the indigenous Australian people on acquiring primary healthcare services.
It is the remote locations of various residential zones of minorities and health treatment inaccessibility which creates challenge for a GP to reach care assistance that takes 4.5 times more travel time than that of care facilities in the major cities. The disability rate among aboriginal population segments in Australians is ineffectually handled without a balanced proportion from primary healthcare policy regulation execution. This depicts a challenge where expectation and actual results revealed a large gap. There is additional health deficits which are incapacitated by the primary healthcare to manage especially with the exceptional burdening in case of chronic disease cases reported across aboriginal population community Australia. The ratio of one in every for indigenous Australian adults getting detected with obesity creates an alarming clinical impact posing challenge up on the overall requirement of primary healthcare which is implying significant deficit as they are considered minority and deprived groups there (Alexander et al. 2021). The rapid aging population in indigenous Australia community is another health hazard causing agent which is disproportionately managed with proper quality of care from primary healthcare services.
SWOT Analysis of Primary Healthcare in Australia
Strength -
Primary healthcare Australia is one of the largest providers of professional level public health care and non government sector. Both acute as well as chronic health crisis is managed by exceptionally talented and skilled doctors, GP, nurses and management Staffs. It is with the incorporation of unique person centred approach that care provision is provided to care seekers building up community feeling for all Australians (Ng et al. 2021). The general practitioners encompass the nurses, community workers, social healthcare workers and professional doctors. The midwife, dentists, pharmacists, health professional and specially trained aboriginal health workers also constitute the primary healthcare service setting. With adequate health promotion, prevention of diseases and rapid spread of chronic ailments like diabetes, fatigue and mental diseases I tried to be made aware to people to seek proper professional treatment under Primary Health care management.
Weaknesses -
The primary healthcare is dispersed into multiple segments which create confusion and chaos while handling increased demand of care services. The advancement in technologies incorporated within primary healthcare services are incapacitated by different professionals to be handled with proper expertise and skill. Lack of training and development progress with continued assessment creates sense of inadequacy of resources which makes the overall health sector suffer across Australian region (Cornwall, 2014). The exceptional rise in health deficit and acute conditions like sexual disorders, drug abuse, extreme alcoholism, cardiovascular diseases, diabetic problems, asthma, oral health, obesity, cancer and mental health deterioration across different segments of Australian population further contributes to the primary healthcare challenges.
Opportunities-
Primary healthcare service across Australia needs to segment there cares program operation so that the multispecialty features are possible to undertake the issues on the basis of separate department. Teams need to be channelized into specialty oriented services rather than shuffling duties to overlap across departments with the same operator and service provider (Balasooriya, Bandara & Rohde, 2021). The social determinants that impede health condition across Australia needs to become the survey assessment monitoring factor for analysing a sustainable and effective health service provision from primary healthcare systems.
Threats -
During the current pandemic let through COVID -19 situations created imbalance in demand and supply of medical care services from primary healthcare service operations across indigenous Australians. Connecting with stakeholders and getting regular supplies of normal treatment other than COVID word hampered and carried out on a irregular nature which challenged the health conditions of overall Australian aboriginal population community regions. The National Health priorities directed towards COVID management necessarily created a significant neglect towards other issues where the National Safety and quality primary healthcare NSQPH Norms and policy standards got hindered (Druce et al. 2021). Hospital bed unavailability and rural service network inefficiency due to technological lag led to threats upon lives of people across Australia especially those living in remote locations particularly the aboriginal community people.
Program priority created by primary healthcare services Australia towards aboriginal population segment
Patient care and safety of residents across Australia is the fundamental responsibility of primary healthcare service (Halcomb et al. 2020). People living in the rural areas and remote locations particularly the aboriginal trade community who are deprived of adequate health facility are tried to become the new focus group of Australian Primary Health service community. With the National Safety And Quality Primary Healthcare Standard along with national general practice accreditation scheme the committee tries to establish review and survey programs to analyze the general health statistics like mental health, physical general conditions like blood pressure, heart rate, cholesterol, diabetic level and other ailments. This enables rapid detection and the primary healthcare nurse, GP and other skilled professionals to cater to aboriginals at a fast rate possible.
Spreading the service operation even across remote locations and focusing more upon infrastructural development with latest clinical equipments for reaching faster solution and care facilities to reduce hazards towards aboriginals as a neglected sector of Australia can help build new opportunities of community healthcare. Aspects like housing education, infrastructure, employment and transport also needs to be simultaneously exploited for providing enhanced quality of health services across Australian people.
Conclusion
It is the great enthusiasm governed by policy regulation that enables the Primary Health service providers to operate even in rural along with remote regions to serve the aboriginal segment of population across Australia. Special service training towards older people, child health and maternity issues along with young health and eradication of drug abuse and alcoholism is also a part of primary healthcare support program. The GP qualification and the nurse services are incapable of creating a balance between demand and supply curve in terms of care facilities.
The primary care committee performed under directives of Australian government to handle acute as well as chronic were incapable of following the elements regulatory policy standards which made the patient safety and immediate help to risk prone diseases other than COVID to be handled with deficiency and lack of facility.
References
.png)
Reports
PUBH6013 Qualitative Research Methods Report Sample
Context:
This assessment is prescribed to advance literature searching, critical analysis, research question development, research planning skills, and reflexivity as a researcher. This assessment involves developing a research question, preparing interview and probe questions, identifying four people that you can interview on this topic (for example, your family or friends, colleagues), and reflecting on your motivation and justification of your research proposal.
It assesses the key understanding necessary for conceptualising and developing a qualitative research proposal, which will prepare you for the use of qualitative methods in research and evaluation as a public health practitioner. There are three steps to completing this assignment.
Instructions:
Step 1:
Develop a research question (similar to the ones you have explored throughout this subject) that supports qualitative exploration of a topic of your choice. Review the materials from Module 1 to familiarise yourself with the scope and purpose of qualitative research.
Warning: Topics must be low risk. This means that the topic should not be likely to cause distress or humiliation, and should not focus on vulnerable groups (such as children or people with a disability). You should discuss with your learning facilitator if you are unsure whether your topic is suitable.
Step 2:
Write 6-8 interview questions that:
• Focus on obtaining information that will help you to answer your research question
• Are qualitative (focusing on experience, opinion, values, perceptions etc) in nature
• Comply with best practice principles for interview question design (Module 4) Obtain feedback from 2 (two) people to refine and improve your questions, and keep records of this feedback for submission with the project proposal.
Step 3:
Write a research proposal for your qualitative project. You must include:
• A brief literature review to summarise the existing knowledge in this space, and justify your proposed project.
• Your research question and the knowledge gap that it will address.
• A summary of the key elements of the methodology that you think would be the most appropriate methodology to use to explore your research question (ie grounded theory, phenomenology etc), and why it is appropriate for exploring your research question.
• Your methods, including how you will select your participants (in this case, four people whom you already know) and your interview process.
• Your interview questions.
• A personal reflection on your motivation for exploring this research question, any ethical or cultural considerations for your project, and anything that could create a risk of bias in your data (ie interviewing friends).
• An appendix containing records of the feedback received on your interview questions (such as a copy of the interview questions with tracked changes).
• Your assessment submission must address all of these points
Solution
Introduction
The likelihood of diabetes is quite common among the indigenous community of Australia. The key reason behind the diseases and its major consequences on the life of community members are still considered as a key concern (Titmuss et al., 2019). For Assignment Help Thus the topic holds a significant relevance.
The project proposal details a brief background on the topic of discussion with the indication of methodology and the process of selecting participants for the current project.
Literature review
Diabetes affects Indigenous peoples around the world for a variety of reasons, but one unifying connection is a shared history of colonisation. Colonisation has been identified by the World Health Organisation as the most major social factor of indigenous peoples' health across the world. Many countries, especially those with advanced statistics systems, have health inequalities between Indigenous and non-Indigenous people. The International Group for Indigenous Health Measurement was formed in response to the need to enhance the evaluation and comprehension of Indigenous health inequalities (Crowshoe et al., 2018). The group is made up of Indigenous and non-Indigenous peoples, the ruling party and non-governmental organisations, experts, and healthcare providers. Health and data statistics are critical for finding and analysing inequities, tracking progress between and within groups, and, eventually, lowering health burdens. However, if the aim of health equality is to be accomplished, information is needed to show that these discrepancies are not merely a third-world concern and that Native peoples in developed countries such as Australia, the USA, Canada, and New Zealand have much worse health outcomes. Consequently, medical information for Indigenous peoples in these countries is inaccurate and incomplete, as are statistics on the underlying social, financial, social, and political variables. The IGIHM was established in 2005 and gathers together a wide group of individuals, including both Indigenous and non-Indigenous peoples, governmental and non-governmental organisations, statisticians, academics, and healthcare professionals (Yashadhana et al., 2020) The declared goals of the IGIHM are to inform people of the gaps in health statistics for Indigenous populations in the four nations and to cooperate worldwide on improved procedures and policies that will greatly boost Indigenous health.
The difference in the health of Torres Strait Slander Australians, Aboriginal Australian, and non-indigenous Australians is widely documented and several policies and programmes are presently striving to close the gap. Even after all these efforts, Indigenous Australians have a ten to eleven year lower mortality rate than non-Indigenous Australians, with 65 percent of fatalities occurring before the age of 65, compared with 20 per cent in the non-Indigenous community (Kirkham et al., 2017). The majority of the difference in life expectancy is due to diabetes and cardiovascular disease illnesses, which are linked to greater hospital admission and mortality rates. Indigenous individuals were 1.6–2.5 times more likely than non-Indigenous Australians to be hospitalised for heart disease in 2013, based on their age, and Indigenous adults are six times more probable to die from diabetes than non-Indigenous Australians. Indigenous adolescents who have type 2 diabetes are ten times more likely to be admitted to hospitals than non-Indigenous adolescents. While hospitalisation is a poor estimate of the prevalence rate of diabetes-related problems in the population, they do show that the burden of disease linked with a diabetes diagnosis is higher in the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities (Zimmet, 2017). Furthermore, the development of cardiovascular disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and heart disease occurs at a younger age among Indigenous Australians than that in non-Indigenous Australians and the occurrence of these conditions is on the rise among Indigenous kids. Nonetheless, the incidence of diabetes among indigenous youths is unknown due to a lack of national statistics (Koye et al., 2019). Indigenous Australians have greater rates of youth-onset type 2 diabetes than the general population, according to studies from several jurisdictions. While there has been an increased incidence of new diagnoses among all Australian kids over the last 20 years, Indigenous younger folks have seen a significantly bigger increase. To determine the exact incidence and disease burden of type 2 diabetes among Indigenous young people, physicians and scientists from all over Australia have collaborated.
Research question
The main research question is as follows
What are the causes and effects of high diabetes occurrence among Australian indigenous communities?
Knowledge gap
The topic of discussion has high importance since it attempts to promote the good health of the people of Australian indigenous community. However, there is a limited discussion about the spread of awareness which the current study will address. Awareness and proper learning about the diseases is necessary for a consistent recovery.
Summary of methodology
Here, the project will be conducted using a primary qualitative approach. The researcher will arrange an interview session for the participants. Here no secondary approach will be considered since the researcher wants to make a direct interaction with the participants for a better understanding of the topic. Primary approach is a key methodology used in projects which influence the data collection technique. In a primary mode of data collection, raw data, facts or information is gathered which justifies the relevance and authenticity of the information. Collecting information about the occurrence of diabetes among the Australian native communities from a secondary approach might not be relevant and current. Although it requires limited time and researchers get a sequential and organised form of data, the criteria covered by other researchers may not fulfil the requirement of the current study. This is why the primary approach is appropriate in this present context. Besides, the researcher will also select a qualitative approach through an interview session. With the interview session, it is possible to get an elaborative point of view from the respondents (Snyder, 2019). This approach is better and suitable compared to a quantitative approach which comprises numerical and objective information or facts which will not be suitable to discuss the matter of diabetes likelihood among indigenous people of Australia. This approach will thoroughly help the researcher to explore the framed research questions. The current project will be based on grounded theory in this regard since it will let the researcher develop a perception based on the collected response and related principles.
The interview will be conducted through a face-to-face session for a better assessment of the participant's expressions and their attitude. The researcher will not be able to meet the criteria in an online interview session. Moreover, the questions will be open-ended to give a scope to participants to present their point of view and elaborate their knowledge on asked questions. Close-ended questionnaires would have restricted the researcher to obtain subjective responses or answers which will not be suitable for this present study. Here, researchers will consider a non-probabilistic stratified form of sampling that will be used to select the 4 indigenous workers as the key participants of the interview session. Here, since all the known indigenous workers will be allowed to take part in the session, the mentioned sampling techniques will be suitable. Selecting simple random probability sampling will not help the researcher to get in-depth information about the health condition and extent of diabetes in the entire community.
Interview Questions
1: What is your lifestyle in terms of the work that you do and the diet which you consume on a daily basis?
2: Do you feel difficulty in accessing health care facilities in your locality?
3: Do you feel that the significant prevalence of diabetes has a negative impact on both the physical and mental health of people and the family? Explain your point of view?
4: What are the general measures that you will take to prohibit the occurrence of diabetes occurrence from your community?
5: What steps have been taken by your government to create awareness about diabetes occurrence?
6: How often do you get a routine check-up for yourself and your family members?
7: Is diabetes genetic diseases which has been running in your family over time or do you feel this is due to unhealthy consumption of food with high sugar content?
Personal reflection
The topic in research for this article is the assessment of the occurrence of diabetes among indigenous communities. While researching questions related to the matter of discussion, I have been motivated to the most since the prevalence of diabetes amongst the indigenous communities across the world has been concerning. While measures of prevalence and incidence are useful in determining the magnitude of a disease's burden in society, they are insufficient in determining the individual's risk viewpoint and I wanted to get into depth of it. For this research, I am committed to doing right by the people whom I will be interviewing; ensuring every type of confidentiality is maintained. I will make sure they get fair, honest and honourable treatment from my end apart from the feeling of security. It is necessary for them to feel comfortable given they belong to a completely different culture. After that, it will ensure that there is no biased interview happening even if the individual I’m interviewing turns out to be my colleague. Any kind of bias can harm the outcome for the project. There will be full transparency maintained between the people I will be interviewing, researching and my research team. I will abide by every ethical conduct and make sure things are in order.
Conclusion
Project proposal and a strategic plan form the base of a project. It needs to be framed with proper planning. The main aspect of a project proposal is the specification of the methodology which consists of the approach, methods and data collection techniques that researchers will consider while conducting the project or the study. It also includes the research question that will be focused at the foremost level. Here, the researcher will be focused on understanding the occurrence of diabetes among the native community people of Australia. Thus, the methods and the techniques have been specified accordingly.
References
.png)
Case Study
PUBH6000 Social Determinants of Health Case Study Sample
Context
The social determinants of health play a major role toward disease, health and wellbeing of the community. This assessment is aimed at consolidating students understanding of how the social determinants of health affect the health outcomes of a population. The assessment gives you an opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of the fundamentals of public health practice and apply theoretical and conceptual health intervention frameworks to analyse the health of a population. This assessment task is also designed to further develop your ability to reflect on your practice. As a public health practitioner, it is important to develop your ability to reflect on personal experiences, feedback and assess your own capabilities. This practice of reflexivity supports personal and professional growth.
Task Summary
In this assessment you are required to read a case scenario provided by your Learning Facilitator, using critical thinking skills develop a report demonstrating your ability to apply theory into practice. Your report should be 1500 words (+/- 10%) in length. In addition to submitting assessment 2 Part A, you are required to provide another 200 words of learning journal demonstrating your ability to reflect on personal experiences and challenges working to complete Assessment 2 Part A . Use the assessment template provided to develop this assessment.
The scenario will be provided separately.
Please refer to the Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Instructions
1. Read carefully over the given scenario provided by your Learning Facilitator.
2. Research health issues and relevant social determinants of health that would influence health outcomes of the population in the given scenario
3. Use the Ecological Model to analyse factors relevant to the scenario that influence health behaviours and health outcomes of the population in the following perspectives.
• Intrapersonal level
• Interpersonal level
• Community level
4. Reflect on your thoughts/activities and challenges in preparing the assessment in the Learning Journal such as information provided to complete the assessment, class activities, searches for further information and references.
Solution
Introduction
The key focus of the assignment is on the disability system in Australia and the impact of relevant social determinants on the health outcome of the Australian population. Accourding to The Assignment Helpline, The case study of a disabled Leo has been used to refer to the various challenges disabled people in Australia might go through although the theoretical perspective is mostly generalized health system. The ecological model consisting of intrapersonal, interpersonal and community level factors have been used to determine the influence on health behaviours and health outcomes. Reflective summary of the experience regarding the assignment has also been provided as learning journal at the end.
Context of Potential Health Issue Among The Population
The survey report of Disability, Ageing and Carers in 2009 revealed that 18.5% of the Australian population or about 4 million people are disabled. In addition to this, another 21% is affected by long-term health condition but is not restricted from everyday activities. 87% of the people with reported disability suffer from specific limitation that restricts them from performing mobility, communication and self-care activities("About People with Disability in Australia | Department of Social Services, Australian Government", 2021). Although there are other health issues that is covered under the entire healthcare system of Australia, the key focus in the case study scenario is disabled people with Leo being one of them. It is quite difficult to define disability but from a general perspective it can be referred to the condition that can hinder a person from their ability to carry out day to day activities (Emerson & Hatton, 2014). However, there are varied degrees to which the disability can hinder a person ranging from mild like needing to wear reading glasses to severe where there is brain injury. According to the Report on Government Services 2002 the three core activities that form the basis of disability includes self-care, mobility and communication. Based on these activities, the ABS Survey of Disability, Ageing and Carers defines 4 levels of disability namely mild, moderate, severe and profound.
There are several issues that people with disabilities have to face and are more likely to experience than people without any disability. Issues like social isolation and fewer opportunities to participate in community life are more probable for disabled people ("Face the facts: Disability Rights | Australian Human Rights Commission", 2021). Moreover, such people are also more subject to living in poor quality, experience poverty, acquire low levels of education and obtain insecure housing. Studies show that some of the greatest causes of disability include mental illness and mental health problems which also diminishes their quality of life and reduce productivity levels. In the Australian population, workforce participation of disabled people is only 54% as compared to 83% of non-disable people ("Disability Support and Services in Australia – Parliament of Australia", 2021). Also, among the OECD countries, Australia has the lowest rank for the relative income of disabled people. Although the Australian government has planned on making all public transport accessible to disable people by 2022, reports show that about 1.2 million disabled people are still struggling to use them properly ("About People with Disability in Australia | Department of Social Services, Australian Government", 2021). Young people with disabilities like cognitive impairment in Australia are six times likely to end up in prison as compared to their non-disable counterpart. On the other hand, 90% of women with intellectual disabilities are subject to sexual abuse where more than a quarter of all disabled people are sexually assaulted in Australia("About People with Disability in Australia | Department of Social Services, Australian Government", 2021).
Social Determinants of Health
The social determinants of health issue refer to the disadvantages that contribute to their poor health and disabled people and their carers are the most disadvantageous group in Australia. The ecological model has been used for critical analysis of the multiple levels of influence on health behaviours of the disabled people in Australia. These include intrapersonal or individual factors, interpersonal factors and community factors ("Ecological Models - Rural Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Toolkit", 2021).
Intrapersonal/ Individual Factors:
The intrapersonal factors influence behaviour such as personality, beliefs, knowledge and attitude and are directly impactful on the individual with the disability. The social determinant that impact on an intrapersonal level is education. The more people participate in the workforce, they acquire higher levels of education and as a result of this achieve better health. Regardless of the impairment types, people with disability have on average lower levels of education as compared to other non-disabled population. Only 24% of the disabled people have completed year 12 or equivalent in terms of educational qualification which quite low than non-disabled people with 46% completing the same educational level ("Social Determinants of Health - Integrated care", 2021).
The National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) provided support through local provider in town for Leo as part of their mission “no one is left behind” which includes 430,000 disabled Australians ("Social Determinants of Health - Integrated care", 2021). Leo lived on his own with the help of the services received from the local provider and was meant to be learning skills that help him live a more independent life. However, the behavioural concerns and continence issues prevented Leo from acquiring the learning skills which has impacted him on an intrapersonal level.
Interpersonal Factors:
The interpersonal factors include social support acquired from interaction with other people or create limitations in enhancing interpersonal growth that can lead to healthy behaviour. Employment can be considered as such a factor that offers opportunity for social support. Both people with disabilities and their carers have lower employment levels which lead to lower incomes and higher rates of poverty. In addition to this, enrolling in the workforce also involve social inclusion, decision-making and autonomy for the disabled person. Disabled people in Australia are almost 50% less likely to be employed which is also well below the OECD recommended 60% (Carey et al., 2017). Even more, disabled women are less likely to be in the workforce as compared to men which further limits their chances of social inclusion.
In the case study, as Leo received services from the NDIS, he lived on his own but was still unemployed as he failed to acquire the learning skills. Moreover, the notice from the service provider to cease all support further worsened the long-standing behavioural and incontinence issues of Leo and his family was quite insecure about his future. It was the complex disability of Leo affecting his cognition, emotional regulation and ability to perform daily task that prevented him from getting employed in the first place.
Community Factors:
These factors include the formal and informal social norms that can limit or enhance healthy behaviours of disabled people through interaction among individuals, groups and organizations. Housing is one such factor and is also linked to health of the disabled individual. Affordable, secure and suitable housing for the disabled is rarely available which makes them vulnerable in the Australian housing market. Instead of residing in cared accommodation establishments, almost 95% of disabled people in Australia live in regular households ("Social determinants of health - Australian Institute of Health and Welfare", 2021). As a result of this, people with disability might often fall out of home ownership and become rental tenants.
The reason the chief executive of Leo’s provider stated of withdrawing the services is the unhygienic condition due to the mess made by Leo. This was considered as an unacceptable risk for everyone and might also compromise the safety and well-being of Leo and the staff members. However, as Leo was suffering from continence issues, a regular household instead of cared accommodation would result in such mess and unhygienic conditions.
Influence of The Key Determinants on Health Behaviours and Health Outcomes
The social determinants from all three levels of the ecological model influence the health behaviours and health outcomes of the disable Australian populace. The lowered rate of employment leads to lower income and increased poverty for the disabled people. As compared to other OECD countries, Australian disabled people live in much worse conditions. As a result of this, the median personal income for disabled people was $225 per week while the non-disabled people had $480 ("SHUT OUT: The Experience of People with Disabilities and their Families in Australia | Department of Social Services, Australian Government", 2021). The intrapersonal factor of education is also linked to this outcome as there is existing income inequality for disabled people regardless of their educational qualification. The higher poverty rates in turn make it eve harder for disabled people to acquire care services which affects them on a community level as well. For this reason, government backed general resources, support and services provided by NDIS helps disabled people overcome the health outcomes caused by the key social determinants (Kavanagh, 2020). Disabled people like Leo and others can live an independent life on their own without worrying about employment and income.
Conclusion
It is evident from the assignment that as compared to other OECD nations, Australia currently is ranked lower in terms of services provided as well as well-being of the disabled people. The critically discussed social determinants from all three levels of the ecological model indicate that Australian population of disabled people are far more likely to suffer from unemployment, poverty and homelessness as compared to non-disabled populace.
Learning Journal
References
.png)
Reports
PUBH6005 Epidemiology Report Sample
Context
In Part B, you are able to apply their knowledge of causation and association. The skills gained from this assessment allows you to make a judgement on causality and association based on the epidemiological research and evidence. You will demonstrate your ability to apply the Bradford Hills criteria, a key tool in determining association and causality within epidemiological studies. Establishing association and causality are key skills in epidemiological disease investigation.
Task
Part B requires you to choose one of the articles that you have critically appraised in Part A, and using the Bradford Hills criteria as a guide, write within 1000-words on your judgment of association and causation. You will need to provide your opinion/decision/recommendations for a couple of the Bradford Hills criteria. Headings can be utilised where required. You may need to search for additional research articles to support your findings. Please refer to the Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Instructions
Select 1 of the 2 articles that you critically appraised in Part A. Address a couple of Bradford Hill’s Criteria's to present your opinion/decision/recommendation in establishing the causality and association of the findings. Your assessment should include should include the following:
1 Give the title of the article and introduce the objective of the paper
2 CHOOSE ANY TWO of the following criteria's and and address them accordingly
2.1 Temporality
2.2 Strength of association
2.3 Consistency
2.4 Dose-response relationships
2.5 Biological plausibility
2.6 Specificity
2.7 Experimental data
2.8 Coherence
2.9 Analogy
Solution
Introduction:
The paper aims to apply Bradford Hill’s criteria to a chosen article to determine the causality of the article. In the year, 1965, 9 viewpoints have been published by Austin Bradford Hill in order to check whether the “epidemiologic associations” are causal. These criteria have been the popularly used for determining “causal inference” within epidemiologic studies. Here in this article, two of Bradford Hill’s Criteria have been chosen to establish the causality (Shimonovich et al., 2020). For Assignment Help These two factors are “temporality” and “strength of association”. “Strength of Association” is basically critical to the ‘assessment of significant causal relationships” (Fedak et al., 2015). Temporality on the other hand is perhaps the only aspect which is agreed to is important to the “causal inference” (Fedak et al., 2015).
Title of the Chosen Article: “Case-Control Study of Risk Factors for Human Infection with a New Zoonotic Paramyxovirus, Nipah Virus, during a 1998–1999 Outbreak of Severe Encephalitis in Malaysia” by Parashar et al., (2000).
Purpose/Object of the paper:
The article mainly discusses the outbreak of “encephalitis” that had affected 265 patients and amongst them, 105 got fatally affected by the virus between 1998 and 1999 within Malaysia. This outbreak was associated with the “paramyxovirus, Nipah”. This is the virus that affected human beings, pigs, cats and dogs (Parashar et al., 2000). The main purpose of the chosen article is thus to examine and to determine the aspects of exposures to Nipah infection amongst human beings while the outbreak of the encephalitis tool place (Parashar et al., 2000).
Assessment of two Bradford Hill’s criteria:
Temporality:
Temporality is regarded as one of the most important criteria for a “causal association” amongst a particular “exposure” and an effect. In other words, the exposure should precede the effect, though it is not required to measure the exposure before measuring the effect (Fedak et al., 2015). Also, it has been explained by Bradford that in the criteria where the relationship between the cause and the effect is casual in case cause or the exposure results in the onset of the infection or the disease (Cox, 2018).
Within the temporality criteria, the effect or the outcome has to take place after the cause and if there is any delay after the cause or the exposure occur, the effect takes place after that delay. The chosen article by Parashar et al., (2000) conducts a case-control study in order to characterize the exposures linked with the “Nipah Infection” of the human beings during the spread of the virus. This study suspected an association of “human Nipah infection” and the “proximity to sick pigs” earlier than the outbreak as most patients were “male pig farmers”. Also, the “viral isolates” from the infected pigs and from the “encephalitis patients” demonstrated the same sequence of nucleotides. Applying Bradford Hill’s Temporality criterion here, it can be said that the cause here is the exposure to the sock pigs or proximity to the infected and the outcome of the effect is the “human Nipah infection” (Cox, 2018). It is clearly observed from the study that after the exposure to the sick pigs takes place, the pig farmers get infected by the virus and thus temporality can be justified here to be causal. Another demonstration of the study that justified the temporality criterion of the article to be causal is that the outbreak was stopped after the “pigs” were slaughtered and were buried. Thus, it can be said that the direct contact of the proximity of the human first took and then the effect, that is the infection within the human body took place and thus cause had clearly preceded the effect.
Strength of Association:
The “Strength of Association” is one of the most important criteria amongst the 9 criteria proposed by Bradford Hill for measuring the causality of an epidemiology study. He explained that the greater the relationship between the “diseases” and the “exposure”, the more it is likely to be causal (Shimonovich et al., 2020). In other words, the stronger the risk magnitude of the association between the “risk factor” and the resultant disease the more probable it is for the relationship to be “causal”. In order to study the relationship between the Nipah infection in humans and the exposure to infected pigs, case patients and control subjects have been chosen (Fedak et al., 2015).
After carrying out the case-control analysis of the study, the activities involving proximate contacts with pigs have been combined in the form of a “single variable”. The study of the results of the article suggests that the exposure to the infected pigs (cause) is potentially associated with the “effect” that is the Human Nipah infection with 86% of “case-patients” as compared to 50% of control subjects (Fedak et al., 2015). In addition, Bradford Hill’s “Strength of Association” criterion can thus be verified here and thus the relationship is said to be causal the as the findings of the study suggests that there is a potential strength of association between the cause (contact to sick pigs) and the effect (Nipah infected humans) and also show that the activities like close proximity with the infected pigs were associated with the “infection”. This argument can be further strengthened by considering the fact the outbreak was prevented by slaughtering and burying the pigs (Fedak et al., 2015). The strength of association is very significant here and thus the relationship is “causal” (Shimonovich et al., 2020).
Conclusion:
In this study, two of Bradford Hill’s criteria have been applied on the study by Parashar et al., (2000) and the application and the analysis of these two criteria on the study demonstrates and establishes a strong causal relationship between the “presumed cause” (contact with sick pigs) and the “observed effect” (Nipah infection in humans). It can thus be concluded that there is a close association between proximity with encephalitis infected Pigs and Human Nipah infection and thus the exposure to these pigs can be considered as the primary source of the disease.
References:
.png)
Reports
Healthcare Systems Report Sample
Assessment Description
The purpose of this individual assessment is to foster students’ capacity to utilise a systems-thinking approach further to develop an understanding of the Australian healthcare system and its ability to provide care and prevent illness. Students will use data to predict the role and influence of preventative strategies and technology on demand for healthcare in the future, focusing on vulnerable populations. They will debate the ethical issues that can arise in managing health care systems and actively consider ways for systems and management challenges to be resolved. In addition, they will create an inventory of resource requirements applicable to a variety of healthcare settings, focusing on vulnerable populations.
Assessment Instructions
This assessment requires students to build on the analysis undertaken in Assessment 2, where a specialist health service’s preparedness to meet the needs of Australia’s ageing population was considered.
The analysis, to date, has used systems thinking approach and has been based on the WHO six building blocks of a health system framework.
1) Service Delivery
2) Health Workforce
3) Information
4) Medical Products, Vaccines and Technologies
5) Financing
6) Leadership and Governance (Stewardship).
In this assessment, students should provide a concise overview of the service and the main findings from Assessment 2. Then, through their research and analysis (systems thinking), focus on identifying how quality services and responsiveness to the needs of an ageing Australian population are maintained and enhanced by the service and its service providers.
To achieve the assessment requirements, the report should be constructed accordingly:
1) Executive summary
2) Concise overview of the service and the main findings from Assessment 1.
3) Examination of how quality service provision is maintained and enhanced by the service.
4) Examination of responsiveness to the needs of an ageing Australian population and how it may be enhanced by the service.
5) Examination of ethical issues and considerations related to service delivery decisions and vulnerable populations.
6) Recommendations for future action.
7) References - A minimum of 15 references, at least 8 of these should be academic journals. Harvard referencing method applies.
To explore the full breadth of maintaining and enhancing quality service provision, students should consider the interconnectedness between the health service and the broader system of the National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards, the National Registration and Accreditation Scheme (NRAS) for health practitioners maintained by the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Authority (AHPRA) and other professionals who self-regulate under the banner of the National Alliance of Self Regulating Health Professions (NASRHP).To provide a context for discussion, students should utilise appropriate standards to assist them in providing substantial examples of how quality services and responsiveness to the needs of an ageing Australian population are maintained and enhanced by the service and its service providers. For example (this is not an exhaustive list):
• NSQHS: Clinical Governance Standard, Action 1.8, 1.9, 1.10, 1.15.
• NSQHS: Partnering with Consumers Standard, Action 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6.
• AHPRA: Continuing Professional Development.
• AHPRA: Recency of Practice.
• SA Health: Allied Health Clinical Governance Framework.
Solution
Overview
The service that has been selected in this study is screening and treatment of breast cancer among the aged woman along with prevention measures that are formulated to mitigate the various risks. 25% of the total population of Australia are aged 65 years and above. It is also found out that the rate of aged population is going to increase by the end of 2055 (Manyazewal 2017).
In Australian health care system hospitals in the state of Victoria have upgraded organizational website that are effective in providing regular updates about each department. For Assignment Help They also provide updates so that elderly women can access the right treatment of cancer, books appointment on time in radiology section and more. Government also supports these elderly people with providing healthcare insurance, regular training session, interconnected and interdependent approach among the hospitals. In this study Breast Cancer screening service and treatment process in Bendigo Hospital has evaluated including challenges in their service process, gaps as well as opportunities. This report also identify the ethical considerations that the organization follow maintaining the privacy and dignity of their aged women patients who are suffering from the breast cancer. A future recommendation also given after this to mitigate the gaps those are existing in their service process.
Organizational overview
Bendigo hospital is the largest regional hospital in the Victorian region. The development project that has initiated in this hospital are worth $AUD 630 million with a specific aim in providing the welcoming, holistic and supportive environment for the service users (ArchDaily 2021). In the previous assignment it has observed that organizations in Victorian region are facing issues like fund unavailability, high staff turnover rate however at the same time use of latest technology and digitalization are being helpful to develop a smoother service. In external aspect, the political impact is highly evidenced through the changes of policies. The most challenging factor is the economic condition that is affecting the budget of the hospitals. From the Assignment 2 it has evaluated that the healthcare system of is constantly evaluating itself along with upgrading their tools, learning process in order to enhance the quality of their service and also for supporting the health progress in ageing population.
Analysis of the Challenges, Gaps and Opportunities
Standard of Care and Support
Bendigo hospital offers a range of comprehensive specialist care across the medical and healthcare disciplines. This organization provides services in emergency, maternity, women’s health, pathology, cardiology, aged care, cancer service and more. Referring to the interconnectedness of organizations and broader system of healthcare standards a detail understanding can be made to define the key standards of healthcare support and practices. Referring to the NSQHS (National Safety and Quality Health Service) clinical governance standards ensure that organizations must follow a clinical governance framework that ensure that the consumers can receive high quality care and safe service (Australian Government 2021). With this guideline, the organisation also provides a transparent informative guideline for patient who is taking an appointment for breast cancer screening. Through the website of the organization they clearly inform about density measurement, radiation, diagnosis and various screening programs.
The Bendigo hospital has built up a multi-disciplinary workforce which includes a skilled medical team that also has sub specialdepartments. In this aspect, the hospital is following the patient safety, quality improvement and safe environment in delivery of care for the cancer patients. In detailing about Bendigo hospital the organization follows Optimal Care Pathways for safe, consistent and high quality delivery of evidence based care system for people with cancer (Australian Commission 2021). This clinical governance framework is acquainted with the process of partnering with other health care bodies. As in this case of Bendigo hospital the health organization provides radiotherapy and radiation services with the partnership of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre (Bendigo Health 2021). While this service standard is properly maintained by the organization, another aspect that is highlighted at the same time is National Registration and Accreditation Scheme (NRAS) which is highly important for all regulated health professionals for ensuring to deliver high quality care and maintain the consistency. It is helpful in saving time for health professionals who works in states and territories of Australia (The Department of Health 2021). According to the organizational website the health organization has included diagnostic imaging accreditation scheme in relation to policies and procedures. For the registration process of the medical practitioners the hospital focuses to use the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) registration documentation. Under this, Bendigo hospital provides scope for every health service user that they can complain about the health professionals in case unsafe behavior, disrespect or inattentiveness.
Understanding of The Challenges
Referring to the strong consistency level with the above standards in medical practices, it can be referred that Bendigo has been continuing to focus on the effective health practices and development. They are committed in maintaining their employment relationship with strong focus on the policies and procedures (Bendigo Health 2021). Despite these excellences the area where this organization is giving issues in providing effective care towards the aged women breast cancer patients is the impact of Covid-19 for which they are facing difficulties for giving radiology appointments, support service and sometimes basic medical treatments. It is also seen that the hospital staffs are notifying about the emergency needs of patients due to irregular medical intervention among the breast cancer aged women (Dinh-Le et al. 2019).
Besides the barrier of pandemic impact, Bendigo hospital has been facing issues of the inadequate co-operation from the aged women of breast cancers as they often ignore the daily activities, food or nutritional suggestions. Along with this, the treatment phases are also intervened as there are only 7 radiation oncologists in this hospital (Peter Mac 2021). Apart from breast cancer these group of medical practitioners also assigned to take care of various other cancers. Additionally, while it comes to deal with the cancer patients and adult ones they require more time and attention to be supported with proper medical help. Being the largest hospital with consisting service support in Victoria region, a large number of adult women with breast cancer comes to this hospital. It is really challenging for the hospital to deal with a large number of consumer with limited number of medical practicing teams. In addition to this as identified in above part the projected number of cancer patients will increase rapidly in future years. From this aspect the present capacity of supporting the need of aged women breast cancer patients is rare.
Identification of The Gap
Referring to the future health opportunities, it is evident that the use of technology will be the most in delivering the most effective service and care support management. Clinical decision support system is the computer based information process where the health care providers can access strong aid with the help of technology. Though the Bendigo hospital is efficient in dealing with the strong consistency of care support yet their role is limited in developing a collaborative care support or depending completely on the medical practitioners’ knowledge and skills. While the development of the technology is highly effective to deal with the medical ground, Bendigo has still not implemented any such automation process within their service system. It is highly possible that the organization may face issues regarding the extended dosage and flaws in medical checkup of the patients who will be suffering from the breast cancer. Another aspect that requires to be mentioned here is that Bendigo hospital does not have its own radiation treatment service. They have to depend on another clinic in providing chemotherapy for the cancer patients. Identification of this gap in their service process is effectiveto reduce the trust and dependency of the cancer patients on the organization.
Referring to The Opportunities
There are multiple opportunities that can be referred for the support and development of the gaps of Bendigo hospital. Among these the aged women breast cancer patients will be supported if they are treated with technological development. For instance, delivery of remote checkup, home based care support will be highly appreciated if properly implemented by this organization. They also require implementing completed in-house cancer treatment process including radiology system so that the process of chemotherapy will be easier (McAlearney et al. 2016).As for example, the use of genetic mapping still under research and it is assumed that there is high possibility for the cancer cure from the interchange of genetic structure. Xenotransplantation is also another process that is still under concern however will be effective to support the individual patients with transplantation of living cells.
Ethical Considerations
Bendigo Health Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) is responsible for all type of ethical practices including the patients, clients, staffs and resources. Referring to the ethical guidelines it is seen that HREC of Bendigo has the role of protection and welfare of the rights of the participants. They specifically focus on the National Health and Medical Research council for proposing of the research projects, monitoring on the projects and approval of the project to maintain the ethical standards. In terms of providing the support to the aged women who are suffering from cancer it is essential that each of the individuals are equally treated and supported. HREC of Bendigo hospital usually provides strong guidelines, training and support for the medical practitioners who are in the service of vulnerable groups (Bendigo Health 2021). Along with this they also evaluate the work force operation process in order to determine wheather they are maintaining the ethical standard in clinical process and follow the organizational rules or not. Along with this evaluation of ethical support is also provided at Bendigo with the feedback evaluation and accessing feedback from the customers. At this area organization provides scope to the customers to tell on behavioral conduct, disrespect towards the privacy and safety issues. These are helpful in managing the entire organizational process efficiently and enable the ethical guidelines throughout the organization. Apart from this, they have to follow the basic consent level including autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence and justice (Runciman, Merry& Walton 2017).
Concerning these ethical points, Bendigo is highly concerned for their cancer patients that all of their medical practitioners must take consent from the patient before providing any specific treatment to them. They take care that before any screening process individual disclosure is maintained by the medical practitioners about possible risks, benefits, nature of the procedure and more (Bendigo Health 2021). In terms of beneficence, the best interest standard that is every breast cancer sufferer assured that they are being treated by the most skilled and knowledgeable person. Though providing ration therapy or chemo treatment is not entirely helpful in physical wellbeing yet the cancer patients have to undergo this process. In terms of ethical guideline of non-maleficence it can be said that patients are properly informed about the harm that they can face while taking the radiation therapy. Finally, Bendigo also maintains the ethical practice of justice that is treating every of their breast cancer patients equally and support them with every possible technology that they have to provide earliest cure as possible by them.
Recommendations for Future Action
Reviewing the present needs of the patient care and management of the Bendigo hospital it can be referred that the Clinical decision support system will be the one that will be most effective in managing decisions timely and quickly. As opined by Zikos&DeLellis(2018) inclusion of CDSS analysis is helpful in managing clinical decisions and diagnosis every time the medical staffs providing care or medical help. Under this process, Bendigo hospital can create a digital log book where they can review every clinical parameters of the patient while treating them or making them ready for an operation. It is specifically helpful for the medical practitioners who are dealing with breast cancer patients as they can review allergic reactions to medicine, previous medical history, and therapeutic duplication alert. People who have to undergone a surgery due to breast cancer at old age require strong monitoring and observation which will be more effective to make with this system.
Reference list
.png)
.png)
Reports
PUBH6004 Leadership and Effecting Change in Public Health Report Sample
Instructions:
In this assignment, you will be provided a scenario (problem) involving a public health leader that you will need to analyse using the knowledge gained from this subject for 3 modules. Subsequently, immersing yourself in the scenario, you will evaluate yourself as a public health leader.
Note: Case study will be provided after Module 2
You will be writing a 2000 word report in three parts, as follows:
.png)
- Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar:
- Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and bibliographical details(including reference list)
- Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper sentence and paragraph construction
- Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Solution
Introduction
Australian Health care sector has been evolving for years coupled with increasing complexities due to rising disease & patterns of infections. The pandemic has created pressure on the already pressured healthcare organization accompanied by a shortage of labor and an increasing number of patients (Walshe & Smith, 2011). Since resources are scarce and the management directly impacts the well-being of the workforces.
Part A- Evaluating public health leader
Since the healthcare system is highly complexed, thus, NSW has defined leadership traits that are important for managing complexities in the public health domain. Health Leads Australia has created a leadership framework that is embedded in the principles like owing leadership, development of capable leaders, and mediating personality in the leadership role (Health workforce Australia, 2013). For Assignment Help In addition to this, Dr. Tania has been recognized as one of the most effective public health leaders during her tenure in varied positions in international health organizations. Thus, the leadership traits will be analyzed through the framework designed by Health Leads.
.png)
.png)
.png)
Also, the leadership framework includes aspects like partnering and collaborating across boundaries, which relies on deploying collaborative approach, mobilization different types of people, creating of cross- sectional collaboration, encouraging fresh insights from varied types of sources for fostering innovation (Bercaw & Poole, 2013). In all the sub- aspects of partnering and collaboration, I lack initiatives for creating cross-sectoral collaborations for service delivery agreements while I also lack competencies for mobilizing people for undertaking collaborative actions to fostering service transformation. Leaders need to possess the capability for delivering high patient outcomes eliminating redundancies and improving the transformation of the systems. Thus, the core ideas of transforming the system include shaping the preferred future, demonstrating critical system thinking, assessment of work through resistance while also being politically astute to foster changes. This aspect contains several sub-parts which are often used by me while working in the healthcare systems.
.png)
Part C- Identifying Strengths and leadership style
The self–assessment tool has been very helpful in identifying gaps and improving them for higher efficacy in healthcare management. In addition to this, in the aspect of achieving outcomes, I have acted according to the sub-sections of this component whenever I work in the healthcare domain. In addition to this, I was in the place of Dr. Tania, I would have also collaborated with different stakeholders like consumers, colleagues for setting the goals for achieving the common vision that is well- being of all socio-economic classes in epidemics and crisis. Since I focused on achieving outcomes, it would help me in aligning resources and influencing decisions for providing a quality and patient-centered approach. Thus, I will continually monitor and celebrate achievement by realizing being accountable in both the outcomes that is failure and success.
The second approach is leading self and developing, as it is very important for the leaders being self-aware thereby understanding strengths and limitations. I also realized that I am highly committed to improving myself, thereby displaying integrity in the roles and context. In addition to this, this strength would help in actively reflecting on the performances, thus responding to engage others for fostering learning and growth. I try achieving outcomes as I am self-aware and thus, apply honest and ethical principles while making crucial decisions in epidemic events. As per the self-assessment tools, my third strength will be engaging others, by recognizing values and cultural responsiveness in different countries I would work in. Since I have efficient skills for engaging others, I am approachable, possess active listening, with a clear presentation of ideas and issues. This strength would also help in actively and easily participating in very difficult conversations displaying humility and respect.
Engaging with others also helps me in inspiring others while enabling them for sharing ideas and information, thereby reaping opportunities for growth and opportunities. Besides, I have strengths in shaping the system as I can understand and can effectively communicate system awareness with all the stakeholders. As a leader, it is very important for involving consumers and varied types of health policy for creating policies, education, training, and other factors that impact well- being of societies at large. However, if I were in the position of Dr. Tania, I would have portrayed good outcomes as I lack competencies in partnering and collaboration. When placed in a leadership position, it is very important to be part of lower socio-economic background, without which equal distribution of resources cannot be assured. Thus, my weakness in forming a coalition would impact the lives of vulnerable populations in times of crisis and epidemics. In addition to this, I also lack competencies in managing myself and being aware as I am majorly focused on uplifting others; hence I am not able to recognize my strengths and reaping opportunities for seeking personal growth.
An action plan for improving gaps has been provided below.
.png)
Conclusion
Healthcare leadership is important in all industries as it is embarked by rapid changes in population demographics supported by a lack of efficient resources. Also, leadership has direct and indirect impacts on the health and well-being of all levels of the community. Leaders in the public health domain hold a crucial place thus, every individual like me must work hard and focus on continuous development to managing healthcare infrastructure effectively.
References
.png)
Case Study
PUBH6003 Health Systems and Economics Case Study Sample
Context
Systems thinking helps us to understand the elements and relationships/interconnectedness of parts to a system. Currently, the use of systems thinking is being advocated in public health as a new paradigm shift. It aids in the solving of complex and intractable public health problems and the identification of risk factors for the achievement of health systems goals/good population health outcomes.
You are required to thoroughly research and write a critical individual report on systems thinking and its application to strengthening the six building blocks of health systems for the reduction/prevention of a chosen public health problem/issue for a selected country.
Instructions
You are required to:
• Identify a country (e.g., Australia or any other country) and a public health issue. Public health problems/issues include excessive alcohol consumption, food safety, heart disease and stroke, road traffic accidents, nutrition, physical activity and obesity, tobacco use, water, sanitation and hygiene, HIV, drug abuse and mental health;
• Provide a critical analysis of the concept of systems thinking and how it can be applied to public health;
• Discuss the six health systems building blocks as proposed by the World Health Organisation (WHO);
• Discuss why the chosen public health issue is complex in the context of the chosen country based on the building blocks and thus requires systems thinking; and
• Apply and analyse how systems thinking can be used to reduce/mitigate the selected public health issue along with the building blocks of the health systems of the chosen country.
Solution
Introduction
Australia is one of the economically stable and developed economies of European Nations, however, the health and infrastructure are considered to be complexed owing to its funding and payment issues. For Assignment Help In the year 2019, 169, 301 deaths were reported within the region of which coronary heart disease was the leading cause in men that is 12% while 12% of females died due to mental health issues like dementia and Alzheimer's (OCHA, 2021). The child death rates were reported to be 76 per 100000 which is lower than in 2009. In addition to this, life expectancy at birth (females) has improved from 1960 which was 74.2 % as compared to 2019 that is 85% (AIHW, 2021a).
In addition to this, life expectancy at birth for males has also improved from 1962 that was 67.9 which has improved to 81. 9% in the year 2019. In recent times, COVID-19 has been the leading cause of death which is 898, however, the disease and incidence rates in Australia have been reducing for the past several years due to which mortality rates have also declined (Australian Bureau Statistics, 2021). The deaths induced by consumption of alcohol reported an upward trend in 2020. The mortality rates during the pandemic were highest with a median age of 86 years with preexisting conditions like dementia, hypertension, cardiac chronic ailments, and hypertension.
Additionally, in the public healthcare units of Australia, the hospital-bed density is 4.0 per 1000 individuals, however, in private houses, there is an average of 4.8 beds for 1000 people (AIHW, 2021b). Also, the Australian public healthcare access is lower or free treatment as costs are majorly covered through Medicare while 46% of the population receives medication from private healthcare units. Besides, the physician density recorded in the year 2015 was 3496 on 1000 population while the population on nursing and midwifery is reported as 12566 on 1000 people.
The chosen healthcare issue is obesity as average Australians are overweight which increases various health risks. More than 70% of Australians are detected with obesity with an underlying chronic health condition that increases the cost of healthcare by more than 30%. Thus, addressing this issue is important for ensuring prevention at an early stage (American Academy of Pediatrics, 2018)
The report will aim at discussing a system thinking approach for addressing obesity as a healthcare problem in Australia.
Obesity as a Healthcare Problem
Concept of System Thinking in Healthcare
System Thinking is referred to as a holistic approach for understanding the interrelation of components, and how each subset operates over a given time frame within larger contexts. In healthcare, it is assumed as a problem-solving approach for evaluating an issue. It analyses the interaction of surrounding elements which greatly impact the problem thus, the evaluation helps understand the entire process for suggesting goals and objectives (WHO, 2010). Thus, in a healthcare context, it is commonly referred to as system-based practice. For instance, for detecting public health issues, system-based practice overviewing individual rehearsal on patients is evaluated within the entire system of healthcare (Brennan, Kumanyika&Zambrana, 2014). Thus, it aims in making healthcare successful by undertaking goals for individual patient levels. However, many diseases like obesity have not been addressed appropriately through system-based practice due to the population with existing conditions coupled with overweight has been increasing for years.
Six Building Blocks proposed by WHO
Service Delivery- Service delivery is commonly assumed as the output of all resources used for making the healthcare system efficient. It might include workforce, supplies, finances, and others. Thus, for improving the outcomes, it is important for aligning the inputs in a way for enhancing the overall service delivery models (WHO, 2010)
The service delivery for providing healthcare resources to treat and prevent obesity includes in-patient and outpatient services. The hospitals face the struggle of huge managing patient counts which impacts early intervention strategies. However, several local governments like NSW have devised strategies like obtaining free health coaching through calls on toll-free numbers which helps individuals in receiving assistance on health goals.Dietitians Association of Australia is also created for publishing campaigns and devise strategies for controlling weight and supervising health-related objectives. However, the Australian Healthcare system has been facing issues like increasing costs, experience for the patients, accessible points of care which have impacted service delivery due to which obesity is considered to be one of the crucial healthcare issues from the past few decades (Clarke et al., 2021).
Healthcare Workforce - The capability of nations like Australia for meeting health goals relies largely on knowledge, motivation, and skills. There is a direct link between the health workforce and the health outcomes of the entire population (WHO, 2010). Australian Healthcare Industry has been facing acute healthcare shortages thus reducing capabilities for meeting the increasing demands from aged care and child care. It is estimated that by 2015, there will be a shortage of approximately 1000000 nurses in inpatient and outpatient services for managing the underlying condition of chronic disease like obesity.
Health Information System- WHO defines that every healthcare organization is only successful if it has reliable data for making an efficient decision. The health information system is highly dependent on the main key factors that are the generation of data, compilation, synthesis, and communication of information to vital stakeholders (WHO, 2010). Australian Healthcare is on the stage of technical transformation with digital strategies proposed by the government, although the application of technology is at infant to mature stage which poses issues in treatment and flow of information from service providers to insurance companies.
Accessing essential medicines- A health care system that is characterized as well functioning ensures that the population receives equitable medicines, vaccines, and other healthcare resources with approved quality, costs, and efficiency (WHO, 2010). For achieving equitable supply of medicines and other healthcare resources, national healthcare policies, guidelines, trade practices, pricing strategies must be effectively aligned with healthcare goals. Australian Healthcare system has an efficient supply of generic and specialty medication, although indigenous populations are provided medication through the community sellers for improving life expectancies.
Financing of Health system- Finances holds a crucial place for ensuring the efficacy of healthcare resources. If necessary, funds are not allocated then workforces would not be employed, no medicines will be supplied while the entire functioning of the healthcare system will be paralyzed (WHO, 2010). The financing healthcare system is dependent on two objectives that are for raising sufficient funds and providing financial risk protection to the entire population. Major issues of healthcarein funding from local and state governments. Also, Medicare increases the complexity of healthcare outcomes as payments are delayed due to a lack of transparency and efficient flow of information in treating chronic ailments like obesity.
Leadership and governance- Leadership and governance ensure the existence of a strategic policy framework that is combined with coalition, regulation, addressing system design, and accountabilities. As per WHO accountability is one of an intrinsic part of leadership and governance as it relates to balancing & managing relationships amongst the population, governmental organizations, non-governmental organizations, households, and other entities (WHO, 2010). Leadership gaps are quite prevalent at every stage of governance which has impacted efficient utilization of resources that has patient outcomes for people with obesity.
Barriers for Applying System Thinking Approach
The system Thinking approach includes the integration of elements for understanding the core issues. Australian Healthcare industry has been witnessing an increase in obesity rates in younger as well older populations. Thus, the system lacks implementation, integration, and evaluation of public health strategies at the community level. One of the profound steps taken by the Australian Government includes banning fast-food advertisement in prime time accompanied by restrictions on retail sectors for selling, promotion, and display of sugary drinks. Lack of uniform monitoring and supervision of meals served in schools and college canteens is one of the implementation issues which is owned barrier of leadership and funding. It is observed that the younger population has a greater inclination to barging on sports drinks, cheesy items, and other foods with trans fat (Clarke et al., 2021). The complex healthcare model accompanied by workforce shortage has increased obesity and related conditions. Technology can be a great facilitator for improving system thinking, although building IT infrastructure requires substantial investment due to which digital strategies have been delayed. Also, privacy and security-related issues have been increasing in past years that have impacted the larger implementation of digital tools for managing service delivery and patient outcomes.
Recommendations for Improving System Thinking
Australian Healthcare system is recommended for prioritizing whole food consumption policies accompanied with physical activities in school and colleges. Also, healthcare practices and campaigns that promote water and vegetable consumption must be introduced. The healthcare leaders are suggested for engaging the wider communities for meeting malnourishment targets while initiatives must be undertaken for improving food environment at school.
Conclusion
Obesity has emerged as one of the chronic health problems of Australia, thus, six building blocks by WHO have been used for identifying issues in detail. System-based approaches lack health policies for managing obesity. Thus, leaders need to collaborate with different stakeholders for applying a system thinking approach to improve the health and well-being of the Australian population.
References
.png)
Research
PUBH6008: Capstone A: Applied Research Project in Public Health Sample
Instructions:
By the end of module 3, student must provide to their learning facilitator a brief review of the literature on their chosen topic. The literature review must contain key references/theorists/researchers for the public health topic chosen. The literature review assignment must be designed to address the following questions:
• Who are the key theorists/researchers in your public health topic?
• What are the key issues?
• What are the gaps in the existing body of knowledge?
The literature review should provide a basis for justifying a clear research question or hypothesis to be explored further.
You must also indicate the search strategy used for your literature review. For example, what were the key words you searched for, and which key databases or other sources did you use to conduct your literature review? (e.g. CINAHL, Proquest Public Health, Informit, Medline, Google Scholar).
Assessment Criteria:
• Critical and comprehensive review of the literature (70%) Clarity of research question/hypothesis (10%) General assessment criteria (20%):
• Provides a lucid introduction
• Shows a sophisticated understanding of the key issues
• Shows ability to interpret relevant information and literature in relation to chosen topic
• Demonstrates a capacity to explain and apply relevant concepts o Shows evidence of reading beyond the required readings
• Justifies any conclusions reached with well-formed arguments and not merely assertions
• Provides a conclusion or summary o Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar:
• Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and bibliographical details (including reference list)
• Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper sentence and paragraph construction
• Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Solution
Introduction
Sexual abuse of minors has long been recognised as critical issue in India. As a result, the "Protection of Children against Sexual Offenses" law was passed, making CSA actions like rape, pornographic exploiting, abduction, and so on illegal. This study will provide a quick review of the reasons for the rise in child abuse cases in India. For Assignment help, There are 430 million toddlers in India as per the official calculations. Children are seen as an important pillar in the growth of a country. Since independence, India's legislation and judiciary have worked hard to ensure that children have fundamental rights from conception until the legal age of adulthood. According to a report, there are four stages of developmental psychology in which an individual not only undergoes physical or biological modifications, but also undergoes changes in psychological, mental, and emotional health, as well as diversity in morals, theories, and language skills.
Protecting these younger generations is thought to be important since it leads to a healthy life for a person and the development of the country as a whole (Atim 2017). A child's essential human rights must be secured from all forms of abuse, including emotional and physical assault, as well as unscrupulous and defenceless conditions. Childhood is the most vulnerable time of a person's life. Children are regarded as a nation's most valuable asset since they are the ones who will define the development and children are the ones who will determine the nation's well-being. In the nation, the child is thought to have personal rights and responsibilities.
The study's goal is to examine the state of child safety by emphasising on incidences of sexual abuse involving Indian children. The research will look into the Indian government's preventative strategies. The goal of the study is to determine what is needed to improve India's current child abuse problem. In this contrary, the research will describe the current situation of Indian society in child abuse cases. The proportion of child abuse cases in rural and urban areas are analysed gradually (IGI Global. 2018).
Search Strategy
Several keywords regarding the child abuse in India are searched on various online platforms such as “Proquest”, “Google Scholar” and much more. Some methodologies are followed to conduct this study. In this regard, a research onion is selected to pick the most suitable methods for this study. The idea is to pick the most representative journals and articles in the field of child abuse within the Indian context. All selected journals are chosen from the 2017-2021 timeframe to avoid the chances of old journal inclusion. Reference and reviews of the selected journals are analysed before the inclusion of relevant data along with the monitored citation.
A "descriptive" study design has been followed to include a detailed explanation of the chosen topic. Selective study philosophy and approach are followed to take part in this study in detail. Special attention has been provided in including relevant data that can support reaching a concrete conclusion in this matter (Cockbain, & Bowers, 2019). All relevant information is included to strengthen the discussion to understand the current condition of Indian child abuse cases. Journals concentrating in prevention strategies of child sexual abuse in Indian framework are prioritised in the search strategy.
Definitions
Harming, ill-treatment, cruelty, abandonment, or starvation of any kid is considered child abuse. Physical, emotional, sexual, and psychological abuse can all be perpetrated against a kid. According to the "National Crime Record Bureau", one hundred and nine minors were sexually molested every day in India in 2018, which shows a 22% increase in the statistics of child abuse cases from the previous year (Tiwari et al. 2018). According to a UNICEF study, Indian parents utilise 30 distinct types of physical and verbal abuse on children aged 0 to 6 years as part of their discipline measures. Unfortunately, the research shows that young kids are more likely to be exposed to conflict, violence, and mistreatment as their families try to adapt, which can have long-term consequences for them. Not everyone understands the impact of such cases on their child and that is why the effect is so vulnerable. The differences between several type of abuses and molestations are described in the below area.
Physical abuse: Physical abuse is defined as the intentional infliction of pain. When most people hear the word "child abuse," they immediately think of physical violence. Molestation manifests itself in injuries, bruises, fires, cracks, and muscle aches, but it can also manifest itself in brutal acts of discipline. Physical abuse is also indicated by damages that do not match the narrative and ignored medically needs.
Emotional abuse: Emotional abuse is defined as behaviour against a child that causes mental distress. Shouting at the child frequently, restricting love or affection, long periods of quietness, and cruel jokes at the child's benefit are all examples of mental neglect. Emotional abuse is defined as calling the child insults or uttering other degrading remarks to the child, which usually leads to low self-esteem. Emotionally abused children may experience depression or a yearning need for affection (Oyekola, & Agunbiade, 2018). Stigmatisation and postponed or incorrect psychological maturity are among the other signs.
Sexual abuse: Sexual abuse includes touching a kid in a sexual situation or having sexual contact with the child, as well as any action directed at the child for the purpose of sexual excitement. Touching, forced sexual actions, and obscene bodily exposure are all signs of this sort of abuse. Both sorts of sexual abuse of a kid are regarded sexual abuse of a child, whether the abuse happens as a one-time occurrence or as a pattern of behaviour that persists for years. Often, the attackers are the child's relatives or family members. These are mostly people that no one would expect to do such crimes (Parmley et al. 2019). Actions in a child may indicate sexual abuse include awareness or promotion of sexual conduct before the child's age, unexpected difficulties with toilet habits in a young child, genital pain or itchiness, injuries, or bleeding. Other signs include difficulty sitting or jogging, stains in their underwear, and other youngsters being sexually abused.
Abuse of any kind can result in long-term consequences. Child abuse has ramifications that go far beyond the physical scars left behind. Relationship troubles and trust concerns may arise in the child. Feelings of worthlessness or low self-esteem are prevalent, and the youngster may have trouble controlling his or her emotions. The study's main goal was to describe how sexual assault affects a child's mental and psychological well-being. Some preventative measures are also aimed towards elucidating.
Literature Review
The purpose of a literature review is to select a variety of publications related to child abuse cases in India. Human trafficking, rape, harassment, exploitation for pornography, and other forms of child abuse are common (Harder et al. 2020). By reading various journal and news articles, the study will expose the exact situation of child abuse in India. The Indian government appears to be working on legislation to stop abuse that is more sexual. Abusers of children are dealt with harshly by NGOs and government organisations, including the police. According to the preliminary findings, the court system is successful in averting societal evil. Several search engines are used to find suitable literary sources for this study.
Discussion of literature
Cases of Child Sexual Abuse in India
One of the most serious issues is that our culture has prioritised adult rape, but child sexual abuse is as important. The only difference is that most youngsters are either unaware that they have been sexually assaulted or are too afraid to tell their parents. Some people are afraid of privacy (Mashayo et al. 2017). Hundreds of millions of children are victims of abuse and exploitation. Kids are physically and emotionally fragile, and they could be permanently traumatised by emotional or psychological abuse. Child sexual abuse is a pervasive problem in our society, although it is rarely spoken. The national of formation of women and children manages this act and aims on removing sexual abuse of children, improving education about child molestation, ensure a stable space for children who are victims of aggression, and imposing harsh penalty on offenders.
It is the basis of a slew of health issues as well as a slew of other issues. Although there is no strong demonstration of a source, reported cases of child sexual abuse are decreasing. One out of every ten children is sexually molested before they reach the age of eighteen, according to statistics. Despite declining rates of registered sexual abuse, the public is unaware of the magnitude of the problem. In India, child sex exploitation has long been an issue, and incidents of horrible atrocities have been documented over the years, prompting a continuing effort to abolish such evil from society.
Effect of Child Sexual Abuse on Children
According to the evidence presented to the Inquiry, child sex exploitation can have far-reaching and serious repercussions (Jones et al. 2019). These impacts can last a lifetime for some victims and witnesses. Child sexual abuse can have a negative impact on a child's cognitive and emotional well-being. This affects their familial and intimate connections, faith, training, and job opportunities. People who have suffered are also two to substantially more likely to be sexual, physical, or mental abuse victims in the future. Victims and survivors blame themselves for changes in family relationships and relatives' well-being. Some victims’ child sexual abuse may become overly protective of their own children and grandkids. They are desperate to make their kids and grandkids feel sympathy for, and to ensure that their own abuse has no negative consequences for them.
It can also cause feelings of loneliness by disrupting friendship groups and leading to bullying or being talked about by others. Some victims of abuse have had their family connections harmed because their parents, siblings, or other members were aware of the sexual abuse but did nothing to stop it. Parents of victims are seen to be affected as well. Parents' mental disorders can be harmed because they blame themselves for being helpless and are unable to safeguard their children (Reiner et al. 2019). Some victims fear that the sexual abuse they experienced as children will make them unfit parents, or that others will regard them as harm to their own children.
There is no single metric by which a child can assess sexual abuse he or she has experienced. As a child, a person is oblivious of some things that he/she learns as time passes, so when he is a sufferer of child sexual abuse, he/she conjures up a variety of images in his/her head while living in fear. The impact of child sexual abuse and neglect on physical, psychological, behavioural, and societal results is studied on a regular basis. Mental implications might be seen in physical effects. Mental health difficulties lead to risky behaviours. Depression and anxiety, for example, may compel a person to consume, abuse, drink, or utilise illegal medications. Some of the major effects are,
Fear: CSA is such a heinous deed that it shatters a youngster's mind, and as a result, a child lives in the shade of terror and never escapes it (Boittin 2018). Most kid maltreatment is unreported due to children's fear of being taken away from the family.
Self-harm: Sexual abuse frequently results in anger toward oneself, such as self-blame, self-harm, and suicide. Those who were sexually assaulted as children are more likely to attempt suicide than the general population.
Sexual health: Being physically manhandled as a child, especially when the abuse is not discovered, might lead to perplexing notions about links and sexual habits.
Emotional harm: Victims of sexual abuse face a variety of medical effects, including sexually transmitted infections and infertility. These physical effects compound the abuse's significant emotional and mental suffering. All of these victims had a variety of issues, including anxiety, anxiousness, disordered eating, and attempted suicide. "Panic disorder", "psychological symptoms", "hyperactivity disorder", "post-traumatic stress disorder", and "reactive attachment disorder" are some of the other side effects of CSA.
Arrival of shame and guilt: In most situations, the attacker is able to persuade the sufferer that it is his own fault (Xu et al. 2018). Some persistent abusers engage in the same abusive behaviour repeatedly. It causes scars on the victim's body and spirit, and he/she feels guilty and ashamed. The person finds e it hard to inform anyone about the abuse because of remorse and humiliation of person commits suicide because of the terrible experiences that he/she had because of the maltreatment.
Post-traumatic stress: CSA can have a significant physical, mental, and sexual impact on a child. It may have long-term consequences for the child's physique (Motsa, & Morojele, 2021). If a youngster suffers multiple traumas to his body and spirit because of this traumatic experience, and their parents and caretakers ignore him/her, the child may develop "post-traumatic stress disorder". They do not increase their ability to believe anyone after being rejected by their well-wishers. In addition, a lack of appropriate counselling pushes individuals to face this issue more.
Abusive behaviours: The victim's behaviour deteriorates into abuse. That person is unable to trust anyone, which has a negative affect both his/her present and future lives. Approximately one-third of abused youngsters will go on to victimise their own children.
Reasons Behind The Sexual Abuse and Torture
The primary cause of this social problem is a lack of knowledge. The Indian government must take firm measures in this regard. The Indian society is thought to be unconcerned about sex education. Child maltreatment is on the rise in India, particularly in rural regions, because of these similar conditions. Another explanation for this is poverty. Due to their poor financial situation, the majority of families send their children to work at a young age. India's overcrowding is another issue (Joseph, & Bance, 2019). Poverty makes it difficult for parents to feed their children, forcing them to stop going to school. This is why there is an increase in illiteracy and child maltreatment.
Because Indian culture has always been patriarchal and dominant, a child is always under their protection and care. Furthermore, they utilise physical force on youngsters to chastise them, believing that this is beneficial to their growth. Many studies show that not only are single causes not to blame for child sex abuse, but that a combination of factors is also to blame for this heinous crime. Some of the most common causes of childhood sex exploitation are discussed in depth.
Poverty: Poverty is a major contributor to child sexual abuse. The majority of incidences of sexual abuse occur in low-income homes. There is a growing trend of selling children to meet their necessities. Parents frequently believe that because they have given birth to a kid, they have the right to place the child in a bond. It is not true that all incidences of child sexual abuse occur in poor homes; some cases occur in middle-class and rich families as well (Rocha-Jimenez et al. 2018). Adult abusers pretended to help truly needy youngsters, but instead reaped the benefits of them.
Illiteracy: Education is crucial to a child's future success. If this is not the case, everyone will suffer greatly. Because they are outside the shielding reach of school and provide assistance agencies, illiterate children are more exposed to abuse.
Poor Health Issues: Children with a mental illness, a learning difficulty, or a physical impairment are more likely than others to disclose childhood sexual abuse.
Homelessness: Children who have been homeless are much more likely to have experienced sexual abuse. Some of them are children who have been sexually abused at a young age. Spousal abuse, physical molestation, and other forms of relationship violence are common among these homeless kids.
Increasing Unemployment: Unemployment is also a significant contributor to child sexual abuse. It can also lead to divorce, alcoholism, poverty, and a variety of other issues. To cope with the stress of unemployment, a person may resort to any form of abuse, including sexual abuse (Reiner et al. 2019). Joblessness has a greater influence on young children, according to heterogeneous effects as this gives birth of depression and mental sickness, which directs towards sexual abuse.
Acquaintances: Children have a strong belief in the person with whom they are connected. They find it difficult to oppose his or her behaviour, even if it is unsettling.
Current Condition of The Situation
With regard to the country's children, the vision of the country's constitution makers was to ensure their extensive development, protection, wider benefits from their deprived and retrograde conditions, preservation of children through a decrease in rate of death, and involvement of children in the nation's overall progression. Four out of five kids are the victims of sexual abuse at an early age. It is sad to mention that despite the digital transformation and social development, people are still so sick that they target kids to harm. These are nothing but mental sickness. Parents must not be too strict or too casual with their kids. Kids who grew up with troubled childhood happen to be molesters in the coming life. That is why child support and sex education are so important.
Increasing Cases in The Rural Areas
According to statistics, children in rural areas endure more sexual abuse at home than those in urban centres. While 41% of youngsters in the poll indicated they had been slapped, almost 58% children said they had been slapped (Uzochukwu et al. 2021). According to the study, 34% of children had their ears pulled by elders, while 66% of youngsters had their ears pulled. While 45% youngsters reported they were put in a room, nearly 57% indicated the same treatment is applied to them.
According to a survey conducted in rural Maharashtra to assess the amount of sexuality and AIDS consciousness in a school, the majority of the girls believe that sex education should be offered at an early age because the age of puberty varies for each of them. Early understanding of sex and menstruating cycles would help children better comprehend metabolic responses and be equipped for the circumstance without feeling ashamed or guilty. According to the findings of this study, the majority of educators believe that sex instruction can be part of doing something recreational but not part of the syllabus.
Preventive Strategies
Most of the child abuse case takes place due to the lack of education. Indian government must include sex education mandatorily within the course curriculum from the early schooling days. Conservative parents often hesitate to talk about sex with their children, which make kids more curious about their sex life. Improper guidance and lack of support from the elders are the reasons behind the increasing cases of child abuse (Li et al. 2017). Sex education must start from home. Parents must educate their children with honesty and patience. The more educated they will become; the less amount of curiosity will rise. That is the only way to get rid of the increasing child abuse cases. Parents must be well aware of their own actions as well. Children's mental troubles arise from their parents' relationship difficulties. Parents must control their actions for the sake of their kids as this can provide a negative impact on them and may lead to dark intentions in the future. In case, parents feel that their child needs help in such cases, they must consult a psychiatrist or put their kids in a "support session" for the betterment of their health.
Literature Gap
The literature has performed a great understanding of child sexual abuses in India. Most of the literary sections have been picked in the subject of the cause and effect of child sexual abuse. A little more attention can be provided on the prevention strategy of child sexual abuse in India. Prevention strategies are usual; however, child sexual abuse prevention strategies in the Indian context seem to be missing hugely in this study (Iheanacho, Stefanovics, & Ezeanolue, 2018). The topic is mostly covered. However, the differences between the child sexual abuses in the past and in recent times are not described. The area is useful to drag the importance of Indian rural areas in increasing rate of child abuse. However, the proportion of child sexual abuses in cities is not rare, which has received least importance in this area. Government of India's policies to prevent child abuse is not mentioned in this study as well.
Conclusion
Given the facts and the outcomes of many past studies, the study has many data to back up the findings and study topic. Child sexual abuse is a global issue, not just a problem in one society. Child sexual abuse can have both short and long-term implications, including underlying injustices, psychological disturbances, cognitive impairments, educational challenges, low self-esteem, and self-harm, as well as the possibility of suicide. The abuser who used the children had a negative impact on his life and damaged his future.
The majority of incidents are recorded in families, schools, communities, on the street, and at work. Many victims are too young or defenceless to speak up about abuse or protect themselves. Even with so many legal measures and child welfare groups in place, if this crime continues to rise, everyone will be forced to take action. Adequate child safety policies and preventive measures are urgently needed to safeguard children from all forms of abuse. Such policies offer a secure environment in which a child can be cared for and thrive.
References
.png)
.png)
Reports
7069SOH Global Healthcare Management Report
Critically evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of resource planning and management in a health system you are familiar focusing on the following key areas:
1. Priority setting and decision-making processes
2. Workforce planning and development
3. Human resource and talent management
Conclude your evaluation with recommendations for improvement of the health system in each of the three key areas.
Coursework 2
3000-word individual report addressing Learning Outcomes 2 -4
This assessment component counts for 15 credits
In 3000 words, addressing learning outcomes 2-4, complete the following assessment
Task:
Critically evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of resource planning and Management in a health system you are familiar with, focusing on the following key areas:
1. Priority setting and decision-making processes
2. Workforce planning and development
3. Human resource and talent management
Conclude your evaluation with recommendations for improvement of the health system in each of the three key areas.
Your individual report will be assessed using the HLS Faculty Postgraduate Assessment Marking Rubric and the coursework 2 assessment guidelines, which you will find in the appendices in the module guide.
For coursework 2 please comply with the following submission guidance:
It is important to you and the tutors that your project is written and presented in a professional manner. The following requirements must be adhered to in the format of assignments:
1. Your limit does allow for +/- 10% words in length. The limit includes words used in Tables, graphs, charts and diagrams, but excludes the front cover, references list and Appendices. If you exceed the word limit you will be penalized 10% from your mark
2. The front cover page - see appendix 4 for the template in the module guide.
3. The font type should be Arial and the font size for the body of the text 12 point.
4. One and a half (1.5) line spacing must be used.
5. All pages should be numbered consecutively, in the footer on the right.
6. Your student number should be in the footer on the left.
7. References, citations, and quotations should be in Coventry University APA Referencing only. Ensure that all statements and arguments are supported with reference to the evidence in the relevant literature.
8. Any diagrams, tables, photographic images etc. should be appropriately labelled and referenced.
SOLUTION
INTRODUCTION
The primary objective of the resource planning and management is to ascertain and achieve and suitable number, mix, and distribution of employees at a price that is affordable by the community. For Assignment help It should be noted that, resource planning and management consists of priority setting and decision-making procedure, workforce planning and advancement, and human resource and talent management (Baldwin, & Hamstead, Mark, 2015). In the present study, Ramsay health care is chosen and its management emphasizes on the connection among doctors and employees, providing a high quality of results for patients regarded as the most significant element of being at the forefront for its achievement. Further the weaknesses and strength in context of this is provided below and recommendation to the organization accordingly.
Main Context
Overview of health system
Resource planning and management plays significant role as it is orderly procedure for sake of explaining and undertaking the methods with respect to health connected elements of the people and to abide through the values of professionalism (Abu Madi, 2018). In relation to the resource planning and management, critical analysis of the priority setting and decision making process, workforce planning and advancement, and human resource and talent management at Ramsay healthcare is explained. Further the Ramsay Australia owns 72 private hospitals and is the largest operator of private hospitals in Australia. The operations performed by Ramsay include three public facilities and mental health related facilities. In addition to this the company has established a retail franchise network for Ramsay pharmacy which is supported by 59 or more pharmacies community. The health care centres in Australia admit around 1m patients on annual basis. Further the Ramsay employs around 31000 or more employees annually to its centers which are located in Europe, Asia etc (Ramsay healthcare, 2021). Company is committed to ongoing improvement in healthcare of individuals in each sector in some management elements like medical reimbursement, implementing more security to patients, and scanning models and safety. Ramsay healthcare acquires well reputed position across the globalized healthcare industries. They are engaged in providing efficiency and quality healthcare operations and keeping a superb record in caring of patient as well as hospital management.
Assessment of Current Key Approaches of Resource Planning and Management in the System
Priority setting and decision making procedure is defined as method of making decisions with respect to the manner in which organization allocate the restricted resources for improvement in the population health. At the Ramsay, effective priority setting is primary to creating resilient health system that could assists towards adoption and responding to the changing requirement of health needs and demands by individuals in effective way (Reed, & Ulrich, Dave, 2017). Further the company recognizes that its employees are essential resources which would help it to strives the improvement and excellent in its practices at workplace. Further this would also promote the healthy and positive harmonies at the centers where people would love to work. Therefore currently the strong focus of company is on its human resources and is representing unique workplace culture and values, also has embedded the ethos within the organization that “people caring for people”. Also the key business principle of the health care is to stay committed towards the safety and health of employees and other people visiting in the centre. In order to keep its journey continuously improving the company is committed towards- Monitoring, improving, Legislative compliance, consistent safe practice across our businesses, fostering a culture that empowers and encourages everyone, Being consultative and reviewing its measurable objectives and targets. Further the current approach of Ramsay towards its resource planning and management in the system is to deliver with diversity. The company delivers problem solving, innovative, decision making diversity through its people. Also polices, programs and procedures of its HR is currently reasonably practical and is inclusive to all the age groups. This diversification assists the strategic goals and objectives of the global value and sustainability. Further the company is also consistent in application of all the human and labor rights and laws in its operations (Susanto, et al 2020). The company commits at sustainable development for its people and also balances its global presence which helps in providing career development opportunities for the localities.
Evaluation of Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Ramsay is one of the leading firm in the industry has various strengths that it helping it to thrive in market place. The highly skilled workforce of the firm and successful training and learning programs is resulting in increased market share as well as penetrating in new markets. The organization is also employing over more 30000 employees annually which results in diversified skills and talent availability in the organization. Further the organization has successfully integrated with the technology companies in current years to build a reliable supply chain (Panik, 2019). The firm is currently focused on building new revenue stream through this which turns out as its strength. Also it track its record related to development and innovation in the resources successfully which helps it to make timely improvement in such resources (Cantoni, et al. 2018).
Weaknesses
Workforce planning is the critical and strategic part of the resource planning and management in the system. It is meant to ensure that company is implementing all the HR functions and is delivering sustainable development to it workforce. Ramsay Health Care is notably proactive in deploying its human resources, but there seems to be some issues and potential problems turning out to be weakness for the organization. The main concern is towards the recruitment of new employees in the company. As there is an issue of ageing workforce within the organization, as sustainable no. of employees are older and have attain at their retirement age (Collings, & Szamosi, Leslie 2019). Yet there is no such group available to replace them, their skills and talent. Additionally the company is facing challenges in managing the new entrants and this is resulting in its loss of market share in niche categories. Further there is low level of current assets availability as compare to its liability and this would create issue in liquidity areas. In addition to this the poor diversification and performance appraisal programs at the company is resulting in low morale. Further this is due to recent development of low culture and politics regulations in the organization and hiring of more local people which is creating diversification issues (Crumpton, 2015).
RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT
In the current report, the concerning issue of organization that has not attained yet is the matter regarding the retention of its employees. Therefore the Ramsay is bound to face the potential issues in it employment due to the steps that have been taken to maintain employees who are 50 years and over (Baldwin, & Hamstead, 2015). This has resulted in high ratios of aging workforce in the organization as the maximum number of employees working in it has attained their retirement age and yet there is no such substitution for them is available (Leatherbarrow, & Fletcher, Janet, 2019). Keeping in mind such issues related to generational gaps, the option are provided to the organization to resolve this issues (Wehrmeyer, 2017). .
Purpose
The main objective behind providing this recommendation is to suggest the Ramsay health care to incorporate the younger employee’s recruitment in the workforce to mitigate the issue of transitional gap in case the aged employees leave the organization (Friedman, et al, 2018). This would help them to maintain the generation gap too in the workforce. It could be done when embracing employee performance programs, the team must considers all the employees of various age groups instead of focusing on certain generation of employees. Within the duration of 6months to 1year such transition is to be done to fulfill the generation gap issue.
The strategic priority of the company is to provide with the improved outcomes for the current as well as future generation equivalently. Therefore the modern HRM managers of the organization must be tasked to sustain the workforce that allows easy transition of skills from a given set of employees to the other (Wickramasinghe, & Bodendorf, Freimut, 2020). This would help them to bridge the generation gap and the rate of compatibility would also increase at local as well as at national level.
Options
Encouraging multi-generational team working by hiring from local region as well as from outside to improve the balance of diversification too (Chiva, 2021).
Set of clear cultural values- There are some fundamental difference in working patterns of the different generation. For instance the older people wishes to work for fixed duration and hours while the current generation prefers to work as per their convenience (Seropian, et al 2020). This issue could be resolved by set clear cultural objectives such as output and goal must be the concerning issue at the end not the time and location of work (Das Gupta, 2020).
Another option is, encouraging use of technology which drives collaboration (Davies, Malek, & Rushmer, Rosemary 2017).
Benefits
Multi- generational workforce
At the national level, as per the world economic forum study states that investing in multi- generational workforce would help in raising GDP per capita almost by 19% in the coming three decades (Multi- generational workforce as a key to economic growth, 2021).
Clear cultural values as per the different generations-
These cultural values would help the organization to bind the workforce together and make a strong and united team (Journé, et al. 2020).
Costs
For the purpose of motivating the employees, keeping the morale and productivity of the organization and its employees high the employees who are under fifty’s must be included (Hall, 2019). The programs to establish such culture would steer the employee’s performance, which assists towards enhancement in cost (Nankervis, & Connell, Julia, 2020).
Risks
Stereotypes and discrimination
The multi- generational workforce could create discrimination around the age groups at the organization (Lawler, et al. 2018). The aged generation might perceive the younger one as oversensitive, open minded, while the younger one might perceive the aged generation as stubborn. This could easily disrupt the internal culture of the organization (Mateev, & Nightingale, Jennifer, 2020).
The Solution
Provide educational trainings to the employees to boost understanding respect and provide them with the opportunities to reflect the generational differences. Working toward dispelling stereotypes can lead to a more harmonious work flow.
Apart from this, company should implement management tool such as SWOT analysis for betterment of resource planning and management –
.png)
On the basis of this, company can take action for responding on weaknesses and threats by utilizing its strength and opportunities (Journé et al. 2020)
Further, Ramsay can also implement PESTLE analysis, by which it could ascertain about external environmental factors that are affecting business activities.
.png)
.png)
Risk assessment and management analysis:
Apart from this, risk assessment and management analysis should be used by company for betterment of resource planning. There are five stages of risk assessment and management such as identification of risk, assess and prioritize risk, development of risk response strategies, implementation of strategies, and monitoring of risk.
Further, by the following manner, risk management strategies could be improvised by company –
• Building a transparent culture of company.
• Creation of safeguard for protection of employees from digital threats.
• Continuous monitoring of risk assessment.
• Building internal team to remain aware of trends.
• Link with external security resources.
• Development of contingency plan
CONCLUSION
In nutshell, it is concluded that Ramsay is a well reputed organization across the globalized healthcare industries. They are engaged in providing efficiency and quality healthcare operations and keeping a superb record in caring of patient as well as hospital management. In its workforce planning and development there are certain loopholes such as high ratios of aging workforce, lack of diversification etc. For them the organization id recommended to encourage the multi- generational workforce which would help them to increase the productivity as well as resolve the issue of generational gap in the organization (Ogunyemi, 2016).
At the Ramsay, effective priority setting is primary to creating resilient health system that could assists towards adoption and responding to the changing requirement of health needs and demands by individuals in effective way. Further in context of workforce planning and advancement the health and safety of the workers at the workplace is the major priority of the business culture. The company is committed to the safety issues for all the workers and other peoples entering in the organization whether they are patients, employees or any other individuals (Rey et al. 2019). In order to maintain their journey of improvement consistent the company is focused on followings commitments- continuously improving a model of consistent safe practice across our businesses, fostering a culture that empowers and encourages everyone to uphold these objectives and policies, being consultative and communicating with all key stakeholders, maintaining systems which add value etc. Everyone at the organization is encouraged to speak up and stand for their safety and health in case it is been violated or observed to be violated. Ramsay values its people and is delivering the services as per the terms and conditions of the employment and is further consistent in application of laws related to labor and human rights at its maximum. These policies requires the human resource managers of the organization or the risk chief officersto contract on terms and conditions that are consistent with the realization of those rights for each employee and which comply with or exceed regional minimum wage standards (Crumpton, 2015).Further the organization is committed in ensuring the flexible working hours for its employees, they focus on the fact that their people won’t have to work for excessive hours. Therefore in order to stick towards this commitment the organization regularly monitors and tries to reduce in case such excessive working hours are been noticed. The promotion of labor standards and norms in the regions where the organization is operating is done by them through representing and involving the key industrial and workforce bodies within the relevant jurisdiction.
REFERENCES
.png)
.png)
Reports
PUBH6012 Applied Research Project in Public
Context:
This assessment advanced skills in reporting the justification, methods, results, and conclusions of a research project. Key understanding contained includes how to justify a research project using literature, how to implement a research proposal to collect and analysis data, how to report the results of the analysis of data, how to contextualize one’s own research in the context of the wider body of literature, and how to draw conclusions about future research and recommendations based on research. This prepares students for the conduct and reporting of research, which is an important skill set for public health practitioners.
Instructions:
Part 1: Due Sunday end of Module 1 Week 1 Based on the feedback from your Capstone A Research Proposal, revise your research plan and GANTT chart.
Submit these to your Capstone A facilitator by Sunday end of Module 1 Week 1. You may not proceed with your data collection until this has been approved by your supervising facilitator.
Part 2:
The final assignment for this subject will be the write-up of the findings of your research into a final report. This will be comprised of the following parts:
1) Abstract
a. Summary of your report (as you would find in a published research article)
2) Introduction
a. Introduction to and justification of the topic area, drawing upon your literature review (from Capstone A), and including the knowledge gap your project addresses
b. Your research question
3) Research design and methods
a. Summarise your research design/methods (from Capstone A) – what type of project did you do?
b. How did you collect the data (ie search strategy and process/ policy consultation process)? If a policy consultation, explain how any organizations/individuals that you consulted with were approached
c. How did you analyse the data (ie thematic analysis, systematic review process, consultation synthesis)?
d. Briefly explain the ethical issues that should be considered
4) Results
a. Report the results of your findings, e.g. key themes if a qualitative study, results in table
format if a quantitative study
b. Clearly explain key figures, tables and graphs
5) Discussion: Interpretation and contextualisation of yourresults
a. Place your results in the context of your literature review
b. Contextualise the results within the academic literature
c. Describe any limitations of your study
6) Conclusion
a. Conclusions from this study
b. Recommendations for future research or policy change based on feasible solutions
7) Supplementary material
a. Reference List
b. Any appendices
This research report format has been based on the standard format for a journal article, and thus may be submitted to a journal in the future if the student is interested.
Solution
Introduction
Background
In December 2019, a continuous bout of pneumonia associated with a new COVID was reported in Wuhan, Hubei Area, China (Sallam, 2021). Contaminations quickly spread throughout China and other countries around the world (Broockman, et al., 2021). The disease caused by the new was dubbed "Covid infection 2019" by the WHO on February 12, 2020 (Lee, 2021). Even while the majority of Corona virus cases are asymptomatic or accompanied by mild, influenza-like signs, select populations, particularly the elderly and persons with concealed illnesses, might develop severe lung harm and severe respiratory miserable condition (Sallam, 2021). For assignment help As the number of Corona virus cases continues to climb and medications are constrained to symptomatic treatment, there is an undeniable need for a preventative approach, such as a vaccination, capable of preventing or decreasing the severity of COVID-19 (Broockman, et al., 2021).In less than a year before the World Health Organization (WHO) declared Coronavirus to be a pandemic, ten distinct vaccines have been approved for use in various countries throughout the world (Edwards, et al., 2021). Nonetheless, there is widespread opposition to Coronavirus vaccines in the United Kingdom, Australia, and a number of other countries (Roope, et al., 2020).Even with vaccinations that are very successful at preventing and stopping corona virus epidemics, large levels of immunisation coverage in communities will be necessary (Lee, 2021). According to the World Health Organization, countries should take a proactive approach to vaccination hesitancy hotspots based on social and behavioural data (Roope, et al., 2020).
Rationale
With more than ten vaccines manufactured by various nations in a single year, it is critical to do global research on their action, efficiency, effectiveness, safety, side effects, and so on (Vanderslott, et al., 2021). While many countries in the Global North are likely to achieve universal vaccination by late 2021, middle and low-income countries may not have essential antibody availability until 2024 (Lee, 2021). Vaccine aversion by even a small percentage of the population can jeopardise the plan's success (Sallam, 2021). As a result, this research is being performed to focus on the efficiency and safety of these vaccinations, as well as to explore their adverse effects in order to reduce the uneasiness associated with Covid-19 immunizations (Vanderslott, et al., 2021).According to current research, COVID-19 vaccination intentions differ significantly among nations (Lee, 2021). Vaccine hesitancy, or being doubtful about obtaining a vaccine, generally accounts for a larger proportion of people who will not get vaccinated than vaccine resistance, or those who refuse to vaccines (Sallam, 2021). Vaccine reluctance to a COVID-19 vaccination was reported at 9% in Australia, with vaccine resistance at 5%, although this information came from a non-representative online poll (Edwards, et al., 2021). According to national representative polls conducted in the United Kingdom, 25–27 percent of respondents were apprehensive (Edwards, et al., 2021). Hence, considering the information, it is deemed important to conduct a systematic review to understand the factors more intricately.
Research Aims
The research aims to highlight and shed critical focus on the vaccine efficacy and safety while also identifying any side effects such that nervousness from their administrations can be reduced to a considerable amount.
Research Objectives
The research aims to address the following objectives:
- To outline the efficacy of the vaccines manufactured for COVID-19
- To highlight the safety that is associated with the vaccines manufactured for COVID-19
- To identify any perceived side effects experienced by the administration of vaccines manufactured for COVID-19
Research Questions
The research aims to answer the following questions:
- What is the difference between the efficacy and safety of different COVID-19 vaccines in Australia, the United Kingdom and its neighbouring countries?
- What are the side effects of the each of the vaccines manufactured for COVID-19?
Research Hypothesis
The research aims to conduct following explorations and tests to achieve:
- Decision on effectiveness of which vaccine in regards to its action of protection against being infected by COVID-19
- A clear understanding of safety and efficacy of each vaccine manufactured, thereby reducing fright spread and anxiety among people to administer vaccines
- A clear understanding of the side effects that are observed in each vaccine and to outline the severity in people with pre-existing health conditions
- A detailed action of the vaccines in countries such as Australia, the United Kingdom, and its neighbouring countries
Methods
When doing any type of investigation, it is critical to discover a reasonable technique that can enable showing up at the exploration location. An efficient technique will be used in the flow extent of investigation. Because the goal of this investigation is to determine the efficacy and security of Covid-19 antibodies, as well as their incidental effects in Australia, the United Kingdom, and neighbouring European countries, a few articles must be investigated, and an orderly audit of various articles will be intended in the research.
Search Strategy
For the current research, 9 databases were searched for the retrieval of appropriate research studies in regards to the topic. Databases like Libraryof Torrens University Australia, PubMed, and open data sets like Scopus, ProQuest, Elsevier, BMJ, Global Public wellbeing, Mendeley, and Google researcher were searched. The publication date of the articles selected for the study were restricted to year 2020 and 2021 as the incident of COVID-19 is recent. For the retrieval of articles in a relevant manner and to gain an appropriate understanding of the research objectives, no restriction on the study design being adopted by authors in studies were done. However, language restrictions were put in place in order to understand the meaning of the content of the articles in an appropriate manner and not being lost in translation.
Study Selection
For the selection of the appropriate articles, it is necessary to outline the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the journals selected for the current systematic review. The following are the criteria for exclusion in the current study. The remaining articles have been selected for the study.
- Articles for which the authors have not adopted research methods concerning the topic and their eligibility for critique
- Articles for which only the abstract is available in the databases searched
- Articles which do not highlight the perceived efficacy of the vaccines and their perceived side effects
- Articles which are not published in English Language
- Articles which are not published by their authors since the year 2020 and 2021
Data extraction
The PRISMA protocol flow diagram depicts the flow of data during the various stages of a systematic review. It describes the number of records recognised, included, and rejected, as well as the reasons for rejections. The flow diagram is depicted below:
Data Analysis
Data were descriptively synthesised to map various parts of the literature as indicated in our central questions. The studies were classified based on the instrument, audience, and research design, with RCT data being studied in greater depth. Because conversation boards are not included in the initial classification method, results are reported for all included research as well as studies that evaluated tools other than discussion boards. Data analysis must be carried out in accordance with the 'Systematic Review,' utilising the PRISMA protocol checklist and flowchart. The PRISMA declaration provides a starting point for organising a systematic review. It includes a checklist of topics to keep in mind for the report analysis.The PRISMA Statement includes a 27-item plan or agenda that is downloaded in Word format for participants to re-use, as well as a four-stage stream diagram in their investigation. The purpose of the PRISMA Statement is to support makers with the declaration of methodical audits and meta-examinations; nevertheless, PRISMA may also be employed as a rationale for discovering precise orderly surveys of various forms of investigations, specifically assessments of medicine mediations. Nonetheless, the PRISMA plan is not a quality evaluation tool for quantifying the concept of systematic audits. PRISMA's general concepts and focuses are typically applicable to any intentional audit, not only those whose goal is to summarise the benefits and drawbacks of clinical consideration mediation. Regardless, a few alterations to the agenda's focuses or the flow diagram will be critical expressly in particular circumstances.As a result, the PRISMA Protocol will be used to conduct an ordered survey for this exploration endeavour. The rationale for employing this mindset is to determine whether the examination disclosures are reliable throughout the targeted countries.
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
Ethical Considerations
In the current research study, no participants have been undertaken as it is a secondary research. Hence, in regards, ethical considerations for the articles for analysis have already been taken by their respective authors.
Results
According to Badiani et al. (2020), Pfizer vaccine showed a significant amount of effectiveness against the COVID 19. It has been seen that the results of the study highlighted a significant rise the effectiveness in the percentage from 90 to 95 per cent. Among 43538 participants 170 people affected with COVID 19. Among all these cases, 162 are from the control group and 8 are from the vaccinated group. Hence, it can be highlighted that the study effectively provided the idea of the effectiveness of the vaccine in terms of the immunization process against the COVID 19. The results have been seen after the phase III trial. This study also highlighted that the impact of the vaccine can be long lasting and the priority group that is over the age of 65 the vaccine showed effectiveness almost 94 per cent. Hence, this can be stated that the Pfizer vaccine is very much effective against the disease of COVID 19. Moreover, the vaccine has not shown any kind of negative health concerns for the participants that is there is no safety issues involved for the vaccine. In this consideration, it should be stated that the study effectively provided a proper idea regarding Pfizer vaccine for the COVID 19 immunization.
As per the views of Nasreen et al. (2021), Pfizer-BioNTechComirnaty, ModernaSpikevax and AstraZeneca Vaxzevria are the most prominent vaccines in Ontario, Canada. The authors conducted the test-negative design study and found out the effectiveness of the vaccine products against the alpha, beta, gamma and delta strains of the COVID 19 virus and the SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are more transmissible and pose increased threats regarding the disease severity. Based on this study, the vaccine products are more effective if the two doses of the vaccines are provided to the patients and the effectiveness of the vaccine products are similar mostly. It has been seen that the vaccine showed effectiveness against alpha strain from 89 to 92 per cent, against beta strain by 87 per cent, against gamma strain it is 88 per cent and delta strain it showed 87 to 95 per cent of effectiveness. Hence, in scenario of Canada the impact of the vaccines are mostly similar and the rate of the effectiveness of the vaccines are higher in case of double dose completion compared to the single dose and also the impacts are more prominent among the elderly people over the age of 60. Hence, it is clear that the vaccination if completed then the immunisation of all the vaccines are mostly similar and the chances of the SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are reduced by these vaccination process. On the other hand, the impacts of the vaccines are mostly positive for the disease reduction.
Based on the views of Boytchev (2021), it has been seen that the AstraZeneca vaccine is mostly used in the European context and the impact of the vaccine can be seen positively in most of the cases. It can be stated that the impact of the vaccine is mostly found against the younger population and the elderly population have not effectively immunized with this vaccination process. In case German newspaper reports it has been seen that the AstraZeneca vaccine can be effective for the elderly people only up to 8 per cent which is a concerning factor for the vaccination of the elderly people of the country as the contamination and the impacts of the COVID 19 disease is very high. Thus, it should be stated that the factor of the vaccination through AstraZeneca should be changed and other effective vaccines should be considered for the change in the situation and increase the effectiveness of the vaccination of the same.
According to Heath et al. (2021), the effectiveness of the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine against the COVID 29 is considerably high. It has been seen that the study conducted by the authors considered 15187 participants in the randomised group and 14039 participants were from the placebo group and the results highlighted that the from the vaccinated group 10 people and from the placebo group 96 people showed onset of the symptoms after the double dose for 7 days. No cases of hospitalisation and deaths were seen among the participants and on the other hand, the study showed that the vaccine 86.3 per cent efficacy against the alpha strain and 96.4 per cent against the non alpha strains with the confidence interval of 95 per cent. Hence, as per the data it can be stated that the vaccine is more effective for the later strains came into action of the COVID 19 than the alpha strain. However, the efficacy of the vaccine is very much prominent for the improvement in the situation considering the decrease in the impact of the disease.
Mahase(2020), highlighted that the Moderna showed a higher efficacy in case of the US and UK population as the rate of the efficacy is found to be 94.1 per cent. However, in several situations in UK it has been seen that the impact of the vaccine is 87 per cent and that can be marked as the true efficacy for the vaccine. Moreover, the vaccine showed several safety and security related impacts on the patients. The vaccine is still less effective for the elderly population over the age of 65 and it can be a concerning aspect for the considered country and the population of the country. It should be stated that the effectiveness of the vaccine can be considered for the improvement of the situation of the COVID 19 situation. However, the consideration of the safety of the elderly people needed to be considered and proper recombination of the vaccine to improve4 the safety should be implemented.
As per the views of Chavda, Vora and Vihol (2021), COVAX 19 is one of the most prominent vaccine against the COVID 19 situation and this vaccine is focused on the spike protein of the virus and nullifies the impacts of the vaccine on the human body effectively. Moreover, it can effectively blocks the ACE2 receptor of the humans and it will reduce the effectiveness of the COVID 19 virus on the body. Thus, it should be stated that the impact of the vaccine is very much prominent as this can impact of the receptor activity and inhibits the growth of the COVID 19 virus. In this consideration the practical studies on the vaccine through experiments required to be considered for the better view on the vaccine.
Baden et al. (2021), conducted a study on 30420 participants among them half of the participants were selected randomly and the people of this group are provided with the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine and the other half of the participants were provided with the placebo treatment. The placebo group showed 185 participants with infection and the confidence interval was 95 per cent. On the other hand, the participants from the random group showed 11 infection cases. Thus, the efficacy rate of the vaccine is 94.1 per cent. Moreover, the affected people with the infection were found to be over the age of 65. Thus, it is evident that the vaccine is effective against the virus and it can effectively reduce the impact of the CIVID 19 cases though the elderly people are more vulnerable to the COVID 19. Hence, it should be stated that the importance of the improvement of the quality of the vaccine for the improvement of the outcome of the elderly people. It should be stated that the impact of the vaccination is prominent and effective for the participants and it should be considered for the further processes of the immunisation.
Based on all the above studies, it should be stated that more or less all the vaccines highlighted prominent impacts and efficacies against the virus and the disease reduction was prominent. However, the Moderna and AstraZeneca vaccine showed some safety issues for the elderly people and that should be improved for the further effectiveness and proper efficacy identification. However, the vaccines are comparably very much effective for the people of the world and the countries should try to improve the quality of the vaccines. Moreover, it should be stated that the improvement of the situation should be considered for future of the disease.
Limitations
The impacts and the efficacies of the vaccines can be seen through the studies. However, the impact of the safety and the security of the disease reduction should be considered and the recommendations should be provided which are missing and the practical studies should be considered for the future context.
Discussion
There are not many literary sources which can give an account of the efficacies of vaccines prepared by many countries. Although a number of pharmaceutical companies are coming up with vaccines and vaccination has already started rigorously, the research on vaccine development is still and scientists all over the world have been at their best to bring out the best version of the vaccines to fight with the evolving strains of the virus. Multiple vaccine candidates are in the phase 1, 2 and 3 of the trial, while many other had been finishing the preclinical trials. Some of the vaccines developed are the Messenger RNA based vaccines, which is a novel technology and had been used in vaccine preparation of other diseases before the pandemic. Results from phase 1 and phase 2 of the trial have showed the safety of the vaccines.Many of the vaccines had been showing some promising effects like recombinant vaccine AZD1222 conducted by the University of Oxford and Astrazeneca. The imperial college of USA has developed the mRNA 1273 vaccine by the Moderna. Other vaccines which has already been approved by WHO are Covaxin developed by Bharat Biotech and Covishield developed by the Serum Institute of India.
While searching for papers to find out the effectiveness of the vaccines, one of the papers have claimed the effectiveness of the Pfizer- Biotech and Astrazeneca vaccines. A paper by Bernalet al., (2021) have conducted a case control study in England, where 156930 adults have been chosen for the administration of vaccine Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 and Oxford-AstraZeneca ChAdOx1-S vaccines. It has been found that a single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine has been 6-=70 % effective in preventing the symptoms of Covid-19. Those who were vaccinated and still had the symptoms were had 45 % lesser chance of getting admitted in the hospital along with 50 % lower risks of death. However, One paper has referred to the side effects shown by the Astrazeneca vaccines. Similar types of results have been shown by a study conducted by Solomon et al., (2021), where it has been stated that just like the other vaccines, the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine have certain side effects which showed its peak within the first 24 hours after the administration of the vaccination and lasted for about 1-3 days. The severe symptoms were not very common, but were the main reason for the avoidance of the vaccines by the recipients or they did not wanted to pursue for the second dose. Most of the symptoms identified were headache, tiredness and dizziness. Another paper by
Badiani et al., (2020) have explored on the efficacy of the Pfizer vaccines on reducing the symptoms of Covid-19. Similar type of results have been shown in the study by Tenforde (2021), where a study has been conducted to find out the effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines. It was found that there was significant effectiveness of the vaccines was detected after the first dose. Effectiveness was shown after the second dose of the vaccine has been completed. However, the adults had been recommended to abide by the hand hygiene protocols and wearing of masks for at least 14 days after the second dose has been administered. However, this study has also admitted that a total vaccination course might not prevent an individual from contracting the disease but can prevent Covid-19 associated hospitalization and death. Vaccinations can also have impact on the post Covid situation in an individual. Similar types of results can be found in the study conducted by
Mahase,(2020), where only one case was found in the vaccination group and for in the placebo group. This study also mentioned about the adverse effects related to the vaccines like short term mild to moderate pain in the site of the injection, hand pain, headache and fatigue. The adverse events were low and similar in the vaccine and the placebo groups respectively. Apart from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Moderna, another vaccine that is available in UK is Novavax(Sacks, 2021). ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 has been referred to be having a pretty safety profile which has been important for the Covid -19 symptoms. One of the most important thing is that it is well tolerable for the elderly people (Sacks, 2021). The Australian government had also approved the Spikevax or the Moderna vaccines for people above the age of 12(Sacks, 2021). A study by Mahase, (2020), analyzed severe Covid cases. It was found that most of the severe cases were found in the placebo group than that of the vaccine group. One death had occurred in the study, that also in the placebo group. However, considering lesser side effects, this vaccines have been rolledout. Another vaccine that has been accepted are vaccine developed by the John & Johnson, which is likely to be the third COV 2 vaccines. Rosenblum et al., (2021),on the other hand have stated about the adverse effects related to Janssen vaccine. On July 202, a warning was issued by FDA about the number of GBS cases after the vaccine administration. The GBS is a rare neurological disorder which is characterized by the sudden onset of fatigue and weakness. GBS can be lethal and can cause permanent paralysis as well as death. Another adverse report noted for the Janssen vaccine was blood clotting, due to which the vaccination trialwas discontinued in a study (Rosenblum et al., 2021).
Covax-19 is a recombinant protein based Covid-19 vaccine that has been developed by a South Australian based biotech company Vaxine. Only one paper found in the systematic review contained information about the effectiveness of Covax-19. There are almost no papers that can validate its efficacy, as it is based on the interim data that has been collected from a Phase III SpikoGen trial which has recruited about 17000 volunteers(Kim, Marks & Clemens, 2021). The interim data has shown that the vaccine has surpassed 60 % of the efficacy of the virus. However, a rigorous trial for this vaccine is still needed considering its partial efficacy(Kim, Marks & Clemens, 2021). It should be mentioned that the primary goal for the implementation of Covid-19 vaccine is to protect against the disease and mortality. Since the production of the vaccine are still at its early stage, it is very difficult to predict or point out the methodological constraints. Secondly, many persons have dropped out from the real RCTs after the administration of the first dose probably due to vaccination hesitancy that, is unjustified speculations about the effects of vaccinations, which can differ from half-truths and unsubstantiated guesses to deliberate misinformation on the basis of the conspiracy theories(Sharma et al., 2021).A very close attention is given to the attendance of the study visits, the cold chain requirement as well as the administration of the study products. All these parameter are difficult to control incase of general population (Solomon et al., 2021). Hence, such randomized controlled trials can overestimate the extent of protection provided by the vaccines in comparison to the real world. Additionally, it is also necessary to say that after the administration of the vaccines, the recipients should be informed of all the side effects, the ways to treat them and when and whom to seek help in case any such adverse effects are seen(Solomon et al., 2021). Thus, from these limited number of papers, it can be said that among the many vaccines that are still under trial, only the vaccines produced by Astrazenaca, Moderna and Pfizer had been showing a promising effects with minimum side effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be stated that although vaccines are the ultimate tool to save the mankind from the paws of this pandemic, the vaccines needs to be carefully wielded and should definitely be used along with other safety protocols. For example, even after the second dosage of the vaccination has been completed, it is necessary to wear masks in public places, wear gloves, use sanitizers and avoid unnecessary crowding, considering the fact that the virus is continuously evolving and the question lies whether misinformation, politics, vaccine hesitation, division and deception be able to make community vaccination possible and lower the burden of Covid-19. Although, many countries and organization are still carrying out researches on vaccination, there are 3-4 main vaccines that has been approved by the World Health Organization and FDA, considering the minimum side effects. This scoping review has explore the differences in the efficacy of the vaccines developed in countries like US, UK and Australia.Among the vaccines, the vaccines developed by the University of Oxford and Astrazeneca and the one developed by the Pfizer had shown good effects. More research trials are required to understand the mode of action of these vaccines and how they can be improved.
References
.png)
.png)
Reports
MBA622 Comprehensive Healthcare Strategies Assignment Report
Assessment Description
This assessment provides students with an opportunity to research and analyse a particular healthcare segment to gain an initial insight into the opportunities and challenges that currently exist for organisations that deliver healthcare services in Australia in that segment. Students will present that research and analysis in the form of a formal report which requires students to adhere to a report structure including an Executive Summary.
Instructions
Students are to investigate an industry segment of the Australian healthcare sector and examine and evaluate its model of operations and growth over the last ten years. Recommended industry segments include:
- General public hospitals
- General practices
- Private hospitals
- Specialist medical services
- Pathology or diagnostic imaging services
- Dentistry or other related services
- Oncology services
- Mental health services
- Allied healthcare services
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Aged care
Information
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969
This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Kaplan Business School pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (‘Act’). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Kaplan Business School is a part of Kaplan Inc., a leading global provider of educational services. Kaplan Business School Pty Ltd ABN 86 098 181 947 is a registered higher education provider CRICOS Provider Code 02426B.
Document Classification: Public
This consultation should take place to help guide students to think ahead. Choosing an industry segment where information cannot be easily found will make the task of analysis much more difficult not only for this assessment but may require students to change their chosen industry for the subsequent Assessments 2 and
3.
The industry analysis must be in report form and should present appropriate criteria or business analysis tools as a framework in which to identify and analyse the challenges and opportunities confronting the segment. It should draw from a range of government and academic sources, as well as industry reports. It should cover:
- A definition of the industry, outlining its main activities
- An overview of the competitive landscape, identifying and describing major competitors or organisations within the segment and their business models
- Industry trends, presenting an overview of operating conditions and factors influencing operating conditions
- Ethical issues faced within the industry
Your analysis should focus on the broader environmental factors influencing operations within the sector. The report may also include charts or diagrams, which are not included in the word count. The findings presented in this report must be based on scholarly and peer-reviewed sources of information that were published no longer than 5 years ago and relevant to the field of strategic healthcare. These sources must be presented in the report in the form of in-text citations and a reference list adhering with Kaplan Harvard Referencing Style. Wikipedia and other ‘popular’ sites are not to be used.
Solution
Introduction
The report is mainly focused on Australia's health care industry, specifically the aged health care sector. The fundamental objective of this report is to demonstrate the overview of the chosen healthcare industry in Australia, including it's the trends, challenges and weaknesses that impact the operations of the chosen healthcare industry. For assignment help The study is very important to briefly represent the current scenario of the aged healthcare sector in Australia and identify the major concerns present in the industry.
Health Industry Segment Overview
The health industry process of Australia is complex as it includes different kinds of services about the physical and mental well-being of the residents of Australia. There are various sectors where experienced and dedicated medical personnel offer the best medical care (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2021). The cost of expensive medical care is borne by Australia's state and tertiary governments. There are three kinds of healthcare available to the people funded by the government: residential aged care, home care, and home support. Medicare claims are also available to the aged people to get benefits. Some of the major competitors in this segment are Allity Aged care, Arcare Aged care, BlueCross and others (Healthcare Channel 2021). The main business model used by BlueCross is the value proposition to its patient to promote dignity, respect and choice of its people. On the other hand, Allity care and Arcare aged care use respect and value proposition-oriented business model to provide adequate services to people.
Application of Analytical Tools
PESTLE Analysis
.png)
.png)
.png)
Table 1: PESTLE analysis
Source: (Developed by the author)
Porter's Five Forces Analysis
.png)
Table 2: Porter's five forces analysis
Source: (Developed by the author)
Identification of Industry factors influencing operating conditions
Multiple factors influence the operating conditions of health care for aged people. The foremost factor that affects is the culture of the aged people. Australia has a diverse culture, and many people belong to the Aboriginal and Strait cultures.
Healthcare organisations need to anticipate this issue by considering the solving methods. This pollution in the environment affects the health of aged people (Panda 2021). Thus, it has a significant impact on the aged health care sector. A high amount of disease in Australia impacts people's lives typically because the organisation needs to focus on the organisational ecosystem to improve its services. The introduction of various new viruses and bacteria can be a threat to the aged health care sector, as aged people are prone to be attacked by viruses and bacteria causes' disease. Psychological factors can also be a crucial one in the aged health care system of the country. Negative thoughts, stress about personal health and others can affect the health of old aged people. Industry, specifically the BlueCross, must initiate some steps to counter that, like positive counselling the aged people to get rid of negative thoughts and lead a healthy life. Alongside this, financial conditions can also affect aged health care. Due to the recent pandemic, every country has suffered in financial crisis, which creates problems regarding the accumulation of proper health treatment to the aged ones. Thus, steps of mitigation regarding this can also be formulated. Another significant factor that impacts quality medical care is the inaccessibility of certain places (Van Gaans & Dent, 2018, p. 12). There are remote locations that are out of reach. Setting up the infrastructure to support the aged people can be expensive and, at times, impossible. Providing care to aged people in remote areas can be extremely difficult.
Trends, challenges and weaknesses confronting the health sector/segment
The number of older adults is escalating, and the infrastructure has to be improved to accommodate the growing number. Challenges faced by the Australian health segment of elderly age care include:
1. Chronic conditions like obesity and overweight are becoming more prevalent among aged people. Conditions like these demand attention as these can lead to far-reaching consequences.
2. Lifestyle-related diseases are also growing in numbers. A sedentary lifestyle can take a toll on health, impacting bodily functions.
3. Disability is also a common trend among aged people. They require additional precautions, and the health systems must handle the operational procedures.
4. A distinct challenge faced by the health systems of Australia is to deal with aged Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders ("Health system overview - Australian
Institute of Health and Welfare", 2021). They have a unique culture and are unaware of modern medical practices (Rheault et al. 2019, p. 8). They comprise a significant number of the Australian population. Aged Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders may not be well-versed in the language and are apprehensive about the advanced health care facilities. Making them understand can be a significant challenge.
Strategic Response:
For the short term and long term (following the Commission's recommendations and the government's response to budgetary investments), proactive aged care providers will outperform their peers in evaluating their activities. Such include a strategic measure which includes:
1. Priorities must be clearly articulated, actively supported, and appropriately funded, spanning the organisation's entire spectrum. Additionally, providers may consider diversifying certain customer segments (like wealth, age, cultural needs) or the scope of their services (i.e. home care service) so that they can make a name for themselves and stand out from the rest. The associated risks should be carefully managed.
2. The sector needs to implement a strong support-oriented policy in Australia that can prevent people from pollution-oriented things that can assist aged people to live a healthier life.
3. The industry needs to seek strong government support that can help promote and enhance the living standard of older people.
4. Transparency and accountability should be considered. Providers must respond. Strategic goal setting, measurement of key performance indicators, and rapid interventions to address/correct gaps will be critical for operations in the aged care sector. As consumer expectations rise and the level of care becomes increasingly standardised, providers need to differentiate themselves. This requires providers to articulate unique market offerings for their target segments that align with consumer preferences (PWC 2021).
5. A different type of approach should also be considered with indigenous peoples. Cross-cultural communication will play an important factor, and there is a need to recruit people from the same community in such a situation.
Ethical Issues
The aged people have the right to decide about their health care system, and they can choose the mode of mediation or whether to follow the instructions of a doctor. The doctors are also mandated to provide detailed information about the health conditions of an aged person so that the person can make informed decisions. However, it can be not easy to follow these ethical principles. A person who may require immediate medical care but is not interested in availing of the facilities can threaten that person (Maile et al. 2018, p. 373). Managing ethical principles can be tough in these situations. Also, different cultures have different beliefs, like the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders have different value systems(Sivertsen, Harrington & Hamiduzzaman 2019, p. 12). They might deny some medical practices. These ethical issues may hamper the overall quality of services.
Conclusion
The health care industry is one of the most crucial industries of any country, and hence it has the utmost importance. Based on the above analysis, it can be stated that infrastructural development is needed in aged care services, and Blue cross needs to offer a better-customised service.
References
.png)
Research
GAL613 Grief and Loss Assignment Sample
Assessment Brief
Length 800 words (+/- 10%)
Learning Outcomes
The Subject Learning Outcomes demonstrated by successful completion of the task below include:
a) Identify the needs and appropriate support services for people experiencing grief and loss.
b) Develop a plan for a holistic approach to grief and loss counselling
Task
This assignment requires you to produce a two paragraph scenario and a corresponding session plan for a client experiencing a complex emotional response to the experience of complicated or disenfranchised grief and/or on-going and ambiguous loss. (200 words +/-20%)
For the purposes of this assessment you are required to assume that you have seen the client over a number of weeks (at least 6) and that you are aware of triggers. Ensure you identify at least 5 possible strategies for working with the client. For example, you may decide that you wish to work with metaphor, or encourage connection with the subconscious via a particular technique, or use a narrative or story telling method or use a focusing technique to connect with something you have observed the client to be shying away from. This should be presented as a table. Please refer to the Task Instructions for details on how to complete this task.
Instructions
To complete this assessment task you must:
Consider the following questions/elements:
• Write a two paragraph scenario introducing a client who is experiencing complex or disenfranchised grief and /or ambiguous loss and who is not in touch with their feelings and emotions. (200 words +/-)
• Produce a session plan for working with the client that includes 5 possible strategies for working with the client. For example, you may suggest a mindfulness based Hakomi strategy to encourage the client to re-experience an event in a safe space.
• You will be assessed on your ability to
o Use your creative abilities to write a scenario that describes an experience of a complex emotional response to the complicated or disenfranchised grief and/or ongoing and ambiguous loss.
o Provide a session plan that includes 5 potential approaches to support a client to work though elements of their functioning that could realistically be associated with complex grief.
Referencing
It is essential that you use appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research. Please see more information on referencing in the Academic Skills webpage. However, References are not required for this assessment.
Solution
Introduction to Case Study
Denise, 59, is a widow who had been living alone for the previous 12 months. After Denise's husband was diagnosed with brain cancer three years ago, he passed away a year ago. She raised two children, both are now adults (27 and 25) but were neither married nor in the military and were instead pursuing jobs in various regions of the nation. Denise finished her bachelor's degree and worked until she was 30, when she got married. Denise's main issues are isolation, sadness (which she'd been experiencing for a year and a half), and trouble dealing with everyday life. She is having a significant depression once before, around the time she was 25 years old, when her father had passed away.
Denise said that she had been more reclusive since her husband's sickness had begun (brain cancer). She had typical childhood, adolescent and early adulthood friendships. Together, she and her husband had enjoyed a tranquil life, devoted to their children and their careers.
During their leisure time, they had participated in academic and cultural pursuits together with great enjoyment (museums, lectures, concerts, and fine restaurants). However, amid the husband's sickness, the couple's few close acquaintances had gone to places like Florida and Arizona, leaving them socially isolated. Her major depressive symptoms were a lack of enjoyment, impatience, retreat from social situations, indecisiveness, exhaustion, guilt, a lack of motivation, and loneliness.
Session plan for assignment help
Session 1: Denise will start by discussing her "sad sentiments." I will quickly elicit Denise's instinctive thoughts.
Session 2: In Denise's second appointment, I will develop an agenda together.
Session 3: I will guide to be socialise
.png)
.png)
.png)
References
.png)
Assignment
BEHL2009 Bachelor of Social Science Assignment Sample
Question 1
Provide a brief literature review on the social issue being addressed -
Immigration and mental health is one of the social issues that are being addressed among our society. Immigration is a life-changing that may result in compromised mental health, especially when personal demands exceed resources.
Mental health is accumulated by three components, these include emotional, psychological and social wellbeing. Having poor mental health is a result of people whose wellbeing has been affected by others or uncontrollable events in varies substantially race, ethnicity, national origin, gender and socioeconomic status which they encounter difficulties and obstacles. These hardships may have included:
Finding quality jobs in safe-work environments.
Achieving economic integration.
Overcoming barriers in accessing basic social and health services.
Engaging in a smaller set of social networks that provide instrumental and emotional support.
Coping with systematic discrimination and racism.
Throughout immigration, most immigrants experience in four common pathways of social determinant of health and health inequalities are material deprivation, psychosocial factors, local enforcement, and access to health and social care. Material deprivation is related to disruption of social support, roles and networks which exposure to harsh living conditions (Unemployment or underemployment). Immigrants mental health often add trauma as part of the psychosocial factors which exposure to violence as being treated appropriately through childhood to adulthood. Political movements is also likely to disrupt family and community network by reduce their social interactions and use of essential public services or uncertainty about outcomes of migration as increasing the vulnerability for reunification of their families. Moreover, difficulties in language learning (especially for elderly migrants), acculturation and adaptation.
The most common disorders that immigrants experience refers to depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorders and phobias.
The first-generation members of the immigrants have the most significant traumatic experience in a new society where they have no English-speaking background, lack of social support, undergo prolonged separation from their family and socioeconomically disadvantage position; hence, the level of psychological stress and demographic characteristics all contributed to the mental health and well-being of immigrants. Furthermore, the role of family is an important component of most support network where family members or relatives have sponsored an immigrant. Social resilience processes may be important in buffering the stress and disadvantage experienced by this substantial and growing population.
Question 2
Provide an outline of the group (dot points), including topics for 6 -8 weeks/ sessions
(free-flowing or set agenda) - a hybrid model (some set agenda, some free-flowing)
.png)
.png)
.png)
Solution
Question 1 - Immigration and mental health
Immigration can be defined as the action of leaving one's home country for relocating to some other country to find employment there and settle there either on a temporary or permanent basis. People who leave their country to settle in other countries are called immigrants (Definition, 2022). Mental health includes three dimensions of the emotional, psychological and social health of a person. It is a determinant of an individual's ability to handle stress, make social relationships, and make life decisions. It plays a crucial role in the overall development of an individual at every stage of his life. It has an impact on the cognitive ability, thought processes, emotions, and behavioral outcomes of an individual (mental health.gov, 2022). There is a significant difference between the terms " mental health " and mental illness. A person with a mental illness may experience some phases of perfect mental health whereas a person may have mental health issues but may not be diagnosed with any mental disease. The mental health of an individual is as important as biological health and long-term poor mental health can result in chronic mental illnesses, pathological symptoms, and various other health issues (cdc.gov, 2022).
Immigrants and refugees are vulnerable to various stressors and mental health issues before they decide to migrate, during the migration process itself, and after the migration process during settlement. A higher rate of mental diseases like anxiety, panic attacks, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is noticed in the immigrants than in the local population of that country. Migration not only reduces the access to mental health care for the immigrants, but it also proves to be a disruption in the continuity of the treatment. Various issues are faced by immigrants at different stages of migration. Before migration, there are faced with challenges like war, conflict, poverty, inadequate employment and livelihood opportunities and lack of educational opportunities. During migration, there are exposed to the threat of detention or violence or unacceptance in the host country or fear or uncertainty. After the migration, during their period of settlement, they are again faced with multiple issues like family separation, and unhealthy living conditions. Cultural or religious challenges, racism and ethnic discrimination, legal and statutory issues, unemployment, and lack of social acceptance (Who. int, 2022).
Shekunov (2022), also explained the process of migration in the three stages of pre-migration, migration, and post-migration and stresses the risk of mental and psychiatric health issues at all three stages of the immigrants. Immigrants are prone to depressive symptoms, and somatic issues, and have almost 10 times higher chances of having post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) than the host population. Cultural gaps and cultural remembrance add to their vulnerability. Issues like language barriers. Changes in social and political systems and lack of societal support contribute to their adverse mental health. Immigrants to Eastern and Western Europe are at a higher risk of developing schizophrenia. Stressors in immigrants for assignment help are caused due to the difficult situations and challenges of the migration process and also inadequate administrative and social support in the host country. Salami, Salma, and Hegadoren (2019), conducted a thematic analysis to understand the various issues that contribute to the adverse mental health of immigrants. Some of the identified issues were language barriers, cultural shock, cultural understanding of the term mental health, the stigma associated with the mental illness, fear of social boycott due to mental illness, and the economic and emotional impact of being diagnosed with mental illness.
Becerra et al (2020), researched to understand the impact of immigration policy and legal compliances on the mental health of Latino immigrants in Arizona. It was concluded that the immigrants who had a higher sense of personal loss and suffering due to immigration were found to have severe symptoms of depression, stress, and anxiety. Immigrants with a higher sense of family loss reported severe symptoms of stress and anxiety only. Wylie et al (2018), explains that the rise in the numbers of immigrants relocating from war-zone or conflict-prone area to various locations across the world has proved to be a huge challenge for mental health care professionals across the globe. These immigrants carry with them a baggage of war episodes, torture, and a difficult migration process. the trauma of war and conflict is difficult to be mitigated within a short period and takes considerable time to overcome them. PTSD is considered to be not adequate to explain the complex traumatic experiences of immigrants that are characterized by somatic issues, depressive symptoms, and anxiety.
Question 2 – Group Outline
.png)
References
.png)
Research
PBHL20006 Participatory Health Research Assignment Sample
This is an individual task assessment. You will be required to write a reflective essay (1500-2500 words). You will reflect on the application of your learning related to the readings, lectures, tutorials, and prior assessments. You will be tasked to address these two points:
• Your positionality and what you thought to be true in relation to public health research.
• How you would seek to undertake research with Indigenous communities.
Solution
Research Positionality
Public Health Research
.png)
.png)
.png)
Figure 1- Positionality
(Source- Author)
Concrete experience:
I had been a part of this research related to the public health for assignment help risk rising in Australia. The issue that I focused on was diabetes. While doing my research on this topic and looking for resources, I came across and learnt that diabetes is one of the major issues rising in Australia. This disease has affected not only adults but also children till 14 years of age. To deal with this issue, the government of Australia has also been working proactively. As much as they can do, they have done and are still trying to do. To help individuals who have diabetes, the government is trying to provide the best medical help and high-quality and affordable medicines. After finding out the number of people affected by this disease, I feel this research is important to be worked on. I feel bad that about 1 million, more than half of the population residing in Australia, have been affected by this growing disease which also leads to deaths. So Australia ranks 10th among all other countries for the deaths that are taking place due to type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Reflective observation:
As per research on this issue, I have understood that diabetes, more than just being a disease, has turned out to be a silent pandemic rising daily and affecting both adults and children. As per the research, it has also been seen that there are two variants of diabetes type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is seen to arise in the early stage. It is common to see it arising in childhood but can affect individuals of any age. It arises when the tissues in the human body and the autoimmune in the pancreas are disrupted. Whereas type 2 has been seen spreading recently among both adults and children. The reason behind type 2 diabetes is when the body tissues are unable to respond to the insulin. Thus, as per my finding, I have seen that type 1 diabetes is highly common among children aged 0-14 years and is the 6th highest incidence. Of all, Australia is considered to be 7th highest in the cases related to diabetes.
Abstract conceptualisation:
Per my understanding, diabetes is not just a public health risk arising in Australia. It also affects the psychological health of individuals already affected by it. When they feel unable to cure their problem, they go through stress, depression, anxiety, and feel ‘burnout’. This is the major issue that is also leading to many deaths. If I were allowed to work on resolving this issue, I would have first advised the individuals who were diagnosed with diabetes to go and seek psychological help first. Because seeing the cases and researching them, I understood that any health issue, even if it can be controlled, if the individual is psychologically being affected, would still lead to death. More than just giving a list of medicines which is also a way of de-motivates an individual who is already in trauma, simple ways should be suggested, such as drinking a lot of water, working out more to reduce extra weight and quitting smoking if they do. Many other things are related to daily life. All this would help the individual to feel motivated and work on curing themselves.
Active experimentation:
In my opinion, people facing the issue should not be treated differently and should not be made to feel like a fish out of water. Rather every individual should be provided with a proper understanding of this, and they should be encouraged to fight against it. Campaigns should be set up to provide the people diagnosed with diabetes with a proper understanding of what it is, how it is caused, and how they can fight against it. This is a disease which cannot be completely cured but rather controlled. Rather than just providing them with high-dose medication, they should be advised to follow a normal life routine where they are required to keep themselves fit, consume sugar-free products, follow a strict diet, keep themselves hydrated, etc. To encourage them, they should be named some famous people who face the same issue but still lead a very normal life. While doing my research, I also came through that even the government of Australia has taken the initiative to provide essential required help to the people and children in terms of medical health.
Research with Indigenous Communities
.png)
Figure 2- Research with Indigenous Communities
(Source- Author)
Concrete experience:
My finding relayed the spread of diabetes among the people belonging to the Indigenous community. I have understood the risk of diabetes is higher among the people of Indigenous people of Australia than among the people belonging to the non-Indigenous community. In my finding, I came across the reason behind the rising cases of diabetes among them, which are reduced physical activities, increased obesity, changes in diet, and the high risk among the ageing population of the Indigenous community. The cases have also reflected that people are mostly affected by type diabetes, which is caused when the body tissues cannot control the insulin present in the body, leading to type 2 diseases. This has increased the rate of deaths taking place between the years 2015-2019.
The people of the Indigenous community residing in remote areas have a high risk of blood pressure, kidney failure, and diabetes. This research work is important being it is important to figure out the main cause of this issue, and recommendations need to be provided or suggested to control the spread of diabetes in the Indigenous community.
Reflective observation:
It was shocking to see the rising cases of diabetes in the indigenous community in Australia. Australia ranks 7th position, which is the highest in diabetes cases. Some of the other reasons due to increased cases of diabetes among the people of the Indigenous community involve alcohol consumption, mental health issues, and smoking. Most of the deaths are caused in the Indigenous community due to avoidance of health care effectively and timely.
In my opinion, public health issue needs to be educated to the people of the Indigenous community. In my finding, I understood that Indigenous people are spiritual and believe in orthodoxy. For them, good health is more than the absence of illness and diseases. They believe that diseases are caused within an individual when they are cursed. Thus, rather than help fight the disease, they distance the person believing they would cure it naturally or die.
My research is based on first educating the Indigenous individuals about the rising diseases. They need to understand what public health is, what risks it can lead to, and what measures need to be taken to cure it. They also need to understand the reasons behind the increased cases of type 2 diabetes in their community: increased obesity, decreased physical activity, and constant changes in their diet. This highly affects the body's immune system and weakens the body tissues. In my research, I will try to find strategies to help the people of the Indigenous community fight diabetes. To make them understand the importance, I have to plan a strategy to link with their spiritual beliefs and help them understand easily.
Abstract conceptualisation:
To cure the issue of type 2 diabetes, which is seen to be high among people, the major issue is the beliefs that these people have surrounded themselves with. The cases are not to be seen as high among the non-Indigenous people because they try to understand things more practically and immediately take precautions. The only problem with the Indigenous people is that they focus on spiritual understanding, and diabetes is an issue which cannot be linked with spiritual reasoning.
As a researcher, if I want to work on improving this issue, the major thing that I need to focus on is their understanding level, what they believe or understand about diseases, and what measures d they take to cure or fight against them. They need to be provided with natural medications which would help cure them. They need to understand what activities would help them cure this rising issue.
Active experimentation:
In my research work, I have understood that special ways need to be strategised to make the Indigenous people understand the issues related to diabetes, especially the reason behind the rising type 2 diabetes among them. Usually, they should not try to accept it or would look for religious reasons for it.
In my opinion, they should be recommended naturally grown medication which might not help them fully but still have some effect. They need to be introduced to the percentage of deaths that occur in their community due to negligence of medical health for the people affected by type 2, diabetes.
Reference
.png)
Research
PUBHLTH7113 Environmental and Occupation Health Assignment Sample
Imagine you are a Public Health Officer in a government health department and you receive a call from a local general medical practitioner (GP). The GP informs you that they have attended to several patients with food poisoning where they have identified Salmonella spp as the causative factor. Salmonella infections are a Notifiable infectious disease in your jurisdiction. The GP further informs you that all cases reported consumption of orange juice from a local manufacturer prior to getting sick.
Using the human health risk assessment model and basic epidemiological principles what steps would you take to investigate this public health concern?
Note that you will need to inform the Health Minister of this matter in a brief. What would you say?
Consider also that you would need to:
• Provide a prompt response time frame
• Provide a media note to the Minister
• Confirm the extent of the problem
• Understand the human health risks (exposure, outcome)
• Identify the most sensitive population (who is at most risk?)
• Initiate communication protocols (risk communication)
• Confirm the source of the problem (where is it originating from?)
• Initiate corrective action (What, when, who and how?)
Solution
Potential sources of lead exposure
The potential sources of lead exposure in the community where child care centre is located are as follows:
Paint:
Lead in residential paint and dust is a major source of lead exposure in the community. Most of the houses in the community are painted with lead-based paints. Moreover, the paint in several houses is peeling off or has deteriorated. Young children often take this paint in their mouths, or the paint falls on meals which exposes people to lead.
Soil:
The factories beside the childcare centre and the depositing of lead-based gasoline often contaminate the soil. Children breathe in this lead-contaminated soil when they are playing outside. Consumption of vegetables or fruits that grow near or in contaminated soil also exposes the children to lead.
Drinking Water:
Drinking water can be a major source of lead as the service lines to which the main water lines of the centre are connected lead-based. Lead faucets, plumbing materials, and pipes carry the drinking water to the centre. However, a chemical reaction that happens in lead plumbing fixtures called corrosion results in the mixing of the metal into the drinking water, making it contaminated with lead.
Population health impacts of lead exposure
Most likely to be affected
The most vulnerable population to lead exposure are children, specifically below six years of age. It has been reported that even a minor level of lead in a child's blood can have severe, devastating effects, and usually, these effects are permanent (Kuang et al., 2020).
The main impacts of lead exposure in children are as follows:
- The nervous system and brain can be damaged.
- The children would face difficulties in learning.
- The development and growth will be allowed down.
- The children would have problems in speaking and hearing.
How would we know
Since no immediate symptoms of lead exposure can be identified, it is necessary that the parents or the guardian consult their child's doctor the very first time they predict a change in a child's behavior or health. They should get their blood tested for lead.
Steps for conducting an environmental health risk assessment for assignment help of lead exposure
An accurate environmental health risk assessment of lead exposure demands a specific understanding of the sources, highly-vulnerable populations, and appropriate medical testing. In the immediate case, the assessment is to be conducted in a childcare center. The steps taken for the purpose are listed below:
Identification of sources of lead poisoning:
Since the child care centre is an old building, it is most likely that the paint on the building's interior and exterior and window sills have deteriorated. Even if the paint was fixed later, it is possible that leaded paints have been used for the purpose. Moreover, the building is situated near a busy main road which was formerly an industrial area. This means that the centre is likely to be exposed to additional sources of lead, such as deposits of lead-based gasoline, dust, and contaminated soil. The drinking water may also be a source of lead since the area has a significant indigenous community who are often exposed to lead sources.
Risk groups assessment:
Since a larger population that is vulnerable to lead in the child care centre involves children, they would be identified as the target groups for the assessment. To conduct the assessments, a few questions to gain an understanding of the current situation would be asked to the caretakers and managers of the child care centre. The questions would be related to the hobbies of the children, their habits, both good and bad, their field of interest, and their health profile. The analysis of the responses will provide insights into the level of lead the children are exposed to.
Medical testing:
Usually, the symptoms of lead poisoning are difficult to identify at the initial stage. Therefore, a blood lead test can be conducted to examine the effect of lead on children (Reuben et al.m 2019). The blood sample for the test can be collected by two methods, namely, heel-prick or finger-prick sample collection and the Venus blood straw collection method. The healthcare providers can test and provide a report on the level of lead in the child's blood. Once the reports confirm the effects of identified sources, steps to mitigate the severe impacts on children's health can be taken.
References
.png)
Research
UMH207 Understanding Mental Health Assignment Sample
Task Summary
In this 1800-word Report, respond to the challenges and issues in the case scenario. You are asked to research and find studies/research/journal articles/government and international health agency reports relating to the case study. These peer-reviewed articles will help you support your line of reasoning.
In this report, you will describe key points in relation to legal and ethical factors and the mental health act. You will also discuss your role as a mental health nurse in this case scenario and consider how you would respond to the client in a practical situation.
Finally, you will critically evaluate the importance of the “therapeutic relationship” in a male client with chronic schizophrenia, who is currently admitted involuntarily under a community treatment order in an acute mental health ward.
Instructions
1) Read the case study provided via Assessment 3 area of the subject.
2) Address the following questions in your Report.
• Discuss how and why the mental health act applies to the case scenario.
• Summarise and Identify specific examples of legal and ethical issues in relation to the patient’s rights.
• Compare the concepts of mental health, mental illness and mental disorder. Determine which category the patient in the case scenario fits. Accurately identify the main symptoms of schizophrenia as outlined in the case.
• As the registered nurse looking after the patient, explain how do you advocate for his rights as a mental health consumer?
• Identify and illustrate the main symptoms of schizophrenia as outlined in the case (this can be done in table form)
• Determine a medication that may be clinically indicated for the patient in the case scenario. Provide a rationale for why it is indicated.
• Evaluate and explain three (3) techniques you would use to develop trust, rapport and begin a therapeutic relationship with the patient when first admitted to the hospital.
• Express how you would explain the need to give the patient a depot anti-psychotic medication.
• Given the patient’s mental state at this time, identify one (1) technique you would use to ensure your personal safety (during the explanation about the depot medication outlined above).
Writing Guidelines
• Be formal and objective in your writing.
• Be analytical and demonstrate critical thinking.
• Keep to the set word limit.
• Answer all questions in your report.
• Use in-text references to support your ideas.
• Use information from academic texts and credible sources only.
• Format in-text references and the reference list according to APA 6th ed. referencing style.
• Proofread your work to check that each paragraph links to the previous or the thesis and that it is easy to read.
• Check your spelling, grammar and punctuation.
• Use a size 12 font (Times New Roman, Calibri or Arial).
• Include a footer with your name, student number and page numbers.
• Include a cover page with your name, student number, subject name, title of assessment, learning facilitator’s name and the final word count (not including referencing).
Case Scenario
“Jason” is a 32-year-old male living in housing commission in Western Sydney. He was diagnosed with schizophrenia when he was 19 years old. At that time, he was living with his parents and he increasingly experienced auditory hallucinations with voices telling him to burn his parent’s house down. Fortunately, these voices reduced when Jason started taking an antipsychotic medication.
Jason has been unemployed since he was 19 years old, and has been taking his medication every day since.
Six months ago, Jason moved out of his parent’s home and entered a shared apartment with 3 other males in the local housing commission. Jason stated he felt “fine” and decided to stop taking his antipsychotic medication.
Over the next 2 weeks, his mental state quickly deteriorated, with auditory hallucinations “louder than ever”. He became paranoid that his flatmates were poisoning his food and he believed a tracking device had been inserted under his skin and that he was being “tracked with a satellite by the CIA”.
His paranoia was so intense that he did not leave his bedroom for 3 days before the ambulance arrived.
Jason was scheduled under the Mental Health Act and admitted to the local acute mental health ward as an involuntary consumer..
You are the student nurse looking after Jason on the ward. He appears agitated, moving around erratically and is not making eye contact with you. He swears occasionally and appears frustrated at being “locked up inside the hospital”.
Jason is refusing to take his oral antipsychotic medication tablets. The doctor has charted an intramuscular “depot” antipsychotic medication, which you have been asked to give to Jason. After assessing Jason’s mental state, you agree that the depot is clinically indicated and is in Jason’s best interest, even though he has not agreed to take the medication.
After a discussion with a senior nurse and the psychiatrist, the team makes the decision that Jason should receive a depot antipsychotic medication against his will.
One week after having the depot, Jason’s mental state is stabilising and he is now agreeing to take oral anti-psychotic tablets. However, he still feels “very tired” and would sleep the whole day if he could. He is still unsure if the psychotic symptoms he recently experienced were real or not, but he is “thinking a lot about it”.
His psychiatrist reviewed Jason and he is hoping to transfer to the sub-acute mental health ward soon, and be discharged home soon as he feels “uncomfortable” in the hospital and “can’t wait to go home”.
Solution
Introduction
Schizophrenia can easily be identified as a severe mental disorder that manifests in an abnormal interpretation of reality. Several studies have been conducted to establish the genetic linkage between the diseases, with little success, therefore, presently, the condition is attempted to be treated through clinical intervention strategies (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2022). The present report is based on the case scenario of Jason, who is suffering from severe auditory hallucination, after the withdrawal from antipsychotic medications. The report addresses the mental health act applicable in the scenario, building knowledge over the difference in mental health, disorder, and illness, advocating for the patient's rights. The main schizophrenia symptoms have been outlined, along with the appropriate rationale for medication. The report also sheds light on the relationship development with the patient ensuring their personal safety for assignment help.
Application of Mental Health Act in the case scenario
Jason has been administered under the “Mental Health Act” within a local health ward specializing in acute mental health. In this situation, the Mental Health Act is the most appropriate legal aspect for the improvement of the patient. As per the Act, mental health practitioners and psychiatrists are encouraged to develop a strong relationship with the patient, which is critically needed in the present situation, as the patient is unable to trust (health.vic.gov.au, 2022). Moreover, as the Act has provisions for compulsory and voluntary treatment, makes it even more preferable in the situation, where Jason’s auditory hallucinations deteriorated leading to paranoia, and requiring compulsory intervention.
Legal and Ethical Issues Pertaining To Patient Rights
The legal rights of a patient, who has sought care within the Australian Health System, are ensured by the “Australian Charter of Healthcare Rights”, which ensures communication, respect, safety, privacy, participation, and comment of the patent (healthdirect.gov.au, 2022). According to Sperling (2021, p.25), patients bear the right to refuse medication. On the contrary, Jason has been seen to refuse medication, which has made the schizophrenia condition worsen. An additional legal right issue that emerges is the access to care facilities that are equipped to handle such critical cases, as Jason has been struggling financially owing to unemployment. The medications being forced upon the patient raises an ethical issue of patient rights (Rhodes, 2019, p.3). Taking into consideration the ethical issues, the privacy of the patient is needed to be ensured and the patient is needed to be treated with respect.
Schizophrenia Symptoms and Contrast of Mental Health, Mental Illness, and Mental Disorder
Mental health is inclusive of psychological, emotional, and social well-being. Mental health bears the potential to heavily influence the nature in which we act, feel, think, handle stress, relate to others and make choices (Happell et al., 2018, p.12). In contrast, mental illness pertains to the health conditions that bring about changes in individual behaviour, thinking, or emotions behind them. According to Zumstein & Riese (2020, p.15), the occurrence of mental illness is closely associated with problems and distress, preventing the ability to perform adequately in family, social, or work environments. According to the World Health Organization, a mental disorder is characterized by clinically significant disturbances in one's emotional regulation, behaviour, and cognition (who.int, 2022). These are associated with impairment and or distress in important areas of functioning. The case study of patient Jason and the details, therefore, provided align with the concept of mental disorder. Moreover in support of the mental disorder and linking it with schizophrenia Müller (2018) has opined that, the disorder results in a combination of delusion, hallucination, and disordered thinking, that impairs daily activities. Symptoms of schizophrenia that have been outlined in the case study are auditory hallucination and paranoia.
Advocacy of Mental Health Toward The Patient
Jason had been suffering from schizophrenia when his age was only 19. Due to his auditory hallucinations, he has been treated with antipsychotic medications. Though Jason has taken antipsychotic medicines for a long time and after stopping the medication, symptoms became aggravated he has been considered and hospitalized under Mental Health Act. The Mental health Act of Australia encourages mental health practitioners and psychiatrists to create a strong relationship with patients applying services of mental health and to give them support and information to make an informed choice about their care (Health.vic.gov.au,2022). In the case of Jason, it has been observed by the student nurse that Jason disagreed to take medications. Therefore, the student nurse has discussed with the psychiatrist and senior nurses and made the decision to provide a “depot antipsychotic drug” for Jason. It has been observed that in this case, mental health practitioners have made the decision for the patient related to taking medications. As per the opinion of Livingston (2020, p. 12), in Australia, mental health patients have the right to access support, assessment, treatment, care, services, and rehabilitation for wellbeing and recovery with the same equality as others. Jason is a mental health consumer here because he is taking services from the mental health hospital. As a nurse, the student can advocate a facilitate communication with all other healthcare members relevant to the preferences of the patient. Based on the research by Bégin et al., (2020, p. 40), it is the role of a nurse to integrate patient-oriented goals into the treatment plan and give objective guidance. Here, after observing aggravated schizophrenia symptoms the nurse has discussed with other team members and advocated the care for Jason. Reid et al., (2018, p. 1210) have stated that to promote advocacy for the mental health consumer a nurse must inform the total team, exhibit appropriate nursing care, give assistance with social problems, and teach patients about their personal advocacy. Therefore, the student nurse who is taking care of Jason has already started advocacy for the right of Jason as a mental health patient.
Identification and Illustration of Schizophrenia Symptoms (Case Scenario)
Critical analysis of the case of schizophrenia patient Jason it has been observed that different symptoms of this disease have occurred in Jason. The problem started when he lives with his parents in Western Sydney and became aggravated after moving to a shared apartment and topping medications. According to Menon (2019, p. 133), schizophrenia is a chronic disorder of the brain that appears with active symptoms like hallucinations, lack of motivation, issues with talking, delusions, disorganized speech, and others. In the case of Jason, during his 19 years of age, he suffered from auditory hallucinations, in which a voice continuously told him to burn the house of his parents. After feeling fine, six months ago, Jason stopped taking medicines and his situation became deteriorated. In the second phase, again auditory hallucination symptoms of schizophrenia have started. In this situation, Jason became paranoid that flatmates are going to poison his food. In addition to this, he has started believing that a tracking device has been inserted under his skin and that he has been tracked by CIA satellites. Moreover, not making eye contact, frustration, agitation, erratic movement, and tiredness are some other schizophrenic symptoms of Jason [Refers to appendix].
Medication and rationale
It has been obtained from the case study that, antipsychotic medicines have been taken for Jason from the start of the symptoms. Since the 19 years old, he has been taking this medication every day. Recently, to treat his deteriorated situation, the psychiatrist of a local “acute mental health ward” has prescribed “intramuscular depot antipsychotic medication”. Based on the research by Haight et al., (2019, p. 780), depot injection is a slow-release configuration of medication. The injection applies a liquid that emits the antipsychotic medication slowly and provides a long-lasting effect. Other authors have stated that depot antipsychotic medication is beneficial for schizophrenia because it overpowers the issues of covert non-compliance (Ling et al., 2019, p. 60). Therefore, depot injection is suitable for Jason in his aggravated situation.
Identified Three Techniques for Developing Trust, Therapeutic Relations, and Rapport
With respect to the case study when Jason was admitted to the local acute mental health ward under the Mental health Act of Australia, the doctor started to give intramuscular “depot” antipsychotic medication. However, Jason did not agree to take the medications rather he refused due to a poor therapeutic relationship. In this condition, three techniques can be used by the mental health ward staff to develop trust rapport with the patient for starting a therapeutic relationship. These are,
1. Accepting: It is really important to acknowledge what the patient tends to say and ensure that they have listened carefully. It is found that acceptance is the best thing to make eye contact and understand patients (van Belle et al., 2020, p.2). Patients like Jason who feels that their doctors and nurse are listening to them are more likely to become receptive to care
2. Encouraging descriptions of the perception: Sutanto (2021, p.14) opined that for patients who tend to experience hallucinations like Jason, it might be useful to ask about them nonjudgmentally. It helps patients to understand that doctors and nurses will not judge them and they can cast their perceptions in an effective manner. This results in developing better trust between patients and doctors.
3. Expressing empathy: When Jason was first admitted to the hospital he refused to take depot anti-psychotic medication. However, the doctors are required to empathize with the patients without being so emotionally overwhelmed. The doctors and nurses are required to manage their emotions so that the issues of the patients might not affect them emotionally. The goal of the mental ward staff should be related to overcoming the issue that the patient is going through. This can help them to make an objective decision during suggestions for the patient. This is how the therapeutic relationship between the doctor and patient can be built.
Explanation of The Need To Give Antipsychotic Medication
It has been found from the case study that Jason was in a bad condition when he was admitted to the mental health ward. This is because he did not leave his bedroom for 3 days and he stopped taking his anti-psychotic medications for days and held poor auditory hallucinations. His mental state was so poor and motivation for treatment was lacking in Jaso with heavier psychotic disorders like schizophrenia. This is why a patient might be less willing to take antipsychotic medications for engaging in treatment activities. As argued by Galderisi et al., (2021, p.12), as a negative symptom of schizophrenia disorder, lack of motivation to take the medication is known to be a common issue and difficult for patients as well as clinicians to recognize. The depot antipsychotic medication was in the best interest of Jason in order to raise the benefits of the treatment. This is considered to be easier to observe and holds long-lasting impacts. However, it also decreases the rates of relapse compared to oral medications. This is why it was required to give the patient a depot anti-psychotic medication.
Technique for Personal Safety
One technique to ensure the safety of the patient with respect to giving him the depot medication as discussed above includes,
1. Z-track method: This method of administrating the IM injection to give the depot anti-psychotic medication is effective (Gee et al., 2018, p.6). Since it aims to prevent the medication from being tracked via the subcutaneous tissue and swaling the medication in the area of muscle. This results in reducing any irritation from the medication. Using this method, the skin can be pulled in a lateral way from the site of infection prior to the injection, and then the medication can be injected. Followed by this the needle is removed and the skin can be released.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that Jason was suffering from schizophrenia issue. However, taking the antipsychotic medication regularly tended to reduce the impact of schizophrenia. On the other hand, when Jason managed to move out of his parent's house, it is seen that he tended to stop taking his antipsychotic medications. With respect to this situation, the impacts of schizophrenia were greater such as louder auditory hallucinations. However, concerning the condition of Jason, he was admitted to an acute local mental health award. It was the proper legal movement to improve the condition of the patient. Although, Jason refused to take the medication in the mental health ward and he was facing financial issues due to unemployment. Despite his unwillingness, the doctors gave him the medication. However, this situation could be improved by developing proper therapeutic relationships between doctors and patients by considering the three techniques discussed above.
References
Essay
PBHL20008 Engaging with Cross-Cultural Communities Assignment Sample
The assessment task for this unit is a reflective essay. Each student will write a reflective essay based on his or her experience of engaging with a cross-cultural community. Student can use example from their previous or current experience of working with a community group and reflect on communication and cultural challenges they experience. Students should then discuss learning they achieved from this experience and how they will apply that knowledge to improve their current or future public health practice.
The reflective essay will be assessed on the following criteria.
- The essay shows evidence of understanding of cross-cultural community engagement: 25%
- Reflection demonstrates use of appropriate language, personal learning and change in practice: 25%
- Reflexivity in linking personal experience, practice examples and evidence: 25%
- All work is the student's own, all information is properly referenced, and essay is written according to academic convention: 25%
- Students must achieve 50% in this assessment to pass the unit.
Solution
Introduction
The reflective assessment for assignment help will describe the personal up-liftment from the cross-cultural involvement with the indigenous groups. I will mention how the different communication obstacles would explore the opportunities so that the health care values and practices in Australia will be developed professionally.
Discussion
During the last summer in Adelaide, I participated in the international summer camp. This was the confluence of all the communities across different indigenous cultures in and beyond Australia (Lin et al., 2019). Amidst the sea of human heads, I found the people of Strait Islander interesting. I did works with the aboriginal community to get a taste of indigenous history. I was inspired in setting up cultural links with them getting past all the cultural constraints. The abundance of religious and cultural diversities supports the root of the culture. The intensive engagement with the different perspectives inculcates a renewed sense of cultural consciousness in me. They shared with me how they came into being, how they pass the present moments, and their future agendas. I felt a certain pride connecting to the home culture and knowing the minute details. It can be seen and felt how the communities share a warm bond trying to navigate the tricky corridors of life. They have a deep reverence for traditional values and community standards (Usher et al., 2021). The community prioritises authenticity, sincerity, and passionate deliverance. The rich cultures and beliefs are attuned to sustainable principles and value creation. I learned that the community people
Cultural and communication challenges were there that put me unease to accomplish the cultural mission objectives. I could not communicate properly and always hesitated in letting my thoughts unfold. I apprehended if the missions of the workshop would be successful. Some pervasive risks and challenges predominantly afflicted the emotional and social well-being of the islanders. Ethnocentrism struck me as the key barrier through which we get partial regarding the lens we look at the dimensions of the cultures. When these perspectives turned into prejudices a blind beliefs, the problems got worsened (Tynan et al., 2020). There was also a widened gap between their cultures and mine; anyhow, I tried to be in their shoes and perceived the communicational impediments. Along with that, comes the traditional tag of stereotyping which is also harmful to cultural cohesion and productivity. I was moved by the psychological barriers that amounted to the fact that widespread loss and grief have been part of the culture and I discovered the unresolved trauma therein. The lack of connection to the enlightened world led to their ignorance of health issues and the determinants of redressal (Yashadhana et al., 2020). The community governance is strong yet they have vulnerabilities to the various life-threatening dangers and losses. The indigenous community loves to pass on their cultural heritage and traditions but the sense of rootedness and belonging is overshadowed by the presence of negative factors. At some points, I felt that the practices in the system could have been more flexible to cope with the modern progression. Racial discrimination was something that entrenched its roots in the pristine soil. Moreover, the linguistic barriers were dominant that aggravated the communicational disputes. In addition, the geographical distance was much more than what I had previously idea and thought. The cultural disparateness added to the miscommunication, flawed mindsets, norms, and gestures (Moodie et al., 2021). Studying unfamiliar cultures and languages was the toughest part of working with the community and being exposed to cultural setbacks.
Personal experience is one of the best parts of the human life. I shook hands with some aboriginals and they considered it disrespectful. The respect for the community bonding was something they considered praiseworthy and I had lessons on the community rituals and customs. I had gathered lessons for them about the aboriginal arts and the ornamental designs on the physique are something they carry as a token of cultural heritage. The cultural baggage was abandoned and I took interest in the basketry and their values of social organisation (Russell-Smith et al., 2021). I learned the protocols and customs of the indigenous individuals and the overall well-being of the community people. IKSPS has been absorbed by me in harbouring the genuine feeling for the system and community values. I have understood that culture is the most symbolic asset for the community who are engaged in the making of history and traditions. All aspects of life have been permeated by cultural lineage and local diversity. I have gained another important knowledge regarding the conservation of policies and wealth. Other participants from abroad also came in contact with the different attributes and therefore, the culture was replete with all the resources and native pride. The cross-cultural symbolism made it easier to contact the different cultures and the people.
In the future, I shall apply the learning in public health practice and implement the protocols to remove the risks that can be harmful to the aboriginals. They are believed to have been the sufferers of chronic diseases like pneumonia, heart disease depression, and many more. Therefore, I will be sincere in offering value-based care to the patients. I have decided to apply the value theory proposed by Walras, Jevons, and Menger. The encompassing theory takes into consideration all the moral practices, ethics and responsible duties to safeguard the lives of the people. Many aboriginals are victims of paranoia, stress, and distressing mental condition due to the loss of lands, and separation from family and children. Many of them are suffering from identity issues and cultural estrangement that gave rise to health problems and many more additional health crises. Incarceration, substance misuse, and violence can be seen among the cultures that decreased the values and increased panic. I will teach them about the indication of environmental degradation, industrial activities as well as many more on health and comprehensive development. If the illicit abuses of drugs and alcohol can be stopped, better immunisation practices could be developed (Yashadhana et al., 2020). I feel that the indigenous community must be sincere in protecting their rights, and stopping their involvement in the criminal system, and better health practices can be created.
Conclusion
This is clear from the above discussion that a deeper connection with the culture can empower the historical and culturally conscious self. I have gained deep learning from the involvement at a deeper level and this is beneficial for protecting the health care sector.
Reference List
.png)
Essay
NUR5011 Contemporary Nursing Assignment Sample
Mr George is a 65 year old widowed father of Giovanni and Maria. He was admitted to your ward for elective lumbar surgery after several years of back pain resulting from a workplace injury. His ability to mobilise has been significantly reduced and he uses a walking aid. Mr George does not speak English and relies on his son to translate for him.
Mr Georges admission paperwork was completed with Giovanni’s assistance. Mr George is allergic to morphine. Giovanni thinks it caused an itchy rash, but Mr George cannot recall. RN Sriya has written this in the paperwork but forgot to put on a red allergy wrist band. His neurological limb assessment shows a left foot drop with full feet numbness and his vital signs are unremarkable. Mr George has a past history of atrial fibrillation. He is on digoxin (0.25 mg/day) and aspirin (100 mg/day). He is noted to be on the organ donor register and Giovanni is the documented medical treatment decision maker.
Giovanni has advised that his father does not wish to be resuscitated in an emergency, but Giovanni is not supportive of this and would like all measures taken. Giovanni has also advised that Mr George is quite anxious about his brother, Steven who is also in the hospital, having been admitted for surgery after falling in the garden. Professor Charcot, the surgeon, visited Mr George and Giovanni on the ward to see that Mr George is settling in well and reminded Mr George and Giovanni that he would perform an L2/3 laminectomy the following morning. RN Kate looked after Mr George on night shift but had difficulty communicating with him. As she thought he might have had a stroke, she placed an electronic order for an emergency CT Brain. In her hand over to the AM nurse (RN Chan), she advised that the CT results were not back but did not documented this.
When RN Chan took Mr George to theatre, they noted that a consent form signed by the patient and the surgeon was not in the file and inserted a blank form into the file for completion. RN Chan alerted Professor Charcot to this. Professor Charcot responded by yelling at RN Chan in front of other nurses and surgeons “You’re so incompetent. Who do you think you are?
If you dare speak to me like that again I will have you fired! Of course, I have already consented the patient! He would not be here if he did not know what was happening. Are you the idiot who ordered a CT Brain on my patient?. RN Chan returned to the ward, upset. They told their manager what had occurred and that they felt bullied and harassed by Professor Charcot. After surgery when Mr George returned to the ward, RN Chan noticed that the hospital consent form had still not been signed and when listening to the Registrars talking to each other about the case, overheard one say, Prof didn’t use xray and did the L4/5 by mistake. RN Chan did not say anything to their manager as they thought that the doctors would advise the patient and his son. They were also too scared to say anything because they didn’t want to be yelled at further and lose their job.
RN Chan went home very upset at the day’s events and wrote on their Facebook status update that “some surgeons are so arrogant! At least I am not the incompetent surgeon who operated on the wrong spinal level!” During the next shift and about 8 hours after surgery, it was noted by the PM nurse, RN Sriya, that Mr George had not passed urine. The protocol of the hospital requires a urinary catheter be inserted if the patient has not passed urine 8 hours after spinal surgery. RN Sriya contacted the Registrar who advised she could not arrive to insert the catheter for 2 hours as she was in surgery with another surgeon and that RN Sriya would have to do it herself. RN Sriya had not inserted a catheter into a male patient before and, assuming it couldn’t be much different to inserting female catheters, undertook the procedure. As a result, frank haematuria occurred with a large amount of blood loss. A MET (Medical Emergency Team) was called, and the patient assessed. Mr George was in a lot of pain and the attending MET doctor, Dr. Pratt orders 5mg of morphine intravenously stat. Mr George was rushed to emergency theatre and a Urologist, Miss O’Donnell, called to surgically repair the damaged urethra. During the operation Mr George went into cardiac arrest and died.
When Giovanni and Maria arrived at the hospital to see their father, RN Sriya asked “Didn’t they call you? He died in the operation”. Maria was understandably angry and upset and stated “No one called me! I am going to sue the hospital and Professor Charcot for negligence, and I am going to the coroner, media, and escalating this as far as I can take it!”.
The case study is designed to prompt your thinking and analysis of the various legal issues/considerations that may arise in health care. Please note that you are not asked to provide a personal view of the case study. The purpose of the essay is to present a coherent argument for the legal considerations that are relevant to the case study. This essay provides an opportunity for you to demonstrate in-depth understanding, and sound, logical and academic argument to support your thoughtful position on the legal considerations present in the scenario.
Structure: Your essay should follow the parameters of the marking rubric; You may use subheadings to develop your paper; The suggested assessment structure in line
- Introduction: should clearly introduce the assessment task and provide an outline of your essay
- Main body: the argument for each of the legal considerations is developed logically & demonstrates critical analysis. It is recommended that the body of your essay is separated into the three legal issues.
Conclusion: summarises the main points of your essay.
Solution
Introduction
In Australia, both the government and the private sector provide healthcare. The Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia (NMBA) registration is mandatory for nurses seeking employment in Australia. Every Australian nurse must adhere to the NMBA's code of conduct. This article outlines the professional and ethical requirements for Australian nurses. The nursing profession is controlled by both customary and legislative laws. These laws include the Nurses Act, the Health Practitioner Regulation National Law, and the Privacy Act, among others (Harrison, 2018). Common law is the body of law that develops through judicial decisions. Professor Charcot often disregarded the responsibility of care he owed to Mr. George. He failed to get Mr. George's consent for the therapy, performed surgery on the improper level of the spine, and threatened and mistreated RN Sriya throughout the procedure. During each of these complications, the patient was anaesthetized.
The hospital's incapacity to provide its patients with adequate care may also be asserted. The hospital did not take sufficient measures to verify that the required authorization form was filled out and that Sriya, the RN, had enough training in the implantation of urinary catheters. Furthermore, no effort was taken to inform Mr. George of the potential risks associated with the treatment. The complaint must establish that the alleged loss or damage was directly caused by the alleged breach of duty (Dixit & Sambasivan, 2018).
Legal Issue 1: Negligence
Specialists, such as surgeons, may often commit the tort of negligence on the job. The term "tort" is often used to refer to reckless behaviour. It happens when a professional breaches their duty of care and causes damage to a patient. The patient alleges professional negligence has the burden of proving that the professional owed them a duty of care, that the obligation was breached, and that the loss or harm was caused by the breach.
A professional has a reasonable duty of care to the patient under their care, which requires them to take all reasonable precautions to avoid harming the patient. Regarding surgery, this entails taking all necessary steps to guarantee that the right patient receives the correct therapy and that the patient is aware of any potential dangers (Buss et al., 2018).
In this scenario, Professor Charcot's actions might be seen as a breach of his duty of care owed to Mr. George. The first problem was that he was unable to convince Mr. George to agree to the therapy. The second error was operating on the wrong portion of the patient's spine. Thirdly, he failed to inform RN Sriya about Mr. George's possibly fatal allergy to morphine. Fourth, he persistently harassed and intimidated RN Chan.
In addition, due to Mr. George, the hospital may have violated its duty of care on many occasions. It did not thoroughly verify that a legitimate authorization form was submitted and signed. The second worry is that RN Sriya was not adequately screened to ensure she has the required skills to insert urinary catheters (Rosebrock et al., 2020). Thirdly, nothing was done to ensure that Mr. George was informed of the dangers involved with the procedure, which would have been considered reasonable under the circumstances. The complaint must establish that the alleged loss or damage was directly caused by the alleged breach of duty. In this case, the loss or damage at issue is Mr. George's death. If Professor Charcot hadn't been so careless, Mr. George would be alive and well today. If he had gotten adequate care and been informed of the risks, he could have lived. If the hospital had been more responsible, Mr. George may still be alive today. Mr. George would have gotten proper care, a valid permission form would have been completed, and he would have been informed of the possible hazards of the surgery if the hospital had been more diligent.
The Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974 (HSWA 1974) mandates that companies preserve the health and safety of their employees at work. This obligation for assignment help involves protecting workers from intimidation and harassment (Chun Tie et al., 2018). It is hard to establish whether the hospital exceeded its obligation by failing to take adequate safeguards to protect RN Sriya from intimidation and harassment by Professor Charcot. Alternatively, it is likely that the hospital ignored this requirement.Under the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act of 1974, employers are required to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of their employees in the workplace to the greatest degree practical (HSWA, 1974). This duty comprises safeguarding employees against intimidation and harassment in the workplace. It is arguable whether the hospital breached its duty by failing to take enough safeguards to protect RN Sriya from intimidation and harassment by Professor Charcot. It is possible, however, that medical workers neglected their responsibility.
Professionals, such as surgeons, may incur the tort of negligence in the course of their employment. Liability results from a violation of the professional's duty of care to the patient, which results in the patient suffering some kind of harm. Patients who allege medical professionals broke a duty of care due to them must also demonstrate that the violation directly resulted in the losses or damages they're seeking compensation for.
A professional owes their patient a duty of reasonable care, which entails doing all in their power to prevent the patient from suffering any damage that may reasonably be expected to result from the professional's actions. For a surgeon, this means taking all necessary precautions before surgery, such as checking the patient's identity and medical history to make sure they are a good candidate for the treatment and explaining the potential dangers to the patient.
The most common tort faced by healthcare personnel is carelessness. The patient may suffer physical hurt, pathological harm, mental harm, or even death as a consequence of the nurse's carelessness. Damages are incurred when something terrible happens, such as an accident induced by medical treatment that prolongs a patient's hospital stay and/or leaves them permanently incapacitated after discharge, or even causes death. This sequence of events begins with the imposition of a duty of care and continues through the exercise of inadequate or non-existent care (henceforth termed "negligence"), the occurrence of an adverse event, and the inflicting of injury. In cases of negligence or wrongdoing, the court may award damages to the injured party. In some circumstances, a negligent person may be held accountable for compensating damages to compensate for economic or non-economic losses, in addition to extraordinary damages. Long ago, carelessness was characterized by common law. In 2002, in response to the conclusions of Justice Ipp, all Australian jurisdictions enacted Civil Liability Acts with provisions addressing medico-legal malpractice (Cross& Cross, 2020).
Employers have a responsibility to protect their workers' health, safety, and welfare as much as possible under the Health and Safety at Work Act of 1974 (HSWA). This obligation includes safeguarding workers from hostile work environments. It might be argued that the hospital in this instance failed in its obligation to safeguard RN Sriya from the bullying and harassment of Professor Charcot.
The obligation to guarantee, so far as is practically feasible, the health, safety, and welfare of workers at work is imposed on employers by the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HSWA 1974). This obligation includes taking measures to prevent bullying and harassment of staff members. It might be argued that the hospital in this instance failed in its obligation to provide RN Sriya with enough protection from the bullying and harassment of Professor Charcot.
Patients like Mr. George who have been injured by unintended side effects may or may not choose to file a lawsuit. Patients who successfully obtained compensation may not have been under the supervision of a nurse at the time of the occurrence. Unbelievably frequent prescription errors and failures to recognize negative consequences among Australian healthcare practitioners are among the most serious concerns affecting the nation's patients. There is a surprising mismatch between the reported occurrence of medical misbehaviour and the amount of money paid out in settlements, according to new statistics on negligence claims in Australia. according to current research, the number of new claims submitted has decreased, or the pace of new claims has remained constant (Kirkegaard et al., 2022). The effectiveness of conflict resolution is growing. There is tension between the need to maintain a high standard of care and the prevalent practice of rewarding patients for unexpected outcomes. In contrast to their colleagues in New Zealand, who have access to a no-fault medical reparations scheme, health professionals in Australia must adhere to common law and statute-based negligence regimes.
As a basis for responsibility, carelessness is rapidly extending to all spheres of human activity and is today the most important and pervasive tort. In recent decades, the legal notion of carelessness has expanded to include economic loss and psychological illnesses in addition to bodily suffering and property damage. In order to achieve justice and lessen the burden on society as a whole, it was difficult but necessary to develop a legal system that is both predictable and consistent.
Despite the fact that each doctor has a unique set of beliefs and values, they are all bound by a set of professional standards that serve as the foundation of their work. Doctors must always act in the best interests of their patients and adhere to the most stringent standards of safe and effective care. They must be dependable and possess a solid moral compass. Patients have faith in their doctors because they perceive them to possess not just the required medical expertise, but also exemplary character traits such as honesty, dependability, and compassion. Patients have confidence in their doctors and expect them to safeguard their confidentiality. Physicians are obligated to safeguard and enhance their patients and the general public's health. In a successful medical facility, the patient’s needs are always first. Medical practitioners must recognize that each patient is unique and collaborate with patients to adjust therapy to each individual's requirements and goals. This requires cultural awareness, which includes knowing and respecting one's own culture and values as well as those of others, and recognizing that cultural differences may affect the doctor-patient interaction and the delivery of health care. Every aspect of safe and effective medical care requires superior communication (Sotomayor-Castillo et al., 2021).
Legal Issue 2: Misconduct
The "right to be treated with dignity and respect" refers to a patient's legal entitlement to treatment that respects and upholds their inherent worth as a person. Patients have the freedom to refuse medical practitioners' degrading or disrespectful treatment. This privilege was thus created for this purpose (Broom et al., 2022). Professor Charcot was the aggressor in the continuous bullying and harassment issue between RN Chan and Professor Charcot.
A physician is not required to provide care to anybody who seeks it, but he must be prepared to meet injured or unwell patients at any time. His duty is to offer compassionate treatment to his patients. Unless required by law, the confidentiality of a patient's medical records must always be maintained. Without exaggerating or trivializing, he must convey the gravity of the patient's illness. Once a patient has been admitted to the hospital, they must not be forgotten (Fisher et al., 2022).
When decisions concerning terminal care are made without comprehensive information or without engaging the patient or the patient's family, both ethics and the law are put to the test. Certain decisions regarding Mr. George seem to have been made without his complete consent or awareness. In addition, it seems that Mr. George and his family were not supplied with crucial information, which led them to believe they had been misled and lose faith in the medical professionals' abilities to care for them (Zheng et al., 2021).
Respecting the dying person's right to autonomy is crucial while making decisions concerning their care. Patients should participate in treatment decisions to the extent that they are able and willing to do so. Consent based on education is a crucial part of this operation, and it is essential that the patient has all the information necessary to make an educated decision. If the patient is incapable of making decisions, family members should be included.It seems that Mr. George was not given sufficient information to make an informed decision about the treatment he would receive. This is troublesome given the circumstances since it suggests that his autonomy was not respected (Minnican& O’Toole, 2020). In addition, it seems that Giovanni was not given all the information he need to make an informed decision on his father's treatment. In the case of an emergency, Giovanni would not have been able to make an informed decision on his father's resuscitation, which is problematic for a variety of reasons.
It is feasible for doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals to use their specialized knowledge outside of their regular work environment. Some physicians may not fully appreciate the responsibilities of medical professionals outside of their expertise. If there is no established therapeutic relationship between a doctor and patient and the doctor has no intention of aiding, one of three outcomes may occur (Gao, 2021). It is conceivable for a doctor to assert they are one but refuse to assist in any way, to acknowledge they are one but refuse to identify themselves as one, or to vehemently deny they are one. Regardless of ethical problems, a physician's actions and public image may have significant legal consequences. Elements of state legislation related to legal duties to aid, which vary widely from state to state, have been recommended for national study and revision.
The doctor-patient relationship can only endure if both parties adhere to the highest professional standards. This needs impeccable manners, respect for others, compassion, and honesty, all of which must be shown. Keeping in mind that every patient is unique Except for exceptional circumstances such as where disclosure is required by law or is in the public interest, respecting patients' right to privacy and keeping their medical information confidential. Patients and, if appropriate, their family members who help them manage their health care should be encouraged and supported in their attempts to become active participants in their own health care (Burström, 2022). Supporting and assisting patients in their efforts to improve their health literacy and make decisions based on enhanced information about their conditions and treatment options is essential in patient care. recognizing the power dynamic between doctor and patient and abstaining from exploiting the patient in any manner (including but not limited to physical, emotional, sexual, or financial means). When a doctor and patient are able to communicate successfully, their connection becomes stronger. This means not just listening to the patient, but also responding to their health-related worries and goals. You should inquire about your patients' use of conventional, alternative, and complementary therapy, as well as any other health recommendations. They should include any other health recommendations they have received. Patients should be given enough opportunity to contest or reject intervention and treatment, and they should be informed of the nature and need of all aspects of their clinical care, including exams and investigations. The process of teaching patients about their illness and available treatment options, including the advantages and disadvantages of each (Vardoulakis, 2021). Assuring that the patient has understood the information provided and is aware of any significant risks associated with any component of the treatment plan suggested for their illness. When possible, accommodate patients' special linguistic, cultural, and communication needs, and be aware of how these needs affect patients' ability to comprehend what is being communicated; respond to patients' questions and keep them abreast of the progression of their clinical condition. Learn about and use qualified language interpreters and cultural interpreters to meet the linguistic and cultural needs of your patients. The Department of Immigration and Citizenship provides a website providing information about government-funded translation services in Australia (Allen et al., 2020).
When all employees involved in a patient's care are able to communicate efficiently and treat one another with respect and compassion, the quality of care offered to the patient is enhanced. Transparent, efficient, amicable, and prompt communication with the other medical personnel and doctors caring for the patient is essential to the success of medical practice. recognizing and celebrating the efforts of everyone involved in a patient's care Maintaining a professional and courteous manner at all times, particularly while conversing online with coworkers. suggesting, allocating, and transferring work to others You may delegate care by requesting another healthcare practitioner to treat the patient in your place; but, you will retain ultimate responsibility for the patient's health (Kirkegaard et al., 2022). If a patient needs a second opinion or specialized care, their primary care physician may refer them to a specialist. When you refer a patient, you normally delegate (at least a portion of) the patient's care to another medical professional, either temporarily or permanently, depending on the circumstances, such as when the patient requires treatment outside of your area of expertise. The phrase "handover" refers to the transfer of full responsibility for patient care from one healthcare practitioner to another. A good medical practice consists of taking all steps to ensure that the individual you are entrusting with a task has the training, skills, and experience to provide the level of care you expect (Osborn et al., 2022). Remember that even if you absolve yourself of responsibility for the choices and actions of those to whom you delegate authority, you will still be held accountable for the overall care of the patient and your decision to distribute authority. This is true despite the fact that you will absolve yourself of accountability for the behaviour of people to whom you have delegated power. Never break the chain of continuous care for a patient by failing to provide pertinent information about the patient and the necessary treatment by failing to give the necessary information.
Legal Issue 3: Consent
In this instance, the nurses' actions have far-reaching ramifications that may be pursued via the judicial system. According to all parties concerned, Mr. George did not provide authorization for the procedure that was performed on him. Because his rights have been infringed, he may opt to file a lawsuit against the hospital and the physician. Consent based on education is a crucial part of this operation, and it is essential that the patient has all the information necessary to make an educated decision. Certain choices concerning Mr. George were made without his knowledge or consent (James et al., 2021). It had a bad influence on him as a result. This is troublesome given the circumstances since it suggests that his autonomy was not respected. Mr. George's experience highlights the need of making ethically and legally sound choices regarding end-of-life care. It is essential to respect patients' preferences and give them all the information they want to make an informed decision (Penman & Tighe, 2019).
As the situation presents, it is debatable whether or not Professor Charcot acted responsibly toward Mr. George. The first problem was that he didn't bother to get Mr. George's approval for the operation. Second, he cut into the patient's spine at the improper level. Third, he didn't do enough to make sure RN Sriya knew of Mr. George's morphine sensitivity. And last, he harassed and threatened RN Chan. The hospital may have broken its duty of care to Mr. George in various ways. To begin with, it didn't check to see whether the right permission form was signed. Second, it didn't check whether RN Sriya had had enough instruction on how to place urinary catheters. Third, it didn't do enough to warn Mr. George about potential complications from the operation. All of the plaintiff's suffering must have resulted from the defendant's alleged breach of duty. The death of Mr. George is the alleged loss or injury in this lawsuit. It might be argued that if Professor Charcot had followed protocol and warned Mr. George of the potential dangers, Mr. George would still be alive today. Mr. George may not have died if he had received the appropriate treatment, signed the appropriate permission form, and been informed of the potential consequences of his decision, all of which were overlooked due to the hospital's carelessness.
Consent is one of the mandatory requirements in a healthcare setting as it ensures the patient or the particular individual is aware of the actions that will be considered. It will help to avoid legal tribunals in case of any misery. From the following case study, it has been observed that Professor Charcot was too much arrogant and without any consent, he performs critical surgery to the patient Mr. George. After the action, the patient encountered severe physical issues due to the inability to urinate and died facing severe pain and medical complexity. It also indicates a lack of duty of care which is a major legal issue. As per the study of Yildirim et al, (2021), it is mandatory for any medical professionals to sign proper consent before proceeding with medical operations that might lead to serious consequences. The same is missing in the case which was found the very next day when RN Sriya was on duty for the next shift. Due to such actions, the family members and relatives claim that they will lodge complaints against all the staff. Despite informing by juniors about the consent the professor acts in his own interest. It is clearly a violation of National Human Right Committee guidelines. Therefore, as per this regulatory and legal framework also the medical practitioner is responsible for the punishable offences.
Considering the perception of the family members l, they are not wrong as none of them is informed about the consent or any of them are not aware of the serious condition or death of the patient. Here, the legal issue associated with lack of duty of care also comes into the picture. As opined by Waterhouse, (2019), the guidelines of "duty of care" clearly indicate that if any casualties occur due to any kind of negligence of individuals assigned in the responsibility, then the other party can sue. Hence, as per this rule, the hospital authorities might face serious legal consequences if the family members of Mr. George claim. However, the claim will be much stronger if it will be against the professor because from the case study it has been found that he is the main culprit.
Informed consent clearly indicates that both parties agree with the terms and conditions along with the consequences of the actions (Nouwens et al. 2020). In the following case, there is no question about the acceptance as no consent has been provided. Apart from that, there was also no verbal confirmation from the patient on the basis of which the entire result can be considered a consequence of the contract. Apart from that, as per the contract law, all medical professionals must check all patient-related documentation before considering any serious actions. In the current case scenario, it has been found that rather than checking the updated medical records the professor had considered the treatment actions that finally resulted in the death of the patient. Therefore, as per the contract law also the professor is guilty.
The case study reflects that there is a linguistic barrier associated with Mr. George as he was unable to understand English properly. As per the knowledge of Gerke et al., (2020), any linguistic challenge makes informed consent invalid as it does not serve the purpose of complete understanding. Hence, in that case, it was the responsibility of the medical professionals at the health care to elaborate everything to the patient. Then the criteria of verbal acceptance can be fulfilled which might lead to less legal trouble. Apart from that, it was also the responsibility of the medical professionals to discuss everything in front of the translator. Then it would make the understanding level superior that could be better to fulfil the criteria for informed consent.
From the case study it has been observed that l, there is no concern about the perception of Mr. George. Medical professionals execute their work as per their own interests. It is also a violation of consent guidelines. According to Döhlaet al. (2020), informed consent endures all the actions or experimentation that will be done, with the permission of the individual. As approval is missing in the case, therefore, it can be also counted as a legal issue associated with the context of consent.
The case study indicates that the professor threatened RN Chan with interference. It was her duty to inform the professor as well as it also falls under the basic rights considering the health and safety of the patient. The self-biased mentality in this case causes the severe problem of a patient's death. Therefore, such offence must be punishable as per the available legal guidelines. Moreover, the operating process of healthcare also needs to be changed to ensure the avoidance of such incidents in future.
Vulnerable people and groups are other aspects associated with the case of Mr. George. In this case, the professor protects his own interest through unethical actions rather than the actual actions that need to be considered. As per the study of Coleman et al. (2022), healthcare professionals must serve community interests rather than their own to match the nationalised treatment standards. Hence, considering this legal aspect also the professor is solely liable for the situation of Mr. George.
By analysing all the aspects, it can be stated that the family members need to lodge complaints specifically against the professor rather than all individuals to get a better response. Apart from that, the healthcare authorities need to organize investigations into the professor and consider strict punishments for such actions. It will help to prevent such unwanted events in future and avoid any legal obstacles in the operations.
- The nurses conduct in this instance have a lot of potential legal ramifications.
The problem of permission comes up first. Mr. George obviously did not provide informed permission before his procedure. This is a potential violation of his legal rights, which might result in a lawsuit for compensation.
The second problem is the CT scan. Whether or if Mr. George gave his permission for this surgery is unclear. If he didn't, the hospital may be in violation of federal law for executing an intrusive surgery without permission.
The urinary catheter is a problem, which brings us to point number three. Evidently, the nurse in question lacked the skills essential to perform a proper catheter insertion. The resulting anguish was so severe that it ultimately proved fatal for Mr. George. There is a possibility that the hospital may be held responsible for any damages that occur because of their carelessness.
The surgeon's actions are a problem, which brings us to our fourth point. The surgeon's behaviour toward the nurse constituted bullying and harassment, given his hostile and insulting tone. The nurse may file a lawsuit as a result of this.
Mr. George's passing is a last concern. This happened because the surgeon and hospital workers were careless. The hospital and the doctor might be held liable for Mr. George's family's suffering.
Conclusion
In this instance, the nurses' actions have far-reaching ramifications that may be pursued via the judicial system. To start, there is the problem of permission requests. According to all parties concerned, Mr. George did not provide authorization for the procedure that was performed on him. As a result of this infringement of his legal rights, he is entitled to monetary compensation. The second issue is a fault with the completed CT scan. Unknown is Mr. George's level of collaboration with this operation. If he hadn't given his consent, the hospital may face legal implications for performing an invasive procedure on a patient without his consent. In the third situation, the urinary catheter represents a major concern. Clearly, the nurse lacked the required expertise to insert the catheter into the patient. Mr. George passed away as a result of his trauma. The hospital may be held accountable for negligent treatment given the circumstances. Fourthly, the surgeon's behaviour is unsettling. The surgeon's behaviour toward the nurse, which included being rude and disrespectful, might be seen as an attempt to intimidate or harass the nurse. A nurse in this situation may choose to file a lawsuit against the medical institution for compensation. The final issue is Mr. George's passing. This happened due to the carelessness of the medical personnel and surgeon. The family of Mr. George may file a lawsuit against the hospital and the doctor for compensation.
References
.png)
.png)
Essay
NURBN1015 Introduction to Evidence-based Practice and Research Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
This assessment task requires you to build on the evidence you summarised and evaluated in Assessment task 2a in order to respond to the clinical question in the form of an essay. The clinical question you chose for task 2a must be used for assessment task 2b. You will need to use at least SIX (6) peer-reviewed primary research articles in total. THREE (3) of these articles will be the three you used in the annotated bibliography, and you need to source at least THREE MORE articles yourself.
CLINICAL SCENARIO CHOICE – USE THE SAME CHOICE AS TASK 2A
Choose the same topic you used to complete Assessment tasks 2a.
Clinical scenario choice 1: Pressure injury prevention
Dario is a student nurse working in an aged care facility and is looking after Mr George Florentine an 82-year old man who suffered a stroke four months ago. He is not able to mobilise without assistance. It was handed over that Mr Florentine needs re-positioning every 2 hours. However, Dario’s buddy nurse says that is not necessary as he has a pressure relieving mattress.
Clinical scenario choice 2: Nutrition in wound healing
Amelia is a student nurse working in a residential facility caring for Iris Johnson a 92-year-old female with a ulcerative wound to her left lateral malleolus. The ulcer is 2cm in diameter and sloughy in appearance with minimal hemoserous exudate. Iris has been prescribed vitamin D and folic acid supplements to help with the healing process; however Amelia’s buddy nurse says that this is silly because nutrition has nothing to do with wound healing.
WORD LIMIT
The word limit is 1500 words (+/- 10%). The reference list is not included in the word count. In-text citations are included in the word count.
ESSAY STRUCTURE
The ‘applying evidence to practice’ essay is to be written using an essay structure with an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The essay format provides you the opportunity to concisely present the findings from the research articles that directly respond to the clinical question/s, compare and contrast the findings, and then apply what is known to your own clinical nursing practice.
The essay should be structured as follows - do not include headings/subheadings in your submission:
Write the clinical question you have developed from the chosen scenario at the top of your essay – this is your essay title.
Introduction: Word limit allocation (approximately) 150 words
What to include
Introduce the topic (the clinical question you are answering), outline the scope of the paper (what you will cover) e.g., evidence-based strategies, how they are applied and evaluated (follow the paragraph topics below)
Paragraph 1: Word limit allocation (approximately) 300 words
What to include
What new knowledge from the research studies can be applied to improve nursing care or patient outcomes?
Compare and contrast findings – paragraph 1.
Paragraph 2: Word limit allocation (approximately) 300 words
What to include
Compare and contrast findings – paragraph 2.
Paragraph 3: Word limit allocation (approximately) 300 words
What to include
Apply this new knowledge from paragraphs 1 and 2 to nursing practice: What strategies will you use to implement new knowledge into patient care?
Paragraph 4: Word limit allocation (approximately) 300 words
What to include
State the methods you can use to demonstrate that nursing practice or patient care is improved.
Conclusion: Word limit allocation (approximately) 150 words
What to include
Summary of the main points
Reference list: (Not included in word count)
Include all references used in text in APA 7th style
Total word count = 1500 (+/-10%)
ESSAY PREENTATION GUIDELINES
Solution
Brief introduction
Immobility, such as that brought on by protracted bed rest at a medical facility, can lead to pressure injuries also termed as bedsores. Most pressure injuries are preventable, and they contribute significantly to patient treatment needs in the healthcare industry. Pressure damage is included on the national list of hospital acquired problems (HACs). The national list of 16 HACs is the product of a detailed methodology that involves literature reviews, clinical interaction, and concept testing with both public and private institutions (Hajhosseini et al., 2020). The hips, heels, tailbone, elbows, head, and ankles are among the skeletal parts of the body that are commonly the locations of these injuries. Pressure injuries can be treated in a number of ways, depending on the stage. Once the wound's stage and severity have been determined, it must be cleaned, frequently with a saline solution (Dalvand et al., 2018). After being cleaned, the wound has to be kept clean, moist, and properly wrapped. To cover the wound, the doctor may select from a range of bandages. This assignment would help to understand the preventive measures that must be taken to prevent the chances of pressure injury.
Body paragraph 1
Topic sentence: Keeping the skin clean and clear of bodily fluids can prevent pressure injury
Evidence: The first stage in skin care is routine assessment of the skin itself. In high-friction areas, patients and/or caregivers should pay careful attention to the skin and keep it dry, clean, and protected from pressure injuries by keeping an eye out for early warning signs (especially at high-pressure spots). Sensors can alert patients or caregivers to any changes in the environment that can make pressure injuries more likely to occur (Jiang et al., 2020). These sophisticated monitoring techniques include pressure mapping and real-time patient monitoring. This is an opportunity for early management and the reduction of pressure injuries for assignment help.
The following best practices for skin care in this patient population are recommended are every day, examining the skin, moisturizing at least twice daily to keep the lipid barriers functioning optimally, using additional skin barriers if the patient experiences incontinence, cleansing, rinsing, and drying the skin after incontinence or when there is too much moisture present, to cushion and protect sensitive areas, using the appropriate therapies, and whenever necessary, or every two hours, changing into breathable clothes (Cox et al., 2018). Dressings are one pressure ulcer therapy strategy. There are many different types of dressings, and they can range widely in price (Sala et al., 2021). Hydrogel dressing is one type of available dressing. The high-water content of hydrogel dressings keeps ulcers moist, preventing them from drying out. According to popular belief, wet wounds heal more quickly than dry ones. Numerous research has examined the possibility that hydrogel dressings for pressure ulcers have a faster rate of healing than other kinds of dressings or topical treatments (Alderden et al., 2018).
Body paragraph 2
Topic sentence: Pressure Redistribution resulting in pressure relief might help to prevent pressure injury
Evidence: Pressure injuries can be avoided by controlling friction and shear. There are mainly two approaches to doing this. The first step entails choosing the optimum materials for the patient's surroundings and support surfaces like beds, mattresses, and cushions. Equal weight redistribution is another goal of these support surfaces. The choice of fabric can also significantly affect how much mechanical stress the patient receives; for instance, it has been demonstrated that textiles made of silk have far lower friction forces than fabrics made of cotton (Padula et al., 2019). On pressure redistribution surfaces, skin contact is increased, resulting in a continuous, even IP. The best material for foam and low-air-loss mattresses is this one. Polyurethane foams that are lightweight are made to contour to the patient's body and account for pressure points in certain areas. With pressure redistribution incorporated directly into their characteristic shapes, cut-foam mattresses and laminated surfaces are only two examples of the increasingly sophisticated material architectures that have resulted from this. Low pressure treatment mattresses also offer pressure redistribution since they continually circulate low air pressure throughout the mattress to spread the user's weight. It is comparable to low air loss therapy, with the exception that the air is kept in the mattress to prevent full deflation when the pump is switched off (Cox et al., 2020). Pressure relief effectively prevents pressure accumulations by focusing on high pressure areas of the body. These surfaces typically contain air-filled cells that might expand and contract based on the surrounding conditions (Fulbrook et al., 2019). For instance, it may be useful to regularly reduce pressure in the lowest third of the mattress if the patient's heels and lower legs are more prone to pressure sores when lying on a mattress. In this case, alternate-air technology can be useful. This cyclical mechanism uniformly distributes pressure over the mattress in response to the patient's needs, reducing the chance of pressure buildups for a lengthy period of time (which also gives the mattress an undulating IP measurement).
Body paragraph 3
Topic sentence: Repositioning of the patient would help to reduce pressure injury
Evidence: Another element of effectively managing mechanical stress is repositioning the patient as needed, ideally every two hours (Sharp et al., 2019). To alert the patient or the staff when repositioning is necessary, auditory aids like alarms or sensors may be used. Repositioning may also be assisted by tools, pillows, or slings that make it easier to move the patient. The application of pressure mapping technologies can also help with patient positioning. This device enhances the visual assessment of a patient's skin by examining the cellular-level processes and biomarkers connected to the early formation of pressure ulcers (De Meyer et al., 2019). Patient positioning includes maintaining neutral body alignment in compliance with the requirements of the treatment. It is accomplished by preventing hyperextension and excessive lateral rotation. Because it lowers the possibility of harm and the negative effects of immobility, proper patient placement is an essential aspect of nursing. Correct patient positioning optimizes exposure to the treatment region while minimizing exposure. Furthermore, there is no evidence that gradually shifting one's position or weight would affect how much pressure is applied at the contact between the sacrum and buttocks (Yap et al., 2022). However, there is evidence that even little adjustments to weight or posture can have an impact on the gravitational equilibrium. Further research must be done to determine how well modest modifications to weight or posture might minimize pressure injuries in patients receiving critical care.
Body paragraph 4
Topic sentence: Usage of medical devices and physical barriers can prevent pressure injury
Evidence: Any object that comes into contact with the patient's skin might result in a pressure injury. This is compounded worse in the pediatric inpatient environment where device-related pressure injuries account for the majority of all pediatric pressure injuries due to the underdeveloped skin barrier and decreased tissue tolerance (Lin et al., 2020). As medical care becomes more complex and includes more devices, nurses must effectively assess patients' requirements and protect patients' skin from getting device-related pressure injuries. creating a physical barrier that shields moisture and irritants from the skin's health and regeneration. By producing a transparent barrier, the wipes lessen diaper rash and skin irritation caused by incontinence without altering the absorbency of incontinence products (Padula et al., 2021). Barrier wipes have been shown to minimize redness and discomfort when used in diaper cares by avoiding breakdown and may be applied similarly to traditional barrier lotions. Barrier wipes do not need to be removed and permit ongoing integumentary examinations.
In addition to the aforementioned fundamental measures, patients and caregivers should pay particular attention to food and water. People who are undernourished are far more susceptible to get pressure injuries. A healthy diet that is balanced, enough hydration, and the use of supplements as needed can all significantly reduce the incidence of pressure injuries in patients (Munoz et al., 2020).
Brief conclusion
From the above discussion it can be concluded that pressure injuries occur when pressure causes a localized damage to the underlying skin and soft tissue. Hospitals and long-term care facilities continue to have a lot of concerns about these skin and soft tissue injuries. They are costly for patients and in the healthcare system, and they have a detrimental effect on patients' quality of life. If the considerable morbidity and death rates linked to these pressure injuries are to be avoided, they must be immediately identified and treated. When different kinds of tension are applied to the skin's surface, a pressure injury happens. When dealing with a pressure injury, infection prevention is essential. If the wound becomes infected, the rest of the body might be in risk. Pressure injuries should be avoided whenever practical since they could have a negative effect on patient outcomes. The first measures in preventing pressure injuries are a comprehensive skin assessment and suitable skin care. Making a management decision for pressure injuries will be aided by the assessment of patients upon arrival. Care plans may also include other things like moisturizing the skin, protecting bony prominences, shielding it from dampness, redistributing pressure, and more.
References

Research
PUBH7033 Foundations of Public Health Assignment Sample
Assignment Details
12 – 15 references should be included in the literature review.
Need to select two contrasting determinants to make title of report. Chose different title than sample report.
Title (10 words)
- Introduction -100-150 words
- The health status of [insert your chosen population] (approximately 150 words)
- Social determinants and their influence on the health outcomes of [insert your chosen population] (approximately 300 words)
- How these social determinants interact with each other to impact health outcomes of [your chosen population] (approximately 300 words)
- Conclusion (approximately 100-150 Words)
- Academic Honesty and Integrity (approximately 150-200 words)
Types of social determinant of health
(Please take notes of what are some starting points to discuss under)
- Education
- Health Literacy
- Class
- Gender
- Culture
- Employment
- Location
- Social Exclusion
- Restricted Finance
- Discrimination
Solution
Introduction
Indigenous people in Australia have experienced great suffering in the last two hundred years of the history of Australia since the arrival of the Europeans accompanied by genocide, subjugation, dispossession, segregation and the introduction of European diseases. This had a huge impact on the Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders who made up the majority of Australia's indigenous population, saw their numbers plummet by more than 90% during the next 200 years (Jalata, 2013). The aim of this literature review has been steered to comprehend the long-term effects of Racism and Health Literacy among the Indigenous population of Australia. The literature review discusses the effects of social determinants like racism and lower levels of health literacy among the indigenous population like Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders for assignment help.
Health Status of the Indigenous Australian population
Research has indicated that before European colonisation more than 15,000 indigenous inhabitants of Australia used to live in Victoria, but that figure was devastatingly shrunken to a meagre 850 by the year 1901(Russell, 2015). This is evidence of the institutional and interpersonal racism that the indigenous Australian people have faced over the years and continue to face in present times. This has reduced their socioeconomic status drastically along with their exclusion from land ownership and economic rights. It has been found that the life expectancy gap between Indigenous men and women is 8 years lower than the non-indigenous population (AIHW, 2021). There are numerous researches that depict institutional racism as the basic determinant of health among the indigenous Australian population, yet most of the existing aspect in today's discourse based on racism completely denies its existence (Kairuz, et al., 2020). The indigenous population of Australia is burdened with diseases twice that of their non-indigenous counterparts which include chronic ailments, mental illness, respiratory, cardiovascular diseases and renal as some of the main concerns. The life expectancy of Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders remains to be 17 years lower than other Australian populations (Marmot, 2011).
Social Determinants and their influence on the health outcomes of the Indigenous Population of Australia
Racism
Institutional Racism has led to the suppression of political efforts in addressing racism while making a way to strengthen racism within society and communities. 17% of the Indigenous adult population in the state of Victoria have experienced racism from 2011 to 2014 when compared to the non-indigenous population (4.5%) have been found in a study. This shows that indigenous adults are four times more probable to experience racism than non-indigenous people in Australia. These statistics increased by 7 times when the experience of racism by Indigenous Australians was compared with the largely white Anglo-Celtic origin people of Australia as only 2.8% of them had experienced racism which was mostly based on the religious background rather than ethnicity, race or culture (Markwick, et al., 2019).
In research, it has been found that there is an association between health outcomes and racism depending on the severity of racism experienced as indigenous people who have been racially abused severely had a higher risk of psychological distress (Markwick, et al., 2019). Racism has been associated with numerous health issues through research like depression, sleeping difficulties, hyperactivity, obesity, asthma and cigarette consumption among indigenous adults and children (Kairuz, et al., 2021).
Health Literacy
Health literacy has been defined as a social construct where the ability or skill of a person to understand the basic services and information regarding healthcare is limited while being unable to decide on suitable resolutions regarding health concerns (Liu, et al., 2020). There is very little exploration of the effects of health literacy on the indigenous population of Australia but they indicate the significantly lower score in education attainment, numeracy scores and school-based literacy programs than the general population of Australia. The indigenous Australians experience hindrances in an array of socio-economic pointers like employment, education and income and thus making them highly susceptible to lower individual health literacy (ACSQHC, 2014). One of the prime reasons for the exhibition of low health literacy among indigenous Australians is the difficulty in understanding, navigating or accessing mainstream healthcare systems as the healthcare system is not designed concerning the culture or language of the indigenous people. The healthcare providers do not try to understand their traditional healing techniques and are culturally sensitive about such issues. Thus, making it one of the prime reasons for the lack of propagation of health literacy among the indigenous people (Thewes, et al., 2018).
Interactions between Racism and Heath Literacy for the Indigenous population in Australia
There is significant racism directed towards indigenous Australians which cannot be attributed to any specific determinant like lifestyle risk factors or socioeconomic status. The policymaking approach which is characterised by human rights aimed at eliminating interpersonal and institutional racism towards indigenous Australians is dominated by a paternalistic approach which in turn reinforces inequalities and racism within the policies rather than eliminating them (AHRC, 2015). The government with its initiatives like the "Close the Gap" initiative has considerably failed to accomplish what it was intended for and such inadequacies in bureaucratic requirements had not been accounted for the cultural differences among the indigenous people. The Indigenous Australians do not have the right to proclaim their right to accept information and unbiased treatment as racism is deeply seated within the bureaucracy of the healthcare system. The health providers and government have also been found to have normalised policies and practices which tried to discriminate against the Indigenous Australians irrespective of their level of health literacy (Durey & Thompson, 2012).
Because of a lack of health literacy, indigenous patients have difficulty understanding terminologies when dealing with primary care providers, which leads to a lack of follow-up care. The lack of cultural sensitivity among primary care providers can be classified as a form of interpersonal racism. It displays the rescindment of accountability for unacceptablehealth literacy communication towards indigenous people and disdain for their cultural associations within the healthcare system. This displays a form of interpersonal and institutional racism against indigenous people and also the existing lack of heath literary education among the indigenous population (Henry, Houston, & Mooney, 2004).
Conclusion
The Australian government needs to respect the connection between racism and health literacy as the former needs to be abolished institutionally and the latter needs to be reinforced within the healthcare systems. Problems of racism and paternalistic approach to policymaking have been discovered within the government policies is the biggest challenge, which has been forcing the indigenous people to adapt or wither away rather than trying to understand their predicament. The report suggests that without abolishing institutional and interpersonal racism, the government cannot be able to bring about health literacy among the indigenous people.
Academic Honesty and Integrity
The above report has been compiled while upholding the University Academic Honesty policy through accurate representation of APA guidelines throughout the report. The topic was assumed through a thorough background study of the history and struggles of Indigenous Australians. The information, concept and thoughts have been attained through the study of current trends of healthcare policies in Australia and the various journal articles, online reports and proceedings of the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, Australian Human Rights Commission (AHRC), Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) and published medical journals on the Australian healthcare system. Some of the trends have also been accumulated through personal experiences of fieldwork done through Youth Work.
References
.png)
Research
PUBH6007 Program, Design Implementation, and Evaluation Assignment Sample
Assessment Task
Needs assessments are crucial in program design, implementation and evaluation in public health, as they form the foundation for the evidence-based approach required to design and evaluate relevant, credible and contextually appropriate programs.
In this assessment, each individual in the group will need to perform a needs assessment associated with your group’s chosen health challenge/target population. To generate a comprehensive understanding of the community need, the group discussion should inform the different areas that each student will focus on under a particular public health theme. Each individual will submit a 1,000 word (+/–10%) needs assessment report.
Task Instructions
Your needs assessment report should include the following information:
1. Background
This should include:
- A clear title of your allocated problem/topic.
- A brief literature review of the current literature that outlines the types of needs (e.g., normative, expressed, comparative or felt) in your chosen population.
- A brief discussion about the need analysis and methodological approaches (e.g., quantitative and qualitative research and systematic reviews) you have chosen to use.
2. Prioritisation of Needs
- In this section, you will prioritise the needs based on the current evidence reviewed and develop and present a problem and solution tree.
3. Justification
In this section, you need to justify your choice of priorities and outline how your needs
assessment will benefit the population.
4. SWOT Analysis
In this section, you will need to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) of your needs assessment:
a. Strengths: What unique needs did you identify that others have not?
b. Weaknesses: What are some things that your needs assessment failed to consider?
c. Opportunities: What are some areas in which you could thrive that are not currently taken advantage of?
d. Threats: What are some external factors (e.g., competitors, consumer demand or economic conditions) that could make it more difficult for you to do a needs assessment?
Solution
1. Background
1.1. Background Information
The problem of anxiety in the younger is has been one of the common concerns in recent times where the young people artificial is centered on the body looks, social acceptance, and the conflict about independence. The avoidance of usual activities or refusal to the engagement in new experiences becomes the key signs of anxiety in college-going students. Some of the symptoms of anxiety in college-going students include irritability, trouble concentrating, withdrawal from social activity, avoidance of difficult or new situations, and chronic complaints above the stomach and headaches. Anxiety is regarded as one of the most common mental health conditions in Australia with an average of 1 in 4 people (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2022). The graph given below shows the number of people experiencing mental and behavioral conditions in Australia in 2018:
.png)
Figure 1: People experiencing mental health conditions in Australia
(Source: Statista, 2022)
The above graph for assignment help presents the statistical data of people experiencing mental and behavioral conditions in Australia in 2018 which shows that around 2.5 million Australians have suffered from aggression or feeling depressed (Statista, 2022). The percentage of anxiety in college-going students is increasing in Australia at a variable rate which shows a spike in the mental health impacts in 2021 (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2022). It also creates concern about the growing rate of mental disabilities in the younger ones and therefore becomes a matter of concern.
1.2. Need Analysis and methodological approaches
The need analysis involves the overall process of the identification and evaluation of the needs with a successful development in the effective training program. It is a systematic process for determining and addressing the needs or gaps between the current conditions and desired conditions (Anderson et al. 2017). The need analysis becomes a formal and systematic process in order to identify and evaluate training with an individual group of employees with consumers and suppliers. The main purpose of this analysis is to provide user satisfaction focusing on the needs of the human and need analysis addressing the requirements of the software. Therefore qualitative and quantitative secondary data analyses were done in order to focus on the background information and understand the relationship between the issues and the availability of the resources. The steps utilized in this paper to understand and analyze the need of the Young communities of Australia are shown in the figure given below created by the author:
.png)
Figure 2: Process developed by the author in order to execute the anxiety needs in the assessment dealing with the Australian population of the University students
2. Prioritization of Needs
The problem analysis proposed the appropriate data collection which is extremely important to understand the effective relationship between the cause and effect along with the contribution of the problem to the specific population. The key understanding is to have the specific knowledge of the population of the university-going students in Sydney and different use of problems and solutions for the various situations to identify and prioritize the potential interventions (Stocker et al. 2021).
It also uses Maslow's hierarchy of needs to understand the problem and prepare a solution in order to have the community's needs of the physical self-fulfillment understanding the impact on the population.
The figure shows the problem and solution tree for the anxiety problems in the university-going students of Australia given as below:
.png)
Figure 3: Problem and Solution tree for Anxiety disorders in college going students of Australia
Priority 1: Relaxation Practice initiatives
- Solutions: The community supports the educational program regarding the relaxation practices and yoga in order to support the community leaders along with the University initiatives and social media
- Problems addressed: Poor education in relaxation techniques, psychological factors, a healthy diet, and having a busy lifestyle
Priority 2: Exercise
- Solutions: The community exercise program
- Problems addressed: lack of exercise which results in both psychological, physical, and psychosomatic factors
Priority 3: Education on healthy eating and opening-up
- Solutions: Increase the frequency of the health services in the remote communities and educate on the healthy eating habits and opening up in order to relieve stress
- Problems addressed: Stress, limited access to the Healthcare services, Busy life
3. Justification
The target population addressed in this case study is the university-going students in Sydney, Australia and therefore several environmental factors impact the individual and the community such as economic, social, and physical (Reavley et al. 2011). The problem and solution tree are created for the needs of the community in order to understand the prioritization of the initiatives that are based on the areas of efficiency, flexibility, and acceptability.
The first priority is based on the relaxation of the mind and promoting the relaxation practice initiatives in order to create peace in mental health. It increases the awareness of the mental health situation which is being faced by the young population of Australia. The end priority focuses on Exercising as a basic need that has been lost in the younger generation promoting the use of social media in order to address the problem and have a higher chance of bringing the benefits. The third prioritization is based on the healthy eating habits opening up which focuses on building strong community relations and addressing the problems that are related to psychological, physical, and psychosomatic disorders.
4. SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis presented below presents the various factors that potentially impact the study and therefore the evaluation is done through the process and outcomes.
.png)
5. Conclusion
This paper is focused on understanding the potential initiatives by knowing the root causes of the problem of Anxiety in the young minds of Australia. It analyses the main priorities focusing on the population-based Healthcare services and education. It also includes the SWOT analysis to evaluate the outcome of the process in order to have a sustainable benefit in the overall process and the situation promoting improvement. The result concludes with several initiatives taken by the community and the government in order to reduce the problem of anxiety in the growing population.
Reference List
.png)
Case Study
NRSG374 Principles of Nursing Assignment Sample
Assignment Detail:
Students are to provide an 1800 word critique of the provided case study using only ONE CPG.
To complete this task you will need to discuss and critique relevant elements of the CPG and case study whilst upholding the National Palliative Care Standards at least one of:
- NSQHS
- NMBA standards and/or
Assessment criteria: The assessment will be marked using the criteria-based rubric.Please note that in-text citations are included in the word count whilst the reference list is not included in the word count. Words that are more than 10% over the word count will not be considered
Now that you have read the case study and selected ONE of the CPG provided you are required to:
- Review and critique the care given to the patient against the CPG you have selected and provide evidence to support your critique through additional research that you will undertake
- Highlight the importance of the National Palliative Care Standards and at least one of the NSQHSS and/or the NMBA Standards and how they influence our practice
- Demonstrate knowledge on the illness trajectory of Motor Neurone Disease (MND) in line with Palliative Care Principles
- Provide links between the case study and your chosen CPG to identify highlights or limitations in care
- Ensure that your sources are all contemporary (within the last five years) and from evidence based sources)
- Read all instructions and the rubric very carefully
Case study – Care of the dying patient CPG
.png)
.png)
Solution
Introduction
Palliative care is a type of care that is a person and its family-centred care with a progressive, active, advanced disease who is going to die or has such prospects of cure. The goal of this type of treatment is to maintain as well as optimize the quality of life (Cheluvappa & Selvendran, 2022). On the other hand, there is a need to mention that the Palliative Care of Australia stated that the chosen palliative care must be strongly responsive to the needs of the diseased person and their family. On the other hand it also strictly considers that all living persons must be provided with the respective care for advanced, progressive diseases and also regardless of the diagnosis (Borbasi et al., 2019). In the respective case study of Tyler, there is palliative care provided by the palliative care team as per his wish, the respective report is trying to critically evaluate CPG with the usage of an appropriate standard to provide the respective person more support and also help his family.
Chosen Clinical Practice Guidelines or CPG with Reason
First of all, there is a need to understand Motor Neuron disease, the illness trajectory of motor neuron disease and the patient's background. In the case of the respective disease of MND, death takes place within a year of diagnosis in most cases and in some cases, it takes two years (Brown et al., 2017). On the other hand Mr Tyler is a young man as his age is only 40 years and has a nice family, so there is a need to consider the EBP means the evidence-based practice and also appropriate standard of care to provide END of life care CPG (Wardle et al., 2019). The respective CPG is that Tyler's death is really unexpected for his family. His babies are too young and he just started his journey of life only a few years ago. On the other hand, Tyler wants to spend quality time with his family as he knows about the disease; he also wants his family reunited though he is not there with his family in future. Sixt, considering all this, there is a chosen END of life care CPG takes place to provide appropriate palliative care to Tyler.
Demonstrate knowledge on the illness trajectory of Motor Neurone Disease
(MND) in line with Palliative Care Principles
Motor neurone disease or MND is a type of progressive disease related to the neurology of a person. The respective disease leads to paralysis in hand, leg. As times go there are the issues of swallowing and problems of breathing also develop in the patient of respective disease (Oliver et al., 2020). As per the principles of the Palliative care, the care always is patient, family and carer centred, so it is able to provide support to Tyler to get appropriate care as well as of to his family and also to carer. On the other hand it is also based on the assessed need. It was the desire of Tyler that his family must be reunited before his death and he can die with honor that must be provided by the palliative care. On the other hand, Palliative care also ensures that the patient, family and carer get the help of local networked services, as per the respective case study Tyler and his family get the help of the local network. On the other hand, palliative care always ensures that the treatment must be evidence-based, clinically and culturally safe. The trajectory of Motor Neuron Disease always needs to be considered. Care is integrated and coordinated, that is also the principle of Palliative care. The integrated and coordinated care supports the patient of motor neuron disease to get physical and mental relief. The sixth principle is in palliative care there is also a clear understanding developed between the care provider team and the patient and his or her family to understand what is the meaning of the care to each of them (Oliver et al., 2020) . So for the respective case study there is at first clear understanding that must be needed to develop what is the meaning of palliative care for Tyler, Catherine and also for the other family members.
Critical Evaluation of the applied care
The respective palliative care that is provided to Tayler needs to consider not only the care of the respective diseased person there are also need to consider the condition of the family members also (Palliative Care Australia, 2018). Because the Australian Palliative Care stated that there is a need to include the care of the family of the ill person also in the respective care (Abbott et al., 2020). Through the case study, it is visible that there are conflicts among the Joycee which means the mother of Tyler and the wife of Tyler means Catherine. On the other hand, it is their wish of Tyler that his children also consider his situation before his death so that he can spend quality time with his family. But such initiatives take place from the side of the Palliative care team, due to the fact that at the end of his life he cannot get his all family members together and close to him except his wife. On the other hand, it is the duty of the registered nurse to provide Evidence-based nursing and consultative nursing and promotion of health and do holistic assessments (Sharplin et al., 2020). In the respective case study, also needs to mention that no such usage of the SAS tool takes place. According to Heslop (2019), SAS tools mean the Symptoms Assessment scale is supportive to understand breathing, pain, insomnia, appetite problems, nausea, fatigue and so on together. On the other hand as per the guideline of the PCOC the usage of the SAS tool is important to measure the appropriate cause by understanding the most important seven symptoms (Eagar, Clapham & Allingham, 2020). There is also a need to consider the Problem Severity score on the time of providing the palliative care to the patient that is also not considered the respective case study and the palliative care team to handle the case of Tayler. Basically, the 4 - point scale is used to understand pain, family problems, spiritual family and so on (Tian et al., 2020). The measurements that take place are either absent, mild, moderate or severe through the respective scale. Hereby also need to include that there is no such usage of the karnofsky Score also takes place within palliative care (Kolakshyapati et al., 2018). The respective score is effective to understand the capability of a diseased person to do some common activity based on the care also provided to increase in quality of life of the family members as well as of the affected person.
NSQHS
The registered nurse has a crucial role in preventive, socio-cultural, therapeutic and also in the promotion of quality patient-centred and family centred palliative care. The World Health Organisation also considers palliative care as an approach that is able to improve the life of patients whether they are adults or children also to their families, especially in the case of life-threatening diseases (Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2020). On the other hand as per the view of Palliative Care of Australia the Registered nurse plays one of the important roles in the case of providing the END of Life care. The respective care is included with appropriate goals, advanced care planning and monitoring with the appropriate acknowledgement that the patient is improving or not. The National Palliative care of Australia is supported by the nine standards that need to be considered by any registered nurse during the time of providing Palliative Care to a patient. On the other hand the National Safety and Quality Health services provide the appropriate support to the patient (Ritchie et al., 2018). On the other hand, there is also a need to mention that the consideration of NSQHS was also chosen as it in some of the case overlaps with the NMBA nursing standard. This Means NSQHS is able to provide proper care to the patient by maintaining the respective standard.
.png)
Figure 1: National Palliative Care Standards
(Source: Cheluvappa & Selvendran, 2022)
Highlights
If the respective standard is considered by the registered nurse at the time of providing care to Tayler about the Palliative care then continuous changes take place within the developed plan as deterioration takes place in the case of the affected person. On the other hand there are psychological, metaphysical theological and emotional aspects that help Tayler to manage his grief and he may be able to give strength to his family members by reuniting them. As per the respective and considered standard once a patient is identified that due to disease the person is going to be dying soon then appropriate terminal care is provided to the patient. All the spiritual convictions and preferences of the affected person must be considered by the respective standard. So it can be stated that implementation of the NSQHS standard is able to support Tayler to fulfil all his wishes about his family before his death, ultimately able to complete the End of life care CPG. The treatment of Tayler must be incorporated with ACP means the Advanced Care plan, Medical treatment decision maker and Advanced care document ( Cheluvappa & Selvendran, 2022). There is the selection of the final rites, final venues also take place. In the case study it is recognised that the recommendation takes place from the side of the Medical Officer to admit in the hospital though Tayler was not interested in that.
Application of standard 2 of Quality and Safety Management as per the case of Tyler cover underlying theme was "Partnering with Consumers," which necessities for efficient execution of the medical field dealing directly with patients. The foundation for quality and security is laid forth in Standard 2 (Quality Health Service, 2022). Thus, by laying up the typical organizational features and operational flow inside a secure institution adequate palliative care could be given as per NSQHS. Partnering with Tyler standard calls for efficient and relevant patient participation in reviewing, designing, and deployment of services, given that evidence supports doing so that indicates patient participation may lead to enhanced reliability, productivity, and security. Further, if the quality and safety management standard is implemented properly then no such recommendation takes place during the time of providing Palliative Care. The patient’s goal is also not considered by the respective treatment that is also a drawback of the given care that also can be handled through the respective NSQHS for assignment help.
Further with application of standard 1 of Governance for Health Service Quality and Safety. Palliative care team in the health care sector use governance frameworks to establish, and raise the company's productivity while spreading the word of quality management and the patient experience to all employees. In the workplace, the governance systems are used by clinicians and others. Standards for Effective Governance for Health Security and Improvement require adequate Qualifications for Service Organizations and improvements in Quality and Governance techniques for progress. Now, there are unified regulatory frameworks in place to managing the potential dangers to the health of the patient aggressively. Applying Theory to Practice in the Clinic Care given by the clinical staff is governed by NSQHS of the present day (Quality Health Service, 2022).
Management of performance and competence and leaders and the medical staff possess the
Having the necessary training, experience, and attitude to treatment to Tyler with palliative care is effective and risk-free. In order to enhance security measures, data is analyzed along with Liberties of the Patient and Active Participation. A patient's participation and rights are recognized and helped by being under their care (Quality Health Service, 2022).
Limitations
The most important issue that is related to the chosen standard of NSQHS is partnering with consumers and governance for health and safety lack of knowledge and skills among the service provider that in most cases fail to fulfill the expectations of the patient and also to the family members of the patient in the case of Trajectory Motor neuron disease. Improper infrastructure and incorporation of the family members of the patient is also a big issue and limitation for NSQHS.
Conclusion
Based on the respective case study it can be concluded that Palliative care needs to consider a lot of things and also a particular or more that one standard to provide appropriate relief to the patient not only from the physical pain but also from mental pain. There is not only the consideration of the health of the diseased person that takes place within the respective care by the registered nurse there are also need to include the family members' care. The care that is provided to Tayler was able to support the physical condition of Tayler but no such consideration takes place about his family care. On the other hand there are no such consideration of tools like SAS, PSS, RUG-ADL Score and modified Karnofsky takes place in the care of Tayler by the registered nurse of palliative team, if that is considered with the standard of NSQHS then Tayler must be provided with best palliative care as per the guideline of the Australian Government. The proposed care that takes place with the NSQHs must be provided in the future to the same condition of the person like Tayler it can be hoped.
Referens
.png)
Research
CAM528 Introduction To Epidemiology Assignment Sample
Task description
For this task, you are required to critique a journal article. A number of articles will be made available towards the middle of the semester. They will be chosen to reflect some of the key areas of interest that emerge from the first discussion board.
Task length
Maximum 1500 words.
Please follow CASP report as a format to write critique of journal and find the answer from the article “Early life determinants of cardiovascular health in adulthood. The Australian Aboriginal Birth Cohort study".
There are some questions on the following pages are designed to help you think about these issues systematically.
1. Did the study address a clearly focused issue?
2. Was the cohort recruited in an acceptable way?
3. Was the exposure accurately measured to minimise bias?
4. Was the outcome accurately measured to minimise bias?
5. (a) Have the authors identified all-important confounding factors
(b) Have they take account of the confounding factors in the design and/or analysis?
6 Was the follow up of subjects complete enough?
Early life determinants of cardiovascular health in adulthood. The Australian Aboriginal Birth Cohort study
1. Introduction
Life expectancy for the Indigenous population in Australia in 2010– 2012 was 10.6 years lower for males and 9.5 years lower for females when compared to the non-Indigenous population. The differences are particularly high in the Northern Territory (NT), where death rates for Indigenous Australians are 2.3 times the non-Indigenous rates.
2. Methods
. Participants
Details of the recruitment and follow-up of the ABC have been previously published in detail [15, 16]. Of all Aboriginal children born between 1987 and 1990 at the Royal Darwin Hospital, 686 of the possible 1238 were recruited into the study. There were no differences for mean birth weights or sex ratios between those recruited and those not recruited.
3. Results
The baseline characteristics of the study participants are presented in Table according to sex. Among female participants, baseline house- hold size was higher compared to males. Attrition analyses comparing baseline characteristics of follow-up study participants and non- participants were performed. Compared to non-participants, those participating in the follow-up were more often females, and they had higher IRSEO scores
CASP-Cohort-Study-Checklist_2018.pdf (196.13 KB)
Sjoholm P et al. Early life determinants of ca... (688.02
Solution
Introduction
The journal critiqued for this report is "Sjoholm P et al. Early determinants of cardiovascular health in adulthood. The Australian Aboriginal Birth Cohort study. International Journal of Cardiology 269 (2018) 304-309." The CASP appraisal tool is used to correctly assess the validity of the author/s interpretation of results and conclusions. The aim of this article was to 1) illustrate the occurrence of perfect cardiovascular wellbeing metrics utilising the AHA guide and its factors and 2) to investigate the association of socioeconomic aspects and birthweight with cardiovascular wellbeing in old age in the ABC.
Critique
The study addressed a focused issue. The study had a particular population Indigenous population in Australia and studied Early life variables of Wellbeing in the middle age of this population. The study highlighted the risk factors, including tobacco smoking, inactive way of life, harmful food behaviour, psychosocial pressure, extreme body heavy, dyslipidaemia, and hypertension. The study tried to detect the harmful effects of these risk factors on the heart health of indigenous adults in Australia (Sjöholm et al., 2018). The outcomes of the study are also considered for best assignment help. The present study showed a relationship between early life forecasters associated with socioeconomic and familial rank and upcoming CV wellbeing in the indigenous populace.
The cohort was recruited acceptably. Of all indigenous kids born between 1987 and 1990 at the Royal Darwin Hospital, six hundred eighty-six of the likely twelve hundred thirty-eight were hired into the research. There were no disparities in mean birth mass or sex quotient among those hired and persons not employed. All actions adding to this research meet with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as amended in 2008. All contestants offered printed clued-upper mission to contribute to this research, and all actions were accepted by the Human Research Ethics Board of the Northern Territory section of Health and the Menzies School of Health Research, counting the indigenous Ethical Sub-committee which has the authority to reject (Sjöholmet al., 2018). Families in metropolitan regions were categorised as metropolitan and persons in distant sites as not cities. The similarity of the mom on the occasion of the contestant's birth was documented. Family dimension was assessed through a survey by enquiring the contestants how many individuals were sleeping in their homes the previous night.
The measurements used in the study have been validated by the Helsinki Declaration of 1975. However, there are no additional considerations visible in the study.
The outcome was accurately measured to minimise bias. A proper analysis like Attrition analysis was used to assess the outcomes. After that multivariate model attuned for age, sexual category, metropolitan/not metropolitan, and groups for birthweight, motherly BMI, IRSEO rank, family volume, and similarity were examined (Sjöholm et al., 2018).
The authors have listed important confounding factors. Relations between numerous in utero features in addition to ecological aspects in both early days and parenthood and afterwards cardiovascular wellbeing have been accepted. These aspects comprise weight at the time of birth, postnatal development outlines, motherly obesity, parental smoking, familial socioeconomic rank and neighbourhood weakness, amongst others. The authors have also listed the American Heart Association (AHA) factors (Sjöholm et al., 2018). It described a sum of seven perfect cardiovascular fitness actions or features for describing and checking cardiovascular wellbeing. These incorporated not smoking, being bodily energetic, keeping standard body mass, blood pressure, blood glucose plus cholesterol stages, and consuming a healthy food habit.
Socioeconomic factors were considered during the analysis. At delivery, birth weight was calculated and information was collected regarding the families and their livelihood circumstances. Families existing in city regions were categorised as metropolitan and individuals in secluded places as not metropolitan. Equivalence of the mother at the instance of birth of the contributor was traced. For areal drawbacks, the Indigenous Relative Socioeconomic Outcomes (IRSEO)directory was utilised. Links between socioeconomic aspects and perfect cardiovascular fitness levels were examined utilising multivariable logistic regression (Sjöholm et al., 2018). Initially, univariate analyses attuned to age and sexual category were done. After that, multivariate models accustomed for age, sexual category, urban/not metropolitan, and groups for birthweight, motherly BMI, IRSEO count, household volume, and uniformity were examined.
The final follow-up occurred in 2014–2016 and offered a follow-up pace of seventy per cent of existing contestants. The follow up might not be complete. The current follow-up inhabitants might not symbolise the creative birth group, since follow-up contributors were further frequently women and had superior IRSEO scores evaluated to non-contributors. At last, the contributors were yet young grown-upsthroughout the previous follow-up (Sjoholm et al., 2018).
The follow-ups are not long enough. It is recommended that following upcoming follow-ups, cardiovascular morbidity and clinical actions might be examined for even enhanced consideration of the scientific significance of the cardiovascular danger outlined in this group (Sjoholm et al., 2018).
The current study demonstrates that perfect cardiovascular fitness was unusual in the ABC grown-up inhabitants. The most ordinary score gathered were ultimate glucose (eighty-three per cent), cholesterol (seventy-four per cent) as well as blood pressure (seventy-three per cent) levels. The slightest ordinary metrics were linked to fitness actions: non-smoking, perfect food, as well as best stages of bodily movement were gathered by not more than half of the group. Major sex distinctions were seen in both the full score in addition to blood pressure and bodily action. Numerous early life variables were seen to separately forecast upcoming cardiovascular wellbeing (Sjöholm et al., 2018). Family dimension and motherly BMI foresee BMI in parenthood. The areal difficulty is linked with potential blood pressure and stages of bodily movement. Metropolitan livelihood surroundings were linked with non-ultimate blood pressure stages. Family volume was linked with the smoking position in middle age. Similar to the results, both family and areal socio-financial positions have been significant variables of cardio metabolic threat aspects. Regarding the scientific and community health standpoint, the current results offer significant backdrop knowledge on the premature existence determinants of cardio metabolic wellbeing in an aboriginal neighbourhood. The current research demonstrates a link between early-life forecasters correlated to socioeconomic as well as familial position and upcoming cardiovascular wellbeing in the indigenous inhabitants (Sjoholm et al., 2018). This research demonstrates that exceptional consideration requires to be placed on health actions such as smoking and dietary lifestyle and gender parity in well-being to attain these objectives.
8. The results of the study are pretty accurate as the results match with the statistics from longitudinal groups in Australia, Finland, and the USA (Sjöholmet al., 2018).
The longitudinal character and well-prearranged follow-ups with comparatively excellent maintenance rates permit us to consider the outcomes established. though, because of the alterations completed to the innovative AHA description of perfect cardiovascular fitness concerning proper food and glucose stages that were required for this research, the outcomes might not be straight equivalent to former alike resaerches (Sjoholm et al., 2018). There was no bias in selecting the participants or measuring the outcomes. The participants also went through a follow-up, which made it easier to believe the results.
The results cannot be applied to a local population. This is because the conventional variables of family earnings and learning were not accessible and might not forever be well-appropriate in distant neighbourhoods. The study populace though is comparatively small causing a few restrictions to afterwards understanding of the outcomes. consequently, it might be right to relate the outcomes to a diverse populace (Sjoholm et al., 2018).These dissimilarities might be of even well-built implication in a comparatively minute cohort. The current follow-up populace might not entirely symbolise the creative birth cohort.
The results fit other evidence. The relationship between site and cardiovascular danger outlines in indigenous Australians has been beforehand learnt in the Heart of the Heart research. It was seen that contestants from city surroundings (Alice Springs) had elevated blood pressure, superior lipid stages and inferior kidney roles than their isolated livelihood complements. Superior earnings were linked with the prominent danger of CVD in city sites but not in Alice Springs or distant neighbourhoods (Sjoholm et al., 2018). Related findings are observed in the ABC group, where city inhabitants had elevated blood pressure. Contestants from generally further privileged regions consistent with the IRSEO countpresented with superior blood pressure andinferiorstages of physical movement in this research.
Research inferences propose how the resultsmight be significant for policy, exercise, hypothesis, and following research. This research demonstrates that unique concentration requires to be placed on health actionssuch as smoking and food behaviour and sexual category equality in well-being. From the findings, policies can be put in place to help improve the CVD health of Australians. With the help of policy implementations, malnutrition can be taken into account. Cardiovascular morbidity and clinical actions might be examined in the following study for even enhanced consideration of the clinical significance of the cardiovascular danger reports in this group. The insinuations can be authenticated by study, for instance earlier research.
Conclusion
It can be said that the article follows all the criteria of the CASP checklist. The article has a focused issue that it discusses throughout the article. Many of the previous research also matches the article and therefore it can be said that the article is valid and genuine.
Reference
Sjoholm, P., Pahkala, K., Davison, B., Juonala, M., & Singh, G. R. (2018). Early life determinants of cardiovascular health in adulthood. The Australian Aboriginal Birth Cohort study. International Journal of Cardiology, 269, 304-309. https://ris.cdu.edu.au/ws/files/26063476/21264048.pdf
Research
SHI104 Sociology of Health and Illness Assignment Sample
Assignment details
Individual/Group Individual
Length 2,000 words (+/- 10%)
Your report should cover the following:
1. Choose 4 social and environmental determinants of health from the listing below, and explain how they may influence your chosen health issue from the video case study used in Assessment 1 and 2 (i.e. Video 1: David - hypertension, Video 2: Rhonda – diabetes and Video 3: Theo – depression).
• social gradient
• poverty and deprivation
• where you live (housing and neighbourhood)
• education
• environment (climate, pollution, sanitation)
• employment status (and conditions of employment)
• transport,
• early childhood life
• personal health strategies
• social support and exclusion
• food
• health systems
• gender and violence
1. Describe examples of ways in which to engage and empower the community and increase health literacy on the health issue presented in your chosen case study video. Consider what communication and cultural issues need to be considered?
2. What impact on a nurse might there be when working with this health population and what self-care strategies could be employed to maintain own well-being and model self- care?
Please note: this report should contain an introduction, body and conclusion (see below for further information on writing reports).
Referencing:
It is essential that you use appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research. Please see more information on referencing here https://library.laureate.net.au/research_skills/referencing
• Assessments cannot be emailed directly to the lecturer.
• If you are late with your assessment submission, you need to follow the late assessment procedure relevant to your campus.
• Feedback can be viewed in My Grades on Blackboard.
Solution
Introduction
The socioeconomic, environmental, demographic, as well as cultural elements that affect people's daily lives and places of employment are all considered social and environmental predictors of health, along with the health system (Who.int, 2022). In this context, for assignment help a comprehensive discussion would be done where the social determinants of health would be related to the case study of David, Rhonda and Theo.
Discussion:
Social determinants of health and depression
It has been seen that health of individuals in a society is significantly associated with social determinants of health. It has been seen that the social determinants of health might contribute largely and directly impact on physical and mental health of population, well-being of them and the SDOH might include safe areas, transportation, and housing, racial bias, prejudice, violence, education, employment prospects, and income, possibilities for engaging in physical exercise and access to healthy meals, contaminated water and air as well as reading and language abilities (Health.gov, 2022). In this context, the social and environmental determinants which would be focused are poverty and deprivation, education, social support and exclusion, as well as gender and violence that are directly related to the case studies.
The first determinant is the poverty. Globally, there is a direct correlation between poverty and unhealthy lifestyles. The health of individuals is at danger due to inadequate nourishment, overcrowding, a lack of clean water, and other severe conditions. In addition, being sick makes it more difficult to work and puts families in a tough financial situation while trying to pay for medical expenses (Braveman & Gottlieb, 2014). Diseases that afflict the broader populace, such as mental problems, can affect persons living in poverty at a far greater incidence. The same is true with depression. Although depression may affect everyone, regardless of socioeconomic level, poverty exacerbates the condition and makes it more difficult for a person to get the proper medical care. However, if the aspects of poverty that fuel sadness are lessened, then fewer people should experience depression.
The following SDOH is education, which plays a significant influence in health through influencing possibilities, employment, and income, which are all substantially correlated with average lifespan, morbidity, and lifestyle factors (Adler et al., 2016). Teenagers who struggle with depression grow social phobias as a result of social contact, which can happen in a school environment. Depression in adolescents causes a feeling of numbness that makes them fear social interaction and failure. Having less education increases your likelihood of developing depressed symptoms.
The following factor is social exclusion that refers to social disadvantage and a lack of opportunities, resources, involvement, and skills that significantly affect the health condition of the patients and lead to development of acute or chronic diseases (Braveman & Gottlieb, 2014). In hierarchical multiple regression, social exclusion characteristics such as lower income sufficiency, unfavorable living conditions, and loneliness substantially linked with higher depressed symptoms after controlling for demographic and health factors.
Lastly, gender and violence are major determinants as females often experience discrimination in accessing the health and other services compared to males and more prevalently experience violence that largely affect their mental health condition. After puberty, girls are more likely than boys to experience depression. Girls are more prone than males to experience depression at a younger age since they generally hit puberty sooner. There is data that suggests the gender discrepancy in depression may persist throughout the course of a person's life. Some girls' risk of experiencing depression may rise when they enter puberty due to hormonal changes. One of the most pervasive societal problems in the world is domestic violence. It causes a number of issues in society, including those related to lifestyle, physical health, family, children, and even mental health. In actuality, there is a strong correlation between domestic violence and depression.
Methods to engage and empower community and increase health literacy about depression
Individual health education
Doctors and nurses have many possibilities for individualized health education since they have daily interaction with patients and their families. The subject chosen must be appropriate for the circumstance. For example, a woman who is seeking treatment for depression should be informed about depression and its effects rather than malaria (Hurley et al., 2020). The ability to debate, argue, and persuade the individual to alter his behaviour is the primary benefit of individual health instruction. The fact that we only reach tiny numbers is a drawback.
Group health education
There are several groups at whom we might target health education, including moms, students, patients, and industrial employees. In group health education, the topic selection is crucial and must closely correspond to the group's interests. For instance, mothers of teenagers might learn about the causes, signs, and situations that can lead to depression in children; school children might learn about sexual abuse that can result in mental illness and depression; a group of patients might learn about mental health that can lead to depression as a result of chronic illness; and industrial workers might learn about work-life balance and burnout (Morrison et al., 2019).
Group discussions are regarded as a very effective teaching strategy for health as a part of group health education. It is a “tow-way technique” of instruction (Zhou et al., 2019). By exchanging ideas and experiences, people grow. The group should consist of at least 6 and no more than 12 persons in order to be effective. A group leader should be present who introduces the topic, guides the talk in the right direction, stops side discussions, motivates everyone to engage, and wraps up the discussion.
Lectures from doctors to a mass population of institution
The most common format for teaching about health is lectures. The majority of the communication in this is one-way, meaning that the individuals are only passive listeners and are not actively engaging in the learning process. The speaker's personality and reputation will have an impact on how impressive and successful the speech is (Tay et al., 2018). A lecture does convey the fundamental knowledge on the matter, but it might not succeed in altering peoples' attitudes toward their health. Nevertheless, lectures play a significant role in small group health education.
Workshop
There are several meetings that make up the Workshop. Small groups will be formed for the duration of the session, and each group will elect a chairman and a recorder. With the assistance of resource employees and experts, each group resolves a portion of the issue. Under the direction of experts, learning takes place in a welcoming, joyful, and democratic environment.
Education for mass approach
The health care professionals can use "mass mediums of communication" such as posters, health periodicals, movies, radio, television, health exhibitions, and museums to educate the general public. In general, group or individual tactics are more effective in changing people's behaviour than mass media (Liu et al., 2020). However, they are really helpful in connecting with a lot of individuals who may otherwise be out of reach. Media should be utilized in conjunction with other strategies for health education to be effective.
Communication and cultural issues associated with health literacy
A common communication challenge for people and their healthcare professionals is inadequate health literacy. Ineffective decision-making, non-adherence, negative results, and a loss of confidence in the medical community can all be caused by patients' incapacity to adequately absorb, process, comprehend, and act on health information (McQuaid & Landier, 2018). Inadequate health literacy can also result in patient expectations being misunderstood and managed incorrectly, increasing the liability risk for healthcare professionals.
Speaking simply, avoiding jargon, using terms that patients understand, decreasing repetition and ambiguity, and other tactics are frequently used as strategies for increasing health literacy. Even while these tactics are essential, cultural competency, another important component of effective communication, is occasionally disregarded.
Although cultural competency and health literacy are occasionally seen as distinct concerns, a patient's views, values, and experiences may greatly affect how they interpret and comprehend health information, which in turn affects their level of health literacy. Furthermore, cultural variations between patients and clinicians can cause misunderstandings, interpersonal problems, divergent opinions about health issues and treatments, and poor results, just as low health literacy does.
Impact on nurses while working with patient with depression
The provision of safe and high-quality treatment and the retention of healthcare workers are both impacted by the workplace environment. Professional settings may have an impact on nurse satisfaction and retention, care quality, and patient safety. When compared to mental health nurses working in the community, institutional nurses had a more unfavorable perception of the workplace. When nurses work in mental facilities, there are decreased perceptions of job motivation, leadership, and autonomy. As a result, it is probable that using an appropriate model for problem-solving and making decisions, such the nursing process, will help RNs recognize depressive symptoms and/or depression (Kim et al., 2021).
Self-care related to depression
The more the patient neglects their own needs and self-care, such as obtaining enough rest, eating wholesome meals, and relaxing, the more likely the symptoms of depression are to worsen. Although the patient may wish to speak with a mental health professional for support and treatment choices, a healthy self-care practice can also assist the patient manage day-to-day living. Depression may be difficult to manage, particularly if the patient is plagued by gloomy, pessimistic thoughts. The patient could feel guilty, unworthy, despondent, and unable to change their mental condition (lovino et al., 2020). That is normal. However, the patient might be able to rewrite or replace these ideas with more uplifting ones rather than just ignoring them. The patient may find it difficult to care about anything at all when the people, places, or things that used to make them happy no longer seem appealing. Self-care may become more challenging as a result.
Giving oneself the chance to try something novel, though, could be the secret to reviving interest in the patient's life.
Conclusion
Social determinants of health might contribute largely and directly impact on physical and mental health of population, well-being of them. In this study, the assessment was done on the basis of three patients David, Rhonda and Theo and the factors that has been associated with the patients are: poverty and deprivation, education, social support and exclusion, as well as gender and violence.
Reference
.png)
Case Study
NRSG367 Transition to Professional Nursing Assignment Sample
Assessment Task Overview
Critically analyse the following case study to answer the essay questions.
Case Study Background
Harry is a Graduate Registered Nurse (RN) who is 8 weeks into his first graduate rotation at the local metropolitan, tertiary hospital. He is currently working on a Medical Ward. For the first four weeks Harry worked alongside his nurse preceptor, predominately rostered on morning shifts. Harry has just completed his first five (5) night shifts yesterday morning and is back on an afternoon shift today (Saturday).
Harry is still trying to manage his roster and other commitments like social touch football with his friends and mountain biking. Today, Harry is feeling tired and frustrated because he slept through his alarm this morning and missed his sister’s birthday breakfast celebration. He is also disappointed that he can’t join his team for the touch football end of season breakup in the evening.
On Shift
Harry has arrived 15 minutes prior to this shift starting. On arrival, he realises that he hasn’t worked with the Nurse-in-Charge before but there are other nurses on the shift that he has met.
Harry feels a little nervous, but he knows two (2) of the patients he has been allocated from his recent night shifts and he is allocated a further two (2) patients who are to be discharged this afternoon. He has not arranged a discharge before so he prioritises these activities as he prepares his shift planner.
A short time later the Nurse-in-Charge tells him that his patient allocations have changed due to skill mix. A different nurse will arrange one (1) patient discharge and Harry will be receiving a new patient from Emergency Department.
Harry feels overwhelmed with the admissions and discharge. He is unsure how he will cope with the rest of his shift. Harry has not looked after a patient (Mr Somersby) who is confused, high risk of falls and wanders around the ward. He is reluctant to ask the Nurse in Charge for assistance as he does not want to appear ‘incompetent’. He decides he must push on, and soon it is time for handover.
At handover, Harry realises that after he had not given Mrs Williams her IVAB. To help with his time management, Harry had set the observation machine to take automatic observations. However, he had forgotten to go in and check this patient for the last 3 hours. Harry has not yet completed the admission documentation for Mr Sommersby as he has been trying to stop him from wandering out of the ward.
Additionally, he has not completed any of his patient notes on the computer on wheels (COWS) machine. The nurse he his handing over to rolls her eyes when this information is handed over. Harry stays 30 minutes after the end of his shift to complete his work.
Following his shift
On his commute home, Harry feels anxious and feels that he did not provide sufficient care for his patients, in particular Mrs Williams. He is frustrated with himself that he may have missed other things this shift and that he had to stay late to finish his patient notes. At home, he spends some time reflecting on his shift and plans to ask his nurse preceptor for any advice/tips on their next shift together.
Harry appears to be struggling during his clinical shift. He also seems to be having difficulty maintaining a work/life balance. Critically analyse the provided case study to answer all the following three questions within an essay format:
1. Determine and justify whether the graduate RN met (or did not meet) their role and responsibilities as an RN during his shift. Provide at least two (2) case study examples and support your discussion using evidence, including Nursing and Midwifery Board Australia (NMBA) Registered Nurse Practice Standards (2016).
2. Construct at least three (3) recommendations as to how the graduate RN could have undertaken this shift differently. Consider in your discussion the knowledge, skills and attitudes inherent in the RN role, including utilisation of technology and teamwork skills, and support your discussion with literature .
3. Transitioning from student to Graduate Registered Nurse can be difficult. Construct at least two (2) evidence-based strategies that could be implemented to promote resilience, build capacity, and support work/life balance during the graduate RN’s transition period .
Instructions:
• Word limit is 1800 words (+/- 10%), including the introduction and conclusion.
• Paper to be written in essay format, must answer the above questions, and should be written in academic writing style (not first person). You may use headings.
• Ensure you consider the AT2 Rubric, Appendix 2 in the Unit Outline, when undertaking this assessment task.
• Submit your paper to Turnitin by the due date.
Solution
INTRODUCTION
This study will answer three questions based on a case study for assignment help in which Harry failed to perform his Registered Nurse (RN) role. This will also examine the negative examples that have made Harry agitated due to his poor performance in this workplace and taking proper care of patients assigned to him. Moreover, some recommendations will also be given along with strategies that help Harry balance his work and personal life.
DISCUSSION
Meeting the RN Role
Harry is a newly appointed graduate Registered Nurse who joined his workplace 8 weeks prior. He was assigned his duty during the morning shift and was suddenly given night shifts and again allotted an afternoon shift the next day. This has made some issues for Harry in balancing a professional and personal life. Moreover, time management was one of Harry's biggest challenges that impacted his working pattern. The day when Harry was allotted an afternoon shift, Harry was depressed and agitated because he wanted to join a football match; however, due to his duty, he had to miss that match. This has impacted his professional life as he has failed in appropriately playing his duty. Work and personal life balance help a person to enhance the level of productivity that helps in career development (Zhu et al., 2022). Due to a lack of time management, a skill that every RN must possess, Harry has failed to take care of his allotted patients. He has failed to give proper medication to Mrs. William. Lack of Time Management is one such negative example of Harry as he has failed to balance his personal and professional life properly, failing to attend the football match. It is significant to note that time management is quite important for RN in getting huge success in their career (Popejoy et al., 2022). Another negative example was that Harry failed to look after Mr. Somersby, who has a high fall risk. Harry was confused and even failed to ask the head nurse for help.
Mr. Somersby would receive proper treatment.
Notably, a registered nurses role is to coordinate the treatment and care of every convalescent. Their responsibilities also vary from drawing blood and educating convalescents regarding their health (Henshall et al., 2018). An example of the case study given in the Nurse and Midwifery Board of Australia is that Ms. Jaclyn Stratton, who was working as a psychiatric nurse, was suspended from her job role as she failed to diagnose the vulnerability of the patient with whom she was dealing. It is important to note that she has failed to perform her duty as she needs to balance her personal and professional life properly. One of the biggest responsibilities RNs play is assessing, observing, and speaking to the convalescents regarding their health issues (Halcomb, Smyth & McInnes, 2018). They are also responsible for recording the symptoms of the ailments, results of the diagnosis and all other essential records regarding the patient's history (Mahoney et al., 2020). Preparing the patients for operations and various tests and offering them essential treatment facilities and care is also a significant duty of an RN. It was also found in one of the case studies in 2018 that two people die due to poor performance standards of registered nurses. The family members of the dead persons have complained that one of the registered nurses was responsible for providing the wrong medication and that impairment has taken away the lives of two people (Chang & Daly, 2016). According to the Nurse and Midwifery Board of Australia, professional conduct is concerned with significant values that can be easily outlined in the set of obligations; codes of midwives and nurses must be prepared for explaining and justifying the actions and decisions. Nurses offer services to the convalescents to be easily cured of their ailments. A lack of time management and balancing work/life are the biggest reasons registered nurses become agitated and fail in performing their job roles (Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia, 2018).
Moreover, they must possess certain skills which are significant in maintaining patients' health and giving them better healthcare and treatment amenities. Harry lacks one of the basic skills that every RN must possess: emergency assistance in medical care. When Mr. Somersby's condition deteriorated atrociously, he failed to call for emergency help so that he would be able to give him better treatment. Rather he remained silent and did not ask for help, which could have taken away the life of Mr. Somersby.
Recommendations for Harry to improve his skills as an RN
The following recommendations are given so that Harry can improve their time management skills and give proper treatment facilities to the patients. This includes emergency cases when the health of the convalescent deteriorates.
Teamwork in nursing is concerned with patient-centric behaviour focused on accomplishing targets working with other nurses (Rosen et al., 2018). Harry must learn to work within a team as it will help give proper care facilities to the convalescents. It also helps in enhancing the standards of outcomes for the patients. Hence, the major motive of the teams in healthcare must work in a team to make other nursing staff learn how to provide high standards of healthcare amenities that aid a patient receiving from ailments (McLeod et al., 2021). Nurses are required to purposefully integrate teamwork and their working patterns to further assist in seeing better responses from the patients and more enhanced accomplishment of the goals.
Registered nurses must work together in collaboration that helps develop solid safety and security outcomes for patients. In addition, it is recommended that when registered nurses work in collaboration, it helps improve the level of communication and productivity of these nurses and helps the healthcare centers to gain maximum benefit in the competitive edge (Zajac et al., 2021). This will help Harry improve his conversation skills with other nurses, which will help reduce his nervousness and enable him to approach other nurses without fear when an emergency occurs. This also helps improve strong nursing care facilities and interdisciplinary linkages (Herzberg et al., 2019). Teamwork skills must be learned so that the efficiency standards can be enhanced in caring for the convalescents, which leads to more brand awareness of the healthcare institutes and more competitive advantage.
It can be concluded that Harry, a registered nurse, must develop certain skills so that he can be able to provide better healthcare facilities to the patients. It is also analysed that better communication standards, developing resilience and using digital technologies must help healthcare professionals in providing better services and it also helps personal development.
Reference list
.png)
Research
HND731 Learning and Teaching for Health Professionals Assignment Sample
Task description
For this assessment task you are required to apply your knowledge of education program planning to the design of an education session. You have been asked to provide an education session to a local mothers’ group about gestational diabetes.
Explain how you would plan the education session, including:
• The information you need to know about your participants and how you would conduct a learning needs assessment for the group and explain why this information is important.
• Write 3 learning objectives for the session.
• Select 3 different teaching methods and explain the rationale for your choices in relation to the learning objectives, participant characteristics and adult learning principles.
• Explain the reasons for evaluating education and how you might conduct process and
content evaluation for this session.
Instructions for this assessment task:
• Draw on information and references provided in the unit.
• You are also expected to do your own research of peer-reviewed journals, textbooks and evidence-based guidelines.
• Websites, consumer information, Wikipedia are not appropriate for assessment tasks.
• Make sure you self-assess your assignment against the marking rubric and presentation requirements before submission. This enables you to ensure all the required areas have been covered.
Solution
Introduction
The purpose of this study is to make an education session for the Mothers' Groups regarding the significance of Gestational Diabetes. Gestational Diabetes refers to a type of high sugar level in the blood of pregnant women which usually starts between weeks 24 to week 28 during pregnancy. It is during this period when the body is unable to produce an ample amount of insulin which is a hormone that helps in the metamorphosis of glucose into glucose. This study will highlight the information of the participants in the education session along with various ways of conducting the assessment. Moreover, the importance of the session, learning objectives, different teaching methods and demonstration of the rationale will also be concentrated here. It will examine the logic for the assignment help of the session and the manifold ways through which the content and process of the session will be evaluated.
Information of the Participants
The participants in this education session are mothers who are aged between 25 to 30 years of age. These women who have participated in this education session are unaware of gestational diabetes and its impressions on the life of women. The participants who participated in the session were either pregnant women or they were post-partum.It is to note that most of the women who have participated in this educational session have developed symptoms like fatigue, excessive appetite and thirst. It is even significant that pregnant women are more prone to this disease during the time of pregnancy as the level of insulin reduces making complications for pregnant women (Giannakou et al., 2019). All the participants joined the educational session so as to know the symptoms and treatments of Gestational Diabetes. The educational session was conducted physically to the participants are from Richmond area of Melbourne.
Way of conducting the learning needs assessment
Assessment of the learning needs has a distinctive role in training and education. It is important to observe that the requirement of learning helps in underpinning any educational apparatus. Some of the ways through which the assessments of learning needs will be done are as follows:
Analysis of Discrepancy: This is a form of assessment in which the Mothers’ group who are taking lessons on Gestational Diabetes are assessed regularly. This is concerned with the comparison of the performance level along with the self-assessment, assessment of peers and assessment of objectives and outcomes (Cortez et al., 2019). It also helps in comparing the scores of different Mothers based on their intellectual abilities. Earlier, the schools in most of the developed countries were using this model for demonstrating the difference in the learning ability of a child than others.
Reflection on action and in action: It refers to the factors of learning experiments that comprise critical thinking of the standards of performance such as audio and videotapes (Giannakou et al., 2019). Reflection in action is concerned with the assessments of the groups and their actual staging’s (Moghaddam et al., 2020). It also helps in the identification of the strengths and weaknesses of the Mothers’ Group so that they can be able to reduce these problems and make their performances better.
Accessing the learning needs: The learning needs of the participants will be accessed by conducting an interview round. Every participant will be asked a set of 10 questions in order to understand their knowledge and concept of Gestational Diabetes. After the interview round, the results will be evaluated so that the knowledge gap in the participants can be filled.
Peer Review: This has become one of the most important ways of assessing learning needs. It refers to a way in which the teachers usually assess the practices of each other and give reviews and advice on each other's performance (Horntvedt et al., 2018). It makes the process of teach more interesting (Hillier et al., 2021). There are five forms of peer review which consist of external, informal, internal, physician and multidisciplinary assessments. This helps to boost their validity, acceptability and reliability.Learning needs can be assessed to get a knowledge what mothers’ groups has gathered from the entire education session. It needs to be evaluated as it helps to offer clarity and ability to the mothers’ groups. The considerations that are needed to make during the time of education session is that first of all a proper plan must be figured out. Later, the learning objectives, plans of the learning session, assessment of the participants and implementation of the required resources are needed for conducting an entire education session.
The needs, avulses, characteristics and preferences of the participants interest needs to be considered while implementing the learning session. The length of the program and its setting also needs to be fixed before starting the learning session. The aim gaols and expected results of the learning session must be outlined along with considerations of the environmental and organisational context.
Overview of the evaluation plan
The evaluation process is helpful in understanding the main goal of the plan, the questions that this session is aiming to answer and identifying the key stakeholders of the plan. The evaluation process also helps in understanding the types of inputs and resources that are required to implement in the program. The identification of structure and processes while implementing the plan. The activities that are required to be conducted in the learning session, the expected results of the session can also be analysed through the evaluation process.
Importance of the session
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that women usually develop at the time of pregnancy. This disease can be developed even in those women who do not have diabetes. In Australia, it is observed that nearly 2% to 10% of pregnant women have developed gestational diabetes (Sorce& Chamberlain, 2019). The session is important for various reasons which are given below
It aids in offering a comprehensive guideline of the entire session: The education session helps in imparting to all participants the exact regulations of the session plans that help in offering an understandable vision and objective of the entire education session (Sorce& Chamberlain, 2019).
Enhance effective Communication: Education sessions are generally conducted so as to make a group of individuals aware of a particular topic which is unknown to them at times. It helps in making the process of interaction between the educator and the learner more effective. Effective educators adopt manifold strategies for making education plenary more interesting (Adiewere et al., 2018). The communication process is generally enhanced when the participants in such educational plenary ask queries to the educator regarding the topic so as to enhance their knowledge regarding the specific subject matter.
Needs of Learners: An educational plenary is essential as participants from different cultural backgrounds speaking manifold languages possess various requirements and choices. Hence, an educational session which is conducted to provide certain information to a specific group of individuals helps in catering for their needs (Adiewere et al., 2018). In this case, educational sessions are conducted in order to impart knowledge of gestational diabetes - its symptoms and process of treatment to local mothers’ groups. Moreover, it also aids the mothers’ groups in enhancing their skills and apprehension regarding gestational diabetes and its implications (Goodall et al., 2020). The mother groups were postpartum group and the main focus that this session has given is on educating the mothers on the risk associated with GDM and also the risk of T2DM for those mothers who were already diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes.
In addition, educational sessions on gestational diabetes help the mothers’ groups in identifying the threats that gestational diabetes poses to mothers during pregnancy. This also aids mothers’ groups in developing ideas regarding the strategies that mothers must implement during pregnancy in order to lead a healthy life so that gestational diabetes can be avoided. Here, educating the mothers’ groups regarding gestational diabetes helps in reducing complications during pregnancy and makes the quality of viability better (Goodall et al., 2020). The education session is important as it helps in improving the knowledge of the learners who are the mothers’ groups in this case.
Learning aims and objectives of the session
Aim
The main aim of this learning session is to empower and support pregnant women to optimize their lifestyle with Gestational Diabetes.
Objective
The three learning objectives of this education session are:
To evaluate the action plans that the mothers’ groups must take to reduce the challenges of gestational diabetes.
Goal: To educate the mothers on gestational diabetes prevention measures. In order to achieve this objective, the preventive measures of gestational diabetes will be informed to all the participants.
To identify the higher risks that women face during pregnancy due to gestational diabetes.
Goal: To inform the participants about the health risk of gestational diabetes especially during pregnancy. This objective will be achieved by evaluating the knowledge that the participants have regarding the health risk of gestational diabetes and then educate them in the health risk tat are unknown to them.
To identify the basic symptoms and treatment policies of gestational diabetes.
Goal: To educate the participants about the early symptom of gestational diabetes and the treatments that is available. This objective will be fulfilled by educating the participants regarding the health symptoms of gestational diabetes and providing them with information regarding he available treatments.
The learning sessions included pregnancy-specific food recommendations as well as messages about healthy eating and physical activity. Furthermore, modest behavioural modification tactics were gradually implemented in order to set short-term goals and promote self-efficacy and self-monitoring. Individual goals were set by participants, guided by lifestyle messages, and included objectives such as lowering high fat or convenience foods, increasing fruit and vegetable intake, and increasing physical exercise frequency. Pedometers and weight increase charts based on IOM recommendations for weight growth throughout pregnancy were used as self-monitoring tools. Participants in the intervention got the same textual material as controls, as well as resources promoting optimal health, GWG, and lifestyle.
The women who participated in the program were aged between 25-30 and they did not have an in detailed knowledge of Gestational Diabetes. In addition to this, pregnant women have increased chance of Gestational Diabetes and complications in pregnancy might occur. The complications might occur since during pregnancy, the insulin level in the body is reduced which increases the time for glucose to break down and turn to glucose (El Toony, Khalifa &Ghazaly, 2018). This factor might result in health complications, especially during pregnancy. The learning session that was conducted aimed at communicating the measures or steps that these women can take in order to prevent themselves from suffering from Gestational Diabetes during their pregnancy (Guo et al., 2018). The learning session also helps in developing the knowledge of those women regarding this health issue. There are certain factors that will be considered while accessing the learning needs of the mothers. The main factors include language, cultural differences and education. In the learning session, many participants participated and among them, many had different cultural and linguistic backgrounds. The learning session will keep this in mind while educating and communicating with these participants. In addition to this, many participants also didn’t have good education due to which they didn’t know the concept of Gestational Diabetes.
Different teaching methods
There are various teaching methods that can be applied to develop the learning session conducted for communicating the awareness of Gestational Diabetes to women. The three learning methods are mentioned below.
Learner-centred method: In the learner-centred method, the teacher becomes both the educator and the learner. In this process, education plays a dual role so that the classroom extends instead of limiting the educator's intellectual horizons (Choi, Lee & Kim, 2019). In this method, the teacher gets to learn new things and gathers new information about contents that were unknown to him. This process makes the teacher a resource instead of an authority. In the learning session, if this method is followed the educator will teach and educate the participants on Gestational Diabetes and the teacher in this process will also learn and take outputs from the participants.
Content-focused method: The content-focused method requires both the learner and the teacher to fit well into the content of the learning session. In this method, the main focus is given to the content of the learning session instead of the learner or the teacher. The skills and information that will be learned through this process will reflect the content of the learning session. Huge importance is given to the analysis and clarity of the content that is being taught (Correnti et al., 2021). Both the learner and the teacher in this process will not be able to become critical or alter anything about the content. In the learning session, the teacher will mainly focus on the content of the learning session following this process.
Participatory method: The participatory teaching method is different from learner-centred and content-focused methods since this method does not lay any emphasis on the learner or the content.
This method mainly focuses on learning through participation. In this method, both the learner and the teacher collaborate and engage in the learning process (Gal et al., 2018). The contribution of the learner and the teacher plays a significant role in this method. This method is quite effective since it helps in the development of both the learner and the teacher wherein, both can learn from each other through participation. In this method, both the teacher and the learners in the leaning session of Gestational Diabetes will participate together in the learning process and will gain more knowledge on the health issue.
Explanation of the rationale in association with the choices of participants, learning principles of adults and learning outcomes
Choice of participants: The participants that were mainly chosen for this included women aged between 25-30. The main topic that this significant study focuses on is Gestational Diabetes which is a health issue that might occur during pregnancy. Pregnant women are prone to this health issue and this health issue develops in women when they are 24-18 weeks pregnant (Thomas, Pienyu&Rajan, 2020). In Australia, around 2-10% of pregnant women suffer from this health issue every year. During pregnancy, the body fails to produce enough insulin that is required to break down glucose into glucose. This increases the level of sugar in the blood which then gives rise to Gestational Diabetes. The participants were chosen since most of the participants were women and they which increases the chance of Gestational Diabetes in them when they are pregnant. These women were did not have an in-depth knowledge of Gestational Diabetes and they also did not have any knowledge of the preventive measures of this health concern which showcases that most women in Australia would not know about Gestational Diabetes (Dalfrà et al., 2020). If women develop Gestational Diabetes in them, they might face complications during their pregnancy which will be bad for both the mother and the child’s health.
Learning principles: The learning session focused on various learning principles. The educator of the awareness program understood that all the participants are not that well aware of these health issues and educating them about Gestational Diabetes from the root is important in developing their knowledge regarding the health issue (Biswas et al., 2020). The main learning principle followed in the session was in the form of a participatory method. In this process, both the learner and the educator collaboratively participated in the learning process so that through communication all the queries related to the health issue can be solved. Participants from varied cultural origins and speaking numerous languages have different needs and options participated in the learning session. As a result, an educational session was held to deliver specific information to a specific set of people aids in meeting their needs. In this scenario, educational seminars are held to teach local mothers' groups about gestational diabetes, its symptoms, and the treatment process. Furthermore, it assists mothers' groups in improving their knowledge and anxiety about gestational diabetes and its consequences (Saboula, Ahmed & Rashad, 2018).
Learning outcomes: The learning session assisted in instilling in all the participants the expected outcome of the learning session which helped in providing an understandable vision and purpose of the awareness program (Guo et al., 2018). Furthermore, gestational diabetes educational programmes assisted mothers' groups in detecting the hazards that gestational diabetes poses to moms throughout pregnancy. These also helped mothers' groups establish ideas on the techniques that mothers must apply throughout pregnancy in order to live a healthy life and avoid gestational diabetes. The need for leading a healthy life was also discussed as it was noticed that most of the women who participated in the learning session didn’t have in-depth knowledge about the symptoms and preventative cure for this health concern (El Toony, Khalifa &Ghazaly, 2018). The learning session also helped the participants in knowing the accurate treatment that they need to access if they notice any early symptoms of Gestational Diabetes in them.
Reasons for the evaluation of the session
Evaluating a certain activity or a program is quite essential as it helps in identifying the outcomes of the process (Carr, Loucks &Blöschl, 2018). The evaluation also helps in understanding the strength and weaknesses of a certain activity so that improvements can be made accordingly. The evaluation process also helps in understanding the knowledge that has been gained and how that knowledge can be applied in its specific field. Conducting the learning session was quite essential as it helps in understanding the level of knowledge that women have regarding Gestational Diabetes. The evaluation of the session is quite important in understanding the knowledge gap that exists among women (Carr, Loucks &Blöschl, 2018). The way the women were able to understand the health complications of the health issue needs to be evaluated so that the effectiveness of the learning process can be understood(Arora et al., 2021).An educational program must be evaluated to understand whether the learners understand the basic concepts taught during the session. It also helps in showcasing the effectiveness of the session to the learners as well as to the community. Sessions need to be evaluated so that the there must be more engagement of participants.
Process Evaluation: It refers to the assessment of the education session to examine whether the planned session was executed as it was planned. The intention behind this education program is to reach all the population of the target area and to identify the major risks and strategies taken to combat these risks.
Outcome Evaluation: It assesses what changes the community has undergone after the education session has been implemented.
The three teaching methods are Content-focused method where the educator gives more focus on the content that is gestational diabetes here. Moreover, Participative method and teacher-centric methods are also followed for this education session.
The ways of assessing the content and process of the session
Optimal adjustment to diabetic living: The fundamental objective of education on diabetes is optimal adjustments. This is what the learning session tortoises as the chief goal of circulating educational resources (Saravanan et al., 2020). The learners have to address the problems that are responsible for the emergence of the problems. Identification of the problems is to the cohesive orientation of the needs of the learners that is fundamental to self-management. Therefore, the role of need assessment is important for determining the pattern of the disease that shapes that provides the patients with sufficient information. On the other hand, the repetition of information must be avoided that the learner has already acquainted with. Acknowledgment of the learners' needs must be prioritised as it lessens the chances of risks, anxiety, and concerns for panic.
Avoiding hypoglycaemia: The first criterion for avoiding hypoglycaemia is to make sure to monitor the blood sugar and not skip the necessary meals. The concentration of fibres minimises the dangers related to diabetics and this is hopeful to save the lives of both women and the child (AlKhaldi et al., 2019). The prevention of hypoglycaemia is the agent of the learning session that also has its message of the promotion of physical activities. Staying physically active increases good food habits and controls the fluctuation in the sugar level. The assessment of learning can be done by observing if the women are maintaining the nutritional food charts and the enriched foods. The awareness programme categorises the must-take and the prohibited food habits.
Knowledge on Insulin: The consciousness programme focussed on the diabetic problems emerging out of the irregular intake of insulin. The women were given knowledge of the adverse effects of the insulin being missed or not taken on time. The reactions of the imperfect push of injection could bring negative effects and this can lead to changes in the skin colours (McIntyre et al., 2010). The serious side effects are posited depending on the necessities for insulin therapy originate. The unintentional use of insulin more than necessary might bring on serious dangers and damage to the psyche. An education survey must be properly planned so that participants get more knowledge regarding the preventive factors of gestational diabetes.
Conclusion
It can hence be concluded that Gestational Diabetes is a health issue that around 2-10% of women in Australia differ from every year. The plan to conduct an awareness program to educate the participants regarding this health issue was quite necessary. The learning session helped in generating awareness regarding Gestational Diabetes and also helped in developing the knowledge of women regarding Gestational Diabetes and its early symptoms. The learning session also helped the participants in understanding the right treatment that they can seek if they witness any symptoms of Gestational Diabetes in themselves or in others.
Reference List
.png)
.png)
Essay
PBHL20001 Understanding Public Health Assignment Sample
This assessment task for this unit is a reflective practice assignment of about 2000 words that describes your growing understanding of Public Health as a discipline. This is an individual assignment. You are strongly encouraged to work on your reflection throughout the term and to make notes of ideas that occur to you or issues that interest you that you can include when you write your assignment.
Your reflection should focus on how your understanding of Public Health changed over the course of the term, and you should compare your knowledge, perceptions, and attitudes at the beginning of this unit with how you feel at the end. You should also reflect specifically on the following questions:
1. How does an understanding of the history of Public Health contribute to professional practice?
2. How important are the non-health factors that are part of public health practice?
3. What are some of the ethical issues associated with public health practice?
4. How will the things you have learned as part of this unit affect your own practice in the future?
This reflective assignment is an essay. A less formal writing style may be used, and references are not required. If you do use any source material, however, each item must be identified in an in-text reference and also appear fully cited on a reference list.
Solution
Introduction
The concept of public health is very important as it deals with ensuring the health and wellbeing of all the people of a country. However, there are different aspects related to the public health related policies. These aspects may not be medical in nature. Factors such as social aspects and ethical issues can affect public health related decision making. In this context, this essay for assignment help will highlight the history of public health and its contribution to professional practices. Along with this, it will also highlight the ways in which social factors and ethical factors impact public health related decision making. Lastly, this essay will highlight the concepts that I have learned in relation to public health during my coursework.
1. An understanding of the history of Public Health and contribute to professional practice
History of public health had become important in the second half of the nineteenth century in the USA. By the late 19th century, in the USA a public healthcare structure had been established which helped me and healthcare staff to treat the patients with proper guidelines.
History of anything is important to understand the present value of the particular area. In healthcare, the history of public health plays an important role in understanding different aspects for professional practice (Naeem et al., 2021). Public healthcare is always involved with different kinds of risks. Due to different symptoms and different health conditions, there are risks of wrong treatments. Historical facts and information help to avoid such risks. Apart from that, history always shows the ways that have already been considered for public health. The result may be favourable or adverse for the patient. Thus, in order to provide better treatment to the public, healthcare organisations can bring up innovative ways to treat people. Innovation helps public healthcare to be more developed and advanced. With the advancement of Medical Science, public healthcare should also become more developed for the better health of the society.
For a doctor, it is important to know the history of healthcare. A person may have a family history of carrying a disease hereditary and that affects that person at a point of his or her life. In such cases, I should know about the family medical history to go forward with the most suitable treatment method. It helps me to consider the wider range of possibilities rather than narrowing the possible ways of the treatment (Aruru et al., 2021). The history of public healthcare helps me understand the timescale of beneficial health. Exceptions are there too as some of the communicable diseases do not follow the rules of history. Nevertheless, in order to improve the public healthcare activities, I should consider all kinds of facts and figures from the past to understand the nature of the disease more conveniently. It will help me to find relevance with the future plans too.
It is important for the healthcare units to keep a track of every vase of public healthcare to use it as a history of case studies in case of treating the same disease in future. For me, knowing the health history of the family of the patient can be fruitful as it helps me to take necessary steps in order to minimise the health risks of the patient (Estabrooks et al., 2018). For example, a family has a history of diabetes. It is being observed that the family members who are blood related, have a high chance of diabetes at a certain age. In this case, I always advise to have regular checkups and blood tests.
2. Importance of the non-health factors that are part of public health practice
Before enrolling for this course, I had an idea that the non-medical factors had no relation with public health practices. I was unaware of the different aspects of non-health factors and how these aspects can make or break the mere foundation of public healthcare. However, during this coursework I was introduced to this topic in depth. I have been taught that different social aspects such as level of income, level of social protection, food insecurity, education, unemployment, discrimination and social exclusion and others play an important role in public health care facilities (Ford and Airhihenbuwa, 2018). As per World Health Organisation, social determinants are more important than lifestyle choices when it comes to influencing health. We have read those undeveloped countries where the rate of uneducated people is higher face more public health issues. For example, the covid-19 pandemic has also affected the deprived section of the countries in larger proportion. There is a higher chance that people with low-income groups will not be able to get the same healthcare facilities that other people get. Moreover, there is a high chance that diagnosis of dieseases will be late for these people as they often avoid going for checkups (Schuchat et al., 2020). On the other hand, people with a low rate of education are not aware of the different healthcare initiatives. Moreover, they may not be aware of the precautions that they need to take. Factors like low income, higher rate of unemployment and lack of economic growth also leads to depression which can again lead to substance abuse and drinking. Lack of education and social awareness can also lead to taboos and stigmas which can make it difficult for the people to get access to healthcare.
During our coursework, we have also learnt about the different strategies that are being taken to mitigate these issues. I have noticed that governments of different countries have started to make health considerations while making decisions about all the other aspects of society. I think this policy is highly effective as it engages a diversified range of stakeholders and aligns their objectives of promoting health as well as social welfare (Khoury et al., 2018). During the coursework, I have been taught that focusing on job creation, development of agriculture, improving the educational system and ensuring equality can ultimately improve public health. In this context, I have noticed the government making policies for ensuring that there is full attendance in the schools while also ensuring that the students are being educated about different diseases and the way they can take care of themselves. This is a form of responsible learning. Moreover, I have learnt that implementing cross-sector strategies can also improve the health of neighbourhoods which belong to poor sections of the society (Brownson et al., 2018). I know about different coordinated strategies that have been implemented across different sectors with social, cultural, economic barriers. These sections of the society have health disparities and are making cross sectional policies to mitigate the same.
3. Some of the ethical issues associated with public health practice
Ethics is a branch of philosophy which differentiates between right and wrong actions. During my coursework, I have learnt about the ethical issues that can hamper public healthcare practices. As per my understanding, the different ethical concerns that arise in healthcare practices include informed consent, confidentiality, scientific integrity and respect for human rights. In this context, the public health ethics inquiry has three main functions, which include identifying and mitigating ethical dilemmas, resolving the dilemmas by deciding the most suitable course of actions (Wickramage et al., 2018). I have also learnt about different forms of ethics such as bioethics which deals with reproductive or end of life decision making, clinical research ethics, confidentiality and use of emerging technologies. Here, as a healthcare practitioner the focus needs to be given on whether the decision taken will be beneficiary for the patient or it will be non-malefic. Other than this, the concept of justice also plays an important role. This is the reason why female foeticide is banned in India. Moreover, gender determination is also banned in India due to the ethical grounds of healthcare. Moreover, I have knowledge that health care practitioners have the liability to safeguard patient information. Other than this, I have also learned about public health ethics which deals with emergency preparedness, social determinants of health, infectious disease control and others.
As per my knowledge, the covid-19 pandemic was a type of ethical issue for the public healthcare system of different countries as it was the duty of the government to collaborate with the health care practitioners in order to reduce the spread of this infectious disease. I think that setting priorities is highly important as the government as well as the public health practitioners need to identify the way they will allocate financial resources (Estabrooks et al., 2018). The policy makers need to negotiate between different ethical issues as they choose their competing priorities in order to resolve the conflict. Our coursework has also taught us about the five conditions that are developed by James Childress that have to be considered before overriding important morale considerations in healthcare. These are policy effectiveness, least restrictive infringements, proportionality of benefits and burdens, necessity and public justification. Thus, as far as I have understood, public health care has to be followed in alignment with asset goals, benefits and burdens of public healthcare and the actions associated with them.
I also think that the majority of public health practitioners do not have adequate skill sets to consider ethics in their day to day work. In this case, first the healthcare practitioners will have to let go of the normative assumptions they hold. Majority of healthcare practitioners think that relying on professional experience and own personal morale is more than enough in managing challenging ethical issues in healthcare (Khoury et al., 2018). However, in reality there is lack of proper clarification and the boundaries of ethical healthcare are also not properly set. The existing healthcare frameworks also do not have the ability to reduce ethical tensions. The decision makers need to formulate frameworks that can manage ethical conflicts while reducing ethical tensions. Thus, I have learnt from my coursework as well as personal experience that there is a lack of effective policies to mitigate the ethical challenges associated with public health. However, the government is trying to take active measures to mitigate the same on a real time basis.
4. Learned factors as part of this unit affect your own practice in the future
The history of public health plays a vital role in comprehending various facets of my professional practice in healthcare. Various types of dangers are constantly present in public healthcare. There is a danger of incorrect therapy due to a variety of symptoms and health issues. Facts and information from the past can help you avoid such dangers. Aside from that, history always demonstrates the approaches to public health that have already been examined (Brownson et al., 2018). The patient's outcome may be positive or negative. As a result, healthcare organisations can come up with novel ways to treat patients in order to give quality treatment to the general public. Innovation aids the development and advancement of public healthcare. As medical science advances, public healthcare should improve as well, for the betterment of the people's health.
We've also learned about the many ways being used to address these concerns as part of our study. I've noticed that governments in several countries have begun to consider health issues while making decisions concerning other elements of society. This policy, in my opinion, is very effective since it involves a wide range of stakeholders and aligns their goals of enhancing health and social welfare. Throughout my training, I was taught that focusing on job creation; agricultural growth, educational reform, and guaranteeing equality can all help to enhance public health.
In this context, I've noticed the government enacting laws to ensure full attendance in schools, as well as to ensure that pupils are educated about various ailments and how they may take care of themselves. This is an example of responsible education. Furthermore, I've discovered that employing cross-sector techniques can help improve the health of neighbourhoods in low-income areas (Brownson et al., 2018). I'm familiar with a variety of coordinated solutions that have been applied across several industries to overcome social, cultural, and economic constraints. Health disparities exist in these areas of society, and cross-sectional policies are being implemented to address them.
Ethics is a philosophical branch that distinguishes between right and wrong conduct. I learned about the ethical difficulties that can stymie public healthcare efforts during my education. Informed permission, confidentiality, scientific integrity, and respect for human rights are among the various ethical considerations that occur in healthcare procedures, according to my understanding (Naeem et al., 2021). In this setting, the public health ethics inquiry serves three key purposes: detecting and minimising ethical issues, and resolving the dilemmas by determining the best course of action.
As a healthcare provider, my focus should be on whether the decision you make will be beneficial to the patient or non-beneficial. Aside from that, the concept of justice plays a significant role. Female foeticide is illegal in India for this reason (Wickramage et al., 2018). Gender determination is likewise prohibited in India because to ethical considerations in healthcare. Furthermore, I am aware that health-care professionals are responsible for protecting patient information. Aside from that, I have learnt about public health ethics, which includes topics like emergency preparedness, socioeconomic determinants of health, and infectious disease control.
Conclusion
After analysis, it has been concluded that heath care sectors need to inform their employees about different issues and make an awareness program. If the sectors want to improve its issues then it needs to make more charity programs and develop clinical leadership. Through those analyses understand various things and try to practice those days by day to improve it. I need to make my decision-making process more effective for the patient's benefit. I also think that fundamentals growth and education growth can help to develop heaths care services. Non-heaths factors did not have any concern with the heaths care sectors or services.
Reference list
.png)
Research
PBHL20003 Social Epidemiology and Statistics Assignment Sample
Task description
The literature review provides an overview of the social epidemiological aspects of your topic that you chose for Assessment 2. It summarises broad trends in the literature on your topic and highlights important points in selected articles. The review task includes:
The literature review is due in the last week of Term. However, your preparation should commence at Week 1 to familiarize yourself with the Library and its academic databases, how to conduct literature searches, select material and structure your Review. The University library and CQU Student Learning Support provide online guides and individual sessions; and workshops on academic writing, academic integrity and referencing. You also have access to resources such as Studiosity.
Choosing the literature to include in your assignment help is important. Only peer-reviewed scholarly material should be used. You need to note various views and approaches contained in the literature and to choose works to include without bias or preconceived ideas. Journal articles are often more relevant than books due to the long lead time between the writing and publication of books and because journals are often the forum where the latest thinking on a topic appears.
Solution
Introduction
Malaria has been accounted as one of the major global health priorities as the prevalence of malaria has been affected worldwide nations. According to World Malaria Report published in the year 2020, it has been found that approximately 229,000,000 case reports of malaria have been witnessed in the year 2019 (World Health Organization 2022, p. 1). The report highlights that children belonging to the age of five and below are one of the most susceptible and vulnerable target populations for malaria. Also, the report highlights that in the year 2019 approximately 67% of death cases were identified associated with malaria throughout the world (World Health Organization 2022 p. 1). The National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System and NNBSS reported the identification of 9291 case reports of diseases that are suspected to be transmitted by mosquitoes from the year 2010 to 2011 (Knope 2013, p. 3). It has also been evaluated and acknowledged that malaria has been one of the historical endemics for the population of Australia which was significantly declared eradicated since they are 1981. As the condition of malaria has no longer been accounted as an endemic condition, there are still 700 to 800 cases of malaria reported each year within the population of Australia who are accounted as frequent travellers.
One of the target populations of malaria within the premises of Australia accounts for Papua New Guinea’s population has it has been found that more than 95% of the population belonging to the New Guinea are found living in regions where the risk of malaria transmission is significantly higher than any other communities. The case reports of malaria within the premises of the Western Pacific region of Australia highlight that more than three fourth of the cases of malaria on identified within the Papua New Guinea population (Australian High Commission Papua New Guinea 2022, p. 1). The National Health and Medical Research Council has provided $21,860,617.00 to the field of malaria research in the year 2020 which is divided among ideas grants and investigator grants (NHMRC 2022, p. 1). Focusing on the rising prevalence of malaria as well as the increased risk of the infection within the Papua New Guinea population as well as other communities of Australia, the following literature review will focus on assessing significant literature evidence available in terms of malaria in the Australian population. It is necessary to develop significant literature analysis to evaluate the conditions sustained by the general population of Australia as well as Papua New Guinea as well as significant strategies and supportive actions that the government must take into account to provide them with safer and secured health outcomes. The increased prevalence of malaria within the target population, the significant factors which are associated with the increased risk of the condition as well as the services that are provided as well as those that need to be enhanced within the target population will be evaluated in the following Literature review.
Methods
To conduct a significant literature review, it will be necessary to identify, select and further evaluate sets of literature evidence with the help of inclusion and exclusion criteria as well as a literature search. The inclusion criteria focus on highlighting the criteria based on which the research articles will be selected from electronic databases. Articles which are published between the year 2010 to 2022 will be selected as well as those which are published in the English language (Patino and Ferreira 2018, p. 1). Also, the articles discuss the prevalence of malaria as well as associated factors within the target population such as Australia and Papua New Guinea to be precise. Electronic databases such as PubMed will be used to attain a significant set of literature articles which are peer-reviewed and authentic (Patino and Ferreira 2018, p. 2). The literature review will focus on the methodology target population, significant findings as well as the research gap that are identified within the selected research articles to evaluate a significant set of evidence for the assessment.
Literature analysis:
Theme 1: socioeconomic stability and diversity associated with increased risk of malaria in Papua New Guinea population
According to the research carried out by Davy et al. (2010, p. 1), it has been found that malaria has been one of the major burdens of health within nations with low-income values and standards first up the research was carried out focusing on the treatment-seeking behaviour in terms of malaria within one of the low-income population of Australia accounting for Papua New Guinea. The research was carried out focusing on a cross-sectional survey between two linguistically, culturally as well as demographically different regions where the Papua New Guinea population were residing. The cross-sectional survey relied on household evidence which was taken from both sides accounting for approximately 928 individuals (Davy et al. 2010, p. 3). These individuals were suspected and reported to be suffering from malaria within the past month and those evidence were taken into account based on the associated factors. These factors highlighted the significant treatment day accounted for, the factors that were associated with their living condition as well as other environmental aspects which are highly associated with the prevalence of malaria. The results of the study highlighted that formal health care treatment facilities, as well as cultural values, had a significant factor in the treatment-seeking behaviour of these target populations (Davy et al. 2010, p. 3). It was found that traditional healers, cultural practices as well as formal health care facilities are counted as the major treatment factors in terms of malaria within the target population. The research developed a significant gap in highlighting the precise cultural values and perspectives that serves as a major contributing factor to the risk of malaria as well as treatment-seeking behavior within the Papua New Guinea population (Davy et al. 2010, p, 5).
It was also found in a different research studies carried out by Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. (2019, p. 3) that one of the significant causes of the increased risk of malaria within the Papua New Guinea population was lack of significant hygiene maintained within the general household activities. It was also found that personal hygiene, as well as environmental cleanliness, was significantly low within the population which increased the favourable setting of water contamination and further growth of mosquitoes breeding. Also maintaining significant hygiene such as hand cleaning, cooking with clean water, drinking clean water or maintaining sanitation throughout the surrounding was highly associated with the increased risk of malaria as these practices were effectively low within the target population (Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. 2019, p. 3). It was found that behavioural factors such as drinking clean water, eating healthy food as well as maintaining nutritional value were appropriately and effectively low within the target population which does expose them to increased risk of malaria when compared to other populations. it was assessed that poverty as well as diversity web significantly functioning within the target population which exposes them to inappropriate cleanliness maintenance as well as safety measures implementation within a their daily routine (Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. 2019, p. 3).
Theme 2: Climate change, and biodiversity within Papua New Guinea and other Australian communities
It has been found from a research study conducted by Imai et al. (2016, p 4), that climate change, as well as biodiversity, has a significant impact on the pop one new journey population increased prevalence of malaria. It has also been evaluated that malaria being a public health concern in the selected population highlights the vulnerability towards the change in climate as well as their increased sensitivity towards malarial mosquitoes. The research was carried out focusing on the time series method which was intended to evaluate the incidence of malaria associated with the weather as well as changing climate. The changing climate, as well as weather, accounted for increased or fluctuation in temperature, precipitation as well as change in global phenomena associated with climate (Imai et al. 2016, p 4). The research findings confirm that change in local weather has an increased influence on the increased risk of malaria within the target population along with a significant association with the change in global climate. The research highlighted a major literature gap where it appropriately discusses the local weather which is highly identified within the selected region’s weather in Papua New Guinea population colonized (Imai et al. 2016, p 4).
Another significant research was carried out by a researcher Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. (2021, p. 2), which highlighted the transmission of malaria within the depopulation of Papua New Guinea. It focused on assessing the social, cultural as well as other demographic factors which have a significant impact on the change in the epidemiology of malaria within the target population. The research was carried out using a mixed-method design where two significant sites in the Papua New Guinea population were selected as the target sample. These selected target populations were involved in in-depth interviews, and discussions as well as cross-sectional survey based on malaria indicators but further implemented in the research to sustain a wide range of evidence (Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. 2021, p. 2). The reason for the study identified that majority of the population spends this substantial amount of time in the outdoor settings which increased their risk to get exposed to increase mosquito bites. It was found that living within the outdoor setting, sleeping in the outdoor environment as well as increased mosquito bites were the factors highly associated with the increased prevalence of malaria within the Papua New Guinea population. It was also found that adult men had an increased risk of malaria due to working in the outdoor settings still late at night and also sleeping outside (Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al. 2021, p. 2).
Synthesis Table:
.png)
.png)
Conclusion
To conclude it can be stated that Australia has an increased prevalence of malaria despite eradication of the condition as one of the major public health concerns. It has been found that the Papua New Guinea population under administrative rule of Australian territory sustains an increased prevalence of malaria and thus serves as a public health concern. It has been found that there are several factors which serve in increased risk of malaria within the population such as poverty, climate change, diversity, cultural values as well as maintaining significant hygiene and healthy routine. After conducting the literature it has been found that there is a significant gap in the literature which precisely focuses on the Papua New general population as well as the biodiversity and the socio-economic condition they live which exposes them to increased risk of malaria and associated complications first of all so further research must be carried out to assess the significant treatment facilities and policies that are provided to them to fight against the prevalence of malaria.
References:
.png)
Essay
NURS2193 Nursing Therapeutics and Aged Clients Assignment Sample
This assessment for assignment help requires you to use your academic writing skills to produce a 1500-word essay.
This will contribute to 50% of your overall mark for the course and supports several of the course learning outcomes for this course:
» CLO 2: Compare and contrast the various work contexts of the professional nurse
» CLO 3: Prepare written communication relative to the acquisition of nursing knowledge
» CLO 5: Describe the basic principles of reflective practice and evidence their application in relation to particular learning tasks
Essay Topics
Choose any 1 topic from 2.
1. Professional boundaries are an important feature of therapeutic relationships between nurses and patients. Discuss this statement. Within your essay, identify the difference between boundary violationsand boundary crossings and provide an example of each.
OR
2. Reflective practice is regarded as a key skill for nurses that enhance professional learning and growth. Discuss this statement Within your essay, comment on why reflective practice is valuable for nursing students and beginning registered nurses.
Solution
Nursing professionals need to engage with their patients or clients in a dynamic way that demands their participation in maintaining a healthy interaction with the patient ensuring the delivery of quality healthcare practice that is beneficial for the patient (Molina-Mula & Gallo-Estrada 2020). The behavior and relationship between the therapeutic nurses and the patient must be very consistent throughout the treatment and within a framework of professional boundaries. In this academic essay, a thorough discussion on the therapeutic nurse-patient relationship would be done followed by investigation of the importance of the professional boundaries and its importance in therapeutic care would be performed, the concepts of boundary crossing and boundary violation with several examples will be discussed throughout the next few paragraphs.
The therapeutic nurse and patient relationship are one of the foundation blocks in nursing care. Throughout the treatment period, the nurses need to maintain the trust, respect, privacy, and dignity of their patients (Hartley et al., 2020). The nurse-patient relationship is a goal-oriented and fruitful relationship that serves the best interests of the patient as well as for delivering quality care. The therapeutic nurse-patient relationship is based on several foundational pillars as follows- firstly, trust, the therapeutic nursing practitioners must build trust between dim and the patient to deliver the best possible care for them. Secondly, respect, the therapeutic nurse needs to have respect start the values and culture of the patient who they treat. Thirdly, intimacy; The physical, psychological as well as emotional intimacy is required to deliver therapeutic play care and which creates a barn ability in the nurse-patient relationship.
The therapeutic nurse-patient relationship is different from the personal relationship in many aspects such as this relationship is based on several regulations and codes of ethics as per the professional standards and it is entirely goal-oriented and different from the spontaneous or uncontrolled interest-seeking personal relationship (Slobogian, Giles & Rent, 2017).
Boundaries are an important parameter in the case of a therapeutic nurse-patient relationship and the nurses should provide the care while staying within the boundaries of the relationship. Proper knowledge, skills and guidance are extremely important in maintaining the professional relationship between the therapeutic nurses and their patients, which is quite different from the personal relationship, where there is no formal education, guidance or advanced preparation required (Kornhaber et al., 2016). Boundaries that are common in the professional sector will be discussed in the subsequent paragraph of this study.
The professional boundaries are the little window in between the therapeutic nurses inability to control power and indulgence and the patients situational vulnerability. The professional boundary in therapeutic nursing care ensures and determines the lines through which they are professional and therapeutic behaviors are guided and in rectifying any behavior whether intentional or unintentional that serves their own interest rather than the patients care need. The therapeutic nursing practitioners must maintain professional relationships and boundaries to be able to maintain play respectful consistent relationships with their patients throughout the length of their treatment phase. The duty of maintaining professional boundaries lies only with the nursing practitioners but not with the patient. The boundary has some major importance in the therapeutic relationships between healthcare professionals and patients.
The professional boundaries in the relationship between the therapeutic nurse and the patient exist because of ensuring the safety and better care for the patients. The nurses need to follow these boundaries in order to sharpen the best interest of the patient throughout their treatment period, it is beyond their personal characteristics and affection. During the therapeutic relationship with the patient, the therapeutic nurse has access to patient information and they can influence the patient seeking care. These specialized knowledge skills as well as access to personal data create a vulnerability for the nurses to the patient. To ensure that the code of ethics professional boundaries, as well as patient safety, are maintained the nursing practitioners must always remain within their professional boundaries during real life practice. In the subsequent paragraph of this study, the author will specifically focus on approaches that are followed to cross the professional boundary in therapeutic communication and relation.
Boundary crossing in a professional relationship between the therapeutic nurse and the patient could be explained by short misconduct as per the professional behavioral standards during their service for the therapeutic care of the patient. The boundary-crossing incidents as moderate to low significance when it occurs for the first instance but overtime with frequent occurrence of boundary-crossing crossings this may lead to boundary violation and which has a serious impact on the professional code of conduct ( Kristoffersen, 2019).
Several actions that lead to boundary crossings when the therapeutic nurse encounters a vulnerable patient are as follows: Maintaining a personal relationship with the patient. Connecting with the patient through social media. Intentionally disclosing in front of the patient. Maintaining a behavior of gif taking from the patients. Providing favors to the patient outside of the job roles and responsibility. Providing special care for the patient beyond the job role ( Hazen et al., 2018). Providing therapeutic care for friends and family
Boundary violation is a serious concern in the case of the therapeutic relationship between the nurse and the patient. Boundary violations are a clear persistent breach of professional boundaries and underlying trust between the patient and nurse. When the nurse takes advantage of the professional relationship they have with their patients and fulfill their personal needs that is a clear indication of boundary violation. Boundary violations are not acceptable in the therapeutic nursing practice and it can impact the nurse’s career affecting licensing sanctions ( Manral, Pareek & Kaur, 2018). The underlying cause of the boundary violation could also be the lack of understanding and confusion present between the nerds and the patient’s relationship in case of what is the roll-up the nurse and play the therapeutic needs of the patient
Several examples of boundary violations are as follows: Engaging in a romantic or sexual relationship with the patient under treatment. Self-disclosure beyond a certain limit with the patient. Lending money or borrowing money from the patient who is receiving the treatment from the therapeutic nurse. Maintaining a culture of gift taking and giving and asking for a favor in return. Asking for benefit what the nurse by influencing the client’s will or power. Too much involvement with the patient that impacts their personal relationship. Using the patient as a medium for selling or promoting the nurse’s own business. Engagement of the patient in providing care to the nursing practitioner.
The violation of professional boundaries between the therapeutic nurse and their patient has a serious impact on the patient as well as the nurse and on the overall patient care that is given. The professional boundaries are in place to help protect the patient’s valuable information and the safety of their treatment. When the professional boundary is breached there is potential harm to the patient which is not always immediately noticed or recognized. Due to this boundary crossing and violation the negative consequences are faced by the patient ( Hook & Devereux, 2018 ). The altered expectations and behaviors if not sustained and managed can create mentally as well as physical trauma to the patient and interfere with their treatment. Crossing professional boundaries as well as violating the boundaries has a serious impact on the nursing practitioner’s professional career. Lawful action may be taken against the nerds and termination of their employment could be enacted. The violation of professional boundaries also has serious physical and mental struggles for the nursing practitioners which lead to their lack of effort in the daily practice impaired personal relationship and stress ( Reyes Nieva, Ruan & Schiff, 2020 ).
This academic essay summarizes the relationship between the therapeutic nurse and their patients and several parameters associated with this. Boundary crossing and boundary violation with respect to the therapeutic nurse-patient relationship is defined followed by several examples which indicate the behaviors associated with boundary crossings and violation. The impact of boundary crossing and the violation has a play on patient care and patient safety as well as on the professional as well as the personal life of the therapeutic nursing practitioner is critically discussed in this essay.
References
.png)
Essay
PBHL20007 Cultural Immersion and Lived Experience Assignment Sample
We each come to public health with a set of our own beliefs, assumptions, experiences, judgments, and views that reflect our culture and upbringing, as well as the events of our life. For this assignment, you must think about your own health experiences and the way they have been impacted by your cultural background and the way you think about health and illness. Firstly, think about how your family deal with illness or treat illness condition. Do they use home remedies to treat illness? How do they decide an illness is serious? What are their preferred ways of managing health and illness?
Secondly, compare how your own personal experiences relate to the views and actions of other people in the same community. Is your family in the majority when it comes to dealing with health and illness? Do they act differently to the most people in the community? If they are different, then explain why and how their behaviour was shaped that way which made them different to others in the community.
Thirdly, discuss your own assumptions about health.
Who do you think is responsible for health - the individual involved, the family, the society in which he or she lives, the government, health services or others? To what extent, do you think people should manage their own health? Who should carry the risk associated with disease and illness?
Finally, consider the role that culture and social background play in health and illness.
Discuss the ways this might affect professional practice in public health, including why it is necessary for a public health practitioner to be aware of cultural differences in health and illness.
This is an individual 2000 words reflective assessment. Your reflections to these areas should be supported by evidence from literature, textbooks or other authentic sources. All references must be cited appropriately with a reference list. In drawing on your own experiences, you may use pictures and other creative material to help illustrate your reflections, but these must also be appropriate cited if they are not your own materials. You cannot use materials from google or any internet sources which does not meet academic standards and guidelines.
This reflective practice assessment will be assessed against following criteria.
1. A deep reflection with ability to write clearly following academic coherence
2. Logically draw and analyse personal experiences around health and illness
3. Critically examine and compare the familial and social context of health
4. Succinctly provide evidence-based arguments around different conceptualisation and accountability to health
5. Appropriate grammar, citation, and referencing
Solution
Introduction
In the present times, health issues are becoming more significant as the population and portions of the society are getting affected by illnesses such as diabetes, infectious diseases, HIV, mental health challenges and many more. Nutrition and lack of physical activity led to obesity which can cause many of these diseases. This essay for assignment help will discuss my experience with Bangladesh's approach to health conditions. This will take into account my family's experience in healthcare. This will also compare my experience with society's concepts of health issues and treatments. The role of society and culture in health issues will also be stated. This will help in clarifying the idea about health issues in the society and the people of Bangladesh.
Family's approach to dealing with health conditions
The approach of Family-Focused Healthcare is becoming more popular in contemporary times as health professionals believe that the involvement of the family can help many diseases to get cured faster. Many states and nations are adapting the task of reform in healthcare that seems appropriate considering the various merits of the family perspective. Recently through research, it has been considered by various researchers, healthcare professionals and advocates that family has a profound force on the health of an individual. Every country should support and strengthen its family caregiving programs based on this respective research (Wisconsin Family Impact Seminars, 2022). Although in Bangladesh, I have seen that my family has always been very supportive during my illness and provided the best care that helped me recover faster. The approach of family care is also more cost-effective and focuses on individuals' help in the recovery process. Family members also have a high level of influence on the health habits of each other. The nutrition we get from our food is consumed through a pattern that we learn from childhood. The habit of exercising regularly is also a common habit that we acquire from our family. Family distress is also a common cause of individuals' ability to focus on the negatives only. For example, a person suffering from hypertension who lives alone will not be able to provide proper health care to themselves compared to a man who lives with a family with the same disease. The family also plays a very vital part in relapses of various chronic diseases. Families in Bangladesh are quite dependent on home remedies as various areas are below the poverty line and do not have the resources to visit medical centres. The infant mortality rate is also high as many mothers do not make it to the hospitals or the health care providers during childbirth.
In my family and others around me, I have seen several instances, where social support and stress have helped in decreasing or increasing the family member's likelihood to fall ill. This can happen due to several reasons like a bereavement of a spouse or close family member, the detrimental effect of smoking or alcoholism and many more. Any person who is susceptible to stress can fall ill much faster. Families that face prenatal conflict often have cases of children who are lower than five years with high levels of stress hormone in the blood. Marital distress can also reduce the immune system functioning in many individuals. A family's decisions and beliefs about health care are very important to promote a healthy lifestyle. The chronically ill patient is dependent on the family members' setting of care provided to them which is quite important. Many times,it has been observed that the cohesiveness of a family during the acute stage of an illness generally decreases if the illness remains for a prolonged period. For example, a cancer patient is often seen to have less distress compared to their spouse or family members. Families also need therapy and support when their family members are going through those issues.
.png)
Figure 1: Family’s role in healthcare
Source: (Wisconsin Family Impact Seminars, 2022, para. 4)
Comparison of personal experience with people of the society regarding health issues
I would start with my experience of the pandemic that we had faced in the last two years and yet the world has not recovered. I learned during this period that every year new pandemics emerge that may or may not be as widespread as the Covid-19 virus. This period has taught me that health education and responsible practices in agriculture and society will help in combating such issues in the future (Hossain, 2020, p.1). Another global challenge that I see around me is the pollution and climate change that is leading to the formation of many new diseases. In many societies, economic disparity and the lack of access to healthcare often lead to diseases and high mortality rates. As a society, there is not much contribution that is done to erase such economic disparities even when individuals are seen to be unable to afford health care. I believe there is an equal role between society and the government in the health services that are provided to us. Managing one's health is very important before we start blaming the communities around us or the government.
I do not believe that my family falls under the majority of the society and how they tackle health issues. The main reason which I can attribute to this is lack of resources as most Bangladesh citizens do not have sufficient income to visit healthcare centres. This forces them to surrender to home remedies which are in many cases not helpful. Moreover, the lack of education in many such families leads to a misconception about health issues that further leads to the wrong treatment of the disease. This can only be combated if the government provides a proper health care system and education to all the citizens of the country.
.png)
Figure 2: Bangladesh health care spending shows a significant increase
Source: (TheGlobalEconomy, 2022, para. 2)
Personal assumptions about health
Bangladesh belongs to the category of pluralistic health care system where healthcare is highly decentralised. There are various for-profit companies, international welfare organisations, government schemes and NGOs. This has caused various problems that have caused unequal treatment between various classes in society. Shortage of specialists, clinical equipment and physicians is quite common in the country. There are only 1.07 % of nurses available for 10000 people. The number of physicians per 10,000 people is only 3.06 % (Thelwell & Tashin, 2022). The leading cause of death in the country is non-communicable diseases. These diseases include diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, malnutrition and so on. I have seen that most of the physicians and healthcare centres are only concentrated in the urban areas of the country. The rural hospitals are poorly funded which means there is limited access to healthcare options. The government does not provide sufficient healthcare funding as a citizen has to pay 63.3 per cent of the total cost of the treatments (Thelwell & Tashin, 2022).
According to my research, I have found that Bangladesh has shown remarkable progress in healthcare in the last few decades. Bangladesh strategies include out-of-pocket payments, general revenue taxation and development partners' contributions which include insurance (Fahim et al., 2019, p.2). The problem in this case that has been observed is that 5 million people fall into poverty because of exorbitant health expenditures (Sarker et al., 2022, p.4). Unfortunately, I could not find enough data which supports the out-of-pocket costs that are related to the healthcare expenditures in Dhaka. The sustainable development goal of the country is focused on promoting the well-being of every citizen irrespective of their age. This goal will also focus on the socioeconomic factors and the democracy of the population to see if the OOP has any influence on the health care expenditures of the urban citizens. It is also important to understand that despite the various help provided by the government, one should be careful about the various diseases that are surrounding them. The risk of diseases cannot be single-handedly attributed to the government or the nation. I have observed during the pandemic that there were various cases where the public of the nation was casual enough even when they were provided with all healthcare advisories. This had led to the increase in the spread of the virus. Hence, I strongly believe that it is important to be aware of health oneself too.
Role of society and culture on health and illness
The local perception of disease has been seen to vary from community to society all around Bangladesh. Even though long exposure to illness has not enabled these populations to capture a proper explanation based on the scientific background which can be backed by germ theories. diseases are generally divided into subcategories namely lamani (diarrhoea), pansa (chickenpox), dudher haga (watery white excreta), lunti (measles) sardi or kasi(cough and cold). Even while various health education programs like BRAC provide specialised dissemination about diarrhoeal diseases, it has not helped much with the notions of the villagers (Khan, Bhuiya & Chowdhury, 2022, p.2). Although the villagers are aware of the various health risks associated with taking food without adequately washing their hands or even keeping the food in an open area, it has not brought many changes in their attitude. The dependency on various religious beliefs and the older customs have made these villagers not understand the importance of scientific data that backs the diagnosis of the diseases. Other reasons include workload on the head of the household, where, for example, they are not even aware that the soap is bought after the entire consumption. The poor villagers who do not have the access to simple three meals a day would not buy soap or slab latrines to avoid diseases.
Environmental sanitation according to me is also a very important role that plays part in a healthy lifestyle of a society. In Bangladesh, there is a multifaceted sanitation problem that starts from the basic hygiene requirements like safe drinking water and also prevention of excreta disposal methods. Indiscriminate defecation results in various waterborne and filth diseases including diarrhoea, hepatitis, dysentery, hookworm, and so on. The rural housing setup has no arrangement of proper lighting and ventilation. Most marketplaces and public eateries have poor hygiene. There is also a lack of proper disposal of animal waste including inadequate drainage. Rural areas do not receive adequate health education. Some of the severe problems regarding health issues also arise from malnutrition around the country. There are only 35 out of 1000 live childbirths in the lower income strata of the country which is a major reason for the lack of nutrition among young mothers (Joarder, Chaudhury & Mannan, 2019, p.3). This is the direct cause of rapid population growth, inadequate food distribution, illiteracy, poverty and so on. Bangladesh also has a high-frequency tendency of flooding which leads to a huge amount of crop wastage every year.
Practising health in rural areas and countries like Bangladesh requires a clear understanding of the culture and customs of the society. The main reason behind it is most of the patients are not adequately educated and have notions and taboos about treatments. In such cases, the health practitioner must be patient and sensible towards the mindset of the patients, while also providing them with the right treatment (Adhikary et al., 2018, p.1). Moreover, the doctors and nurses also need to ensure that the patients come back for the treatment and do not get agitated by the health care providers.
.png)
Figure 3: Malnutrition in children in the last decade
Source: (Tradingeconomics, 2022, para. 2)
Conclusion
It can be concluded from this essay that Bangladesh is yet to cover a long path to reaching an ideal health care system. I have discussed my family's role and also the other families of the society who play a vital part in the healthcare system and it's uplifting. I have also compared my views with the data that I have collected regarding the health care system and the contribution of the government in various parts of the country. The role of the society has also been analysed to understand why Bangladesh is still behind in the healthcare scenario.
Reference List
.png)
.png)
Research
CAM520 Global Health System Assignment Sample
Prepare a written report for assignment help to improve the capacity of the Australian health care system to address the evolving health needs of a target population. Choose one of the 31 Australian Primary Health Networks as the context for your report. Draw upon the epidemiological and demographic information in the most recent PHN needs assessment done by your chosen PHN. Your report will make four (4) evidence-based recommendations for change in the primary health care sector and discuss possible implementation strategies. Justify the proposed changes against Duckett’s criteria for an ideal health system – equity of outcomes, quality of care, efficiency, and acceptability for health consumers.
Solution
Introduction:
The Primary Health networks or PHNs are funded by the Department of Health of the Australian government in order to manage and coordinate the delivery of Primary Health care within the diverse regions of Australia. PHNs serves as an independent organization which focuses on assessing and evaluating the health needs of a community and providing significant health services to the general population according to their need as well as their favourable situation (Bates et al. 2022 p. 4). There are two significant goals of a Primary Health network which guide and account for the services the particular organization conducts. It focuses on improving and enhancing the effectiveness of the significant health services provided to people with a high risk of depraved health outcomes (Australian Government, 2022, p. 1). It also aims on improvising and supports the coordination of significant and necessary health-related services to the people in need along with increasing available and easy access to better care along with ensured quality service delivery. There are 31 Primary Health networks within Australia which function independently with an aim to minimize the risk of poor health outcomes as well as connect people with significant health services and maintain appropriate care delivery to people within significant time and locality (Australian Government, 2022, p. 1). In the following assessment, North Coast PHN has been selected out of the 31 Primary Health care networks in order to evaluate its significance in maintaining significant health service and quality care delivery within a certain target population of Australia. The assessment will thus focus on assessing the significant target population based on the epidemiological and demographic information accounted for by the north coast PHN in order to provide better health services and facilities to the general population of Australia.
Target population and health needs:
With growing age, the risk of several health issues and conditions develops in an elderly individual. According to World Health Organization, the common health issues or conditions witnessed by an elderly individual throughout the world account for osteoarthritis, diabetes, depression, hearing issues, loss of vision, dementia, a chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, joint pains as well as refractive error (WHO, 2022, p. 1). Within the premises of Australia, one in every five older individuals accounting for 22% of the overall population have reported the issues defies related to stroke, as well as heart or vascular complications. It has been found that 7% of the population sustains the risk of cancer while 15% are accounted to live with diabetes. Also, glaucoma, cataracts, blindness or muscular degeneration are also some of the issues witnessed by the elderly population living in Australia which develops a state of deprived quality of life and unhealthy ageing. With growing age the risk to sustain multiple health issues increases which serve as a depriving factor within their health conditions as well as the quality of living (Israeli et al. 2022, p. 3). The elderly population also sustains the development of several health conditions or stability which comes with growing age and they are generally accounted as geriatric syndromes. These syndromes serve as a prime factor in the development of different health issues and sufferings within an elderly individual such as the risk of falls, pressure ulcers, frailty, delirium as well as urinary incontinence. With growing age as well as significant health complications the basic needs and requirements of aged individual accounts for personal security, safety, financial stability, physical and mental health, significant health care services, management of health challenges along with self-actualization (Nguyen et al. 2022, p. 6). Thus this aged population explains the need of maintaining healthy ageing with growing time which explains the need of enhancing and improvising the significant physical environment they are ageing, the services they are provided with as well as the opportunities they sustain in order to maintain a healthy lifestyle as well as management of their health issues. It has been found that acknowledging the ageing population and significant planning for their benefit is one of the necessary investments for the future of the Australian population as it can ensure benefits for the younger generations as well as those who are growing older (Davern et al. 2020, p. 17).
According to the North Coast PHN, it has been found that more than 20% of the overall population of North Coast belongs to the age group of 65 and above when compared to those of Australia and NSW where the statistics are 15.7% and 18.5% respectively. It also highlights that more than 15.8% of the age population explains the need for assistance in conducting their core activities (North Coast Collective, 2022, p. 1). It was found that healthy ageing and living was the second health issue faced by the population of North Coast as well as a significant regional strategy in order to ensure better ageing within the elderly population. The health need assessment conducted by North Coast PHN highlighted the need for significant collaboration and partnership of health professionals with the elderly population in order to manage their health as well as the risk of sustaining illness. It was found that the elderly population mainly needs assistance based on non-disease approaches such as health care expenses or cost, overcoming the barrier of distance to seek services, and informed and well-guided services based on residential care or home-based care (North Coast PHN, 2022, p. 1).
Evidence-based recommendations and implementation strategies against Duckett’s health system criteria
Recommendation 1:
Access to transportation as well as health care services are two prime factors that serve as a barrier in the process of healthy ageing in the older population it has been found that travelling long distances to seek health care services often becomes a major issue for the older population as with growing edge several disabilities and mobility issues increases (North Coast Collective, 2022, p. 1). Also according to the North Coast PHN, it has been found that distance of travel was one of the issues reported by the general population which serves as a barrier to accessing significant health services. It was found that in order to seek specialist care and service, 42.9% of the population reported having issues due to the distance of travel that they had to meet (North Coast PHN, 2022, p. 1). Also in terms of allied health services such as podiatrists, dentists or physiotherapists the distance of travel was also a common barrier reported by 29.9% of the population. the population living on the North Coast explain the need to travel distance to seek better services in relation to their mental health condition as they lacked significant counselling and psychiatric services within their local premises. Approximately 40.3% of the population reported having a lack of services in their mental health facilities which has a direct association with the increased need for travelling distance (North Coast PHN, 2022, p.1). Hence focusing on the issues of travelling long distances as well as lack of services it is recommended that significant home-based or residential care services are provided to the elderly population on the northern coast. It is necessary that the elderly population or the population with a demand for healthy ageing are provided with significant attention and resources within their homes instead of nursing homes to seek better health conditions and undergo healthy ageing (Gordon et al. 2020, p. 75). Thus the North Coast PHN needs to develop a significant health care team which precisely functions on providing home-based care or residential care two people with increased health needs. In order to implement the strategy, it is necessary to develop a significant proposal with collaboration from other stakeholders such as local government, national government, NGOs, the Primary Health network as well as professionals with skills and experience in delivering home-based care. The intervention or the strategy will highlight the delivery of services to people in relation to their health needs living in every demographic condition in order to maintain equitable outcomes (Siette et al. 2021, p. 997). According to Duckett’s health system criteria equity of outcome explains that every individual belonging to every demographic or epidemiological condition is provided with equal and rightful opportunities in terms of their health and well being. Home-based care and residential care explains the significant delivery of services and health needs to the aged population with disability issues or mobility barriers within their living premises. It serves by minimizing or removing the need of traveling distances in order to seek better services as well as bringing effective specialist care and interventions at home to the people in need (Doh, Smith and Gevers, 2020, p. 1371). The recommendation in relation to the Primary Health network will ensure that people living on the North Coast with the need for home-based care will sustain a significant opportunity for healthy ageing with minimized risk of travel discomfort. Also, home-based care will reduce the increased health expenditure which rises with the need to travel long distances in order to seek specialists and professionals in relation to their health issues such as mental health, physiotherapies as well as other underlying health issues.
Recommendation 2:
It was found from the elderly population of the North Coast explains the lack of understanding and guidance related to the services as well as resources that are available in relation to their health issues. From the North Coast PHN, it was found that in relation to mental health services 35.3% of the population reported that they do not understand or are sure about what kind of services are available for their treatment (North Coast PHN, 2022, p. 1). In relation to alcohol and other drug services it has been found that out of 50.4% belonging to the age group of 15 to 64 years, 38.1% reported a similar issue of having a knowledge barrier about the services or facilities that are available. Also, 35.2% of the population belonging to 15 to 64 years reported that in relation to age-specific services these sustain and charity as well as lack of understanding of the diverse range of services or treatment facilities that are available within their communities (North Coast PHN 2022, p. 1). Thus, based on this statistical evidence it is recommended that significant awareness and guidance strategies or measures should be taken into account in order to guide and educate the population regarding the services as well as facilities that are available (Archibald and Kitson 2020, p. 99). According to Duckett health system criteria, acceptability for health consumers explains the suitable and appropriate guidance or services delivery to health consumers in relation to their health and well beings. Thus their recommendation explains that the North Coast Primary Health services need to guide the population regarding the services and treatments that are available to respective illnesses two people in need the implementation strategies for the recommendation explain the usage of primary healthcare services which will function in delivering appropriate guidance and knowledge to the local people as well as the communities.
Recommendation 3:
On assessing the North Coast PHN evidence on the local Health Network as well as services attainment by the general population as well as the issues they witnessed while seeking access to health services it was found that cost was one of the common factors which was identified in each aspect of health service. In terms of seeking specialist care, allied health, mental health services, alcohol and drug services, general practice as well as age-specific services. In each of the health service aspects, more than 25% of the population reported witnessing issues with cost in terms of their health care (North Coast PHN 2022, p. 1). With a lack of knowledge about available services the increased risk of spending a higher amount of economy on inappropriate diagnoses, medicines as well as services (Le et al. 2021, p. 5). By providing significant guidance and knowledge in relation to the available services the elderly population sustains the ability to invest their healthcare funds and economy in relatable and appropriate health services in terms of their underlying issues. Also, elderly health care funds must be ensured to people with financial instability in order to assist them in seeking better ageing and sustain efficient and effective services in terms of health according to Duckett’s criteria.
Recommendation 4:
It was also found from the North Coast PHN statistics it was found that in terms of age-specific services approximately 31.1% of the population reported having difficulty in organizing their services and care along with the daily necessities. They reported having issues with managing doctors’ appointments, normal domestic support and assistance as well as care packages with funding. Thus, it is recommended that significant home-based nursing care is provided to patients with deteriorating health conditions where they lose their ability to manage home-based services as well as their health care needs (North Coast PHN 2022, p. 1). According to ducats criteria, the recommendation will focus on providing effective and efficient services to elderly people and guide them through healthy ageing.
Conclusion:
It can be stated that the elderly population of Australia explains the increased need for significant and necessary services related to their health and well being in order to restore the process of healthy ageing. The North Coast PHN highlighted the significant needs explained by the elderly population of the North Coast related to their health and the ageing process. Thus focusing on the needs as well as the risks sustained by these populations significant recommendations had been made and guided in the assessment which will serve in ensuring the process of healthy ageing. These recommendations are maintained using buckets health system criteria which guide equity of outcomes, quality of cash, efficacy as well as acceptability. The North Coast PHN explains the need for certain recommendations which highlight the implementation of advanced and well-organized home-based or residential care for age populations, cost-effective treatment intervention or health care funds as well as maintaining education and awareness in terms of health services available.
References:
.png)
.png)
.png)
Essay
CAM529 Introduction to Public Health Assignment Sample
Task description
Background:
Cardiovascular disease is considered by the World Health Organisation to be the “world’s number one killer.” This group of diseases causes considerable morbidity and mortality worldwide, and greater than 75% of cardiovascular disease deaths occur in low and middle-income countries
Task:
You are to write an essay describing the global health problem of cardiovascular disease. You should consider how the epidemiology of heart disease differs in low, middle and high- income countries, and the reasons for this. Imagine that you are working for a regional office of the World Health Organisation
You can choose which WHO regional area you wish to focus on. You should then search for and interrogate the literature on current public health challenges and responses to cardiovascular disease for your chosen region and use this information to make recommendations for future action.
Your essay paper should be structured as follows:
• Introduction: Introduce the topic and define the scope of your paper.
• Background: Include the most recent data to illustrate the public health problem in your region, and describe how the problem differs within and between countries in your region. Discuss the determinants of health that are relevant to this issue and explain how they contribute to disease burden.
• Public Health Response: Based on your reading of the literature, describe the current public health policy and strategy responses to this issue in your defined geographical region. Critique this response – identify strengths, weaknesses and gaps, as well as opportunities in relation to the current response. Consider public health approaches that you believe will reap the greatest population health gains. Support your arguments with reference to relevant scholarly literature.
• Recommendations: Based on your critique of the current public health response, provide three policy recommendations for improving the disease burden of cardiovascular disease in your region of choice, and identify the governing bodies that would be responsible for enacting these recommendations.
Task length
The essay should be approximately 3000 words (including references, tables and figures). A word count within 10% of this is considered acceptable.
Solution
Introduction:
It is to be noted that “Cardiovascular Diseases” are the number one killer disease in the world. Globally, an estimated 18 million people had died suffering from cardiovascular disease and amongst all these deaths, more than 85.2% deaths had been due to “stroke” and “heart attack” (Bansal, 2020). Over three-quarters of cardiovascular deaths occur within low and middle-income countries. Amongst 17 million premature deaths in 2019, more than 37% of the deaths had been caused by CVDs (Mehra et al., 2020). The essay discusses the various aspects of cardiovascular diseases and a discussion entailing how heart disease differs in low, middle, and high-income countries (Fuchs and Whelton, 2020). The WHO region that has been taken under consideration in this paper is “South-East Asia” (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018). The various public health challenges and responses towards “Cardiovascular diseases” for the chosen region would be carried out and some relevant and suitable recommendations would be made for future actions (Dehghan et al., 2018). It is needless to mention that it is of utmost importance to detect cardiovascular diseases at the earliest so as to manage, counsel, and discover effective cures and medicines for the disease (Thomas et al., 2018). The scope of the paper is that it would help future epidemiologists to find the spread, and measures of Cardiovascular diseases within the various high, medium, and low-income countries in South-Eastern Asia for assignment help.
Background:
Heart diseases account for more than 33% of all deaths take place in the South East Asian region and as per reports, cardiovascular diseases are responsible for more than 4 million people every year (Oliva, 2019). Within the region some of the majorly identified causes of cardiovascular diseases (Shafiq et al., 2018). In addition to this, the high blood pressure, as well as unhealthy diets, air pollutions, and so on, are some of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in the South East Asian regions and they account for more than 18 percent of the total number of deaths and 28 percent of the cardiovascular-related deaths (Jankowski et al., 2021). According to the study by Zhao (2021), amongst all deaths from CVDs, 39% percent of deaths in Southeast Asia are caused by Ischemic heart attacks, 49% percent of deaths are caused by Stroke, and 12 percent of deaths are caused by other cardiovascular diseases (Zhao, 2021).
Low income countries: Bangladesh:
Bangladesh is one of the low income countries of South-east Asia and a recent study from the rural Bangladesh has demonstrated that a there had been drastic increment in the cases of cardiovascular diseases between 2010 to 2019. The age-oriented cardiovascular diseases had increased by 30 times (Islam et al., 2016). Also, it can be said that Bangladesh has exhibited some prominent increment in the prevalence of some non-communicable chronic diseases and the related ates of mortality and morbidity in the previous few years (Islam et al., 2016). Some of the major health determinants pertaining to the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in Bangladesh include hypertension, diabetes, body-mas index, raised blood pressure, education and so on. As Bangladesh has experienced some rapid urbanization within the last few decades and also exhibited fast economic growth and thus has recently emerged as “a developing nation” (Sharif et al., 2021). As a result of this increased urbanization and growth, there is an increasing concern about further risks of chronic diseases due to the habits of people to adopt sedentary lifestyles (Barua et al., 2018). Bangladesh has also undergone changed food habits and increased inclination of young and middle aged people towards processed foods and inconsistent means and reduced physical activities (Islam et al., 2016). It is to be noted that poor lifestyles are being increasingly adopted by the people of Bangladesh, and as a result, more and more people have been suffering from Coronary Heart Diseases and renal failure than ever before (Hahn et al., 2021). Also, within Bangladesh, the males, unmarried people, the non-slum urban people and the non-Muslims tend to greater possibilities towards the risks of cardiovascular diseases (Barua et al., 2018). In addition to this, according to many studies, the Cardiovascular disease risks had been seen to be conversely proportional to the level of education amongst the males and females and Bangladeshis. For the people having more than 1 years of education, the chances for them to suffer from elevated cardiovascular disease risks is less than 10% (Sharif et al., 2021). Thus, education can be an effective way to prevent and control the risks of CVD within the country.
Middle-income countries: India
In the of the Southeast Asian regions, India is a developing nation with middle-income, and in this country, hypertension, stress-related brain activities, and so on have been reported as some of the most potential factors attributing to cardiovascular deaths (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018). In the 21st century, Cardiovascular diseases had been one of the most significant causes of mortality in India (Geldsetzer et al., 2018). As compared to the people of Europe, the Indians are affected by cardiovascular diseases 10 years earlier and mostly during the most productive period of their lives. In India, amongst all deaths caused by cardiovascular diseases, 52% are middle-aged. It is to be noted that the most prominent health determinants pertaining to cardiovascular diseases in India is include age, gender, unhealthy food habits, sedentary lifestyles, consumption of tobacco and alcohol abuse.
Moreover, the case of fatality that is attributable to cardiovascular diseases within the middle-income countries like India is significantly higher than high income countries (Kundu and Kundu, 2022). As estimated by the World Health Organization, with the present burden of cardiovascular diseases in India, the nation might loose more than $230 billion from productivity losses and expenditure within the healthcare in the coming decade. In India, the high propensity to develop Cardiovascular diseases can be attributed to various biological mechanisms, various social determinants and other interactions (Nambiar et al., 2020). Migrant Asian Indians have three-times greater prevalence of coronary artery diseases within the rural parts of the country (Kundu and Kundu, 2022). Moreover, the prevalence of Coronary artery diseases within Indians is more than 22 percent for the diabetic patients and 11 percent for the non-diabetic ones. The coronary artery disease prevalence within the rural parts of the nation is more or less 50 percent than within the urban population (Nambiar et al., 2020). Therefore, in order to address the significant burden requires a thorough understanding of all sociological and biological determinants and the complex dynamics underlying the various interactions as well.
High-income countries: Thailand
As per the latest World Health Organization data for 2018, cardiovascular diseases including coronary heart diseases in Thailand has reached more than 60,372 which is equivalent to 12.35% of the total deaths in the country (Juntarawijit and Juntarawijit, 2020). The “age adjusted Death Rate” of the country as per WHO report is approximately 63.10 per 100,000 of population ranks the country #157 in the world. In this country, the main health determinants relevant to cardiovascular diseases include “high blood pressure levels”, “high cholesterol levels”, “diabetes”, smoking, and so on (Juntarawijit and Juntarawijit, 2020). In the last decade, there had been a drastic increase in various chronic diseases within Thailand and Cardiovascular diseases and coronary artery diseases had a significant rise. In the year 2019, in Thailand there had been more than 350 thousand patients undergoing “ischemic heart disease” (Jensen et al., 2019). In that same year, the highest number of patients suffering from Cardiovascular diseases was from Bangkok and there were nearly 48 thousand patients. In the last decade, the number of Thai people suffering and dying from CVD including coronary heart diseases had been increasing in a drastic manner and had been considered to be one of the major causes of deaths in Thailand (Gheewala et al., 2019). The most potential factors that can be attributed to these diseases are unhealthy food habits, and the drastically changing eating behaviours of the people. The Thai people often eat high fat content and high carbohydrate content foods and also they barely exercise but exhibit high levels of stress. In the increasing rates of cardiovascular diseases in Thailand, genetics also play a significant role (Hahn et al., 2021). Apart from that, hypertension, high cholesterol, increasing rates of obesity, smoking and adoption of sedentary life styles are also some of the major factors contributing to the increasing cardiovascular disease rates in Thailand (Krittayaphong et al., 2019).
Public Health Responses within the region
At present, the South Asian tends to account for one-fourth of the total world population, and yet it already claims nearly 60 percent of the worldwide burden of heart diseases (Hahn et al., 2021). It is to be noted that the burden of cardiovascular diseases ion would continue to increase in a drastic manner within the region of Southeast Asia in the future few decades. Substantial public health achievements had been made in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases and strokes; however, they are not sufficient to prevent or reverse the epidemic (Zhao, 2021). Public health services societies by guaranteeing conditions of life where the people can be healthy by addressing 3 major functions, namely, assessments, policy development, and assurance (Thomas et al., 2018). Fruitful achievements within these areas include effective assessment, policy development, and assurance (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018). For many decades, Southeast Asian public health agencies and epidemiology researcher’s has gathered data on cardiovascular diseases and had carried out research on the ways to measure and prevent them. Despite the persistence of some crucial gaps, the collected information tends to provide a great evidence-base for effective decision-making by public health (Oliva, 2019). Moreover, a wealth of various policies had been developed based on the gathered knowledge and some policies had been implemented in an effective manner but await broader and more intensive applications in order to gain the optimum impact (Dehghan et al., 2018). The others had yet to be acted on. The evaluation of all these policies needs the implementation on an optimum scale and enough resources for evaluation. It is important to note that assurance is evaluated by the level at which the society is protected from the cardiovascular diseases and strokes that can be attained in spite of the latest progress (Dehghan et al., 2018). Therefore, it can be said that the public health agencies can out the recent knowledge for working through a targeted plan of action. However, it is unfortunate to note that most public health agencies are not yet “well-equipped” for these tasks. Within the region of Southeast Asia, this is considered to be further complicated by the provisions of “care split” amongst public and private systems (Shafiq et al., 2018). Primary care services can one of the main contributors to heart and cardiovascular diseases and should be strengthened for realising the actual integration of care for “secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases”.
However, in the public health response in Southeast Asia, there is a lack of patient participation in the various rehabilitation programs and there is poor adherence to the medication (Fuchs and Whelton, 2020). These are the two main issues associated with the public health responses within south-east Asia and these must be addressed to strengthen the secondary prevention responses for heart diseases. It is to be noted that the evidence-based patient education and empowerment initiatives tend to be lacking all over the region and thus must be prioritized. The uses of technologies might provide scopes within the area. Improving and expanding the registry data coverage is important for understanding the actual views of the disease and informing policies (Fuchs and Whelton, 2020). The data integration via “electronic health records” is lacking at present, however, might contribute to that goal. Strengthening the monitoring of the “secondary prevention goals” within the non-communicable diseases or cardiovascular plans and auditing services, delivery based on the establishment of quality standards, and the patient outcomes must be regarded as high priorities for studying economies for refining the healthcare offerings and assure that the requirements of patients are met (Jankowski et al., 2021).
The gains against cardiovascular diseases, in particular, and the impact of the better interventions are, without a doubt a great news. At the same time, they tend to introduce a new problem. Within high-income countries like Singapore, there are an increasing number of people who are now the supervisors of heart attacks and strokes (Mehra et al., 2020). The more the supervisors the more likely it is that there would be more survivors of heart attacks and the more there will be a recurrence of the diseases. The data sets that describe the prevalence of ischaemic heart diseases and strike certainly tend to tell a story of “long-term growth” (Hahn et al., 2021). Thus, it can be said that an ever-increasing part of the population is considered to have cardiovascular disease and might survive a heart attack or a stroke (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018). This tends to demand some urgent attention but also tends to represent a realizable opportunity for assuring those individuals get appropriate care. For instance, the fight against tobacco can be considered the most important public health success (Thomas et al., 2018). The prevalence of smoking between 1990 and 2015 has declined in all study economies, minimizing the risks of cardiovascular diseases. During the same period, a considerable increment in the population percentage of those who are obese in the economies (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018).
It is to be noted that the “WHO south-east Asia regional office” had coordinated the development of “national cardiovascular control programs that focus on secondary prevention of community and primary care settings within the countries like Thailand, Indonesia, and so on. Moreover, the “Global cardiovascular atlas report” of 2011 depicts a list of some “best buys” of some immensely cost-efficient interventions, strategies, and policies for preventing and controlling cardiovascular diseases which can be feasible for the implementation within the middle and low-income nations of the region (Dehghan et al., 2018). These include various effective public health strategies that address various behaviural risk factors like tobacco and the use of alcohol or unhealthy diet practices. Combined with some interventions for secondary preventions like the use of “aspirin, beta-blockers, angiotensin” turning enzyme inhibitors and the lipid lowering therapies, the risks of “recurrent vascular events can be reduced by approximately 75%. It is to be noted that within Southeast Asia, the cardiologist density is decreasing while the need for cardiology is increasing at an incredible rate, especially within the low and middle-income nations (Babatola, 2018). Therefore, cardiologists tend to feel overloaded and frustrated with the trends. In spite of that, the health administrators and the policy makers would need some comprehensive data for considering the aspects for some future planning of the health workforce, provided the rising prevalence of the heart diseases and the requirement for “coordinated care”. This would continue to exert pressure on the health systems (Thomas et al., 2018). The need for balancing the other public health policies must be recognized, but the most significant challenge here is that it is not just about increasing the number of the cardiologists, and even if there are an adequate number of doctors to take care of the elderly population in a more generic manner, many cardiologists would just move out of the “public services” to the private service due to the financial incentive and the flexible workloads (Cheong et al., 2019).
Recommendations:
It is important to note that the World Health Organization demonstrates the public health surveillance as a continuous, and systematic collection as well as analysis of interpretation of various health-associated information required for the planning, implementation, and evaluation of the “public health practices” (Cheong et al., 2019). The most important aspect of policy development for Cardiovascular diseases is that effective data should be collected, analyzed, and should be well-communicated to the stakeholders. The main bodies who would play the prior roles in the policy development include the policy makers, the scientific communities, and the planners of the program along with the medical institutes, the Public health authorities, and the funding agents (Roth et al., 2020).
The most significant feature of an effective action framework for preventuig and reducing Cardiovascular diseases is that the framework should entail the present reality which should briefly summarize the current knowledge of the progressive development of cardiovascular diseases and stroke. A vision of the future that summarises the most favorable situations that should be achieved if the cardiovascular disease hazards are to reverse or arrested. Also, the framework must also consist of a set of strong “intervention approaches” that should include a number of wide approaches that when completely and effectively implemented can help to bring out the transitions to the future healthy people and partnership goals for minimizing the heart diseases and the stroke and the way the 6 intervention approaches could fulfill the various stages of the disease and can facilitate the achievement of these goals. In addition to that, the policy framework must also consist of the target population that indicates the way people can reach the successive intervention approaches (Baddour et al., 2020).
In The Southeast Asian region, the framework for combating the rising urgency of cardiovascular diseases, especially in the low and middle-income countries includes taking action by translating the current knowledge into effective public health actions (Cheong et al., 2019). The policy must have strengthening capacities for transforming the public health agencies with the new and advanced resources and competencies and by expanding strategic partnerships with the high-income countries within the region such as Singapore, and Malaysia in order to sustain and mount those actions (Baddour et al., 2020). Moreover, the policy framework must be efficient enough to evaluate the impact of the actions by monitoring and evaluating the health impact of the interventions (Thomas et al., 2018). The Policy makers and the government bodies within the regions must generate advancing policies that demonstrate the most crucial policy issues and pursue the required preventive actions and research practices to solve those issues and expedite the development of policies (Cheong et al., 2019). The scientific communities and the program planners must also engage in various regional as well as global partnerships by multiplying the resources and by capitalizing on the shared experiences with the others throughout the global communities who have been addressing similar types of challenges.
Conclusion:
The paper has entailed a detailed discussion of the epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases within a chosen WHO region, that is South East Asia and it entails a brief evaluation of the spread of the disease within low, high and middle-income countries and the various measures and preventive actions taken by the region against the epidemic followed some recommendations entailing how the preventive measures, and the controlling policy framework within the region can be strengthened and made more effective. From the study, it can be concluded that in order to develop an effective public health policy within the Southeast Asian region, it is important for the policy makers to communicate the plan to the public at large and to establish some significant awareness and concern about the disease. It can thus be said that a comprehensive and a highly effective public health strategy for the prevention of heart diseases and strokes tend to depend on a broad understanding of the fact that the cardiovascular diseases in the Southeast Asian region tend to threaten the health of mainly the middle aged and the older adults and this can be prevented and controlled by the reversal fo the various acquired behavioral practices such as sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, smoking and so on.
Reference list:
.png)
.png)
.png)
Coursework
7138SOH Global Healthcare Challenges Assignment Sample
Description of the coursework
You are required to write an essay addressing either TYPE-2 diabetes or Tuberculosis. For either option, your essay will be provided with a case-study to inform or use as knowledge- base to write your essay exploring and analysing factors in globalisation and global change that influence aspects of the disease that you chose to write on.
OPTION 1: A Global Health Perspective in Fighting Diabetes – The China Case-study
Type-2 diabetes, a consequence of malnutrition, is now one of the commonest non- communicable diseases whose emergence, control and management are influenced by globalization process and global change.
Critically analyse how factors within globalisation process and global change contribute to the increased global burden of type-2 diabetes, and set out the challenges facing global and public health agents in their fight against the disease.
Guiding Instructions for doing the essay
Through analysing and interpreting globalisation issues beyond those identified in the case- study on fighting type 2 diabetes in China, use guidance 1-4 below to structure a 2,500 word essay in response to the task described in Option 1.
Students will be required to analyse a case-study of a global healthcare issue and use it as knowledge base to do the essay coursework.
Word count: 2,500 words (± 10%), Credit worth: 20 credits
1. Identify and describe FOUR globalization factors and explore to clarify how EACH factor influences global emergence and prevalence of type-2 diabetes [1000 words].
2. Identify and describe the role of FOUR categories of agents involved in activities for the prevention, control and management of type-2 diabetes [375 words].
3. For each of the FOUR categories, identify and examine the challenges facing specific Organisations or initiatives in performing their role to reduce the global burden of type-2 diabetes [1,000 words].
4. Draw your conclusions about (i) globalization and type-2 diabetes emergence, and (ii) challenges facing global efforts to reduce impact of type-2 diabetes [125 words].
An effective essay should demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the connections between complex globalisation processes and malnutrition leading to type-2 diabetes. The essay should therefore critically analyse the meaning of globalisation and clarify how its processes influence malnutrition, health inequalities and emergence of type-2 diabetes. An effective essay also shows evidence of thinking about global and public health systems’ response to type-2 diabetes crisis by discussing the challenges facing global agents and partnerships in fighting the disease.
For further advice on writing the essay see module guide subsection 6.3.3 General essay guidelines Assessment
OPTION 2 – Fighting Tuberculosis: A Global Health Perspective
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the commonest communicable diseases whose emergence, and effectiveness of the control and treatment strategies are influenced by globalization process and global change.
Critically analyse how factors within globalisation process and global change contribute to increased emergence, spread and global burden of tuberculosis, and set out the challenges facing global and public health agents in their fight against the disease
Guidance for doing the coursework
(i) Guidance for doing the coursework will be provided in synchronous sessions in Week 5 or Week 11.
(ii) The weekly student-led seminars are also designed to help students develop the skills to critically analyse and interpret ideas about globalisation and health that are highlighted in case-studies. We expect students to actively participate in seminar discussions to familiarise themselves with the approaches to critical analysis of the concepts that feed into their coursework because they will be expected to use the approaches to do their coursework.
(iii) As the module progresses students will complete a Proforma Essay Plan (use template provided) for weekly review with the tutors to show how they plan to logically respond to the coursework task in order to achieve the module learning outcomes.
Structure of the essay
(i) The work should have a concise and informative essay title that shows full interpretation of the coursework task. Title of the case-study being used as the knowledge base for the essay is therefore NOT appropriate.
(ii) The case-study will be accompanied with FOUR clearly numbered instructions to follow in structuring your essay responding to the coursework task.
(iii) Introduction - The essay should have a helpful introduction that interpret the assessment task, clarify about its aim, and an outline of the argument to be presented in response to the coursework task.
(iv) Main Body - The essay should be structured as A FLOWING RESPONSE to the coursework task and must logically follow the order of the guiding instructions provided with the case-study.
• No subheadings
• No bullet points or listing of ideas, and
• No graphs, maps and / or tables.
The task requires students to instead verbally interpret, describe and explain the information presented relevant to the topic being discussed.
(v) Conclusion – In line with instruction 4 on the guidance for doing the coursework, the essay should summarise the discussion so that the reader gets a clear overview of what you have argued in response to what the coursework required you to do.
Referencing
Arguments in the essay should be referenced using APA style of referencing. As a guide, every 1,000 words used in the essay should have at least 10 references to show evidence of wide reading
Solution
OPTION 2 – Fighting Tuberculosis: A Global Health Perspective
Introduction
Tuberculosis could be referred to as a potentially serious infectious disease that to measure only impacts the lungs (Churchyard et al., 2017). The bacteria which causes this disease tends to spread from person to person through tiny droplets that are released into the air through sizes and cops. Most people that have been infected with the bacteria do not have any symptoms. However, the common symptoms of tuberculosis include coughs that are blood tinged, night sweats, weight loss, and heavy fever. Treatment isn't always required for those individuals who do not report any symptoms. Patients with active symptoms require a long course of treatment which involves multiple antibiotics. It is a highly common disease in the world right now which is easily transmissible (Pescarini et al., 2017). It could be partially preventable by vaccine and is treated by a medical professional. In order to do so the individual needs to gain a medical diagnosis.
Main body
The globalisation factors that contributed in to spread and prevalence of tuberculosis on a global level are discussed as follows:
Migration: it has been identified that up to 2% of the world's population is living outside the country of their birth. It has led to an impact on the population mobility on use of health services and the entire health paradigm (Oppong, 2020). They have now become a burden on the host Nations and the importance of this particular aspect is regularly increasing. The drivers of mobility which includes the process of international movement along with back and forth transition between different risk environments have been major factors in the management of infectious disease in the areas which receive heavy influx of migrants. It is vital to note that the issues of Management and high level and broad which have also been cross-cutting in the past (Lönnroth et al., 2016). These include policies and managing the migration process for skilled labour requirements. It is upon the host country to make sure that people and the territory for fulfilling their purposes are not acting as the agent of diseases and imposing a burden on the Healthcare system. They also need to take into account biometric characteristics and population demographics for assessing the labour coming into the country and the ways in which they could impact others around them. Family reunification has also become a considerable factor with in the migration paradigm as it dictates the behaviour of the person entering another country and the ways in which the individual would contribute to these issues are also encompass Health Care professional. Training and maintenance of competence as the need to cater to the migrant population as well as the citizens while dealing with the communicable diseases such as tuberculosis (Lee, 2018). It is essential on behalf of the host country to monitor the health service use and health outcomes in both local and migrant populations in order to make sure that communicable diseases such as tuberculosis are not studied at white scale due to the influx of people in the country.
Global travel and tourism: it is vital to note that movement is associated with the spread of disease in many ways. One of the major ways in which travel helps infectious diseases to spread is by introducing new microorganisms into a new Geographic area. When a novel pathogen enters a population that did not have an experience of this microbe it is likely to cause disease outbreak. Microbes that mostly cause symptomatic and mild infections intended to spread widely and still manage to cause disaster outbreaks (Allen & Feigl, 2017). Microorganisms that survive in the human host completely such as the tuberculosis bacteria readily spread in a new area. However, if one or more intermediate vectors or hosts are involved or the microbe has a complicated life cycle the introductions of bacteria and to a new Geographic area really lead to outbreaks because the requirement of a catalyst can act as a barrier. It is necessary to understand that a permissive condition can exist in a new location that introduces the pathogen to infect and spread (Laranjo et al., 2018). For instance, in that location where people do not cover their mouth and face while sneezing and coughing can lead to a severe spread of Tuberculosis. However, in a particular location where people are educated about the disease and unaware that the need to cover their faces with masks when visiting in public for controlling the spread of diseases are likely to restrict the spread of tuberculosis on their own behalf (Abdisamdov & Tursunov, 2020). Introduction of a new micro oven use of graphical areas has been considerably facilitated by global travel and tourism because the countries now do not have many restrictions while welcoming people into their territory and are highly flexible which makes it easy for people to go to another region and infect the population for best assignment help.
Lack of monitoring measures: it is necessary to note that tuberculosis almost feels like a coughing and sneezing which is highly common. When an individual travel through a global border and reports coughing and sneezing it is highly unlikely on behalf of the airport authorities or other individuals to stop the individual and check the symptoms (Zumla & Abubakar, 2018). Due to this, most of the patients suffering from tuberculosis are able to enter another country without too many restrictions and monitoring measures which expose the people of a foreign Nation towards the development of the disease. However, it is vital to understand that people who themselves are suffering from tuberculosis do not have the slightest idea that they are suffering from this particular disease and hence act as an agent of spreading the same without the required information (Wirth, 2018). This is also because of lack of monetary measures where the first people tend to view fever and sizes as a response to the weather and not as something that could be life threatening diseases.
Lack of education and awareness: there are some nations that do not have the required education and awareness for detecting the diseases and end up acting as agents for spreading them in other developed countries. The World Health Organisation reported that eight countries accounted for around two third of the total disease count which was led by India. It was then followed by China, Philippines, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, South Africa, and Bangladesh (von Delft et al., 2016). All of these countries are developing countries and due to lack of awareness and education within the citizens contributed to the Global spread of Tuberculosis. Lack of education and awareness is a globalisation factor because now people have taken diseases and their spread very lightly as compared to the times when they were living their secluded borders (Schaller et al., 2019). For instance, there are still some countries in the world which have no idea about the existence of tuberculosis in the first place and feel that fever and sneezes are just a common response of the body and nothing they should be looking out for while screening people coming into their country or checking them.
Agents are of paramount importance as the preparation of documents by the health agencies requires specific knowledge of these agents (Verma et al., 2019). It is necessary to note that the role of four categories of agents which are involved in the activities of the prevention control and treatment of tuberculosis are discussed as follows:
International Healthcare Institutions: it is necessary to note that as tuberculosis processes a serious threat to people on a worldwide basis, Health Care Institutions are among the first agents who are responsible for treating and preventing tuberculosis in the region. International Institutions include Public Health Care facilities, World Health Organisation, CDC, NHS, etc. It was the World Health Organisation which declared the will clauses to be an international emergency 1993. It has helped the world to recognise the presence of tuberculosis and then develop ways for fighting the same. Presence of international Healthcare Institutions enables the entities to develop and implement a strategy on a global level for controlling tuberculosis and preventing the disease. It also streamlines the treatment because when a drug is developed in one country it could be given to the other regions as well so that they could minimise the impact of the bacteria (Mason et al., 2017).
Primary Health Care providers: when an individual suffers from basic symptoms of cough and sneezing the person is likely to visit the nearby hospital or clinic. The doctors there uh are known as Primary Health Care providers if they are in near to people and perform the early diagnosis of the situation (Camacho et al., 2020). They play an important role in detecting tuberculosis because the Primary Health Care provider needs to look out for all the symptoms and not classify TB as a common cold due to cough, sneezing, and fever (Armocida & Martini, 2020). It is essential that they take the required measures otherwise the cases can go undetected that can lead to a global epidemic of the bacteria. If the cases are not identified then it is highly unlikely that they could be prevented because the world would not have the information about an eruption of tuberculosis in a particular region.
Scientists and researchers: they are one of the most important agents because they work in order to develop vaccines and other Diagnostic procedures that could be used for identifying the prevalence of tuberculosis in the first place and then we used the antigenic method for developing the required vaccines (Rohde & McNamara, 2018). However, it is necessary to note that researchers also closely work with advanced and improved drugs which are effective for controlling the strains that are sensitive and resistant to existing medicines. Advancements in Global Medical Science have led to the duration of several drugs that have helped in controlling as well as curing tuberculosis such as MDR-TB (Balogun et al.., 2021). It is because of the efforts of researchers and scientists that it has been possible.
Non-governmental organisations: there are also vital agents in the treatment and prevention of tuberculosis on a global level. This is so because these organisations work in favour of underprivileged and economically backward people who might not even have the required awareness and education of identifying the tuberculosis in the first place. Non-governmental organisations work in order to spread awareness and educate people about how to distinguish TB from common cold (Kaplan et al., 2018). In many parts of the world it has been because of NGO that people have been given the required vaccination and drugs which are very costly if procured on a private level.
It is necessary to note that the agents also face challenges while performing their role to reduce global impact of tuberculosis. The challenges are as follows:
International Healthcare Institutions: One of the major challenges faced by the international Healthcare institutions in reference to control, prevention, and treatment of tuberculosis is the early detection of bacteria. This is so because it is highly difficult to distinguish tuberculosis from common cold and in order to do so speciality centres have been developed that have the required equipment (Lanza et al., 2020). International Healthcare Institutions tend to monitor these activities because they need to allot emergencies and provide the required material for global management of diseases.
Primary Health Care providers: The major challenge faced by Primary Health Care providers is the lack of resources (Burzynski & Keshavjee, 2020). This could be both physical as well as human resources. This is so because Primary Health Care providers are unlikely to have all the machinery and equipment that is needed to test every particular disease including tuberculosis. In some cases, they also fall short of nurses and other Health Care staff which makes it difficult on their behalf to manage the patients.
Scientists and researchers: Researchers and scientists tend to face the challenge of time (Rizzo et al., 2016). This is so because after a disease has been declared as a global emergency or a local epidemic that they need to collect the samples of antigens and test it along with the performing experiments in order to identify the ways in which particular bacteria reacts to different vaccines and chemical compositions (Denecke et al., 2019) . It takes a couple of months or an entire year depending on the complexity of the disease. It is a challenge because until the researchers and scientists develop vaccines through extensive R&D procedures the patients continue to develop adverse symptoms without an effective drug or medicine to help them deal with the same.
Non-governmental organisations: However, it is necessary to understand that Non-governmental organisations also face tough challenges while dealing with Global diseases because of lack of proper funding and the strategic direction (Demetriades, 2017). On some occasions they tend to collaborate with the government or private business Institutions for making the vaccine or drug easily accessible to people. It is necessary to understand that funding can play a major role because if an NGO would not have the required money it is highly unlikely that they would be able to procure vaccines or other resources for helping underprivileged people (Brown & Savulescu, 2019). However, the money is not only used in procuring vaccine supporters for also spreading awareness and educating people against tuberculosis and the ways in which they could minimise the impact on their own behalf. It is because of these and those that if people in remote areas are aware about the existence of TB and able to distinguish the same from the common cold so that they could seek for advanced treatment and not contribute to spreading on a community level.
Conclusion
From the essay, it can be concluded that globalisation has facilitated the spread of tuberculosis. This is so because globalisation has made it easy for people to travel around the world along with the flow of goods and ideas. This has not only contributed to the emergence of opportunity there but it has also made it easy for diseases to travel across borders and become an epidemic.
The major factors include migration, travel, lack of education, and lack of monitoring measures. Lack of education and monitoring measures are globalisation induced factors because the countries around the world have eased the restrictions of entering into territory and do not test people against common cold or other aspects which exposes them towards the risk of welcoming tuberculosis as an epidemic. The four categories of agents that are involved in the activities of prevention control and treatment of tuberculosis include International Healthcare organisations, Primary Health Care providers, scientists and researchers, and non-governmental organisations. It is necessary to understand that these agents deal with their own challenges in order to handle the epidemic of tuberculosis. Have a comma the common challenges include lack of resources and funding.
List of References
.png)
.png)
.png)
Research
HCT343 Research Methods and Data Analysis in Healthcare Assignment Sample
Assignment Task
Title: - Correlation of socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life in parents of children with Autism in India
PURPOSE OF STUDY:
The purpose of this study is to determine the correlation between health- related quality of life and socioeconomic status in caregivers of autism children in India.
OBJECTIVES:
1) To assess the Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores of HRQoL using SF 12 in parents of children with Autism in India
2) To evaluate the association between socioeconomic status and Health- related quality of life (HRQoL) in caregivers of children with Autism in India.
• Inclusion Criteria:-
Parents of children with Autism
Child with autism should be from the age of 4 yrs to 18yrs.
• Exclusion Criteria:- Parents of children with autism who have morbidities.
Methods: -
Study design: - A cross-sectional, non-experimental design. The primary variables of interest are HRQoL and socioeconomic status by modified Kuppuswamy socioeconomic scale
• Data Analysis: - Paired sample t-tests will be used to assess the Physical Component Summary (PCS) and Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores of HRQoL.
• The Pearson Product Moment Correlation will be used to measure the relationship between socioeconomic status and HRQol in caregivers of children with Autism.
NULL HYPOTHESIS:
1) There is no correlation between health-related quality of life and socioeconomic status in caregivers of children who are autistic in India.
Solution
1. Project laid Summary
Autism is one of the most severe neuropsychiatric disorders that affect children. The subject's Autistic can be characterised by the impairments of interactive social behaviour in a stereotypical manner (Joseph et al., 2022). The absence of the ability to perform tasks properly can impact oral health. The sense and constant care of helplessness drastically affect the quality of life. The respective disease occurs due to the neurodevelopment that is identified at the early stages of growth of the children and prior to attaining three years of age of a child. The presence of the condition Autism delayed the development of social and communication skills and fixed or restricted behavioural patterns. Many types of research are carried out to understand the condition of Autism in India and provide the information that around 18 million people in the country are suffering from the condition of Autism. It is also reported that the number of children affected by Autism is increasing day by day (Divan et al., 2021). Some of the researchers also claim that socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life of the parents of children are correlated with Autism; however, most of them are unable to provide deep information. A lack of primary research is also found regarding Autism to establish a correlation between this and socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life in parents of children for assignment help.
The issue with most of the previous studies is that those consider small sample sizes and also consider healthy parents, so the aim of the research is not gratified. Hence, the respective study aims to investigate the relationship between the health-related quality of life in parents and socioeconomic status in a total of 50 participants. All the participants have at least one child with Autism. The data is collected by using 12 scales of HRQL, and the socioeconomic status of the participants is modified and collected through the scale of Kuppuswamy. The collected data is presented in tabular form, followed by statistical analysis to establish the research objectives.
2. Background of the study
The disorder of Autism is a type of complex disability that is increasing day by day throughout the world and also in the country of India. The disability of children not only brings a financial burden for the family members, especially the parents; it also impacts the social health, psychological health and physical health of the families (Goldberg, McCormick and Virginia, 2021). In most cases, parents with Autism affected children revealed a lower quality of life if that is compared with the other parents who have healthy children and also the parents with physically disabled children.
Physicians and caregivers provide the information that children with the condition ASD not only develop neuro-developmental disorders yet also lead to problems that require proper treatment and medical attention (Keeley, 2021). Hence it can be stated that it impacted the quality of life of the parents due to the pressure of treatment of the child and related expenses. However, the respective disease develops a lifelong disability that limits the child's educational, social, and occupational demands in all stages of life. Hence the children require lifelong support from parents, which is a kind of burden for the family. The World Health Organisation also shows worry regarding the condition of Autism because it not only affects children and families, it also dismantles the growth of society (Grinker, 2020).
The diagnosis process of Autism is also complicated and difficult due to the absence of specific medical tests. There are various tools discovered by physicians to test Autism in children. WHO recommended the requirements for a diagnosis of behaviour and mental conditions. The ICD-10 test is preferable in the UK, while the USA prefers DSM-5. “The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)” is used in India (Kim et al., 2022). At the same time, there are various risk factors that are associated with Autism, parental age, heredity or family history and so on. The research provides the information parents who have one child affected through Autism also have the chance of having Autism in a second child also. Consequently, a clear understanding of Autism and its correlation with socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life require enlightenment to change the lifestyle of parents (Prakash et al., 2021). Recommended improvement of quality-of-life families with children of Autism also supports the growth of societies.
a) Data Search
.png)
b) Critical appraisal of research literature, Analysis, synthesis and evaluation of research literature
Autism is the third most developed disability in the world. According to Abbeduto et al. (2014), the developed countries, due to a lack of awareness regarding Autism, are affected mostly. Not only lack of awareness, poor diagnosis and lack of primary needs for Autism also increase the risks and numbers of affected people. As per some of the studies, the condition of Autism is developed due to genetic and environmental causes. While some others provide the information that low birth rate, viral infections during the time of pregnancy, metabolic imbalances and family history are responsible for the development of Autism. Detection of Autism in the early stage of childhood is challenging. However, the condition is properly diagnosed at the age of two years. As per Adler and Ostrove's (1999) view, though Autism cannot be diagnosed at an early stage, it can be understood through observation, as most of them develop difficulties in communication and the development of appropriate social relationships. Parents try to hide their conditions of Autism due to a lack of awareness about their mental health. Even many people are unaware that their conditions can impact newborn children. The affected children with age exhibit various abnormal behaviours and are subjected to filthy remarks, humiliation, bullying and so on.
There is no such cure for the condition of Autism in children due to the absence of drugs. However, appropriate awareness is effective for performing and adopting appropriate requirements to manage Autism. Based on the view of Bromley et al. (2014), Cognitive behaviour therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, behavioural management therapy and so on. On the contrary, another research provides the information that Autism in children can be managed through medication treatment, school-based therapy, nutritious food and so on. Speech therapy is also considered by the physician in most cases of Autism. There upon it can be stated that the supportive system of Autism requires appropriate investment, which brings huge economic pressure upon the parents and to family. Children with Autism can lead happy lives if they are raised in a proper healthy, and happy environment. However, economic pressure, in most cases, brings disturbance within the environment of the home (Ahmed, Buheji and Fardan, 2020). In some of the cases, it is also observed that parents lose their ability to parent due to the economic pressure of treatment in a place where psychiatric and physical challenges take place.
As opined by Harman (2014), mothers experienced higher levels of stress. Some societies blamed mothers for the condition of Autism. At the same time, some parents try to find out the reason for Autism that, delays the whole process of diagnosis. With the reference of Hicks, Jason, (2018), incorrect diagnosis also increases the issues of the parents and family members. Secondly, children with Autism require support on their everyday chores, which decreases the occupational involvement of parents and ultimately impact economic conditions (Hastings et al., 2005). The schools that are run by the country's government are not effective due to the absence of infrastructure, which ultimately leads the parents to take private support services. Socioeconomic conditions are also impacted because Autism affected children are unable to travel by public transport in most cases for their mental and physical conditions. Thus, it can be stated that socioeconomic conditions are related to the life of parents of children with Autism.
The health-related quality of life means HRQoL is one of the most important measures that are not only effective for understanding the health of people with Autism, but it is also effective for understanding mental health. Based on the view of Algahtani et al. (2021), HRQoL is a kind of approach that is effective in measuring various health outcomes by proper evaluation of an individual's emotional, psychosocial and physical well-being as well. As stated by Meadan, Halle and Ebata, (2010), Paediatric Quality of life systematically addresses various problems such as social functioning, school functioning, and emotional functioning. Further, every domain of this is broken down into various factors. All of this is to support the children with Autism as well as the parents.
Most of the literature focuses on the families and parents with Autism and also disabilities and disorders. However, very few focus on increasing the quality of life of the affected children and their family members (rehab council.nic.in, 2022). While detection of Autism is quite difficult, increasing the quality of life can be able to support the parents and also the affected child. Treatment of Autism has also involved the education of parents and the spreading of awareness and also of caregivers. According to Rizk, Pizur-Barnekow and Darragh (2011), Caregivers are able to support children with Autism. However, lack of knowledge and investments from the sides of Government and infrastructure related to the respective care increase the issues of them. Pharmacological treatment for Autism is mostly preferred and widely practised in developed countries like India.
3. Purpose of study
The aim of the respective study is to evaluate the correlation between socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life in the family members and parents of children with Autism on the basis of a case study of the country India. The aim of the research is to recommend to parents with Autism children some remedies that are effective in maintaining the quality of life of themselves and also of their children.
a) Null hypothesis
There is no such correlation between socioeconomic status and health-related quality of life in the parents of children with Autism in country India.
b) Objectives
The objectives of the respective study are as follows:
? To evaluate the correlation of socioeconomic status of life in parents of children with Autism in India
? To evaluate health-related quality of life in health-related quality of life in parents of children with Autism in India
? To develop appropriate awareness in a married couple to manage the risks of Autism in pregnancy
? To recommend some remedies to the parents for managing the lifestyle of Autism Children
4. Research design
The socioeconomic status of the individual is an important parameter for determining the status of the individual in society (Wani, 2019).In this regard, importance is given to occupation, earnings as well as education. Henceforth it can be regarded that these parameters play a pivotal role in shaping the nutritional condition and the subsequent health condition of individuals and families in general (Nielsen et al., 2021). In the current topic, thus, it becomes imperative to determine the socioeconomic status of the parents of the children who are suffering from Autism in India. Thus, this determination of socioeconomic status would help to reflect the quality of life that the parents of autistic children are leading in India. Thus, the correlation study helps to understand the association that exists between socioeconomic status and the quality of life that these parents are leading.
In this regard, it is essential to formulate the categories in which these parents can be classified. These categories would help to understand the exact choice of the participants who will be chosen for conducting this study (Patino and Ferreira, 2018). The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the selection of the participants are as follows
a)Inclusion Criteria:
• Parents who have children suffering from Autism
• Parents are strictly from India
• Parents who have given consent to participate in the survey
• The parent can respond to the questions of the survey.
• The different parameters of threw socioeconomic status have been taken into consideration.
b) Exclusion Criteria
• Parents who do not have children suffering from Autism.
• Parents who are residing outside of India.
• Since Autism is a sensitive topic, the parents who have not given consent to participate in the survey have been excluded from the survey.
• The parents who are not in a mental or physical situation to respond to the questions have been excluded from the survey.
• The socioeconomic status of the patients has been considered in this respect, and the other aspects of life, like the physiological or the psychological parameters of the concerned, have been excluded from the survey since the focus is on the determination of the socioeconomic status of the parents and their relation with the quality of life that they are leading.
Thus, it can be inferred that the study is strictly concentrated on evaluating the socioeconomic status of the parents whose children are suffering from Autism. The parents of autistic children are only taken for conducting this survey. Moreover, it can be inferred that the parents' consent was taken before conducting the survey since Autism is a sensitive issue and ethical consideration must be given utter priority in this regard. The parents who have not opted to answer the questions of the survey have not been included in this research study. The study is this directed towards the goal, and it diverts itself from the unnecessary consideration of the aspects unrelated to the survey. For instance, this study avoids focusing on the parents who are residing outside India and thus focuses only on the estimation of the scenario of the parents who are residing in India. Furthermore, the physiological or psychological aspects of the parents have not been considered in this regard. The focus of the study is thus centred on finding the socio-economic status of the parents whose children are suffering from Autism in India.
c) Sample size
In this case, it is essential to determine the appropriate sample size, and this can be determined by the calculation of G power. The sample size is a crucial factor in the determination of the statistical accuracy of the results (Kang, 2021). The difference between the alternate and the null hypothesis is also determined by the sample size, and this can be predicted with the help of G power. Thus, the G power estimation is quite essential in the development of the research design of the scientific study.
The sample of 50 participants was taken by considering the G power of the population. In this case, the previous research has shown that the result of the correlation test has a tendency to have a positive value (Kivimäki et al.,2020). The p-value of 0.05 has been considered in this regard since the 5% level of significance is taken. In this kind of condition, the power of 0.8 is quite instrumental in diminishing the occurrence of the type-II error, and the effective sample size is 0.3. Thus, by considering all the necessary coefficients of correlation(r), the effective size is 0.478, and thus, in this respect, the sample size of approximately 35 would be quite conducive for performing the statistical analysis. Thus, we have considered the sample size of 50, and this is in good agreement with the G power of the sample size. In this respect, it must be noted that the smaller sample size would lead to the depleted statistical accuracy of the calculation that would be conducted, and this would also imply that the standard deviation from the mean would also be low. Thus, an accurate idea about the G power will help in ensuring that the size is adequate and it does not lead to the generation of excessive standard deviation, which can be regarded as an impediment to the accuracy of the statistical analysis. As discussed earlier ethical considerations have been taken into consideration, and thus it is essential to take the consent of the parents. The sample number of 50 reflects the number of participants who have agreed to participate in the study. A total of 62 participants had been approached for the survey, and among them, 12 participants opted to stay out of the survey. Henceforth the sample size of 50 has been considered for conducting this survey.
d) Data Collection
It is essential to evaluate the appropriate research methodology that will be conducive to procuring the research goals and objectives. The two types of research methods that are predominant in the scientific world are quantitative and qualitative types of research (Thelwall, and Nevill, 2021). In this research context, it was essential to evaluate the relationship between the socio-economic status and the healthy life of the parents whose children have been suffering from Autism. Firstly, it can be noted that the survey was conducted with the aid of the randomly chosen 50 parents whose children have suffered from Autism. This survey was conducted to evaluate the correlation between the socio-economic status and the healthy lifestyle of the concerned individuals. Thus, in this context, primary quantitative research has been performed to determine the effect of socioeconomic status on the health-related quality of life of the parents whose children have been suffering from Autism in India.
In this respect, the modified Kuppuswamy scale will be used, and 5the scoring will be done accordingly to measure the different parameters of the socio-economic status of the participants in India. The first aspect of measurement is the educational qualities of the parents of autistic children. In indicating this regard, the highest education is awarded a score of 7, while the illiterate participants are given a score of 1. The occupation of the participants will also be marked accordingly, with the people holding important positions in the government or private sectors getting a score of 10 while the unemployed participants are awarded 1. Again, in the case of income, the people belonging to the highest income categories will be awarded a score of 12, while people earning the least amount will be awarded a score of 1. Furthermore, it should be noted that according to the latest Kuppuswamy scale, the upper classes of the society are awarded a score of 26-29, while the people belonging to the lowest strata of the economic ladder will be given a score of 5. Thus, the higher scores of the participants indicate that they enjoy a better socio-economic position in society than the other participants.
The datasets will be properly estimated with the aid of the appropriate methods, and this will be instrumental in establishing the research goals (Sovacool, Axsen, and Sorrell, 2018). In the current research, the randomly selected parents whose children have been suffering from Autism were chosen, and their socio-economic status was estimated with the aid of the SF-12 and taking the modified Kuppuswamy scale for determining the socio-economic status of the parents. The data was collected after the completion of the survey, and it contained information related to the economics and education of the participants. The appropriate statistical test will help to depict the scores of the participants in the survey.
In this regard, the descriptive statistics will be calculated with the aid of Excel, and this will help to form a comprehensive idea about the responses that will be collected from the participants, and this will reflect the overall socio-economic status of the participants. A blank model 0f descriptive statistics is given below.
.png)
Table 1: A blank model of descriptive statistics
(Source-Self created)
The statistical analysis of the data collected from the survey will help to analyze the effect of the socio-economic status on the health-related quality of life. Here in this context, the Excel analysis was performed to conduct the correlation of the data that was collected from the survey (Miot, 2018). Table 2 determines the meaning of the values that are obtained from the statistical analysis of the data set which is available. Again, this relationship can be both; positive and negative (Mat Roni et al., 2020). The positive value determines that the variables in question get increased with the enhancement of the variable. A negative association can also exist, which implies that with the increase in one variable, another variable gets diminished.
.png)
Table 2: Meaning of the correlation values
(Source-Self created)
5. Ethical governance and consideration
Ethical consideration has been taken by the Ministry of Health and family welfare under the government of India. In this case, 50 people have been considered for undertaking the survey since it deals with a sensitive issue like child autism. Thus, the parents will be made to sign a petition of consent to affirm that they do not have any issues with sharing the relevant personal information. In this regard, the research design of the study has been made in consideration of the ethical aspects, and the consent forms of the parents will be submitted to the ministry of health and family welfare. The parents will be sent the questions through email, and this inline survey will ensure that the parents won't have to bear unnecessary trouble for participating in the survey. The parents whose children have been suffering from Autism can respond to the questions from the comfort of their homes since the survey will be conducted online mode. Thus, the parents would also feel comfortable sharing their personal details since this project will be conducted under the governance of an appropriate state agency. The reliability of the project would ensure the proper response from all the participants. Moreover, a detailed report about the progress of the survey will be presented to the learned experts after conducting the survey. These experts will review the scenario of the project properly and will also strategize some necessary recommendations that are related to the research study. These recommendations, according to the review of the scenario by then experts in the field, will be submitted to the government organization from time to time. Thus, the project related to the evaluation of the socioeconomic status and the quality of life of the parents whose children are suffering from Autism has been depicted by considering the ethical aspects and the proper governance of the project. The supervision of the concerned experts and the government agency would aid in fulfilling the research goals.
References
.png)
.png)
Research
HCT199 Evidencing Learning in Specialist Professional Assignment Sample
Assignment aims:
1. To enable students to recognise and optimise professional learning opportunities in relation to the practice setting;
2. To enable students to critically evaluate their professional practice, synthesise this in relation to their on-going role and professional development; and
3. To articulate the critical evaluation of professional practice through oral and written presentation of reflections on practice/practice related issues.
On completion of the module a student should be able to:
• Knowledge and Understanding [K)
• Intellectual Skills [S 1]
• Discipline Specific (including practical) Skills. [S 2]
• Transferable Skills [T]
1. Define and articulate personal learning outcomes via a learning contract relating to an aspect of their professional practice (K).
2. Use case studies/specific examples of practice to engage in a structured process of individual, critical and dialogic reflection on their own advanced, professional decision making in relation to this aspect of practice (S1).
3. Recognise and articulate through formative and summative assessment personal and professional learning, linked to personalised learning outcomes (S1, S2).
4. Clarify issues which define generic versus specialist practice, acknowledging professional identity whilst understanding where skills merge and others’ roles supersede in practice (S2).
5. Synthesise understanding of the philosophy of the relevant profession in order to suggest future advancements/changes to their own professional practice and where appropriate, that of the profession (K, S2).
Syllabus content:
The majority of content will be directed by the chosen specialist study, but the following areas will be explored for all:
Concepts underpinning professional development in the workplace:
- Individual responsibility for professional development
- Identification of professional development needs reconciling individual professional development needs and organisational / service development needs
- Clarification of generic versus specialist practice
- Concept of reflection and processes of reflective practice
- Evidence-based practice / Evidence-based decision making.
Processes of formalising work-based learning:
- Defining and writing individual learning outcomes through learning contract design
- Approaches to evidencing learning through work-based practice e.g. portfolios, professional diaries and significant incidents
- Using case studies as an approach to critical, dialogic reflection
- Principles of accreditation of work-based learning, if applicable
Solution
A Critical Reflection on the Development in Management of Neurophysiological changes in Autism from the Perspective of an Aspiring Advanced Physiotherapy Practitioner
Introduction
Most Forth Valley primary care surgeries now employ Advanced Physiotherapy Practitioners (APPs). To address any musculoskeletal issue, APPs serve as patients' first point of contact. Patients may bypass the doctor's office and schedule an appointment with the APP via the clinic's front desk (Tawiah et al. 2021). Advanced physiotherapy practitioner has a broader autonomy of practice, allowing them to triage, assess, evaluate independently, and diagnose patients with extremely complex illnesses and maybe numerous pathologies across the health and social care landscape to enable integrated treatment (McGowan et al. 2018).
While expert physiotherapists still strive to give their patients as much autonomy as possible, they also take on leadership and management roles, deal with complicated decision-making processes, and know how to mitigate risk. Expert physiotherapists have advanced knowledge and training in a narrow field of medicine, such as injectable therapy; some even have prescription skills and the ability to diagnose and treat complex capabilities (Tawiah et al. 2018). In addition to directing the client's rehabilitation, their duties include collaborating closely with medical experts and acting as the initial point of contact, with the power to request diagnostic practitioners such as x-rays, scans, and blood tests.
Discussion
My earnest goal is to become a successfully advanced physiotherapy practitioner whose main focus will be on the neurophysiological changes that occur from Autism. This paper is reflective in nature, discovering and broadening my continued professional development (CPD) perceptions to date, which has allowed me to broaden my clinical skills, knowledge, and comprehension of the topic of neurophysiological changes that occur from Autism. This paper is intended to be read by healthcare professionals. According to the Health and Care Professionals Council (2019), continuing professional development may be broken down into the following four categories. These are self-directed learning, work-based learning, formal education and professional activity. Reflection is at the core of all continuing professional development (CPD), and doing so is necessary in order to make sense of my experiences and advance my work for assignment help.
Self-reflection is analogous to explaining what one sees while staring into one's own eyes. It is a method for gauging how I operate in the world and how I study. To think about something is to engage in "reflection," in the simplest sense. Writing a reflective essay or study on one's own experiences is a vital part of the educational self in modern times (Roy and Uekusa, 2020). Instead of doing things with the same effectiveness I always have, reflecting may help me improve my skills and review how well they work. Positivity in this context refers to asking oneself whether there is a better or more efficient way to accomplish something and then acting on that inquiry (Chen et al. 2019). The ability to reflect on oneself is personal for development. Without it, we respond automatically to our surroundings and to our own selves. If I have ever had an intense reaction to something or said something that I have since come to regret, then I may acknowledge how reflection can assist me to use the better nutritious feedback and modification lifestyles (even opinions) which are not providing me. If this is the case, then I may also comprehend how it can support me in changing behaviours that are not serving me. We all self-reflect regularly, almost subconsciously, and we also do it on purpose when we want to learn something new about ourselves (Stefan and Cheie, 2022). What we see when we reflect on our own activities or routines is usually not a skewed reflection of reality but rather a minor distortion.
Clinical criteria for autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) include deficits in the ability to communicate, engage socially, and adapt communication (American Psychiatric Association, 1994). As per my understanding, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is defined as the process that encompasses the whole group of effects from the most severe form of the condition, autism, to the milder forms, such as pervasive developmental disorder and Asperger syndrome (AS) not elsewhere defined (PDD-NOS) (PDD, NOS). A broad variety of IQs may coexist inside a single autism diagnosis. In other words, there is no universal ASD diagnosis (Miyazaki et al. 2007). Also, I realised that there are several potential causes of the ASD phenotype, including genetic disorders and ecological exposures and preterm delivery.
Variation in phenotype is also shown in areas such as the rate of language acquisition, the prevalence of epilepsy, and the spectrum of cognitive capacity. Nonetheless, abnormal responses to sensory information seem to be shared by those on all ends of the spectrum (Coskun et al. 2009). I came to know that over ninety-six per cent of children with ASD report both hyper- and hypo-sensitivities. There is a broad range of severity throughout the spectrum for sensory and behavioural impairments, just as there is for communication and social deficiencies, and these differences may persist into adulthood (Minshew et al. 2002).
From the two original fundamental findings by Asperger (1994) and Kanner (1943) through first-person experiences, sensory processing difficulties have been a consistent theme in clinical diagnoses of ASD (Asperger, 1994). I acquired that those who are unable to express their discomfort when confronted by certain sensory inputs may resort to self-harm or violent conduct. Hyper- and hyporesponsiveness to sensory input are not limited to those with ASD, although they do seem to be more common in this community than in those with other developmental disabilities (Leekam et al. 2007). It is less well known how these sensory abnormalities are distributed in individuals with ASD. In the past, it was believed that the more local senses were more susceptible to damage and served as indications of immaturity in development (Baranek et al. 2006). According to my understanding, despite increased evidence for disturbance in auditory and visual processing pathways and a renaissance in interest in multimodal integration, these individuals ’ experience are frequently the ones that get the least amount of research. This is the case in many cases (MSI).
There is evidence in the literature that points to observable changes occurring in early auditory circuitry, especially in response to increasingly complex stimuli. However, anomalies in the cerebellum do not appear to be sufficient to explain the inadequacies for all individuals who fall within the autism spectrum (Roberts et al. 2010). I realised that the ability to take in and make sense of a variety of incoming sounds is the fundamental prerequisite for both language and effective communication. Therefore, it is very necessary to have an understanding of the characteristics of this preliminary stage in the auditory sensory stream. Ordinarily, event-related potentials (ERPs) obtained using magnetoencephalography (MEG) and electroencephalography (EEG) have been utilised in order to explore cortical auditory sensory processing that occurs further than the brainstem (Koh et al. 2010). I learned that brain responses are gathered across numerous trials to simple auditory stimuli and averaged to produce information on the temporal and spatial resolution of responses.
The main and association auditory cortices are assumed to be responsible for the abnormally late peaks seen in both EEG and MEG investigations (150 ms). These findings, unfortunately, disclosed to me that there are directional disparities in delay. Cortical latencies were shown to be shorter for longer tones at 1000 Hz in two separate investigations. Tone durations of 100 and 4 milliseconds were utilised, respectively, by Ferri et al. (2003) and Martineau et al. (1984). Delays in onset and latency in others have been observed compared to controls. Bruneau et al. (2003) demonstrated late auditory evoked potentials using a tone with a frequency of 750 Hz and a duration of 200 milliseconds. MEG was employed by Roberts et al. (2010) to report a delay in the M100 response of the right hemisphere to tones of various frequencies lasting 300 milliseconds (200, 300, 500, and 1000 Hz).
Whitehouse and Bishop (2008) observed, in instance, that the early peak latencies of the typical repeating tones varied across vowel sounds, sophisticated nonspeech sounds, and complex tones. This was the case regardless of whether the sounds were speech or nonspeech. This was the case despite the fact that each of the noises was considered to be a tone that repeated itself. Researchers Bruneau et al. (2003) and Oram Cardy et al. (2008) observed that stronger language ability was reflected in this area of low-level processing by greater and earlier right hemisphere cortical peaks. This discovery was made by the researcher Martineau et al. (1984). Differences in age, diagnosis and research paradigms may account for contradictory results. The future of this study is expected to benefit from the incorporation of behavioural phenotyping and correlations.
When Swiss psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler developed the term "autism" to describe an individual who withdrew into their own world, he drew inspiration from the Greek word for "self" (Blatt, 2012). As per my knowledge, due to sensory processing difficulties, autistic youngsters may seem to be living in a separate universe from their peers. These kids won't stop talking about the same thing, do the same things again and over (such as wring their hands or rock their bodies), say the same words over and over, and refuse to change to new situations. Psychiatrist Leo Kanner analysed the cases of 11 very bright kids who all showed characteristics of autism, including an intense need for isolation and sameness (Kanner, 1968). Kanner hypothesised that these children lacked the capacity for social-emotional development from birth (Grandin and Panek, 2013).
The frequency of the autism phenotype has remained consistent, but the number of people who are clinically diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder has grown significantly, according to a 2015 study conducted in Sweden that looked back over a 10-year period (Lundstrom et al. 2015). Because it is based on the observation of gene expression in people and their relationships to genetic variables, phenotyping is a valid method for evaluating autism neurophysiology. I understood that the significant rise in autism diagnoses is due to the fact that phenotyping has been largely abandoned in favour of a subjective checklist of symptoms, with little to no knowledge of the probable origins of these symptoms.
According to a nationwide study conducted in the United States in 2015, many children who were first labelled with autism spectrum disorder were subsequently determined not to be autistic (Bloomberg et al. 2016). I acquired that children who were given an incorrect diagnosis were less likely to be sent to a professional for further evaluation and treatment, and they were also less likely to have ever been diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder or Asperger syndrome. According to a study published in Psychology Today in 2015, many children initially labelled with autism really suffer from a mix of language delay, sensory difficulties, and apraxia (Schrader, 2015). If a kid has apraxia, it means that he or she (a) understands language conceptually but has trouble expressing it vocally and (b) has trouble blending sounds in words to make meaningful communication. I also learned that it is true that some of these youngsters have trouble paying attention during tests. Others have difficulties digesting information and hence cannot reply in time to be assessed.
From an article published in 2016, I witnessed that Between 2006 and 2012, the number of people in Germany who were diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder rose by almost 70 per cent. The authors of this study clearly imply (Bachman, 2018) that a substantial percentage of this huge rise was attributable to an incorrect diagnosis. Some researchers speculate that rather than having autism, many of these kids just had a low IQ, learning problems, or ADHD (Knight, 2017). Overdiagnosis of autism is common, according to the results of a 2019 thorough study published in JAMA Psychiatry (Rodgaard et al. 2019). There has been an over-expansion of the autism umbrella. I understood how autism is increasingly used as a catchall term for a wide range of conditions in neurology and child psychology that have just a superficial relationship with autism. In many cases, medical professionals will diagnose autism symptoms in people whose presenting symptoms are really just ADHD and poor social skills.
Many youngsters with sensory processing disorder (SPD) are given a diagnosis with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), according to a story in the Irish Times from 2019 (McDonagh, 2019). I acquired that poor eye contact, disliking hugs, poor play, and meltdowns are being used to label children with autism.
The German government provides financial assistance to autistic children and their families and provides special services in the classroom for autistic students. However, the vast majority of kids who have autism can succeed in a traditional classroom setting without any additional support. In Ireland, children with an autism diagnosis have better access to special care and education programmes tailored to their unique needs than children with other diagnoses. Due to this advantage, doctors are more likely to identify a kid with autism rather than another disorder (Rose, 2016).
Autistic children who live in the United Kingdom and need special assistance get a Disability Living Allowance. I learned that in order for the parents to obtain this benefit, neither a diagnosis nor proof of financial need is necessary. In the United States, parents may have Risperidone and Aripiprazole prescribed for their children if they have been diagnosed with autism. The antipsychotic medications approved for use in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression cannot possibly help those with autism. The only reason parents give their kids medication is so they can behave (Talsma et al. 2010).
As per my research, children who are antisocial, struggle with anxiety and refuse education are often incorrectly classified as autistic in the United Kingdom. To the mother's benefit, a fraudulent diagnosis of autism might be used in custody proceedings (Garber, 2011). The autistic brain has the same basic neurological structure as any other brain. The neurophysiology of the autistic brain is what sets it apart. The cingulate gyrus (CG) is like an automated transmission that smoothly shifts focus between the frontal lobes in a neurotypical brain. However, in autism, a dysfunctional CG prevents access to the emotional/creative processing right frontal lobe, which is pivotal in spontaneity, social behaviour, and nonverbal abilities. While some neurotypical individuals are primarily right-brain thinkers, others tend to favour the left side of the brain. However, autistic individuals can't function well without using their left brain exclusively (Rolland, 2020). This may take up to a day. Anxiety is a distressing physiological reaction (not an emotion) that goes straight to the body and ignores the brain.
I understood that an autistic person's hyperfocus is so strong that they are unable to juggle competing thoughts. An autistic individual will accept your every statement at face value since they lack the cognitive capacity to process two sets of information at once. Autistic persons are unable to monitor how they are being received or viewed by their audience when speaking at length about a favourite subject (Kallstrand et al. 2010). I learned that people on the autism spectrum need organised activities because they cannot focus on both the task at hand and the task of predicting what could happen next.
Different forms of sensory overload are also brought on by hyperfocus. As a result of their hyperfocus, autistic people hear loud or high-pitched noises with far more intensity than their neurotypical counterparts. An autistic individual may experience cognitive impairment and a frightening void of thought if exposed to too many words on a page (Jemel et al. 2010). From my knowledge, I understood that anxiety might be brought on by shopping for too long or by overhearing private conversations. Anxiety attacks are often triggered by hardware shop lighting displays. Some people find that their hyperfocus amplifies their sensation of touch, which may make wearing tight clothes or receiving a hug uncomfortable.
These 52 autistic characteristics are all attributable to autism's distinguishing feature: hyperfocus (Churches et al. 2010). The mental state of hyperfocus consists of undying, laser-like attention on a single thinking process to the exclusion of all others. My research says that about a third of the following characteristics may also be attributed to other factors. This is why collecting a list of symptoms isn't a reliable diagnostic tool. The categorization of symptoms leads to more questions than answers if we don't know what's causing them (Vlamings et al. 2010). Autism's distinctive symptoms result from hyperfocus, a condition that is causally unique. If I suffer from hyperfocus, I won't be able to process several inputs or thoughts at once. The autistic person on the other end of the line cannot sense anything you or I am saying to them right now.
The concept of an autism spectrum needs to be abandoned because it is unproductive. Many erroneous autism diagnoses may be traced back to this flawed idea. The condition of autism does not belong on any gradable spectrum (Monk et al. 2010). I understood that autism is not a spectrum disorder but rather only has one form. No autistic autism disorders exist, and neither do autistic tendencies. True autism exists at a one hundred per cent rate. The sole difference between people with autism is the degree to which they experience hyperfocus. Individuals with autism disorder (low functioning) tend to be completely inaccessible due to their intense attention (Annaz et al. 2010). While communicating with people with Asperger syndrome who are high functioning, I understood that they exhibit hyperfocus less severely. If a visual representation is to be of any use, it must take the form of a vertical bar chart, with the highest intensity (lowest functioning) at the bottom and the lowest intensity (maximum functioning) at the top.
Children with autism who are unable to communicate are especially vulnerable to being stuck in a state of hyperfocus from which they cannot be rescued. Some severely autistic youngsters, as Einstein did at age four, develop an interest in communication and begin speaking on their own (Iarocci et al. 2010). Children with developmental, learning, language, communication, or social disorders not associated with autism are the only ones who can be taught to talk. When compared to the clinical phenotypic approach that was the norm in the 1960s, the symptom survey method of autism diagnosis represents a huge step backwards. Phenotyping relies on studying gene expression in people and establishing links between circumstances and genetics.
Conclusion
Autism is a neurophysiological disorder that affects how the brain processes information and is not caused by external factors. The inability to react to external or social stimuli is a major problem for a brain that is stuck in hyperfocus. Similarly, it cannot be treated using behaviour change techniques. Autism-related hyperfocus cannot be reasoned away. Hyperfocus, or intense, single-minded attention on one thought pattern at a time, to the exclusion of everything else, including one's own emotions, is a defining characteristic of autism. It seems that the cingulate gyrus (CG), the brain region responsible for focusing attention, is malfunctioning in those with hyperfocus. When compared to the clinical phenotypic approach that was the norm in autism diagnosis in the 1960s, the symptom survey method has been a severe setback.
Phenotyping relies on studying gene expression in people and establishing links between circumstances and genetics. Autism is a neurophysiological disorder that affects how the brain processes information and is not caused by external factors. The inability to react to external or social stimuli is a major problem for a brain that is stuck in hyperfocus. Similarly, it cannot be treated using behaviour change techniques. Autism-related hyperfocus cannot be reasoned away. Hyperfocus, or intense, single-minded attention on one thought pattern at a time, to the exclusion of everything else, including one's own emotions, is a defining characteristic of autism. The brain of the attention-focusing cingulate gyrus (CG) seems to be at the root of hyperfocus.
References
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
Case Study
NURBN2025 The Health and Cultural Diversity Assignment Sample
Assessment Description:
Students to explore impacts to health and health outcomes for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples, as well as demonstrate the importance of incorporating cultural perspectives in clinical practice as future healthcare professionals.
Overview:
The purpose of this task is to demonstrate cultural safety in clinical practice. You will critically examine a case study identifying the necessity of culturally safe practice to improve the health and health outcomes for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples.
In assessment task 1 you identified an understanding of your own identity, along with social and cultural factors and how this has influenced your own beliefs about, and interactions with, Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander Peoples. In this assessment task you have the opportunity to apply this self-reflection to practice when exploring the events of the following case study. Your responses are to be evidence-based.
Case Study
Annie is a 59 year old Aboriginal women from the Atherton table lands near Cairns, in north Queensland. Annie is passionate about being an Aboriginal community member, enjoying yarning with her community and attending local community events. Annie has one daughter Sharelle, 32 years old and one son Tony, 30 years old. Sharelle has 3 children, Sarah 12 years old, Kelly 9 years old and Alex who is 3 years old. Sharelle lives close to Annie in the Atherton Table lands.
Annie has lived independently for many years and was employed as a Murri Primary School Teacher which she loved. Annie retired 3 years ago to support her daughter with caring for her children. Annie had separated from the father of Sharelle and Tony many years ago.
Annie is visiting her son Tony and daughter-in-law Kate in Melbourne (within the Monash health catchment area). They have a baby, Lily who is 9 months old. Kate is returning to work so Annie has come to Melbourne for an extended stay to help care for baby. Annie enjoys caring for and getting to know Lily. Lily is relatively easy to look after, sleeping through the night. Annie takes over the care of Lily once Tony and Kate go to work. Annie loves signing songs to Lily. She also takes on the usual care like feeding and changing nappies. Lily will sleep about 3 hours in the middle of the day, so this gives Annie time to rest or tidy the house. Annie will take Lily for a walk if it is warm enough once she wakes up. Tony and Kate will take over the home tasks when they arrive home from work.
Annie is a bit lonely as she does not really know anyone. Annie is missing the mob in the Aboriginal Planned Activity Group where she is involved in yarning, gardening and walking activities. Annie’s favourite was art as she was creating a piece for a local exhibition. Annie does not like hospitals; she has a fear of hospitals because her community have had bad experiences.
Case Study Instructions
Move through this case study by addressing the following situations:
Section one: How do you ensure you are committed to a journey of cultural safety?
You are on a morning shift at Dandenong Hospital, Monash Health and have been informed that you need to admit a patient being transferred from the Emergency
Department. You receive the handover:
Annie is a 59 year old Aboriginal women from the Atherton table lands and has Type 2 diabetes and Hypertension, diagnosed when she was 50. She has managed her diabetes with the support of the
Local Aboriginal Health Service (Wuchopperen Health Service Limited:
https://www.wuchopperen.org.au/health-support). Annie had been informed that her kidney function was deteriorating which she had been following up at this service. Shortly after arrival in Melbourne Annie becomes unwell and is admitted to hospital. Annie was experiencing intense ear pain and had become very unsteady on her feet, later diagnosed with a severe ear infection requiring intensive intravenous antibiotic treatment.
Annie arrives on the ward; you greet Annie while taking her to her bed. How do you ensure you are committed to a journey of cultural safety?
1. Provide an evidenced based strategy that enables you to continue your cultural safety journey.
2. How do you welcome Annie into the ward?
3. Annie reveals her current situation with you, as outlined in the case study. What actions would you take following this conversation? You are advised to investigate an Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Service that would be able to support Annie while she is staying in Melbourne.
Section two: Addressing culturally unsafe practice.
You are now at handover. You are presenting Annie to the nursing team. You have just described Annie’s symptoms. You have said Annie is very unsteady on her feet and before you can continue you hear two nursing colleagues say, “I bet she’s an alcoholic. We will make sure we limit her pain relief”. To unpack this situation please answer the following questions
1. In NURBN2025 you were introduced to racism, the causes and impact on health outcomes Identify from peer reviewed literature the possible reasons why non-Indigenous people make racist assumptions about First Nations peoples. Include the following:
a. The potential beliefs, values and attitudes that have influenced these non- Indigenous nurses to be culturally unsafe.
b. Describe how these nurses have used power differentials related to their beliefs, for nursing care.
2. How would you advocate for Annie in this handover?
Section three: Promoting Cultural safety
You make an appointment to meet with your nurse unit manager (NUM) to address this culturally unsafe practice. What team based solutions could you present to your NUM. Think of this in terms of:
1. How could cultural safety be promoted within this ward?
a. What antiracist group learning strategies could be implemented?
b. How could power differentials be minimised?
Please note the word counts are a guide. The reference list is not included in the word count.
Solution
Section 1:How do you ensure you are committed to a journey of cultural safety?
The case scenario conveys that Annie is afraid of hospitals as her community has had a bad experience with care services. It is very common that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander patients mostly confront several issues or challenges as the medical practices including nurses and doctors carry biased attitudes toward the community (Arrow et al. 2018). Thereby for a patient like Annie confirming cultural safety and equality in accessing healthcare is very important to confirm a safe environment for the healthcare setting. In order to confirm cultural safety for Annie, stakeholder engagement is much more important to confirm openness, respect, and offer safe care to a patient like Annie. It can justify a trustworthy, flexible, respectful relationship during the period of treatment. In order to confirm cultural safety, maintaining the privacy and secrecy of the patient is another important consideration as most of the aboriginal people do not have such type of offering during their intervention in the healthcare setting for best assignment help.
Considering Annie's fear regarding her healthcare setup, it is very important to welcome her to the ward with all warmth confirming a friendly environment. It would even help to justify cultural safety in the process. The nurse needs to be skilled and professional enough to carry an unbiased attitude and treat them in the same way as other patients. A welcoming attitude can even be confirmed by behavioral attempts where maintaining eye contact can offer assurance to Annie to be comfortable in the setup. Cultural safety can even be accommodated in the practice through effective communication where more focus would be on listening as most effective communication is mistaken by speaking. More listening to patients like Annie can help the nurse to be more acknowledged of her culture, and background to address her needs accordingly. It would help to sustain cultural safety in the setup. Before proceeding with any intervention for her difficulties taking her decision and discussing the intervention procedure with her is a must to avoid ethical issues like informed consent, autonomy, etc (Beks et al. 2019). Addressing to the referred ethical issues can even help to sustain a positive, safe, cultural environment in the healthcare setup. Having an understanding of Annie's difficulties as well as cultural considerations, it would be better for the nurses to arrange a support system to confirm that her main health issue is being addressed.
Annie does not have an extended family to help her out and her son and daughter might not be that much effective to offer her support. Thereby to confirm her continuous improvement regarding all types of health issues, it will be better to take the help of community services so that she can recover first. Annie is already getting the help of services to manage her diabetes but the service is not available in Melbourne as it belongs to Queensland and Annie is in Melbourne right now. Thereby it is important to arrange for another type of health service for Annie which is available and accessible in Melbourne. The help of any local aboriginal network can be communicated to confirm cultural safety afterward. As this particular network would help to be connected with the support service for the community; thereby it would be a better consideration to confirm cultural safety. The service needs to be such where several segments like raising awareness, building partnerships, information determination, etc which would be much helpful for Annie to be self-dependent in all terms. There are services like ACCHO and NACCHO that can help Annie in her situation through their programs and policies (Bovill et al. 2021). It would even help her to get rid of her fear of hospital services as these particular support services are for the community she belongs to and it is definitely help her to be comfortable and feel culturally safe and secure in all terms.
Section 2: Addressing culturally unsafe practice
In legal considerations, it has been confirmed in Australia that equality would be there in the health sector with no discrimination for race, gender, background, tradition, custom, etc. However, the practical scenario does not get properly aligned with the same; rather there are several nonindigenous people who consider aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people as discriminated, against, and unequal, and make them marginalized. It can be confirmed undauntedly that everyone has their own attitude, value, and beliefs but individualism should not lead to racism including hatred, discrimination, or prejudice due to their origin, or color. It even extracts the negative image of the sector as well as the societal structure of the country. Health Care sector belongs to emergency services and racism cannot be overflowing in such a sector; still, nurses often exercise power differentials as per their values, belief, or attitude. They often ignore Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people and do not pay proper attention to their symptoms to offer them safe care intervention (Jayakody et al. 2020). Such a type of attitude immediately confirms culturally unsafe practice on the part of the nurses. Most of nonindigenous nurses believe that aboriginal people can be only one community and there cannot be any variation regarding that. However, that is a complete misconception regarding aboriginals which eventually leads to improper addressing of cultural diversity followed by culturally unsafe practices. Furthermore, most of the non-indigenous people believe that aboriginals or indigenous people are illiterate, ill-mannered and live a gross life where they always get involved with drinking, smoking, and the use of drugs. Research even confirms that they are not very interested to work but rather always ask for everything for free. Such type of wrong information or improper belief regarding indigenous people on the part of non-indigenous people eventually attracts unsafe practice by creating a barrier in the care intervention (O’Donnell et al. 2020). Due to such type of wrong beliefs, nurses often do not share enough concern or focus for the patients or their symptoms and rather carry a biased attitude which becomes the main barrier for the entire care process. Such a type of attitude will definitely make Annie very uncomfortable, hurt, and angry due to the involved discrimination. She can even think of racist activities in the health care center which eventually can increase her uncomfortable regarding the healthcare setting. Thereby, it would be better for the nurses to exercise an open flexible environment in the setup. It is even important to exercise effective communication and shared decision-making in the process where the patient like Annie would not feel left out but rather can play an active role in the entire intervention. As the nurses of the next shift have a misconception regarding the aboriginal community and already have confirmed their biased attitude towards Annie, thereby, it is important for the nurse of the present shift to make them aware of some important considerations while the handover. It is very important to convey human rights, patient rights, and several ethical issues to be followed by the nurses during handover to assure or informed them about consequences. It would help them to be more focused on the patient without sharing any biased attitude toward her aboriginal background. It would be even more relevant if the nurse on the present shift would convey her experience with Annie (Quinn, 2019). Such information can remove the misconceptions of the nurses conveying the fact that all aboriginals are not involved in features like smoking, drinking, taking the drug, etc to confirm a culturally safe environment for Annie.
Section 3: Promoting Cultural safety
Such unfair practices need to be stopped as well as promoting cultural safety is another important consideration to be taken care of. In order to promote cultural safety in the hospital care setting, the nurse unit manager needs to be conveyed of such unfair practices. Apart from conveying the thing, it is even important to take some initiative to promote cultural safety. The first and foremost concern to promote cultural safety in the practice can be training (Skoss et al. 2021). Training would be much helpful to make the nurses informed or acknowledge about cultural diversity. The training can make them more efficient, skilled, and effective to remove the issue of cultural diversity and promote
cultural safety. If the nurses of the next shift had enough information about aboriginals then they might not have such type of generalized attitude or behavior towards Annie rather they can secure a friendly safe environment for her treatment. Hence, it immediately can confirm cultural safety in the process. Decision makers and nurses in the healthcare sector are the main stakeholders to exercise or initiate action to attain sustainability as well as success for their efforts. There are some nursing principles and foundations to avoid ethical issues. The training even needs to accommodate the same so that the nurses would have enough knowledge regarding informed consent, authority, non-maleficence, and beneficence which eventually would help them to avoid improper addressing to the patient and automatically culturally safe practice will be aligned in the setup (Tremblay et al. 2020). The training even needs to convey the consequences of otherwise situations to make the nurses aware of all positive and negative to secure cultural safety in the process.
References
.png)
Case Study
NUR1203 Cultural Safety and Professional Practice Assignment Help
Brief task description
This assessment task supports you to be an effective Bystander in the workplace and will hopefully extend beyond this. It is a requirement that student nurses and registered nurses are Culturally Safe practitioners. Part of this is when we witness culturally unsafe practice, that we have the skills to navigate this and bring change to the workplace setting.
Length 1500 words +/-10% (word length includes in-text referencing and excludes your reference list and appendices)
Task information
This Assessment requires you to respond to the following case scenario.
You are to identify ONE of the culturally unsafe care points within this scenario and use the four components of the Bystander Intervention Framework as the basis of this essay.
Case study
You are doing a clinical placement on a busy surgical ward, and you are working with a Registered Nurse (RN). Both of you attend to an adult patient, Elliott, who has been admitted for a surgical procedure and requires a blood transfusion intra-operatively. The family identify their religious faith as Jehovah’s Witness, where the belief in the administration of blood and blood products via transfusion is against their faith. Elliott has no vision and is able to communicate using speech.
The RN assumes that Elliott is unable to communicate for himself and talks only to her mother who is in attendance for admission.
The RN turns to face the mother and makes the following comment, “Hello there – who do we have here today? Thanks for bringing Elliott in for his admission. How long has he been unwell for? Do you know? I have his chart here with me and just want to ask you some questions regards his medical history if that’s OK? It says something here about him not consenting to a blood transfusion.... we’ll need to sort that out, because he’s going to need it you know!”
After finishing off admitting Elliott to the ward, you walk back to the nurse’s station with the RN. The RN turns to you and states “What a weird religion that stops you from having a blood transfusion. Why would anyone want to be in that religion?”.
1. Identify ONE of the culturally unsafe care points and explain its relevance to this case study and explain why it is culturally unsafe.
2. Identify 2 Direct interventions that you could use in this scenario. Your response cannot be a replication of any responses that have been provided with, in your Bystander training
3. Identify 2 Indirect interventions that you could use in this scenario. Your response cannot be a replication of any responses that have been provided in your Bystander training.
4. Identify 2 Distraction interventions that you could use in this scenario. Your response cannot be a replication of any responses that have been provided in your Bystander training.
5. Protocol intervention/s: Identify the NMBA Codes of Conduct that this culturally unsafe care is breaching.
Writing Style
• This assessment piece to be written as an report and in third person.
• Do not use headings
• Correct Academic writing as per USQ guidelines
• All discussion is to be appropriately referenced using APA 7th Edition Referencing
• Contemporary Literature must be sourced (no more than 7 years old).
Solution
Introduction
As per professional standards for registered nurses (RN), nurses must reflect dignity and professionalism through their practice and ensure patient right over person-centred and well-informed treatment practice. This report focuses on identifying culturally unsafe care reflected by RN in the case of Elliot, who belonged to Jehova's Witness believers and denied blood transfusion as per religious belief. This report also highlights 2 direct interventions for this case and 2 indirect interventions for this case, and 2 distracting interventions for nursing assignment help.
Culturally unsafe care points
In the case of Elliot, culturally unsafe care practice has been witnessed by an in terms RN responsible for the care of patients disrespecting the religious belief of the patient for not consenting to intra-operative blood transfusion rather than making the patient and family members of the patient agree on the procedure through empathy. The RN has also breached patients' right to the confidentiality of personal information as RN has communicated about patients' religious beliefs and treatment outcomes openly in nurse stations and reflects disrespect towards the religion. As mentioned by Poorchangizi et al. (2019), nurses have the responsibility of safeguarding patients' right to confidentiality. This right has been breached here by the RN, along with disrespect to the patients' culture. The RN has also avoided directly communicating with the patient even though the patient can talk. These are the areas where RN has reflected culturally unsafe care practices, lack of dignified behaviour, and respect towards patients' cultural needs and health conditions. This incident reflected unprofessional behaviour by the RN's breach of patients’ rights.
Direct intervention
The case here is to ensure a culturally safe care environment for Elliot. Direct interventions that can be considered in this case include training RN to deliver care in a culturally competent manner and ensuring collaboration with community health service providers. Authority of care service-providing organisations can consider arranging training for RN to enhance their cultural competence. Cultural competence among nurses can be enhanced by making them aware of different cultures and the importance of reflecting respect for the culture and religion of patients in the nursing profession (Kaihlanen et al., 2019). For example, during training sessions, the RN can be made aware of legal consequences associated with not respecting the religion of a patient, as well as improve the RN's ability to communicate with patients in a culturally competent way for incorporating changes in the RN's behaviour. Further such training can also improve other RNs' perception regarding the importance of maintaining culturally safe care practices to avoid the recurrence of such incidents.
On the other hand, including community healthcare professionals in the care team of Elliot can be beneficial for reducing the cultural barrier in care. The main concern here is no consent for the intraoperative blood transfusion, which is necessary for the patient. Community health service professionals can communicate with the patient and his family to make them understand the consequences of which blood transfusion becomes necessary during treatment and ways the patient can avoid breaching their religious values without impairing the treatment requirement (Bolcato et al. 2021). The community health professional can also help RN to understand patients' perspectives associated with treatment measures that can help to solve complications associated with the treatment plan
Indirect interventions
As the RN has reflected on culturally unsafe behaviour in terms of not respecting the cultural beliefs of patients and not prioritising patient confidentiality, strict measures can be taken against RN by making management aware of the situation. Further, appointing a different RN with professional knowledge of cultural competence and knowledge of managing patients with Jehovah’s Witness beliefs can be beneficial. RN can lose their license and job for not following professional standards and ensuring respect toward the cultural needs of patients. As mentioned by Handke et al. (2019), cultural competencies-related practices in healthcare settings allow limiting cultural disparities associated with treatment specification and help to minimise the consequences of inequality. Thus the respective case reflecting the poor understanding of cultural competencies highlights the presence of inequality in the case of the patient belonging from a significant religious belief only for not providing consent to a treatment requirement. Thus making authorities aware of the situation and taking strict action against the RN can help to limit the recurrence of such a situation in the future.
As the current RN appointed for Elliot has reflected a poor understanding of cultural competence thus, another RN having profound knowledge about the requirements of cultural competency can be appointed to manage this case. Ensuring a cultural competence care environment for the patient can help to limit the cultural barriers arising in the treatment plan as well as the dignity of the patient can be maintained. Further, replacing the existing nurse with an experienced professional will provide understanding regarding patients’ consent redefining other treatment methods that can be applied to replace the intraoperative blood transfusion. Thus it can be considered a strategy for dealing with the current situation.
Distracting intervention
Application of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and counseling sessions with family members of patients in the presence of community service providers knowing dealing with issues of care associated with a patient with Jehovah’s faith can be considered in this case. As mentioned by Babiano-Espinosa et al. (2019), CBT allows the development of an interacting treatment environment for service users and service providers for better delegation and patient care needs. In the current case of Ellitor thus CBT based approach can be applied to reduce resistance to blood transfusion. Under this approach safety of blood transfusion in terms of their religious values and consequences for not considering the blood transfusion can be communicated. The CBT approach focuses on including changes in the behaviour of patients by encouraging and guiding them to judge a situation from a positive side. Thus this technique can be beneficial for making Elliot and his family members provide consent for blood transfusion.
A set of counseling sessions can be arranged for Elliot and his family members, and during the secession, it will be ensured that privacy and confidentiality are maintained. During the counseling session, it can be ensured that the patient and the family members actively participate in the communication to clarify the issues of not considering blood transfusion and the current health condition. Such sessions can also be used for reforming their existing experience due to poor behaviour of RN to ensure the trust of the patient and his family member over the services provider. It will help to ensure a cultural safety care environment and limit the issues associated with consent.
Protocol interventions
NMBA code of professional conduct forces nurses' duty to ensure patients' rights and respect for patients' decisions. In this respective case of Elliot, there are certain arise that RN has avoided and neglected. The first area neglected was the patient's condition, as Elliot could speak; however, the RN preferred to communicate with his family rather than the patient, which highlighted impairing patient-centered practice and informed-making. This activity of RN breaches the first code of conduct of NMBA, which is focused on nurses' practice safely and competently. As per this code of conduct, nurses must act safely and competently without being compromised by patient health limitations (Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia, 2022). In this case, RN neglected Elliot’s personal views on the matter of blood transfusion though can communicate this code of conduct 1 has been breached. Code of conduct 4 NMBA standard focuses on ensuring nurses respect and dignity towards patients' culture, ethnicity, and values as well as beliefs while receiving care (Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia, 2022). However, in this case, Elliot, while communicating with his family member RN considered a very informal way of communicating, reflecting the less interest in the patient's cultural and religious identity.
Further, while communicating with other RN, the respective nurse became very disrespectful to Jehovah's Witness's religious beliefs by saying the religion was weird and questioning the following religion. This incident signifies disrespecting the cultural and religious identity of the patient, thus breaching the code of conduct 4 of NMBA standards. Code of conduct 5 has also been breached in this unsafe cultural practice as this code highlights nurses' responsibility to maintain the confidentiality of the personal information of patients as per the National privacy principle 2001 and Privacy Act 1988 (Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia, 2022). However, the RN, in this case, avoids confidentiality of the patient's details, such as cultural and religious specifications, by openly communicating about it in the nurse station. This code of conduct 5 of the NMBA standard has been breached in this culturally unsafe practice.
Conclusion
Thus it can be concluded that here RN has breached the NMBA code of conduct 1, 4, and 5 through culturally unsafe practice. The issue that arises can be solved through training sessions to improve RNs' knowledge regarding cultural competencies and CBT, as well as community healthcare service providers' engagement for making such patients and their families actively involved with care requirements. These techniques can help to ensure patient rights without impairing treatment specifications.
References
.png)
Research
PUBH6002 Global and Environmental Health Issue Assignment Sample
Individual/Group - Individual
Length - 1000 words (+/- 10%)
Learning Outcomes - The Subject Learning Outcomes demonstrated by successful completion of the task below include:
a) Examine environmental factors from the local to the global levels that influence health and interpret the relevance to the health of populations.
b) Interpret and analyse the impacts of globalisation on the social, economic, and political determinants of global and local health.
c) Critically analyse ethical elements relevant to environmental health protections, policies, and industry practices, including identification of vulnerable groups
d) Investigate the relationships between environmental risk factors and social, economic, and political determinants of illness and injury.
Instructions
Review the given policy provided by your lecturer. Public health policies are evidence-base
structured targets, aiming to provide the practical strategies that governments can apply to regulate key structural factors that contribute to the burden of, and the risk factors associated with the disease that is targeted by the policy.
To review the given policy, read carefully the given policy provided by your Learning facilitator.
Research the academic literature related to the policy and then conduct a review in 1000 words
(±10%) a report guided by the following four questions:
Introduction/Background (Approx. 150 words)
- In the introduction present the burden of disease and risk factors before the implementation of the current policy.
- Finally, briefly discuss the impact of the health-related issues related to the specific burden of disease(s) and population.
- Include an overview of the assessment as part of the introduction. Policy analysis (Approx. 600 words)
- Discuss how the policy was developed? Who were the key stakeholders in this development and what were their role?
- Describe the expected outcomes and the strengths of policy based on its successful achievements?
- Discuss 2 challenges or strategies that have been less successful or unsuccessful related to the policy. Recommendations and conclusions (Approx. 250 words)
- Provide 3 evidence-based recommendations to improve the implementation and/or efficacy of the policy based on your policy analysis.
Annexes
Solution
Introduction
Though in comparison with most of the countries of the world, Australia can boast of a clean and healthier quality of air, it has almost 5000 of its citizens that succumb every year due to diseases caused due to air pollution. The increase in population, urbanization, industrialization, air mode of transport, deterioration of the climate, and injudicious use of energy resources has been contributory factors to Australian air pollution. It has been predicted that with any remedial steps, a substantial increase in summer smog will be noticed after the year 2030, along with drought-driven bushfires and dust storms (science.org.au, 2022). Prolonged exposure to air pollution can increase the chances of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and lung cancer. The vulnerable population like children, the elderly, the economically backward, and people with an already compromised immune system are more at risk of health hazards caused by air pollution (Who. int, 2022). Glencross et al (2020), researched that air pollution has a severe adverse impact on the immune system of the population. This report for assignment help will cover an analysis of the National Clean Air Agreement, Australia which was formed in December 2015.
Policy Analysis
In April 2014 Commonwealth Environment Minister of Australia Greg Hunt Conceptualized this agreement with the proposal of united efforts of all Environmental authorities of Australia for improving the air quality. Though the primary responsibility lies with the local governing authorities, all the levels of statutory and government authorities play a significant role in improving air quality. The Commonwealth, state government, and the local territorial government were identified as the key stakeholders responsible for the successful implementation of this agreement. This agreement was formulated to identify the main areas that contributed to poor air quality and to set priorities to work on those identified target areas. Identification of key air pollutants and their sources, and strategies to mitigate their impact was the objective of this agreement. Strategies to reduce air pollution need to be devised. This agreement aimed to meet three fundamental outcomes: improvement in environmental condition and health of citizens of Australia, society empowerment through increased awareness, access to authentic and genuine information and ways to combat air pollution, and an updated tracking system of air quality based on information, evidence, scientific principles and facts specifically for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and ozone. This agreement is a complementary tool for other government and commonwealth-enabled initiatives for environmental sustainability. The Commonwealth Government launched a National Environmental Science Programme that has a dedicated fund of $8.88 million for ensuring air quality in urban areas. An additional fund of $2.55 billion has been created to reduce the emission of harmful gases and air pollutants to establish the Emissions. Some notable achievements of the agreement over the years include the establishment of standards for emissions from marine engines and power equipment that will operate outdoors, and an increase in the quality of air for particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone gases (dcceew.gov.au, 2022). Various air champions have been identified who will work for this cause, and spread awareness and education. Non–statutory initiatives to improve air quality have also been identified (awe.gov.au, 2022). The main strength of this agreement is its holistic and comprehensive approach to dealing with the poor air quality whereby it attempts to garner support and collaboration at all levels of multiple stakeholders. Participation from local to national level improves the commitment towards the objective and reduces the resistance if any. Another strength is not only its short-term objective that will be met with a reduction in emissions but also a long-term vision of creating a culture or lifestyle change in the citizens of the country through awareness and education which is going to yield long-term sustainable benefits in maintaining air quality.
There has been criticism of this agreement by various environmental groups on the ground that the standards laid down by the Australian government in its clean air agreement do not comply with the norms established by the World Health Organization. Owing to this criticism, Australia has now set upper limits on the air pollutants PM10 which denotes the coal dust, fumes, and other coarse air particles, and PM2.5. a limit of 25 micrograms per cubic meter has been set for PM 10 (Abc.net.au, 2022). Another shortcoming of this policy is the lack of focus on industrialization as a contributor to air quality. There should be a stringent upper limit on the industries in the emission of air pollutants, the type of air pollutants, and also the consumption of natural resources.
Recommendations and Conclusions
The standards set in this policy should be following the standards set by the WHO for a universal and global approach and adherence to air quality. WHO has set various upper limits for different gases, fumes, and air pollutants which can serve as a benchmark for this agreement (C40knowledgehub.org, 2022).
The Australian government can also study the cases of other developing countries that have been facing air quality issues and understand the initiatives taken by them to curb this growing menace.
.png)
Figure 1: Initiatives to improve air quality across various countries
(Source: Safety4sea.com 2022)
Eco-friendly public transport systems that are pedestrian- and cycle-oriented, purchasing energy-efficient electronic appliances and machinery, reduction in domestic as well as industrial waste, and reduction in agro incineration, are some of the steps that can be undertaken at the community level (Financialexpress.com, 2022).
Australia has been frequently criticized for its lack of regulation and enforcement of air pollution. The harmful impact of air pollutants, even when under the permissible limit, cannot simply be ignored. The agreement along with other environmental pacts are found to be lacking in monitoring mechanisms, established universal standards, and lack of coordination between government authorities. The main cause of air pollution in Australia is particulate matter (PM) which is generated by industry and transport vehicles, mining, and coal-related activities. The National Clean Air agreement should have it in its priority area as the adverse impacts of PM on health such as neurodevelopment disorders, lung, and respiratory diseases and increased mortality cannot be ignored. The Agreement must identify high threat zones through the data related to air quality and the cost of health damages in that area and treat those areas as a high priority. The agreement should reflect the financial burden of health hazards on the economy of the country. The agreement ignores the huge expenditure incurred because of health hazards due to air pollution. Approximately $5.9 billion is spent on health issues due to transport and energy per annum in Australia and its economic impact on the bottom line of the country should be reflected in the agreement (Vlies, 2022). The agreement should also focus on vulnerable areas like Hunter Valley in New South Wales which is targeted not only by environmental pollution but also by social and economic disparity. Being a hub for coal mining, it causes tremendous air pollution due to the emission of hazardous and toxic fumes, and huge amounts of waste (amansw.com.au, 2022).
References
.png)
Essay
EBP107 Evidence-Based Practice Assignment Sample
Instructions:
Students are required to conduct an evaluation of one journal article in an essay format. The article may be the selected one used in Assessment 2 Article Summary task. Alternatively, you may choose to select an article of your choice from the range of research articles supplied for the previous Assessment 2 assignment.
This task requires using one of the critical appraisal tools supplied from a link below. Choose an appraisal tool that fits the chosen article to evaluation.
• CASP. (n.d.). CASP Checklists. Retrieved from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
• Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (CEBM). (2014). Critical Appraisal Tools. Retrieved from
https://www.cebm.net/2014/06/critical-appraisal/
• Equator Network.(n.d.). Reporting guidelines for main study types. Retrievedfrom
http://www.equator-network.org/
• Joanna Briggs Institute (n.d). Critical appraisal tools. Retrieved from
https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools
Essay Format:
The article evaluation must be presented in an essay format, with an introduction, body and conclusion.
Introduction:
The introduction must introduce the article, including proper referencing of the article, and a discussion about why you chose that article to evaluate.
Body:
In the body of your essay you must:
1. Use the critical appraisal tool you have chosen to evaluate all the sections of the research study, including the title, abstract and declarations.
2. Throughout the body of your essay you are to refer to the chosen critical appraisal tool and use additional references to support your evaluation. Subheadings may be used.
3.. Provide a referenced definition of Evidence Based Practice (EBP), and a recommendation as to how well the findings from this study may be incorporated into EBP. Give reasons and offer evidence to support your evaluation.
Conclusion:
A brief discussion of the overall quality of the study with reference to the strengths and weaknesses as outlined in the body of the essay.
Referencing: It is essential that you use appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research. Please see more information on referencing here: https://library.torrens.edu.au/academicskills/apa/tool
Word count: Please include the word count - excluding in-text citations and reference list at the end of the assessment. Please adhere to the word count, if you exceed 1,500 words (+10%), the excess may not be graded.
Appendix: Include a copy of the completed critical appraisal tool as an appendix.
Solution
Introduction
This study aims to conduct a critical evaluation of a journal through the assimilation of the CASP tool. Long et al., (2021) in this comment that CASP is a potent tool that is employed predominantly to assess the limitations and soundness of qualitative research methodologies. In this particular context, a journal is integrated that identified whether the consumption of eggs and cholesterol impacts the cardiovascular health of an individual. This particular article has been chosen here to know whether the consumption of egg is dangerous for the people having cardiovascular disease. The essay aims to bifurcate the legitimacy and transparency of the study and its applied method critically for best assignment help.
Discussion
Employment of critical appraisal tool
To evaluate the essay critically CASP checklist has been incorporated as it embodies some prompt questions to assist the research study effectively. After going through the journal systematically, it can be said that the study from the very beginning made it absolutely clear whether the consumption of eggs and intake of cholesterol plays a vital role in the cardiovascular health of an individual. Additionally, the aims of the study clearly state that it aims to associate the study with cholesterol intake and morality rate from CVD in the US population.
In this particular study, the cohort is recruited in a coherent manner. The NIH-AARP study was a vehement perspective cohort that was integrated between October1995-may1996 when a questionnaire was forwarded to around 3.5 million AARP (Zhuang et al., 2021). The final analytic cohort consisted of around 500,000 participants and this particular study is assimilated as per the strengthening of the conducting of observational inculcation in epidemiology statement. Additionally, through answers to study-oriented mailing, the “US postal service national of address database”, and direct conversation with cohort members, all the participants were scrutinized for the changes in their address.
The researchers integrated data of 521,120 participants from the NIH AARP diet and health study while integrating a median follow-up of over 15 years to examine the impact of egg and cholesterol intake with specific morality. However, since it is a "randomized controlled trial with random modeling," the approximation cannot be considered to be entirely accurate.
The result demonstrated around 129,328 deaths including 38,747 deaths during the integration of median follow-up of over 15 years. It demonstrated that both whole egg and cholesterol intake were positively associates with all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality. Additionally, a multivariable adjustment model was integrated to minimize the bias to a comprehensive extent.
It was found that the additional half of a whole egg daily was around 1.07 for cancer, 1.07 for CVD, and 1.07 for all-cause mortality (Zhuang et al., 2021). Mathematically speaking if an individual consumes 300 mg of dietary cholesterol maximized around 19 percent, 16 percent, and 24 percent mortality rate associated with all-cause, CVD, and cancer.
The methodology has effectively integrated multivariable models and meditation models to individually examine the impact of cholesterol and egg simultaneously. In both cases, the statistical analysis puts forward a positive correlation of morality rate with consumption of eggs and dietary cholesterol. However, the approximation cannot be regarded as being truly accurate nevertheless, as it is a "randomized controlled trial with random modeling". Here, the confidence intervals give a "range of values" rather than a "single value" for the forecast, allowing one to assess the degree to which the conclusions of the study may be believed.
The follow-up has been maneuvered for more than 15 years (Zhuang et al., 2021). It enables the researchers enough time to establish the proficiency of their findings.
The result states that the intake of eggs and dietary cholesterol are closely intertwined with CVD, all-cause, and cancer mortality. Hence, all individuals must limit their cholesterol intake while incorporating egg white instead of whole eggs to lead a healthy life. In terms of the result, the table of Baseline Characteristics and All-cause Mortality has been mentioned properly. Additionally, the abbreviations and table headings were noted to retrieve accurate outcomes. The research examined and analyzed the relationship between the “consumption of eggs and cholesterol”, particularly in terms of morality from various causes among 521,120 participants with a “mean follow-up” of 16 years. The results are quite precise as the study utilized “cause-specific hazard models” for considering competing risks to calculate hazard ratios as well as 95% confidence intervals of “all-cause” and “cause-specific” mortality based on different categories of consuming egg and cholesterol. However, as it is a “randomized controlled trial with random modeling”, the approximation cannot be considered genuinely accurate. A “range of values” is provided here by the confidence intervals instead of a “single value” for the forecast, hence allowing to determine how much the research findings can be trusted.
The results of this study are identified to fit with other accessible evidence. It is so as the ultimate outcomes have demonstrated consistency with joint research of “6 prospective US cohorts”. The study has finally reported that consumption of an additional half egg/day is closely associated with an 8%, 6%, and 8% higher risk of CVD mortality, incident CVD, and all-cause mortality. Meanwhile, a similar pattern has been reported by the study for the association between consuming non-fried and fried eggs while observing an inverse alliance between consuming “egg-white substitute” with mortality. Therefore, underscoring the negative impact of “egg yolk” and “cholesterol” in premature deaths. The research has explained the clinical relevance well and it has been observed that the study would not exceed a statistical significance. Additionally, the “internal validity” of this research was high as it identified and presented the entire structure in an appropriate manner. The protocols were analyzed and approved despite the actuality that all the collected data have a significant value. However, the research is not limited to any particular population and can be applied to the local population. Additionally, the study is that its external validity failed to meet the standard level, though it has an enormous impact on the health and longevity of human beings. Therefore, it can be used for acknowledging and reducing risks associated with diet and lifestyle.
Critical evaluation of the appropriateness of the chosen cohort study
In this study, 521,120 participants were involved from all across the United States. The study has finally reported that consumption of an additional half egg/day can cause a higher risk of CVD mortality, cancer, and all-cause mortality. As stated by Zhuang et al., (2021), it is important to limit “cholesterol intake” and replace whole eggs with egg whites or other alternative sources of protein to facilitate “cardiovascular health” and “long-term survival”. On the other hand, Zhong et al., (2019) have included and analyzed 29 615 participants to shed light on the associations of egg consumption and dietary cholesterol with the “incident cardiovascular disease” and “mortality”. However, the result showed that a higher consumption rate of “dietary cholesterol” can increase the risk of incident CVD as well as all-cause mortality among US adults, particularly in a dose-response manner. Additionally, Panizza et al., (2018) have created “The Healthy Eating Index-2015” for assessing the accordance of dietary intake with the “Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA) 2015–2020”. The result showed that there is an inverse association between high “HEI-2015 scores” and “risk of mortality” from CVD, cancer, and all-cause for both men and women. Moreover, Mazidi et al., (2019) have identified that there is no direct link between total as well as CHD mortality with egg intake in men and women. The study has also resulted that egg intake has a “reverse association” with stroke mortality among men, though it is not significant among women.
Evidence-based practice
EBP is a procedure employed to review, examine and transcribe the latest scientific research. The key goal of this particular process is to integrate the best possible research into medical and clinical practices. It enables medical professionals to integrate informed decisions (do Vale et al., 2021).
The study integrates a positive correlation between mortality from all-cause, CVD, and cancer, and increased in-take cholesterol. However, they completely discarded the fact of the difference between good cholesterol and bad cholesterol. It integrated a hypothesis and considered cholesterol derived from the egg as LDL. On the other hand, the study also completely discarded that the majority of the cholesterol in our body is made by the liver itself. Hence, a series of discrepancies is prevalent in the present study. Numerous reports suggest that the cholesterol derived from eggs is not LDL. On the other hand, the liver is being stimulated to formulate cholesterol by saturated and Trans fat in our diet which acts as a prerequisite for the body (Li et al., 2020). Additionally, the nutrients present in Eggs such as Lutein, zeaxanthin, choline, and others work wonders for the eye and brain. However, it cannot be denied that the fried egg puts forward a positive correlation with bladder cancer. The risk is mitigated automatically when it is consumed or boiled (Chen et al., 2021). Therefore, one egg a day can be a belling in disguise to meet the prerequisites of protein, vitamins, and good cholesterol. However, people suffering from cardiovascular disease must take expert opinion and consumes it in modulation. It is also recommended that the egg must be consumed boiled rather than fried to mitigate the chances of cancer.
Conclusion
In this particular situation, a journal has been included that determined whether egg and cholesterol consumption affect a person's cardiovascular health. Since it is a "randomized controlled trial with random modeling," the approximation cannot be considered to be entirely accurate. However, the researchers integrated data of 521,120 participants who have been followed up of over 15 years to examine the impact of egg and cholesterol intake with specific morality, hence, the result of the study clearly shows a strong temporal succession between the research cohort and the result which shows the reliability of the research outcomes. However, since it is a "randomized controlled trial with random modeling," the approximation cannot be considered to be entirely accurate.
The confidence intervals in this case provide a "range of values" rather than a "single value" for the forecast, enabling one to judge how much the study's findings may be trusted. Hence, the recommendation has been modified after the identification of the gap in the study.
References
.png)
Research
NSG3NCI Chronic Illness Management Plan Assignment Sample
Write a 1000-word report for assignment help explaining what telehealth is and why the type you chose may be beneficial for a client with the described chronic illness
Points to consider:
Definition of telehealth and different types
Why a particular type would be beneficial for your client
The multidisciplinary needs of your client
Description of the client’s chronic illness and why telehealth may be an option
Positive aspects of telehealth for the client
Negative aspects of telehealth or issues for the client
Solution
Chronic Illness
Arthritis is characterized by the painful and swollen swelling of one or more joints. Arthritis is characterized by a range of joint symptoms, the most prominent of which are pain and stiffness, which often get worse with age. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two forms of arthritis that are diagnosed most frequently.
Introduction
Definition of Telehealth and Different Types
Telehealth is the delivery of healthcare and related services through electronic and digital communication technologies, including but not limited to remote medical diagnosis and treatment, healthcare professional and patient education, health information services, and patient self-care. Telehealth makes use of a wide variety of technologies, including remote patient monitoring (RPM), video conferencing (both live and on-demand), "store and forward" electronic transmission, and mobile health applications (Knudsen, 2018).
The desire to stay in touch with patients, no matter where they may be, is what motivates the many manifestations of telehealth. Telehealth is the electronic exchange of health-related information between a care provider and a patient. This broad definition gives rise to several subsets of telehealth. Here are a few of the most notable:
? Patient Tracking at a Distance: In the first place, one of the most important things that telehealth is good for is keeping an eye on patients from afar. Caregivers may keep tabs on their patients' well-being from afar with the help of remote patient monitoring.
? Store-and-forward: The ability to "save and send" telehealth data is also crucial to the concept's existence. Telehealth with a "save and forward" capability improves long-distance access to patient histories and other medical data (Maeder, 2021).
? Telehealth in real time: A doctor may provide round-the-clock, anywhere-in-the-world treatment to a patient via real-time telehealth.
? Remote Monitoring: The use of telehealth to enable patients to have certain parts of their health monitored from the comfort of their own homes is becoming an increasingly popular alternative. Providers are able to address both acute and chronic diseases because to remote patient monitoring.
? Medical advice from a specialist: Because of telehealth, doctors may collaborate remotely to offer more comprehensive treatment options to their patients.
? Telehealth for Rheumatoid Arthritis: One can check in and follow up with the healthcare provider when they have rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thanks to telehealth.
? Radiology and other medical imaging: Sharing medical pictures like X-rays, scans, and more is now much quicker thanks to advancements in telehealth technology. By making these pictures accessible, any board-certified radiologist with network access can evaluate them whenever necessary (Tigerconnect, 2021).
Why a particular type would be beneficial for your client?
Our client who’s suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and has restricted mobility or significant symptoms, such as persistent pain, exhaustion, and joint stiffness, which make it difficult to attend in-person consultations, may find that telehealth’s remote monitoring is an intriguing choice. Telehealth’s remote monitoring has the potential to make receiving treatment for RA less intimidating, which may encourage people living with the illness to seek treatment sooner for any changes in the symptoms they are experiencing (Bergman, 2021).
.png)
Because they don't need to take time off from work or pay for transportation to go to their appointments, persons who have RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis) can save a considerable amount of time and money by using telehealth’s remote monitoring. Appointments with a healthcare provider are also made a great deal more convenient for this patient demographic as a result of this (Saini, 2022).
The multidisciplinary needs of your client
With the help of a team of professionals from different fields working together, patients can get the best possible treatment. With everyone's input, the team as a whole can provide better care to its patients. This strategy is effective because it guarantees that each patient receives personalized attention (Freeman, 2021).
Although members of a multidisciplinary team have to put in more time, the patient benefits from coordinated services and a standard operating procedure (SOP) that enhances the quality of care they get. Communication within a multidisciplinary team makes coordinating efforts simpler, even if not all team members are present when a patient is being treated (Healthie, 2022).
Describe the client's chronic ailment and explain how it might be treated via remote monitoring
There are more than a hundred different varieties of arthritis and related disorders, and our client has a form of arthritis that is not a single disease but rather specifies a mix of symptoms including pain and inflammation in the joints. Arthritis affects people of all ages, races, and sexes equally, making it the biggest cause of disability in the United States. Despite the fact that some forms of arthritis are more prevalent among the elderly, arthritis itself is not a disease that is tied to advancing age (Gogia, 2019).
It's possible that remote monitoring is something brand new for both us and patients. Knowing as much as possible about the tools that will be utilizing to treat patients is the most effective way to provide care. This includes how they operate as well as how the data will be transmitted from the device (Reifsnider, 2020).
.png)
Advantages of telehealth from the patient's perspective
Benefits from telehealth remote monitoring is that they are easily accessible. As was previously said, no travel is necessary, and participation is global. Both of these factors contribute to the efficiency of telehealth visits, since they minimize the time away from work or school that would otherwise be required (Arthritis, 2021).
Concerns or drawbacks that the patient may have when using telehealth
Utilizing these technologies, on the other hand, comes with both positives and negatives, just like any other emerging or cutting-edge technology would. Some of the disadvantages (or restrictions) of remote monitoring are relatively insignificant problems that can be circumvented by service providers or resolved by IT departments.
? There are a few disadvantages associated with remote patient monitoring, such as the fact that it is dependent on expensive technology that not all patients can afford.
? Connections to the internet that can be relied upon are required for RPM systems. It's possible that some of the patients don't have access to broadband internet, which makes it more difficult for them to engage in RPM settings. However, basic vital signs data transmission does not always necessitate the use of broadband. (D’Silva, 2021).
Conclusion
Rapid adoption of digital health records (DHR), which are essential for providing remote care, has accompanied telehealth investments. Half of healthcare leaders (49%) cite digital health records as a major investment, reflecting government attempts to make healthcare data-driven, the report found.
Patients in remote locations now have easier access to care thanks to the widespread use of telehealth following the COVID-19 epidemic. According to the report, the attention is now more on technology driven healthcare, and healthcare leaders are overwhelmingly supportive of the adoption of remote care solutions, with 33% listing a shift to virtual care as one of their top priorities and 51% listing telehealth as a top investment area.
References
.png)
Essay
PUBH6006 Community Health and Disease Prevention Assignment Sample
ASSESSMENT BRIEF
Learning Outcomes
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
1. Examine health promotion principle and strategies.
2. Apply concepts of community capacity building and empowerment
3. Integrate health promotion theories and public health frameworks into practice
4. Demonstrate clear and assertive communication across a range of settings and situations
Instructions
Review one existing community-based health promotion program provided by your lecturer. Then use the assessment template to develop a report drawn from your critical analysis and applying theory into practice. The list of health promotion programs and the assessment template will be provided separately.
1. Critically explain the target group of the chosen program in the following topics based on the evidence derived from the chosen program. Use creditable evidence to support you point of view.
• Explain the target population of the chosen program in the context of community health.
• Explain the importance and significance of this prevention among the target population.
2. Use the following topics to critically analyse the appropriateness of the chosen program. Support your point of view with the evidence derived from the chosen program and creditable evidence.
• Aims and level of disease prevention of your chosen program.
• Health promotion strategies (Ottawa Charter strategies) that had been applied to the chosen program.
• Health promotion activities/interventions that had been incorporated into the chosen program such as lifestyle change program, health education session, screening test etc.
• Community capacity building and empowerment strategies (Laverack’s ladder) that had
been applied to chosen program.
• Main communication channels used in the chosen program.
Solution
REVIEW OF CHECK.PROTECT.CONNECT PROGRAMME
Introduction
Lung cancer has become a burning health concern in modern times due to the poor lifestyle quality of people and the rapid increase in addiction to cigarettes. Symptoms of lung diseases are difficult to understand, and people often avoid them. Check.protect.connect provides an opportunity for people to assess their lung health condition. This study focuses on analysing the health promotion intervention considered under Check.Protect.Connect program based on the Ottawa charter strategies. It includes a description of the aim of this program as well as the targeted population. Based on a conceptual framework, it evaluated the concept of community empowerment considered under this program.
Target population
Community health issues addressed by Check. Protect. Connect program are lung diseases and lung cancer. This program focuses on increasing awareness among the community regarding the symptoms of lung diseases. The targeted population of this program is not specific to age groups as this program tagged people who are suffering from lung diseases or people who are on the verge of developing acute lung disease or lung cancer (Lung Foundation Australia, 2021). This program targets Australia's population for making them access help for their lung diseases at the right time.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide, and in the year 2012, lung cancer became the cause of death for 1.6 million people. As suggested by Parker et al. (2017) Severity of death due to lung cancer increases as per increase in age. The premature death, disability, and loss of productivity due to lung cancer cost $895 million in the year 2017. Thus it becomes necessary to prevent the severity of lung cancer through early diagnosis. As mentioned by Clark et al. (2020), online screening programs allow individuals to access necessary information for understanding symptoms of lung diseases. Lung cancer prevention is necessary for maintaining the wellbeing of individuals as well as increasing awareness regarding the health consequences associated with poor lung health.
Conceptual Framework of a Community-Based Program
Aim
Check.protect.connect program is developed by Lung Foundation Australia, and from the year 1990, this organization is promoting awareness regarding lung diseases among people (LungFoundationAustralia, 2021). This program developed by this foundation aims to increase awareness among people regarding lung diseases and their symptoms as well as the providing opportunity for equality in care for treating and diagnosing lung diseases.
Level of prevention and approach applied.
This program focuses on preventing the diversity of lung disease through increased awareness and engaging with people who are suffering from lung diseases. Making people aware of the necessary measures for maintaining good health of lungs is the primary approach for prevention considered under the program. The activities of this program are divided into three sections, including Check, protect and connect. In the check section, a checklist is provided to the user that allows the user to identify lung diseases (LungFoundationAustralia, 2021). On the other hand, in the protection section, this program allows users access to advice regarding immunization and areas about health concerns needed to be communicated with the health professionals. Whereas in the connecting section, this program means regular communication with people suffering from lung diseases to ensure needed care and support. Health literacy is the approach applied in this program. As stated by Nehemiah and Reinke (2020), health literature allows increasing the capacity of individuals to understand basic health information. Based on their approaches, the support services of the program include communication with respiratory care nurses, communication with lung cancer support nurses, and other lung disease support groups. Further support for regular exercises for people having serious lung conditions also falls under the service provided under this program.
Explanation of health promotion strategies through Ottawa charter strategies
Ottawa charter health has been developed for achieving health promotion for the areas mentioned by the World health organization (WHO) for the betterment of community health. As per this charter, essential resources of good health include peace and shelter as well as education. Further stability income, availability of resources, and equity also fall under the essential resources as per the charter (Betterhealth, 2021). Strategies for health promotion mentioned under this charter include advocacy, enabling, and mediating. Advocacy approaches of health promotion focus on favourable conditions in terms of environment, cultural and social equity, and economic stability.
On the other hand, enabling a focus on ensuring equality in health services through a supportive environment. Whereas meditating focuses on prerequisite the prospects of health that cannot be addressed by the health sector alone. This strategy ensures coordination of better health service providers and the government for the delivery of health care aids. Based on these strategies, promotions activities under Check.protect.connect programs can be evaluated. The advocacy focuses on enhancing people regarding the right care, which is done through the check stage of this programmer.
On the other hand, enabling people to avail the right facilities within protecting strategy of this program where people are provided an opportunity to communicate with health service providers to access aid. On the other hand, mediating focuses on maintaining coordination which is included under the connect stage of health promotion under this program. Ottawa charter focuses on priorities of health for delivering successful health promotion (Betterhealth, 2021). These areas include building public health policy, creating a supportive environment, strengthening community-based activities as well as developing personal skills, and on the other hand, reorienting health services and moving into a healthy future fall under prioritisation areas under the charter. These areas are considered under the Check, protect, connect program. This program focuses on enhancing public awareness and allowing people to access the required assistance to cope with lung diseases. Further, to avoid issues due to lack of support services to individuals diagnosed with lung diseases and cancer through the science strategies, this program allows supportive aid to people.
Analysis of health promotion activities
The health promotion activities considered under the Check, protect, connect program are based on increasing health literacy and bringing positive lifestyle changes. Health promotion activities considered under the program falls under the criteria of health education and lifestyle change. As opined by Pizon (2019), health education allows people to identify which habits are good and bad for health. Health education allows improving health awareness among people and reducing risk behaviors. Check, protect, connect programs focus on increasing health awareness among people regarding maintaining a healthy lifestyle for avoiding lung diseases. The services provided under the program include special services for users with lung cancer. The other support service provides an expert opinion regarding health conditions and allows users to identify the symptoms of lung disease. As per the views of Haber (2019), health awareness regarding the activities that lead to health wellbeing provides an opportunity for healthy aging. The severity of lung disease in spread the overall age groups, thus guiding people for bringing healthy changes and identification of symptoms at the right time fall under the primary health promotion activities of this program. Health promotion activities considered under this program for best assignment help, focus on improving lifestyle quality of service users for reducing occurrence of lung diseases.
Concept of community empowerment
The strategies considered under Check, protect, and connect program focus on sustaining individuals' awareness of lung diseases. Based on Lavarack’s ladder, this community empowerment made through the strategies considered under the program can be defined. The primary motive of Lavarack’s ladder is to increase community-based interaction that leads to community empowerment. In the considered health promotion program, lavarack’s ladder is applied for establishing interaction between health professionals and people for making them understand that the symptoms of lung diseases and healthy lifestyle need for prohibiting lung diseases. As mentioned by Starns(2019), equality is care facilities that allow delivery services equally to individuals. This program also focuses on maintaining equality by ensuring accessibility of health assistance services to users.
In community programs, communication channels play a vital role in understanding communication needs. As mentioned by Swanwick & McKimm (2017), communication allows understanding the needs based on the need for health interventions that can be further developed. In the Check.Protect.Connect program the service users are communicated through online platforms as well as media platforms. The media platform is utilized for making users aware of the changes in services, and the online platform for making people access the services. Based on the forms filled up through online platforms, different services are provided to users as per their health needs. Online platforms allow better engagement with service users. Online platform provides opportunity to engaging with large target group.
Conclusion
Thus it can be concluded that the Check, protect, connect program focus on maintaining user interaction through online communication platforms. This program includes advocacy, enabling, and mediation of an approach to understanding the risk behaviours that lead to lung diseases. This program allows people to understand the symptoms, whether they have any lung disease or not. Further, this program ensures advocacy that helps to rescue lung cancer which has been a burning health concern. This program includes advocacy as well as focus on enhancing health care policy as well as assistance by ensuring support for people dealing with lung diseases.
References
.png)
Case Study
HAS108 Health Assessment Sample
Individual/Group Individual
Length 2000 words (+/- 10%)
Learning Outcomes
The Subject Learning Outcomes demonstrated by successful completion of the task below include:
b) Identify and demonstrate interview techniques used to enhance communication during history taking
c) Discuss ways to incorporate health teaching as part of the health assessment
d) Perform a thorough and accurate holistic health assessment
e) Discuss the importance of understanding the diversity of society and cultural safety approaches that influences the approach to healthcare
f) Recognise elements of the development of person centred care plans
This assessment requires you to answer 3 questions. The questions are the same for each character however, given the different circumstances, socio-economic and medical histories of the characters, each case study is to be uniquely considered.
Short Answer Questions for case study assignment help -
1) Using resources provided in this subject, identify and explain what information is needed to a gain a more comprehensive past history for your chosen video character. Consider the patients level of health literacy and cultural safety issues in your answer.
2) Based on the information given for each character, identify and explain what abnormalities/concerns you can identify in the physical observations and patient history.
3) Identify and explain what additional physical assessments are needed in order to facilitate a diagnosis for your chosen character, and identify and describe what body systems need to be explored further.
Theo
PULSE: 70 bpm (resting), 100 bpm (on exertion).
TEMPERATURE: 37.5 ?C
RESPIRATION: 18 (Theo reports thick secretions, ‘worse when getting up in the morning’, primary auscultation- audible moist cough that Theo states ‘is hard to get rid of’).
SaO2: 95% room air (RA)
WEIGHT: Body Mass Index (BMI) 16.
BP: 100/70 mmHg
CNS: GCS 15
GENERAL APPEARANCE: Dishevelled, tooth decay, nicotine stained fingers, initial visual inspection
Theo observed to have to have minimal body fat.
Mobility: ambulant does not appear to have any deficits.
Urinalysis: Leukocytes ++. Slight Specific Gravity increase of 1.010.
Solution
1. Title and a brief summary
Personal Improvement Plan
From this project, it can be understood that my BMI score is increasing gradually (32.4). This is quite high. So, to improve my health, I have set an aim to reduce my weight by 5 kilos in 5 weeks and increase my daily walking by 10,000 steps more daily. In this project, I have steed various ways through which I have achieved this aim of mine.
2. Introduction - Why did you choose this project?
a. Problem description
My major problem is my increased body weight. I need to lose some weight since my Body Mass Index (BMI) is much higher than what is considered healthy for someone of my age and height (health.gov.au, 2021). My doctor says that the back discomfort I've been having is related to my weight gain and that my latest blood test reveals an increase in cholesterol. As a result of my recent commitments, I have been too busy to maintain my usual level of physical activity. When I was routinely going to the gym, at least twice a week, I never had the back issues I'm having now. After a consultation with a nutrition specialist, I will also make certain lifestyle adjustments under my power, such as giving up junk food and switching to vegetables and fruits.
This is a major issue. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2016, over 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and over 650 million were obese. In the same year, 41 million children under the age of 5 were overweight or obese (Who.int, 2021). The prevalence of obesity has more than tripled since 1975, and it is a major risk factor for several chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer (Who.int, 2021). The increasing prevalence of obesity has been attributed to several factors, including changes in diet, sedentary lifestyles, and environmental factors.
b. Available knowledge
From my problem, I understood that I have a major issue with obesity. Previously I did not know the negative impacts obesity can have on our bodies. After some, I understood that one of the most significant impacts of obesity is an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. Obesity can also lead to physical limitations, such as reduced mobility, joint pain, and difficulty performing everyday activities (Gibbons et al. 2019). In addition, obesity can negatively impact mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
c. Rationale
Lewin's Change Management Model is a framework for managing and implementing change within an organisation. The model consists of three stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing (Bashori et al. 2020). The unfreezing stage involves preparing anything for change by creating awareness of the need for change and breaking down the existing mindset and habits. During this stage, I will develop my aim to reduce my weight and enter into a healthy lifestyle. The changing stage involves implementing the change, which may involve changes to organisational structure, processes, or culture. During this step, I will change my eating habit and regularly go for a walk to make up to 10000 steps daily. Finally, refreezing involves stabilising the new changes and embedding them into the culture (Cone & Unni, 2020). Under this step, I will make new changes, such as consuming vegan foods and giving up on meat.
d. Aims statement
My proposed aim is to “Reduce my weight by 5 kilos in 5 weeks and increase my daily walking by 10,000 steps more daily”.
3. Methods - What did you do?
a. Context
Previously when I did a check-up, I understood that my BMI score was 32.4, which is higher than a normal person's. With a score above 30.0, I understood that I have obese. A high body mass index (BMI) score indicates being overweight or obese, and it can have several negative impacts on an individual's health. A high BMI can increase the risk of developing chronic health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, and some types of cancer (Dadar Singh et al. 2022). However, after fulfilling my aim, my BMI score decreased to 26.2. Though it means that I am overweight, I have completed my goal and will focus on having a healthy weight range in the future. To measure my BMI. Firstly I used a scale to measure my weight accurately. Before stepping on the scale, I was sure to remove any heavy clothing, shoes, or accessories. I recorded my weight in kilograms (kg). Then, I used a measuring tape or a wall-mounted height rod to measure my height accurately. Next, I used the following formula to calculate my BMI: BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m))^2. Finally, I interpreted the data and determined my BMI.
b. Intervention/s
To ensure that I can lead a healthy lifestyle, I will take various measures. The interventions include walking 10,000 steps more daily. I will also ensure that I will consume less junk food and healthier food. This will be done by including more fruits and vegetables in my diet. Eating junk food regularly can lead to obesity, which can increase the risk of developing chronic health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and some types of cancer. Junk food can also negatively impact mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. The tools that have been used to measure BMI in this project are digital or analogue scales to measure weight accurately, a measuring tape to measure height accurately, a calculator or a BMI chart to calculate BMI based on the weight and height measurements and BMI apps that use the height and weight inputs to calculate BMI automatically. It is important to note that BMI is not a perfect indicator of an individual's health, as it does not consider factors such as muscle mass, body composition, and overall fitness level. Therefore, it should be used as a general guideline and not as a definitive measure of an individual's health.
c. Measures
I want to keep track of the following for a week or two before I start my 5-week programme to establish a baseline. The data from these items will be used as part of my benchmark.
? My BMI
? Average calories I consume in a day
? Factors include the number of drinks I have each week, the amount of coffee and water I drink, and other things.
? In the course of my normal, regular strolls
? What I eat in terms of produce daily
? My consumption of high-fat, high-sugar, and high-salt meals
I just had a blood test done to get a sense of how my blood is doing right now, and I want to do another one at the end of the five weeks to see if anything has changed.
d. Analysis (if relevant)
From the entire effort given, I have witnessed that, to a certain extent, I was able to improve my health condition. Previously I was obese, but after achieving my aim, I saw that I had become an overweight person. Previously my BMI score was around 32.4, and after achieving my goals, the BMI score reduced to 26.2. My BMI score was reduced by 6.2 scores. This was a huge achievement for me. However, another goal of mine was to walk 10,000 steps more daily. This was not possible for me. With my maximum effort, I could only make up 5000 steps more daily. I tried to control my junk food craving and started having only vegetables and fruits. However, it seemed impossible. So, to please my taste buds, my nutritionist gave me permission to have junk food once a month. In the future, I wish to control all these cravings and keep a target of becoming a healthy person with a normal BMI score.
e. Ethical considerations
Losing weight was a personal goal for me, but ethical considerations need to be taken into account. I ensured that I did not use fad diets or extreme weight loss methods. This is because it can be dangerous and harmful to health. Another ethical consideration is the pressure to conform to societal beauty standards, which can lead to body shaming and discrimination against people who do not fit those standards (Brytek-Matera et al. 2019). Additionally, there is a concern about weight bias and discrimination in healthcare, which can affect the quality of care that individuals receive. It is important to approach weight loss in an ethical and responsible manner, focusing on health and well-being rather than conforming to societal expectations or harmful weight loss methods.
4. Results - What did you find?
BMI
.png)
.png)
Figure 1: BMI Score Improvement
(Source: Author)
The table above shows my improvement in BMI score week-wise. The BMI score in 5 weeks has been stated above. From the graph above, it can be seen that my initial BMI score in week one was 32.4, it can be seen that my BMI score in week two was 31.9, it can be seen that my BMI score in week three was 29.6 it can be seen, that my BMI score in week four was 27.3 and it can be seen that my BMI score in week five was 26.2. From the graph, it can be witnessed that my improvement from week one to week two. However, from week two to week three and week three to week four was quite impressive.
Steps covered
.png)
.png)
Figure 2: Steps Covered
(Source: Author)
The table above shows my improvement in steps covered week-wise. The steps covered in 5 weeks have been stated above. From the graph above, it can be seen that I covered around 2000 steps more daily in week one, it can be seen that I covered around 3210 steps more daily in week two, it can be seen that I covered around 4200 steps more daily in week three, it can be seen that I covered around 3600 steps more daily in week four and it can be seen that I covered around 4980 steps more daily in week five. From the graph, it can be witnessed that my improvement from week one to week two. However, from week two to week three and week three to week four was quite impressive.
5. Discussion – What does it mean?
a. Key findings
Losing weight was a challenging task for me, and it was not uncommon to lack motivation at times. There are various reasons I struggled with motivation when it came to losing weight. It was due to a lack of my self-discipline, not seeing results fast enough, or feeling overwhelmed by the process. The main reason was due to the absence of a support system. Losing weight was challenging, and having a support system of friends or family can make the journey easier. Again, it was due to a lack of enjoyment in the weight loss process. When exercise and healthy eating became a chore, it was easy to lose motivation. Finding an activity or food that I enjoy can make the process more enjoyable and sustainable. It was not uncommon to hit a weight loss plateau, where weight loss stalled even with consistent efforts. This was discouraging and led to a lack of motivation for me. For me, eating is a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or other emotions. Breaking this habit was challenging and led to a lack of motivation. Initially, I did not know how to lose weight effectively, which led to frustration and a lack of motivation. Understanding nutrition and exercise was important for success.
b. Interpretation of results
From the entire process, I have understood the negative impacts of junk food and unhealthy lifestyles that can hamper the human body. With excessive consumption of junk food and an unhealthy diet, I became obese with an increased BMI score of 32.4. From research, I understood that according to my age, my BMI score was quite high compared to normal. So, to focus on my health, I developed a plan and set an aim of losing 5 kilos in 5 weeks. After 5 weeks, from the data presented above, it can be stated that I have improved a lot, although I still have to take more action. However, I witnessed that there are still many areas of improvement that I have to focus on. For example, in week three, my steps covered was 4200, whereas, in week 4, it was around 3600. This reduction in the steps was because of my busy schedule. I was so engrossed in my office that I could not give much time to my health. Due to a meeting, I had to delay my walking time. This issue was resolved in the next week as my steps covered increased to 4980. However, this did not have an impact on my BMI score in week 4 because I kept my diet intact. I did not consume any junk food and only ate vegetables and fruits.
c. Limitations
One of the major challenges that I faced while doing this project was searching for a good nutritionist who could guide me in this journey. Another issue that I faced while doing this project was giving up on my favourite food. This was initially very difficult for me as I used to live on junk foods. Losing weight also required lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and healthy eating habits. These changes were initially difficult for me to implement and maintain. I also received unsolicited advice from others about their weight loss journey, which can be unwanted and demotivating.
d. Conclusions
This project has positively impacted me as I was able to improve my health and lead a healthy life. I could improve my diet and avoid junk foods that were hampering my health.
Losing weight reduced the risk of chronic conditions and improved my overall health. Carrying excess weight can put stress on joints, making it difficult to move around. Weight loss helped me to reduce this stress, making movement easier and less painful. My back pains were alos reduced. It also helped me to reduce or eliminate sleep disorders, leading to better sleep. I will work to maintain a healthy weight range in the future, even if I am now overweight. I want to become a healthy person with a normal body mass index score in the future by controlling my junk food cravings.
6. Critical reflection
My realisation of how unhealthy my life has been was one of the surprises I encountered throughout this transition journey. Although I've always held the opinion that nutrition has no direct connection with back pain, I was surprised to see that various writers have focused on the causes of back pain (Pasdar et al. 2022). The more I've dedicated myself to making this transformation, the more I've learned about various diseases, and health conditions that I may face in the future or that may enhance the chances of their occurring. As a result, people are more likely to believe that they can avoid the ill effects of any area of their lives by just making an effort to do so.
Over the first three weeks of putting the change into action and treating the issue, I mastered the insights that led to its success via in-depth research and concentration on the main keywords involving health, BMI, contributing factors and causes, and prevention. Pain in the axial lumbosacral region, pain in the radiculopathy, and pain that is transferred from elsewhere in the body are the three most common causes of low back pain (Urits et al. 2019). Back pain affects between 10 and 30 per cent of adults in the United States in any given year. This realisation has motivated me to continue taking preventive measures and making efforts to ensure that I do not become one of the many people whose day-to-day activities are hampered by back pain brought on by the additional weight they are carrying, which is the case for me because of the additional weight I am carrying. (Attention is paid to preventive measures)
In addition to this, I came to the conclusion that before I could consider the new method to be completely functioning, it would need a significant amount of time and effort on my behalf to include all of these new aspects into my routine and maintain a record of them. I neglected to carry out what are known as "initial background studies." I should have spent more time researching the issue before making a change, such as how to take into consideration my age in the transition process or how difficult my exercises would be during the first week due to lactic acid and agonising pain in my body. I should have done this before making a shift. When a change is launched, one of my study interests is to investigate the influence of factors such as social pressures, structural adjustments, and preparation for change (Rogerson et al. 2016).
What went right:
- Results are seen during the first three weeks
- I felt better in general (Back pain, general happiness, and similar)
- There wasn't a lot of variation in the process I mapped.
- As a result of my investigation and implementation of the structured change, I now understand the issue better and am less resistant to future adjustments (Kept my motivation high)
? The responsibility for the transition and the difficulties lay with me.
I feel that I have gotten a great lot of insight into the process, and if I were to do it again, I would probably change it so that it is relevant to a wider range of situations. Despite the fact that the change I decided on is extremely individualised, I would want to expand more while yet being focused on the same topic matter.
If I were to carry out this project once again, there are a few aspects of it that I would change in order to guarantee that I get the results I want and am able to classify it as a triumph.
- Some of my measurement tools may be off, so I will have to upgrade them.
- I want to investigate transformation projects of greater length, during which I expect to include outside parties for advice and guidance.
- Nothing else will be ruled out entirely at this time.
- In the process, I will examine rewards.
- I plan to evaluate a potential shift in my lifestyle on many occasions, taking into account the potential influence of external factors like climate, season, and time of year.
? I'd analyse my plan's immediate and distant outcomes.
In addition to this, I would consider how the medication would influence my eating habits, what kind of assistance from the outside world I might need in order to be really effective if a customised or standard solution would be preferable, and the total cost of the process (Chang et al. 2017).
References
.png)
Essay
HEAPH6007 Public Health Ethics Assignment Sample
Task: Health Promotion Program Plan: In this assignment – as an actual/potential health promotion professional/practitioner - you are going to explore/develop a population health promotion strategy to address an identified health need in your community that reflects the health need and target group that you identified in both Assessments 1 & 2. There are two different scenarios here. These being:
1. It may be an existing/recent comprehensive health promotion programme that you are detailing and critiquing.
2. It may be a purely 'hypothetical' (mock) example of a comprehensive health promotion that you would like to see in practice in your community.
Whichever scenario you choose - it is probably best to highlight (early on) in your assignment which option you are adopting and identifying your role within it.
Plan a program that is based on the principles of comprehensive health promotion process; including community development, community stakeholders and their various roles - and include your own role.
Your Program Plan will include:
• the background to the problem (what do we know about the problem and how to address it)
• the program goal (what you hope to achieve)
• objectives (what factors you need to address to achieve the goal)
• delivery strategies (what you are going to do)
• an evaluation plan (how you are going to know that you have been successful)
Word count - 2000 Words
Solution
Introduction
Research conveys that asthma is an international health issue though it is not much acknowledged internationally. Globally 300 million people are suffering from asthma. Extra mucus in the airways causes coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing (Kuruvilla et al. 2019). There can be life-threatening asthma attacks for which consultation with the doctor for the person and symptoms is required. The paper thereby will share its concern for health promotion programs for asthma where it will offer a background of the problem to identify goals and objectives so that delivery strategies can be identified accordingly. An evaluation plan even will be justified to understand the success or failure of the health promotion program.
The Background of The Problem
In an emergency, a person with an asthma attack can apply some of the techniques like sitting up straight, avoiding triggers, calling the emergency number, and exercising the Buteyko breathing technique (Abrams, 2020). Due to several factors like weather changes, stress, the side effect of medication, allergies, colds, and flu, asthma can take place. Considering the illiteracy or ignorance regarding asthma and its prevalence internationally, a health promotion program for the same is much required. Understanding the causes and symptoms of asthma and its prevalence in society, it is very important to address the issue properly. As it is stated that prevention is better than cureness thereby avoiding severe asthma attacks, it is better to address the disease from its route. The health promotion program needs to focus on every possible prevention strategy to make society free from this disease as much as possible (Hartley et al. 2020). The main focus of the program needs to be acknowledgment or awareness in society regarding its severity, causes, and symptoms to be well aware of.
Program Goal
The program aims to assist people with asthma in initiating asthma control to reduce asthma rates and deaths. It even objectifies inclusive health promotion programs where communities like military members, children, pregnant women, senior adults, Hispanic individuals, and black individuals get included.
Objectives
The main objective of this essay assignment help is to have effective strategies to make the health education program successful. The strategies thereby would be-
• Establishing managerial and support systems in the societal structure
• Offering appropriate health and mental health services for people with asthma
• Offering asthma education with a proper awareness program (Backman et al. 2019)
• Providing a healthy environment to make it safe to not to trigger asthma
• Suggestion for physical education and activity to reduce the chances of the attack
• Proper coordination between all the stakeholders of the society to make it acknowledged by everyone
Delivery Strategies
In order to meet the aim and objective of the health promotion program, the program adopts EXHALE strategies for controlling asthma which eventually can Educate for asthma self-management, eXtinguishing secondhand smoke and smoking. It even confirms Home visits to trigger reduction as well as self-management education to Achieve proper asthma guideline-based medical management to confirm proper Linkage to co-ordinate with care across the setting with a special focus on effective Environment policies or practice to reduce at work, outdoors, or indoor asthma triggers (AAFA, 2022).
Initiating community health, the health program would accommodate the promotion of updated guidelines as per caregivers, patients, and clinicians. It is further been objectified that the promotion of guideline-based asthma care for referred communities or groups gets accommodated in the process (Danvers, Lo, & Gaillard, 2020). Communication with community health workers for reducing asthma triggers at home is important to comprehend. Further launching three national awareness campaigns for lung infections like flu to impact on asthma, controlling symptoms, and use of asthma inhalers and allergic asthma for children are important strategies to include. Most importantly the community health program needs to take care of developing education with effective resources to make the community health promotion program successful to protect the community or society free from such types of issues.
For delivering strategies, proper strategy development is an important consideration to make the pre-planning aspect effective. In the referred strategy delivery the program has taken the help of Asthma Prevention Management And Treatment Communities Approaches For New Millennium and Two National Asthma Education And Prevention Programs (CDC, 2022). 8 interactive components are even accommodated to coordinate the health program.
Strategy development is the pre-planning and planning stage where a strategy implementation is most important to make the health promotions program successful while proper execution. In order to serve the referred communities who are directly involved with the entire concern, the health promotion practitioners need to adopt proper implementation strategies which need a team effort to involve parents, students, medical staff and faculty, medical administrators, social administrators, etc can be used for developing the plan to address asthma for a particular society to make the program tailored as per the need. Such narrowing down can be even helpful to make the implementation or execution successful as every strategy might not be feasible or appropriate for every society. Hence it is important for the social administrator as well as promotion practitioners and medical administrators to determine which strategies can have the highest priority as per the need of the particular society and can have the support of available resources (CDC, 2022). The society and the medical administrator wherever possible initially need to focus on asthma programs to be conducted in society as much as possible accommodating all stakeholders to get rid of emergency situations or hospitalization. As research conveys that residents, minority populations, and low-income experiences higher emergency and hospitalization as well as death than the general population thereby promotion practitioners with the help of social administrators need to confirm if such type of scenario is involved for this particular health promotion program in that area.
Specific Strategies
1. Establish management and support system for an asthma-friendly society - for proper implementation of this particular strategy, it is very important for the promotion practitioners to identify existing for that area as well as resources to meet the needs with proper cultivation of potential barriers. The promotion practitioners would be responsible for proper coordination regarding asthma activities in the area. He even needs to share coordination with the local administrator and health administrator to confirm if asthma coordination can better be integrated with other types of activities (CDC, 2022). It would be better for the promotion practitioners to share the strategies with District Health Council to get help as per need. It eventually helps him to better convey asthma management in society with all support of the health department considering it a higher priority. He can even opt for the implementation or development of written policies and procedures regarding asthma education as well as management to promote the program which is language and culturally appropriate. He is responsible to cultivate recent records of that particular area to be well assured about the need of that particular community. Conducting a survey can even help him to be particular about every individual to use that regular data in health promotion programs for further betterment. The use of individualized education plans with physical activity can help him to spread awareness or acknowledgment in society to confirm support as per need (Isik, Fredland, & Freysteinson, 2019). It will be better for him to take the help of administrative support to have better trust or loyalty in the society which eventually can help in promoting communication with the society stakeholders to confirm the better provision of care. Availability of private, state or federal funding needs to collect to initiate the success of the program.
2. Provide effective health Services for the community with asthma - accommodating a written asthma action plan for all people with asthma can help to accelerate the success of the program. The plan however needs to be developed by the primary care provider to provide it to the parents most importantly. It even needs to include emergency contact information, environmental triggers, peak flow, monitoring medication, individualized emergency protocol, etc (Chen et al. 2019). Promotion practitioners, however, are responsible to share the plan with appropriate people and medical staff to abide by the family educational rights and privacy act guidelines to get parental permission. It is important for the promotion practitioners to ensure that everyone can have immediate access to medication as prescribed by the physician with the approval of the parents. It is important to use standard emergency protocol for the endangered community in respiratory distress if they are left from an asthma action plan. The promotion practitioners are liable to ensure case management as per the database to provide a full-time registered nurse for an emergency situation as well as proper access to consulting physicians. Proper coordination among all the stakeholders is most important to make the delivery of the promotion program successful (George, 2018).
3. Provide awareness programs and asthma education for people - it is important to ensure that all people with asthma can have education regarding asthma basics, emergency response, and asthma management for which it is important that parents are encouraged in participation of the program. Integration of awareness as well as health education to endangered as well as other people to make them prepare for emergency situations. Assistance needs to be provided for cessation programs as well as smoking prevention specifically for the students.
4. Provide a healthy and safe environment for reducing asthma triggers - promotion practitioners need to convey to society that tobacco is prohibited in all media for all the time (Cicutto et al. 2020). He is even responsible to make people acknowledge about prevention of indoor air quality problems by eliminating or reducing allergenic including tobacco smoke, debris, and dust from the construction as these trigger asthma. The use of Integrated Past Management Techniques for controlling pests can be effective.
5. Offering safe, enjoyable physical education as well as activity opportunities - promotion practitioners need to encourage full participation in physical activities specifically among children as well as modified activities for other endangered people like pregnant women, etc. Proper access to preventive medications before activity and emergency medication immediately needs to be comprehended.
6. Better managing asthma symptoms - education support with proper involvement of all family members can help the promotion practitioner to convey the main aspect of the entire asthma health education program to everyone to fight with the issue from a better position. Cooperation or partnership with local community programs can help the promotion practitioners to reach the vast range of society to confirm a wide grasp of the health education program. Arranging seminars, and awareness through social media, print media, and every possible way can be adopted to make the program successful as much as possible (McClure et al. 2018).
Evaluation plan
Evaluation of the health promotion program is important to confirm the success or failure of the respective program. In order to confirm the same, the promotion practitioner with his team would access perceived health status for 3 months to get an idea about healthy behaviors and changes the society has accommodated through the health promotion program. Feedback-giving programs even can be arranged to understand if the taken policy or awareness seminars served the purpose of the same. By making a comparison between initial data to collected data by every 3 months the success or failure of the health promotion program can best be evaluated. The evaluation plan would surely accommodate the purpose of the evaluation, evaluation questions, and criteria along with time table and work plan to collect data in an effective manner. Such type of inclusion can be much helpful for the health promotion program to be evaluated in a proper way.
Conclusion
The paper has confirmed that asthma can even be life-threatening though it is either ignored or neglected in the societal structure which eventually increases the number of severity or death of asthma. Thereby the health promotion program is been formulated to prevent asthma for which the discussed 6 main strategies are establishing a management and support system for a friendly environment, offering appropriate health and mental health services for endangered people, offering asthma education and awareness program for everyone, offering a safe and healthy environment to reduce asthma triggers, offering safe, enjoyable, physical education and opportunities for the community, effective communication, coordination, and cooperation among all the stakeholders. Promotion practitioners are seen as the main responsible person to execute all the strategies in a better way where evaluation plan is much helpful to confirm success or failure for him.
References
.png)
Thesis Writing
Evaluating Knowledge and Attitudes of Undergraduate Nursing Students Regarding Pain Management Assignment Sample
Chapter 1
Introduction
Given that millions of cancer patients experience chronic pain from illness, surgery, or trauma on a daily basis, unmanaged pain has come to the attention of many healthcare professionals in the oncology environment (Deandrea, Montanari, Moja & Apolone, 2008). This approach of nursing assignment has greatly advanced the development of evidence-based recommendations and research on the management of pain in cancer patients with both acute and chronic illnesses (National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2010). The number of cancer patients experiencing unrelieved pain has been increasing exponentially despite these recent advancements (American Cancer Society, 2009). In fact, the problem has gotten so bad that pain has been designated as the fifth vital sign (American Academy of Pain Management, n.d.).
Unmanaged pain has been highlighted as a significant barrier to the overall care of cancer patients in the oncology population. According to estimates, more than 75% of cancer patients will experience breakthrough pain at some point over the course of their illness (American Pain Foundation, 2010).
Cancer pain, which can result from a variety of problems, severely reduces the quality of life for both patients and their carers (American Cancer Society, 2009). As a result, the Ad Hoc Committee on Cancer Pain of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) said in 1992 that 70% of cancer patients would feel significant pain at some time in the course of their disease, with more than 80% receiving poor treatment. The committee therefore created crucial and urgent guidelines for better pain management in the oncology population by encouraging better pain assessment and treatment abilities as well as formal training and education of healthcare professionals about pain management (ASCO, 1992). The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality likewise revised its 1994 guidelines for the treatment of cancer pain in 2001. Due to the widespread belief that many cancer patients are still receiving inefficient pain relief methods, this was also intended to improve cancer pain management skills. Nevertheless, despite the existence of all these recommendations for efficiently managing cancer patients' pain, uncontrolled pain is still a common issue.
Problem Statement
Pain actually affects all psychophysiological levels and practically all facets of a patient's life, including interpersonal interactions, everyday living activities, and the ability to execute their job. As a result of incapacity, lost workdays, and decreased production, pain is estimated to have a 90 billion dollar economic impact (Turks, 2006). The American Nurses Association (ANA) states that nurses must keep up-to-date on pain assessment and management (ANA, 2001).
So, if pain is the most prevalent reason people seek medical attention, why is it the condition that is treated the worst? Many professionals in the area believe that the inexperience of nurses and doctors is one factor in why people continue to needlessly suffer from incorrect pain treatment (Lasch, Greenhill, Wilkes, Carr, Lee, & Blanchard, 2002). Many medical personnel are unprepared and unmotivated to manage pain adequately, which causes many patients to have a lower quality of life (American Cancer Society, 2009). This ignorance starts with fundamental educational initiatives.
A review of the literature over the past few years has revealed that neither the medical nor the nursing curricula contain enough educational material to adequately equip students to handle their patients' pain demands. This problem could be caused by the fact that nursing professors are not effectively equipped to teach students about pain management, either because they lack understanding in this area or because they do not stay up to date with current evidence-based methods (Ferrell, McGuire, & Donovan, 1993). Additionally, this educational shortcoming may have influenced nurses' unfavourable attitudes about patients seeking pain relief as many of these poorly prepared nursing students went on to become nurses. For instance, many nurses lacked appropriate knowledge of the dosages, applications, and fundamental mechanisms of action of many drugs, as well as other pain management techniques (Lasch, et al., 2002).
Few studies have examined baccalaureate nursing students' skills and attitudes in successfully managing the pain of their patients with reference to the undergraduate nursing programme (Diekmann & Wassem, 1991). Due to a lack of material in their curriculum, these children have also demonstrated a profound lack of knowledge. This curricular gap could be caused by out-of-date textbook content, poor instruction by teachers due to their own ignorance of the subject, or a combination of these factors (Ferrell et al., 1993). The combined impacts of these have a significant negative impact on baccalaureate nursing students' ability to effectively manage pain. Since there are few studies that focus on this topic and many students still struggle to manage their patients' pain successfully, the goal of this study was to investigate the knowledge and attitudes of undergraduate students regarding pain management.
Assumptions
In this study, there are two presumptions made:
1. The majority of cancer patients do not effectively control their pain.
2. By instructing nursing students, pain management will be improved.
Research Questions
The following research queries are addressed in this study:
1. What amount of expertise in pain management do baccalaureate-level nursing students have?
2. How do nursing students feel about treating pain in cancer patients?
3. Is there a connection between baccalaureate students' views and knowledge about how to treat pain in cancer patients?
Definition of Terms
The following terms are defined for this study's purposes:
1. Pain management: According to the American Pain Society Quality of Care Task Force, (2005) any interventions used to comprehend, lessen, and explain the causes of pain are included in pain management.
2. Pain: According to the American Academy of Pain Management (n.d.), pain is a complex combination of emotions, culture, experience, spirit, and sensation that is transmitted through the nervous system and sensed by the body. In other words, each patient who experiences pain is an individual with their own complicated psychological and physical experience.
3. Knowledge: Understanding of facts, concepts, and information acquired through instruction, experience, and learning for a specific purpose (Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary, 2009).
4. Pain attitudes: A steadfast set of convictions and principles that influence how one responds or behaves in the presence of pain (McMillan, Tittle, Hagan, Laughlin, & Tabler, 2000).
Significance of Study
The purpose of this study was to shed light on baccalaureate nursing students' attitudes and understanding regarding pain treatment. Compared to other healthcare workers, nurses spend the majority of their time at the patient's bedside, hence they are crucial in the assessment and evaluation of pain. As a result, nurses must take the lead in bringing about change for better pain management results among patient populations. As a result, the patient suffers if nurses are inadequately trained and unprepared to properly relieve pain. For this reason, in order to enhance patient outcomes and effectively work with other healthcare professionals to treat pain, student nurses need to be well-educated and knowledgeable about pain and pain management.
Chapter II
Review of Literature
This chapter's goal is to give a review of the pertinent literature. The literature reveals a variety of barriers to efficient pain treatment and thereby shows their influence on patient outcomes. The lack of knowledge and the unfavourable attitudes of nurses, nursing professors, and baccalaureate nursing students are among the barriers that have been examined.
Knowledge About Pain Management
Effective pain treatment is being hindered most by nurses', nursing students', and nursing educators' lack of understanding (Chiu, Trinca, Lim, & Tuazon, 2003). In reality, the paucity of information described in early 1990s studies is still blatantly apparent in more current literature. For instance, deficiencies were found in students' responses to questions about the physiology of pain, assessment parameters, and distinguishing between addiction and tolerance and physical dependence, which were based on the criteria for minimally acceptable scores on many pain management questionnaires (Goodrich, 2006). Nurses should do a more thorough assessment of pain rather than just asking patients to rate it. Additionally, there were inconsistencies in the breadth of the material provided about pain in lectures. Most
According to surveys, more than 50% of nurses disagreed that patients were the best arbiters of their own suffering (Bernardi, Catania, Lambert, Tridello & Luzzani, 2007; Rieman, 2006). In fact, the majority of teachers and students admitted that they weren't sure whether to accept that the pain ratings provided by patients were correct. In these situations, nurses and students recorded lower pain scores than what was reported and gave patients lesser medication amounts (Goodrich, 2006; Lasch et al., 2002; McMillan et al, 2000).
Diekman and Wassem (1991) also showed how many nursing programmes had little to no instruction on managing cancer pain, leaving trainees ill-equipped to employ effective pain-relieving techniques. The necessity for more effective integration of pain management content into programme curricula was highlighted by Goodrich (2006), who found that there are various gaps in nursing education addressing pain management and students (both medical and nursing). Additionally, students mentioned that they were unprepared to carry out pain management responsibilities because they had received little to no knowledge about pain management (Ferrell et al., 1993; Lasch et al., 2002). As a result, Chiu and colleagues' 2003 study found that students from Australia and the Philippines also received insufficient pain instruction, which prevented them from properly addressing patients' suffering.
Only a small number of faculty members were found in past studies to have additional expertise in pain treatment. In fact, both academic staff and students said they lacked the knowledge necessary to apply pain management techniques, and supplemental treatments to successfully manage patients' pain. The faculty also concurred that teaching students about pain and cancer pain management would better prepare them for general practise (Ferrell et al., 1993;Lasch et al., 2002). In addition, Ferrell and colleagues (1993) reported that few educators had noticed changes in pain treatment techniques over the previous 20 years and were not aware that new regulations had been put in place to address patients' pain demands. Additionally, educators only minimally met students' demands for pain education in less than one-third of schools, teaching them about current research techniques in pain management (Lasch et al., 2002). The majority of research found that nursing educators must admit that their curriculum lack the requisite course material to adequately train their students on pain management (Goodrich, 2006; Ferrell et al., 1993; Lasch et al., 2002). As a result, curriculum changes are necessary to compel revaluation of current nursing programmes in order to support students' development of stronger pain management skills.
Additionally, a review of the literature revealed that students performed poorly on tests that asked about the administration, dosage, side effects, and mechanism of action of medications (Plaisance & Logan, 2006). Thus, despite improvements in pain management techniques, students showed a lack of pharmacology knowledge necessary for pain management. In order to better relieve pain, doctors, nurses, and students typically underused opioids (Lasch et al., 2002; McMillan et al., 2005). Data also showed that the majority of nurses were unaware that a mixture of medications might be used synergistically to relieve pain in a safe way, without patients experiencing respiratory depression, and they had sufficient knowledge of the World Health Organization pain ladder (Bernardi et al., 2007). Deficits in understanding the maximum dosage of some analgesics, calculating analgesic doses, as well as the mechanism of action and analgesic dosages for pain management, were generally observed in nurses and students' responses in classes (Goodrich, 2006; McMillan et al., 2005; McMillan et al., 2000). Additionally, nurses were not aware that continuous pain medications were more effective at controlling pain than waiting for patients to express it verbally (Bernardi et al., 2007). Additionally, faculty members lacked understanding of the opioids' ceiling effect, the distinction between addiction and physical dependency, and tolerance (Lasch et al., 2002). Since respiratory depression was also believed to be a serious adverse effect of opioid drugs if taken over a 24-hour period, statistically speaking, no changes in scores on the usage of opiates for pain management were seen (Bernardi et al., 2007; McMillan et al., 2005).
Overall, inadequate knowledge and negative attitudes were found to be resolved by continuous education. Nursing knowledge and attitudes can be improved by continuing education in intensive pain treatment, according to McMillan and colleagues' (2005) research. To deliver competent care and enhance patient outcomes, nurses must constantly stay up to date with current treatment guidelines (Diekmann et al., 1991). Although given that knowledge of pain management is a crucial component of effective nursing practise, more research is needed to address the integration of new educational modules in teaching nurses about pain and pain management. The majority of studies showed that there was little correlation between educational attainment and being better at managing pain (McMillan et al., 2005; Plaisance & Logan, 2006). In order to fully teach nursing students at all levels and themselves on how to manage pain in patients, instructors should apply novel educational methodologies. In fact, after receiving pain education, nurses, students, and teachers felt more competent in evaluating pain and applying the right measurements and techniques to successfully relieve it (Lasch et al., 2002; McMillan et al., 2005; Wilkes, Lasch, Lee, Greenhill & Chiri, 2003).
According to two studies, oncology nurses received more formal training on recommended pain management techniques than non-oncology nurses (McMillan et al., 2005; Rushton, Eggett & Sutherland, 2003). Data from both studies indicated that oncology-trained nurses provided better pain management results for patients and were more familiar with suggested practise guidelines than non-oncology nurses. However, neither group of nurses had a good understanding of the pharmacology of drugs used to treat cancer pain (Bernardi et al., 2007; McMillan et al., 2000).
Attitudes Toward Pain Management
Negative attitudes among healthcare workers and students are another another obstacle to efficient pain management. While most cancer patients do experience pain at some point during their illness, as many students and nurses correctly noted, very few thought that pain could be effectively relieved by medication or that it was appropriate for cancer patients to receive maximum tolerated treatment in order to become pain-free (Diekmann et al., 1991). Additionally, nurses believed that patients overestimated their level of pain, thus if a patient was cheery when visiting with the nurses, a lower pain rating was logged and the amount of pain medicine administered was decreased (McMillan et al., 2000).
Second obstacle, as most nurses would permit worries about addiction to influence their administration, pain ratings and drug dosages were also reduced in younger and older patients (McMillan et al., 2005; Rushton et al., 2003). When doctors prescribed patients 24-hour analgesics, a similar pattern was seen. The nurses would let their view that patients should feel agony before receiving medication affect how they gave out painkillers (Ferrell et al., 2003; McMillan et al., 2000). Students and teachers similarly voiced their concern that giving patients too much opioid medication might promote addiction, which was a big barrier to them giving patients analgesics (Lasch et al., 2002).
Inadequate nursing education was another barrier to developing good attitudes for pain care that worked. Nursing professors were more likely to pass along their own misperceptions about the physiology of pain and the pharmacology of drugs to students (who later became nurses) because they were insufficiently knowledgeable about the principles of pain treatment themselves (Ferrell et al., 1993; Lasch et al., 2002). It was also fascinating to observe that instructors and students were more prone to apply their own biases to patients if they were not well trained on pain treatment (Lasch et al., 2002). The data did not make it apparent, nevertheless, if oncology nurses were more sympathetic to patients who were in pain than non-oncology nurses.
Last but not least, the delivery of educational modules shown a significant improvement on attitude questions by nurses. Additionally, it was discovered that attitudes toward recording patients' pain had changed dramatically, demonstrating the need of education in pain management (McMillan et al., 2005).
Summary of Literature
In conclusion, a study of the empirical literature has revealed that the nursing curriculum lacks the instructional content to adequately equip its students to properly manage their patients' pain requirements. This problem can be brought on by the nursing faculty's own lack of readiness to teach students about pain management. Studies found that nursing instructors either lacked expertise in pain treatment or did not stay current with evidence-based procedures. Furthermore, since many of these ill-prepared nursing students went on to become nurses, this educational fault might have crept into their professional conduct, showing extremely negative attitudes and subpar pain management abilities. Therefore, more focus must be placed on teaching students about fundamental drug action processes, doses, and uses, as well as other pain management techniques.
Chapter III
Methods
The study's methodologies are detailed in this chapter. This comprises information about the sample's characteristics, such as the requirements for participation, the variables being studied, and a description of the measurement tools that were employed to gather the data. Additionally, the methods for gathering data and doing analyses are presented.
Sample
The target demographic for this study was undergraduate nursing students, and the sample comprised of willing undergraduate students at the University of South Florida who are currently pursuing a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) (USF). Being a senior BSN student at USF, enrolled in the Leadership and Management in Nursing course, being above the age of 18, being able to read and write English, and having taken undergraduate pharmacology and pathophysiology courses were the inclusion criteria for participation.Through the use of power analytical methods, the sample size was assessed. For a Pearson correlation, a sample size of 30 should produce significant findings with a power of 0.80 and an alpha set at 0.05.
Instruments
The Nurses' Attitude Survey (NAS), the Pain Management Principles Assessment Tool (PMPAT), and a demographic data questionnaire were the instruments used in this study. Both assessments were selected because they clearly distinguish between knowledge gaps and attitudinal barriers in pain management, making them suitable for the study.
Nurses’ Attitude Survey
The NAS, developed by McMillan and Tittle in 2000, consists of 25 items and measures attitudes toward pain management using a four-point Likert scale. Strongly disagree to strongly agree were the range of responses for the instrument, and each item's raw score varied from 1 to 4. The higher the score, the happier the nurses were. The study asked questions on administering analgesics on time, using opiates, assessing pain, its objectives, common myths, and non-pharmacologic pain management.
Reliability and Validity. Using Cronbach's alpha, a satisfactory level of internal consistency reliability (r=0.70) was discovered. When it was pre-tested and post-tested among nursing students, a significant difference (p.01) was found, which further supported its validity (McMillan et al., 2000).
Pain Management Principles Assessment Tool
The PMPAT consists of 31 multiple-choice questions with four possible answers. A test of pain management was intended for the questionnaire knowledge of physiology pharmacology, and the concepts of assessment and management as well as the characteristics of pain, such as addiction, physical dependence, and tolerance. The survey's scores ranged from 0 to 31, or 0 to 100%, with higher scores indicating more correctly answered questions.
Reliability and Validity.The tool's design was based on a framework from earlier research investigations attesting to the validity of its content. Using the pre- and post-test approach, the validity of the instrument was also examined before and after a three-hour pain management course was given to 28 nursing students. From the pre to post test, validity was determined to be highly significant (t=6.76, p0.01). Additionally, reliability was shown to be quite good (r=0.84, p=0.00) (McMillan et al., 2000).
Demographic Data Form
A demographic data form was also given to each participant to complete. The questionnaire asked about the respondent's age, gender, ethnicity, current semester of their BSN programme at USF, greatest level of schooling attained, work history, current employment status, and whether they had ever gotten any kind of pain management training.
Approval
Both the USF Institutional Review Board and the USF College of Nursing gave their approval for the study to be carried out, which allowed students to be approached about participating. The instructor of the Leadership and Management in nursing course was asked for approval before the surveys could be given to the students in class. Additionally, each participant received a letter outlining the goals of the research and the requirements for enrolment. The letter further emphasised that participation was voluntary and confidential, and that completing the questionnaires implied consent.
Procedures
Each student received a questionnaire during class time. The instructor of the Leadership and Management in nursing course was asked to leave the classroom before the questionnaires were given out, and the investigator stayed in the space to oversee the study, give out the surveys, and collect them. There was a brief summary of the study, stating that taking part had no risks or benefits for participants other than advancing the field of nursing research in the area of pain treatment. Additionally, students had the chance to ask any pertinent questions they might have had about the research. Students were also instructed to carefully study the provided instructions and complete their questionnaires on their own, without consulting any textbooks or other students.
Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics, such as frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations, were used to analyse the demographic data. Students' knowledge levels, attitudes toward pain management, and the relationship between knowledge and attitudes were examined using Microsoft Excel and the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS).
Means and standard deviations were calculated to address Research Question 1: What is the amount of knowledge of pain management principles possessed by nursing students at the bachelor level?
Means and standard deviations were determined to respond to Research Question 2: What are nursing students' perspectives toward pain treatment in the oncology patient?
The Pearson Correlations were performed to provide an answer to Research Question 3: Is there a significant association between knowledge and attitudes among bachelor students about pain treatment in cancer patients?
Chapter IV
Results, Discussion and Conclusions
This chapter includes the findings from questionnaires administered to University of South Florida undergraduate nursing students to ascertain their level of knowledge and current views regarding pain treatment. Discussion of the correlation between knowledge and attitude scores is also offered along with the results of the variables. This chapter also covers the study's limits, findings, and recommendations for further investigation.
Results
Sample
41 undergraduate students who are currently enrolled in their senior year of study for a Bachelor of Science in Nursing at the University of South Florida made up the sample for this study. 90% (n=37) of the 41 participants were women, while 10% (n=4) were men (Table 1). The age range of the students was 18 to 42 years, with a mean of 22.5 years. The bulk of participants—73%, or 30, were of non-Hispanic White ethnicity; the remaining participants were 7% (n=3) African Americans, 15% (n=6) Hispanics, and 5% (n=2) Asians (Table 1). According to study, the proportion of students with formal education ranged between 15% to prior to enrolling at USF, whereas 2% (n=1) had bachelor's degrees in subjects other than nursing (Table 1). The majority (75%, n=31) claimed to be full-time nursing students without jobs, while 15% (n=6) were employed as nurse technicians and 10% (n=4) were CNAs (Table 1). 20% (n=7) of students received training in pain management, compared to 80% (n=34) who received no training at all outside of what was provided in their nursing degree (Table 1).Table 1 shows the frequency and percentage of students by gender, ethnicity, and level of education, work experience, and pain management training.
Knowledge of Pain Management Principles
The PMPAT's raw results were tallied and analysed in order to respond to the first research question, which measured the knowledge of undergraduate nursing students on pain management (McMillan et al., 2000). Out of 31 items, the mean knowledge score was 19.4 (SD= 3.0), or 63%. According to the raw results, the 41 students' correct response rates ranged from 39% to 81%. Only 7 students, or 17% of the class, would have passed the pain management knowledge test if a passing score of 70% had been utilised, whereas 30 students, or 73%, would have scored between 50% and 75% and 4 students, or 10%, would have scored below 50%. (Table 2).
When the answers to the individual knowledge questions were analysed, it became clear that students performed poorly in the areas of pain physiology, the pharmacology of pain medications, the right time to take pain medication, the use of cutaneous stimulations as a measure of pain relief, and the primary goal of pain management practises, with scores of 39% or less. On the other hand, the concept of tolerance and patients as the most accurate and reliable judges of their own pain were the two subject areas where items obtained a score of 100%. Patients should be in charge of their own pain management plans, nurses should notify the doctor if a patient's pain worsens while taking the maximum amount of analgesics prescribed, and distraction as a pain management strategy were other categories in which ratings were 90% or above (Table 3).
.png)
Attitudes Toward Pain Management
The Nurses' Attitude Survey was used to gauge attitudes (NAS). Strongly disagree to strongly agree were the range of responses for the instrument, and each item's raw score varied from 1 to 4. The nurses' attitudes were more upbeat the higher their score. A mean score of 17.1 (SD=2.6) was calculated after the raw data from the attitude survey supplied to the sample was analysed, with a range of 48% to 88% of students having favourable views toward pain management.
According to the findings of an item analysis of the NAS, all 41 students (100%) agreed that continual evaluation of pain and drug efficacy is essential for efficient pain management. They also agreed that distraction and diversion could reduce patients' pain levels. Additionally, 95% of students concurred that patients may be reluctant to take painkillers owing to worries about using opioids, and that a nurse should consult a doctor if a patient's pain persists. Following this, 78% of respondents agreed that patients should be kept pain-free, and 71% agreed that cancer pain could be relieved with the proper anti-cancer medications, radiation therapy, and/or painkillers. These results were followed by 85% of respondents who agreed that a constant level of analgesic should be maintained in the blood to control pain effectively. Furthermore, 15% believed that patients in pain may withstand high doses of opioids without sedation or respiratory depression, and 39% felt that the cancer patient and family should have greater control over the schedule for analgesics than the medical professional (Table 4). Contrarily, 98% of students disagreed that a doctor's or nurse's assessment of a patient's pain is a more reliable indicator of that pain than the patient's self-report; 78% of students disagreed that patients should feel pain before receiving their next dose of painkillers; and 73% of students disagreed that patients receiving opioids round-the-clock for cancer pain are likely to develop addiction. In addition, 5% of students disagreed that patients taking 24/7 opioids are at risk for sedation and respiratory depression, while 29% of students thought cancer patients should receive pain medicine before the pain returns (Table 4).
Relationship Between Knowledge and Attitudes
A Pearson correlation between the total scores for knowledge and the total scores for attitudes was calculated to see if there is any association between knowledge and attitudes among bachelor students about pain management in cancer patients. The Pearson correlation coefficient of these two variables was r=0.33 (p=0.038), indicating a modest to moderate but significant degree of association.
.png)
Discussion
Sample
The convenience sample of 41 students from USF's undergraduate Bachelor of Science in Nursing programme responded, and this was enough to provide statistically significant and enough data for the study. The sample gave a clear cross-sectional impression of the USF nursing students that are enrolled in the programme right now. The findings from this study, however, may not be extrapolated to encompass the full population of undergraduate nursing students in Florida or the United States because the data was only obtained in one geographic location and had only a minimal representation from other ethnic groups. Additionally, there was relatively limited participation from minorities in this study because the sample was primarily made up of non-Hispanic Whites.
Since ethnicity and culture have an impact on knowledge and attitudes about pain management, the absence of participants from other ethnicities and cultures may have introduced bias into the data collection. The fact that all students were requested to participate rather than being randomly chosen was another study constraint, and it is unclear what impact this may have had on the data collected as well. The demographic data form's question about pain management training was incorrect since students might have taken it to indicate material covered in class rather than official training provided by a professional.
Knowledge of Pain Management Principles
On the knowledge test, the average score was 19.4 (SD=3.0), or 63%. Data revealed that nursing students have little understanding of how to treat pain. These results were comparable to those of Plaisance and Logan and McMillan and colleagues for nurses in 2000. (2006). McMillan and colleagues (2000) received a mean score of 18.8 (SD=2.9) or 61%, whereas Plaisance and Logan (2006) received an overall score of 64%. Because of this, nurses may not be learning important knowledge in their fundamental nursing programmes, even while the focus on pain remains a national priority.
Students demonstrated strength in some areas of the pain management knowledge test, despite the relatively low overall knowledge scores. For instance, 100% of the students correctly responded that patients are the best judges of their own pain, and 93% said that patients should be in charge of their own pain treatment regimen. This was in line with the results of McMillan and colleagues in 2000, who scored 96% and 81% respectively, but not with those of Bernardi and colleagues in 2007, where only 56% of nurses thought that patients were the most reliable judges of their own pain. This demonstrated that USF's present undergraduate programme does focus on pain management. This agrees well with the NAS, which found that 98% of students disagreed that a patient's self-report of pain is a more reliable indicator of pain than a doctor or nurse's evaluation of discomfort.
Most students were able to define tolerance correctly, describe naloxone's function, and employ a combination of analgesics to treat pain when it came to pharmacologic management. The results of McMillan and colleagues (2000), who reported an 89% score, were consistent with the fact that 100% of students could define tolerance. However, the threshold for distinguishing addiction from tolerance and dependence in the study by Goodrich (2005) was less than 80%. The finding that 93% of students agreed that patients should be in control of their pain management regiment was strength of this study. This result was significantly higher than the 81% score attained ten years earlier by McMillan and colleagues (2000).
Although the data analysis revealed few areas of competency, there were several areas where students' knowledge was significantly lacking.
Most of the inquiries in these categories concerned the physiology and pharmacology of pain. This aligns with earlier study investigations (Bernardi et al., 2007; Diekmann & Wassem, 1991; Ferrell et al., 1993; Goodrich 2005; McMillan et al., 2000; Plaisance and Logan, 2006). For instance, only 29% of students correctly identified that the best time to administer pain medication was before pain began, while only 37% of students were aware of the Gate Control Theory. C-fibers, which are responsible for dull, aching pain sensations, were also unknown to only 20% of students. In terms of pharmacology, just 14% of students were aware that oral administration of medications was the preferable method, 22% were aware that methadone was the opioid with the longest duration of action, and less than 60% were aware that meperidine caused toxicities to the central nervous system.
Less than 24% of students indicated that the main objective of pain management was complete pain relief, and less than 1% of cancer patients develop a drug addiction to painkillers, it was also reported. Additionally, there was a paucity of knowledge regarding the application of non-pharmacologic methods for treating pain of any intensity, such as cutaneous stimulation. Therefore, it is now evident why nurses struggle to manage patients' pain since students don't have a basic understanding of the physiology and pharmacology of pain. These findings imply that pain management issues will persist even after this new nursing generation enters the workforce.
Attitudes Toward Pain Management Principles
A mean score of 17.1 (SD=2.6) out of 25 was determined after the raw test scores from the sample were analysed. The views that many students have regarding pain management may be influenced by their lack of knowledge of the physiology of pain and the pharmacology of opioids. For instance, only 5% of students disagreed with the claim that patients receiving 24/7 opioids are more likely to experience sedation and respiratory depression. This finding is consistent with the low response rates for the question of whether patients in pain can tolerate high doses of opioids without experiencing sedation or respiratory depression. Because of this, students might be aware that increasing opioid doses are caused by opioid tolerance and do not always result in sedation and respiratory depression if they had a better understanding of the physiology of pain and the pharmacology of opioids. These findings, which were in line with earlier research, demonstrate that nurses and students haven't made much progress in this area over the past ten years.
It was also noteworthy that the sample of students who participated in the study were devoted to acting as ardent patient advocates and strongly believed that a patient's self-report of pain was more accurate than that estimated by a doctor or nurse. This was directly tied to the knowledge question, where all students unanimously agreed that patients were the greatest arbiters of their own pain. Only 39% of students believed that cancer patients and their families should have more say in the analgesic schedule than a medical practitioner, nevertheless.
Because cancer patients and their families spend the majority of their time managing chronic pain outside of the authority of doctors and nurses, the notion that they should have control over the analgesic regimen is erroneous.
As a result, we can see that nurses might adopt a more optimistic perspective on pain management if they gained a deeper understanding of the physiology of pain and the pharmacology of analgesics. Additionally, if students see the need of better educating patients on how to manage their own pain and giving patients and their families greater influence over their pain treatment programmes, they can create stronger interactions with their patients and, eventually, better patient outcomes.
Relationship between Knowledge and Attitudes
The data acquired showed that students who often scored highly on the knowledge test also scored highly on the attitude test, despite the Pearson correlation value (r=0.33, p=0.038) showing a weak to moderate association between knowledge and attitudes. The knowledge survey and attitude questionnaire share many items; however there seem to be some differences. As an illustration, students' knowledge of therapeutic levels appears to be lacking, despite their positive sentiments. In contrast to the 78% of students who disagreed that patients should feel discomfort before receiving the next dose of pain medication, only 29% of students correctly responded on the knowledge questionnaire that additional pain medication should be administered on an as-needed schedule before pain returns. This may suggest that students have trouble distinguishing between analgesics taken only when necessary and regimented analgesic treatment strategies.
The question of whether complete pain alleviation is a goal is another area where there appears to be ambiguity. Only 24% of students who responded to the knowledge survey thought that all patients should receive total pain relief, however 78% of students who responded to the attitude survey agreed that patients should be kept in a pain-free state. This could mean that even though students possessed the positive dispositions necessary for good pain management techniques, they lacked the information and justifications for why patients needed complete pain relief.
Another subject where pupils struggled was addiction. Only a tiny percentage (24%) realised that less than 1% of cancer patients developed a drug addiction to painkillers, even though 100% could describe tolerance appropriately. 73% of students who took the attitude test disagreed that cancer patients who get opioids continuously for pain relief are prone to develop an addiction. As a result, we can see that knowledge and attitude ratings on the topic of addiction appear to be unconnected. It's unclear how these nurses' inconsistent knowledge and attitude scores will ultimately affect how well they treat patients.
Conclusions
Despite the fact that pain management has been studied for many years, students' ignorance seems to be a key barrier to effective pain management techniques. Because this study revealed a lack of understanding and some unfavourable views, it is clear that more needs to be done to educate students on the physiology of pain and the pharmacology of analgesics. While students frequently possessed the optimistic outlook necessary for effective pain management approaches, they frequently lacked the underlying information and comprehension of why they were practising certain abilities. So it follows that training nurses and students is a positive step toward improving pain treatment techniques. Therefore, if we want to enhance the information that students receive regarding pain management, a modification in the current undergraduate curriculum is necessary. For this reason, learning about pharmacology, pain physiology, and gaining a better understanding of terms like tolerance, dependency, and addiction would help students become more knowledgeable and better able to care for patients with chronic pain. Therefore, it is essential that methods for improving student education be found if we are to pave the way for patients to receive better pain treatment techniques.
Implications for Nursing
The results of this study have various nursing-related ramifications. Future research on the knowledge and attitudes of undergraduate students on pain management should involve several educational institutions from various geographic regions and a diverse ethnic population to produce more accurate results.
Nursing research should also concentrate on the creation of specialised teaching methods that can be included into the undergraduate nursing curriculum to teach students about pain management in an efficient manner. This will surely give students the chance to treat cancer patients with chronic pain effectively and to encourage better patient outcomes in terms of pain management.
References
.png)
.png)
Assignment
PUBH6206 Health Promotion and Community Health Assignment Sample
Individual/Group - Individual
Length Part B - 1500 words (+/-10%)
Learning Outcomes This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
a) Critically analyse health promotion principles theories at the level of prevention.
b) Apply the principles of the Ottawa Charter to develop health promotion interventions in diverse communities.
d) Apply health promotion principles, theoretical frameworks, and strategies to health promotion intervention for diverse communities.
e) Critically analyse the concepts of community capacity building and empowerment within health promotion interventions
Task Summary
Students are required to develop the health promotion intervention based on the health promotion intervention plan outline developed in Assessment 2 Part A. Students are required to write the program of 1500 words (+/- 10%) in length. The steps below provide clear instructions on how to develop and present your program. Support your point of view with the credible evidence sources.
Instructions for online assignment help
1. Explain the stages of program development in the following stages.
Planning: Review your plan outline against the feedback given by the Learning Facilitator (Target group, Aim, Objective, Timeframe, and Stakeholders developed in Assessment 2 Part A)
Consideration: Consider health promotion principles, theoretical frameworks, and strategies, including Ottawa Charter Area of Action that could applied to your program
Implementation:
Explain potential stakeholders that should be involved in your program and the importance of their roles.
Select health setting where the program would be implemented and explain the appropriateness of this setting/location.
List required resources, including: human resources; equipment; tools and devices (e.g. testing kit, yoga mat, scale, stationary); facilities (e.g. room for education session, space/court for physical activities), printed resources (e.g. flyer, poster, booklet) (this is a critical thinking practice rather than the actual activity).
Estimate your budget required for you program and where could you get funding to support your program (this is a critical thinking practice rather than the real funding)
2. Explain how your program will be monitoring and evaluated.
3. Critically explain timeframe and milestones of your program
Solution
Background
As the health promotion plan outline was completed, a brief knowledge about the risk associated with early mortality of infants and children under the age of 5 years was identified. The outlines help in assessing and highlighting the issues of diarrhoea witnessed by children which thus has been focused as one of the main leading causes of child death worldwide (Shine et al., 2020). As children below the age of 5 years have a lack of ability to self-assess health needs, manage and minimize risk factors and have a proper understanding of the threat. Thus, they witness the enhanced risk of complications related to diarrhea (UNICEF, 2022). The risk of diarrhoea is high among infants and children who lack proper access to clean drinking water, live in a house with poor disposal of human faecal, live in a poor house with shattered infrastructure, lacks proper meal as well as maintain standard hygiene. Thus, these factors explain the social determinants of health related to diarrhoea which increases the threat of infection in infants and children. As children are incapable of managing safety and sustaining a healthy lifestyle by themselves, it is necessary that parents are accounted for their safety and health security (World Health Organization, 2022). The health promotion plan hence focuses on involving children along with their parents in order to generate awareness and safety instructions in order to provide them with an opportunity to safeguard health. As Australia has a well-structured vaccination and clean water supply system, the risk of diarrhoea is significantly low and thus no proper statistics on the issue have been recorded (Thomas et al., 2021). Focusing on which the health promotion plan has been prospered to make sure that the general population do not forget the risk that the infants possess and ensure early management of the risks.
Health intervention
The health promotion intervention focuses on guiding and educating parents regarding the illness, the social factors and the other surrounding environment setting that increases the risk of diarrhoea among their children. The socio-economic approach to health has been identified to be the best application in the case of diarrhoea among children as the social factor the children witness and the economic burden faced by the family together develop a threat of diarrhoea (Lago et al., 2018). It aims to modify the physical and social environment in place of changing health behaviours. As the intervention aims to minimise the risk of diarrhoea, among the general population, it will focus on the primary level of health intervention where the aim is to reduce the risk of illness and ensure management before getting infected (Disease Prevention and Healthy Lifestyles, 2022). Focusing on the Ottawa charter health promotion strategy, the health promotion plan focuses on involving “Advocacy” as the key to success as it guides the need to provide education, awareness and advocacy among the patient and susceptible population as a means to overcome health challenges (Nkangu et al., 2021).
Stakeholders
1. Stakeholder 1: dieticians and paediatricians- provide dietary and nutritional guidance to infants
2. Stakeholder 2: primary care and health care professionals- provide, diagnosis, treatment, care and health education.
3. Stakeholder 3: social service providers and non-governing organizations- support intervention with other services and facilities such as resources, funding, food and coordination.
4. Stakeholder 4: local authorities and Department of health, Australia- fund, policy and guidelines for health promotion intervention (Seymour et al., 2018).
Diarrhoea
Aims: the aim of the health promotion intervention plan is to assess the issue faced by the children in terms of their deprived social determinant of health and in terms of which, to formulate an intervention. The aim highlights the delivery of awareness and prevention guidance to parents of children below the age of 5 years in order to ensure the safety and security of their health. Also, as Australia has no recorded cases of diarrhoea due to vaccination, it is necessary that the health care provider focus on the issue and consider the delivery of guidance (Sommers et al., 2019).
Objectives
Objective 1: the objective of the health promotion plan is to provide awareness to the communities regarding the precautions they must follow to safeguard their children from diarrhoea.
Objective 2: the objective is to maintain recognition among car providers in terms of diarrhoea in order to avoid the development of state public health issues.
SMART goal:
S: the objective focuses in empowering parents as well as communities in terms of diarrhea management.
M: the objective can be measured by assessing change in health care delivery in terms of diarrhoea as well as preventive measures maintained by parents within the communities
A: it is possible to achieve as it requires stakeholder already working within community level and ensure
guidance delivery.
R: it focuses on delivering health promotion within diverse communities.
T: objective is time bound as education and prevention guidance will be delivered within a duration of 8 months.
Setting:
The setting has been selected as in Australia due to Rotavirus vaccination, the prevalence of diarrhoea has come under control and thus no significant data is recorded on the occurring cases of diarrhoea. It is necessary that proper acknowledgement of minor cases is provided and significant guidance among communities is provided to safeguard children (Ruiz-Borrego et al., 2020).
Timeframe: the timeframe of the health intervention plan is identified to be 8 months.
References:
.png)
Dissertation
Mediation and Moderation of Sleep in Arthritis Fatigue Assignment Sample
INTRODUCTION
Background and Significance
Fatigue and Arthritis. The definition of fatigue is "loss of energy and difficulty to keep a regular schedule"
(Cella et al., 2010). Chronic tiredness is thought to be aberrant and pervasive, occurring in individuals who often do not benefit from standard restorative treatments, in contrast to acute weariness, which is typically tied to a particular cause and is frequently cured by rest (Christodoulou et al., 2014). In older adults, fatigue is a worrying symptom since it is linked to functional impairments and predicts 10-year mortality (Hardy & Studenski, 2008a) (Hardy & Studenski, 2008b).
The impact of arthritis on public health is also significant. In the US, the prevalence of arthritis is 23%, or 54.4 million people, making it the most common kind of adult disease (Sandoval-Rosario et al., 2018). For older persons, arthritis is the main source of impairment (Barbour et al., 2017). Co-morbid conditions including heart disease, obesity, and diabetes place a heavy load on arthritis patients (Havens et al., 2017).
A musculoskeletal disorder called arthritis affects the connective tissues around the joints, including the muscles, tendons, and ligaments (Hootman et al., 2012). Two kinds of arthritis that are of particular importance are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. The most prevalent form of arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA), affects over 30 million persons worldwide (CDC, 2020). OA is a chronic degenerative illness and a typical age-related ailment (Anderson & Loeser, 2010). Obesity, physical inactivity, and joint injury are risk factors for OA (Hawker, 2019).
Over 1.3 million persons in the US suffer with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the second most frequent kind of arthritis (Ma et al., 2014). Although the exact origin of RA is unknown, environmental and genetic factors are considered to be involved (Deane et al., 2017). One of the most costly medical illnesses to treat in US hospitals, RA costs $19.3 billion annually (Birnbaum et al., 2010).
Due to its high prevalence (affecting up to 70% of arthritis patients) and interference with patients' ability to participate in everyday activities, arthritis-related tiredness is a serious problem (Gron et al., 2014; Kirwan et al., 2007; Overman et al., 2016). The biggest indicator of future decreased activity is arthritis fatigue (Murphy et al., 2013).
Reduced exercise for arthritis patients worsens their symptoms as well as any other co-morbidities they may have. In the therapeutic setting, where physical exercise is proven to be beneficial in lowering tiredness symptoms and controlling co-morbidities, arthritis fatigue has an adverse effect on patients by restricting physical activity. (2012) Hotman et al.
There are many variables to consider while assessing the covariates of arthritis tiredness (Hackney et al., 2019) for nursing dissertation. In patients with arthritic fatigue, associations between the modifiable factors of physical activity and sleep have been found (Matura et al., 2018). In addition to behavioural variables, heart disease, obesity, and diabetes co-morbidities may be managed by increasing physical activity and improving sleep quality (Hootman et al., 2012). Thus, the emphasis of this study is on the particular factors of physical activity and sleep and how they relate to arthritis weariness.
Physical Activity, Fatigue, And Sleep. Exercise has been demonstrated to lessen arthritis patients' sensations of weariness (Durcan et al., 2014; Katz et al., 2018; Rongen-van Dartel et al., 2016). Additionally, exercise has been linked to better sleep and arthritis sufferers (Durcan et. al, 2014). Numerous research have shown that physical activity, sleep, and weariness are correlated. Poor sleep is quite common and is closely related to tiredness in older adults with OA (Hardy & Studenski, 2008a). Fatigue and inadequate sleep are associated (Austad et al., 2017). RA fatigue is strongly impacted by physical function and sleep quality (Rongen- van Dartel et al., 2016). Poor sleep, depression, and obesity have all been demonstrated to have a role in the indirect relationship between physical inactivity and tiredness (Katz et al., 2016). Cross-sectional study designs are often used in studies examining the connections between weariness, physical activity, and sleep (Loppenthin, Esbensen, Ostergaard, et al., 2015; Puyraimond-Zemmour et al., 2017; Westhovens et al., 2014).
Although cross sectional designs provide insight into a variety of factors, it may be challenging to establish their causal relationships (Nikolaus et al., 2013; Solem, 2015). Although sleep and physical activity are thought to be variables in arthritic tiredness, the part that sleep plays in this association is unclear (McKenna et al., 2017; Nikolaus et al., 2013). The processes underlying the relationships between the factors of weariness, physical activity, and sleep will be better understood via further study employing randomised controlled trials or longitudinal designs. This study broadens our understanding of the interplay between arthritic fatigue, physical activity, and sleep in a longitudinal setting. This study also emphasises the value of second-generation research to enhance therapeutic tiredness therapies.
Second-generation research. Sleep and physical exercise have been shown to be related to arthritic weariness. Understanding sleep's involvement as a third component in the connection is the next step in increasing our understanding in this area. The importance and function of first- and second-generation research were discussed by Guralnick (1993) in the context of his work on early intervention for children. These categories provide valuable insight into the relevance of third variable research and are pertinent to nursing research (Guralnick, 1993).
In first-generation research, the direct link between variables is shown, and the major influence of one variable on another is examined (Hopwood, 2007). In the first generation of study, the link between the independent and dependent variables is the main emphasis (MacKinnon & Luecken, 2008). Direct impact research does not, however, suit everyone, particularly when it comes to how it may be used in a therapeutic situation. There is now mounting research that suggests a connection exists between arthritic weariness, physical activity, and sleep.
The use of first-generation research led to the conception of second-generation research (Guralnick, 1993). Clinical research must demonstrate more than the presence of an effect (Kraemer et al., 2002), and it is crucial to comprehend how such effects function and their boundary conditions. In second-generation research, the features that combine to best cure a certain ailment under specific circumstances are specified (Hayes & Rockwood, 2017).
Second-Generation Research. Looks at the circumstances in which the major effect(s) between two variables operate. Third (3rd) variable study design serves as a representation of this (Hopwood, 2007). In order to provide physicians insight into current therapies and help them be more effective at providing individualized care, it is crucial to examine the function, importance, and consequences of third factors (Kraemer et al., 2002). Through the use of mediation and moderation techniques, this study investigates the contribution of the third variable impact of sleep onto arthritis tiredness.
Mediation and Moderation Methodology
A conceptual and statistical framework for third (3rd) variable designs that include variables (or groups of variables) that affect the relationships between treatments and outcomes is provided by mediation and moderation approaches (Breitborde et al., 2010). Because the mediator is an intermediary in the chain of causes, they are useful in explaining relationships between two variables. This clarifies "how" the three (3) variables are related to one another. Moderators take into account the particular circumstances in which two variables are associated. As the moderator's levels vary, the two variables' relationship changes. This clarifies "when and under what circumstances" the result of a variable may be maximised. Clinicians may fine-tune therapies using the crucial evidence provided by mediators and moderators.
Significance: This longitudinal, second-generation design pilot study investigates the relationships between sleep, physical activity, and arthritis tiredness. Since there are many contributing factors to arthritis tiredness, this research (third (3rd) variable design) focuses on two variables and how they interact to affect the result of arthritis fatigue. The effects of treatment (e.g., medicine) alone on arthritis tiredness are insufficient (Nikolaus et al., 2013). In the current treatment of arthritis, cognitive behavioural strategies, such as health promotion to encourage physical activity, might be targeted to reduce weariness. Understanding the relationship between physical activity, sleep, and arthritis tiredness is important because it allows doctors to modify current therapies to increase their potency and customise interventions. The information from this research is useful for the design of future, more extensive longitudinal clinical studies to examine the impact of exercise and sleep on arthritis tiredness. The study's findings also shed light on tiredness treatment strategies that could be appropriate in situations including fibromyalgia, autoimmune diseases, and cancer-related fatigue.
Purpose
This research looked at the relationships between sleep, physical exercise, and arthritis tiredness. In this study, the variables were investigated for their direct, mediating, and moderating impacts using Baron and Kenny's fundamental methodological framework (Baron & Kenny, 1986). The preliminary investigation found that physical exercise directly reduces arthritic tiredness. The second stage looked at how physical activity and sleep, the link between the variables, affect weariness. The mechanisms by which physical activity and/or sleep restrain or enhance the link to arthritic fatigue were then studied as moderating effects of the variables.
Aims
The study's primary goal was to see whether there was any correlation between arthritic tiredness symptoms and physical activity. Examining the role of sleep as a mediator of physical exercise on arthritic fatigue was the study's secondary goal. The third objective was to ascertain if sleep had a moderating impact on physical activity in the context of arthritic fatigue.
Primary Research Questions
Direct Effects:
1.0 What is the immediate impact of exercise on arthritis fatigue?
Inhibitory Effect:
2.0 Does sleep have a role in the connection between arthritic weariness and physical activity?
Modifying Impact:
3.0 Does sleep mitigate the wear-and-tear on arthritis caused by physical activity?
Theoretical Framework
The conceptual and statistical mediation and moderation model serves as the theoretical foundation for this investigation (Baron & Kenny, 1986). Two models from the literature—the Theoretical Model of RA Weariness and the Biobehavioral Model of Fatigue in Osteoarthritis—were used to guide the selection of the variables for physical activity, sleep, and fatigue (Katz et al., 2016). Through a review of the literature, the Biobehavioral Model of Weariness in Osteoarthritis (Hackney et al. 2019) establishes the connection between fatigue, sleep quality, and physical activity. Based on a cross-sectional study of 158 RA patients, Theoretical Model of RA Weariness (Katz et al., 2016) establishes the association between physical activity sleep and sleep and their relationship to fatigue. Both Hackney and Katz mention a number of variables that have been linked to RA fatigue. But the goal of this research is to investigate the association between the arthritis-related controllable factors of weariness, physical activity, and sleep.
It was shown that physical inactivity had an indirect relationship with exhaustion, which was mediated by other factors including poor sleep (Katz et al., 2016). Other studies have not, however, shown any moderating effects of exercise or sleep on arthritis weariness. The study's remaining theoretical frameworks focus the investigation of the direct, mediated, and moderating effects of simple walking and sleep on arthritis tiredness.
1. What is the immediate impact of exercise on arthritis fatigue?
.png)
Definition of Terms
The Biobehavioral Model of Fatigue in Osteoarthritis (Hackney et al. 2019) and Theoretical Model of RA Fatigue served as the foundation for the study's independent and dependent variables (Katz et al., 2016). The operational definitions for each variable were improved and guided by a study of the relevant literature. The following sections provide explanations of the theoretical and practical definitions for each variable.
Demographic Variables
The survey gathered information on sex, race, ethnicity, education level, marital status, number of people living in the home, and current job.
Independent (predictors) variables
Physical activity and sleep were included as the study's independent variables. Simple walking was used to conceive exercise. Walking involves moving the feet in unison to propel the body forward at a slow to moderate speed. Walking is the movement a person does when engaging in regular activities as well as extra walking sessions. Simple walking may be done both indoors and outdoors and doesn't need any extra gear other than a pair of safe shoes. Simple walking was operationally defined using a step counter accelerometer that is readily available. Off-the-shelf technology is an economical method for measuring at home and offers a fair measurement over time. We utilised a Fitbit bracelet as an accelerometer to track daily steps during the research period.
Sleep was the second independent factor. The situation of being asleep is one in which the body and mind "usually recurs for many hours every night, during which the neurological system is generally passive, the eyelids are closed, the postural muscles are relaxed, and awareness is essentially suspended." Every night, people intentionally engage in sleep, which gives them time for rest and recovery (Cella et al., 2010).
The 8-item PROMIS Short Form v1.0 - Sleep Disturbance 8b (PROMIS SD-SF) was used to assess sleep (Yu et al., 2012). The PROMIS SD-SF evaluates self-reported impressions of the depth, quality, and restoration of sleep during the previous seven days. Greater sleep disruption or sleep-related impairment is correlated with higher scores. The amount of sleep each participant had was gauged at weeks 1, 4, and 6.
Dependent (Outcome) Variable
The study's dependent variable, arthritic tiredness, was assessed. The definition of fatigue is "an overpowering, crippling, and continuous feeling of weariness that reduces one's capacity to do everyday tasks, including the capacity to work efficiently and to function at one's typical level in family or social duties" (Cella et al., 2010). The PROMIS Weariness-Short Form was used to gauge study participant fatigue (Lai et al., 2011). The PROMIS F-SF is made up of eight questions that assess how much sleepiness you experienced last week as well as how much it interfered with your physical, emotional, and social activities. The available responses are listed on a Likert scale with 1 being never and 5 being always. We assessed participant tiredness at weeks 1, 4, and 6.
Summary
An annoying and frequent sign of arthritis is fatigue. Numerous cross-sectional approaches have been used to study arthritis fatigue in great detail. There is ample evidence that arthritic fatigue is a complex problem, and that the factors of physical activity, sleep, and weariness are related to one another. Other co-morbidities might be affected by controllable factors including physical exercise and sleep.
The link between physical activity, sleep, and weariness was investigated in this longitudinal research. The goal of this second-generation study is to comprehend how a third variable—sleep—operates and how its boundaries are defined. In order to evaluate the correlations and add on what is already known, this research adopted a mediation and moderation technique. This study is important in a number of ways. This study's longitudinal results expand upon what is known as a result of cross-sectional research. This study is important because it may help therapists better understand how physical activity and sleep impact, mediate, or reduce the effects of tiredness on clients and how to adapt therapies for them.
CHAPTER 2 - REVIEW OF LITERTURE
Purpose and Search Strategy
This section's goal is to discuss the most recent research on arthritis and the relevant factors of weariness, physical activity, and sleep. This part examines the potential for the conduct of this research project, the search technique, and a review of the literature on the relevant variables.
From August 2018 to February 2020, a thorough search of the literature was conducted to identify researches that investigate the connection between the factors of exhaustion, sleep, and physical activity. PubMed, EbscoHost (Science Citation Index, Academic Search Premier, CINAHL Complete, MEDLINE, PyschInfo, SPORTDiscus Direct), and Web of Science were the databases searched (WoS). The following primary MeSH search phrases were used to conduct searches across all of the databases on the list: "fatigue," "physical activity," "sleep problems," and "osteoarthritis" or "rheumatoid arthritis." Peer reviewed, clinical trial, present abstract, English language, and people were the search parameters for the article inclusion requirements. They were also published after 2000. Pharmaceutical trial, absence of an abstract, and abstract simply were the article rejection criteria. The relevancy and eligibility of the titles and abstracts were then carefully examined. 12 items were found after doing the search. For information, see table 1.
Table 1
Search Strategy
.png)
Arthritis
A severe illness called arthritis affects over 54 million individuals in the US in different forms (Barbour et al., 2017). According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), arthritis is a disorder that affects the joints, tissues surrounding the joints, and connective tissues, resulting in joint pain, stiffness, and deformity. The symptoms of arthritis make it more difficult to move, making it the primary cause of disability (CDC, 2009). By 2040, it is anticipated that more than 78 million individuals would have arthritis (Hootman et al., 2016).
Over 100 different forms of arthritis exist (CDC, 2019). Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis (OA) are the two types of arthritis that are most common (RA). Although the pathogenesis of arthritis is different, the disease burden is same (Chua et al., 2019). OA and RA have long-term repercussions that include joint pain, joint deformity, and disability (Hootman et al., 2012). It is believed that both forms of arthritis cause inflammation (Arthritis Foundation, 2020; Hackney et al., 2019).
The most prevalent kind of arthritis, osteoarthritis, affects 30 million Americans over 65, mostly women (Hawker, 2019). When the cartilage between bones deteriorates from osteoarthritis, it causes the joints to become painful, swollen, and difficult to move (Arthritis Foundation, 2020). Age, sex, previous injury, weight, and heredity are all risk factors for osteoarthritis (Sakalauskiene & Jauniskiene, 2010). According to Ashford and Williard (2014), osteoarthritis is not a normal part of ageing and its symptoms may be treated to stop the condition from becoming worse and causing impairment (Hootman et al., 2012) The second most prevalent kind of arthritis is rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The body assaults healthy tissues and cells since it is an autoimmune illness (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), 2014). Chronic inflammation brought on by RA results in loss of function in the organs and joints as well as pain, edoema, and stiffness (NIAMS, 2017). Approximately 1.5 million individuals in the US suffer with RA (Hootman et al., 2016). According to Scott et al. (2010), the usual age of onset is between 40 and 60 years, and women are more likely than males to have RA (NIAMS, 2017).
Current Arthritis Treatment Overview and Role of Nursing
The management of the disease process, enhancing cognitive behavioural processes, and addressing personal difficulties and individual requirements are the three main areas under which arthritis therapy approaches may be divided (Hewlett et al., 2011). Each of the three tactics need for nursing knowledge. Nursing care influences illness management, makes use of cognitive behavioural strategies, and takes part in the treatment of individualised problems such co-morbidities. The overview of arthritis therapy and the function of nursing are both discussed in this section.
A range of medicinal therapies may be used to manage the arthritis disease process. Joint replacement surgery can be necessary for treatment (Hawker, 2019). In certain circumstances, drugs are utilised to reduce the inflammatory response and restrict the progression of the illness (Scott et al., 2010). The relationship between inflammation and disease activity in arthritis is largely unclear (Hackney et al., 2019; Matura et al., 2018). Not all of the symptoms that patients experience are entirely addressed by medical treatment (Hootman et al., 2012; Walter et al., 2018). Patients with arthritis benefit from medical therapies in terms of pain reduction and improvement. Interventions in cognitive behaviour show promise because they provide additional or alternative forms of therapy.
The interactions between ideas, emotions, behaviours, and symptoms are reflected in cognitive behavioural therapies (Hewlett et al., 2011). Pain and tiredness symptoms have improved as a result of applying cognitive behavioral techniques to manage the complete person and encourage behaviour change (Ferwerda et al., 2017). In sedentary arthritis patients, interventions that reduced sitting time increased activity levels, enhanced physical function, and decreased levels of weariness (Thomsen et al., 2017). Changes in behavior, such as increasing physical exercise for health reasons, may reduce tiredness symptoms and boost function by 40%. (Kelley et al., 2011). Interventions using cognitive behavior to encourage a healthy lifestyle may also be tailored to the unique difficulties each client with arthritis experiences.
The third step in treating arthritis entails controlling each patient's particular personal circumstances. Managing co-morbidities is part of providing care for persons with arthritis (Hewlett et al., 2011). For arthritis patients, co-morbidities are a challenge. Arthritis, and the resulting decrease in physical activity, makes it harder to manage the chronic conditions of heart disease and obesity. About half of all adults with arthritis have been diagnosed with heart disease, and one third have been diagnosed with obesity (Chua et al., 2019; Tournadre et al., 2018).
In order to effectively treat arthritis, medical therapy of the condition must be combined with cognitive behavioral therapies to encourage a healthy lifestyle and personal difficulties specific to the patient, such as co-morbidities (Hewlett et al., 2011). Professionally speaking, nurses are qualified to help in each of these situations. Clients benefit from nurses' knowledge in sickness treatment and health promotion. This research contributes to our understanding of the interaction between sleep and physical activity for health promotion and offers further details on how these activities contribute to arthritic fatigue.
Fatigue in Arthritis
It has been shown that fatigue levels are comparable across various forms of arthritis (Cross et al., 2008). The majority of people with severe arthritic tiredness are women, unemployed people, and those who don't exercise too much (Tournadre et al., 2018). Patients with arthritis state that weariness is their top priority and biggest worry, however healthcare professionals often ignore this fact (Hewlett et al., 2005; Power et al., 2008). Patients' top concerns revolve on arthritis weariness, which is persistent and common.
Physical Activity and Fatigue
Numerous physical activity/exercise therapies, including yoga, low-impact aerobics, dynamic strength training, and pool-based therapy, have been proven to be effective in reducing tiredness (Cramp, Hewlett, et al., 2013; Katz et al., 2018). By enhancing a person's aerobic and functional capacity, physical exercise therapies lessen tiredness and hence require less effort to do everyday activities (Katz, 2017).
According to Kelley, Kelley, and Callahan's (2018) research, aerobic exercise greatly reduces the symptoms of weariness. Katz and colleagues (2018) also noted that a walking intervention that increased physical activity over a twenty-one-week period helped arthritis patients feel less worn out. These physical activity programmes also had a somewhat significant impact, according to two recent meta-analysis studies (Cramp, Berry, et al., 2013; Rongen-van Dartel et al., 2016). Numerous types of physical exercise seem to help with arthritic weariness.
Walking has been recognised a fair kind of exercise when determining which physical activity is best for those with arthritis (Baxter et al., 2016). Walking involves moving the feet in unison to propel the body forward at a slow to moderate speed. The demands of patients with tiredness, who often find it difficult to go to locations outside of their homes for exercise training, may be met by walking, which is simple to learn and requires minimal expert direction and equipment. Accelerometers may be used to count steps as a tool to quantify exercise; for instance, Fitbit has been shown to be reliable for recording walking as exercise in fragile elderly persons with slow gaits (Case et al., 2015; Le Masurier & Tudor-Locke, 2003). (Paul et al., 2015).
Sleeping Quality and Arthritis Fatigue
Most arthritis sufferers complain about poor sleep quality (Fertelli & Tuncay, 2019; Goes et al., 2017). A link exists between insufficient sleep and greater than average levels of reported weariness in older persons with arthritis (Hawker et al., 2010). Some research indicate that increasing physical exercise may help people sleep better (Dolezal et al., 2017). Higher levels of physical exercise among arthritis patients result in greater overall sleep time (McKenna et al., 2018). This implies a connection between exercise and sleep.
Relationship between Arthritis Fatigue, Physical Activity and Sleep
It is difficult to assess the mechanisms underlying the relationship between arthritis fatigue, physical activity, and sleep because there is little research that: 1) considers all the variables simultaneously; 2) employs uniform measurement tools; and 3) is behaviorally based rather than based on a drug trial. The studies that incorporate cross-sectional and single randomised controlled trial (RCT) designs and include at least one of all the relevant variables are expanded upon in this section.
In older individuals, increasing physical activity is linked to better sleep and fewer signs of weariness (Christie et al., 2016). In a research looking at the connection between physical activity, sleep quality, and weariness in persons living in communities, 22 older adults (aged 65-81) took part. This research implies a connection between the factors, however the sample size was modest, the study lasted more than seven days, and the group was made up of healthy individuals rather than those with arthritis.
Loppenthin et al. (2015a, 2015b) looked at a community of arthritis patients in a large research (n=384) to investigate the associations between arthritis, physical activity, sleep, and other characteristics. These research' results indicated that physical exercise reduces exhaustion and that sleep quality and weariness are related (Loppenthin, Esbensen, Jennum, et al., 2015; Loppenthin, Esbensen, Ostergaard, et al., 2015). Although physical activity, weariness, and sleep are discussed in these research, the links between the three variables are not explicitly stated. The cross-sectional nature of these investigations further restricts their scope.
Rongen-van Dartel uncovered factors that support the association between arthritic tiredness, physical activity, and sleep (2016). Poor sleep and decreased physical performance were shown to be directly connected to increased degrees of tiredness in this research of 228 arthritis patients (Rongen-van Dartel et al., 2016). This study suggests a link between the variables, even if the cross-sectional design does not specify the direction of the association.
Indirect links between physical activity and exhaustion were discovered, which were mediated by insufficient sleep (Katz et al., 2016). This study examined 158 arthritis patients to identify factors related to weariness. This research reveals a link between the variables, although its cross-sectional methodology has certain limitations.
Through its connection to pain and exhaustion, sleep quality has an indirect impact on functional capacity, which includes walking. Fatigue and pain were shown to be mediators of the association between sleep quality and disability in a cross-sectional study of 162 people with arthritis (Luyster et al., 2011). The study has limitations in that the factors of interest are not explicitly addressed, despite the fact that it offers some information. The cross-sectional design makes it difficult to determine the cause, scope, or size of the mediators between sleep quality and impairment.
The literature contains one important piece of study. Durcan et al. (2014) used a randomised control trial research design to assess the impact of exercise on sleep efficiency and weariness. Following the baseline evaluation, experts created a customised 12-week workout programme with follow-up scheduled every three weeks. The exercise regimen included a number of therapeutic modalities, such as strength training, range-of-motion exercises, and walking. There were 38 participants in the control group who got standard treatment and information on the advantages of exercise for RA, and 40 patients in the intervention group who received these same services. According to Durcan et al. (2014), the physical activity intervention enhanced sleep quality and feelings of exhaustion since there was a statistically significant improvement for the intervention group in both areas (p = 0.04).
This research does have certain restrictions, however. Experts (a doctor and a physiotherapist) assessed the baseline evaluations to develop a customised 12-week programme with follow-up every three weeks for the expert and time-consuming exercise intervention. A significant amount of resources were also needed for a number of therapeutic modalities included in the intervention, such as weight training, range of motion exercises, and walking. Simple interventions like walking could be enough to have this impact.
Opportunity for Research: The Gap
The Disk implications of the earlier study designs and findings provide a chance to increase the body of research on sleep, arthritis fatigue, and physical activity. According to the research, these factors have been linked to an increased risk of arthritis in people. However, the majority of the research only assesses two of the three important characteristics. Since the majority of the researches examining this link have been cross-sectional, no additional conclusions can be drawn than correlations. The variety of assessment techniques employed in the literature on tiredness, exercise, and sleep is another difficult aspect (McKenna et al., 2017). Comparing the study's findings becomes challenging as a consequence. Physical activity, weariness, and sleep may not be related in a straightforward linear manner. It has not been thoroughly explored how and when the variables interact.
Theoretical Framework: Mediation and Moderation Models
The Theoretical Model of RA Fatigue and the Biobehavioral Model of Fatigue in Osteoarthritis (Hackney et al.) served as the foundation for the development of the theoretical framework in this research (Katz et al., 2016). The mediation moderation model serves as the study's general framework (Baron & Kenny, 1986). The planned study looked at the connection between exercise, arthritic tiredness, and sleep quality.
A comprehensive review was used to create the Biobehavioral Model of Fatigue in Osteoarthritis (Hackney et al., 2019). The correlates of tiredness were built into a model by the authors. The two behavioural components that are recognised as having a direct impact on weariness are physical activity and sleep quality. This model's lack of scientific validation is one of its drawbacks.
The Theoretical Model of RA Fatigue served as the study's second model (Katz et al., 2016). The research utilised data from a study that investigated the causes of tiredness in a sample of 158 people with rheumatoid arthritis. The results showed a statistically significant link between weariness, insufficient sleep, and physical inactivity. Poor sleep acted as a mediator in the link between physical inactivity and weariness, according to a mediation study (Katz et al., 2016). The cross-sectional form of the research and the emphasis on inactivity as opposed to activity are its weaknesses.
But the connections that have been made help us understand the correlations that exist between these factors, allowing for further investigation.
The work of Baron and Kenny serves as the foundation for the general framework that supports the conceptual and statistical technique of mediation and moderation (1986). To represent the interaction between variables outside of the discovery of a causal link, mediation and moderation are two separate ideas and uses (Baron & Kenny, 1986). Here, the conceptual paradigm of mediation and moderation is briefly addressed; Chapter 3 describes the statistical approach.
The literature study reveals connections between arthritis tiredness and may be regarded as first generation research. The evaluations imply that second-generation research focused on "how," "why," "for whom," and "under what conditions" is the next stage in the development of this knowledge (Breitborde et al., 2010). These second-generation research questions may be asked using the framework provided by mediator and moderator methods.
You may think of mediation as the "how" and "why" of variables. Finding a mediator in a causal link helps to understand the interaction between the independent and dependent variables. The mediator is crucial because, if it is discovered, it acts as an intermediary in the chain of events (Breitborde et al., 2010; MacKinnon & Luecken, 2008). Only in situations where there is a causal link may a mediator be present. This study's primary goal is to establish if physical exercise and arthritis tiredness are causally related. If such is the case, the second goal of this research is to ascertain how sleep fits into the chain of events that leads from physical activity to arthritic weariness.
Moderators take into account the particular circumstances in which two variables are associated.Moderators explain how the variables "when" and "under what circumstances" are connected. As the moderator level varies, the relationship between the independent and dependent variables changes (MacKinnon and Lueken, 2008). The investigation of sleep and physical activity, both alone and together, and their impact on arthritic tiredness is the third and final goal.
Summary
An incapacitating chronic illness, arthritis. Treatment for arthritis involves a variety of approaches, including medical management of the disease process (such as surgery or medical intervention), behavioural elements (such as promoting physical activity and sleep), and other personal/individual requirements including co-morbidities. Opportunities for behaviour are promising and fit easily within nursing's objectives and actions.
Using a mediation moderation approach, this study analyses the relevant variables—physical activity, arthritis tiredness, and sleep—and investigates their connection. Additionally, this study makes use of PROMIS standard measuring techniques so that other PROMIS researchers may expand on the findings (Bartlett et al., 2015).
Understanding the connection between physical activity, arthritic tiredness, and sleep offers the chance to enhance clinical care and research efforts in nursing and medicine.
CHAPTER 3 - METHODS
Introduction
This pilot study's goal was to investigate the connection between exercise, arthritic tiredness, and sleep. The goal of this research is to investigate how sleep, over time, affects the link between physical activity and arthritic tiredness. The research design, sample, intervention, tools, processes, and data analysis are all covered in this chapter.
Study Design
Investigation Design An experimental, long-term repeated measurements design was used in this study. Three outcomes were measured for participants (n=24): daily steps, disturbed sleep, and exhaustion. Self-reported questionnaires and accelerometer data were used to gather the results at the baseline, week four, and week six.
Sample
The research, which was carried out in many rural New England villages, was representative of the region's existing elder resident population. The Foundation of State Nurses, a State Council on Aging, a senior facility, and a YMCA in western Massachusetts were used to find participants. The sample included 24 persons with moderate tiredness, ranging in age from 50 to 86. 24 individuals were selected based on the advice that 10-15 per group is sufficient when the goal of the research is to investigate the impact of the pilot intervention, despite the fact that sample size calculation was not done due to the pilot nature of the study (Hertzog, 2008).
1) Participants in the study had to be 50 or older. 2) Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis self-reported by the patient, and 3) PROMIS Tiredness Short Form v1.0 -Fatigue 8a (PROMIS F-SF) score of more than mild fatigue (Lai et al., 2011). Inability to walk or the presence of a condition that would prevent it (such as a foot deformity, surgery on a lower extremity joint within the previous six months, a stroke, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc.) were the exclusion criteria. The Mini-Cog test also looked for overt delirium, dementia, or any conditions that indicated a decline in cognitive status (Borson et al., 2000).
Instruments
The capacity of the research participants' eligible study subjects to engage in cognitive testing was evaluated. Mini-Cog (Borson et al., 2005) was used to measure cognition. The Mini-Cog has two parts: a clock sketching test and a 3-item recall memory test. It is highly sensitive (76%) and specific (89%) and is not negatively affected by age, language, or education (Borson et al., 2005). (Borson et al., 2003).
Steps were recorded using a Fitbit accelerometer worn on a bracelet. The Fitbit wristband was selected because it is accurate for recording step counts of fragile elderly persons with sluggish gaits and has a long battery life of up to 6 months for simple wear without recharging (Case et al., 2015). The built-in Fitbit app was utilised to monitor and log daily steps taken. The PROMIS F-SF was used to quantify participant weariness (Lai et al., 2011). The PROMIS F-SF is made up of eight questions that assess how much sleepiness you experienced last week as well as how much it interfered with your physical, emotional, and social activities. Options for responses are given on a Likert scale with 1 being never and 5 being always. Values might be anything from 8 to 40, with higher scores indicating more weariness. With Cronbach's alphas ranging from.72 to.88, PROMIS F-SF showed high dependability (Ameringer et al., 2016). The scale also demonstrated strong validity in populations with a range of ethnic and racial backgrounds (Ameringer et al., 2016); concurrent validity was supported by moderate to high correlations between PROMIS F-SF and the Multidimensional Fatigue Symptom Inventory-Short Form and between PROMIS F-SF and the Brief Fatigue Inventory (r =.70 to.85); and discriminant validity was supported by moderate correlations with other measures of related but unrelated constructs.The 8-item PROMIS Short Form v1.0 - Sleep Disruption 8b was used to assess sleep disturbance (PROMIS SD-SF). The PROMIS SD-SF evaluates self-reported impressions of the depth, quality, and restoration of sleep during the previous seven days. Greater sleep disruption or sleep-related impairment is correlated with higher scores. The scale demonstrated strong convergent-discriminant validity with high correlations with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (r=0.83-0.85) and low correlations with the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (r=0.25-0.30), as well as excellent internal consistency with Cronbach's alphas > 0.9 (Fogelberg et al., 2015). (Yu et al., 2011).
Procedures
The research received Institutional Review Board (IRB) clearance. A recruiting strategy was employed to concentrate on readily accessible hubs for arthritic customers. Focus areas included a state nursing research network, arthritis activity clubs, and arthritis support groups. Flyers that had been authorised by the IRB were distributed and put in provider care offices, senior centre bulletin boards, and fresh letters from the State Center for Aging. The participants' informed permission was sought after identifying those who could be interested. Then criteria for inclusion and exclusion were applied to the participants (see Sample).
The PI conducted an individual introduction session with all eligible participants (PhD student). The lesson included explanations of the study's methodology and goal, as well as guidelines for using an accelerometer. Participants completed the demographic survey at the conclusion of the session and received a Fitbit accelerometer to wear for six weeks. Participants had to show being able to comprehend the Fitbit screen's step counter and charging instructions. Additionally, everyone received an exercise journal to record their daily step totals before bed. Every two weeks, the participants were given self-addressed, stamped envelopes to submit their activity records in. A 6-week schedule of the study's activities, instructions for using the Fitbit, a copy of the permission form that had been signed, and the PI's contact information were given to the participants at the conclusion of the visit. Participants recorded their daily steps each night before bed in the weekly activity diary, which they completed each week. The PI contacted the participants once a week during the duration of the 6-week trial to check on any Fitbit issues and to address any study-related queries. Participants filled out the sleep disturbance and exhaustion questionnaires at the conclusion of weeks 1, 4, and 6. The list of variables and the timetable for data collection are shown in Table 2.
Data Collection Schedule
Data Analysis
For each of the relevant variables, descriptive statistics like mean, median, mode, and range were computed. To ascertain if randomization and normal distributions were adequate, data on participant characteristics and outcome variables were firstly examined. Using the models proposed by Baron and Kenny, the variables were also examined for a mediation and moderating impact of sleep (Baron & Kenny, 1986; Hayes, 2009; Zhao et al., 2010).
Sleep's meditative effects. The first stage in evaluating the direct effects of physical exercise on arthritic fatigue was to evaluate the connection of mediation.
1.0) What is the direct relationship between physical exercise and arthritic fatigue?
.png)
Mediation Analysis
The following two regression models were created at three different time periods, week 1, week 4, and week 6, to investigate the mediation impact of sleep. Look at Table 3.
Table 3
Regression Model for Mediation Analysis
.png)
To determine if sleep mediates the connection between physical activity-induced arthritic fatigue and the following three conditions (Baron & Kenny, 1986).
1. There is a direct link between arthritic tiredness and physical activity (steps).
2. Physical activity (measured in steps) and sleep have a substantial link; and
2. When sleep is included into the regression, the impact of physical activity (steps) on arthritic tiredness will vanish (or at least lessen).
Moderation Effect of Sleep
3.0) Does sleep mitigate the impact of exercise on arthritic fatigue? Is the third research question.
The following regression model was created at three different time intervals, week 1, week 4, and week 6, to investigate the moderating impact of sleep:
Figure 6
Moderation Analysis
.png)
Table 4
Regression Model for Moderation Analysis
.png)
The statistical significance of the regression coefficient was examined in the regression models. If the result is significant, it suggests that sleep has a considerable moderating influence on the association between arthritic tiredness and physical activity (steps).
CHAPTER 4
REAULTS
Introduction
This pilot study's goal was to investigate the connection between exercise, arthritic tiredness, and sleep. This research was especially created to look at the mediation and moderating effects of sleep over time on the link between arthritic tiredness and physical activity. The findings for each of the three study topics are presented in this section.
Demographics and Descriptive Statistics
The 24 New Englanders that made up the research sample ranged in age from 55 to 86. The sample's ages were equally split throughout the three decades. Rheumatoid arthritis was reported by two thirds of the study group (n=16, 67%) and osteoarthritis by one third (n=8, 33%). Most research participants were married and lived with their spouses (n=16, 66.7%), female (n=18, 75%), and Caucasian (n=22, 92%). 25% (n=6) of the sample population had a high school diploma or less, according to the data. 18 people, or 75%, were college graduates or more. In Table 5, further descriptive information is included.
Table 5
Demographical Background
.png)
.png)
.png)
At weeks 1, 4, and 8, data were gathered for the independent and dependent variables.
6. The HealthMeasures Scoring Service evaluated the PROMIS Fatigue (F-SF) and PROMIS Sleep Disturbance (SD-SF) items. The service generated a T-score for each participant using de-identified survey data. With a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10, the T-score rescales the raw score into a standardised score. The PROMIS Fatigue (F-SF) values for weeks 1, 4, and 6 were used to determine the Cronbach's alpha, which varied from 0.94-0.97. For the PROMIS Sleep Disturbance (SD-SF) findings for weeks 1, 4, and 6, the Cronbach's alpha varied from 0.87 to 0.95. The number of steps was computed using the weekly average of each person's daily steps. Every measurement interval's minimum, maximum, mean, and standard deviation were computed for each variable. Table 6 displays these numbers.
Table 6
Descriptive Statistics for Independent and Dependent Variables (n=24)
.png)
T-scores with an average score of 50 are created from fatigue and sleep scores.
Week 1 Results
What is the direct relationship between physical exercise and arthritic fatigue? A cross-sectional examination of the factors of physical activity, weariness, and sleep is done during week 1. According to the findings (=0.09, t=.42, p=.68), there is no connection between physical activity and arthritic weariness. See Table 7 and
.png)
Research Question #2. Does sleep modulate the impact of physical exercise on arthritic fatigue?
Two regression analyses linking physical activity, arthritic tiredness, and sleep are included in the Week 1 results (see Tables 8 and 9). The data demonstrated that step counts affect arthritic tiredness in both a direct (path coefficient=-.01) and indirect (path coefficient=-.18) manner, but that none of these effects is statistically significant. According to the findings, sleep does not act as a mediator between step counts and arthritis weariness. Look at Figure 5
Figure 8
Week 1 Cross-sectional Mediation Analysis
.png)
Table 8
Week 1 Cross-sectional Regression Results for Mediation Analysis
.png)
Research question #3. Does sleep lessen the impact of exercise on arthritic fatigue?
For sleep to moderate arthritic tiredness, there must be a considerable interaction between physical activity and sleep. There is no discernible moderating impact of sleep in week 1 according to the physical activity*sleep interaction data (=0.06, t=0.17, p=0.87). The link between physical exercise and weariness is not moderated by sleep.
Look at Table 9.
.png)
Figure 9
Week 1 Cross-sectional Moderation Analysis
.png)
Table 10
Week 1 Cross-sectional Regression Results Moderation Analysis
.png)
Week 4 results
Research question #1 what is the immediate impact of exercise on arthritis fatigue?
According to the Week 4 longitudinal data, physical activity and arthritic tiredness are significantly correlated (=-.19, t=-.40, p=.048). Look at Table 11 and Figure 7.
.png)
Research question #2 Does sleep operates as a mediator between the effects of exercise on arthritic fatigue?
Two regression analyses relating physical activity, arthritic tiredness, and sleep are conducted in week four (see Table 12 and 13). The results demonstrated that exercise had a statistically significant direct (path coefficient=-.60) and indirect (path coefficient=-.23) impact on arthritis tiredness. The findings show that adding the sleep variable to the model raised the effect of physical activity from -.60 to -.83, indicating that sleep mediates the relationship between physical activity and arthritis tiredness. Look at Figure 8.
.png)
Research question #3 Does sleeps lessen the impact of exercise on arthritic fatigue?
The interaction terms must be statistically significant in order to evaluate if sleep moderates the impact of physical activity on weariness. The physical activity*sleep interaction is not significant in the week 4 data (=.15, t=.63, p=0.54). Look at Figure 8. The association between physical activity and arthritic weariness is not moderated by sleep. Look at Table 13.
Physical activity and arthritic weariness, however, are significantly correlated ((=-.71, t=-2.16, p0.04).
Figure 12
Week 4 Longitudinal Moderation Analysis
Week 6 results
Research question #1 what is the immediate impact of exercise on arthritis fatigue?
There is no correlation between physical activity and arthritic tiredness, according to Week 6 longitudinal findings (=-.19, t=.60, p=.56). See Table 15 and Figure 10.
.png)
Research question #2 Does sleeps operate as a mediator between the effects of exercise on arthritic fatigue?
Two regression analyses linking physical activity, arthritic tiredness, and sleep are included in the data from week six (see Tables 16 and 17). The tables demonstrate a direct (path coefficient=-.61) and indirect (path coefficient=-.07) relationship between physical activity and arthritic tiredness, although only the direct relationship is significant. According to the findings, sleep is not a mediator of the connection between physical activity and arthritic tiredness. Look at figure 14.
.png)
*Path coefficient is significant at p <.05
Research question #3 Does sleep lessen the exhaustion brought on by arthritis after exercise?
The interaction terms must be significant in week 6 data to evaluate if sleep moderates the impact of physical activity on weariness. Physical activity*sleep interaction is not significant in the week 6 data (=-0.003, t=-.01, p=.99). The association between physical activity and arthritic weariness is not moderated by sleep. Look at
Figure 15
.png)
CHAPTER 5
DISCUSSION
Study Overview
An extremely common symptom of arthritis in elderly persons is fatigue. This longitudinal pilot study's objectives were to investigate the link between physical activity and exhaustion as well as the mediating and moderating roles that sleep plays in this connection. The cross-sectional data at week 1 showed that there is no impact of sleep on arthritis tiredness in terms of mediation or moderation. The impact of physical activity rose from -.60 to -.83 in the longitudinal data at week 4, demonstrating that sleep mediates the relationship between physical activity and arthritic fatigue. The moderating effect of sleep, however, was not seen. The benefits of physical exercise on tiredness were neither moderated or mediated by sleep in the follow-up longitudinal data at week 6.
Mediation Effect of Sleep
Sleep's Mediation Effect Mediators provide light on the "how" and "why" of a causal relationship's third variable (Breitborde et al., 2010). According to the findings of this long-term investigation, sleep mediation started in week 4. The results are in line with those of earlier research by Katz (2016) and Luyster (2011), which found that tiredness symptoms were mediated by sleep. The standardised coefficients () for mediation had a considerable effect size (=-.83) and were statistically significant (Cohen, 1988). When sleep was included to the association between physical activity and arthritic tiredness in week 4, the impact size increased, going from -.60 to -.83. The results point to precise and distinct correlations between the three variables, with sleep playing a particular role in mediation.
Sleep did not operate as a mediator in the data from week 6 between physical activity and weariness. Even if the requirements for mediation were not satisfied, two of the three paths were important. Significant and having a modest impact size were the path coefficients between physical activity and sleep (=-0.61, t=-2.59, p=0.02) (Cohen, 1988).
Sleep and weariness were significantly correlated, however with a minor impact (=.38, t=2.18, p=0.04). The week 6 findings may indicate that the mediation of sleep on the link between physical activity and weariness may be time-limited when compared to the week 4 findings. The mediation effect was diminished after 4 weeks and vanished at week 6.
Comparison of Sleep Mediation in Cross-sectional vs. Longitudinal Results
The Theoretical Model of RA Fatigue by Katz et al. (2016) served as the foundation for this study's framework. Based on the results of their cross-sectional study, which included 158 arthritis patients, Katz et al. identified the probable explanatory factors connected with weariness. Katz et al. discovered that physical inactivity had an indirect relationship with tiredness, which was influenced by other factors including poor sleep. Some of the Katz et al. findings and the outcomes of this investigation were in agreement.
The longitudinal research found a substantial mediation impact of sleep but the cross-sectional study did not when comparing the mediation effect of sleep in the cross-sectional review at week 1 with the longitudinal review at week 4. Because the correlations were not explored longitudinally, the results may indicate that a cross-sectional approach may not always capture precise relationships, particularly cause-and-effect relationships between factors. A cross-sectional research design may not be the ideal method to find variable connections since mediation and moderation interactions are theoretically described as causal links between the variables (Barron & Kenny, 1986).
Moderation
Moderators provide light on the particular circumstances that exist between two closely related variables. In this research, it was expected that when the moderator variable (sleep) level changed, the connection between the independent variable (physical activity) and the dependent variable (fatigue) would also vary. In a cross-sectional investigation at week one or at the study intervals of week four or week six, this association was not discovered. The results imply that sleep may not operate as a moderator in the association between arthritic tiredness and physical activity.
Up until now, there hasn't been much knowledge on how sleep acts as a mediator between physical activity and weariness. In a recent research (n=481) of healthy teenagers, sleep quality was shown to mitigate the link between physical activity and weariness (Herring et al., 2018). There was a dose-response between physical exercise and reduced tiredness feelings in those who had trouble sleeping. The findings of this research do not agree with those of Herring et al. (2018). The research population was different and a cross-sectional design was adopted by Herring et al. (2018).
Strengths
There were a number of advantages to this research. The longitudinal research design with the mediation and moderation technique increased our understanding of how sleep affects the connection between physical activity and weariness. The research added to our knowledge of how sleep affects us over time, particularly the mediating effects of sleep in the fourth week. According to this research, a longitudinal design may disclose the precise mechanism by which sleep and physical exercise interact to affect arthritis tiredness.
The findings of this study back up the importance of second-generation research as a direction for nurse researchers. Finding a connection between variables is the goal of first-generation research. There are often several connections; for instance, arthritic tiredness has numerous correlations. How can a doctor begin to use this in patient care? Although first-generation research offers helpful cause-and-effect knowledge, its therapeutic use is limited (Guralnick, 1993). Second-generation study examines how connections' impacts function and the conditions' boundaries (MacKinnon & Luekin, 2008). For instance, this study's results showed that the association between physical activity and exhaustion is mediated by sleep. This reveals that the interaction takes time since the impact was not felt until week four. We also understand that the impact could only last for a short period of time since we did not detect it by week 6. This could affect the advice we provide to our customers.
The significance of practical behavioural techniques was stressed in this research. Sleep and physical exercise are behavioural elements that may be changed and have effects beyond mere exhaustion. With so many co-morbidities, physical exercise is a health promotion activity that is beneficial. Most individuals can engage in the affordable exercise of simple walking. Poor sleep is considered to interact with comorbid illnesses such pain, falls, cancer, and chronic heart failure as well as have an influence on these disorders (Onen & Onen, 2018). A health promotion activity that helps with tiredness and maybe other comorbidities is promoting excellent sleep hygiene.
The study's use of off-the-shelf technology, the Fitbit, gave researchers insight into instruments used in daily living. Fitbit, an accelerometer, is commonly sold at retail establishments. Globally, there are 100 million Fitbits in use, of which 28 million are active (Associated Press, 2019). The findings of this study may persuade other researchers to keep looking into how common arthritis sufferers may employ tools and remedies.
Limitations
The research has a number of drawbacks, including a small sample size, a straightforward design, effects from the seasons and holidays, and weather. The goal of this research was to serve as a pilot study. There were 24 older persons with arthritis fatigue in the sample. A larger sample size would provide more accurate and trustworthy findings.
The symptom of fatigue is multifaceted. There are over 100 factors that have been linked to arthritic tiredness in some way (Cramp, Hewlett, et al., 2013; Loppenthin, Esbensen, Jennum, et al., 2015; Loppenthin, Esbensen, Ostergaard, et al., 2015; Rongen-van Dartel et al., 2016). Two theoretical models of arthritic fatigue were used to guide the selection of the variables of physical activity and sleep in weariness (Hackney et al., 2019; Katz et al., 2016). In order to adequately represent the complexity of weariness, both models are multifactorial. The mediation and moderation methodology condensed the links to analyse arthritis tiredness in this research.
As a consequence, it's conceivable that our finding was influenced by other important factors. Both the Theoretical Model of RA Fatigue (Katz et al., 2016) and the Biobehavioral Model of Fatigue in Osteoarthritis (Hackney et al.) identify non-modifiable and modifiable variables that influence fatigue symptoms. The following variables are non-modifiable: age, sex, and illness status. In addition to physical activity and sleep, there are other controllable variables that affect weariness. Other modifiable characteristics that the theoretical models identify include depression, pain, and obesity. These other factors may have had an impact on the results even though they were not examined in this research. It is advised that future studies assess how they affect tiredness.
The use of wearable activity monitors, such the Fitbit, by older persons is now being studied. After two months, wearable activity trackers are no longer used by those over the age of 70. (Li et al., 2019). Researchers are still looking into why people stop using trackers, such how easy they are to wear and operate (Shin et al., 2019). This is consistent with mediation at 4 weeks and no mediation at 6 weeks, which may be attributed in part to the novelty of wearing the activity tracker for a brief length of time. Our research did not take into account potential changes in interest in straightforward walking over time.
In New England, the study recruitment was available all year round. The unpredictable New England weather has an influence on older adults who want to go on outdoor walks. Participants in the study were urged to choose secure walking routes. There were occasions when the weather made it impossible to go outside or to drive to a building where one could walk. One of the things that contributes to older adults taking less outside walks is the weather (Rantakokko & Wilkie, 2017). The recruiting period had an average of 46 inches of annual precipitation, 36 inches of annual snowfall, with average high and low temperatures between 82 and 13 degrees Fahrenheit (US Climate Data, 2019). Significant rains fell during 2019 (Page, 2019). One woman said, "I am not a duck," while describing her attitude about walking during a week of rain.
Participants also went on holidays and vacations, which would have reduced the amount of walking they could have done. Our sample included 14 participants, or 58 percent, who were retired. Participants visited family members during the course of the year in order to attend planned and unexpected events, holidays, and/or go on vacation away from their residences. The capacity to walk during part of the research period's weeks may have been hampered by travel time, whether by vehicle or aircraft, and unfamiliar surroundings.
Clinical Implications for Nursing
Complex care requirements must be met for older persons who are fatigued from arthritis. Three broad areas may be used to categorise arthritis therapy approaches: disease management, optimising cognitive behavioural processes, and client-specific demands (Hewlett et al., 2011). The last two of the categories are directly impacted by the study's results.
According to the study's conclusions, sleep gradually influences both physical activity and weariness. In order to increase the behaviorally modifiable parts of treatment, nurses will collaborate with clients to maximise the cognitive behavioural processes. Knowing that promoting physical exercise, such as brisk walking, might help with tiredness symptoms over time, nurses can encourage this behaviour. Additionally, nurses may encourage excellent sleep hygiene, such as a regular sleep pattern and sleep-enhancing activities before bed. The study's findings showed that sleep had a mediating role in the connection between physical activity and weariness, having a cumulative impact on easing sensations of fatigue.
Meeting the unique requirements of clients by treating co-morbidities is the study's second clinical application for nursing care. Comorbid conditions including heart disease, obesity, and diabetes affect older persons with arthritis fatigue at a significant rate (Barbour, 2017). Arthritis-related physical inactivity and the symptoms that go along with it do not aid in the treatment of other co-morbid illnesses. Promoting exercise, getting enough sleep, and reducing tiredness symptoms may give older adults more motivation to keep moving.
Further Research
The study's results recommend that future research concentrate on methods that might keep customers walking for extended periods of time. Patients with arthritis who get motivational counselling and SMS messages had their sitting time reduced (Thomsen et al., 2019). The additional significance of behaviour training in exercise therapies is a subject of growing research in osteoarthritis (Wellsandt and Golightly, 2018). Virtual peer groups and telecoaching are two additional approaches in the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease population that show potential for long-term promotion of exercise (Demeyer et al., 2017). It has been shown that using cognitive behavioural therapy may assist obese patients become more active over time (Grave et al., 2010). No of the approach, future research should incorporate measures and treatments that promote and encourage physical activity in arthritis patients.
Future studies should distinguish between various forms of arthritis and the severity of the disease process in study participants. Although osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis have comparable illness burdens (Chua, 2019), comparing moderation analyses across different diagnostic types would need looking at a larger sample size. This would provide more clarity and give physicians the flexibility to customise advice for arthritic tiredness.
Also included in future study should be more complex statistical techniques like structured equation modelling (SEM). In order to choose the analytic routes, this research used Baron and Kenny's method to mediation and moderation using linear regression. SEM gives researchers the chance to look at the connections between several independent, dependent, and correlated variables in a single, substantial model. SEM also offers the benefit of being able to take measurement error into consideration (Zhao, 2009).
Conclusion
Using mediation and moderation approach, this longitudinal research investigated the effect of sleep on the connection between physical activity and arthritis tiredness. According to the study's findings, by week four, sleep acted as a bridge between physical activity and exhaustion. Sleep did not function as a mediator between physical activity and exhaustion at any other point throughout the 6-week research. In order to comprehend the operation and boundary features of a third variable—sleep—this study engaged in second-generation research. The findings imply that encouraging exercise and sleep may eventually lessen arthritis-related weariness. This study is important in a number of ways. Cross-sectional knowledge is expanded upon by the longitudinal results. The clinical community will be able to adjust their therapies to help people with arthritic fatigue as a result of this study, which is equally important. The results from week four point to a clear and correct association between the three variables, particularly the meditational function of sleep, which may help older people with arthritis fatigue and their healthcare professionals assure sleep promotion while reducing tiredness symptoms.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
.png)
.png)
.png)
Assignment
PHCA9521 Global Health and Development Assignment Sample
Due: 8 September
Length: 500 words (Worth 20%)
Background to this Assignment Task
Module 2 introduced the key players in global health progress such as the World Health Organization/UNICEF, Government and Non-Government (NGOs), Global Alliances, Philanthropic(private) Funding and others. It also provided information on where to obtain current information on global health initiatives and current global health statistics.
This task requires students to search the available resources on-line in global health, decide upon one Program/Initiative of interest; summarise key information and communicate this effectively.
This enables peer sharing of information and resources in your group, and the opportunity to view a range of Initiatives/Programs globally.
Assignment Questions for Assignment Help
1. Select a Global Health Initiative or Program from any of the key players in Global Health
2. Write a 500-word document which describes the program; the need and significance of the disease or situation; and outcomes. This will include global health data (statistics) from a range of sources.
3. This task includes the skill of producing a document which translate more complex knowledge and information and communicates it at the level of your fellow post-graduate students and work colleagues.
A minimum of 3 references are required. One reference can be the Website or link to the Program, one to the site where the data was obtained and one which shows the significance of the disease or situation. References are not included in the word-count and there is no need for an Introduction or Conclusion. Do not write this document as a list or in dot points. This task requires you to set out the document in a way that most effectively translates this knowledge to your fellow students.
Solution
Introduction
The purpose of this study is to analyse the importance of the Global Health program to fight Aids and to make people aware of the importance of this program.
Background of The Study
It is observed from a study that there are nearly 38 million people in the world who are suffering from Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. It is significant to note that this is a disease which is sexually transmitted and one-fifth of the total population in the world is unaware of its consequences. Dr Mike McCune is trying to collaborate with Novartis for developing affordable maiden doses of gene therapy for the affected people. Moreover, this program is being conducted to make the population aware regarding the symptoms, consequences and procedures of treatment for the affected people. The prominent program is Global fund to Fight Aids and the key players of this program are the programming associates and the members of the United Nations and World Health Organisation who in collaboration will be convening this program. The higher officials of both institutions will be responsible to make participants understand the implications of AIDS.
Need and Importance of The Program
Health and well-being are the most important wealth for people. HIV is a virus that demolishes the T-cells of human beings and reduces their immunity of people. Hence, people became weak to fight with diseases and disease prone. Hence, the program is required to make the population understand the implications of HIV-AIDS in the bodies of human beings. This program is important as it will help the students to become cognizant of the action plans to combat AIDS. This program will also help in learning the approaches through which the transmission of the disease can be checked. In addition, the program will give information that human fluids like saliva, tears and urine do not contain the virus, however when fluids are in contact with the blood it becomes infectious (Sherbuk et al., 2020). Moreover, preventive methods like the practice of safer sex and the practise which a person needs to perform after getting HIV positive will be discussed in the program so that people can become more aware regarding HIV-AIDS.
Summarisation of The Outcomes
The major outcome of Global fund to Fight Aids program by the United Nations is to provide information to the people regarding the preventive measures, symptoms and treatment of HIV-AIDS. It is significant to note that due to this program people will come to know that the common symptoms of HIV-AIDS are rash, muscle ache, fatigue along with lymph which gets swollen (Marc et al., 2022). They will come to know that HIV-AIDS is a disease which usually gets transmitted during sexual intercourse, usage of contaminated syringes for vaccination and many more.
Figure: Trends of HIV in Australia
Source: (ABC News, 2022).
The infected mothers will also come to know that their unborn babies can also contract the disease as a result of the body fluids which including amniotic fluids. Blood transfusion and transplantation of organs also lead to contracting HIV. Moreover, In Australia, there are around 28, 180 people who are suffering from HIV-AIDS (NewsGP, 2022). As an outcome of this program, these infected people will come to know that abstinence from having copulation with their partner helps in reducing the chances of HIV-AIDS (Benzaken et al., 2019). Another preventive measure that will be told to the participants of this program is of practising safer sex. In addition, some of the treatment procedures for HIV-AIDS will also be told that will help the infected people to get free treatment facilities from the government. All the participants will be told about antiretroviral therapy (ART) which is a treatment procedure for HIV-infected people (Marukutira et al., 2020). Moreover, Global fund to Fight Aids program will give all the information to participants so that HIV-AIDS can be eradicated from the world.
Conclusion
This study has analysed the background of HIV-AIDS and the challenges that it poses to humans. It has demonstrated what outcomes the program on HIV-AIDS will pose on the participants of the program.
Reference List
Research
NSG3101 Rehabilitation and Community Cares Assignment Sample
ASSESSMENT OVERVIEW AND REQUIREMENTS
“National Health Priority Areas (NHPAs) were established in response to the World Health Organization’s Global Strategy of Health for All by the year 2000 and sought to focus public attention and health policy on these areas that were considered to contribute significantly to the burden of disease in Australia" AIHW (2018). The NHPAs currently consists of nine priority areas in relation to health and chronic disease.
To demonstrate your understanding of the National Health Priority Areas in relation to chronic disease, you are required to complete Parts A & B of this assessment as outlined below.
Part A of this assessment requires you to work collaboratively in groups of 3. Each member of the group will work individually on either sections 1,2 or 3 to produce a 1000-word document that will form part of the overall presentation report. Which member of the group does which section is up to you as a group to decide.
Your individual report must be evidence-based, use current literature and use APA 7th referencing style. A minimum of 10 references is required, and references must be no older than five years except if required they come from required or recommended textbooks.
You will need to research, identify and discuss the following in your report for assignment help
Section 1 - The Australian National Health Priorities
This section should include the following:
1. Discussion of the Australian National Health Priorities, when were they formulated and why?
2. An outline of the priority areas in relation to chronic conditions and prevalence of disease in each relevant chronic disease priority area using current data and
statistics to support your discussion.
3. A brief discussion of the National Strategic Framework for chronic illness used to coordinate the management of Chronic Disease in Australia.
Solution
Question 1
The National Health Priority Area is an initiative that is formed from a collaborative effort that includes the State, the Territory, and the Commonwealth of Australia. This particular health priority seeks to put focus on health policy and public attention on the areas that are deemed to significantly contribute to the disease burden that exists in Australia (Simpson et al., 2021). After years of analysis and decisions, the Health Ministers of Australia decided to formulate a plan which would mainly focus on paying attention to typical public health concerns that exist in the country. After researching the critical health emergencies that exist in the country, this particular health priority plan was formulated.
This plan was formulated in the areas where it has a potential for gain in health (Littlejohns et al., 2018). It was identified while negotiating this plan that there are main health concerns that exist in the country. This National Health priority was implemented in 2000. The main reason behind the formulation of this particular health policy was to ensure the health and safety of the general public. This plan was implemented as an initiative to help in reducing the rates of chronic conditions among the people of Australia. This plan was crafted with the intention of eliminating the diseases that are a burden to the country.
The Australian government realized that there are various diseases that exist in the country which are still not given proper attention and cure. Diseases like mental health issues are still considered to be taboo in many places of the world. Australia wanted to take this initiative in formulating a health care plan that will mainly focus on the diseases that are still undercover and lacking proper care (Bik-Multanowska et al., 2022). This plan will help millions of people in getting better treatment and cure remedies for those diseases that fall under the nine areas of priority.
Question 2
Chronic disease is known as a condition that commonly lasts for one or more years, and it requires ongoing treatment and medical attention and also limits the activities of regular living(Seaton et al., 2019). There are various types of chronic diseases that exist in Australia, which is a burden to the country as it takes away the lives of many each year. People suffering from chronic conditions suffer both physically and mentally. Chronic conditions in cumulative forms are also known as non-communicable diseases. Non-communicable diseases have a mortality rate of 41 million per year which contributes to 71% of the total death rates. There are various types of chronic conditions that contribute to the total death rates in Australia. In the year 2014-2015, more than 3% of the total population of Australia reported having Coronary health conditions for a long period of time (Engelman et al., 2019). It is estimated that more than 1.7 million Australians are diabetic patients. This data represents the number of patients who are registered and known. Cancer is considered to be a major illness in Australia, and it has a substantial economic and social impact on the life of the individual who suffers from this illness (Nisar et al., 2021). Asthma is more common in the 0-14 age group male among which females above the age of 15 have asthma more percent (Xu, Jones & Mishra, 2020).
Figure 1: Yearly date rates in Australia due to chronic conditions
Source: (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2022)
The priority areas of chronic conditions include adherence to medication, behavioral modification, and seeking mental care. It is identified in the NHPAs that various modifications are needed to be implemented in the country's medical system so that chronic conditions can be treated. The priority areas in adherence to medication ensure that all the citizens of Australia are provided with proper medication. Behaviouralmodificationsaim in to increase or decrease a certain type of reaction or behavior. Seeking mental care is considered to be a priority due to the fact that many Australians suffer from mental illnesses that are undiagnosed.
Question 3
The National Framework is helping millions of Australian with health literacy, health workforce, extensive research, governance and leadership, and data and information regarding various chronic conditions. The initiative from the side of the National Framework is helping in reducing the rates of chronic conditions by providing them with health assistance and proper treatment so that the recovery rate can be increased. It is also identified that a lot of proper management practice is required in order to manage the way the health system in Australia works. The National Framework ensures that every chronic condition should be treated well, and it is the responsibility of the health system to ensure that effective medication is provided to all. The framework identifies all the citizens who are suffering from some type of chronic condition and then aims to diagnose that person with medication that will be provided by the Australian health system.
Figure 2: Percentage of people suffering from chronic conditions in Australia
Source: (Abc, 2022)
The National Framework for treating chronic conditions in Australia is an overarching document policy that is formulated especially for chronic conditions that exist in the country (Cardoso, Reis & Manzanares-Céspedes, 2018). This particular framework outlines the outcomes and directions through which the Australian people can be helped, and their lives can be made healthier. This can be achieved by following effective management and prevention strategies that are marked under the chronic conditions identified by the NHPAs. This particular framework moves across a disease-centric approach and helps in providing national directions and strategies that are applicable to a variety of chronic conditions. With the help of recognizing that various other similar principles that underlie the management and prevention of chronic disease do exist. This particular framework is considered to be an effective resource for every player in the space of chronic conductions (Hajat & Stein, 2018). This particular framework was crafted with the intention of providing strategic and effective measures that will aim to make the lives of the Australian people safer and healthier.
Reference list
Essay
PBHL20004 Public Health Action and Evaluation Assignment Sample
This is an INDIVIDUAL assessment. Based on your informal reflections throughout the term, you will explore your ability to develop effective partnerships with others, including establishing relationships and collaborative learning. In a 1500-word essay, reflect on your group partnership throughout the term. In your essay, you will need to focus on following points for assignment help:
• The group process in establishing and maintaining relationships throughout the term
• The effectiveness and experience of collaborative learning within the group
• The relevance of this experience in undertaking community-based public health actions and evaluations.
A minimum of two appropriately cited references is required.
Solution
Introduction
The reflective assessment will shed light on the team dynamic and how my personal growth is determined by collaborative learning within the team. It will also be demonstrated how the relevant experience will be conducive to the effectiveness of healthcare practices that are based on values and ethics.
Discussion
The group process is one of the relevant activities to maintaining relationships. I think maintaining bonds with members of the team is key to professional efficiency. Productivity is guaranteed only when there is no miscommunication in the team. Group partnerships uplift confidence, and make morale strong. I always look forward to fruitful learning that becomes easier to communicate with the team members in a friendly spirit. The group process instils the spirit of togetherness that sharpens the intellect and cognitive powers to flourish to the fullest (Van Leeuwen and Janssen, 2019). Unity in the entire team is very much required that keeps the team going toward the desired destination. At the same time, it channels the energy in a positive direction. I have learned how to stay connected with other people at a critical juncture. Personal connectivity enriches the professional outlook that makes the output attuned to the purpose. The more connections that can be developed within a team, the more growth one can achieve through the discussion. Many people being assembled in one place contribute to the knowledge by sharing valuable opinions on a particular topic. The various perspectives generate strong individual insights and paradigms (Qureshi et al., 2021). The exchange of cultural values and the discussions pave the way for the comprehension of the multiple topics and the various usages of these into the perfect application.
I have enhanced my decision-making process having been involved with team collaboration and dynamics. My leadership qualities have been made to tackle a situation with dexterity. Professional growth has been fuelled by personal determiners. I have comprehended one process that socialisation is being made easier by maintaining relationships with the team in a friendly manner. A positive outlook has grown that removes all complications and odds. Simple manners and outlooks have grown to be developed while discussing with peers. I have highly benefited from the multiple views of different people or cross-cultural ethos, differences and symptoms. The team undertaking the task to finish, it is not difficult to finish the task with alacrity and promptness (Ansari and Khan, 2020). Group thinking has enhanced my analytical skills and this is necessary for the increase of patience, determination, and composure. Without chaos, the decision-making process gets more stable and appropriate to the condition. Contextualisation makes learning fast and effective. Different needs of the individual get fulfilled and when the opinion is asserted, it keeps all the inhibitions at bay. All the insecurities can be dissolved and this is the cornerstone of overcoming challenges with a smile (Van Leeuwen and Janssen, 2019). I have incorporated a lot from the group process and maintained a good connection with the others. I have developed the strongest attitude having been involved in the intensive discussion. I have been insured to take more dangerous risks in my stride and that is effective for the process to be risk-free and devoid of uncertainties and indifferences. I become innovative in solving critical problems with calmness and creativity. Learning from past experiences, I have been able to head-on with the present collisions with steadfastness.
The effectiveness and experience of collaborative learning within group can improve self knowledge’s. The efficiency of collaborative learning helps me focus on my strengths and lets me categorise my weaknesses. After the weakness has been identified, I have been enabled to set up the thinking of the highest capability with strong intuition. My organisational skills have been sharpened which leads to better and proactive management of self and dexterous control over the difficulties in life. Communicational goals have been set and I have strived to the setting of the goal with purpose. The interaction will be developed to widen the scope of understanding and the knowledge objectives. I have increased my self-esteem and encouraged the other members to follow the creative pattern of thinking to shine in life. The development of interpersonal and social skills maximise the educational missions that would demonstrate the goals to the team (Florence, 2020). The chance of miscommunications, risks, and hazards will be less which promotes combative decision and continuous learning. I have been inspired to follow social interaction and dimensions that project the groups in the development of interactional skills. The creation of a diverse atmosphere helps the professionals delve into the depth of concepts and skills. The critical concepts and ideas are related to the emergence of analytical powers. I am now good at offering valid judgments. The power of constructive criticism has been developed by the capacity to influence people with courage, confidence and a people-solving mentality.
Members of the team will work for the same goals and develop the power of empathy and respect for others' feelings. Active listening makes the social skills strongest which helps the future orientation solid and fundamental. I have learned to respond to the various applications and opinions and angles. Open-mindedness has been developed that makes the connections between personal and professional skills. Through collaborative learning, I have gained the trust and learned to place credibility on the onions made by the team. The supportive ambiance will raise the optimism and the growth that are accountable for the future productivity in the group (Ansari and Khan, 2020). The learning experience has been fruitful in making the content fun-filled and true to the experience. I have felt comfortable discussing with the team members and this is effective in the origination of the inspiring content and the evaluation of the ideas in the future. The ideas of different people influence my thinking in making positive contributions.
The experience of learning collaboratively has majorly helped me in undertaking community-based public health actions. The experiences gathered by collaborative learning have helped me to understand what I can do to undertake public health actions better. The experience has given me the ability to judge the strengths and weaknesses of other members in the group. The experience can be used to assign particular sectors to a particular person who is good at it (Omae, 2021). Through using the experience of collaborative learning I and other members can learn faster about what can be done to undertake a community-based public health action. The experience also helped me to communicate my thoughts to the other members of the group which made it even easier for everyone to work towards a single goal. Utilising the experience I learned qualities of leadership which also helped me to lead a group of members in undertaking a community-based public health action. Having the experience of collaborative learning also helps everyone to be more solution-oriented rather than focusing on the problem (Florence, 2020). Through learning new things from each other I managed to be more capable to undertake community-based public health actions, the experience also helped me understand other members better.
Collaborative learning has germinated a sense of values, morality and ethics and I think this will be helpful when I will extend the hand of support to the community people. The relevance of the moments and the experience will let me know each other. It is very important to consider and treat human beings with blue and compassion. Health care demands value-given care where the patients no longer feel stressed and depressed. Community-based actions stimulate hearty efforts and these will regulate the higher concentration and morale in the work people are going to undertake. The more I will utilise the accumulated learning in the professional field, the stronger I will be. Value-based care requires the efficacy of the individual to be a good caregiver (Qureshi et al., 2021). I will be empathetic to assess the real needs of the people and offer the right kind of attention they are craving. Many patients feel estranged from the mainstream of life and they cannot reconcile with their previous experiences. The constant desire to be a part of society makes them more vulnerable and the caregivers must be affectionate enough to make them forget the loss of family and friends.
I will be at my best to question the value of being given care and learn from the entire journey. I will try to create the situation so that they again gain a renewed sense of hope and certainty in life. I will exercise the practices of ethics and morality in each complicated scenario. I will be able to manage the needs of the afflicted people and give them the promises of hope and resilience. The patients will benefit from value-based learning. The sociocultural ambiance will be justified and this will make my purpose strong.
Conclusion
This is identified from the above discussion that group-based learning adds to the dynamic benefits and positive outlooks for the participants in the tear. The reflective account has demonstrated how the gathered learning will come to help in the future period.
Reference List
Case Study
NURS3002 Advance Decision Making and Practice Assignment Sample
Length: 1500 words
Curriculum Mode:
There is a word limit of 1500 words. Use your computer to total the number of words used in your assignment. However, At not include the reference list at the end of your assignment in the word count. In-text citations will be included in the additional 10% word count. If you exceed the word limit by more than 10% the marker will stop marking at 1500 words plus 10%.
Aim of Assessment:
The Aim of this assessment is to develop your understanding evaluating the professional conduct of a nurse/midwife in the case study provided.
The case study provided is a decision statement selected from Decisions of the Professional Standards Committee from the Nursing and Midwifery Council New South Wales - The Health Care Complains Commission (HCCC). You are to identify professional practice issues from the case study and then draw on the professional frameworks and regulatory legislation, to develop sound and appropriate responses to the clinical incident that will inform your future practice.
Details for Assignment Help
This assessment requires you to identify and summarise the professional practice issues in the case study from either a nursing or midwifery practice perspective. You need to identify and evaluate relevant professional errors identified that potentially contributed to the incident happening. Finally, discuss on how your future practice might change and develop as a result of this learning.
Students are to draw on the National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards, NMBA professional practice documents and NSW Health policy documents (where appropriate) to develop informed responses.
Students must refer to and use the case studies located on vUWS under Assessment 2 tab for this assessment. There is one nursing case study and one midwifery case study to choose from. Submission requirements: -
The total word count is 1500 words. - Electronic copy only.
- This assessment is marked online; no paper copy will be accepted. Marks, comments, and the marking criteria will be released online. If you do not receive your marked assessment when all others have been returned, it is your responsibility to contact the Subject Coordinators for assistance.
Solution
Introduction
The professional code of conduct of a nurse embodies an ethical blend of rules and norms that is designed to direct the nurse in providing care to the patients found in critical care situations. The code of ethics comprises veneration for beneficence, autonomy, non-maleficence and justice. The essay consists of three sections. The first section discusses the professional practice issues from the perspective of a nurse. The second section points out the relevant professional errors of two nurses from the case study. In addition, the NSW Health policy documents mark the guidelines to be followed by the nurses rendering service to critical care patients. Finally, the third section discusses the reflection on how the suggested practices might amend and mitigate the issues found in the incident of the case study. The essay identifies the relevant professional errors from the case study and shows that the professional code of conduct followed by the nurses can help to resolve issues.
Section 1
The incident in the case study points out the complaint that has been launched against Ms Nelly Youssef who is a registered nurse. The complaint was launched against Ms Nelley Youssef by the Health Care Complaints Commission before the Administrative Tribunal and NSW Civil.
This complaint was lodged after an inspection of all the allegations charged against her on 13th January 2021 (Gillespie & Reader, 2018). All the allegations were proven, and she was charged with professional misconduct and unsatisfactory professional conduct. The case was filed against her after the Commission noticed an unprofessional act. They alleged her after they found an 80 year patient with a laryngeal stoma unresponsive. Ms Nelley Youssef reluctantly agreed with the junior colleague to dress the stoma and provided the dressing to the patients without proper instruction (Joo & Liu, 2021). Later, the patient was found not responding, thus it was tough for her to remove the dressing. When asked, she provided wrong information stating that she noticed the patient was not responding and the stoma was not covered. When found that the information provided was irrelevant, it was decided that strict actions would be taken against her. She misled her junior colleague (Gillespie & Reader, 2018).
Section 2
The incidents in the case study point out two professional errors committed by two nurses, Ms Nelley Youssef and RN Mc Arthur. Nelly Youssef was accused of unsatisfactory professional misconduct as she improperly responded to a request from a junior colleague who sought advice from her (Caselaw.nsw.gov, 2022). The former stated that it will cause no harm if Meplix occlusive dressing to the stoma of Patient A. By this, she portrayed inadequate knowledge that stoma is the only airway of patient A, covering which will lead to more harm than good. Moreover, the dressing was forgotten to be removed from the patient until he was found unresponsive in the shower. When she was accused of unprofessional conduct under 139B(1), she said she did not find Mepilex border dressing on the stoma. However, later on, she admitted that she lacked knowledge regarding Patient A's anatomy (Caselaw.nsw.gov, 2022). Moreover, she stated that she did not know that the laryngeal stoma was the only airway for the patient.
RN McArthur was also accused of the unprofessional code of conduct under 139B(1)(a). The concerned person also improperly applied a Meplix dressing on the patient's laryngeal stoma before he started to take his shower. Moreover, he also lacked adequate knowledge about the clinical history of the patient (Halcombet al. 2020). He also failed to know that the only airway of the patient is the laryngeal stoma which was unknowingly covered. He further stated that she stayed with the patient for five minutes after applying the dressing. This was falsely stated by the person in a letter sent to HCCC. He had further satiated that at the time of dressing he lacked the information about the underlying anatomy of patient A (Caselaw.nsw.gov, 2022). To everyone's utter surprise, he denies is not guilty of whatever has happened with the patient.
NSW health organisations monitor the incorporation of Policy Documents and guide the implementation as an essential aspect of strong governance, audit formulation and performance. The policy document consists of guidelines, policy directives and information issued by the NSW Ministry (NSWhealth, 2022). Besides encompassing protocols and procedures, it also lays down guidelines that should be strictly adhered to by the health service unit within the local health district. The policy documents formulate superior clinical practices along with the clinical and non-clinical functions. The guidelines are issued by the NSW policy systems and adopted in the NW health units. The components of the policy document are the information bulletin, NSW health organisation and the NSW ministry of health (NSWhealth, 2022). The policy document clearly explains the information bulletin, policy directive and essential guidelines issued by the NSW health organisation.
The organisation found in the case study does not follow the guidelines laid down by the National Safety and Quality in Health Service Standards (NSQSH). So, the company can opt for Safety and quality systems with the help of governance processes so that they can improve and manage the safety and quality of health care for patients (Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2021). In addition, the NMBA guidelines are not ingrained in the mentioned health care unit of the case study. The NMBA states that nurses shall adhere to professional commitment and abide by the respective law (NMBA, 2022). Thus, the nurses are expected to act with professional obligation for the sake of the patient's recovery and well-being. As a result, the convicted nurses are placed under S139B (1) for conducting unprofessional behaviour (NSWhealth, 2022). The Health Care Complaints Commission (HCCC) has done justice to the complainant by identifying the accused and taking legal measures.
The implementation of the NSW policy documents gives an overview of the roles and responsibilities to incorporate the policy directives (Taylor et al. 2020). The policy documents comprise the codes of conduct that medical professionals are expected to follow. It provides a framework of actions with respect to ethical conduct. Breaching the code of conduct mentioned in the policy documents will be held responsible by law (NSWhealth, 2022). In addition, it leads to disciplinary actions and the punishment is decided by the severity of the crime.
Section 3
Reflection
I have been through both the cases and understood that the first case was related to Ms Nelley Youssef, against whom a case was filed due to her unprofessional negligence towards the dressing of stoma for an 80-year-old patient who was found not responding. At the same time, the second case deals with two professional misconducts by Ms Nelley Youssef and RN McArthur for reluctantly applying Meplix dressing to a patient with a laryngeal stoma (NMBA.gov., 2022). All I understand is that both cases are completely careless, or the nurses are not being provided with proper training. As per my understanding, an individual might own a degree and be an official nurse, but they can still be expected to make mistakes. In both cases, the situation could have been controlled if the nurse had asked for help from their other senior colleagues before conducting the method on the patients (Taylor et al. 2020). Both the patients have been found to act unprofessionally, first for misguiding their junior colleagues and second for showing a lack of adequate knowledge.
After summarising the cases, I had been through the NMBA Standards for Practice documents for Nurse and NSQHS or National Safety and Quality Health Service. I learnt about the patients' professional expectations and the nurse's authority. I can conclude that if I had been in place of Ms Nelley Youssef, I should have taken the responsibility and correctly instructed my junior colleague for the dressing of the laryngeal stoma firstly because the patient had not been responding and second because it was 80 years of age. This is not only the main reason but the main because, as a senior nurse, it is my responsibility to take care of the patients and properly guide the juniors (NMBA.gov., 2022). Thus, this would not have led me to any problems like Ms Nelley Youssef had. As per the case of RN McArthur, firstly, I would have strictly followed NMBA and NSQHS and still, if I was unclear about the procedures, I would have consulted someone, maybe a doctor or an experienced nurse. I would not have reluctantly applied Meplix on the patient's stoma before their bath. It is very unprofessional and showcases carelessness to state a lack of adequate knowledge about the wound (NMBA.gov., 2022). Even if that had happened, I would not have just strongly accepted that it was not my fault, even after knowing it was.
Conclusion
This study is concerned with summarising a case study that had been provided related to the issue or complaints that had been launched against the nurses for misleading or misconducting and performing unprofessional techniques of giving medication to the patients. Here the summary has been provided of the patient's complaints. The study has been divided into an introduction to the nursing case study talking about the professional code of conduct in nursing. Sections 1, 2, and 3 highlights the issues and summarise what the problems had been, under what act they have been taken, and what accusation points have been pointed at the nurses and how they had reacted to it. Reflection is the place where the cases have been heightened with the problems that the patients have faced due to the unprofessional acts of the nurses.
References
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care (2021). National safety and quality in health service standards (2nd ed.). Retrieved 27th August 2022, from https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/sites/default/files/2021-05/national_safety_and_quality_health_service_nsqhs_standards_second_edition_-_updated_may_2021.pdf.
Gillespie, A., & Reader, T. W. (2018). Patient?centered insights: using health care complaints to reveal hot spots and blind spots in quality and safety. The Milbank Quarterly, 96(3), 530-567. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1111/1468-0009.12338
Halcomb, E., Williams, A., Ashley, C., McInnes, S., Stephen, C., Calma, K., & James, S. (2020). The support needs of Australian primary health care nurses during the COVID?19 pandemic. Journal of nursing management, 28(7), 1553-1560. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.19.20135996
HCCC v Youssef & McArthur [2021] NSWCATOD 2
Health Care Complaints Commission v Youssef; Health Care Complaints Commission v McArthur - NSW Caselaw. Caselaw.nsw.gov.au. (2022). Retrieved 27th August 2022, from https://www.caselaw.nsw.gov.au/decision/176ee7c5bee2c2cdb86225c8.
Joo, J. Y., & Liu, M. F. (2021). Nurses' barriers to caring for patients with COVID?19: a qualitative systematic review. International nursing review, 68(2), 202-213. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8013562/
NMBA.gov. (2022). Retrieved 29th August 2022, from https://www.nursingmidwiferyboard.gov.au/codes-guidelines-statements/professional-standards/registered-nurse-standards-for-practice.aspx
Taylor, E. V., Lyford, M., Parsons, L., Mason, T., Sabesan, S., & Thompson, S. C. (2020). "We're very much part of the team here": A culture of respect for Indigenous health workforce transforms Indigenous health care. PLoS One, 15(9), e0239207. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239207
Www1.health.nsw.gov.au. (2022). Retrieved 27th August 2022, from https://www1.health.nsw.gov.au/pds/ActivePDSDocuments/PD2016_049.pdf.
Coursework
7069SOH Managing & Planning resources in Healthcare Organisation Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
1. Critically apply financial performance management, budgeting, and cost-benefit analysis to healthcare organizations
2. Critically evaluate the legal, ethical, educational, and professional factors which impact the management of the healthcare workforce
3. Critique the skills and knowledge required by healthcare leaders which impacts upon finance and workforce.
Coursework 2
3000-word individual coursework addressing Learning Outcomes 2 -4
This assessment component counts for 15 credits
In 3000 words, addressing learning outcomes 2-4, complete the following assessment task:
Critically evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of resource planning and management in a health system you are familiar with, focusing on the following key areas for assignment help:
1. Priority setting and decision-making processes
2. Workforce planning and development
3. Human resource and talent management
Prepare a business case for improvement in one of the key areas that maximizes the strengths and addresses the areas of weakness you have identified.
Your individual coursework report will be assessed using the HLS Faculty Postgraduate Assessment Marking Rubric and the coursework 2 assessment guidelines, which you will find in the appendices in the module guide.
It is important to you and the tutors that your project is written and presented in a professional manner. The following requirements must be adhered to in the format of assignments:
1. Your limit does allow for +/- 10% words in length. The limit includes words used in tables, graphs, charts and diagrams, but excludes the front cover, references list and appendices. If you exceed the word limit you will be penalised 10% from your mark
2. The front cover page - see appendix 4 for the template in the module guide.
3. The font type should be Arial and the font size for the body of the text 12 point.
4. One and a half (1.5) line spacing must be used.
5. All pages should be numbered consecutively, in the footer on the right.
6. Your student number should be in the footer on the left.
7. References, citations, and quotations should be in Coventry University APA Referencing only. Ensure that all statements and arguments are supported with reference to the evidence in the relevant literature.
8. Any diagrams, tables, photographic images etc. should be appropriately labelled and referenced.
Solution
Introduction and context
In this particular study, the Midland Healthcare system is being focussed majorly in association with their initiative to provide acute treatment to the mentally ill patients. In order to attain such objectives, this study will look into a specific healthcare system for the purposes of resource planning and management, among other things. The investigation will also look at topics such as decision-making and prioritization, workforce development, and human resource management, to name a few. Midland Healthcare will offer inpatient treatment for a range of acute mental health illnesses and needs, according to the findings of the research (Midland Healthcare, 2021). In order to aid in the rehabilitation of its 40 patients in the acute care center, the organization supplies more than only medicine to them (Mesfin et al., 2020). In addition, the organization provides counseling, support, and therapy to those who are recovering from diseases.
Discussions
The business case for improvement
The high number of readmissions for mental health concerns that Midland Healthcare has witnessed has prompted the organization to focus its efforts on improving patient outcomes after they have been discharged from its facilities. The organization hopes to use this money to extend its services to the general public as well as to aid patients who have been discharged from the hospital in improving their overall health status.
Table 1: Smart objectives
(Source: Self-developed)
In order to be able to provide adequate care to the patient even after the discharge with not only medicine but also therapeutic, counselling, and supporting process the management of Midland healthcare needs to fund a lot in this particular proposal. Besides, preliminary investigations of Midland Healthcare's resource planning and management practices, according to the organization, must be completed before any substantial adjustments can be introduced (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). The activities of identifying, analysing, and obtaining the resources that are required for the project's success are all included in the definition of resource management in project management. What is certain is that, no matter what the nature of the project is, it will always need human and physical resources, including the necessary workers and labor, as well as construction materials and equipment, as well as facilities, information technology, and other resources.
Option appraisal
The health-related obstacles faced by patients, service users, and members of the community are the main focus of resource planning and management in healthcare systems, with the bulk of attention being focused on these difficulties at any one time (Mesfin et al., 2020). The availability of sufficient resources to address the needs of patients is critical to providing them with a decent quality of care. This is particularly true in the case of Midland.
Identifying unmet patient requirements and matching them with available resources within an organization is the purpose of resource planning and management in the healthcare industry. Creating prior goals that are both acceptable and attainable in order to enhance patient outcomes is a priority for the organization, which also acknowledges and analyses the mental health requirements of individuals who are treated by them. The Midland Health System provides patients with access to an array of additional equipment and gear that may be of assistance with their mental health care needs, in addition to medical equipment and drugs. There is also an enormous number of staff that are there to serve customers at any time they want it.
Benefit analysis
The costs and benefits of several different methods must be weighed and compared to achieve a decision on resource allocation before any conclusions can be reached. Other public-sector healthcare organizations are also under the control of the federal government, in addition to Midland Hospital (Midland Healthcare, 2021). All choices, from financial decisions to input and labour decisions to capital decisions, are imposed by the United States federal government (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). The government's use of this budgeting information, on the other hand, is what enables them to categorize expenditures and calculate the amount of money that will be required to complete the project to its completion.
The Midland Institute for Mental Health also has responsibility for human resources and talent management, which is important given that the quality of therapy provided to patients is highly dependent on the growth of current staff members. When it comes to achieving long-term success, companies such as Midland Corporation understand the need of investing in human capital. For example, the company recognizes the importance of recruiting and maintaining highly trained and motivated personnel over the long term. Counselors, social workers, and therapists are examples of professional staff members who are offered opportunities for professional development because they have direct patient contact. Given how critical it is for these professionals to keep up with their education and training, it is critical that resources be given and budgetary choices are made with a strong focus on their continued education and training in mind.
Midland will conduct a review of the present personnel and material levels, as well as how they may be expanded or repurposed, as part of its attempts to close the gap between the actual and expected states of things in the industry. A sufficient number of staff members must be maintained to ensure that both inpatients and outpatients continue to get support and treatment without jeopardizing the organization's goals and objectives. This is especially important in emergencies (Midland Healthcare, 2021). This gives us an idea of the identification and execution of measures to reduce the gap between demand and supply for employees inside the organization as a direct result of this strategy.
It is also feasible to evaluate whether or not more supplies or equipment will be necessary for therapeutic operations by comparing the existing condition to the planned state. In order to make a choice, it is important to first recognize a problem and then communicate with others in order to discover a solution to that problem. A healthcare system's additional responsibilities include the provision of high-quality services that are tailored to the specific needs of each individual patient. As a result of the organization's legal and ethical obligations to treat each patient as an individual, Midland's staffs is ready and willing to treat each patient as if they were a separate and distinct individual.
Cost analysis
Midland organizes its resources in order to maximize efficiency, and it does it via the use of a cost-benefit analysis approach, as well as planning and forecasting procedures. Midland's approach to resource planning places a strong emphasis on incremental budgeting as well as activity-based budgeting, with the kind of budgeting chosen depending on the particular components of a project as well as the demands placed on the workforce. When it becomes essential to increase the percentage of the previous year's budget that is being utilized in the current year's budget, incremental budgeting must be employed to accomplish this. To put it another way, this method is simple and easy to comprehend (Rangachari & L Woods, 2020). As a result of this, the budget may be overstated or underestimated, which may result in inefficiencies in the budgeting process as a result of the budgeting process as a whole over a longer period of time. As a consequence, management is likely to exaggerate the severity of the crisis, resulting in the waste of financial resources as a
Result of their decisions.
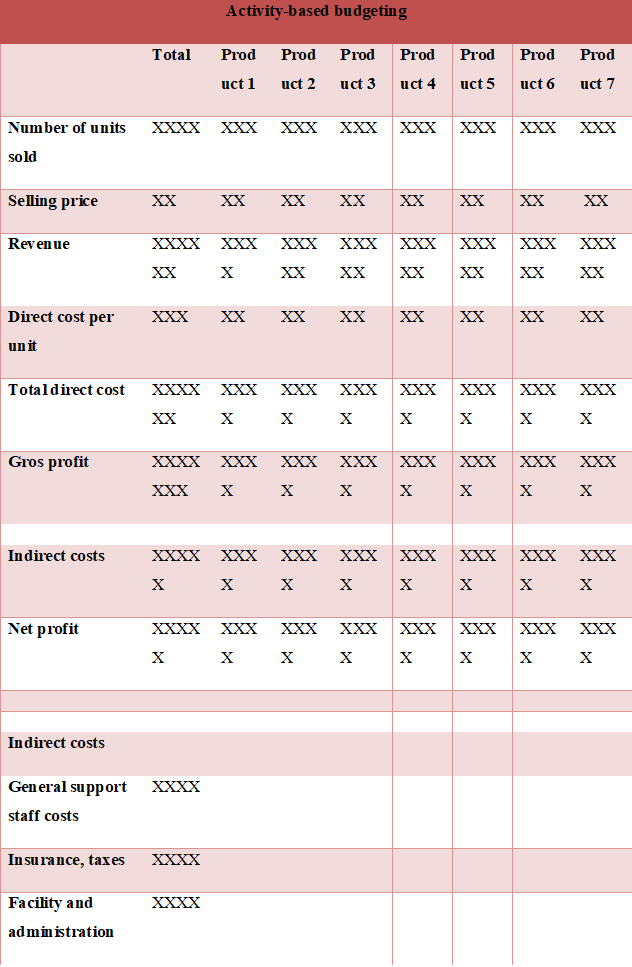
Table 2: Budget template of Activity-based budgeting
(Source: Developed by the researcher)
It is used as an example to illustrate how activity-based budgeting techniques may be used to real-world problems in order to obtain successful outcomes. The project described in the introduction is utilized to demonstrate this. The use of budgets to account for cost drivers and activities that vary from those that occur in the usual course of business is critical when these changes arise. Budgets must be used to account for the differences in costs and activities that have occurred. Identification of the specific amount of money that will be required to achieve the project's objectives, on the other hand, may prove to be a challenging task.
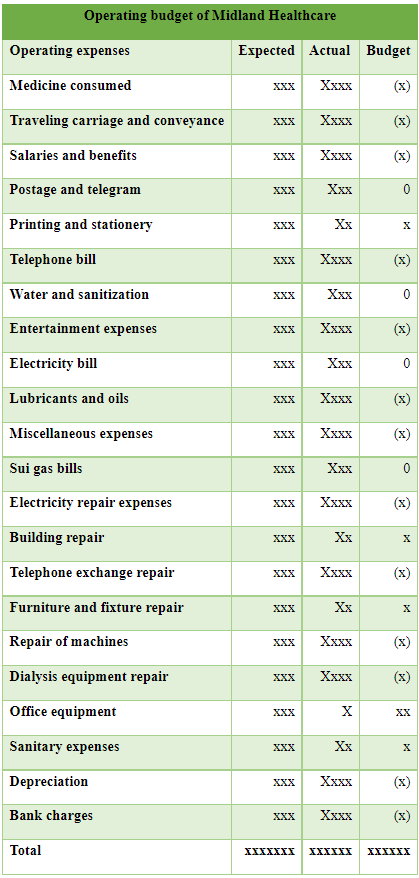
Table 3: Operating budget structure
(Source: Self-developed)
In Healthcare facilities, the operating budget is generally done to forecast expenditures as well as revenues for the upcoming years (Wang & Jobarah, 2021). In this case of Midland Healthcare, the operating expenditures for a new project and expansion of their care to the general public as well, therefore, has been done. A simple operating budgetary structure has been provided for a better understanding of all the possible expenses for Midland healthcare during the course of the project. By the differentiation between expected and actual operating expenses, Midland healthcare can successfully able to generate its operating budget for the project and based upon that can significantly fund better.
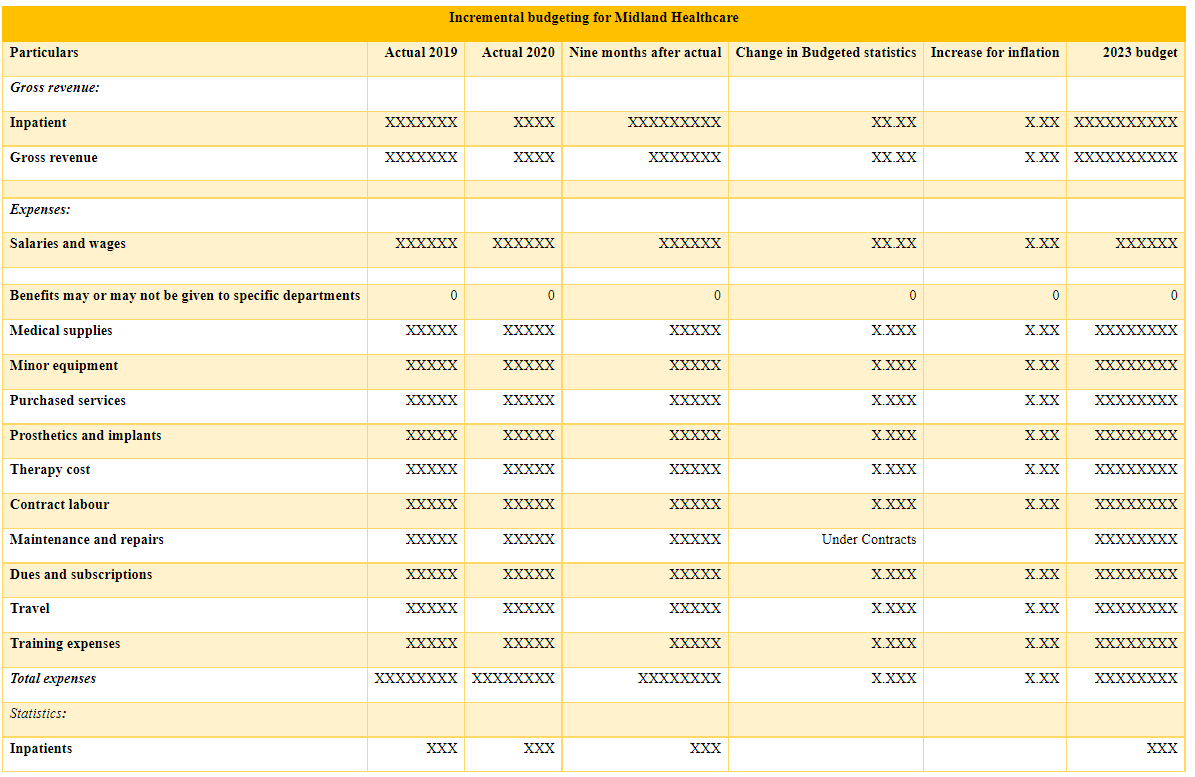
Table 4: Incremental budgeting structure
(Source: Self-developed)
Incremental budgeting on the other side can help the Healthcare financial experts to make small and significant changes to the pre-existing budget for creating a whole new budget (White, 2020). For the case of Midland Healthcare combining the previous budget needs to only add the incremental amounts in this particular budget for getting a clear identification of the new budget numbers. Incremental budgeting is easy to implement as well as a calculator and it can help Midland healthcare in the continuity of the funding. However, this particular process leads to extra spending as well as doesn't consider all the charges.
Risks
Midland has a policy of doing a cost-benefit analysis in order to determine the training and development needs of its personnel. Following that, the technique is used to evaluate the costs of such training to the benefits that may be gained as a result of such training. Despite the fact that this is a simple strategy, it does not offer a comprehensive picture of the desires and objectives that exist inside the labor market (Limbu, Piryani & Sunny, 2020). Along with benchmarking, the organization uses key performance indicators to measure the success of each individual person inside the organization as a complement to benchmarking, and this is in addition to benchmarking (Al-Haroon & Al-Qahtani, 2020). Managers set objectives for the level of the workforce and put a heavy focus on it throughout the workforce and talent planning cycle in order to guarantee that demand and supply are kept in balance. However, the training and maintenance cost is too high. In that case, it is more likely to put adverse effects on the budgetary aspects and planning of the initiative as well. Comparatively speaking, benchmark-based testing delivers a more accurate representation of a product's overall performance than other testing approaches.
Table 5: The risk matrix
(Source: Self-developed)
The development of a business case for enhancing the management of human resources and talent in healthcare organizations was crucial to achieving the aim of enhanced performance in this sector (Berberoglu, 2018). People are a very significant resource in healthcare organizations since they are accountable for providing patient-centred services.
Evaluation
It can certainly be considered, the Midland healthcare in order to take action for all the considered strategic lookout to help the mentally unstable individuals get better health outcomes even after discharging need to follow the "logic model" for monitoring, measuring as well as ensuring the success of the proposed impacts. As per the views of Howarth et al., (2020), the Healthcare facility first and foremost needs to look for adequate resources or inputs according to the logic model. Assessment of adequate resources or inputs or labour can help in understanding the ability of the facility to successfully implement the changes.
Figure 1: The Logic Model
(Source: Howarth et al., 2020)
The second necessity of the logic model represents all the activities of the change implementation. Midland Healthcare, therefore, needs to access all the activities such as upgrading the training process, hiring more experts, restructuring group points of the organization, and more can be utilized for accomplishing the proposed planning for better success. On the other side, as per the opinions of Mills et al., (2020), the logic model also requires the planner to extensively focus on the output as well. After accomplishing the planned initiatives this particular model can help the Midland Healthcare facility to drive the service for acute facility care patients in providing treatments regarding the aftercare of discharge. Last but not least, the "logic model" as for the last movement included help the service providers in analyzing the level of accomplishment to the intention. The Midland Healthcare facility therefore can successfully address whether the service they were willing to provide is accurately meeting their intention of what is actually needed to be.
Conclusion
It can finally be summarised that Midland Healthcare has been quite affected by the alarming rate of increment in the readmission rate in the mental health facilities due to lack of aftercare. After the discharge, there are very few patients that get accurate aftercare, support, adequate therapy, and more to recover. This particular scope is very narrow to the general public as a service in the Healthcare sector. Henceforth, Midland Healthcare has taken the initiative to provide more than medicinal care including counselling, support as well as therapy to the patients for recovering from the disease as aftercare. Initially, this particular organization is willing to guide 40 rehabilitation patients combating mental illness in their own acute care center. Therefore, the resources and finances of this particular business have been evaluated for understanding the scope of running this initiative. Through SMART objectives, various perspectives of the proposal have been analysed. Strategic priorities such as "preliminary investigation of resources and management practices", "analysing the scope of resource management", "provide adequate training" and more have been taken under consideration. Finally, it can be concluded that there are certain skills that are required by the Healthcare leaders to impact the finances and workforce such as "operation knowledge beyond country-specific level", "managers need to have global perspective", "practicing unity" and "mentoring others".
References
Midland Healthcare. (2021). Best Multispeciality Hospital in Lucknow | Midland Healthcare. Midland Healthcare. Retrieved 27 April 2021, from https://midlandhealthcare.org/
Rangachari, P., & L Woods, J. (2020). Preserving organizational resilience, patient safety, and staff retention during COVID-19 requires a holistic consideration of the psychological safety of healthcare workers. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(12), 4267. https://www.mdpi.com/743378
Limbu, D. K., Piryani, R. M., & Sunny, A. K. (2020). Healthcare workers’ knowledge, attitude and practices during the COVID-19 pandemic response in a tertiary care hospital of Nepal. PloS one, 15(11), e0242126. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0242126
Berberoglu, A. (2018). Impact of organizational climate on organizational commitment and perceived organizational performance: empirical evidence from public hospitals. BMC health services research, 18(1), 1-9. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12913-018-3149-z
Al-Haroon, H. I., & Al-Qahtani, M. F. (2020). Assessment of organizational commitment among nurses in a major public hospital in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 13, 519. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc7320227/
Mesfin, D., Woldie, M., Adamu, A., & Bekele, F. (2020). Perceived organizational culture and its relationship with job satisfaction in primary hospitals of Jimma zone and Jimma town administration, correlational study. BMC health services research, 20(1), 1-9. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-020-05319-x
Wang, Z., & Jobarah, H. (2021, December). Predictive Analytics Method Underpin Planning and Budgeting Evolution. In Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference. OnePetro. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://onepetro.org/SPEADIP/proceedings-abstract/21ADIP/3-21ADIP/D031S088R003/474128
White, J. (2020). (Almost) Nothing New Under the Sun: Why the Work of Budgeting Remains Incremental. In Budgeting, Policy, Politics (pp. 111-132). Routledge. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780429336232-8/almost-nothing-new-sun-work-budgeting-remains-incremental-joseph-white
Howarth, M., Brettle, A., Hardman, M., & Maden, M. (2020). What is the evidence for the impact of gardens and gardening on health and well-being: a scoping review and evidence-based logic model to guide healthcare strategy decision making on the use of gardening approaches as a social prescription. BMJ open, 10(7), e036923. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/7/e036923.abstract
Mills, T., Shannon, R., O’Hara, J., Lawton, R., & Sheard, L. (2022). Development of a ‘real-world’logic model through testing the feasibility of a complex healthcare intervention: the challenge of reconciling scalability and context-sensitivity. Evaluation, 13563890211068869. Retrieved on: 10th March 2022, From: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/13563890211068869
Essay
HEALT1113 Effective Communication For Health Professionals Assignment Help
Due Date: Wednesday, 6th April 2022 - 23:59 hour (Week 6)
Value of the Task: 30%
Word Limit: 1800 +/- 10%
Assessment Details:
Building on your understanding of effective communication from Task 1a, you will explore effective communication with patients using a case study. You will assume the role of a Registered Nurse, a Physiotherapist or an Occupational Therapist, who has received a client referral for patient management with the focus on effective communication. You have not yet met this patient/client. You should critically reflect on how communication with the patient/client will take place. You must choose ONE of the two cases provided in Moodle for your essay response.
Assessment Structure for essay writing help
Your essay must include the following:
1. Introduction (10 -15% of total length).
a. Introduce the concept of effective communication in your specific health context
b. Provide an overview of the case study you have chosen.
c. Outline the main points you will discuss in the body paragraphs
d. Use in-text citations and ensure they are reflected in the reference list.
2. Body paragraphs (5 paragraphs)
HEALT 1113 – Effective Communication for Health Professionals - Assessment a. Using the headings and prompts as a guide provided in the essay template, create complete paragraphs applying academic writing style, plus evidence to support your claims using in-text citations.
b. Highlight important elements from the case study that will determine your communication strategies
c. Your writing should include analysis and synthesis of the research.
3. Conclusion (10% of total length)
4. Reference list: APA 7th edition
a. You are required to reference a minimum of eight academic sources (e.g. textbooks, peer reviewed journal articles).
b. Resources such as websites, legislations, and government sites are in addition to the minimum of eight academic resources.
c. Reference list is NOT included in the word count, but in-text citations are included in the word count.
Solution
Introduction:
Communication has been playing a major necessary and critical role in the field of healthcare as it ensures health care professionalssustain a position to understand patient needs, the issues as well as involve them through the process of effective care and treatment process. Patient with misuse disorder of alcohol or any other substances often sustains addictive behaviour and related medical issues or comorbidities (Ratna, 2019). Thus, it explains the need for effective treatment and care for the patient, in order to provide better and accurate treatment and recovery options to the patients, it is essential to understand the underlying factors such as the reason behind the addiction, the difficulties witnesses post addiction as well as the better options available. In such conditions, communication plays a significant role in assessing the patient as well as planning for a better treatment plan involving the patient themselves (Prip et al., 2018). The essay will focus on the case study of a 19 years old Maggie with a state of alcohol abuse and associated complication. In this essay, the different communication goals for the patient, communication strategies, along with potentialbarriers to effectivecommunication and interprofessionalcommunication related to Maggie’s case study will be evaluated using a perspective and critical role possess by a registered nurse.
Body:
Focusing on the case study of Maggie, a few significant communication goals have beendeveloped in order to ensure better treatment and recovery outcomes. One of the effectivegoals of communication in the case of Maggie is to generate awareness about the issue she has been witnessing in terms of her alcohol abuse. Health communication is known to be the study and practice of communicating with the aim to promote health information (Finset et al., 2020). It focuses on guiding and educating the community, public or patients in terms of their illnesses impacts and treatment needs with increased health literacy. Another communication goal for Maggie will focus on developing therapeutic communication in order to involve her in the treatment process and initiate a patient-centred approach to care and treatment (Martin & Chanda, 2016). The main aim of therapeutic communication is to help and assist professionals such as nurses and clinicians in developing trust and a therapeutic bond with the patient. It assists them in developing a collaborative approach with patients and another interprofessional team in order to ensure the physical and emotional involvement of the patient in their own treatment and recovery process (Schwind et al., 2016). It also serves as a way to understand the issues faced by the patient in terms of both their mental and physical health. Thus, focusing on the issue faced by Maggie, the communication goals will help in seeking a better understanding of the issue and difficulties she faces as well as developing a treatment and care plan according toher needs and demands during the treatment and recovery.
Focusing on the case study of Maggie and the communication goals addressing her issues, it will be necessary that certain communication strategies are involved in the care plan in order to ensure better communication establishment and treatment outcome. One of the necessarycommunicationstrategies in the case of Maggie accounts for active listening in orderto evaluate the issue she has been witnessing and the reason behind her difficulties. Active listening serves a crucial and essential role in the entire process of communication as it aims at addressing the significant process of receiving as well as interpreting information provided (Jahromi et al., 2016). It providesanopportunityto understand the chief research behind the progression of the issue as well as understanding patient needs. As Maggie has been identified to be becoming withdrawn and has sustained a state of loneliness along with mood issues in her life due to difficulty communicating with family as well as lacking friends, active listening is one of the necessary strategies that must be included in the communication process. Another significant communication strategy that needs to be incorporated into their treatment and care plan for Maggie accounts for patient teach back. It is one of the necessary and significant communication strategies in their field of health care where nurses and physicians focus on effectively communicating and making understanding information to the patients (Yen &Leasure, 2019). Often patient says they have understood everything guided by the nurses or the physician but the majority of the information is either neglected or not understood by the patient. Thus, in such conditions patients are enquired to repeat along with the professional and often requested to state what they have understood as a way of taking back in terms of communication (Talevski et al., 2020). Thus, it will be used as a process of communication strategy where after ensuring communicationandinformationdeliveryMaggie will be guided through the process of taking back communication. In order to implement these effectivecommunicationstrategies in the care and treatment process of Maggie, a patient-centred approach to communication must be incorporated. In the approach, the nurse or physician focuses on providing care and treatment based on patient values, beliefs, needs as well as preferences such as her need to have better diet, to indulge in physical activity and to communicate with community members to overcome the issue Maggie is currently facing. Focusing on her need, it is necessary to communicate with someone, as it helps her to overcome the sleep disorder, mood disorder and will also help to gain effective weight (Schembre et al., 2018).It aims in involving the patient in active participation in the whole process of communication, treatment plan and recovery services (Wolters et al., 2017).
In order to address Maggie and ensure her involvement of her in the treatment and care process focused on effective communication, it is necessary that a positive rapport is built with her. Building rapport will ensure sustaining her trust and active participation in the process of treatment as she is known to witness withdrawal from family and friends and is in a state of loneliness. (Barkley, 2016) She also was found to lack interest in talking to anyone and remain in her own space with changing mood issues It is one of the chief reasons behind her state of addiction as she drinks more to remove her loneliness and sustain sound sleep. Focusing on the needs, the BATHE protocol of effective communication will be used in order to build rapport with Maggie. It is one of the significant and useful strategiesin the case of health care where professionals are provided with an opportunity to build rapport with their patients and extract them out of suffering to ensure ease and comfort (Pace et al., 2017). It focuses on open-endedinteractionand communication with the patient with an aim to build effective and strong relationships which do not always limitto clinical needs. It helps in understanding the patient’s identity, individuality, traumatic situation, distress experiences, difficulties, issues as well as diverse health needs. It does not focus on reliving the health issue but aims to ensure activelisteningand developing a significant therapeutic and interactive bond with the patient (Chengappa et al., 2020).
The BATHE protocol focuses on 5 stages which include
? Background – about patients and their life
? Affect – the impact of the findings on the patient
? Troubles – issues that the patient is witnessing
? Handling – the way the patient is handling the situation
? Empathetic Statement – show empathy and respect to the patient ensuing different consoling sentences.
Potential communication barriers
After going through the case study and the factors involved in the issues witnessed by Maggie, it has been foundthatthere are two potential barriers that may develop in their process of effective communication. One of the factors accounts for emotional barriers where patient emotional values and conditions often develop a hurdle in establishingeffectivecommunication. Emotions such as anger and lonelinessoftendevelop a wall between the patient and the communication as the patient’s emotional distress keeps them deprived of the ability to understand and evaluate the aim of communication (Mack et al., 2021). As Maggie has been witnessingmooddistress, due to lonelinessas well as a lack of ability to interact with her parents. A state of emotional barrier in communication may develop as she does not sustain the interest or intention to communicate with others. Also, it has dragged her towards the state of increasedalcoholconsumption as it helps her to get through the day and have a sound sleep at night. Thus, in such conditions, it is necessary that effective therapeutic communication must be focused on where initially a rapport is built with the patient in terms of trust and respect (Blake & Blake, 2019). It will help the patent to open up to the professionals and deal with the emotional barrier to communication. Also, in the case of involving her mother in the treatment and care plan focusing on a patient-centred approach, a potential social-cultural barrier to communication might develop (Schouten et al., 2020). Due to having cultural differences and a bad experience in health care due to belonging to the Aboriginal community, her mother hasa state of untrustful interest in healthcare facilities. Maggie belongs to the Aboriginal community and the care process involved themother as next to the kin, thus focusing on their cultural values, culturally safe and sensitive communication must be involved. Thus, it also might develop a potential barrier in the communication process and to resolve and overcome the barrier, it will be necessary to focus on involving culturally safe communication (Brooks, Manias & Bloomer, 2019). Focusing on the cultural diversity of health care settings, often communication must focus on a culturally sensitive and safe process. It will focus on ensuring a communication where the divert of the patient's culture, values and perspectives will be respected and maintained in their communication and treatment process.
In the case of Maggie's treatment plan, professionals such as Psychologists for mood disorders such as changing mod patterns as well as alcohol abuse, the dietitian for loss of weight and inability to eat as well as a family counsellor for the disruptedinteractionand communicationbetweenMaggie and her mother. These three professionals apart fromregistered nurse will be involved and communicated in the treatment plan for Maggie. In case of effective communication with healthcare professionals belonging to different healthcare backgrounds and specializations, it is necessary to ensure clear and accurate communication. It will be necessary to focus on written communication along with interprofessional communication to ensure proper sharing of evidence without the conduction of error (Wei et al., 2022). Often challenges such as diversity in professional dynamic may develop as each professional belongs to a different professional background along with a lack of understanding of their role in their interprofessional collaboration. Thus, in such conditions, an effective collaborative approach with significant interprofessional communication is necessary to overcome these challenges (Chichirez&Purc?rea, 2018). It will help in understanding the dynamics of each professional as well as ensuring sharing of information and understanding related to their role in the treatment plan.
Conclusion:
The essay was to assess the differentcommunicationstrategies and their impact on the case study of Maggie as she has been identified to be suffering from mood and alcoholmisuseissues. After completion of the essay, it has been found that Maggie has explained the need for effective communication in her treatment andrecovery plan as one of the major issues that she faced was a lack of interaction with her family. It dragged her towardsalcoholmisuse, and thus focusing in which, the essay highlights the significant communication gaols and strategies that must be provided to her in order to restore her cognitive and physical health back to normal. The essay helped in assessing the different type of communication strategies as well as their need in healthcare. It also helped in evaluating the type of professionals and professional communication that must be maintained while assisting a patient with alcohol misuse disorder.
References:
Barkley, P. S. (2016). Building rapport with your patient: Positive case management outcomes. http://ocu.course.documentation.s3.amazonaws.com/HS2800/WK1+Building+Rapport+with+your+Patient.pdf
Blake, T., & Blake, T. (2019). Improving therapeutic communication in nursing through simulation exercise. Teaching and Learning in Nursing, 14(4), 260-264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2019.06.003
Brooks, L. A., Manias, E., & Bloomer, M. J. (2019). Culturally sensitive communication in healthcare: A concept analysis. Collegian, 26(3), 383-391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colegn.2018.09.007
Chengappa, N., Honest, P. C. R., David, K., Pricilla, R. A., Rahman, S. M., & Rebecca, G. (2020). Effect of BATHE interview technique on patient satisfaction in an ambulatory family medicine centre in South India. Family Medicine and Community Health, 8(4). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7566425/
Chichirez, C. M., &Purc?rea, V. L. (2018). Interpersonal communication in healthcare. Journal of medicine and life, 11(2), 119. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6101690/pdf/JMedLife-11-119.pdf
Finset, A., Bosworth, H., Butow, P., Gulbrandsen, P., Hulsman, R. L., Pieterse, A. H., ... & van Weert, J. (2020). Effective health communication–a key factor in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Patient education and counseling, 103(5), 873. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7180027/
Jahromi, V. K., Tabatabaee, S. S., Abdar, Z. E., &Rajabi, M. (2016). Active listening: The key of successful communication in hospital managers. Electronic physician, 8(3), 2123. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4844478/
Mack, J. W., Currie, E. R., Martello, V., Gittzus, J., Isack, A., Fisher, L., ... &Bakitas, M. (2021). Barriers to optimal end-of-life care for adolescents and young adults with cancer: bereaved caregiver perspectives. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 19(5), 528-533. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.7645
Martin, C. T., & Chanda, N. (2016). Mental health clinical simulation: therapeutic communication. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 12(6), 209-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2016.02.007
Pace, E. J., Somerville, N. J., Enyioha, C., Allen, J. P., Lemon, L. C., & Allen, C. W. (2017). Effects of a brief psychosocial intervention on inpatient satisfaction: An RCT. Family medicine, 49(9), 675. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5689450/
Prip, A., Møller, K. A., Nielsen, D. L., Jarden, M., Olsen, M. H., & Danielsen, A. K. (2018). The patient–healthcare professional relationship and communication in the oncology outpatient setting: a systematic review. Cancer nursing, 41(5), E11. https://doi10.1097/NCC.0000000000000533
Ratna, H. (2019). The importance of effective communication in healthcare practice. Harvard Public Health Review, 23, 1-6.https://www.jstor.org/stable/48546767
Schembre, S.M., Liao, Y., Robertson, M.C., Dunton, G.F., Kerr, J., Haffey, M.E., Burnett, T., Basen-Engquist, K. and Hicklen, R.S., 2018. Just-in-time feedback in diet and physical activity interventions: systematic review and practical design framework. Journal of medical Internet research, 20(3), p.e8701.https://www.jmir.org/2018/3/e106/
Schouten, B. C., Cox, A., Duran, G., Kerremans, K., Banning, L. K., Lahdidioui, A., ... &Krystallidou, D. (2020). Mitigating language and cultural barriers in healthcare communication: Toward a holistic approach. Patient Education and Counseling, 103(12), 2604-2608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.05.001
Schwind, J. K., McCay, E., Metersky, K., & Martin, J. (2016). Development and implementation of an advanced therapeutic communication course: An interprofessional collaboration. Journal of Nursing Education, 55(10), 592-597. https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20160914-11
Talevski, J., Wong Shee, A., Rasmussen, B., Kemp, G., & Beauchamp, A. (2020). Teach-back: A systematic review of implementation and impacts. PLoS One, 15(4), e0231350. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231350
Wei, H., Horns, P., Sears, S. F., Huang, K., Smith, C. M., & Wei, T. L. (2022). A systematic meta-review of systematic reviews about interprofessional collaboration: facilitators, barriers, and outcomes. Journal of Interprofessional Care, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2021.1973975
Wolters, M., van Hulten, R., Blom, L., &Bouvy, M. L. (2017). Exploring the concept of patient centred communication for the pharmacy practice. International journal of clinical pharmacy, 39(6), 1145-1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-017-0508-5
Yen, P. H., &Leasure, A. R. (2019). Use and effectiveness of the teach-back method in patient education and health outcomes. Federal practitioner, 36(6), 284. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6590951/
Case Study
PBHL20010 Case study Assignment Sample
The first assessment task is a case study of about 2000 words that you will complete on an individual basis.
The case study will require you to choose one of the eight stakeholder groups listed below and discuss their role in a public health emergency; the nature and direction of their interest based on their position in the community and their function in society; and the factors that may affect their actions. You must also choose a specific emergency situation from which you will draw examples to illustrate your discussion. This may be an epidemic of disease (for example, the COVID19 pandemic); a natural disaster (flood, bushfire, earthquake, etc); or an anthropogenic event (chemical spill, industrial explosion, etc). You ust specific the emergency and stakeholder groups clearly in the introduction to the case study. You will also need to use appropriate academic references to support your understanding of stakeholder participation, communication needs, responsibilities, and so forth as relevant.
The stakeholders you may choose from are:
1. Local government
2. Science/health experts
3. Local business interests
4. The media
5. Representatives of the long-term community (people who have lived in a given location for 10 years or more)
6. Representatives of new groups (people who have recently arrived in or moved to a given location)
7. Local health care personnel
8. State (or higher level) government
Your case study must have the following sections for assignment help
1) Introduction – identifies the chosen stakeholder, the emergency and gives a general indication of who they are or what they do;
2) Roles in a Public health Event – for the stakeholder group you have chosen, describe their role in a public health emergency; make sure to consider whether their role is official or non-official and whether they are personally at risk of health impacts and the other kinds of risk they experience;
3) Risks and Responsibilities – for the group you have chosen, describe the nature of the risks identified in the previous section; make sure to consider whether the risk is direct or indirect, whether it is a risk to health or another kind of risk, what the specific health or non-health risk involves, and what the group’s responsibilities are in relation to the public health emergency and its own and the risks of other stakeholders;
4) Role in Public health Decision-Making – for the group you have chosen, consider how they contribute to decision-making in the context of a public health emergency; be sure to discuss whether their contribution is official or unofficial, the channel through which they might affect the decision-making process. and the degree to which their impact is informed by evidence-based and non-evidence-based knowledge; and
5) Conclusion – discuss the position of the stakeholder group you have chosen in a public health emergency; you may want to consider whether they are actors or bystanders, for example, or use some other classification, but be sure to state whether your chosen stakeholder group is likely to be affected significantly, the nature of the impact, and why you believe this would occur. This assignment must be written in a formal, academic style (not first person) and must be fully referenced. Harvard referencing is preferred for this unit. If you need help with referencing, please consult the referencing guides available online and through the Library as soon as possible.
Solution
Introduction
In this paper, a discussion regarding the role of a particular stakeholder group in regard to a public health emergency is going to be elaborated. The stakeholder group that has been chosen in order to make the discussion is the media, and the public health emergency that has been considered in this regard is Covid19. It can be regarded as the most considerable public health emergency in the current situation. The emergency has caused a significant number of deaths throughout the world, and it has caused harm to public health considerably. Along with providing a significant effect on public health, it has caused economic shock to a number of countries. However, the matter is that the media was supposed to play a vital role in regard to the process of making people aware of the emergency and the situational needs, and by considering this key area, the overall discussion is going to be elaborated on here.
Roles in a public health event
Roles
Covid19 is a global infectious disease that emerged from Wuhan, Chin (Anwar et al., 2020). The media can be regarded as the main mean of mass communication that includes radio, television, the internet, newspapers and others. People who are associated with media are mainly responsible to make people aware of the current situation based on every aspect related to society, politics, economic factor, technical area, environmental hazards, health situations, and others. It means that in regard to such a situation where a pandemic has been spreading in an effective manner and causing numerous deaths and affecting uncountable number of people, they were supposed to play an important role in making people aware of the situation. In this regard, their roles have been as follows:
Making people aware of the situation
It can be regarded as the key role of the chosen stakeholder group with respect to the concerned emergency situation. They have been supposed to make people aware of every day’s update, such as the death rates related to Covid19, the way the infection has been spreading each day, what is the current situation of the local area and the world as well. They have been supposed to make people understand the severity of the issue by letting them know about these factors. At the time when people become aware of the severity of a situation, they are able to make the right decision based on the situational needs, and that is why the media has been responsible to make them aware of the situational needs so that they can manipulate their lifestyle and become interested in living a restricted life by considering the emergency of the situation.
Providing authentic information regarding the emergency of the situation
The media, in regard to the situation of a healthcare emergency is responsible to provide authentic information to people so that they can understand the actual scenario and make decision properly based on it. By considering the viewpoint of Mheidlyand Fares (2020), it can be stated that media is a powerful avenue for the dissemination of wellness education. In regard to Covid19, the media was responsible to do the same, From death rates to infection spreading rates, everything are required to be communicated with people while maintaining the highest level of authenticity so that they can understand what they should do in a particular situation in order to be safe. In this case, the media is not likely to be influenced by any political influences. They have been responsible to maintain authenticity with respect to each word they have been sharing with people as the situation has been complex and crucial. Any misleading word of the media might lead people improperly and it would enhance the severity of the issue.
Leading people to the right path in crucial moments
People have been panicked in the situation with the increasing number of deaths and infection rates. At that time period, it has been the responsibility of the media to understand how they should live their lives in order to keep themselves and their family members safe. Instead of making people scared, they have been supposed to encourage them to maintain all safety and precautionary measures so that the situation can be controlled properly.
Whether the role is official or non-official
The roles of the media that have been highlighted in the above-stated passages are definitely official. At the time of public crisis, media is required to ensure to communicate crisis information effectively (Latifet al., 2020). By considering the official responsibilities of media, it can be stated that they are professionally responsible to gather and update information regarding any situation, and correct information throughout the life of a news story. They are also professionally responsible to provide facts that can allow people to be better informed about any issue that matters to the society and the lives of people. It means that covering the Covid-19-based issues can be regarded as the key responsibility of these people and it can also been stated that by considering the official terms and conditions, that these people have to follow, it has been their official responsibility to make people aware of the situational needs, the emergency of the situation, and the way to control the situation. They have been supposed to work by considering that if they can make people aware of these facts and if they can reach people properly, controlling the situation would be easier and battling with the health emergency would also be easier. Hence, it can be concluded that all of the responsibilities highlighted above can be regarded as the official responsibility of these people and they have been supposed to handle these responsibilities by considering the professional ethics of them.
Their personal risk
In this situation, they have some personal risks, and these are mainly about their health. Throughout 2020- 2021 and the beginning of 2022, the spreading rates of Covid-19 were considerable.
Figure 1: Covid19 spreading rates
(Source: Statista, 2022)
The graph is showing the same. In such a situation working with public was a considerable risk for the media as they could be affected anytime as they did not have any scope to isolate themselves from people who were affected. It can be regarded as a major health concern that these people have faced in this situation. In the following section, a detailed discussion regarding the risks is going to be elaborated on.
Risks and responsibilities
Nature of the risk
In the above-stated passages, the risk has been identified, and when the matter comes to making a discussion regarding the nature of the risk it has to be stated that the risk was supposed to impact the stakeholders directly, and it can also be stated that the risk was mainly related to the health of these people and the family members of them. Covid19 is a significant global and public health crisis (Banerjee and Rao, 2020). These stakeholders were supposed to meet with public by considering their professional roles and responsibilities, and that is why they were supposed to be infected in the fastest manner. In this regard, it is also important to state that they have not been free from the risk yet as Covid-19 is still causing harms and death though the infection rates have been decreased, and it means that these people are still dealing with such risks.
Another important risk to be considered here is about their economic and professional security. By considering the information shared by Radcliffe(2020), it can be stated that a number of people have lost their jobs in the Covid19 phase as a number of news companies have been laid off in the Covid19 phase. This situation has actually affected their professional and economic security of these people. It can be regarded as a direct risk to be considered here as it has directly impacted the overall lifestyles of these people in a devastating manner.
Responsibilities of the group in public health emergency
From professional aspect, they are responsible to collect information regarding the current status of Covid19 and it has been the responsibility of them to provide people with accurate information so that they can understand the situational needs and they can take steps based on the same. It has been their responsibility to make people aware of the precautionary measures so that they can deal with the situation perfectly. They have been supposed to provide information not only regarding the impact of the issue on public health but also the impact of the issue on political and economic aspects. In order to avoid risk of Covid-19, effective government interventions have been implemented, and it has been the responsibility of media people to make individuals know about these (Liu et al., 2021). They have been responsible to ensure that people understand the situational needs properly and make decisions based on it.
The risks of other stakeholders
In this regard, other stakeholders were also supposed to face some issues. Along with journalists, press and camera man, some other people work with media people and that includes the drivers of the vehicle that these people are using, their assistants, and others, and these people are supposed to be infected if these people get infected. It means that with the risk of the chosen stakeholders, the risks of other stakeholders are interrelated.
Role in public decision making process
How they contribute to decision making
Bridgmanet al.,(2020) have stated that if people spend time in media that provide misinformation, they are likely to develop wrong attitudes and behaviors. These people are responsible to provide a significant impact on public decision making process. They have been responsible to make people aware of Covid-19 situation that can influence the decision-making process of them. They have been responsible to make people understand the precautionary measures instead of causing them to get panicked. They have been responsible to maintain the highest level of integrity and honesty in regard to the data collection and communication process so that any individual would not be misled and they van make the best decision by considering the actual situational perspectives.
Whether the contribution is official or unofficial
By considering professional aspect, it can be stated that media people are supposed to make people aware of a situation and his kind of awareness can influence the decision-making process of individuals in a considerable manner. From this perspective, it can be stated that the contribution of them that has been highlighted in the above-stated passages is completely official.
The channel through which they can affect the decision-making process
Media people can be associated with any channel that includes newspapers, television, internet and others. From this perspective, it can be stated that all of these channels can be used in order to affect the decision-making process of people. In other words, it can be stated that media people are sharing information by using all of these channels and this information is effective enough to influence the decision-0making process of people, and that is why it can be stated that newspaper, television, radio, and the internet are some channels through which media people can influence the decision-making process of people.
The degree with respect to their impact in this regard
In the above-stated passages, a discussion regarding the way they can influence the decision-making process of people has been elaborated, and by considering the same, it can be stated that the degree to which they can impact the decision-making process is high as they are the primary resource of information for mass people. By considering their viewpoint, mass people have been judging the Covid-19 situation and the way they have to deal; with it. Hence, the degree with respect to their impact in regard to the decision-making process is high.
Conclusion
In the above-stated passage, a detailed discussion regarding the impact of the media on a health emergency (Covid-19) has been elaborated. By considering the discussion, it can be stated that these people have been playing a vital role in the context while providing people with authentic information and making them aware of the situation. They have been contributing to the decision-making process of people in an effective manner as per their professional responsibilities while dealing with considerable risks. By considering the way the stakeholders are playing the role of actors with respect to the situation. Based on the actions of them, the way people can think and manage the issue is being changed, and it means that they are playing the role of actors in this regard. The situation can impacted their lives effectively as it has already been stated that they have been dealing with considerable health risks. Apart from that, they were dealing with job security-layered issues. Health risks can impacted their action with respect to the situational needs and it could prevent them from following their roles and responsibilities. On the other hand, job security issues associated with the situation could affect them physical and mental well-being. The situation-related discussion has been made, and based on the situational perspective, it has been possible to understand that such issues could occur.
References
Anwar, A., Malik, M., Raees, V. and Anwar, A., 2020.Role of mass media and public health communications in the COVID-19 pandemic. Cureus, 12(9).https://www.cureus.com/articles/38293-role-of-mass-media-and-public-health-communications-in-the-covid-19-pandemic
Banerjee, D. and Rao, T.S., 2020. Psychology of misinformation and the media: Insights from the COVID-19 pandemic. Indian Journal of Social Psychiatry, 36(5), p.131.
Bridgman, A., Merkley, E., Loewen, P.J., Owen, T., Ruths, D., Teichmann, L. and Zhilin, O., 2020. The causes and consequences of COVID-19 misperceptions: Understanding the role of news and social media. Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review, 1(3).https://www.indjsp.org/article.asp?issn=0971-9962;year=2020;volume=36;issue=5;spage=131;epage=137;aulast=Banerjee
Latif, F., Bashir, M.F., Komal, B. and Tan, D., 2020.Role of electronic media in mitigating the psychological impacts of novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Psychiatry research, 289, p.113041.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165178120309380
Liu, N., Chen, Z. and Bao, G., 2021. Role of media coverage in mitigating COVID-19 transmission: Evidence from China. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 163, p.120435.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162520312610
Mheidly, N. and Fares, J., 2020.Leveraging media and health communication strategies to overcome the COVID-19 infodemic. Journal of public health policy, 41(4), pp.410-420.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41271-020-00247-w
Radcliffe, D., 2020. Covid-19 has ravaged American newsrooms–here’s why that matters. Available at SSRN 3693903.https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3693903
Statista, 2022. COVID-19 new cases worldwide by day | Statista. [online] Statista. Available at: <https://www.statista.com/statistics/1103046/new-coronavirus-covid19-cases-number-worldwide-by-day/> [Accessed 18 April 2022].
Case Study
NURS3015 Health Variations 4 – Acute Life Threatening Condition
Case Analysis- Case Study of an Acute Life-Threatening Condition
Word Count
There is a word limit of 1000 words. Use your computer to total the number of words used in your assignment. However, do not include the reference list at the end of your assignment in the word count. In-text citations will be included in the additional 10%-word count. If you exceed the word count by 10% (1100 words) the marker will stop marking.
Aim of assessment
The aim of this assessment is to enable students to:
1. Demonstrate knowledge by analysing the information provided in the case study.
2. Apply the clinical information provided in the case study and describe this clinical information within a pathophysiological and patient focused framework.
3. Discuss nursing strategies and evidence-based rationales to manage a patient with acute heart failure
4. Discuss the pharmacological interventions related to the management of a patient with acute heart failure
Details
You are to answer all questions related to the case study provided for assignment help. Your answers must be directly related to the clinical manifestations that your patient presents with. You must submit your work with a minimum of six references from the past 5 years including peer-reviewed journal articles, textbook material or other appropriate evidence-based resources.
Case study
Mr. Aloha Das is a 68-year-old gentleman presenting to the emergency department at 0400hrs with worsening shortness of breath. Onset 2 days ago and progressively worsening. He also developed wheeze and right sided pleuritic chest pain this morning. Vomited x1, ongoing nausea. Has history of non-compliance with medication and adherence to fluid restriction.
Past History
Hypertension, Inferior Myocardial Infarction in 2020, Heart Failure, non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy, Permanent Pacemaker inserted 2021, DM Type II, GORD, Osteoarthritis.
Current medications:
Furosemide 40mg OD, Captopril 6.25 mg TiD, Digoxin 0.125 mg BD, Metformin 500mg TiD, Nexium 40 mg BD.
On 1.2 L fluid restriction; Echocardiogram results in 2021- systolic dysfunction, mild mitral valve regurgitation, dilated left atrium and ejection fraction (EF) 33%.
Plan
• Continuous cardiac monitoring
• 12 lead ECG
• Blood pathology order
• Troponin I High Sensitivity
• Chest X-Ray
• Insert IVC right hand
• Furosemide 40mg IV Stat
• Echocardiogram
Results of Investigations:
Chest x- ray: Left ventricular hypertrophy, interstitial edema noted by Kerley B lines in the costophrenic angle.
Blood Results:
Electrolyte, urea and creatinine:
Result/ Reference Range
Sodium - 137 mmol/L 135-147 mmol/L
Potassium - 3.9 mmol/L 3.5-5.2 mmol/L
Chloride- 105 mmol/L 95-107 mmol/L
Urea nitrogen(BUN) - 14.0 mmol/L 3.0-8.0 mmol/L
Creatinine- 147 μmol/L 64 -104 μmol/L
Question 1
In order to prioritise your nursing actions, you are expected to have a sound understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology.
Explain the pathogenesis and pathophysiology causing the clinical manifestations with which Mr Das presents.
Question 2
Choose one high priority nursing intervention that you will perform for Mr Das
– Briefly explain why you chose this nursing intervention
– Explain how the nursing intervention will alleviate the clinical features of Mr Das using physiological linking
– Describe briefly the impact of not performing the intervention
Question 3
Mr Das has been prescribed Furosemide 40mg IV Stat and Glyceryl Trinitrate IV Infusion 10 mcg/min starting rate.
For both medications explain
– The mechanism of action
– Why your patient is receiving this medication in relation to his symptoms and diagnosis?
– What are the nursing considerations for this medication?
– What clinical response you expect?
– What continuing clinical observations will you need to undertake?
Submission
Refer to Section 2.5 of the Learning Guide- General Submission Requirements Submit your assessment through Turnitin
Format
All assignments are to be typed Typing must be according to the following format:
3 cm left and right margins, double spaced.
Font: Arial or Times New Roman
Font size: 12pt
See further submission requirements below
Submission Requirements
1. Electronic copy only. Students are to submit an electronic copy of the assessment. Students are not required to submit the original hard copy of their assessment on campus
2. Submit your assessment electronically through the Turnitin link on the unit vUWS site.
3. Students are to upload the assessment with the following title: Surname_Firstname_assessment title
4. Your assessment must be submitted in .doc, docx format.
5. This assessment is marked online; no paper copy will be accepted. Marks, comments and the marking criteria will be released online. If you do not receive your marked assessment when all others have been returned, it is your responsibility to contact the Unit Coordinator for assistance.
Solution
Question 1:
RHD (Rheumatic heart disease) indicates a major cause of cardiovascular diseases. In this case study, a brief explanation of pathophysiology and pathogenesis causing the clinical manifestations with Mr. Das. This particular case study is based on the diagnosis and clinical manifestations of RHD for Mr. Das, and this includes pathogenesis, diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention of acute rheumatic, and treatment. According to this case study, a 68 years old gentleman, Mr. Das, presented himself to the emergency department with the condition of shortness of breath. It is seen that, 2 days ago, with progressive worsening, Mr. Das suffered and presented to the department of emergency at 0400 hrs.
Due to this, pathophysiology and pathogenesis caused clinical manifestations, and Mr. Das developed right side chest pain this morning along with on-going nausea and one-time vomiting. As per the case analysis of "Acute Life-Threatening Condition", this cannot be managed with successful results, and that is critically dependent on prompt therapy and early recognition (Caraher et al., 2018). For example, in the case of an "Acute Life-Threatening Condition", the person can face different symptoms before the death, and all the symptoms occur within 2-5 days after facing the first symptom.
Question 2:
A chosen high priority nursing intervention is “monitoring of vital signs and recovery progress” and that is considered as independent nursing intervention for this particular case study. Vital signs are most important component for this case of Mr. Das to monitor patient’s health as well as allow prompt detection for delaying recovery or addressing the breathing problem. Furthermore, several plans like Continuous cardiac monitoring, 12 lead ECG, Blood pathology order, Troponin I High Sensitivity, Chest x-ray, IVC insertion in right hand Furosemide 40mg IV Stat and Echocardiogram are included in the nursing intervention (Burchum & Rosenthal, 2021). Current medications include several medicines which are allocated for the patient where Furosemide 40mg OD, Captopril 6.25 mg TiD, Digoxin 0.125 mg BD, Metformin 500mg TiD, Nexium 40 mg BD are used.
On the other hand, on 1.2 L fluid restriction, Echocardiogram resulted in 2021- systolic dysfunction, mild mitral valve regurgitation, dilated left atrium and ejection fraction (EF) 33% are also utilised ((Lewis et al., 2020)). In the nursing assessment, several details of the patients have been discussed. Thus, “monitoring of vital signs and recovery progress” is best nursing intervention for this particular case of managing the health condition for Mr. Das.
Discussion of how a nursing intervention will alleviate the clinical features of Mr. Das physiological linking
As per the case study, a Nursing intervention will help to give alleviation to the patient, Mr. Das. After that, corresponding to the current medications as different medicines including Furosemide 40 mg OD, Captopril 6.25 mg TiD, Digoxin 0.125 mg BD, Metformin 500mg TiD, Nexium 40 mg BD have been allocated. Furosemide 40 mg OD is mainly used for the treatment of fluid retention blended with heart failure, including left ventricular failure. Besides, Captopril 6.25 mg TiD is used for congestive heart failure (Bullock et al., 2017). In order to treat irregular heartbeats, Digoxin 0.125 mg BD is used for the treatment of DM type 2 as Mr. Das is suffering from DM type 2 as per the case study. Creatinine and Urea nitrogen (BUN) is high from the reference rate. Along with that, Nexium 40 mg BD is utilised for the treatment of erosive reflux esophagitis, including the prevention of rebreeding of peptic ulcers. With several intervention reports like blood reports, x-ray and others report the right diagnosis will be taken as per the case study (Suen et al., 2020).
Describe the impact of not performing the intervention
In such accordance with not managing and performing a well nursing intervention, different issues can occur if the intervention is not performed as several medicines as per the case study is too significant for the treatment of heart failure and DM type 2 (Xu et al., 2018). If the restrictions cannot be performed, Mr. Das may suffer from several symptoms. Along with that, if blood reports and x-ray are not considered, medication will not be procured.
Question 3:
The mechanism of action
According to this case study, Mr. Das has been prescribed two medicines for his "Acute Life-Threatening Condition", and these are Furosemide 40 mg IV stat and Glyceryl Trinitrate IV Infusion 10 mcg/min in starting rate. For Mr. Das, the initial dose is to be administered through an intravenous application with 40 mg Furosemide, and if needed, another injection could have to be given after 30-60 minutes (Huether & McCance, 2019). On the other hand, according to the health condition of Mr. Das, Glyceryl Trinitrate IV Infusion 10 mcg/min has been given, and the dosage of 10 mcg/ min was able to obtain Glyceryl Trinitrate 6 ml of admixture/hour. These two prescribed medicines were helpful to manage his health condition at the starting rate.
Why is your patient receiving this medication to his diagnosis and symptoms?
In case of patient diagnosis and symptoms, Furosemide 40 mg IV stat helps the body get rid of some extra water by increasing the urine in the patient's body. Additionally, another one helps to reduce the tone of "vascular smooth muscle" (Atherton et al., 2018). After that, the action is more suitable to manage venous capacitance vessels compared to arterial vessels.
What are the nursing considerations for this medication?
Medication administration is a nursing intervention, and that includes five major activities for prescribing and managing the health of Mr. Das. These are such as diagnosis, implementation, assessment, planning, and evaluation.
What clinical response do you expect?
The major aim of the clinical response is to evaluate changes in lung volumes, diagnosis, and perception of breathing discomfort intensity with pharmacological intervention.
What continuing clinical observations will you need to undertake?
The major clinical observations in the case of "Acute Life-Threatening Condition" for Mr. Das is to manage the pathogenesis and pathophysiology causing the clinical manifestations along with ECG report, and checking irregular heartbeat and sugar test for DM type 2, and many more.
Reference
Atherton, J. J., Sindone, A., De Pasquale, C. G., Driscoll, A., MacDonald, P. S., Hopper, I., ... & Connell, C. (2018). National Heart Foundation of Australia and Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand: guidelines for the prevention, detection, and management of heart failure in Australia 2018. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 27(10), 1123-1208.https://www.heartlungcirc.org/article/S1443-9506(18)31777-3/fulltext
Burchum, J., & Rosenthal, L. (2021). Lehne's Pharmacology for Nursing Care E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=VGNCEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=PHARMACOLOGY+NURSING+CARE++BOOK+Lehne%27s+pharmacology+for++nursing+care&ots=rRXRiaAdxd&sig=zF4O9V3tIDIScLRzMNYRkvNSLjI
Byrne, J. E., Bullock, B., & Murray, G. (2017). Development of a measure of sleep, circadian rhythms, and mood: the SCRAM questionnaire. Frontiers in psychology, 8, 2105. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02105/full
Caraher, M.C., Sophocleous, A., Beattie, J.R., O'Driscoll, O., Cummins, N.M., Brennan, O., O'Brien, F.J., Ralston, S.H., Bell, S.E., Towler, M. & Idris, A.I., (2018). Raman spectroscopy predicts the link between claw keratin and bone collagen structure in a rodent model of oestrogen deficiency. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1864(2), pp.398-406. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925443917303848
Huether, S. E., & McCance, K. L. (2019). Understanding Pathophysiology-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.http://repository.stikesrspadgs.ac.id/104/1/Study%20Guide%20for%20Understanding%20Pathophysiology-345hlm.pdf
Lewis, P., Wilson, N. J., Hunt, L., & Whitehead, L. (2020). 1 Nursing in Australia. Nursing in Australia: Contemporary Professional and Practice Insights.https://api.taylorfrancis.com/content/books/mono/download?identifierName=doi&identifierValue=10.4324/9781003120698&type=googlepdf
Suen, L. K. P., Guo, Y. P., Ho, S. S. K., Au-Yeung, C. H., & Lam, S. C. (2020). Comparing mask fit and usability of traditional and nanofibre N95 filtering facepiece respirators before and after nursing procedures. Journal of Hospital Infection, 104(3), 336-343. https://www.karger.com/Article/PDF/488001
Xu, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, A., Zhu, J., Tang, H., & Zhu, X. (2018). Effect of self-efficacy intervention on quality of life of patients with intestinal stoma. Gastroenterology Nursing, 41(4), 341. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6078485/
Coursework
7140SOH Health Policy in Organisations and Systems Assignment Sample
Module Learning Outcomes
There are four learning outcomes for the module and by the time you have completed it, it is envisaged that you will be able to:
1. Critically analyse the global stakeholders to determine the key policy actors and organisations and analyse the roles they play in the development and implementation of national, transnational, and global health policy
2. Critically analyse the policy drivers and the factors associated with the development and implementation of health policies in high-, middle- and low-income countries
3. Apply economic evaluation to critically analyse the impact of health policy in high-, middle- and low-income countries
4. Critically review the leadership challenges and skills in implementing policy changes at an international, national, and local level
Coursework 2 (2500 words)
Smoking tobacco is a significant risk factor in developing lung cancer. Policies to reduce the impact of smoking are designed to reduce lung cancer and other smoking related diseases. Critically analyse how the United Kingdom and South Africa have implemented anti-smoking policies and discuss their effectiveness. Discuss 2 or 3 policies in total.
You should include the following for assignment help
• Data demonstrating incidence and prevalence of smoking in each country
• Policy drivers in UK and South Africa and resource allocation
• An analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the policies to reduce tobacco use
• Whether there are any conflicts of interest in national government
• Leadership challenges and skills in implementing policy changes at an international, national, and local level
• Comparison of two countries and the effectiveness of the policies
• Headings to make your work clearer to the reader
Submission Guidance
It is important to you and the tutors that your project is written and presented in a professional manner. The following requirements must be adhered to in the format of assignments
1. Your limit does allow for +/- 10% words in length. The limit includes words used in tables, graphs, charts and diagrams, but excludes the front cover, the table of contents, references list and appendices. If you exceed the +/- 10% word limit you may receive a 10% penalty on your coursework mark
2. The front cover page - see appendix 1 for the template.
3. The type font should be Arial and the font size for the body of the text 12 point.
4. One and a half (1.5) line spacing must be used.
5. All pages should be numbered consecutively, in the footer on the right.
6. Your student number should be in the footer on the left.
7. References, citations and quotations should be in Coventry University APA 7th Edition only (https://libguides.coventry.ac.uk/apa)
8. Any diagrams, tables, photographic images etc. should be appropriately labelled and referenced.
All coursework must be submitted through the assignment links via the AULA page.
Referencing
Coventry University have adopted the CU APA 7th edition Referencing System as the standard format for citations and references. There is a Centre for Academic Writing which can provide detailed support on the APA style of referencing. There is also a useful reference guide on the CU Harvard Style that I advise you to download and keep.
This can be found at:
https://libguides.coventry.ac.uk/apa
Solution
Introduction
Overview of smoking prevalence globally
As per the viewpoint of West (2017), there are about 1 billion tobacco smokers globally, which accounts for 7% of women and 30% of men. Although, the prevalence rate of smoking tobacco varies according to the determinant factors of different countries.
From the above-illustrated figure, it has been found that the overall prevalence of tobacco smoking is 23% globally, whereas it is approximately 32% for men and only 7% for women. Although, the prevalence of tobacco smoking has been decreasing considerably over the years due to anti-smoking advertisements and the implementation of anti-smoking policies.
Introduction to the UK, including the prevalence of smoking
The UK, the abbreviated form of the United Kingdom, is a sovereign nation within the northwest part of Europe, which is one of the most developing industrial countries across the entire world.
From the above-depicted figure, it has been understood that the prevalence or occurrence of smoking cigarettes amongst both women and men has declined substantially since 1974. In the year 2019, only 12.5% of all women and approximately 15.9% of all males smoked cigarettes, which is nearly one third compared to the rate, which was reported in 1974 (Statista, 2022).
Introduction to South Africa, including the prevalence of smoking
South Africa is the northernmost nation within the African continent, which is well-known for its cultural diversity, natural beauty and varied topography.
The above-demonstrated figure shows that approximately 35% of all respondents, participated in the “Statista Global Consumer Survey” smoke cigarettes as one of the most popular tobacco products (Statista, 2021). On the other hand, other tobacco products are Hookah, cigars, pipe tobacco, e-cigarettes, chewing tobacco, oral nicotine pouches and others.
Policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK
As per the report of GOV.UK (2018), the main policy drivers for the reduction or minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption or uptake of tobacco products. Additionally, one of the main policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco is to increase awareness of the citizens of the UK regarding the side effects of consuming tobacco by giving examples of the number of deaths or cancer patients due to this.
Policy drivers for the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa
One of the key policy drivers, which play a major role in the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa, is to increase tax rates on purchasing tobacco (Lau et al., 2018). Another key policy driver is to increase the prices of cigarettes, as it has been helping to minimize the intensity of consuming tobacco amongst the poor of South Africa (Boachie & Ross, 2020). Although, the effects of increasing prices of tobacco products vary based on the gender, race and age groups of the individuals in South Africa.
Main Body
Policy drivers in the UK, including resource allocation
The primary policy, which is involved with the minimization of tobacco smoking in the UK is the "Health Act (2006)”, which was implemented in the year 2007. The primary focus of this policy is to ban tobacco smoking in enclosed workplaces and public spaces for controlling the number of deaths causing due to passive smoking. In this context, this policy has become more effective while making England smoke-free by the implementation of the "Tobacco Control Plan for England” in 2017 (Hackshaw et al., 2010). In this context, the two most important policy drivers are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption of tobacco (Opie-Martin et al., 2020). Additionally, the two important resources while reducing tobacco smoking are initiation by increasing the tax rate and prices of cigarettes and cessation control by increasing the awareness of the citizens (Sun & Mendez, 2019).
Policy drivers in South Africa, including resource allocation
“Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” is the main policy, which drives the minimization of tobacco smoking in South Africa, whose key drivers are increasing cessation and decreasing consumption for restricting or prohibiting smoking within public spaces (South African Government, 2022).
The above-depicted figure demonstrated the phases of reducing tobacco smoking after the implementation of “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” and other “Tobacco Products Control Amendment Acts” periodically (Reddy et al., 2013). The figure also shows that the number of purchasing cigarettes has been decreased after the execution of anti-smoking policies. The resource allocation for this policy is government initiatives, awareness programs, and strict government regulations against tobacco smoking.
Leadership challenges in the UK during policy implementation
While implementing the policy for reducing the consumption of tobacco, the economic impact is one of the most vital leadership challenges, which the government and other regulatory bodies of the UK have been facing. In this context, Ekpu & Brown (2015) stated that the economic effects of tobacco smoking are based on two leadership challenges, such as the expenses of minimizing the prevalence of smoking amongst smokers and expenses of tobacco utilization itself. On the other hand, the government of the UK has also faced challenges regarding the imposing of tax on tobacco purchasing by its citizens (Till, McKimm & Swanwick, 2020). Lastly, it can be said that the lack of penalties for the individuals who violate the laws, rules and regulations of anti-smoking is another significant leadership challenge, due to which the numbers of deaths caused by passive smoking have been increasing considerably.
Leadership challenges in South Africa during policy implementation
The report of the World Health Organization (2022) depicts that strengthening the execution of the agreement of tobacco control is one of the most vital leadership challenges within the African Regions, including South Africa. Due to this particular leadership challenge, the usage and consumption of tobacco by the citizens of South Africa and other African regions have been increasing rapidly (Tukuru et al., 2021). An increase in purchasing power of the consumers related to tobacco is one of the leading leadership challenges, due to which the markets of South Africa have been growing more accessibly. Increasing awareness of the citizens of South Africa is another most crucial challenge, which the government of the country has been facing while implementing the policy (Warner, Tam & Koltun, 2014). In this context, comprehensive monitoring is required to be followed for informing the civil society and government about the purchasing of tobacco products.
Weaknesses and strengths of the policy in the UK
One of the most vital strengths of tobacco smoking control policies in the UK is its execution of a smoking cessation campaign named "No Smoking Day” in the mid-1990s (Owen & Youdan, 2006). The strength of this policy or campaign is its effectiveness in lowering the prevalence of smoking within the country. Due to this policy, the rate of tobacco smoking decreased to 25% amongst adults in 2003 from 33% since its implementation. On the other hand, the most vital weakness of the anti-smoking policy in the UK is the inability of the government to successfully comply and enforce “Tobacco Advertising and Promotion Act 2002” effectively (CPI, 2019). Another weakness is the incapability of the government to invest additional money in this policy.
Weaknesses and strengths of the policy in South Africa
One of the most vital strengths of “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993” is its strict implementation in South Africa for considering tobacco smoking as the second considerable health concern after AIDS/ HIV (Plagerson, et al., 2019). Strength of this policy in South Africa is to become the first country to ban the smoking of cigarettes within enclosed workplaces and public spaces. Another important strength of this policy is to increase the minimum age of the citizens of South Africa to legally access tobacco (Bonnie, Stratton & Kwan, 2015). One of the most vital weaknesses of this policy is the incapability of the South African Government to impose this policy while selling and advertising tobacco products compared to the advertising of anti-smoking products in the country.
Impact of the UK’s economic condition on the implementation and development of the policy
According to the data of the World Bank (2022), the UK is a high-income country whose average income is $12,696 and above. The economy of this country has an impact on the implementation and development of tobacco control policies under the "Health Act (2006)”. In this context, Ekpu & Brown (2015) stated that the government of high-income economies like the UK acquire a huge amount of tax revenues from the consumption and production of tobacco. Additionally, more employment opportunities within the tobacco industry create. The economic condition of the UK helps the government to invest in anti-smoking policies and procedures more effectively so that tobacco smoking amongst adult smokers can be controlled effectively. Sometimes, the government does not focus on the strict rules and regulations of this policy for its own economic gain or interest.
Impact of South Africa’s economic condition on the implementation and development of the policy
As per the data of the World Bank (2022), South Africa is an upper-middle-income country according to its economic condition. Although its economic condition is lower than that of the UK, it is the first upper-middle-income country, which imposed continuous increases in terms of excise tax for reducing the consumption and production of tobacco smoking. In this context, the government of South Africa has been shedding light on the improvement of the health conditions of its citizens by increasing the prices of cigarettes. Additionally, the average price of cigarettes within the retail sector of South Africa has been hiked by 110%, due to which its poor citizens are incapable of purchasing cigarettes due to which, consumption of tobacco smoking has been lowered considerably (Chelwa, van Walbeek & Blecher, 2017).
Conflicts of interest within national government in the UK
For controlling the consumption of tobacco, the government of the UK has been making efforts in terms of conflicts of interest amongst the policymakers. In the year 2017, the government of the UK has recently launched the “Tobacco Control Plan for England” so that awareness of the citizens regarding the side effects of tobacco smoking can be increased effectively. The government has been focusing on the strict implementation of its public health policies under the "Health Act (2006)” so that the health conditions of the citizens can be protected and secured significantly. No economic profits should be considered while imposing the strict regulations of tobacco control policies in the UK.
Conflicts of interest within national government in South Africa
While describing conflicts of interests within national government in South Africa, the role of interest groups can be illustrated as they are the associations within the political system of the nation, which influence public policy based on any social issue (Asare, 2009). Here, tobacco smoking is one of the greatest social issues, due to which the number of deaths has been increasing. In this context, the government has totally banned the advertising of tobacco products along with the increasing advertising of anti-smoking products.
Comparison between the UK and South Africa regarding the effectiveness of smoking reduction
While comparing between the UK and South Africa about the effectiveness of smoking reduction, it has been observed that South Africa is most effective in reducing tobacco smoking compared to the UK as the government of the UK acquire economic gain and advantages of tobacco consumption and production (Nation Master, 2022). While imposing the policy, the government of the UK face challenges regarding economic loss as the tobacco sector of the country contributes a large amount of money to the economy. For dealing with this challenge, the government of the UK started to increase awareness of the public through “No Smoking Day” besides ceasing the production of tobacco. On the other hand, the government of South Africa faced a challenge while imposing an increased tax on tobacco products. Although, the government executed many tobacco control policies for securing the health conditions of its citizens.
Theoretical interventions regarding control of tobacco smoking
While supporting the above-described evidence regarding tobacco control, it has been observed that the theories or models of behavior change are relevant. In this context, some theoretical interventions related to tobacco cessation or control are “Transtheoretical model”, “Health Belief Model”, and “Social Cognitive/Learning theory” (Roberts, Kerr & Smith, 2013). The core aim of these theoretical interventions is to cease the consumption of tobacco by helping the smokers to change their behaviours towards tobacco smoking. In this context, the government of the UK has launched “No Smoking Day” for encouraging the smokers not to smoke to that particular day so that their behaviour can be changed for at least one day. Additionally, the government of South Africa has shed light on the health concerns of its citizens through the application of “Health Belief Model” so that the awareness of the individuals regarding the side effects of tobacco smoking can be understood.
Conclusion
In the above discussion, an overview regarding smoking prevalence has been provided by considering the statistics from across the globe. The research has showcased Africa is having the highest prevalence of smokers in which 7% of smokers can be accounted as female and 30% are male individuals. The above analysis has also provided some statistical information from different sources. From the analysis, it can be noted that the rate of smoking among the citizens of the United Kingdom is being declined since the year 1974. However, during the last few years, the statics have mentioned that more than one-third of the rates identified in 1974 have been recognised in the nation. Following the statistics showcased in the discussion majority of the individuals have responded that they do not smoke or consume any tobacco items, whereas, 35% of individuals in the nation smokes cigarettes daily. In the above discussion, a statistical overview has been presented from the results of “Statista's global survey” where cigarettes have been recognised as one of the highly accepted and consumed tobacco materials in South Africa.
It can be also be concluded that, in the United Kingdom, the government have taken several measures and policies for reducing the tobacco and cigarettes consumptions rates by establishing several healthcare protocols and regulations. One of the major and most effective policy drivers that are used by the UK government is transcending a major awareness regarding the negative impacts of smoking among the citizens of the nation. The government and other healthcare communities are trying to showcase the negative effects of smoking and consuming tobacco by giving examples of an increasing number of deaths and an emerging number of cancer patients as well. On the other hand, the South African Government have also intended to take several actions, such as; increasing the tax rates on tobacco products or taking actions against the uncontrollable supply chain of the substances. Here, the primary motive of the government is to minimise the intensity of smoking among the youth population of the country and increase a major awareness regarding healthy lifestyles as well.
In the above discussion graphical representations have been used for showing the changes in tobacco consumption rates in South Africa from the year 1690 to 2009. The research has also provided the references of several acts, such as; the “Tobacco Products Control Act 83 and 93” along with the “Tobacco products control amendments acts”. At the same time, it is evident that over the decades due to the leadership issues within the nation several challenges have been faced by the UK government for setting the amendments and rephrasing the regulatory systems within the nation. The same account has also been presented in terms of South African governance procedures. It seems that the changes in leadership options and style mainly harmed the civil society and their lifestyle. Also at some point unlike the UK due to the slow speed of development at some parts of South Africa dealing with the consumption rate of tobacco seems to stay less effective even after the establishment of government protocols.
References
Asare, B. E. (2009). Tobacco regulation in South Africa: Interest groups and public policy. African Journal of Political Science and International Relations, 3(3), 099-106. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJPSIR/article-full-text-pdf/FCFC4587529
Boachie, M. K., & Ross, H. (2020). Determinants of smoking intensity in South Africa: Evidence from township communities. Preventive Medicine Reports, 19, 101099. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211335520300590
Bonnie, R. J., Stratton, K., & Kwan, L. Y. (Eds.). (2015). Public health implications of raising the minimum age of legal access to tobacco products. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://tobacco.cleartheair.org.hk/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/18997-2.pdf
Chelwa, G., van Walbeek, C., & Blecher, E. (2017). Evaluating South Africa's tobacco control policy using a synthetic control method. Tobacco Control, 26(5), 509-517. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://scholar.google.com/scholar?output=instlink&q=info:toqmvfMf6Q8J:scholar.google.com/&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5&as_ylo=2010&scillfp=2313872938218841645&oi=lle
CPI. (2019). Smoking ban in the United Kingdom. Centre For Public Impact (CPI). Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.centreforpublicimpact.org/case-study/smoking-ban-united-kingdom/.
Ekpu, V. U., & Brown, A. K. (2015). The economic impact of smoking and of reducing smoking prevalence: review of evidence. Tobacco use insights, 8, TUI-S15628. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.4137/TUI.S15628
GOV.UK. (2018). Tobacco commissioning support: principles and indicators. GOV.UK. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/alcohol-drugs-and-tobacco-commissioning-support-pack/tobacco-commissioning-support-pack-2019-to-2020-principles-and-indicators.
Hackshaw, L., McEwen, A., West, R., & Bauld, L. (2010). Quit attempts in response to smoke-free legislation in England. Tobacco control, 19(2), 160-164. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://tobaccocontrol.bmj.com/content/tobaccocontrol/19/2/160.full.pdf
Lau, Y.K., Tam, J., Fleischer, N.L. & Meza, R., (2018). Neighbourhood deprivation, smoking, and race in South Africa: a cross-sectional analysis. Preventive medicine reports, 11, pp.202-208. From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211335518301141
Nation Master. (2022). South Africa vs United Kingdom: Facts and Stats. Nationmaster.com. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.nationmaster.com/country-info/compare/South-Africa/United-Kingdom.
Opie-Martin, S., Jones, A., Iacoangeli, A., Al-Khleifat, A., Oumar, M., Shaw, P.J., Shaw, C.E., Morrison, K.E., Wootton, R.E., Davey-Smith, G. & Pearce, N., (2020). UK case control study of smoking and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration, 21(3-4), pp.222-227. From: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/21678421.2019.1706580
Owen, L., & Youdan, B. (2006). 22 years on: the impact and relevance of the UK No Smoking Day. Tobacco control, 15(1), 19-25. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2563638/
Plagerson, S., Patel, L., Hochfeld, T. & Ulriksen, M.S., (2019). Social policy in South Africa: Navigating the route to social development. World Development, 113, pp.1-9. From: https://findresearcher.sdu.dk:8443/ws/portalfiles/portal/151844724/Revised_Manuscript._15.8.2018.pdf
Reddy, P., Sewpaul, R., Sifunda, S., James, S., Yach, D., Resnicow, K., ... & Mbewu, A. (2013). A decade of tobacco control: The South African case of politics, health policy, health promotion and behaviour change. South African Medical Journal, 103(11), 835-840. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://journals.co.za/doi/pdf/10.7196/SAMJ.6910
Roberts, N. J., Kerr, S. M., & Smith, S. M. (2013). Behavioral interventions associated with smoking cessation in the treatment of tobacco use. Health Services Insights, 6, HSI-S11092. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.4137/HSI.S11092
South African Government. (2022). Tobacco Products Control Act 83 of 1993 | South African Government. Gov.za. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.gov.za/documents/tobacco-products-control-act.
Statista. (2021). Tobacco product usage in South Africa 2021 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.statista.com/forecasts/856757/tobacco-product-usage-in-south-africa.
Statista. (2022). Cigarette smoking in the UK by gender 1974-2019 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/423001/cigarette-smoking-in-great-britain-by-gender/.
Sun, R., & Mendez, D. (2019). Initiation versus Cessation Control Policies: Deriving Optimal Resource Allocation Strategies to Decrease Smoking Prevalence Under a Fixed Budget. MDM policy & practice, 4(1), 2381468319832036. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2381468319832036
The FINANCIAL. (2020). Efforts to control tobacco undermined by conflict-of-interest among policymakers, new research reveals ? FINCHANNEL. FINCHANNEL ? News Making Money. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://finchannel.com/efforts-to-control-tobacco-undermined-by-conflict-of-interest-among-policymakers-new-research-reveals/.
Till, A., McKimm, J. & Swanwick, T., (2020). The importance of leadership development in medical curricula: a UK perspective (stars are aligning). Journal of healthcare leadership, 12, p.19. From: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7079548/
Tukuru, M.O., Snyman, L., Postma, T.C. & van der Berg-Cloete, S.E., (2021). Dentistry in South Africa and the need for management and leadership training. South African Dental Journal, 76(9), pp.532-536. From: http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?pid=S0011-85162021000900009&script=sci_arttext&tlng=es
Warner, K. E., Tam, J., & Koltun, S. M. (2014). Growth in tobacco control publications by authors from low-and middle-income countries. Tobacco Control, 23(3), 231-237. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://scholar.google.com/scholar?output=instlink&q=info:DeIJWTzNih4J:scholar.google.com/&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5&as_ylo=2010&scillfp=1682438322522218787&oi=lle
West, R. (2017). Tobacco smoking: Health impact, prevalence, correlates and interventions. Psychology & health, 32(8), 1018-1036. Retrieved 14 January, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5490618/
World Bank. (2022). World Bank Country and Lending Groups – World Bank Data Help Desk. Datahelpdesk.worldbank.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519.
World Health Organization. (2022). Tobacco Control. WHO | Regional Office for Africa. Retrieved 14 January 2022, from https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/tobacco-control.
Essay
GDECE101 Early Childhood Care and Education
Assessment 1:
Essay (1000 words) Inclusive strategies and approaches when working with careers/families and communities. Inclusive strategies and approaches when working with carers/families and communities.
Following the guidelines in the EYLF and the NQF, review a range of contemporary inclusive approaches and strategies related to working inclusively with carers/families and communities.
Compare and contrast the recommended practices with some of the historical approaches examined in class.
Please use the APA referencing style.
Weighting - 50%
Learning outcomes
On successful completion of this subject you will be able to:
A. Evaluate historical constructs of childhood and their impact on contemporary early childhood systems and curriculum in Australia.
B. Assess a range of strategies for promoting effective and respectful working relationships with diverse parents/carers and communities.
C. Debate contemporary educational issues in social, cultural, political, philosophical and historical contexts.
D. Appraise diverse Indigenous Australian and Torres Strait issues and epistemologies and their impact on early childhood care and education.
E. Advocate for children’s rights and anti-bias approaches to working with diverse cultures and identities.
Solution
EARLY CHILDHOOD CARE AND EDUCATION
Introduction
Early learning frameworks for the student help in maintaining a holistic approach to the parents for understanding the needs of their child. In this assignment there are detailed strategies for promoting the impact of learning.
Contemporary childhood systems and curriculum
National Quality Framework and Early Years Learning Framework help to create better childcare systems and regulations to maintain an understanding among the caregivers or the families to convey the need of improvement in a child. These two contemporary systems work for a long time to sustain a developmental aspect on the child’s health and mental development (Hamilton et al. 2019). In historical context early stage of student’s development is divided into series of stages such as preoperational or sensory motor operation development. In early education system a common goal of student development is to sustain a better development of the mental health of students at an early age (Petit Early Learning Journey, 2019). Academic success and continuation to traditional process may differ in different countries. Nowadays childcare curriculum is divided into theme based, high scope based and Montessori based.
Theoretical Overview of NQF and EYLF
NQF:
The National Quality Framework, or NQF, established by the Australian Government, regulates the education provision for early childhood and promotes children's first five years’ education (Ghoghra, 2017). NQF includes:
National Quality Standards
National legislation and national legislation.
National Education Framework.
Evaluation and Quality Assurance Process
.png)
NQF
Source: (Petit Early Learning Journey, 2019)
The first impetus for change began with the COAG or Australian Government Council meeting in December 2007. They agreed to make "significant improvements in the educational areas, skills and development at early childhood ". The 2008 discussion paper 'National Framework for Early Childhood Education and Care' explains the reasons for these changes. These revealed that:
? More working parents are starting to work in Australia
? Increased compulsion to provide for families
? Providing high-quality care to multiple children:
? Significant benefits for disadvantaged children
? Improving short-term outcomes such as school readiness
? Less risk of abduction of "vulnerable" children.
? More classroom diversity.
? Establishing a healthy lifestyle and learning
? Significant social and economic benefits
? Differences and gaps in the rules for quality identification, assessment and monitoring in care and education across Australia.
? Removing inappropriate differences between education and care sectors create divisions between child care and kindergarten sectors.
? The children should be the priority above all (Petit Early Learning Journey, 2019).
EYLF:
The EYLF is the first Australian framework of national curriculum for education at early childhood. It emphasizes activities that are play-based to improve early childhood education and the significance of language communication (including early numeracy and literacy). In July 2009, the COAG approved five learning outcomes for children ages 0 to 5 as part of the EYLF and structured according to the following related factors: theory, practice, learning outcomes (Ghoghra, 2017).
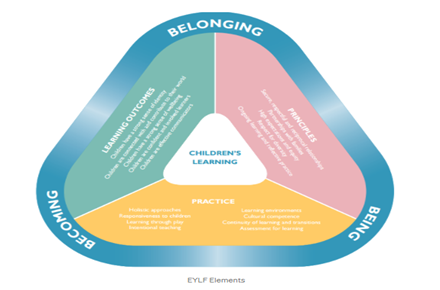
EYLF Framework:
Source: (Ghoghra, 2017)
The framework is based on a vision of children's health characterized by participation, attendance and presence. Children at early stage are mostly connected to community, family, environment and culture. (Ghoghra, 2017).
Belonging: The experience of being a part and is an important part of one's life. Children are part of a cultural group, a family, and an entire community. Being: Childhood is a time to understand, explore and understand the world. Being a child recognizes the value of life in the here and now. Childhood is a preparation not only for the future but also for the present (Ghoghra, 2017).
Becoming: Children's knowledge, relationships identities, abilities &skills, and understanding change during childhood. Strategies of effective relationship
Discovering Identity: Strong sense of identity is another important part for parents in the early age of their children’s of the development. It helps working parents to get a good grasp on identifying the strengths and weaknesses of their children. The EYLF system helps to maintain a proper understanding of the importance of the development of the child system (Quality forum, 2021). Identity development is an essential phenomenon for the growing children for further development.
Connection and Contribution: In order to feel the connection to their external and internal environment it is essential for parents to keep their children in a good situation. It helps to create a better understanding to the children and they can easily learn where to contribute their intelligence. They can generate a strong sense of their rights and community values as well (Press et al. 2018).
The aims of education have different problems in clarification and it is needed to be mitigated quickly.
Mitigating problems and issues of Child care
Strategic plans have been developed for maintaining a better understanding of the indifferent development of the children in a positive environment. NQF and EYLF both have their own version of distinctive plans for nurturing children of working parents (Morrissey & Moore, 2021). Family engagement and care: It is an important step for strategic planning of the child care systems to maintain values to the care systems which in turn helps to the development of the child. They help to generate the thinking skills with the medium of play based learning systems (Hamilton et al. 2019). Mitigating quality gaps: It is important to maintain a better place without any discrimination at an early age. It is important to create awareness from an early childhood to maintain a discrimination free mentality. As “charity begins at home” it is important for parents to maintain these critical aspects of life and respect each other that can develop the mind of a child.
Leadership development: It is another important phenomenon of the child care units to develop the integrity of doing work that can help children in future. Sustainability: It is important for every family to care for their children from any harm whether it is external or internal. It is an important step for a family to maintain such understanding for better development of their children (Petit journey, 2021).
Conclusion
Strategic plans for the parents and the caregivers to create a sustainable environment for the children to thrive upon. It creates an understandable environment for the children and the family both.
Reference list
Ghoghra, R. D. (2017, June 21). NQF, NQS and EYLF. Retrieved November 25, 2021, from Medium website: https://medium.com/@riya.ghoghra/nqf-nqs-and-eylf-2e392cdfc440
Hamilton, A., Jin, Y., & Krieg, S. (2019). Early childhood arts curriculum: a cross-cultural study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 51(5), 698-714. Retrieved on: 12th November 2021, from; https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yan-Jin-17/publication/330949330_Early_childhood_arts_curriculum_a_cross-cultural_study/links/5ce0db2892851c4eabacede4/Early-childhood-arts-curriculum-a-cross-cultural-study.pdf
Morrissey, A. M., & Moore, D. (2021). In whose best interests? Regulating childcare environments in Australia. Australasian Journal of Early Childhood, 18369391211050184. Retrieved on: 14th November 2021, from; https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Anne-Marie-Morrissey-2/publication/355318538_In_whose_best_interests_Regulating_childcare_environments_in_Australia/links/6171623f766c4a211c04f0b1/In-whose-best-interests-Regulating-childcare-environments-in-Australia.pdf
Petit Early Learning Journey. (2019, April 29). What is the Early Years Learning Framework? Retrieved November 25, 2021, from Petit Journey website: https://www.petitjourney.com.au/early-years-learning-framework/
Press, F., Woodrow, C., Logan, H., & Mitchell, L. (2018). Can we belong in a neo-liberal world? Neo-liberalism in early childhood education and care policy in Australia and New Zealand. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood, 19(4), 328-339. Retrieved on: 14thNovember 2021, from; https://researchoutput.csu.edu.au/files/26276662/22831996_published_article.pdf
Quality forum (2021), A Strategic Plan for Achieving the Care We Need, Retrieved on: 14th November 2021, from; https://www.qualityforum.org/A_Strategic_Plan_for_Achieving_The_Care_We_Need.aspx
Case Study
DEME20002 Supporting and caring for people with Dementia Assignment Sample
Learning Outcomes Assessed
1. Analyse the diverse presentations of people with dementia and the impact this may have on their care.
2. Demonstrate the comprehensive assessment of people at risk of or experiencing dementia.
Aim
The aim of this portfolio is for you to demonstrate your ability to appropriately assess the diverse presentations of people with dementia using a comprehensive assessment tool.
Instructions
There are three parts to this portfolio.
Part one: Select two case studies located on Moodle and describe the presentation of the two people with dementia.
Part two: Explain how diverse presentations of people with dementia may impact the care delivered to them by health professionals.
Part three: Describe and justify your comprehensive assessment of the people in the two case studies selected. This assessment must include physiological, psychosocial, and cognitive assessment.
Ensure each part of the e-portfolio is substantiated with peer-reviewed literature.
Literature and references
The number of references you should use is not limited. You should consider using references when you have used material from another source .You may also use seminal scholarly literature where relevant. Additional suitable references include textbooks and credible websites. When sourcing information, consider the 5 elements of a quality reference: currency, authority, relevance, objectivity, and coverage. Grey literature sourced from the internet must be from reputable websites such as from government, university, or peak national bodies: for example, the Australian College of Nursing.
Case study
Case Study 2. Mary Hobson.
Mary is a fifty-three-year-old woman who resides in the Fairfield Elsis Residential Aged Care Facility. She has lived in the facility for three years, after being found by neighbours in her house, on the ground, following a fall. Mary has no next of kin and her medical records indicate that she has previously had children, however, she does not appear to have contact with any of them at present. Mary needs encouragement with all areas of ADL care. She will commonly sit for hours on end unless she is encouraged to move. The facility has asked you to come in and assess Mary and suggest some strategies to motive and inspire her to increase her activity.
Meeting with Mary
When you meet with Mary, she immediately embraces you, and calls you the name of one of her children. She asks you about the football and grins widely as she talks happily of how Collingwood is likely to win the grand final. She talks about many different topics: cake making, cathedral windows, and sings hymns through your conversation. She seems very pleased that you have come to visit. She is less motivated to move from her
seat and when you suggest a walk, she says “No no no no...”. She looks slightly disturbed that you want her to move. You notice that toward the end of the meeting, she begins to become slightly over familiar, and you notice that there is a change in her demeanour.
Significant history
Mary has quite a lengthy medical history listed in her notes, involving injuries from previous falls (one only a few weeks ago), dental issues, bunions on both feet, arthritis in her legs and fingers, vitamin B deficiency, anorexia, previous diagnosis of alcoholism, and a past diagnosis of depression, along with her diagnosis of early-onset dementia, possibly alcohol-related dementia.
SOLUTION
Presentation of two people with dementia:
Mary (53 y, Female): The presentation of her symptoms of dementia indicates that she currently does not have any contact with any of her children, nor does she have any close relative to care for her. Her symptoms show that she has absolute disinterest to move, walk or be active.
In addition, she needs encouragement in all areas of daily-life activities. Also, the meeting with Mary has confirmed that she suffers from delusions and hallucinations because she was taking the names of her children and having some conversations about football matches, cathedral, and cake making that were not relevant indeed.
(Barry &75y, Male): Barry resides with his son at his residence who cares about his food and also gives him company. The case about Barry suggests that he has post-traumatic stress resulted from the Vietnam war. Barry has some frightening memories of the Vietnam war and thus suffers from panic attacks and sleep deprivation. Barry’s disease is called vascular dementia (Gowan & Roller, 2019). As suggested in the case study, Barry had recently suffered a stroke and that might have blocked an artery in the brain.
Part two
The way diverse presentations of dementia patients influence care delivery:
The diverse presentation of dementia affects the care delivery process because all patients have unique symptoms and have unique life experiences. In the case of Mary, she has no interest in moving or having doing activity. She suffers from delusions, hallucinations and many underlined diseases such as deficiency of Vitamin B, anorexia, dental issues, and many others. Her past medical history confirms that she has multiple issues and alcohol-related dementia. Patients like Mary need empathy because emotional support provides patience and insights to them. Thus, treating these patients with empathy would generate better care outcomes (Arvanitakis, Shah & Bennett, 2019).
However, in the case of Barry, he is suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) followed by the Vietnam war. He has traumatic memories of the war and gets panic attacks and sleepless nights. His condition reveals that he is not comfortable sharing much about the experience of the war. In addition, Barry also undergone a stroke which resulted in visio-perceptual difficulties. Since Barry is resistive in nature but is open to discussion for possibilities, an effective CBT would help him combat the issues.
Impact of the assessment on nursing care:
The care delivery process by nurses for dementia patients depends on their age, history of their life experiences, severity of dementia, and the presence of other underlying medical conditions (Kim, 2019). Referring to the case study of Mary, patients like her must be provided with suitable tools like an easy chair where they can feel comfortable. Also, ssome familiar and interesting decorations can make them feel engaged to their surroundings. These might encourage them to be more mobile and be active. Also, caregivers and nurses must empathize with patients like Mary and avoid questioning them (Harrison et al., 2018).
Furthermore, patients like Barry often need psychological therapeutic interventions. Gowan & Roller (2019) suggests that psychotherapies and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy can effectively help patients with vascular dementia and post-traumatic stress. For these patients, the nurses must also consider exposure treatments. Thus, it can be said that the diverse presentation of people with dementia tends to influence the way of care delivery by health professionals.
Part three
Comprehensive assessment for Mary:
Physiological: The falls risk assessment of Mary reveals she has high risk of falling as she was found collapsed on the floor before being admitted to the care unit. Also, she is immobile and has number of underlined diseases like anorexia, previous alcoholism, deficiency of Vitamin B and so on. Additionally, the pressure ulcer risks for Mary are also high as she was an alcohol and thus has high chances of liver ulcers. Moreover, the deficiency of Vitamin B can lead to mouth ulcers.
Psychological: Tools like Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) can be used to assess her depression and anxiety. Diagnosis reveals that she still longs for her children and is lonely. The psychological assessment reveals that refusal to walk or move can be characterized by old-age, increasing severity of dementia, orthopaedic aspects, and decreased functionalities. This assessment is important as this reveals about the psychological status of the patients and hence determines the care giving procedure.
Cognitive: The tools like Cognitive Impairment Scale PAS can be used for assessing her cognitive aspects. The diagnosis reveals that she was suffering from cognitive decline and having hallucinations and hence have been facing difficulties with her ADLs.
Comprehensive assessment for Barry:
Physiological: The falls risk assessment of Barry reveals that he has high risk of falling as he has visio-perceptual issues and depression. His old age can be another contributing reason to his falls risk. The pressure ulcer assessment of Barry’s case reveals that he does not have any symptom of developing ulcers and hence the risk is low. Barry must be exposed to some like-minded people as him with whom he can connect and communicate easily.
Psychological: The psychological assessment tool like Cognitive and neuropsychological tests can be used to determine his anxiety and depression scales (Beckman et al., 2019). The diagnosis reveals that barry has declining thinking skills and he finds it difficult to connect and communicate with people. This assessment would help the care givers to determine the level of care needed and to give the most suitable psychotic therapies.
Cognitive: The cognitive assessment can be done through Dementia Severity Rating Scale (DSRS). This assessment reveals that the type of dementia Barry has entails reasoning, memory, planning, and other types of thought processes resulted from the trauma of the Vietnam war. A recent psychological theory called Emotional Processing Theory states that the exposure treatments can be helpful for these patients’ cognitive condition as it would prevent the trauma memories to be negatively incorporated within their brain (Hayes, 2015).
References
Arvanitakis, Z., Shah, R. C., & Bennett, D. A. (2019). Diagnosis and management of dementia. Jama, 322(16), 1589-1599. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2753376
Beckman, E., Lazar, K., Van Hulle, C., Cole, A., Asthana, S., & Gleason, C. (2019). Association of traumatic brain injury, post-traumatic stress disorder and vascular risk with cognitive function in a veteran population: the brave study. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 15, P1559-P1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2019.08.160
Gowan, J., & Roller, L. (2019). Changed behaviours in people with dementia. AJP: The Australian Journal of Pharmacy, 100(1180), 69–77. https://doi.10.3316/informit.320828203940274
Harrison, S., Cations, M., Jessop, T., Hilmer, S., Sawan, M., & Brodaty, H. (2018). Approaches to deprescribing psychotropic medications for changed behaviours in long-term care residents living with dementia. Drugs & Aging, 36(2), 125-136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-018-0623-6
Hayes, A. (2015). Facilitating emotional processing in depression: the application of exposure principles. Current Opinion In Psychology, 4, 61-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.03.032
Kim, H. (2019). An analysis of the need for aid tools in dementia patients: focusing on the normal elderly, dementia patients, and caregivers of dementia patients. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development, 10(11), 4399. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2019.04300.6
Research
HAGE20005 Health Promotion For Healthy Ageing Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Due date:5.00pm (AEST) Wednesday, 26 May 2021 (Week 11)
Weighting: 50%
Length: 2500 words plus or minus 10% (excluding references)
Unit Coordinator: Ainslie Monson
Learning Outcomes Assessed
1.Evaluate the suitability of a current health promotion strategy to meet the needs of older people using evidence-based research.
2. Assess a current health promotion campaign related to health ageing and devise a health promotion plan to optimize well-being in older people.
Aim
The aim of this assessment is to prepare you to make a high-level contribution to health promotion policy and practice for the older person throughout the health care system.
Instructions
You are writing a critical analysis of a health promotion strategy and related campaign aimed at older persons. Choose a targeted area such as physical activity, smoking cessation, obesity, mental health, or some other focus area requiring health promotion in the community of older persons.
This involves, firstly, choosing a current health promotion strategy and related campaign aimed at older persons.
Your task is to:
• critically evaluate the strategy and
• assess the campaign and
• devise a health promotion plan for the older person related to the strategy and campaign.
Please follow the steps below to complete your assessment task:
1. Introduction (250 words) – Introduce your topic. The introduction outlines the key points of your essay. It will inform the reader what you are writing about – why you are writing about it and how you will discuss this topic.
2. The main body of the essay (2000 words) identify and explain the health promotion strategy and campaign selected. Justify the selection of your strategy and campaign and how it relates to the care of older person. Critically analyze and assess the strategy and campaign selected and its relevance to the older person. Devise a health promotion plan for a local level related to the strategy and campaign. The main body of the essay should be substantiated with reference to the peer reviewed literature (no less than 10 peer reviewed articles).
3. Conclusion (250 words) – no references in this section. The conclusion should summaries the key areas that address the set task. No new information should be included.
Literature and references
In this assessment use at least 15 contemporary references (<10 years) to support your discussion. You may also use seminal scholarly literature where relevant. Suitable references include peer-reviewed journal articles as well as textbooks and credible websites. When sourcing information, consider the 5 elements of a quality reference: currency, authority, relevance, objectivity, and coverage. Grey literature sourced from the internet must be from reputable websites such as from government, university, or peak national bodies: for example,
Requirements for assignment help
• Use a conventional and legible size 12 font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, with 1.5-line spacing and 2.54cm page margins (standard pre-set margin in Microsoft Word).
• Include page numbers on each page in a header.
• Write in the third-person perspective.
• Use formal academic language.
• Use the seventh edition American Psychological Association (APA) referencing style. The University Academic Learning Centre has an online APA
Referencing Style Guide.
• The word count is considered from the first word of the introduction to the last word of the conclusion. The word count excludes the reference list but includes in-text references and direct quotations.
Submission
Submit your assessment via the unit Moodle site in Microsoft Word format only.
Marking Criteria
Refer to the marking rubric on the Moodle site for more detail on how marks will be
Solution
Introduction
The current report covers the subject of health promotion for aged Australians, who are prone to vulnerable health conditions, including both mental and physical. The essay will specifically focus on the subject of mental health promotion for the older people in Australia to reduce the effects of stigma, followed by prevention of depression and suicidal tendencies. The essay will outline the fundamentals of mental health stability for older people in Australia, through the implementation of the National Mental Health Policy 2008. It aspires to capture the core intent of the subject by enabling the older people to come up with self-manageable ways to deal with the associated issues of a disturbed mental health. The survey report of the 2007 National Survey of Mental Health, conducted by the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare showed that people belonging to the age group of 16-85 years are subject to the highest percentage of mental health issues with an increasing percentage of 6% to 7% on an average for the age group of 75-85 years (aihw.gov.au). This figure shows the presence and risks of mental health among the older people in Australia, causing significant mental health damages (Awaworyi Churchillet al.2019).
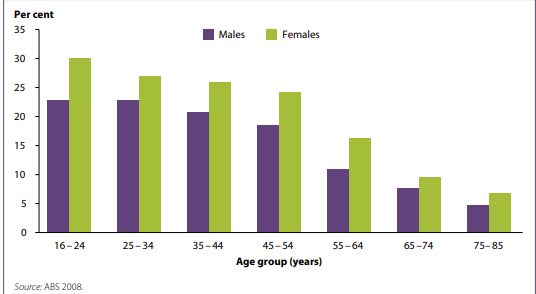
Mental health issues sorted by age group in Australia in the year 2007
(Source: aihw.gov.au)
This is obviously a cause of concern as it essentially affects the process of healthy aging in the country, leading to a possible rise in the number of mental health cases. The structure of the essay follows the standard structure and explains the selected health promotion strategy, along with a critical evaluation of the same, followed by a theoretical interpretation and a proposal for a Health promotion plan for the local aged people in the country.
Discussion
Explanation of the health strategy and campaign: National Mental Health Policy 2008
In order to explain the details of the National Mental Health Policy 2008, it is important to understand the aims and objectives of the policy (Milner, Smith & LaMontagne, 2015). The National Mental Health Policy 2008 aims at reducing the number of cases of mental health issues among the Australians, including the younger and the aged population (aihw.gov.au). The policy design is developed to support enabling recovery, along with prevention of mental health issues, by conducting early detection and avoiding occurrences of severe cases, including depression and suicides (Edwardet al.2015).
The policy has a strategic vision of promoting the mental health and well-being of the Australian community and develops programs to support the cause of mental health issues and enable the individuals to fight social stigmas (apo.org.au). The mental health patient, in every country in the world suffer from social disconnect and are treated differently. This policy ensures a comprehensive check and monitoring of the patients, pertaining to the security of mental health problems and enable participation of the patients in the society, with equal opportunities (Barryet al.2019).
The strategy skilfully aims at maximizing the ability of the children, the teenagers and aged people to cope up, with the normal stresses and encourage the people to participate in enhancing the emotional resilience and reducing vulnerability to mental health (Van Spijkeret al.2019). This strategy encourages in have focused on delivering the coordinated programs, both at the individual , community and system levels and focus on enhancing the security of the mental health patients to ensure that they are able to participate in the functions of securing mental health (Askell-Williams& Murray-Harvey, 2016).
The campaigns under the strategy include de-stigmatisation targeted at the whole community, identifying the populations, which is at the highest risk, ensuring an access to care at the right time, prevent suicidal tendencies by encouraging the people to participate in community activities and even assign carers to them, as and when needed (Slewa-Younan et al.2017).
Justification behind the selected strategy and campaign
Mental health is a serious problem in the world and people of all ages succumb to this condition. From a survey conducted by the Black Dog institute, it has been found that one in every five of the Australians suffer from mental health issues (Mokitimiet al.2018). Approximately 20% of the Australian aged between 16-85 years are affected by mental health issues, which include depression, dementia, self-isolation and the repeated suicidal attempts (aihw.gov.au). Out of the 20% of the Australian suffering, the mental health blockage shows 11.5% of the total count having a single disorder, while the rest 8.5% have multiple mental health disorders (health.gov.au).
The findings from Mission Australia’s Youth Survey in the year, 2014 showed that the onset of mental health issues in Australians occur at the age of 18-24 years, with a significant segment having the teenagers and the aged people in the list (health.gov.au). Therefore, the most affected population in mental health issues in Australia comprise the teenagers and the aged people (Milne ret al.2015).
It has been further found that the second leading cause of death in Australia is that of suicide due to depression or self-isolation, which could be a possible outcome of mental health issues. therefore, the focus is laid on the reducing the number of deaths , along with educating the aged people to refrain from engaging in any sort of mental health issues and self-isolation, caused due to depression and social disconnect (Gupta&Sagar, 2018).
The justification behind the selected strategy is established through its possible implications of enabling recovery and preventing and detecting the mental illness, at an early stage, to prevent all sorts of possible occurrences of such condition (Astell-Burt&Feng, 2019). The policy engages in developing interventions for reducing mental health, which includes both clinical and psychological (Ho&Mussap, 2017). The plan has also been effective in helping the mental health patients, fight the social stigmas, and be a part of healthy community environment.
Therefore, the justification behind the selection of the National Mental Health Policy 2008 is developed through its patient-centric approach and its ability to take care of the mental health patients, by applying the Multi-disciplinary model of care. This Multi-disciplinary model of care caters to the implementation of both the clinical and psychological intervention pertaining to the challenges of mental health, faced by the aged population in Australia (Hashmi et al.2020).
However, critics have pointed out the loopholes in the strategy in terms of the absence of a holistic approach, and integration of an evidence-based program, which may include, use of digital tools like Artificial Intelligence, Big Data to map the exact number, Ginger and Silver Cloud to offer self-help resources and tele-therapy.
Critical analysis and assessment of the strategy
In order to conduct a critical assessment of a health promotion policy or strategy, it is important to evaluate the ratio of accomplishment with the set objectives. According to Zhou et al.(2018), the success ratio of a health promotion policy or strategy is dependent on the development and application of policy levers over time (Coates& Howe, 2015). These policy levers map the percentage of success of a health promotion policy or strategy in compliance with the set objectives (Graceet al.2015). While conducting an evaluation of a health promotion policy or strategy, it is often evident that the key focus is placed on the outcome or impact measures, which draws on the balance sheet of the selected indicators, representing the interventions, control measures and success of the interventions.
Hence, in order to assess the success and failure of the National Mental Health Policy 2008, it is important to understand the kind of interventions that had been implemented by the policy with the objectives and the loopholes. The policy shows that although the agenda behind the designing of the National Mental Health Policy 2008 had been strategic, yet it lacked the holistic approach (van Rensburg&Fourie, 2016). The strategy did focus on early detection of mental health issues among the people in Australia, including the Aged population with allocations of separate carers for them to look after, however, the holistic approach is missing.
The strategy mainly focused on external interventions like psychological and clinical, by assigning doctors to the earliest rescue. However, the emphasis on individual participation and self-education is missing in the strategy along with the absence of an evidence-based program, to continuously monitor the progress of the intervention and apply digital integration for better evaluation.
Health promotion plan for the local people
In relation to the above explanation of the selected health promotion strategy for prevention of mental health issues for the aged people in Australia, it needs to be stated that the percentage of affected people in mental health are much more among the aged compared to the teenagers (blackdoginstitute.org.au,2021). The teenagers have the support from their family members and often engaged in early interventions, likely counseling sessions, active community engagement, social communication and psychologist interventions (Syed& McLean, 2017).
The aged people on the other hand are more prone to mental health issues, as they are mostly aged , may be at the age of 70+ years wherein either of the partners have expired and the children also do not stay with them. Multiple incidents can happen, which could be the possible causes behind the mental health issues of the aged people in Australia (apo.org.au, 2021). This aged population in turn takes to clinical depression, abstinence from taking medicine and even engage in isolation and social disassociation. The eighth stage in Erikson’s model of psychosocial development shows the presence of ego integrity in war with despair. This stage comes to a person, who is above the 65 years of age, until his/her demise.
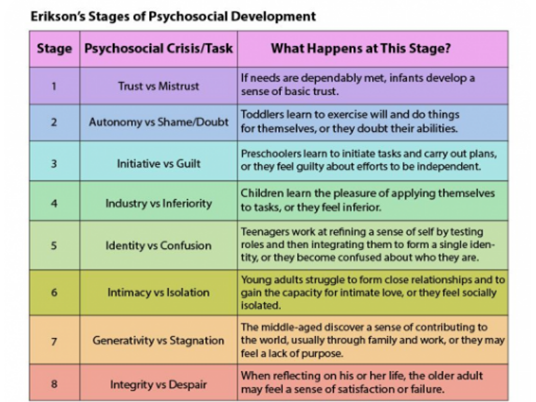
Erikson’s eight stages of psychosocial development
(Source: Syed& McLean, 2017)
At this stage, an individual invests a lot of time in thinking about the accomplishments and failures in life. It is these failures, which often push them towards mental health issues, causing depression and unprecedented suicidal attempts. Hence, this section of the population needs to be targeted to avoid unprecedented suicidal cases and depressive deaths. Therefore, from the above explanation of the selected National Mental Health Policy 2008 policy, it is obvious that although the policy had been effective in the beginning stages, yet there has been an unequal ratio between the objectives met with the policy levers.
Therefore, a separate plan needs to be developed, which will focus on the aged people of the locality and educate them to deal with mental health issues in a stronger and more self-managed manner. The plan is inspired from the National Mental Health Policy 2008 and aims at reducing the occurrence of mental health issues among the older people, at the local level.
Goal 1: To encourage the local aged people to enrol in the nearby yoga classes, ballroom dance practices and physical exercising centres
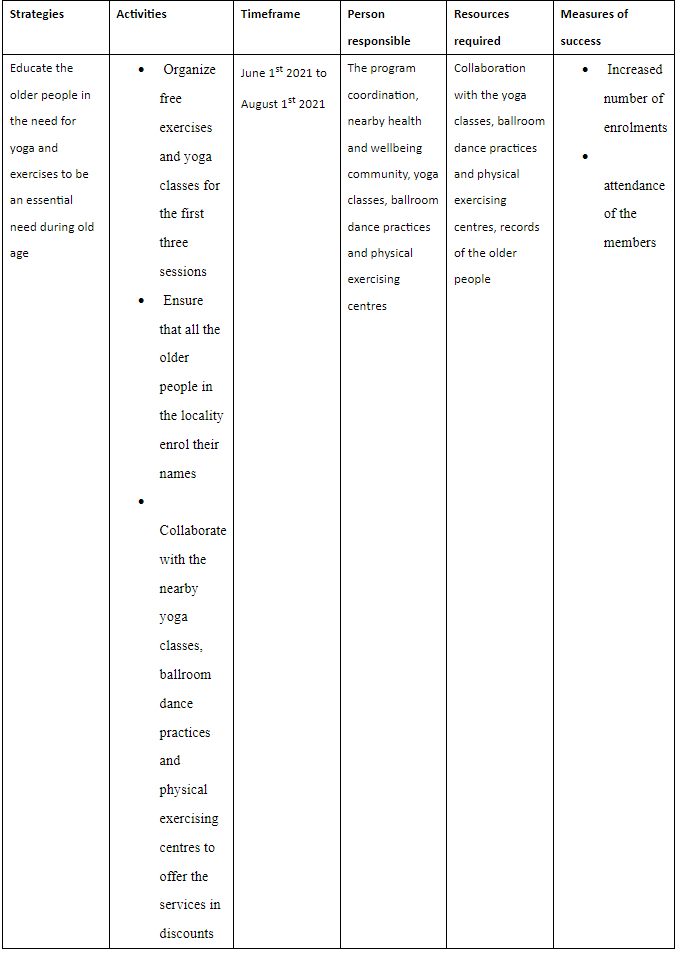
Goal 2: Select two days in a week by the community centres to encourage the older people in community interaction through casual group meets and cultivate friendship
Goal 3: Conduct weekly community centre weekly activities like painting, cooking, walking pets and encourage the aged people to participate in them
Conclusion
In consideration to the above literature, it is obvious that mental health issues happen to be one of the biggest issues in Australia. The highest percentages of the affected group include the aged and the teenagers. However, the findings show that the recovery rates among the teenagers are more compared to the aged population. Therefore, the selection of the aged population for the study is justified. The teenagers are said to receive quicker interventions and participations from the family guardians to help them stabilize, while the aged people mostly subside to isolation and suicidal attempts.
Therefore, the selected National Mental Health Policy 2008 ¸aimed at reducing the number of depression and suicidal cases among the older people in the country, and induce a conducive ambiance to support healthy aging in the country. The selected strategy rationalizes the inclusion of plans and actions to ensure that the mental health promotion of the aged population of the country is secured. The critical analysis of the National Mental Health Policy 2008,policy showed that the primary assessment of the success and failure rate of the National Mental Health Policy 2008 was dependent on the percentage of the objectives met, subsiding with the percentage of the intervention from policy levers.
The study showed that although the plan had been successful in the beginning, yet few areas were left untreated, which automatically questioned the overall credibility of the plan. Hence, the application of the Multi-disciplinary models of care has identified the strategy to have a holistic approach. Nonetheless, the strategy needs to be more robust with a continued focus on using the methods to monitor the mental health conditions of the older people and apply an evidence-based approach. Additionally, a recommended health promotion plan for the local aged people to combat mental health issues has been developed.
References
Aihw.gov.au . (2021). Mental Health of Older Australians. Retrieved from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/getmedia/c2ff6c58-e05e-49ed-afd7-43bd21eef4e2/AW15-6-4-Mental-health-of-older-Australians.pdf.aspx#:~:text=From%20the%202007%20National%20Survey,85%20age%20group%20(Figure%206.4.
Apo.org.au . (2021). National Mental Health Policy 2008. Retrieved from: https://apo.org.au/node/30315
Askell-Williams, H., & Murray-Harvey, R. (2016). Sustainable professional learning for early childhood educators: Lessons from an Australia-wide mental health promotion initiative. Journal of Early Childhood Research, 14(2), 196-210.
Astell-Burt, T., &Feng, X. (2019).Association of urban green space with mental health and general health among adults in Australia. JAMA network open, 2(7), e198209-e198209.
Awaworyi Churchill, S., Farrell, L., & Smyth, R. (2019).Neighbourhood ethnic diversity and mental health in Australia. Health Economics, 28(9), 1075-1087.
Barry, M. M., Clarke, A. M., Petersen, I., & Jenkins, R. (Eds.). (2019). Implementing mental health promotion. Springer Nature.
blackdoginstitute.org.au . 2021. Retrieved from: https://www.blackdoginstitute.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/1-facts_figures.pdf
Coates, D. D., & Howe, D. (2015). The design and development of staff wellbeing initiatives: staff stressors, burnout and emotional exhaustion at children and young people’s mental health in Australia. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 42(6), 655-663.
Edward, K. L., Warelow, P., Hemingway, S., Hercelinskyj, G., Welch, A., McAndrew, S., & Stephenson, J. (2015). Motivations of nursing students regarding their educational preparation for mental health nursing in Australia and the United Kingdom: a survey evaluation. BMC nursing, 14(1), 1-5.
Grace, F. C., Meurk, C. S., Head, B. W., Hall, W. D., Carstensen, G., Harris, M. G., &Whiteford, H. A. (2015). An analysis of policy levers used to implement mental health reform in Australia 1992-2012. BMC Health Services Research, 15(1), 1-11.
Gupta, S., &Sagar, R. (2018). National Mental Health Programme-optimism and caution: A narrative review. Indian journal of psychological medicine, 40(6), 509-516.
Hashmi, R., Alam, K., &Gow, J. (2020). Socioeconomic inequalities in mental health in Australia: Explaining life shock exposure. Health Policy, 124(1), 97-105.
Health.gov.au . (2021). National Mental Health Policy 2008. Retrieved from: https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2020/11/national-mental-health-policy-2008.pdf
Health.gov.au. (2021). Mental Health Promotion. Retrieved from: https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/publications/publishing.nsf/Content/mental-pubs-n-pol08-toc~mental-pubs-n-pol08-2~mental-pubs-n-pol08-2-2
Ho, F., &Mussap, A. J. (2017). Transgender mental health in Australia: Satisfaction with practitioners and the standards of care. Australian Psychologist, 52(3), 209-218.
Milner, A., Smith, P., &LaMontagne, A. D. (2015).Working hours and mental health in Australia: evidence from an Australian population-based cohort, 2001–2012. Occupational and environmental medicine, 72(8), 573-579.
Mokitimi, S., Schneider, M., & de Vries, P. J. (2018). Child and adolescent mental health policy in South Africa: history, current policy development and implementation, and policy analysis. International journal of mental health systems, 12(1), 1-15.
Slewa-Younan, S., Yaser, A., Guajardo, M. G. U., Mannan, H., Smith, C. A., &Mond, J. M. (2017).The mental health and help-seeking behaviour of resettled Afghan refugees in Australia. International journal of mental health systems, 11(1), 1-8.
Syed, M., & McLean, K. C. (2017).Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development.
Van Spijker, B. A., Salinas-Perez, J. A., Mendoza, J., Bell, T., Bagheri, N., Furst, M. A., ...& Salvador-Carulla, L. (2019). Service availability and capacity in rural mental health in Australia: Analysing gaps using an Integrated Mental Health Atlas. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 53(10), 1000-1012.
vanRensburg, A. J., &Fourie, P. (2016). Health policy and integrated mental health care in the SADC region: strategic clarification using the Rainbow Model. International Journal of Mental Health Systems, 10(1), 1-13.
Zhou, W., Yu, Y., Yang, M., Chen, L., & Xiao, S. (2018). Policy development and challenges of global mental health: a systematic review of published studies of national-level mental health policies. BMC psychiatry, 18(1), 1-9.
Assignment
MET414 Applied Epidemiology Assignment Sample
To be submitted via Turnitin by 14.00 on 15 March 2021
Using a public health or healthcare service that is currently being delivered in a population of your choice, prepare a written assignment describing how you would assess whether the service is meeting the health needs of its target population.
The service may be based in any specified patient population, neighborhood, city, or country. Please be very specific about the population. It is recommended that this should be a population and service that you are relatively familiar with.
The assignment should cover the following points:
1. Description of the service, including:
• If you find a strategy with many components, just choose one intervention to evaluate;
• Service aims and objectives;
• Target service users;
• How service is being delivered;
• Underlying evidence-base and guidelines that relate to the service, including evaluation of both clinical and cost-effectiveness.
2. Use a health needs assessment (HNA) approach to assess the:
• Health needs of the target service users;
• What indicators would you include to measure their health status?
• What sources would you use to find data on your chosen indicators?
• The HNA section should include scoping of the epidemiological, corporate and comparative parts.
3. Service evaluation; i.e.:
• Present a logic model to include structural, process and outcome indicators that would allow you to assess the performance of the service;
• Are there any gaps in services?
• Is the service meeting the health needs of the population?
• Are there any associated inequalities?
• Are there any members of the target service users who are not benefiting from the service?
• What would happen if the service was removed?
You are not expected to carry out the HNA itself. However, you are expected to describe your methods and potential sources of data, knowledge and intelligence.
The completed assignment should be type-written with a word limit of 2,000 words, excluding your logic model, tables, figures, and references.
References should be in Harvard style.
This assignment carries 50% of the marks for the MET414 Applied Epidemiology module.
For assignment help you prepare and practice a HNA, you will receive teaching about the principles. As part of your formative assessment, you will be asked to work in small groups to design and present an outline for a HNA. These presentations will offer you the opportunity to work through the design of a HNA and receive feedback.
Please note: whilst the oral presentations are based on group work, your summative assignments writing should be submitted individually, and not be related to the topic of the group oral presentation.
Email the module lead / MPH Office if any questions
Solution
EVALUATING TOBACCO CONTROL ‘STOP SMOKING’ HEALTHCARE SERVICES IN THE UK
SECTION 1: DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE
1.1 BACKGROUND TO THE SERVICE:
There have been considerable advances in health with advancements in research and up-gradation in technology. There is a considerable increase in tobacco smoker worldwide which leads to more than more preventable deaths than ever before. This creates a greater need for health care policy on the prevention of smoking leading to a considerable challenge for the NHS. NHS England partners with various organizations for the prevention of smoking amongst people in England. The Tobacco control healthcare delivery plan aims at a Smoke Free Generation (Wee et al., 2020). The Tobacco Control Plan for England was developed by the Government in 2017-22 as a nationwide initiative to provide support towards tobacco control. The aim of this plan was to focus on reducing the rate of smoking amongst 15-year-olds, who are smokers. Reducing the rate of adult smokers in England and reducing gaps existing in inequalities prevalent amongst routine and manual occupations across England. The policy also aims at reducing the prevalence of smoking amongst pregnant mothers. The Government prepared a delivery plan that engaged inter-departmental collaborations also local partnerships such that appropriate governance regarding the delivery of the plan could be easily achieved. The Government in the UK has high ambitious targets for making England smoke free even with the threats of budget cuts being prominent (Beard et al., 2014, p 280). The Government of England offers specialized services to stop smoking. Though there has been a significant reduction in funds available to stop smoking yet the Government continues their undeterred efforts to prevent smoking services in the entire nation. Thus, the service of the Stop Smoking plan aims at prevention or reducing smoking amongst varied age groups and amongst members of the population.
1.2 SERVICE AIMS AND OBJECTIVES:
The government’s plan of Stop Smoking aims at controlling the use of tobacco in England. Some of the specific aims regarding the service include;
o Prevention of smoking at the national level.
o Supporting smokers to quit their habit of smoking
o Reducing the variations in rates of smoking
o Effective application of the policy of smoking control
This service aims to reduce the overall rate of smokers prevalent in the UK (Department of Health & Social Care, 2018). With the present service being built on the foundations of past successes in tobacco control efforts in local areas. With the support and vision of the NHS, there is a long term plan developed for pursing approaches to adopt a sustainable care system that can bring about significant effects of tobacco prevention and control.
1.3 TARGET SERVICE USERS:
Priority in tobacco control has been given in England due to the high rates of prevalence along with increasing rates of smokers in the nation. A survey conducted by the NHS found a considerable rise in the number of smokers since 2013. There has been given considerable importance on controlling the use of tobacco not only from the national levels but also from local authorities. There remain high rates of prevalence of smokers in England (Bauld et al., 2016, p 1165).
A survey conducted by the Government depicts reveals that the targeted population of smokers in England constitutes young people age 15 years and above, the adult population also pregnant women. There has been a significant rise in the number of smokers at the school level. The ease of availability of tobacco makes them susceptible to becoming smokers early in their lives. 87% were seen to be pregnant women who were using tobacco. Pregnant women seemed unaware of the effects of smoking during their pregnancy period hence there was seen extensive use of tobacco amongst them. 70% had some kind of mental health conditions associated, 67% people were in some routine and manual occupations with low levels of incomes and 60% of smokers were seen to be with acute long-term conditions (Office for National Statistics, 2021). People with mental conditions or with low levels of incomes were seen to be using tobacco greater than people with middle to high levels of income. These high prevalence groups have been the key target population for the Government of England.
The targeted service aims at bringing about considerable effectiveness in either reducing or preventing smokers from their smoking-related habits. Through effective intervention from the NHS along with local authorities, the specialized services will be provided for long-term efforts (Pirie et al., 2013, p 140). Most of the targeted users and participants for the services include those who are taking up services such that they can avoid smoking also it includes those who are yet to adopt but intends to adopt services aimed at preventing or reduction in the incidence of smoking.
1.4 SERVICE BEING DELIVERED:
Prevention and reducing tobacco smoking services in England is adopted by the NHS along with local authorities. The targeted population for the purpose of this service delivery has been adequately identified, also the Government has adopted tremendous efforts with suitable budgetary allocations by setting different levels of priorities for the delivery of tobacco smoking control services (Smith et al., 2020, p 42). Methodology for service delivery aimed at prevention or reduction in tobacco smoking includes the NHS coordinating with local authorities to delivery intervention programs aimed at desired outcomes.
Services targeted at prevention or reduction in tobacco control practices has mainly been delivered through local healthcare authorities rendering healthcare services. They set-up training centers also programs frequently for different targeted groups of the population at different locations to bring about effectiveness in the services (Beard et al., 2016, p 354). Community settings were primarily selected for the purpose of service delivery aimed at tobacco control and prevention methods.
There are varied services that are adopted as a part of this service. There are programs aimed at prevention and reduction which includes interacting with patients, providing them strategies that might be adopted for preventing smoking and so on. Training is provided by healthcare professionals for smoking cessation. Recording outcomes for smoking prevention also assists in accurately measuring smoking beyond self-reporting (Hollingworth et al., 2012, p 165). Through Carbon Monoxide resting, there are programs developed for the prevention of smoking amongst pregnant women. The services also aim at promoting self-care and prevention amongst individuals.
The targeted users are actively invited and referred to this service such that they can accommodate them and prevent or reduce their smoking-related habits. Targeted users are required to attend programs also training sessions such that they are able to take up the course and prevent smoking altogether (Richardson et al., 2014, p 45). Targeted users are contacted by the community such that they can take part in sessions, programs, training and activities aimed at promoting cessation of smoking.
1.5 UNDERLYING EVIDENCE-BASE AND GUIDELINES THAT RELATE TO THE SERVICE, INCLUDING EVALUATION OF BOTH CLINICAL AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS:
The Government publishes reports that include data and statistics of adult smoking in the UK. In the year 2019, it was found that 14.1% of individuals in the age group above 18 years smoked tobacco, accounting for 6.9 million people, as reflected in the Annual Population Survey (APS). Though there has been a considerable decline in the proportion of smokers from 2018 amounting to 14.7% to 14.1% in the year 2019. The highest proportion of current smokers were in the age bracket of 25 to 34 years accounting for almost 19.0% of the population (Office for National Statistics, 2021). There was also 23.4% people in routine and manual occupations who smoked amounting to 2.5 times greater than people who were engaged in managerial and professional occupations, amounting to 9.3%. the NHS aims to adopt tobacco control services as per the WHO Framework Convention for Tobacco Control to be followed at all levels of the nation.
Evidence of the cost-effectiveness of the service can be ascertained by the limited budget and spending undertaken by the government in curbing smoking (Shahab et al., 2017, p 85). All the intervention mechanisms are handled at the local community levels for adopting cost-effective efforts. Though there is a considerable cost component attached to the training and programs which are advertised for tobacco prevention and control mechanism.
2 SECTION 2: ASSESSING THE HEALTH NEEDS OF THE TARGET SERVICE USERS
2.1 INDICATORS TO MEASURE HEALTH STATUS
The services on stop smoking of tobacco have been built and developed on the basis of past efforts for the prevention of smoking. Initiatives in the domain include working in a joint manner with individuals in the local authority services, partnering with the NHS and also pursuing approaches for the population for the development of a sustainable and integrated system of care. The Government in England has very ambitious targets for attaining smoke free ambition in England by 2030 in spite of threat pertaining to budget cuts remaining (Cancer Research UK, 2021). Ascertaining the health need assessment of the targeted population, the aims of the service has been ascertained. The health needs of the targeted population are being ascertained especially for pregnant women, school-going children and adults such that the impacts of smoking on their health can be reduced. Tobacco control can be seen to be of considerable importance when reducing the impact of adverse effects on the health of individuals also reduce the incidence of cancers amongst the population. Survey data reveals a considerable impact on the health of the targeted population also a rise in the incidence of cancers associated with tobacco smoking (Hunt et al., 2018, p 314).
2.2 SOURCES OF DATA ON INDICATORS
Cancer research organization in the UK publishes relevant data which reveals that tobacco smoking has been seen associated with cancers of 15 different types affecting the nasopharynx, oral, lung, oesophagus, larynx, ovarian, stomach, pancreas, bladder, pharynx, liver, kidney, bowel, leukaemia, and bowel and also many more. The organization reveals that tobacco remains one of the biggest forms of preventable cancers and death in the UK. Smoking was seen to be associated with 125,000 deaths in the UK. 15% of cancers were seen to be caused by smoking. There was also seen considerable deprivation associated with cigarette smoking in 2019 (Ash, 2017).
2.3 SCOPING OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL, CORPORATE AND COMPARATIVE APPROACHES:
Cancer research organization in the UK also ASH organization revealed that in every 2 people born after 1960 in the UK is diagnosed with some forms of cancer during their life and approximately 1 in every 4 will die from tobacco smoking disease. Tobacco smoking is estimated to be causing one-fifth of cancers every year and causing 27% of deaths related to cancers in the UK (Raupach et al., 2015, p 374). A recent survey conducted by Ash organization reveals that 19% of cancers are connected to some form of tobacco smoking. These bodies are the leading research organizations in cancers in the UK. Data search conducted in these organizations reveals the health needs of the population to prevent cancers.
2.4 EVALUATION OF SERVICE
Logic model to adopt structural, process and outcome indicators which will allow assessing the performance of the service (Brain et al., 2017, p 914). There will be adopted prevention-related indicators for assessing the intervention of the service for understanding the effectiveness of the service performance.
Figure 1: Service Evaluation Model
Source: Author
Using an epidemiological approach, the HNA has been conducted and then an evaluation approach is undertaken for ensuring effective intervention. This approach will enable the meeting needs of the target population (Jones, and Hamilton, 2013, p 565). The health service is evaluated using the above methodological approach. Limitation on the service includes budgetary constraints remaining with the need of the target population. Though budgetary constraints cannot be addressed by the services.
2.5 GAPS IN THE SERVICES
The services in the UK is made available to all possible types of users such that inequalities can be removed with the best possibilities. Targeted users in the service have been benefitting tremendously from this service. There does not remain any significant gaps that remain in attending to the services for the targeted users. Intended targeted users such as adults often restrain from the services provided. A possible explanation for this includes their unawareness regarding the impacts associated with the consequences of tobacco smoking.
2.6 IN CASE THE SERVICE WAS REMOVED
In case the service was removed or withdrawn then there might arise significant consequences reflected in the direct rise of cases of tobacco smokers. The relevance of this service is regarding its sustainability aspect, which otherwise in case not implemented then will lead to considerable impacts on the health of the targeted population. School going children and pregnant women will be the most impacted group in case the service was removed. As the service focuses on considerable behavioral change to have a positive impact on the targeted population.
3 REFERENCES
Ash, 2017. Smoking and Cancer. ASH Fact Sheet on Smoking and Cancer. Accessed from [https://ash.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Smoking-Cancer.pdf]
Bauld, L., Hiscock, R., Dobbie, F., Aveyard, P., Coleman, T., Leonardi-Bee, J., McRobbie, H. and McEwen, A., 2016. English stop-smoking services: one-year outcomes. International journal of environmental research and public health, 13(12), p.1175.
Beard, E., Brose, L.S., Brown, J., West, R. and McEwen, A., 2014. How are the English Stop Smoking Services responding to growth in the use of electronic cigarettes? Patient education and counseling, 94(2), pp.276-281.
Beard, E., West, R., Michie, S. and Brown, J., 2016. Association between electronic cigarette use and changes in quit attempts, success of quit attempts, use of smoking cessation pharmacotherapy, and use of stop smoking services in England: time series analysis of population trends. bmj, 354.
Brain, K., Carter, B., Lifford, K.J., Burke, O., Devaraj, A., Baldwin, D.R., Duffy, S. and Field, J.K., 2017. Impact of low-dose CT screening on smoking cessation among high-risk participants in the UK Lung Cancer Screening Trial. Thorax, 72(10), pp.912-918.
Cancer Research UK, 2021. Tobacco statistics. Together we will beat cancer. Accessed from [https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/risk/tobacco#heading-Zero]
Department of Health & Social Care, 2018. Tobacco Control Plan Delivery Plan 2017 – 2022. National Archives of the Government of the UK. Accessed from [https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/714365/tobacco-control-delivery-plan-2017-to-2022.pdf]
Hollingworth, W., Cohen, D., Hawkins, J., Hughes, R.A., Moore, L.A., Holliday, J.C., Audrey, S., Starkey, F. and Campbell, R., 2012. Reducing smoking in adolescents: cost-effectiveness results from the cluster randomized ASSIST (A Stop Smoking in Schools Trial). Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 14(2), pp.161-168.
Hunt, D., Knuchel-Takano, A., Jaccard, A., Bhimjiyani, A., Retat, L., Selvarajah, C., Brown, K., Webber, L.L. and Brown, M., 2018. Modelling the implications of reducing smoking prevalence: the public health and economic benefits of achieving a ‘tobacco-free’UK. Tobacco control, 27(2), pp.129-135.
Jones, S.E. and Hamilton, S., 2013. Introducing a new stop smoking service in an acute UK hospital: a qualitative study to evaluate service user experience. European Journal of Oncology Nursing, 17(5), pp.563-569.
Office for National Statistics, 2021. Adult smoking habits in the UK: 2019. Office for National Statistics. Accessed from [https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/healthandlifeexpectancies/bulletins/adultsmokinghabitsingreatbritain/2019]
Pirie, K., Peto, R., Reeves, G.K., Green, J., Beral, V. and Million Women Study Collaborators, 2013. The 21st century hazards of smoking and benefits of stopping: a prospective study of one million women in the UK. The Lancet, 381(9861), pp.133-141.
Raupach, T., Al-Herbie, G., McNeill, A., Bobak, A. and McEwen, A., 2015. Smoking cessation education and training in UK medical schools: a national survey. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 17(3), pp.372-375.
Richardson, S., Langley, T., Szatkowski, L., Sims, M., Gilmore, A., McNeill, A. and Lewis, S., 2014. How does the emotive content of televised anti-smoking mass media campaigns influence monthly calls to the NHS Stop Smoking helpline in England? Preventive medicine, 69, pp.43-48.
Shahab, L., Dobbie, F., Hiscock, R., McNeill, A. and Bauld, L., 2017. Prevalence and impact of long-term use of nicotine replacement therapy in UK Stop-Smoking Services: findings from the ELONS study. Nicotine and Tobacco Research, 20(1), pp.81-88.
Smith, C.E., Hill, S.E. and Amos, A., 2020. Impact of specialist and primary care stop smoking support on socio?economic inequalities in cessation in the United Kingdom: a systematic review and national equity analysis. Addiction, 115(1), pp.34-46.
Wee, L.H., West, R., Hiong, T.G., Yeap, L., Chan, C.M.H., Kiau, H.B., Perialathan, K., Mohamed, M.H.N., Michie, S. and Jackson, S.E., 2020. Effectiveness of training stop?smoking advisers to deliver cessation support to the UK national proposed standard versus usual care in Malaysia: a two?arm cluster randomized controlled trial Addiction.
Essay
NUR7003 Leadership Changing Healthcare Landscape Assignment Sample
Question
Write a 1000-word reflective assignment help of your approach to leadership,
acknowledging strengths and limitations.
You should acknowledge recent learning and how this may now be
influencing a change in your leadership behaviour
Please refer to the academic guidelines in assessment. You should:
• Attach your work to a completed front cover sheet
• Include an accurate reference list
Leadership skills enhance the communication by delivering the mission and vision of the firm to its employees very effectively. This further helps in identifying the roles which can best fit for the academic skills. Leadership techniques have helped me in understanding the influence of others and the capacity towards determining a particular goal. When the leadership techniques come into play, it can be beneficial both at the workplace for the delegation of work as well as it enhances a personal wellbeing of an individual. In my personal experience, the leadership techniques have helped me to establish effective communication and encourage the team members for the task performance. During my college days, I have observed that when working in teams, the leadership and managerial practices helped in minimising the errors and also gaining constant progress in the work. I tried to help the team members initially by setting up effective communication. In the starting of the project, I mentioned the team members that they can feel free to express their views on how to precede with the work. This gave them the confidence to further understand the work details and set up meetings which can help in the better understanding of the work.
Solution
Leadership has also helped me to improve my communication skills and to enhance my self-confidence. This can be mentioned as the way in which enthusiasm it involved. Often,I used to find it difficult to understand a certain task and would find lack of time in performing it. After I had implemented the leadership techniques, it has helped me to understand the details of the work in a far better manner. I have also been able to focus on the group activities more. Confidence is increased when the targets of the group assignments are met and the team members are satisfied with the leadership technique that had been followed for the completion of the work (John and Bertram, 1959).The main challenge that I observed during the practice of the leadership skills is that it was sort of difficult for me to comprehend my own values and principles. I would always jump to assumptions and conclusions really quick which made me fail a couple of time. Those failures were the times I learned the most. I have also observed that when the most appropriate leadership technique is not followed then the organisational complexities are increased. Similarly, Michael Hartsfield(2010) also stated, “Managers do things right and leaders do the right thing.”
Gibbs Reflective Cycle helps in encouraging people to think and reflect on the experiences they had faced during a certain situation, activity or even event. With the help of a circle, a reflection on those experiences which they went through can be structured in several phases. This I can relate to an incident when I did an internship with an organisation, there the leadership practices were not followed and it became hard for the members to understand as to how they should behave within theworkplace and how to proceed effectively with the tasks. This is the main reason why I failed in submitting most of the projects on time because that had to be done in the group activities and it was hard for the members within the team to understand as to how to discuss and delegate the different responsibilities within the project. This has helped me to become more flexible in understanding the group approaches and further lead myself into the team and help all the members to achieve progress. This incident helped me in reflecting upon the skills that I never thought I inherited. The next course of action would be to enroll in courses related to leadership that could enhance my managerial skills and abilities in order to effectively manage change and nurture the people around me.
.png)
Figure 1: Gibbs reflective cycle
(Source: Mindtools, 2022)
The four E’s framework also been a great help to me for identifying the actual context of leadership in the global concern and to differentiate within the national and the global leadership techniques. These includes the energy, energising ways, the edge of the technique which is considered for moving ahead with the leadership practice, the way of execution of the leadership technique which can be beneficial for an individual or the organisation. Passion of the leader is also considered in the global context where the work proceedings of the leader are considered. Here the passion of the leader is noted as to how they try to manage the team and follow the guidelines of the workplace and how far they are successful in making the team understand about the work details (David, 2012). The way they try to manage the working of the team, support them in time of need and further guide them with the necessary training and support as required can help the leaders to maintain the leadership technique which is appreciated by the people.
.png)
Figure 2: 4 E’s framework
(Source: Researchgate, 2022)
There are several approaches to leadership as well which also contains the ethical norms. As stated by French & Raven, the power bass procedures are handled when it comes to understanding the stakeholders care and the ethical concerns (Alan & James, 2018).As stated by Yukl and Yukl,ethical leadership technique also played a great role in building my leadership skills. The ethical values consider the practices such as trustworthiness, honesty and responsibility. When I tried reading the leadership approaches, it helped me to understand the benefits of being more honest and trustworthy within the workplace or in any group activity. When such practices are considered, it has not only helped me to increase the transparency in the group activities but has further helped me to understand the ways in which the team can be managed. When I asked the team members to be honest regarding their work, they tried to provide me the details and the areas which they find it hard to understand.
Therefore, it can be stated that following of the leadership techniques can not only help in better performance at workplace but can further help in making the team more authentic. My self-confidence has been boosted after the utilisation of the leadership practices as I got much appreciationregarding the team work. I also got the support of my team members in the work proceedings and they also tried to help me in times of need which further made our team strong. Hence, I would like to conclude that the best leadership technique suitable for the workplace needs to be considered for the development of an individual as well as the team.
References
Michael, H (2010). Leadership Reflection: Leaders Do the Right Thing: A Popular Phrase or a Real Practice?https://www.regent.edu/journal/journal-of-biblical-perspectives-in-leadership/leaders-do-the-right-thing/
Alan, C. and James, S. (2018) Sources of Leadership Power - French and Ravenhttps://www.businessballs.com/leadership-philosophies/sources-of-leadership-power-french-and-raven/
John, R. and Bertram,R. (1959) The Bases of Social Powerhttp://www.communicationcache.com/uploads/1/0/8/8/10887248/the_bases_of_social_power_-_chapter_20_-_1959.pdf
David, C. (2012) Continuing Confusion -Are Managers and Leaders Different?https://scholars.fhsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1047&context=jbl
Researchgate, (2022) 4 E’s framework https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-4Es-model-for-delivering-behavioural-change_fig1_284187722 (Accessed on March 23, 2022)
Mindtools, (2022) Gibbs reflective cycle.https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/reflective-cycle.htm (Accessed on March 23, 2022)
Coursework
AC7026 - Master of Public Health (Nutrition) Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Module Title: Nutrition related diseases
Distributed on: 26.01.2021 / Teaching week 27
Submission Time and Date: To be submitted by 9:00 am GMT on Tuesday 4th May 2021
Word Limit: 3000 words (+/-10%)
Weighting -This coursework will be mark out of 100 and accounts for 70% of the total mark for this module
Submission of Assessment
Electronic Management of Assessment (EMA): Please note if your assignment is submitted electronically it will be submitted online via either Blackboard or Turnitin by the given deadline. You will find a Blackboard/Turnitin link on the module’s eLP site. It is your responsibility to ensure that your assignment arrives before the submission deadline stated above. See the University policy on late submission of work.
Assessment Instructions:
Funding for nutrition research comes through research councils (MRC, BBSRC, innovate UK), industrial sponsors or charitable organizations. In almost all cases funding is awarded competitively based on written grant applications. Here we will mimic that process, you are asked to create a three-year research grant project to address a pressing issue in the area of diet and disease.
Your project needs to be conducted by one person, working with limited support (i.e. technical help) and within three years. Strong projects will have the capacity to make meaningful improvements to health and will build upon topical issues covered in the module. (These improvements may be direct or indirect, i.e. your project might directly stimulate behavior change, or it might better inform those who set nutrition policy). You are encouraged to talk to the module leader about the suitability of your project ideas at an early stage.
Typically, a grant application is structured as:
Lay summary (500 words max) This is a plain language overview of your project, written for a non-expert audience.
Background and significance (850 words max) A concise literature review showing that you have something new to add, you need to be selective with your literature here, identify the most important work, show what questions are not yet answered.
Hypothesis and Aims (250 words max) be very implicit, what is your question and what do you hope to achieve?
Deliverables (400 words max) What will you determine and by when (include time points)? Structure as bullet points, GANTT charts are also useful.
Study design (650 words max). What work will you do? can it be done within 3 years? Please provide details of the study.
Impact (350 words max) This can be the hardest section to write. Why is this work important? Who will benefit and how? What steps will you take to make sure that the maximum benefit is realized?
Costings. (A page showing that you have planned how much money you will need, this includes yearly costs for staff, equipment, travel expenses, etc. Please be realistic, the project needs to deliver value for money but without costs affecting the quality of the work.
Module Learning Outcomes for assignment help
Learning outcomes assessed by the assignment:
1. Understand priorities in public health nutrition
2. Critically evaluate the scientific basis of current public health nutrition concerns
3. Independently develop plans to interrogate the nutrition evidence base.
Word Limit Guidance: For assessments where a word limit is indicated, a student’s ability to write within the word limit is part of the assessment concerned. Where a word limit is indicated students should provide a final word count by highlighting all text included in the main body of the assessment (the main body of the assessment does not include the reference list) and simply stating that word count.
The main body of the assessment includes:
-the title (if applicable)
-an abstract (if applicable) -the main body of text (including any sub-titles)
-in text citations e.g. (Smith, 2018) -direct quotations, case studies etc.
-tables, figures (including any table/ figure titles), illustrations and footnotes
Referencing Guidance.
Referencing is a key aspect of the academic assessment process, as it allows students to:
• acknowledge the contribution that other authors have made to the development of their work (and
therefore, help avoid plagiarism)
• evidence students independent research and depth and breadth of reading i.e. student ‘scholarship ‘
• demonstrate understanding of concepts proposed by other writers while developing their own ideas
• inform their readers of the sources of theories, datasets, quotes etc. that have been referred to, and enable readers to find the sources quickly and easily themselves.
Solution
Beriberi
A nutrition deficiency disease
Overview
The purpose of this project is to ensure better solution to a nutrition deficiency disease, beriberi, which causes fatal illness. The disease was first discovered in the year 1593 in England and is still an issue in most of the underdeveloped countries such as Bangladesh, Thailand and Kiribati. The purpose of the project is to eradicate beriberi by spreading awareness among people who are affected, providing medical aid to those people with the help of the local government and presenting schemes and policies to the government including financial aid. Many poor, underdeveloped and developing countries such as Kenya, Uganda, Kiribati, Bangladesh etc. are still facing these issues due to lack of public healthcare facilities, nutritional policies and lack of medical supplies to the people suffering from these nutrition deficiency diseases. Poverty is one of the major reason to cause beriberi as a person in unable to consume nutritional diets due to lack of capital. Proper nutrition and diet plans will help prevent this disease (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). Through this project, I would like to address such a problem with a solution to how we can eradicate this kind of disease from spreading. Arranging proper nutrients foods will also help people with thymine deficiency to gain thymine in their body. The awareness campaign should be done in different parts of the world where the problem regarding this issue is very widespread.
A sever thymine deficiency or vitamin B1 deficiency causes Beriberi. Wet and Dry beriberi are the two of its kind which causes due to low intake of Vitamin B1 or thymine rich food. Wet beriberi affects cardiovascular system resulting, in extreme case, blockage of heart and increase in heartrate affecting the circulatory system of a human body. Whereas, on the other hand, dry beriberi cases sever nervous breakdown and affects the nervous system causing paralysis, in extreme case. Consuming alcohol in a large amount and in a disorderly manner may also be the cause of thymine deficiency resulting to cardiovascular issues. Enlargement of heart, nausea, swollen legs, loss of appetite and lactic acidosis can be observed in infants affected with chronic or acute beriberi (Buttriss, 2015). Due to lack of thymine, cardiovascular and nervous system do no respond and function well as lack of thymine prevents doing so. 80 Percent of the people, due to abuse alcohol, which prevents their body to absorb thymine which in turn causes deficiency of thymine inside the body. These diseases are mostly found in third world countries rather than the developed countries. Low standard of living and ignorance towards healthcare plans lead to these kind of deficiency and causes many other nutrition deficiency diseases.
Background and significance
A forgotten disease that is still a clinical issue in many countries in southeast Asia including Bangladesh (Smith, H. A. 2017). Thymine was the first vitamin B that was discovered. In July 2009 an unknown illness caused death to a large number of African Union soldiers in Mogadishu which was later identified as wet beriberi. Laboratory investigations did not show any metabolic, infectious or toxic abnormalities which is why it was difficult to understand the nature of the disease (Emukule G, et al. 2011). After examining the blood sample of 16 soldiers it was identified that the levels of erythrocyte transketolase activation coefficient was high which caused thymine deficiency. This is considered to be an ancient disease but it is still existing in many parts of the world. The question is why is this disease still exist and how nutrition research will help control these diseases? Nutrition research will help understand the deficiencies and the food supply chain which will help people lead a healthy life and providing better outcomes for the economy. The main issue is to understand that a high number of diseases are caused due to deficiency or excess of nutrients consumptions (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). A proper nutrition and diet research will help understand the food consumption cycle which will be the stepping stone to eradicating diseases caused due to improper consumption of nutrition. Though cases of beriberi can be still seen with the introduction of advance technology and scientific methods deficiencies diseases like beriberi can be controlled.
Individual response to diet and food
Due to different metabolic rates, diet cannot be same for all people rather it should be according to the genetics, epigenetics and ethnics differences. The discovery of variability in diet will help in personalizing the diet for different people resulting in a better inform policy. The first thing is to understand the variability of metabolic responses in different people to different diet and food which can be done with the help of the following:
Omics:
Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics are the two omics research that helps identify how nutrients reacts to different genes, proteins and metabolites that will help identify the individual health and its issues (Buttriss, J. L. 2015). It will help understand how nutrients are digested, metabolized and absorbed in different human bodies. This will help create new biomarkers which will help identify health deficiency of an individual.
Microbiome:
Different microbes such as bacteria and virus that are present inside a human body contributes to microbiomes. Microbes varies from person to person and each has a unique microbe that makes microbiomes identical and different from each other though the subpopulation may consist same microbiomes. The microbiota that changes due to change in age, diet and physiological rates should be determined accordingly to adjust the diet of an individual. Research is needed to determine different microbiota that reacts differently to different nutrients. It is also important to understand its role in disease prevention and progression.
Genome:
The role of DNA and RNA and its determination is important so as to understand the proper diet that an individual need. Genome gives a complete information about an organism as it provides all the information which is required for an individual to function (Gropper, & Smith 2013). By identifying this it will be easier to analyze what deficiencies an individual has which will help in overcoming the deficiencies diseases like beriberi.
Impact of nutrients in healthy growth and development
The research will help improve the health and well-being of an individual. Early determination of the nutrients (Buttriss, 2015) will help resist the diseases later to affect individual’s livelihood and development progression.
Early nutrients:
The role of diets is essential for the parents while preconception and during pregnancy which will help respond to early nutritional events. The introduction of an infant to solid food is a major decision as this may lead to obesity in future. The assessment of the nutrition in the early life is essential as this may cause a lot of diseases if not taken care of at an early stage.
Nutrition and reproduction:
Nutrition greatly impacts on maternal and paternal fertility. So this is an area that needs to be researched as it affects in preconception as well as post conception. Impact of nutrients are huge and it plays a key role in preventing diseases relating to reproductive organs such as prostate and ovarian cancer. The determination of the factors and mechanism is important for change in health of an individual.
Role of nutrition in health maintenance
Health maintenance requires continuous research to understand the role of nutrients and novel ingredients and its contribution in health (Chern, & Rickertsen, 2003). To rely on researches that help to dietary guidance including DRI is essential for health policy. At an early stage it is recommended to better understand the nutrient needs which will help in maintaining health in all population and subpopulations.
Optimal body functions:
It is better to determine the role of nutrition and fitness, together and individually to maintain the functions of the body that includes muscular, skeletal and nerves system.
Energy balance:
Researches require to identify system wide changes that important to reach optimum energy of a body. Experimental approach has not proven to be much effective in the past as it was unable to reach the population whereas system wise approach will help to reach wide scale of population to understand the energy balance.
Role of nutrition in medical management
Nutrition researches play an important role in connecting the diseases with their treatments. Researches that are evidence based results in more effective policy making that ensures proper patient care
Disease Progression:
To understand the medical management of the diseases, research plays and important role. It helps understand how a body response to different disease when nutritional factors influence both disease initiation and its progression. Research will also help us understand the role nutrition plays in prevention of the diseases.
Nutrition Support:
Nutritional researches are required to determine to understand the best support that is needed to for survival and growth of an individual and subpopulation (Eilender, 2016). It will help understand how nutrients helps with chronic disease among infants and the elderly people.
Understanding nutritional related behaviors
Drivers of food choices:
The drivers that influences food choices are:
• Government policies
• Cultural differences
• Environment
• Food marketing and social media
Nutrition and brain function:
The marketing of healthy food behaviors will greatly help the population to consume healthy diets. The diets will influence hormonal changes which in turn will help in metabolism (Gropper, & Smith, 2013). of an individual. Factors such as consumption of the different diets, variety, eating frequency etc. will help researchers to understand the pattern of the intake of the nutrients. It is important to understand how eating influences neural biochemistry and brain functions.
Food supply
• Collaboration between nutrition and agricultural production
• Identifying the quality factors that influences the consumption of food
• Introduction of biotechnology and nanotechnology to influence food production and providing novel nutrients to individuals
• Enhancing the knowledge of food to understand its availability.
The above factors will help identify and control nutrition deficiency diseases. In many countries there are people who still follows culture ignoring the biological harm they bring to themselves. Awareness campaigns with the help of the local leader may convince them to take precaution and understand the essentiality of consuming medicines.
Hypothesis and Aims
As beriberi is one of the many diseases that is caused by deficiency of vitamin, thymine, it is necessary to understand how food environment affects the dietary patterns and what is needed these to solve the problem.
Below is a few question that needs to addressed:
• What kind of dietary change is needed and is the current dietary change significant?
• How does assistance program helps reach and promote proper dietary patterns?
• What are consequences of negative dietary responses?
• How is marketing playing an important role in influencing dietary choice of food and how are its impacts?
• How do we monitor, assess and evaluate the dietary change changes?
• How does inclusion of quality of food influences its consumption?
• How does promoting local production of food and its supply influence dietary patterns?
The above questions are very important to address as the dietary patterns of an individual is directly related to its health care. Proper nutrition intake is far less costly then taking medicines at the stage where the disease will be chronic. The rise in number of beriberi cases in southeast Asia including Japan helps us understand that this is not only a concern in the underdeveloped countries but also in the developed countries.
As this is a disease that is caused due to deficiency of nutrition the aim and objective should be to make policies that will provide proper nutritional diets to every individual. With the help of the local government the following schemes and policies can be implemented:
National food policy plans:
Making Desirable Dietary Plans, which will formulate the requirements of energy such as needs of micronutrients and macronutrients are essential. It can influence the future of agriculture and food policies of the country. Desirable dietary plans are adaptive and improving in nature as it changes according to the growing needs of the people (Shi, 2019). A plan that will help change the idea of food nutrients and its intake not only for the urban people but also for the rural people, poor people, people living in hilly areas and people under poverty. The USP of this plan is that it is not static in nature and it will vary according to the nature of the requirement.
School feeding programs:
This is a step that can be taken very actively as it will nourish the children from a very basic level. This is a part of right to food to everyone. Introducing feeding programs in schools will not only feed them but also will encourage them to come to school every day. The countries that have a high level of poverty such as Bangladesh and Pakistan (Shi, 2019) should introduce feeding programs in the government schools so that the children are exposed to multi nutrients. In this way government can also observe the intake of the food at a large scale and plan the production and availability of the food accordingly.
Anti-poverty programs:
In this program the idea is to pay an amount to the poor section of the society directly so that they can consume adequate amount food to feed their family. This can be given according to the number of members of family members present in the family. In 2003 Mexico came up with such a plan to provide direct money to the needed class of the people. This will help the government to understand the food consumption of the country according to which policies can be made.
Deliverables
It is better to find ways to identify these diseases at a very early state so that it can be addressed accordingly. The following things should be done at an early stage to avoid these deficiencies:
• Medical checkup for every individual once in a year funded by the government
• People who are affected with these diseases should be able to access free medicine
• Involving the funded organisations to conduct medical camps in the areas with large number of cases of beriberi are high
• Making locally produced food more feasible to the people through government subsidized markets where people can afford local vegetables and food at low cost
Inadequate thymine consumption, less absorption of thymine and abnormal metabolism will result in a loss of thymine through urinary track. Transketolase is an important factor that reduces thymine in the body, when it functions improperly (Carpenter, K. J. 2000). Irritability, insomnia, loss of appetite are also the symptoms that effects the psychological stages. Factors that are influencing the thymine requirement are as follows:
• Composition of the diet: The dietary requirements of carbohydrates and fats are to be maintained in proportion. Increase in fat containing diets though does not effect at large but the consumption of carbohydrate in a large quantity happens to increase the requirements of thymine
• Climate: This influences the requirement of thymine as climate is directly proportional to energy consumption.
• Age: For the individuals those who are actively involved in work will have to increase the intake of minimum thymine.
• Body weight: The requirement of thymine will differ according to the body weight. More is the weight more is the consumption of energy and more is the requirement of thymine.
• Physical activity: More workout and activity will lead to more loss of energy resulting in more requirement of thymine.
• Pathological condition: Pathological condition influences the consumption of thymine. Patients having gastronomical disorder, alcohol issues, thyroid disorder etc. will require to consume their thymine accordingly that’s will not affect their health further.
The GANTT chart below shows the planning and duration that is needed to initiate the project. As most of the cases are observed to occur in the backward areas like Bangladesh, Pakistan, Kenya etc. choosing one of these places is important. In this project we will work in the areas of Bangladesh and try to eradicate this disease with the help of the government by making policies and schemes. Below is the time frame shown in GANTT chart to initiate the plan.
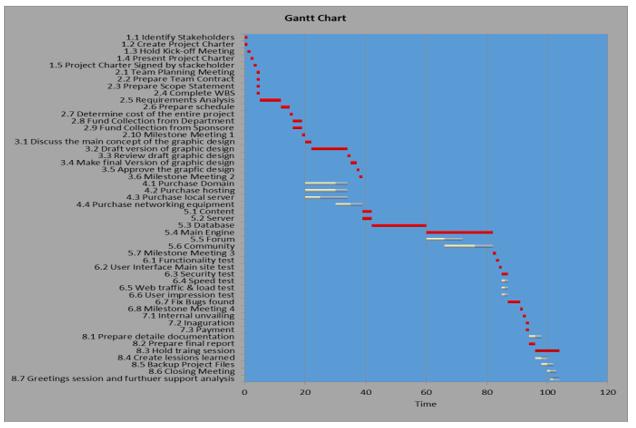
GANTT Chart
Study design
Availability of the food ingredients should not be the reason for inadequate food intake or dietary composition. Cultural diversity and changes in food habits according (Eilender, E. 2016). to that must also be the key points while making dietary plans and policies. Integration of human rights education in school level is an important policy (Battle-Fisher, M. 2014) that should not be ignored as it will help people would realize of the right to food. To identify food insecurity in the vulnerable groups and the reason for their inadequate supply of food (National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). 2013). Measures should be taken according to the results found about why is their insecurity of food among these groups.
With the help of the local government of Bangladesh the following work is to be done to address the issue:
• Collaborating with the human rights groups and nutrition community which can be a stepping stone towards success in overcoming nutrition deficiency diseases
• Conduct education and awareness programs that are essential as this will help people to understand their right to food and why is it important to all
• Educating the people about nutrition sensitive food with the help of local volunteers which will not only help them understand the importance of food nutrients but also will help them choose from the diverse food options which they can afford and will be available to them easily
• Collaborate with the NGO’s to organise camps and programs for free medical checkup to the people holding below poverty level cards.
• It has been estimated that about 40% of the population is have inadequate thymine intake which needs to addressed by appointing free volunteers in different areas where the poverty level is spiking (Shi, L. (2019).
The project will take more or less two and a half years to conclude where we can set up people andorganisation who will carry on with the work. Research is one of the most important part which will take first two quarters after the grant approval. The reason why it should be done is because this is a kind of disease that can be eradicated with the help of a little awareness. The only reason this disease is existing is because of poor food and nutritional policy of the government in the country and that is the target of this project which is to make policies and programs, collaborate with the human rights groups, ask for help from the funded organisations and collaborate with the pharmaceutical companies providing vitamin B1 medicines at a subsidized rate.
Impact
One of the overriding challenges is to identify the group of people that requires right to food which will help in further studying about how and what to plan. Next comes the identification of the food insecurity and finding the root cause of this inadequacy of food (Chern, W. S., &Rickertsen, K. 2003) should be the ultimate priority. The fundamental approach should be taken to identify these problems and when the plans are in action to monitor its implementation to venerable groups. Socio-economics factors will highly influence these plans and it may happen that sometime the plan may not works as expected but the basic idea and the plan should not be altered. Human rights principal make human right framework more effective (Ho, L.-sang. 2013) as it will involve multiple stakeholders to get involved that will help in proper implementation of the plan and its smooth running. Right to food involves nutrition benefits as well and if these two are constantly been involved together the outcome will be sustainable development (Ho, L.-sang. 2013). Education and information on human rights and right to food will also play a vital part. This will help people of different vulnerable groups and ethnic groups to follow their culture without suffering from nutrition deficiency diseases.
Costing
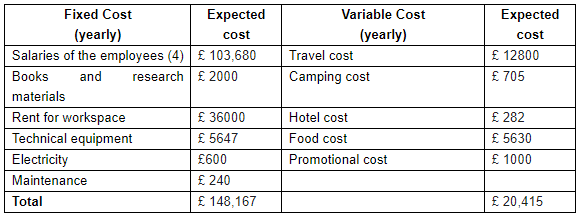
Grand total: £168,582 per annum
References
Battle-Fisher, M. (2014). Application of systems thinking to health policy & public health ethics public health and private illness
Buttriss, J. L. (2015). Public health nutrition (2nd ed., Ser. The nutrition society textbook ser) John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Carpenter, K. J. (2000). Beriberi, white rice, and vitamin b: a disease, a cause, and a cure
Chern, W. S., &Rickertsen, K. (2003). Health, nutrition and food demand.
Eilender, E. (2016). Public health and community nutrition (First, Ser. Nutrition and
dietetics practice collection). Momentum Press.
Gropper, S. A. S., & Smith, J. L. (2013). Advanced nutrition and human metabolism (6th ed.)
Wadsworth/Cengage Learning
Ho, L.-sang. (2013). Health policy and the public interest. Routledge
National Center for Health Statistics (U.S.). (2013). National health and nutrition
examination survey (Vol., estimation procedures, 2007-2010, Ser.
Shi, L. (2019). Introduction to health policy (Second, Ser. Gateway to healthcare management)
Health Administration Press
Smith, H. A. (2017). Forgotten disease: illnesses transformed in chinese medicine
Watson JT, El Bushra H, Lebo EJ, Bwire G, Kiyengo J, Emukule G, et al. (2011) Outbreak of Beriberi among African Union Troops in Mogadishu, Somalia. PLoS ONE 6(12): e28345. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028345
Research
PUBH6003 Health systems and Economics Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Individual/Group - Individual
Length - 1,500 words (+/- 10%)
Learning Outcomes
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
• Apply systems thinking and an intersectoral approach to public health issues.
Submission - 12-Week Module
Due week 5 on Sunday at 11:55pm AEST/AEDT*
6-week Module
Due week 3 on Sunday at 11:55pm AEST/AEDT*
Weighting - 40%
Total Marks - 100 marks
Instructions for assignment help:
To prepare for this assessment, choose one public health issue (e.g. diabetes, obesity, cancer, heart disease, mental health, substance misuse, air pollution, water and sanitation, road accidents, suicide, etc.) in any country and examine how systems thinking can help to identify the broader system issues, and recommend solutions for better management. This is a research- based assignment which requires to conduct literature review on the selected topic on the specific country context.
Then in approximately 1500 words (+/- 10%), please answer the following questions considering your selected public health issue and country context.
• Describe the public health issue from systems thinking perspective (consider all direct and indirect factors and explain the complexity of the issues or interconnectedness of the issues)
• Explain the roles of stakeholders, both within the health system and in other sectors in addressing this issue (consider intersectoral action perspective)
• Drawing on research evidence, explain the obstacles (e.g. lack of cooperation among stakeholders or lack of shared vision and leadership, feedback delay, lack of healthy policy, fragile and fragmented health system, funding limitation, time constraints) that are preventing the application of systems thinking and intersectoral approach to the issue.
Report Structure
Your report should follow the following structure. The word count includes the introduction, body and conclusion.
(Title of your assignment)
Assessment 1: PUBH6003: Student name, Student ID
Executive summary
Provide a short summary which gives the reader an overview of the report.
Introduction
Provide a short introduction which gives the reader an overview of the whole assignment.
Briefly introduce the public health issue in your chosen population (country).
Influence factors
Describe the public health issue from systems thinking perspective (consider all direct and indirect factors and explain the complexity/interconnectedness of the issues.
Health system
Explain the roles of stakeholders, both within the health system and in other sectors in addressing this issue (consider intersectoral action perspective)
Challenges
Drawing on research evidence, explain the obstacles (e.g. lack of shared vision a leadership/cooperation, feedback delay, lack of healthy policy, fragile and fragmented health system, funding limitation, time constraints) that are preventing the application of systems thinking and intersectoral approach to the issue.
Recommendations
Based on the identified obstacles and literature, offer suggestions (e.g. developing shared vision
and leadership, policy change or reform, creating supportive environment, strengthening, and
reorienting health system, increased budget allocation, empowering community and individuals)
for how systems thinking and an intersectoral approach could be applied to the issue.
Conclusion
In a short paragraph, provide a useful overall summary of your assignment for the reader. Do not introduce any new information/ideas.
Submission Instructions:
Submit via the Assessment 1 – Report link in Assessment on main navigation menu in Blackboard
Assessment Criteria
• Demonstrated knowledge and understanding ofsystemsthinking and anintersectoral approach (20%)
• Showsthe ability to interpret and analyse relevant information and literature on systems thinking and an intersectoral approach (30%)
• Demonstrates the ability to apply knowledge and understanding ofsystemsthinking and anintersectoral approach to a public health problem (30%)
• Use of academic conventions including appropriate resources and referencing (20%)
o Uses key readings and shows evidence of reading beyond the key reading
o There is a lucid introduction and clear conclusion or summary
o Complies with normal academic of referencing and bibliographical details (including reference list, use 6th version APA style)
o Is written clearly with accurate spelling, grammar and sentence
Solution
APPLYING SYSTEMS THINKING IN PUBLIC HEALTH ISSUE OF PREVALENCE OF DIABETES
Introduction
The global health domain is rapidly transforming and advancing. The domain of public health issue has emerged to even greater heights, posing challenges to humanity, which is evident from the surge in the recent Covid-19 pandemic. Tackling issues in the public health domain requires not only insight into the problem but also capabilities applied to resolve them easily. Systems thinking approach in public health issue is a new approach being integrated that offers more durable insight for understanding and for taking action (Johnson et al., 2018). There are various benefits offered by the systems thinking approach while other approaches are confusing due to their enormous body of theories, methods or tools they engage. Systems thinking is being currently adopted for resolving various issues related to public health as it can provide powerful language for communicating as well as investigation of complex issues (Frank et al., 2016). The current scope of discussion relates to the application of systems thinking approach to a particular issue in public health and the ways it offers beneficial solution over other methods. While there exist enormous public health issues within Australia, one prominent issue that bears a tremendous burden of costs and responsibilities on the government is Type 2 Diabetes. Though there has been various intervention mechanisms as well as methodologies for tackling the issue yet it remains one of the most prominent which is still growing in Australia amongst the aged population. This discussion reveals ways systems thinking approach can provide a better solution for the management of the public health challenge.
The public health issue of the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Australia
Influence factors
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition depicted by high levels of glucose in the blood. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes amongst the aged population is associated with modifiable lifestyle factors, also genetic and family-related risk aspects. According to the National Health Survey (NHS) conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), 2014-2015 almost 1 in 6 people aged 65 years reported diabetes, amounting to almost 574,000 people. Such prevalence was seen to increase with age with men reporting higher rates of prevalence as compared to women. There were a greater prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes amongst the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people as against other Australians.
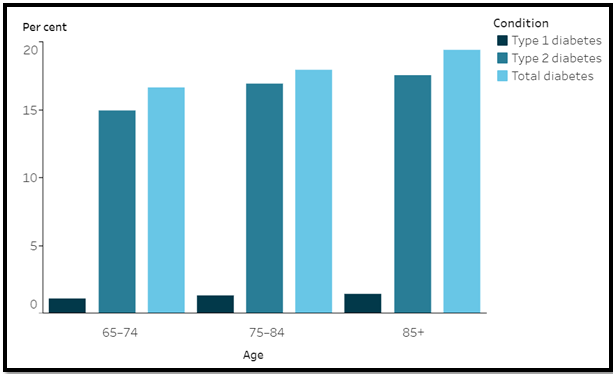
Figure 1: Rate of self-reported diabetes
Source: (AIHW, 2018)
Systems thinking perspective allows considering all direct as well as indirect factors associated with the disease type 2 diabetes (Hassmiller Lich et al., 2016). Type 2 diabetes being a large public health issue in Australia, there are various factors and system actors that have tremendous roles in this complex issue. While there remain considerable factors that leads to the challenge of type 2 diabetes, there are various system actors (participants) who are unable to tackle the issue effectively, making it a highly prevalent disease in the population. Some of the direct and indirect factors leading to type 2 diabetes are unhealthy lifestyle factors, lack of awareness of the disease, lack of physical exercise, sedentary lifestyles, genetic issues, family history of diabetes, lack of balanced diet, inefficient management of diabetes, a high body mass index (BMI), high blood pressure, lack of professional help for managing diabetes as rural locations in Australia and so on. The complexity of the issue arises from the interconnectedness of the issues and also arising from the lack of it (Keane, 2014). For instance, a lack of awareness regarding the impacts of type 2 diabetes often leads to not professionally approaching the management of the disease. Prevalence of genetic factors also sometimes the presence of type 2 diabetes individuals in the family leads to ignoring lifestyle factors, BMI, heart disease, high blood pressure that might lead to the onset of type 2 diabetes amongst aged adults and inability to tackle them as well. Australia is a country that is dominated by public health actors supported by the Federal along with State Government funding. Hence role and responsibility in tackling a public health issue by the government are of enormous importance. The public health intervention approach is primarily determined by public health policies determined centrally by Federal efforts. Hence participants (actors- stakeholders) play a predominant role in tackling the prevalent type 2 diabetes. Issues that arise in this public health issue is lack of focus of government, or governmental agencies and their healthcare providers in eliminating type 2 diabetes from Australia (Leveson, 2012). The prevalence of numerous disease and the recent outbreak of Covid-19 has to a certain extent diverted the government's attention from reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
Health System
Stakeholders in the public health system include patients, GPs, doctors, hospitals, nurses, healthcare professionals, government, professional bodies and agencies aiming to tackle the challenge of type 2 diabetes. As this a dominant public health issue in Australia is primarily tackled by governmental intervention, they are the primary stakeholders apart from their healthcare providers, who in turn are supported by the policies approved by the government (Buttigieg et al., 2015). The government in the country hence has a crucial role in developing policy, procedures and fund initiatives for tackling the growing issue of type 2 diabetes amongst the aged population, which in turn bears tremendous costs on the government. The role of healthcare providers which includes doctors, nurses, and other professionals are directed by governmental policies. Hence they focus their efforts on eliminating the prevalence of the disease based on funding available or focus provided on the issue by the government. This intersectoral perspective provides relative less importance to tackling the issue as there is another major prevalent health issue in the country currently.
Challenges
Hence drawing from the discussion above, it can be easily understood that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes as a public health issue has remained not due to lack of shared vision and leadership or cooperation, lack of healthy policy, delays in feedback, or fragile health system, or time constraint rather due to lack of focus and funding limitations (Battle-Fisher, 2014). There is a present tremendous intersectoral approach to the issue. The prevalence of several public health issues and especially the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic has posed tremendous constraints on the government as well as healthcare providers to tackle the issue of type 2 diabetes (Liedtka et al., 2017). With the government having a varied focus such as controlling outbreak or coronavirus, tackling child mortality issues, comorbidity issues, prevalent public health diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart problems or high blood pressure challenges goes to the backdrop. The importance of the issue has reduced over the years considerably with limited funding available with the government in tackling health challenges and constraint arising out of the increase in costs of healthcare.
Recommendations
Based on the literature and obstacles identified, certain recommendations have been developed that can assist in tackling the issue. Also, such recommendation includes systems thinking and intersectoral approach applied to the issue.
? Policy reforms: From the perspective of systems thinking, the government has a large number of different policies in healthcare. A consolidated policy on a disease affecting the aged developed can create a consolidated effort impacting the health systems to adopt an approach that is easy as well. With systems thinking approach, it is possible to realise the interconnectedness of the various disease affecting the aged and then tackling their root cause by consolidated efforts form healthcare actors can provide a solution to the challenge.
? Creating a supportive environment: Again, this is in connection with the previous point that aims at undertaking a consolidated effort from the government as well as from the side of healthcare providers. With systems thinking approach developing a supportive environment from the side of the government in the healthcare sector can render tremendous effectiveness in tackling this complex issue of type 2 diabetes amongst the aged population in Australia.
? Increasing budget allocation: With increasing costs especially in the healthcare sector, the budgetary allocation has not been revised. Budget allocation for tackling public health issues such as type 2 diabetes and other prevalent diseases amongst the aged Australian population needs a revision. This will enable creating an allocation for tackling this issue in the long-term as well.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the complex issue of type 2 diabetes prevalent amongst the aged population in Australia is growing tremendously. Such complex issues cannot easily be tackled by single-handed efforts which bring into role systems thinking approach. The systems thinking approach has the capabilities to handle complex issues like this one. By adopting a consolidated approach of systems thinking, this issue of type 2 diabetes can be tackled with efforts assumed by the government and healthcare providers.
References
AIHW. (2018). Older Australia at a glance. Australian Government – Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Accessed from [https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/older-people/older-australia-at-a-glance/contents/health-and-functioning/diabetes]
Battle-Fisher, M. (2014). Application of systems thinking to health policy & public health ethics : public health and private illness (Ser. Springerbriefs in public health). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12203-8.
Buttigieg, S. C., Rather, C., & Eiff, W. von. (2015). International best practices in health care management (Ser. Advances in health care management, v. 17). Emerald.
Frank, M., Shaked, H., & Koral-Kordova, S. (Eds.). (2016). Systems thinking : foundation, uses and challenges (Ser. Management science: theory and applications). Nova Science Publishers.
Hassmiller Lich, K., Frerichs, L., Fischbein, D., Bogachev, G., & Pentz, M. A. (2016). Translating research into prevention of high-risk behaviors in the presence of complex systems: definitions and systems frameworks. Translational Behavioral Medicine : Practice, Policy, Research, 6(1), 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13142-016-0390-z
Johnson, J. A., Anderson, D. E., & Rossow, C. C. (2018). Health systems thinking. Jones & Bartlett Learning, LLC. https://public.ebookcentral.proquest.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=5555416.
Keane, C. (2014). Modeling behavior in complex public health systems: simulations and games for action and evaluation. Springer Pub. Company, LLC.
Leveson, N. (2012). Engineering a safer world: systems thinking applied to safety (Ser. Engineering systems). MIT Press.
Liedtka, J., Salzman, R., & Azer, D. (2017). Design thinking for the greater good: innovation in the social sector (Ser. Columbia business school publishing). Columbia Business School Publishing.
Essay
PSYC20036 Assignment 3 Sample
Question
Reflective journal Task Description In Assessment 3, you will write a reflective journal to chronicle your reflections, insights, and ongoing development of knowledge and skills regarding the implementation of a self administered positive psychology intervention for Assessment 2. You will produce two reflective practice journal entries (600 words each, +/- 10%) documenting: • your growing understanding of how to design, implement, and evaluate positive psychology interventions in an applied setting. This will include personal reflection on why the specific positive psychology intervention was expected to be useful to your own personal or work circumstances. • evaluation of changes in perceptions, beliefs, and behaviour during the self administered positive psychology intervention. What have you noticed about yourself, your emotions, relationships, or other aspects of your wellbeing since undertaking the intervention? • reflections on progress and challenges in implementing and completing a self administered positive psychology intervention. What specific challenges did you face or how did you ensure that you continued to implement the specific aspects of the intervention? It is expected that you will relate your experiences (e.g., challenges, progress, outcomes) to what the positive psychology literature tells us about the particular intervention and, more generally, processes of change. While you will submit both journal entries at the same time, it is recommended that the first be written within the first 2 weeks of beginning your intervention and the second be written at the end of the intervention/shortly after completion of the intervention. Maximum word count: 600 words (+/- 10%) per entry. This word limit includes in-text citations but excludes any reference section. Meeting the assignment help word count is included as a part of the marking criteria in your marking rubric on Moodle. See the Psychology Word Count Information document on Moodle for a rationale for using this type of word limit restriction.
Solution
Journal entry One
The positive psychological intervention has always been one of the most powerful aspects for the development of individuals and it has focused on the overall development through building the consciousness and sense of power among all the individuals in a definite manner. I would like to discuss different aspects that are very important for my overall development in both the personal and professional aspects. The implementation of the psychological behavioral strategies for the betterment (Donaldson, Lee & Donaldson, 2019). The self-administered strategies will need to be implemented for the best results in this scenario. The treatment types of structured counseling would be very relevant to the challenges that could be addressed. Throughout this positive psychology intervention, I have found that I am not much extrovert and I like to keep shy (White, Uttl & Holder, 2019).
I understood that this habit should have to be changed so the best outcomes could be addressed. This would also help me to understand how I would communicate better with everyone in the society and workplace. To achieve better results, I should have indulged in different meditation methods and feel gratitude for everyone who has helped me in this entire process. I also came to know that I have to give my efforts to different acts of kindness (Pawelski, 2020). I have to maintain a proper relationship with everyone in society so I can ask for assistance whenever I need them. I have to present my best possible self mine so I can become what I have always wanted. I have to undertake assessments of my strengths and weaknesses. I should build the leadership components within me because this will help me to achieve the best results in the future (White, Uttl & Holder, 2019).
Psychology has come up as one of the most impactful aspects for the growth and development of individuals. This is the reason why I should learn to be optimistic all the time. This would guide me to be strong everytime (Donaldson, Lee & Donaldson, 2019).The impact of positive emotions is always high on human minds and I have felt it all the time. I believe that I should perform the best roles as a human being when I can see everything positive in the other human beings. I should learn to appreciate the efforts put in by others for the betterment of all the fields. If I appreciate them, I will get them back when I try to put in some effort. I focused on my well-being and how I can achieve it despite so many challenges (Carr et al., 2020). I was not able to lead my team effectively and get the highest sales figures. This is when I began to understand how I should try to be optimistic and influence all the team members to work collaboratively and spread the light of positivity through their works. These positive vibes have always helped me to understand different factors about success.
I will need to think of these aspects and cater to the needs of the time. I feel that the gratitude visit intervention is very important for me because this always helps in the improvement of communication in different ways. I indulged in the self-guided happiness exercises after watching videos on YouTube. It helped me to gain lots of positive vibes and I want to improve my skills and capacities to become a better person altogether. I believe this will surely help me to understand the points of understanding the relevance of showing gratitude to everyone (Woodworth et al., 2017).I felt very good and my mind was full of joy when I was doing all of these exercises. I would also continue this exercise to be my positive self.
Journal Entry Two
In this journal entry, I would describe the positive psychology intervention and how I have faced the challenges only to overcome them fruitfully. In the meantime, I had very little confidence about the works that I was going to undertake. This is why I wanted to provide more efforts to become successful in all the cases. I had to rely on my understanding and knowledge I have. I was not able to understand how I could boost up my confidence for the best outcomes (Carr et al., 2020). I have had the aim of performing at my very best so I could follow the proper process and get the best outcomes wherever needed. The above journal entry was at the beginning and during the time of positive psychology intervention. In this second journal entry, I would like to describe the aftermath of completing these positive psychology interventions. I would like to say after two months of completion of this intervention that I have been greatly benefitted from all of these strategies (Woodworth et al., 2021).
It has helped me a lot to understand how important it is to deliver the best performance by being confident and implementing the best strategies for the improvement of individual capacities. Through developing the best possible self, I have become all the more confident about my ideas. I am also able to align between my ideas and the potential strategies that I would like to execute (Proctor, 2017). I have gained knowledge about the importance of teamwork in different aspects indeed. I have become more helpful in all the works that I have participated in. Previously, I became morose after every failure and did not dare to get back stronger. Now, after this positive psychology intervention, I have highlighted the idea that I would be able to get more support from everybody around me if I show the same support to others (Gander, Proyer & Ruch, 2016). This would make the entire collaboration happier all the time. I have become more energetic about my projects and I can complete them with full authority.
These aspects have changed my life forever through positive psychology interventions. The practice of gratitude also helped me to understand that I can become one of the most successful persons in the world if I can deliver all of my works in my personal and professional lives with full confidence (Donaldson, Lee & Donaldson, 2019). I have improved my confidence and capabilities through daily strength awareness measures as well. I have gained several traits that would later help me out to become a better human individual. Some of these traits are humanity, courage, and wisdom. These traits have helped me to treat people differently and understand their challenges in life. I have become more sympathetic than before and I like to help people out in their difficult times (Gander, Proyer & Ruch, 2016)
I believe this will lead me to become a successful leader in my professional workplace. Otherwise, I cannot shine and survive in my professional career if I do not possess all of these traits. These are some strengths that I have found within myself. I am relentlessly trying to provide my best efforts and improve my performance (Donaldson, Lee & Donaldson, 2019).I have made self-administered tests and identified all the potential challenges that I still have. I will look forward to improving on my capacities that could give me a better place in society also (Woodworth et al., 2021).I felt that the stress level has reduced and I can take the decisions very calmly as well. I am more flexible in my cognitive responses. All of these factors have guided me to improve my position and status within society.
References
Carr, A., Cullen, K., Keeney, C., Canning, C., Mooney, O., Chinseallaigh, E., & O’Dowd, A. (2020). Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 1-21.
Donaldson, S. I., Lee, J. Y., & Donaldson, S. I. (2019). Evaluating positive psychology interventions at work: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Applied Positive Psychology, 4(3), 113-134.
Donaldson, S. I., Lee, J. Y., & Donaldson, S. I. (2019). The effectiveness of positive psychology interventions in the workplace: A theory-driven evaluation approach. Theoretical approaches to multi-cultural positive psychological interventions, 115-159.
Gander, F., Proyer, R. T., & Ruch, W. (2016). Positive psychology interventions addressing pleasure, engagement, meaning, positive relationships, and accomplishment increase well-being and ameliorate depressive symptoms: A randomized, placebo-controlled online study. Frontiers in psychology, 7, 686.
Moskowitz, J. T., Cheung, E. O., Freedman, M., Fernando, C., Zhang, M. W., Huffman, J. C., & Addington, E. L. (2021). Measuring positive emotion outcomes in positive psychology interventions: a literature review. Emotion Review, 13(1), 60-73.
Pawelski, J. O. (2020). The elements model: toward a new generation of positive psychology interventions. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 15(5), 675-679.
Proctor, C. (Ed.). (2017). Positive psychology interventions in practice. Springer.
White, C. A., Uttl, B., & Holder, M. D. (2019). Meta-analyses of positive ps ychology interventions: The effects are much smaller than previously reported. PloS one, 14(5), e0216588.
Woodworth, R. J., O'Brien?Malone, A., Diamond, M. R., & Schüz, B. (2017). Web?Based Positive Psychology Interventions: A Reexamination of Effectiveness. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 73(3), 218-232.
Research
PUBH6004 Leadership and Effecting Change in Public Health Assignment 2 Sample
Assignment Brief
Individual/Group - Individual
Length - 2,000 words
Learning Outcomes
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
1. Critique theories, styles, approaches and strategies of leadership in public health
2. Analyze the influence of diversity on leadership (gender, culture, professional discipline and community)
3. Evaluate personal leadership strengths and areas for improvement through analysis of public health leadership frameworks
Submission - Due Sunday end of Module 3 (Week 6) by 11:55pm
Weighting - 30%
Total Marks - 100 marks
Instructions:
In this assignment, you will be provided a scenario (problem) for assignment help involving a public health leader that you will need to analyze using the knowledge gained from this subject for 3 modules. Subsequently, immersing yourself in the scenario, you will evaluate yourself as a public health leader. (Note: Case study will be provided after Module 2).
You will be writing a 2000?word report in three parts, as follows:
Part 1: Analyze the scenario of the public health leader, presented in the Australian public health
context using the Australian Health Leadership Framework [1000 words]
(Australian Health Leadership Framework: https://www.aims.org.au/documents/item/352)
Part 2: Undertake a self?assessment using the Leadership self?assessment tool [500 words]
http://www.springboard.health.nsw.gov.au/sat/documents/leadershipassessmenttool.pdf
Apply the tool to obtain your results. (The tool is not automatic – you need to apply it honestly)
Part 3: Imagine yourself to be in the situation. Reflect on your leadership style, its strengths, and apply them to this scenario. How would you have responded to the situation based on the self?evaluation in part 2? Where do you see the gaps in your profile? Prepare an action plan. [500 words]
Assessment Criteria:
Your graded assignment will be assessed against the following specific criteria:
• Demonstrated ability to analyze public health leadership scenario in the context, applying the Australian Health Leadership Framework to the scenario presented (40%)
• Demonstrated ability to self?assess leadership style, summaries and critique (10%)
• Demonstrated ability to contextualize, reflect on leadership style, assess gaps and prepare an action plan for improvement (30%)
• General assessment criteria (20%):
o Provides a lucid introduction
o Shows a sophisticated understanding of the key issues
o Shows ability to interpret relevant information and literature in relation to
chosen topic
o Demonstrates a capacity to explain and apply relevant concepts
o Shows evidence of reading beyond the required readings
o Justifies any conclusions reached with well?formed arguments and not merely
assertions
o Provides a conclusion or summary
o Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar:
• Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and
bibliographical details (including reference list)
• Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper
sentence and paragraph construction
• Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Solution
Introduction
The following essay will analyze the scenario of the public health leader using the Australian Health Leadership Framework. Furthermore, a self-assessment will be undertaken and a reflection based on the personal leadership style, its strengths and application to be scenario will be discussed in detail.
Part 1: Analysis of Dr. Tania’s situation
Leadership is comparable in all businesses even if the complexity and purpose of health is acknowledged. Health leaders are trying to enhance clinical, quality of life and the health system's well-being. Research demonstrates that the quality of health leadership influences the quality of patient care directly and indirectly and promotes optimal practice (Schaye, et al., 2020). Leaders impact people, their satisfaction, management confidence, dedication, personal and team effectiveness and organisational culture and environment. Leaders play an essential part in the mobilisation of people for a shared purpose, while others are significant. Health leaders work with others to affect the quality of health and welfare and the quality of treatment for birth, disease and life (Tay, et al., 2021). Capable leadership, governance and management are crucial to success in improving the quality of life and maximizing health-related investment effect. Distributed leadership involves everyone with the ability and will to lead the way to enhance their activities to create a lively and achievable vision of an equal, effective and sustainable human centre health system. Everyone may exhibit leadership in their area of influence in order to enhance health outcomes. The Australian health leadership framework comprises of five dimensions which help in understanding the leadership character of an individual in any given scenario. Hence, for the current scenario of Dr. Tania, this framework has been implemented to understand the qualities that are present in her while managing a health situation in a clinical health setting.
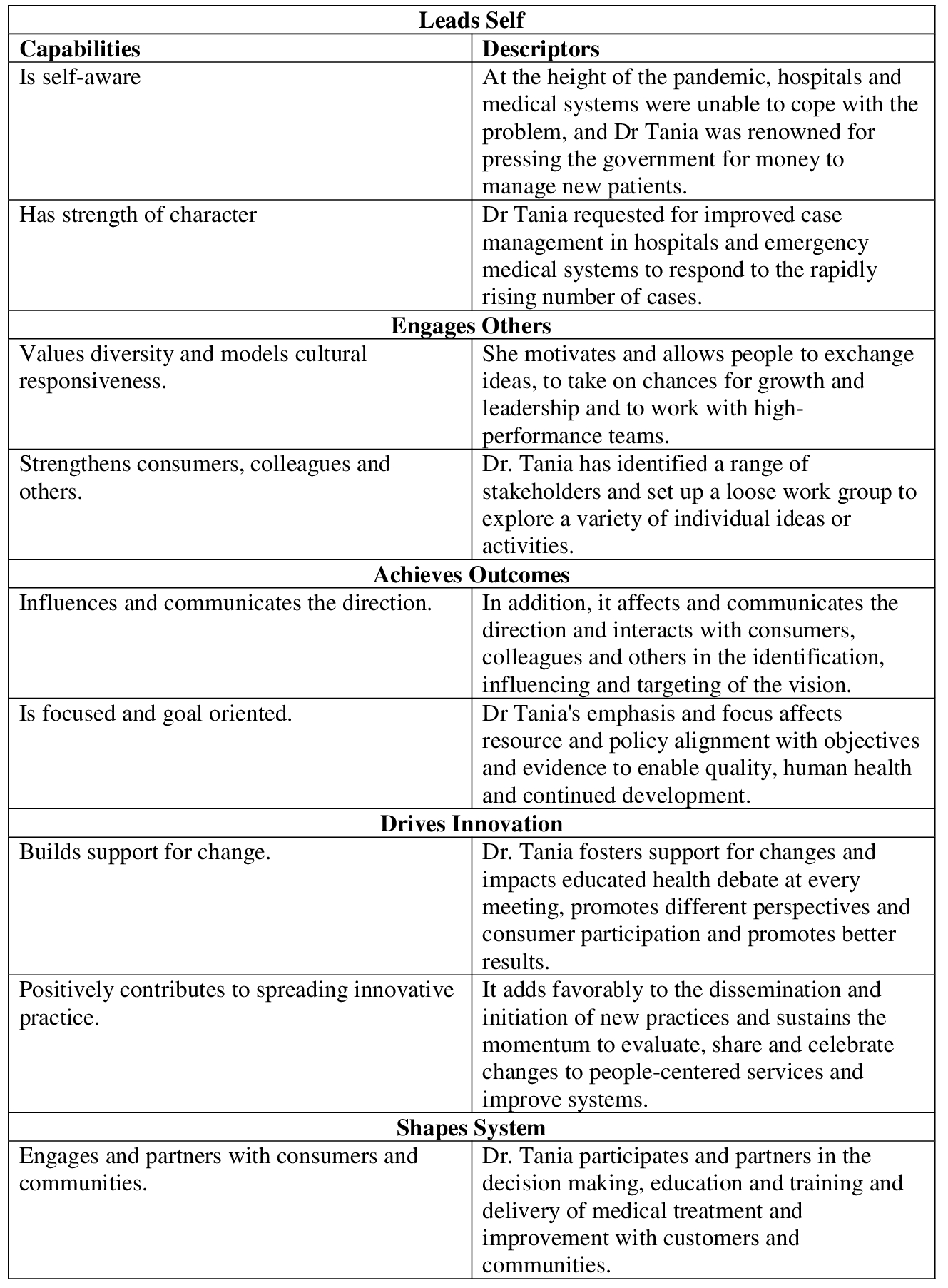
The first dimension suggests leading oneself in a clinical health care setting (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). Leaders are always ongoing. They recognize their skills and their limits and dedicate themselves to reflecting on themselves and improving them. Self-awareness, self-reform, drive, empathy and social competence are seen and demonstrated. In their position and context, they show integrity and perseverance in situations that are hard (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). Dr. Tania was responsible for coordinating the national response to the Nipah virus in the first occurrence of a national health catastrophe. Hence, it can be understood that Dr. Tania is self-aware and has strength of character. It is because of this she is able to understand the background of the pandemic and has ethical integrity, resilience, and courage to face the situation by her.
The second dimension displays the ability of leaders to engage others. Leaders allow others to engage with a vision or objective by use of complicated tales and explanations (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). Leaders encourage others to recognize, learn and grow possibilities. Dr. Tania identifying stakeholders shows its capacity to depict diversity of values and cultural reactivity models (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). It recognizes first Australians and guarantees that all individuals, consumers and employees in all healthcare environments are treated with decency and respect. She also enables consumers, co-workers and others to be strengthened. She motivates and allows people to exchange ideas, to take on chances for growth and leadership and to work with high-performance teams. It is with the help of this dimension that she is able to structure an appropriate action plan to deal with the pandemic in an efficient manner.
The third dimension displays the leader’s ability to achieve outcomes (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). Leaders are those who work to change things. They create an inspirational and motivational direction, they allow energy and effort to achieve and keep an eye on your objective. Health executives are compassionate about the quality of the health care system and the sustainability (Health Workforce Australia, 2013).
The fourth dimension revolves around driving innovation of leaders (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). Health innovation is not only a new product. It incorporates significant changes in business and care paradigms in order to deliver quality services centered on people. Passionate leadership, without which the status quo cannot be challenged, is a crucial component in effective innovation (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). The fifth dimension revolves around shaping systems by leaders. Health is a complex system in development that connects all components, including services, law and finance (Health Workforce Australia, 2013). A change in one element has consequences for the entire. Leaders who know patterns of interdependency are able to explain trends and to enable solutions to maximize benefits and reduce unintentional damage or injury (Health Workforce Australia, 2013).
Part 2: Undertake a self-assessment using the leadership self-assessment tool
I have assessed my own leadership potential with the help of the leadership self-assessment tool provided by the “Health Education & Training Institute”. In order to be a successful healthcare leader, the leader must have some key skills, expertise and traits. This NSW Health leadership framework helped me to assess my leadership potential on these leadership skills (heti.nsw.gov.au, 2021). I have performed the assessment through answering some survey questions and the results of my assessment have discussed below (See appendix). This framework helped me to identify the areas of improvement for strengthening my leadership capability.
Achieving outcomes (Score = 2+3+3+3+2+2+2+3 = 20) – In this domain, I have gained a score of 20, a mixed score in different areas. For instance, I found myself accountable for performance and resources, while being able to use patient outcomes and service agreement for driving performance. However, I can improve focus on what makes a difference in results and for building a common vision for health outcomes.
Developing and leading self (Score = 3+3+3+3+3+2+2+1 = 20) – In this domain, overall I have shown strength in developing and leading self, in most of areas, I have scored the maximum point. I am good at demonstrating self-awareness, actively seeking personal growth and taking responsibility of own performance and service. However, I can improve the area of modelling desired behaviour and values. Besides, I need to improve my patience, while working under pressure (Sutherland, 2014).
Engaging people and building relationships (Score = 3+3+2+3+3+3+3+2 = 22) – I am also good in engaging people and building relationships. Relationship building and communication is one of my strengths. I got the highest score in this domain, which highlights this area as my strength. I am effective in facilitating effective team process and fostering others’ development. Harnessing talent and diversity is also plus point, but I can work more on developing ability to create workplace culture environments, where people can contribute.
Partnering and collaborating across boundaries (Score = 2+2+2+2+3+3+3+3 = 20) – I have significant scope to improve this area, as I got mixed grade, showing a lot of areas with medium points. I scored well in creating cross-sectorial collaboration and encouraging fresh insight from diverse source to foster innovation. However, I need to build ability for working across formal boundaries and inspire people through my own action to collaborate for change (AU, 2020).
Transforming the system (Score = 3 + 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 3 + 2 = 15) – I scored poor in this domain, the minimum score among all five domains in the self-assessment framework, .e. 15. This is indicating significant need for improving this area. In demonstrating critical and system thinking I have significant room for improvement, which is crucial for a leader. I also need to improve my political astute and ability for building support for change. My score was also poor for assessing and working through resistance and other obstacles towards change.
Part 3: Reflection on leadership style and Action plan
Reviewing the scenario of Dr. Tania, I revealed that the leader has met all the necessary leadership criteria and the domains highlighted in the leadership framework by NSW. If I was in her situation, I would adopt the “transformational leadership style”. It is because, the situation Dr. Tania faced, showed that there was a significant need for change in the healthcare system for making the workforce and system ready to deal with the crisis situations effectively. Transformational leadership is a highly regarded leadership style supporting change and innovation in organizational and industrial context. The key strength of this leadership style is the integrity and fairness and its ability to inspire others to accept and face challenges. Following this leadership style in the scenario of Dr. Tania would have helped me to inspire the workforce towards bringing change in the healthcare system, transformation of the system, proper resource management, eliminate discrimination and promote diversity and inclusion, which was highly needed in the scenario of change for equalization of medical system (van Diggele et al., 2020). Additionally, it would promote collaboration and community mobilization, required for standardization of process and increased adherence of community people towards the preventive measures. I have identified some gaps in my profile, based on the above discussed self-evaluation, based on the scores I got upon attaining the self-assessment. The following action plan would help me to fill those gaps.
Action plan
Key strengths – Communication, relationship building, team building and management, openness, self-awareness, visionary
Key priorities – Developing patience, modelling desired behaviour and values, ability to create workplace culture environments, where people can contribute, ability for working across formal boundaries, problem-solving skill, analytical skill, working through resistance and other obstacles towards change.
Development needs – I have found a lot of areas for improvement, which could contribute to my future strength and leadership ability, but currently, I need to work on developing my problem solving skill and improving patience level, while working in crisis situation. It is because, a leader has to undergo crisis situations every day and patience is foremost aspect that would help the leader to be calm and handle the situation tactfully and make effective decision. For this, I also need to have excellent problem solving skill.
Goal – My key goal is to become a patient and assertive leader, with excellent problem-solving ability by next year.
S – It specifically emphasizes upon problem solving skill development.
M – It can be measured through formative and summative assessment through leadership role play
A – It is attainable via field-specific action plans listed below.
R – It is relevant for developing leadership skill and ability to handle crisis situations like the scenario of Dr. Tania.
T – It would require 6 to 8 months to be completed.
Benefits of goal – This goal is SMART and would enrich my leadership potential and would help me to work in crisis situations like Dr. Tania.
Risks involved – No such risk is involved.
Potential obstacles – Lack of resources, lack of guidance or support, political or cultural barrier
How to overcome obstacles – I would take guidance from my supervisor to access resources and support required.
Resources – Problem solving tools, training session, supervisor’s guidance, peer support, organizational simulation, internet, computer, pen, paper
Where to access resources – These resources can be accessed online, from library and from the supervisor.
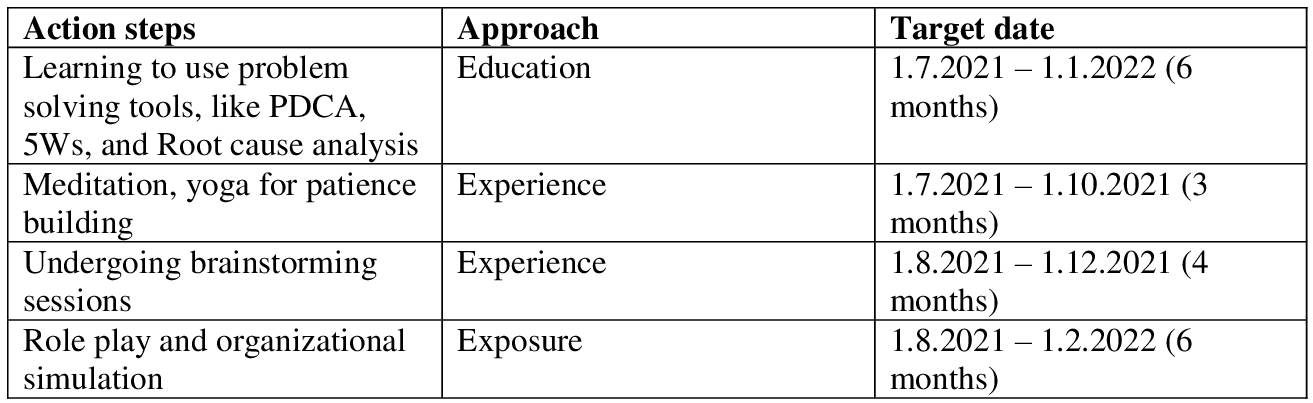
Conclusion
In conclusion, this framework for NSW Health leadership enabled me to evaluate my leadership potential in these leadership qualities. Following a transformative style of leadership in the Dr Tania scenario, I would have helped inspire people to change the health care system, transform the system, manage the right resources, eliminate discrimination, and promote diversity and inclusion, something that was so necessary in the changing scenario for equalization of the health care system.
Reference List
AU, H. N. G. (2020). Mentoring for Leadership and Management Development. https://www.heti.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/621707/LMDED-A-Guide-for-Mentees-2020.pdf
Health Workforce Australia. (2013). Health LEADS Australia: The Australian health leadership framework.Aims.org.au. Retrieved 25 June 2021, from https://www.aims.org.au/documents/item/352.
heti.nsw.gov.au. (2021). The Leadership and Management Framework – Self-Assessment Tool. Retrieved 25 June 2021, from https://www.heti.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/622950/LMDED-Framework-Self-Assessment-Tool-2020_PRINT.pdf
Schaye, V. E., Reich, J. A., Bosworth, B. P., Stern, D. T., Volpicelli, F., Shapiro, N. M., ... & Bails, D. B. (2020). Collaborating Across Private, Public, Community, and Federal Hospital Systems: Lessons Learned from the Covid-19 Pandemic Response in NYC. NEJM Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery, 1(6). https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/CAT.20.0343
Sutherland, D. (2014). Assessments Using the NSW Public Sector Capabilities Framework. https://www.duncansutherland.com.au/images/stories/downloads/PSC_Capabilities.pdf
Tay, K. H., Ooi, C. C., Mahmood, M. I. B., Aw, L. P., Chan, L. P., Ng, D. C. E., & Tan, B. S. (2021). Reconfiguring the radiology leadership team for crisis management during the COVID-19 pandemic in a large tertiary hospital in Singapore. European Radiology, 31(1), 468-474. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/8644093669 van Diggele, C., Burgess, A., Roberts, C., & Mellis, C. (2020). Leadership in healthcare education. BMC Medical Education, 20(2), 1-6. https://lesa.on.worldcat.org/oclc/8787670639
Research
PUBH6012: Capstone B Applied Research Project in Public Health Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Individual/Group - Individual or Group
Length - 5,000 words
Learning Outcomes for assignment help:
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
1. Integrate and apply their knowledge and skills in public health
2. Apply research skills to a public health issue
3. Analyse the results of data collected from research, taking into consideration prior evidence and theory
4. Understand the ethical implications for conducting a piece of public health research
6. Create a final research report
Submission - By 11:55pm AEST/AEDT Sunday of Week 10
Weighting - 80%
Total Marks - 100 marks
Context:
This assessment advanced skills in reporting the justification, methods, results, and conclusions of a research project. Key understanding contained includes how to justify a research project using literature, how to implement a research proposal to collect and analyse data, how to report the results of the analysis of data, how to contextualise one’s own research in the context of the wider body of literature, and how to draw conclusions about future research and recommendations based on research. This prepares students for the conduct and reporting of research, which is an important skill set for public health practitioners.
Instructions:
Part 1: Due Sunday end of Module 1 Week 1
Based on the feedback from your Capstone a Research Proposal, revise your research plan and GANTT chart.
Submit these to your Capstone A facilitator by Sunday end of Module 1 Week 1. You may not proceed with your data collection until this has been approved by your supervising facilitator.
Part 2:
The final assignment for this subject will be the write-up of the findings of your research into a final report. This will be comprised of the following parts:
1) Abstract
a. Summary of your report (as you would find in a published research article)
2) Introduction
a. Introduction to and justification of the topic area, drawing upon your literature review (from Capstone A), and including the knowledge gap your project addresses
b. Your research question
3) Research design and methods
a. Summarise your research design/methods (from Capstone A) – what type of project did you do?
b. How did you collect the data (i.e. search strategy and process/ policy consultation process)? If a policy consultation, explain how any organizations/individuals that you consulted with were approached
c. How did you analyse the data (i.e. thematic analysis, systematic review process, consultation synthesis)?
d. Briefly explain the ethical issues that should be considered
4) Results
a. Report the results of your findings, e.g. key themes if a qualitative study, results in table
format if a quantitative study
b. Clearly explain key figures, tables and graphs
5) Discussion: Interpretation and contextualization of your results
a. Place your results in the context of your literature review
b. Contextualise the results within the academic literature
c. Describe any limitations of your study
6) Conclusion
a. Conclusions from this study
b. Recommendations for future research or policy change based on feasible solutions
7) Supplementary material
a. Reference List
b. Any appendices
This research report format has been based on the standard format for a journal article, and thus may be submitted to a journal in the future if the student is interested.
NOTE: due to the time constraints around submission and peer review, a submitted article will not be required as part of this subject. If you wish to develop a journal article, you may seek advice on how to do this at the end of the Capstone.
Assessment Criteria:
• Revised and approved project plan and GANTT chart (5%)
• Clear executive summary/abstract which condenses the findings of the report (10%)
• Clear justification and outline of the significance of the topic (5%)
• Justification of the research design and methods, including ethical considerations (10%)
• Clear presentation of results, with transparency of findings (20%)
• Comprehensive discussion of the results within the context of previous studies/theory, and identification of the limitations of the study, with recommendations for future research (30%)
• Conclusion with logical recommendations related to the findings and wider literature (10%)
• General assessment criteria (10%):
• Provides a lucid introduction
• Shows a sophisticated understanding of the key issues
• Shows ability to interpret relevant information and literature in relation to
chosen topic
• Demonstrates a capacity to explain and apply relevant concepts
• Shows evidence of reading beyond the required readings
• Justifies any conclusions reached with well-formed arguments and not merely assertions
• Provides a conclusion or summary
• Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar:
• Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and bibliographical details (including reference list)
• Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper sentence and paragraph construction
• Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Solution
Introduction
In reproductive aged women, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a very common endocrine disorder. Also, PCOS is common in ethnic diversity in its manifestation. The study has focused on genetic and phenotype studies in Asian women with PCOS. It is very common that East Asians hirsutism score cutoff is lower than the Caucasian counterpart, and they are less hirsute. Across ethnicities, it is not clear about any significant differences in the characteristics of polycystic ovary (PCO), or prevalence, or severity of irregular menstruation (IM). In East Asian patients, the IM/PCO subgroup is a relatively common phenotype, but it is not the same among Caucasian patients (Kim & Choi, 2019). The prevalence of insulin resistance acts as a major determinant of PCOS among Asian women. In East Asian patients, a lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome and lower body mass index (BMI) were reported. However, as per comparative report, Asian women with PCOS were likely to have metabolic complications and diabetes than Caucasian patients, despite lower BMI. South Asian patients showed severe metabolic risks and insulin resistance, an increased degree of hirsutism, early onset of symptoms compared with Caucasians. In the pathogenesis of PCOS, genetic components play an important role, and between Asian and Caucasian patients, similar genetic risk factors exist suggested by the wide association studies of PCOS. Across different ethnicities, ongoing comparative studies are required to manage PCOS and the standardization of the diagnosis (Kim & Choi, 2019).
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) has clinical manifestation, which varies from mild to severe disturbance of metabolic functions and reproductive functions. As PCOS affects 1 woman out of 5 women of reproductive age, it has clinical and public health importance across the various regions. The high level of androgen in women could lead to PCOS in women. It has diverse clinical implications such as reproductive features (hirsutism and hyperandrogenism), impaired glucose tolerance, and psychological features (anxiety, depression). Moreover, itis an X-linked dominant condition. PCOS in women is widely dependent on ethnicity, environmental, genetic factors, including body weight and lifestyle of the women. Therefore, weight loss increases the chances of ovulation and pregnancy and improves the endocrine profile. With medications such as aromatase inhibitors, clomiphene citrate, tamoxifen, and gonadotrophins, PCOS can be treated. When other treatment fails, the last option for fertilization is in vitro fertilization. According to different studies based on Spain and the USA, its prevalence is estimated at 4-8%. Moreover, fertility can be improved by maintaining a lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and behavior therapy (Qureshi et al., 2016). As stoutness initiated insulin opposition fundamentally exasperates PCOS highlights, it has interesting collaborations with the steadily expanding heftiness commonness around the world. How PCOS affects long-term health should be provided to women through education. Also, this education can make the women feel physical and psychological benefits so that with their health care providers, they could engage themselves more freely (Qureshi et al., 2016).
Polycystic ovarian condition (PCOS) is believed to be the most widely recognized endocrine problem in ladies. Regular indications incorporate unpredictable polycystic ovaries, hirsutism, and feminine cycle, just as an expanded danger for a huge number of conditions, including dyslipidemia, insulin obstruction and barrenness. The commonness of polycystic ovarian disorder is by and large idea to be somewhere in the range of 3% and 10% however it is broadly obscure for explicit subpopulations dependent on geological area and race/nationality. In light of the serious level of inconstancy and irregularities between the diverse analytic standards, there is a one of a kind test that exists while deciding the commonness of this disorder. There is a huge level of people that stay undiscovered even in the wake of visiting different medical services suppliers. Most examinations led across the world are restricted by little example size, determination inclination, and absence of similarity across considers. There have been not very many investigations that have analyzed the commonness of polycystic ovary condition across the United States. In view of the National Institutes of Health (NIH's) symptomatic measures, there is a comparable commonness of PCOS recorded across the United Kingdom, United States, Greece, Spain, Mexico, and Australia. Different examinations have shown a few contrasts between geological area and race. The current data isn't enough persuading to choose if there are any basic differences in the inescapability of PCOS across geological territory, racial or ethnic get-togethers. This audit will try to decide the commonness of polycystic ovarian condition dependent on geological area and race/nationality
Justification of the study
In this study, it is essential to monitor the women's metabolic and cardiovascular wellbeing and upgraded the related dangers to distinguish ladies with the analysis. Based on geographical location and race or ethnicity, the prevalence of the polycystic ovarian syndrome is widely unknown for specific subpopulations, which is generally thought to be between 3% and 10% (Wolf et al., 2018). While deciding the predominance of this disorder, a one of a kind test exists dependent on the serious level of fluctuation and irregularities between the distinctive analytic measures. According to many researchers, South Asian women have the lowest prevalence of PCOS. The geographical location plays a key role to influence the prevalence of PCOS (Wolf et al., 2018). So here, it is important to focus on Asian Women to understand various determinants of PCOS in the regions.
Literature Review
The epigenetic change can explain the difference illustrated in the twin studies combined with the genetic loci. This could contribute to PCOS pathogenesis and symptom development if external factors alter the expression of these genes. According to the epigenetic theoretical model, an individual is more in control of his mental and physical health condition that he thinks. The vulnerability relating to PCOS condition in Asian women can be minimized by making positive changes (Raperport& Homburg, 2019).
Making lifestyle changes to curtail obesity, ensuring frequent and timely health screening and diagnosis and living in a healthy environment are few measures to control risk factors and determinant of PCOS (Ding et al., 2017). Generally, Chinese women are at the lowest risk of developing PCOS and Caucasian women and females residing in the Middle East, with Black women having the highest risks of developing the syndrome under the same diagnostic criterion of PCOS. The healthcare management priority, ethical variation in screening, and diagnosis play an integral role in influencing the prevalence of PCOS (Ding et al., 2017).
In the etiology, predominance, and adjustment of polycystic ovary condition (PCOS), an assortment of ecological variables is conceivably included. Other than this, ecological poisons, diet and nourishment, financial status, and geology are the fundamental natural variables. In upsetting conceptive wellbeing, ecological poisons assume a part is obvious in some examination, however what these poisons may mean for the advancement of PCOS has very limited research study. Much research explained that PCOS symptoms could be reduced with weight loss among obese women and certain dietary supplements (Merkin et al., 2016). Further, more research is required in preventing or mitigating the development of PCOS to compare various approaches to nutritional factors and weight loss that may play a role. Some research explains with certain PCOS phenotypes has some association with low socioeconomic status. But socio-economic conditions during youth or pre-adulthood that might be more applicable to the formative beginning of PCOS requires more focal point of the specialists (Amiri et al., 2020). The worldwide examples of PCOS are conceivably important pointers of hereditary, social, and ecological variables that may add to abundance hazard in specific districts of the world, which should be tended to the restricted extent of tantamount global investigations on PCOS (Merkin et al., 2016).
The Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Questionnaire (PCOSQ) and the Short Form-a day and a half (36) were managed in a cross-sectional study to 129 Caucasian ladies and 42 South Asian determined to have PCOS enrolled from the gynecology outpatient centers of two college showing clinics in Sheffield and Leeds. Extra clinical information was disconnected from clinical notes. Regularizing information, gathered as a component of the Oxford Health and Lifestyles II review, was acquired to contrast SF-36 outcomes and ethnically coordinated with ladies from the overall UK populace. Utilizing the SF-36, regulating HRQoL scores for ladies of South Asian source were lower than for Caucasian ladies. Given this lower benchmark we tried whether a similar relationship remains constant among those with PCOS
Research questions
1. What are the major driving determinants of PCOS?
2. Why this region influences the prevalence of PCOS?
3. What are the measures that can be taken to control risk factors?
Research Design and Methods
A systematic investigation and a secondary research design pertaining to the topic ‘Determinants of PCOS among Asian Women’ has been conveyed in this paper. For getting a though insight into the public health issue with involving the associated determinants, the existing data relating to the topic has been considered for the research. A huge source of secondary data has been used to gather data for the research paper on the public health issues such as journal papers, institutional library and textbooks, previous research article studies, and reports from international agencies like the World Health Organization (WHO). Secondary data are quite helpful as it helps to get already published and incorporate with this research in order to get the better understanding. Online sources are used to gather the secondary sources and after going to various studies and their data this research paper was written.
Chart-1: Gantt Chart for the designed research paper
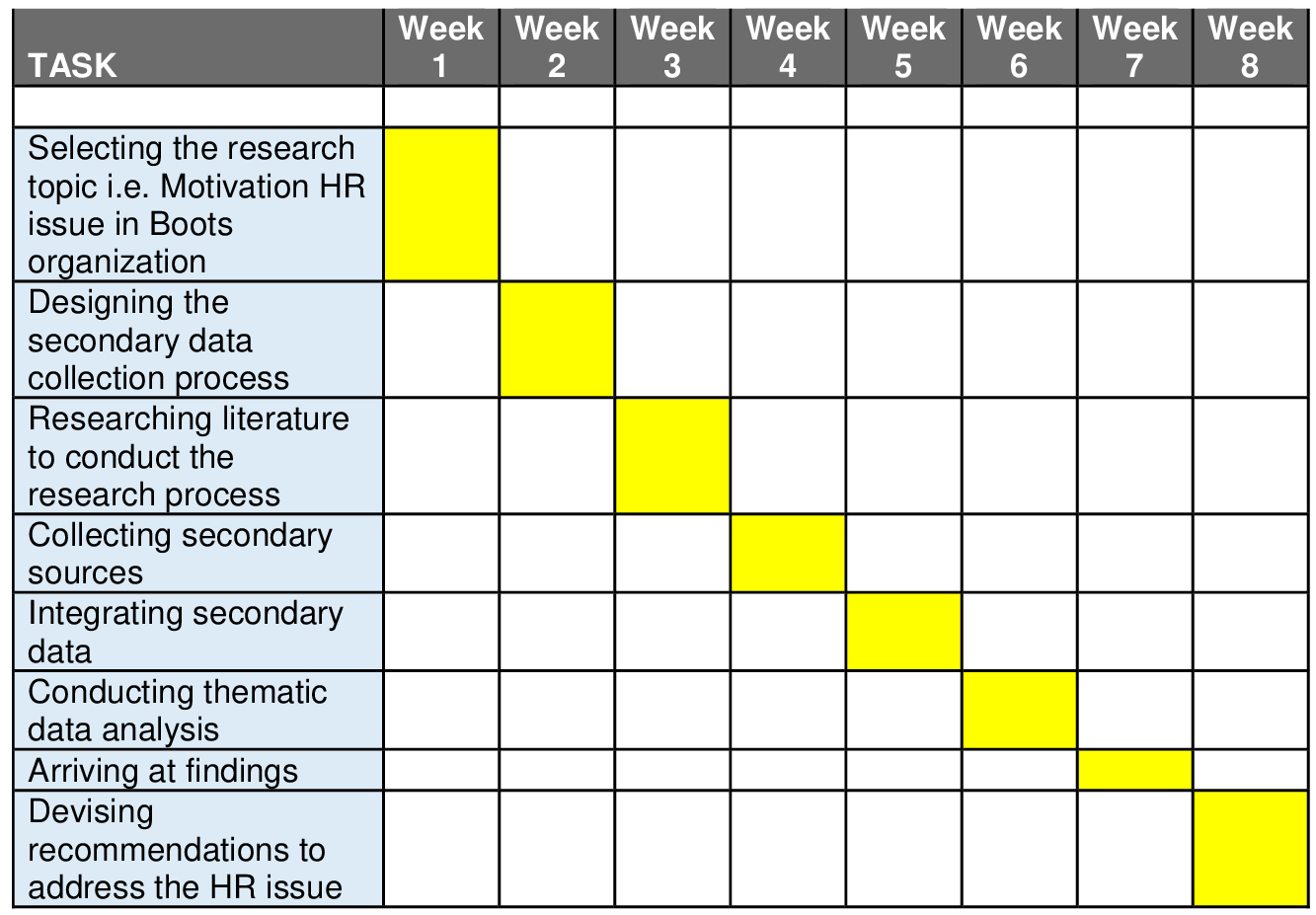
While designing the research paper, the researcher has taken the help of Gantt chart to identify the tasks with targeting some week. According to the planned schedule in the week 1, selecting the research topic i.e. Motivation HR issue in Boots organization has been covered. In the second week, the researcher has covered designing the secondary data collection process. In the third week, the researcher has focused on the literature to conduct the research process. Next, collecting secondary sources has been conducted in the fourth week (Aversa et al., 2020). Moreover, integrating secondary data has been evaluated in the fifth week. In the sixth week, systematic data analysis has been conducted. In the seventh week, the findings have been structured appropriately. At last week that is eighth week, devised recommendations to address the issue.
Hence, the research paper is designed to understand the ladies' metabolic and cardiovascular wellbeing and improved the related dangers to distinguish ladies with the analysis and in future it can monitor properly. The main aim of the paper is to do the critical analysis of the geographical location and race or ethnicity, the prevalence of the polycystic ovarian syndrome and identify why PCOS is widely unknown for specific subpopulations. In this research paper, major driving determinants of PCOS has been analysed and it has also focus on the prevention measures that can be taken to control risk factors has been analysed and interpreted. Accordingly, the research paper is designed to cover its primary research question that is what are the major driving determinants of PCOS? Why this region influences the prevalence of PCOS? What are the measures that can be taken to control risk factors?
Data Collection process
In this research paper, the research data is collected focusing on the secondary sources of data that includes articles, reports, and institutional library and textbooks focusing on the symptom development among women, socio-economic conditions, demographic factor, clinical issues of the geographical population referred to as risk factors among the Asian women. Further, the data collection has also focused on the internal and external factors influencing the PCOS among Asian women (Chaudhari et al., 2018).
Search Strategy and Process
There are various academic sources such as ncbi, science direct, Google scholar, ijrr journal, WHO and many more has been identified over various articles and reports on PCOS among Asian women for the search strategy of systematic review. The research paper has involved various authors’ perspectives over the topic with referring the abstract and findings between 2010 and 2020 period of time. For this paper, the researcher has specified Asian women population with identifying the assessment criteria such as analysis and interpretations containing prevalence of PCOS women, key determinants and risk factors, racial and ethnic PCOS prevalence, prevention programmes and PCOS prevalence provinces. In this paper, the contributions of the secondary source of literature and their outcomes, considered for the analysis of the data. Further, the research paper has gone into more detail to find out the research gap that is discussed (Dos Santos et al., 2020). The researcher has avoided some narrative reviews, and editorials publications, which are not specific to the PCOS Asian women. Moreover, the researcher also did not consider summarized evidences for the analysis of the research (Fokunang et al., 2013).
Data Analysis
The systematic literature review of PCOS among Asian women has been considered in the analysis of the research paper. By conducting these literature reviews, the researcher has identified the research gaps in the study ofPCOS among Asian women. Further, the research gap has been helpful to analyse and interpret the major driving determinants of PCOS and the region influences the prevalence of PCOS (Lim et al., 2019). In addition, the literature reviews also helpful to interpret the prevention measures that can be taken to control risk factors with specific recommendations. In this paper, the recent ten years’ data published between 2010 to 2020period of time has been taken to updates the systematic review of the PCOS among Asian women. Various sources of articles and reports related to public health and PCOS are studied for the systematic review. The hypothesis regarding incidence rate of PCOS in Asian women, prevalence of PCOS and risk factors has been analysedthrough studying the literature review. In the next part, the study has focused on the interpretations of prevalence and incidence among women and the association among the incidence, and prevalence of the PCOS.The research paper focused on a wide range of factors that are responsible and significantly influencing the prevalence of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) in Asian women. The paper analyzed that the PCOS in women is widely dependent on ethnicity, environmental, genetic factors, including body weight and lifestyle of the women. Comprehensive approach by healthcare professionals and individuals is necessary to control its burden. Controlling factors relating to diverse aspects such as lifestyle changes, occupational factors, and individual habits are vital to curtail PCOS-related risks (Rani et al., 2021).
Brief Descriptions of the Included Literatures in the Data Analysis
According to Qureshi et al. (2016), the high level of androgen in women could lead to PCOS in women. Kim and Choi (2019), mentions that the prevalence in insulin resistance acts as a major determinant of PCOS among Asian women (Kim & Choi, 2019). According to Wolf et al. (2018), South Asian women have lowest prevalence of PCOS (Wolf et al., 2018). The geographical location plays a key role to influence the prevalence of PCOS. Andini et al., (2019), mentioned that some of the chief factors impacting PCOS in Asian women are insulin resistance, obesity, genetics, etc. According to Ding et al. (2017), the healthcare management priority, ethical variation in screening and diagnosis plays an integral role to influence PCOS (Ding et al., 2017). Merkin et al. (2016), mentioned that some of the chief environmental determinants of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome include environmental nutrition, diet and nutrition, etc. (Merkin et al., 2016) According to Kshetrimayum et al., (2019), the lifestyle factors and environmental factors play a key role to influence the PCOS condition among women (Kshetrimayum et al., 2019). According to the author, the PCOS is a genetic disorder, which is influenced by diverse factors (Ünlütürk et al., 2016). Rani et al. (2021), mentioned that hormonal imbalance is a major determinant of the medical condition (Rani et al., 2021). Raperport & Homburg (2019), explained that the ethical background of a person plays an influential role and impacts the prevalence of PCOS (Raperport & Homburg, 2019). The prevention measures require to be considered to reduce the PCOS prevalence rate among the women, looking into the risk factor examined in the research gap from the literature review.
Ethical considerations
While conducting a research work, research ethics is an essential element of the research work. A researcher must require to adopt the research ethics, which relates to the code of conduct. If a researcher is considering ethical practices in to the research study, it is always considered as the qualified research work as the adoption of ethical practices has a direct implication on the research paper quality (Buchanan& Miller, 2006). According to the public health perspective, a research ethics always supervised with providing more preferences and taking into consideration to the benefits and risks to the society along with the research participants, who are involved in the research study (Buchanan& Miller, 2006). While working on a public health research topic, there are some of the chief ethical principles that must be adopted by the researcher such as non-maleficence, beneficence, autonomy, and justice (Moghadam et al., 2018).
Key determinants of PCOS and Risk factors for high Prevalence among Asian women
The exploration of the secondary data has revealed that various determinants of PCOS exist among Asian women. Some of the chief determinants are genetic factors, obesity and insulin resistance.
Genetic factors
For the delayed follicular growth of women with PCOS, the anomalies in calcium balance may be separately responsible. Further, it may follow up to PCOS syndrome pathogenesis. In PCOS metabolic syndrome and Insulin Resistance (IR) pathogenesis, the vitamin D deficiency may be a causal factor. A major candidate gene for PCOS is the gene of the vitamin D receptor (VDR). It is also called as the calcitriol receptor NR1I1 (Andini et al., 2020). VDR is a ligand activated transcription factor to control cell functions including homeostasis of calcium phosphate and bone metabolism, and control many endocrine functions, which mediates the vitamin D genomic activities. For potential effects of complex disease susceptibility and functional significance, various VDR polymorphisms have been examined like obesity, cardiovascular disease, tuberculosis, osteoarthritis (OA), hypertension, and high myopia.
Obesity
PCOS has various factors and obesity is one of the major factors among them. The obesity has three parameters for its evaluation, which are the Waist Circumference (WC), Body Fat Percentage (BFP), and Body Mass Index (BMI). These three parameters have further divided into two categories such as the PCOS group and the balanced control group (Varanasi et al., 2018). The above-discussed three parameters are important in supporting PCOS diagnosis and screening as compare to the balanced control group, in the PCOS population the BMI, WC, and PBF have increased significantly. For predicting PCOS, Rotterdam recommendations are preferred as a gold standard (Andini et al., 2020).
Insulin resistance
Jin Ju Kim and Young Min Choi (2019), mentions that the prevalence in insulin resistance acts as a major determinant of PCOS among Asian women. In East Asian patients, a lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome and lower body mass index (BMI) were reported. However, a comparative study reported that Asian women with PCOS were more likely to have metabolic complications and diabetes than Caucasian patients, despite lower BMI. South Asian patients showed severe insulin resistance and metabolic risks, an increased degree of hirsutism, early onset of symptoms compared with Caucasians. In the pathogenesis of PCOS, genetic components play an important role, and between Asian and Caucasian patients, similar genetic risk factors exist suggested by the genome wide association studies of PCOS. Across different ethnicities, ongoing comparative studies are required to manage PCOS and the standardization of the diagnosis(Kim& Choi, 2019). Insulin resistance plays an important role in PCOS pathogenesis, which results in compensatory hyperinsulinemia. Therefore, the women with PCOS have an increased risk of prediabetes, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome (MetS), and type 2 diabetes. Obesity is prevalent among women with PCOS although the prevalence across background populations differs. A research report has mentioned that indicating the Asian women with PCOS have metabolic complications as they were more likely than Whites to have diabetes. Moreover, depending on the measure used and the threshold, the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in PCOS patients differs accordingly (Kim& Choi, 2019).
Results or findings
In this research paper, various manuscripts are described in description section, from where the collected articles provided ideas for the key determinants of the PCOS and its risk factors. The manuscripts have been analysed, and defined the table-1 explaining to categorize Complications, risks stratification, biochemical abnormalities, associated clinical features in PCOS. The overall research has implemented qualitative study in the research paper (Wijeyaratne et al., 2014).
Table- 1: Complications, risks stratification, biochemical abnormalities, associated clinical features in PCOS
The table has explained the possibility biochemical derangement of acyclic oestrogen excess has associated clinical features such as menstrual irregularity or oligomenorrhoea. It has complications like ovarian cancer, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, which has probable risk, remote risk and increased risk among the PCOS Asian women. In insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia biochemical abnormalities, the associated clinical features in PCOS include acanthosis nigricans obesity, which may result in some complications such as pregnancy induced hypertension, diabetes mellitus, gestational diabetes and hypertension. Accordingly, pregnancy induced hypertension has some probable risk, diabetes mellitus has increased risk, gestational diabetes has increased risk and hypertension has probable risk stratification. Moreover, the dyslipidaemia biochemical abnormalities may leads to resulting complications coronary artery disease with having probable risk stratification. Further, the high testosterone or androstenedione, decreased sex hormone binding globulin of biochemical abnormalities has associated clinical features in PCOS such as hirsutism, frontal balding, acne, and hydradenitissuppurativa. The above table has mentioned all the risk stratification, which are resulting complications among the PCOS Asian women (Dos Santos et al., 2020).
Table-2: In an unselected female population estimated prevalence of PCOS
In the table -2, an unselected female population has estimated for the prevalence of PCOS. Looking into the 1990 NIH, the estimation of 5.5% (95% CrI: 4.8–6.3%) hasthe prevalence of PCOS for White women. In the Middle East, 6.1% (95% CrI: 5.3–7.1%), and 7.4% (95% CrI: 6.3–8.7%) has taken respectively for the corresponding figures for women residing and Black women (Ding et al., 2017). Next, jumping to the 2003 Rotterdam, the Middle East women (16.0%, 95% CrI: 13.8–18.6%) and Chinese women (5.6%, 95% CrI: 4.4–7.3%) has prevalence estimation, which is feasible. Among Chinese women, the prevalence of PCOS has almost risen to the triple in the Middle East women. For females in Middle East, under the 2006 AES, prevalence of PCOS is12.0% (95% CrI: 11.3–14.2%), under the 2003 Rotterdam it is 16.0% (95% CrI: 13.8–18.6%), and under the 1990 NIH it is 6.1% (95% CrI: 5.3–7.1%). Under the 2006 AES with the prevalence is lying in-between and under Rotterdam more than doubles the prevalence that is under the 1990 NIH (Ding et al., 2017).
Graph-: Prevalence of risk factor among PCOD women in Asia
According to the research study, the urban regions have a considerably higher proportion resided among the PCOS women. The rural regions are in middle stage and the controlled regions are found very less according to the graph. The research has mentioned that lifestyle and dietary factors are attributed for the major difference in the various regions. The Asian PCOS women requires to focus on the long?term health consequences (Deswal et al., 2019). Women can be at risk of serious if they ignore the PCOS, later which can be difficult to manage in their health condition. In this context, for better management continuous surveys and lifestyle changes should be promoted with taking initiatives (Deswal et al., 2019).
Discussion
In this study, it is essential to monitor the women's metabolic and cardiovascular wellbeing and streamlined the related dangers to distinguish ladies with the determination. In view of geological area and race or identity, the commonness of the polycystic ovarian disorder is generally obscure for explicit subpopulations (Wolf et al., 2018). While deciding the pervasiveness of this disorder, an interesting test exists dependent on the serious level of changeability and irregularities between the diverse demonstrative rules. According to many researchers, South Asian women have the lowest prevalence of PCOS. The geographical location plays a key role to influence the prevalence of PCOS (Wolf et al., 2018). So here, it became very important for the Asian Women to understand various determinants of PCOS in their regions and accordingly they can change their lifestyle.
In this paper, Epigenetic theory has been used to comprehend the research findings in detail. According to the epigenetic theoretical model, an individual is more in control of his mental and physical health condition that he thinks. The vulnerability relating to PCOS condition in Asian women can be reduced by making positive changes(Raperport& Homburg, 2019).A few measures to control risk factors and determinant of PCOS such as living in healthy environment, ensuring frequent and timely health screening and diagnosis and making lifestyle changes to curtail obesity(Ding et al., 2017).The Research analysis has focused on the prevalence of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome among Asian women that has influenced by a wide range of factors. It is anlysed that comprehensive approach by healthcare professionals and individuals is necessary to control its burden (Kshetrimayum et al., 2019).
The research paper has found that to curtail PCOS-related risks, controlling factors relating diverse aspects is vital and significant. These controlling factors are individual habits, occupational factors and lifestyle changes. There exist factors like generic factors and geographical placement which cannot be controlled to influence the PCOS condition (Wolf et al., 2018). The following figure has explained Safety measures to control the determinants of PCOS among women, which can be considered in the future studies and women can get serious about the issues.
Figure-1: Safety measures to control the determinants of PCOS among women
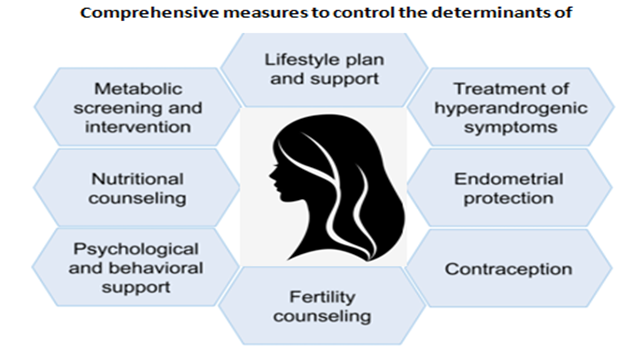
Limitations of the study
The research paper has regional boundaries to study the determinants of PCOS among women. It has given more focus on the Asian region and the study was also focused to the gender specific. This research paper can be helpful for the state interventions to identify the gaps in the public health sector. This paper helps to find out the safety measures to control the determinants of PCOS among woman, but as it’s depends up on the secondary research so finding data is major limitation of this research paper (Aversa et al., 2020).
Conclusion
It is concluded that, the identification of the determinants of the PCOS among the Asian women was essential for the study as it has highlighted the chief determinants such as genetic factors, obesity and insulin resistance issues. The analysis of complications, risks stratification, biochemical abnormalities, associated clinical features in the Asian women with PCOS has also discussed. A few measures to control risk factors and determinant of PCOS such as living in healthy environment, ensuring frequent and timely health screening and diagnosis and making lifestyle changes to curtail obesity can be taken into consideration for the future studies. In future there is a need to implement intervention as the research on the PCOS public health concern has highlighted its seriousness. It adversely affects the health condition of Asian women with PCOD. There is the requirement to implement measures to control its prevalence. The prevalence of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) condition among Asian women has been examined in the research, which acts as a serious public health burden. Suitable measures need to be adopted to control the associated risks and determinants. It is recommended that the government and social workers should raise various initiative programmes for the PCOS women to spread awareness. Based on the feasible solutions the controlling factors such as individual habits, occupational factors and lifestyle changes should be taken into consideration to make changes in the health policy and research.
Essay
PUBH6001 Health Policy and Advocacy Assignment Sample
Assignment Brief
Individual/Group - Individual
Length - 2000 words (+/?) 10%)
Learning Outcomes
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
Analyze different theories and approaches to policy agenda setting
Apply knowledge of policy development to a public health policy issue
Analyze issues in contemporary Australian health care policy
Develop processes for the evaluation of and accountability for policy
Critique the role of networks and coalitions in the policy agenda setting process
Submission - Sunday of week 8 at 11.55pm*
Weighting - 40%
Total Marks - 100 marks
Instructions:
In this Assessment, you will engage in policy analysis. For assignment help Choose a health policy (either current or past), either at the state or federal level, to analyses in this Assignment (e.g., mental health policy, women’s health policy, preventative health policy, men’s health policy, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health policy). The Assignment should be approximately 2,000 words (+/? 10%) and presented in essay form. Address the following questions in your Assessment but please do not answer the questions as a series of short answers:
Firstly, provide a short introduction to your essay. Then proceed to analyses your chosen policy, and in doing so, consider the following issues:
The Problem and Context
• Describe the current and historical policy context of the problem.
• What is the problem which the policy seeks to address?
• What problems are highlighted?
• What problems have been overlooked?
Frame of Reference/Dominant Discourse
•What is the common frame of reference or dominant discourse evidence within this policy???
•Are certain words and phrases commonly used?
•Are there any underlying assumptions behind these?
Targets, Stakeholders and their Representation
•Who is the target of the policy (the subject of the discourse)?
•Who are the other stakeholders identified in the policy? Describe key institutional structures, agencies and workforce capacity building.
•How are the subjects of the policy being represented?
•How are different social groups portrayed in this policy and what implications does this have?
•Are there any moral judgements expressed in this representation?
Policy process
•Who were the stakeholders involved in the development of the policy? Who was overlooked?
•Whose interests were represented in the development of the policy? Which voices were not heard?
•What were the potential competing interests and power differentials of those involved in the development of the policy?
•What was the motivation for stakeholders in creating this policy?
•Were there any particular windows of opportunity that enabled the development of this policy?
Policy Solutions
•What solutions are put forward to address the problems?
What alternative solutions might have been overlooked?
•Are there any social/power/ethical implications of this policy?
Effectiveness
•Consider the implementation of the policy. How effectively do you think the current policy has been implemented?
•What are the accountability processes for the policy?
•Consider evaluation measures (indicators) and any evaluation which has been undertaken.
•How effective has the policy proven to be?
Finally, finish your essay with a conclusion.
Assessment Criteria:
• Knowledge and understanding of the policy issue (30%)
• Critical analysis of the problem, frames of reference used, the policy process and policy solutions (30%)
• Application and synthesis of knowledge about policy theories (25%)
• General Assessment Criteria (15%) Assessment fulfills general academic standards, including: Provide an introduction and conclusion
• Complies with academic standards of writing, including legibility, clarity, accurate spelling, presentation and grammar.
• Uses appropriate APA 6 style for citing and referencing research
• Upholds standards of academic integrity, as demonstrated by acceptable report from text?matching software (e.g. Safe Assign).
Solution
Women’s health policy
Introduction
Australia was among the first countries to adopt a health and wellness related strategies specifically for women. The National Women’s health Policy was embraced to strengthen and to enhance the health and well-being of every Women and girls living in Australia, especially those who are more susceptible to poor health. The National Women’s health Policy 2010 was created on the concrete foundation of the first National Women’s Health Policy: Advancing Women’s health in Australia. The National Women’s health Policy now helps to address the challenges faced by Women in sustaining good health in the 21st century. There has been a serious rise in diseases affecting women today. But, unfortunately, there are major inequalities in the wellness status of several Australian women (Dc.cod.edu, 2021). The woman from lower socio-economic groups, Aboriginal background and Torres Strait Islanders still face hardships regarding health care. The aim of the new and improved health care policies for Women strives to enhance the health care conditions of all women, especially those prone to poor health. Based on the National Women’s health Policy 2010, the National Women’s health Strategy for 2020 to 2030 was adopted for even more improved health care for Women (Nakray, 2013). This report shall dive deeper and find out more detailed information about Women’s health care polices of Australia.
The problem and Context
Women’s health has been neglected in the society for long. It was time that women are treated as equal subjects in the society whose health needs must be catered to. Thus, the policy makers felt the need for framing policies that would help in the upliftment and improvement in the health of women in the country. The window of opportunity when the framing and implementation of the women health policy is the fact that it will help in improving the health index of the country which will consequently help in enabling growth and development in the country.
The 1stNational Women’s health Policy of Australia was adopted in the year 1985. In the Adelaide conference (September of 1985), more than 700 Women together produced a bipartisan agreement stating that the National Women’s health Policy, should be focus on Women ’s position in the society, how it affects the status of their health and accessibility in wellness treatment facilities.
In order to create the Women’s health policy, an extensive consultation process was followed yearning to discuss the ‘Women’s health: a framework for change‘. Meetings were held across all capitals cities and few handpicked villages, 300+ written documents were submitted, which clearly conveyed the message to the government to know the real situation and how it impacted the lives of the women in the country. The Women of Australia contributed a huge deal in the development of the First National Women’s Health Policy.
The problem prioritised in the 1989 policy were Health of aging Women, Reproductive health and sexual health, Personal and mental health, Livelihood Health and Safety, Violence against Women, Women’s health as care givers and the impact of prejudice against women on Women’s health. Some strategies also recognized five field regarding Women’s concern about structure of health care and information –Outlay of health services for Women, provide with health related information, collection of data as well as research, participation of Women in making decisions in health sector, equipping health care providers A majority of health problems were established with the aid of study and analysis, which represent the significant problems related to mortality and diseases among women in the next twenty years.
Firstly, the health focus area is preventing severe illness by controlling the danger, targeting severe illness like diabetes, cardiovascular illness, and cancer. And also by preventing risk factors like nutrition, obesity, drug consumption, inactivity in life style, alcoholism. The policy encourages getting a detailed insight of Women’s lives, containing the obstacles that prevent Women adopting healthy lifestyles and behaviours. Secondly, the focus area is taking care of the mental state and health, depression, targeting anxiety, and suicide for women. Thirdly, the focus area is reproductive and sexual health; providing information and educating people on sexual health, safe coitus practices, reproductive health, and maternal health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and staying fit before, during and in the postpartum period may have a significant and long-term impact on both the mother's and the kid 's health. And finally, good ageing focuses on illnesses such as musculoskeletal injuries, dementia, and disability. The strategy emphasises that the economic, cultural, and environmental conditions in which women reside and age can have an effect on their later years. However, despite the policies and strategies that have been implemented by the government of Australia in context to women’s health, not much improvement has been seen in the overall health of the women of Australia. This is probably because of the lack of a procedural means to implement the policies and strategies of women health as a result of which desired outcome is not attained.
Frame of Reference/Dominant Disclosure
There has been significant improvement in Women’s wellness care since the introduction of Women’s health treatment strategies. However, these improvements are not equally achieved throughout Australia. Women from certain group like the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders involvement much worse health. Even though some agenda of the National Women’s health Policy 2010 has initiatives to eradicate inequality in health care, there are little evidence of how much it has been able to achieve success in real situations of those Women (Phaa.net.au, 2021).
There is a severe lack in fund for these policies, which is not highlighted like its principles are. Apart from that some Australian Women feel that NWHP and NWH Program only address the interests of Anglo-Australian women from middle class background (Awhn, 2021). The problems of the Aboriginal Women were however left out as discussed earlier. The National Aboriginal Health Strategy, was adopted to deal with Aboriginal Women’s health. But regrettably, it was never funded sufficiently. An evaluation in the year 1994 brought to light -gross under-funding by all governments, absence of accountability, absence of political support for the National Council of Aboriginal Health that was created to supervise implementation.
No satisfactory long term outcome was achieved even after positioning immigrant and refugee women differently. The National Non-English Speaking Background Women’s health Strategy (NESBWHS) was created to help these women.
Keywords like Women, Aboriginal Women, National Women’s health Policy, strategy, health, health issues can be seen throughout. It is assumed that the National Women’s health Policy and other programs are enough for resolving all issues and problems related to Women but in reality they fall short to cover the entire aspect of Women’s health.
Targets, Stakeholders and their representation
The main target of the National Women’s health Policy, National Women’s health Strategy, National Non-English Speaking Background Women’s health Strategy (NESBWHS), etc. is Women of Australia (Dalinjong & Homer, 2018). All these policies are targeted towards improving Women’s health. Australia launched the National Women’s health Policy in 1989 and became the only country to have a comprehensive policy on Women’s health care. The policies are meant to deliver conventional and diverse Women’s health services. The other stakeholders of the women health policy include the healthcare professionals including doctors and nurses as well as the government as they play an important role in improving the overall health of women in the country. They also have a very big role and representation to play in the implementation of the women health policy aimed at improving the overall health of the women of the country. Both the government as well as non-governmental organizations ensure that the health needs of the women in Australia are catered to. They constantly monitor the policy and the impact that it has on the overall health of women in the country.
The idea of Women as central principal of the policy was widely supported. One of the main principles of the policy was equality among women regarding health care. Because of the high risk that the Torres Strait Islander Women and Aboriginal Women faced in poor health, they were oftentimes prioritised (Vasilevska & Fisman, 2012). The other groups of Women who were at high risk of inferior health were- Women with disability, Women who are caregiver, Women living in remote areas or rural areas, refugee Women, migrant Women, Elderly Women, and bisexual and lesbian Women. Active participation of the different groups of Women in designing the policy, implementing the strategies which affect them, helping to facilitate that the health aids and information are designed keeping in mind the needs of people who require it the most (Awhn.org.au, 2021). The participation of women in making these policies strongly suggests involving expert opinion of women from various communities in implementation of the local programs which aim to improve the health of women in the country.
Policy Process
The National Women’s health Policy is a unique proposition specifically designed for women and girls in Australia. The policy was created specially with women prone to poor health in mind. The 1989 policy was designed to solve the problem related to Women’s health of that era (Wohler & Dantas, 2017).
Over the past decades, the 1989 policy for women’s health has been the footing for expansion of new programs for women’s health. A majority of health care establishments were built or renovated; health care providers were trained in a new and integrated way. Australian Longitudinal Study on women’s health was established because of 1989 policy.
The National Women’s health Policy was developed on the basis of 1989 policy. This policy had a dual approach addressing immediate and future health challenges of Women. It equally prioritised- Administration and advancement of health care facilities and preventive strategies to care and prevent through targeted health issues that will have a massive effect on the following twenty years and dealing with the social determinants of health in order to curb health inequalities.
Policy Solutions
The government of Australia is based on improving and motivating decent wellness of everyone and supports obstructive efforts which may help to address particular health problems raised by Women through this policy.
Chronic diseases are one of the biggest health issue faced in Australia, which causes death, disability and sickness among the population. But chronic diseases can be reduced by prevention, modifications of lifestyle and providing support. The Australian Government has taken numerous initiatives to help prevent and manage chronic diseases, one such example is the Australian Chronic Disease Prevention Alliance. Over the past decade, ACDPA has operated with the government, stakeholders and public health groups to boost nutrition, increase physical activity and reduce obesity among the population.
Mental health conditions can be a silent killer. In today’s world mental health issues are rapidly increasing and affecting huge masses of the population all around the world (Hajizadeh & Butler, 2014). Women are more prone to experience mental health problems from various issues like domestic violence, family pressure, post partum depression etc. The Australian Government has taken multiple initiatives to help prevent and cure mental illnesses. Some of them are The National Mental Health Policy of 2008, beyond blue: The National Depression Initiative, Forth National Mental Health Strategy and headspace
Most deadly and dangerous sexually transmitted diseases can be prevented very easily. The Australia’s Health Ministers Committee (AHMC) promoted the New National Strategy for prevention of STIs, BBVs, and HIV.
The Australian health ministry has taken several initiatives to help mothers before, during and after child birth. Initiatives like- the Australian National Breastfeeding Strategy 2010–2015, National Maternity Services Plan, et al to support mothers and reduce mortality rate in new-borns. Apart from this, the government must also employ volunteers who shall spread awareness regarding women health, this will help in educating people on serious issues like women’s health. The social implication of these policies implemented by the regulatory bodies is reflected by the importance that the government bestows on the health of women. This empowers women who feel important and cared. Apart from this, this is the ethical thing to do as women have been neglected in the society at large and now, it is time to give them equal importance as the men of the society.
Effectiveness
Australia launched the first National Women’s health Policy in 1989 and since then Women have experienced significant economic, social and technological changes. Based on the policy of 1989, the National Women’s health Policy 2010 and the National Women’s health Strategy 2020 to 2030 has been created to make improvements in women health policy. The overall health of women in the country has witnessed considerable improvement over time (ray Jamieson, 2012). Diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancer, smoking rate in women have noticed a declining trend.
On one hand it can be said that the women’s health care policies have changed the National health policy to a great extent. We now have a modified and integrated women’s health policy that is inclusive of the arguments made by feminist like a national plan to combat violence against Women and the National Disability Strategy that meets the ethical needs and engages a sex inequality (Long& Baer, 2018). While on the other hand much of the changes clearly reflect a substantive political action. Health care for Women or anyone else, at the decision making help is still limited to primary health care and hospital levels, as the investments made for it is very small. The accountability of the success or failure of the policy lies in the hands of the policy makers who frame and implement the policies aimed at improving the health of women in Australia. The improving overall health of women as reflected by the statistical data is an evidence of the effectiveness of the women health policies and strategies implemented by Australia.
Conclusion
The National Women’s health Policy of 1989 was a remarkable mile stone that set the tone for future developments of health care specially tailored to fit the needs of women. In all, the government has taken great initiatives, and helped prioritize and endorse Women’s health care system. The Australian government has formulated lots of collection of policies, strategies, initiatives, programs and plans to health. The NWHP was the first of its kind health policy specially designed for women which inspired many such models across the world (Awhn, 2021).
The separation of women’s health sector has resulted in a plethora of successful achievements. Differentiation of access to health care of Aboriginal, Torres Strait Islanders, Women with disabilities, has considerably lowered.
With improved health care the quality of life of Australian Women has improved considerably (health.gov.au, 2021). Thus it can be concluded that the National Women’s health Policy has proven be a great achievement and has considerably been able to enhance wellness protection requirement of Australian Women, specifically the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Women
References
Awhn.org.au. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from http://awhn.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/38_NationalWomensHealthPolicysummary.pdf
Dalinjong, P. A., Wang, A. Y., & Homer, C. S. E. (2018). Has the free maternal health policy eliminated out of pocket payments for maternal health services? views of women, health providers and insurance managers in northern Ghana. Plos One, 13(2), 0184830.
Dc.cod.edu, (2021). [online] Dc.cod.edu. Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://dc.cod.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1630&context=essai
Hajizadeh, M., Connelly, L. B., & Butler, J. R. G. (2014). Health policy and equity of health care financing in Australia: 1973-2010. Review of Income and Wealth, 60(2), 298–322
health.gov.au. (2021). Department of Health | Women's Health. Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/national%20womens%20health-1
Long, D., & Baer, H. (2018). Health anthropology in australia: special section on medical anthropology. American Anthropologist, 120(3), 560–565.
Nakray, K. (2013). Gender-based violence and public health: international perspectives on budgets and policies. Taylor and Francis.
Phaa.net.au. (2021). Retrieved 24 March 2021, from https://www.phaa.net.au/documents/item/875
ray Jamieson, G. (2012). Reaching for health: the australian women's health movement and public policy. ANU E Press.
Vasilevska, M., Ross, S. A., Gesink, D., & Fisman, D. N. (2012). Relative risk of cervical cancer in indigenous women in australia, canada, new zealand, and the united states: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Public Health Policy, 33(2), 148–164.
Wohler, Y., & Dantas, J. A. (2017). Barriers accessing mental health services among culturally and linguistically diverse (cald) immigrant women in australia: policy implications. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 19(3), 697–701.
Research
PUBH6004 Leadership and Effecting Change in Public Health Assignment Sample
Assessment 2 - Public Health Professionals
In this nursing assignment help, you will be provided a scenario (problem) involving a public health leader that you will need to analyse using the knowledge gained from this subject for 3 modules. Subsequently, immersing yourself in the scenario, you will evaluate yourself as a public health leader. (Note: Case study will be provided after Module 2). You will be writing a 2000?word report in three parts, as follows:
Part 1:
Analyse the scenario of the public health leader, presented in the Australian public health context using the Australian Health Leadership Framework [1000 words] (Australian Health Leadership Framework: https://www.aims.org.au/documents/item/352)
Part 2:
Undertake a self?assessment using the Leadership self?assessment tool [500 words ] http://www.springboard.health.nsw.gov.au/sat/documents/leadershipassessmenttool.pdf Apply the tool to obtain your results. (The tool is not automatic – you need to apply it honestly)
Part 3:
Imagine yourself to be in the situation. Reflect on your leadership style, its strengths, and apply them to this scenario. How would you have responded to the situation based on the self?evaluation in part 2? Where do you see the gaps in your profile? Prepare an action plan. [500 words] Assessment Criteria: Your graded assignment will be assessed against the following specific criteria: • Demonstrated ability to analyse public health leadership scenario in the context, applying the Australian Health Leadership Framework to the scenario presented (40%) • Demonstrated ability to self?assess leadership style, summarise and critique (10%) • Demonstrated ability to contextualise, reflect on leadership style, assess gaps and prepare an action plan for improvement (30%) • General assessment criteria (20%): o Provides a lucid introduction o Shows a sophisticated understanding of the key issues o Shows ability to interpret relevant information and literature in relation to chosen topic o Demonstrates a capacity to explain and apply relevant concepts o Shows evidence of reading beyond the required readings o Justifies any conclusions reached with well?formed arguments and not merely assertions o Provides a conclusion or summary o Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar: ? Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and bibliographical details(including reference list) ? Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper sentence and paragraph construction ? Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Introduction
In this assessment the analysis of the case study of the public health leader is being done by using the knowledge of the subject and further the self-assessment test for being a leader has been conducted. In the end the analysis of the self-leadership position considering the case study provided is being presented.
Part 1
Public Health Leader Role
According to research, it has been seen that the quality of health leadership tends to affect directly and indirectly the quality of patient care and is one of the most critical factors for supporting the practice that is best in the industry (aims.org.au, 2022, p3). Health leads Australia had been made by the research and dialogue and had been made on the existing and validated work of the global platform and tends to focus on the capabilities needed to deal with the health issues in Australia (Pinto, & Bloch, 2017, p3).
Health LEADS Australia: leadership framework
1. Leads Self: The leadership process is never complete, and it is always a topic of work in progress (aims.org.au, 2022, p7).
2. Engaging Others: Leaders tend to enable the people to engage with the vision or goal by stories and explanations that relate to the complexities (aims.org.au, 2022, p8).
3. Achieving the outcomes: The people who are the leader need to work to make an individual difference (aims.org.au, 2022, p8).
4. Driving Innovation: It tends to include the fundamental business changes for the business and the models of care for achieving people-centered quality services (aims.org.au, 2022, p9).
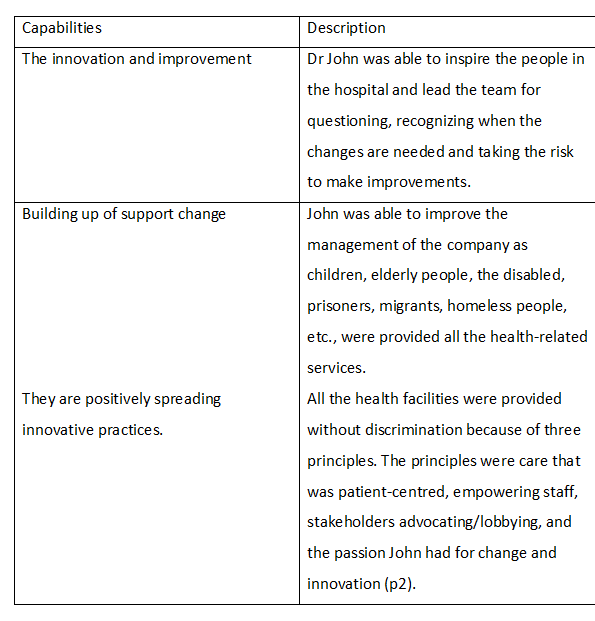
5. Shape system: Health is a complex system that is evolving where all the parts involving the services are interconnected with the legislation and the funding (org.au, 2022, p9).
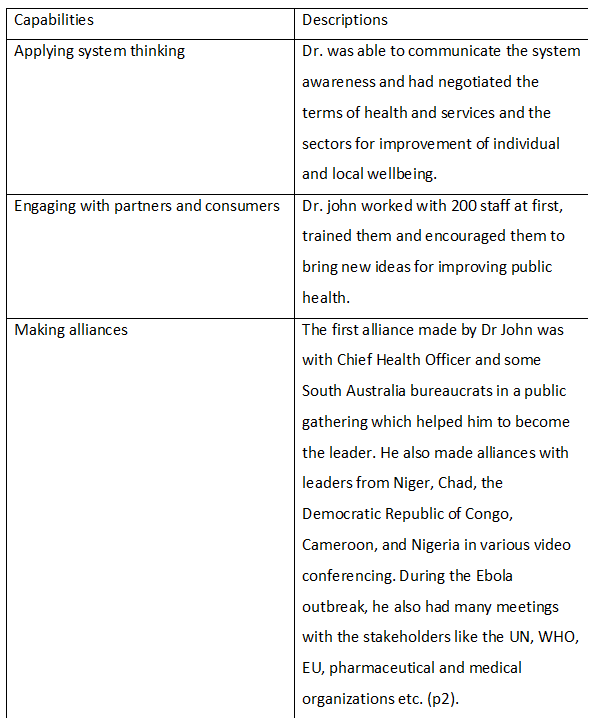
Part 2
Defining Leadership
Leadership is an art through which a person can motivate a group of people for acting towards achieving a common goal (Kiral, 2020, p1). According to the report of R. T. (2021, para 28), leadership does not tend to rely on the attributes of the individuals as well as it does not focus on the relationship dyadic between the leaders and the followers that tends to be the starting point of the leadership. In other words, it can be said that leadership is essential collective by nature and involves the activities of initiating, developing, deciding, and supporting as well as challenging and executing the elements that are independent (R. T. 2021, para 28).
It has been observed from the self-assessment that often I don’t tend to be engaged with other people in order to follow proper services direction that can be made and a vision for the health (heti.nsw.gov.au, 2022, p5). I also found out that I sometimes discuss only those factors which I feel are important that can impact the future of the health of a person.In Achieving Outcomescategory I have got 3 ‘a lot of the time’, 4 ‘some of the time’ and 1 ‘very little/never’. Through the self-assessment, I have also found out that before speaking, I sometimes keep my attitudes, beliefs, and behavior of mine in consideration and how it will affect others. I continuously look for opportunities that I need to learn and develop. However, I sometimes lose my calm and fail to ‘walk the talk’ with the values and beliefs of mine.In Developing and Leading self category I have got 2 ‘a lot of the time’, 5 ‘some of the time’ and 1 ‘very little/never’.In order to solve specific problems, I sometimes spend time with the team and discuss the work together while assisting them in finding out different issues that tend to affect the performance. However, I sometimes fail to create opportunities for people from other professions so that they can learn from one another. In Engaging people and building relationship I have got 1 ‘a lot of the time’, 7 ‘some of the time’ and 0 ‘very little/never’.
I have also observed that I have failed to challenge the work related practices and has failed to inspire people to change. In Partnering and collaborating across boundaries I have got 0 ‘a lot of the time’, 5 ‘some of the time’ and 3 ‘very little/never’.I also fail to take every stakeholders perspective when making decisions. Further I ask people to come up with new ideas as well as apply new information in the delivery nut fails to put forward the solution that are designed to meet the requirements (/heti.edu.au, 2022, p17). In Transforming the system I have got 1 ‘a lot of the time’, 5 ‘some of the time’ and 2 ‘very little/never.
Part 3
Reflection according to Case Study
Leadership Style: If I was in the situation of Dr John and wanted to make changes in the hospital while making improvement in public health, then I would be using Transformational leadership as it is one of the most effective styles (Eliyana, &Ma’arif, 2019, p1).
Strengths: Some of the strengths of my leadership style include having the ability to motivate others. I can encourage the employees to move from a self-interest attitude to the mindset in which they have been working for the common good. I am also able to hold emphasis on authenticity cooperation and make clear communication.
Application: There is a difference between being a leader of the business and a leader of public health; according to (TRIMESTER 1 Module 1. (2022, p3), Rowitz stated that a successful public health leader refers to the one with vision, decisiveness and who are the excellent communication and change agents as well as who are willing to take risks. In this case, I would have been having the convictions of the value and will be committed deeply to improving the health of everyone in the community. I would also be mentoring and providing the right set of training to the team so that the desired results could be achieved (Rasa, 2022, p4). Also, my emotional intelligence is highly energetic, and I am passionate regarding my work as a health practitioner (Mollah, et al., 2018, p7). I have strong moral values and try to encourage other people to follow the same (Bonsu, &Twum-Danso, 2018, p11). I believe in working in an ethical manner and with clean values and clear priorities. Using transformational leadership will be necessary because it is a type of leadership where the leader and follower are empowered each other’s motivation and morality (Louw, Muriithi&Radloff, 2018, p 2).
Gaps: From the self-evaluation, I have found out that along with the strengths of emotional intelligence and empathy, I also have specific gaps. I tend to become nervous during times when there is enormous pressure. Often because of my busy schedule, I am not much able to assist other people in their work. I also find it challenging to negotiate with the stakeholders, and keeping everyone's perspective in mind while making decisions becomes difficult.
Action Plan
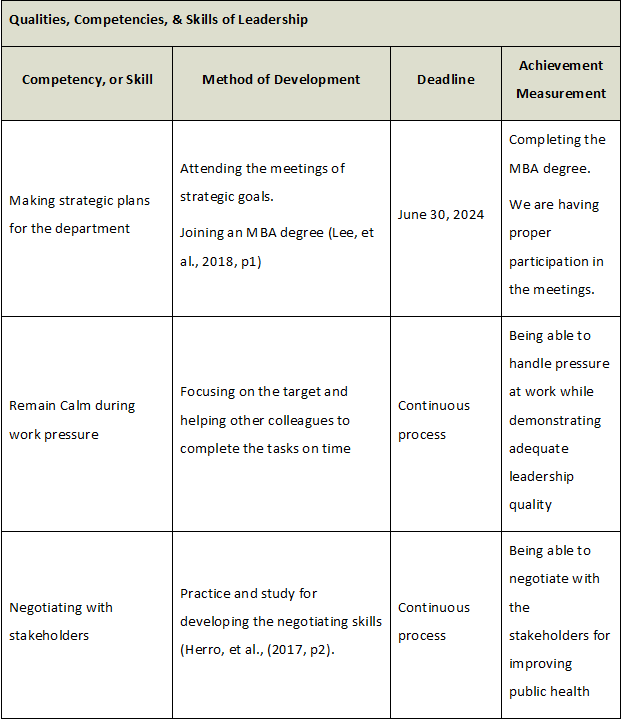
Conclusion
From the above analysis it has been seen that Dr John was an effective public health leader. He was able to identify the changes that were needed in the hospital and also was able to grab the opportunity of becoming an leader by meeting the bureaucrats at the public gathering. He had full determination and strong values on which he worked upon. He also treated other people equally and encouraged the team to come up with new ideas. The self assessment shows that I have strong emotional intelligence and ethical values with the help of which I can motivate and encourage the team in an effective manner. However, I need to work upon the negotiation skills and the quality to remain calm during work pressure.
References
Bonsu, S., &Twum-Danso, E. (2018). Leadership style in the global economy: A focus on cross-cultural and transformational leadership. Journal of Marketing and Management, 9(2), 37-52.https://gsmi-ijgb.com/wp-content/uploads/JMM-V9-N2-P04-Samuel-Bonsu-Global-Economy.pdf
By, R. T. (2021). Leadership: In pursuit of purpose. Journal of Change Management, 21(1), 30-44.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jakhongir-Shaturaev/publication/357271334_SCIENTIFIC_HORIZON_IN_THE_CONTEXT_OF_SOCIAL_CRISES_68_THE_DIFFERENCE_BETWEEN_EDUCATIONAL_MANAGEMENT_AND_EDUCATIONAL_LEADERSHIP_AND_THE_IMPORTANCE_OF_EDUCATIONAL_RESPONSIBILITY/links/61c46747abcb1b520adb0440/SCIENTIFIC-HORIZON-IN-THE-CONTEXT-OF-SOCIAL-CRISES-68-THE-DIFFERENCE-BETWEEN-EDUCATIONAL-MANAGEMENT-AND-EDUCATIONAL-LEADERSHIP-AND-THE-IMPORTANCE-OF-EDUCATIONAL-RESPONSIBILITY.pdf
Eliyana, A., &Ma’arif, S. (2019). Job satisfaction and organizational commitment effect in the transformational leadership towards employee performance. European Research on Management and Business Economics, 25(3), 144-150.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2444883418300196
Health Education and Training Institute Higher Education Academic Quality Assurance Framework. heti.edu.au. (2022). Retrieved 26 March 2022, from https://heti.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/485708/HETI-Academic-Quality-Assurance-Framework-v1.1.pdf.
Health LEADS Australia: the Australian health leadership framework. Aims.org.au. (2022). Retrieved March 23 2022, from https://www.aims.org.au/documents/item/352.
Herro, D., Quigley, C., Andrews, J., & Delacruz, G. (2017). Co-Measure: developing an assessment for student collaboration in STEAM activities. International journal of STEM education, 4(1), 1-12.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40594-017-0094-z
Kiral, E. (2020). Excellent Leadership Theory in Education. Journal of Educational Leadership and Policy Studies, 4(1), n1.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095771817300944
Lee, C. S., Ooi, A. S., Zenn, M. R., & Song, D. H. (2018). The utility of a master of business administration degree in plastic surgery: determining motivations and outcomes of a formal business education among plastic surgeons. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Global Open, 6(6).https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6157935/
Louw, L., Muriithi, S. M., &Radloff, S. (2018). The relationship between transformational leadership and leadership effectiveness in Kenyan indigenous banks.http://dspace.daystar.ac.ke/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/3609/The%20relationship%20between%20transformational.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Mollah, T. N., Antoniades, J., Lafeer, F. I., &Brijnath, B. (2018). How do mental health practitioners operationalise cultural competency in everyday practice? A qualitative analysis. BMC Health Services Research, 18(1), 1-12.https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12913-018-3296-2.pdf
Pinto, A. D., & Bloch, G. (2017). Framework for building primary care capacity to address the social determinants of health. Canadian Family Physician, 63(11), e476-e482.https://www.cfp.ca/content/63/11/e476.short
Rasa, J. (2022). Developing influential health leaders: the critical elements for success. Jhmhp.amegroups.com. Retrieved March 23 2022, from https://jhmhp.amegroups.com/article/view/5595/html.
The Leadership and Management Framework. Heti.nsw.gov.au. (2022). Retrieved 26 March 2022, from https://www.heti.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/622950/LMDED-Framework-Self-Assessment-Tool-2020_PRINT.pdf.
What is Leadership?. TRIMESTER 1 HE 2022 PUBH6004 ONLINE M1831 CRN 529 Module 1. (2022). Retrieved March 23 2022, from https://docs.google.com/document/d/1-vDbVuYJIuE9UFXCZIMV3UTxv7Px7DUsI2L40ARFEhA/edit.
Assignment
PUBH6005 Epidemiology Assignment Sample
Instructions:
Part A: covering modules 1 to 3 (due at the end of each modules, 1, 2, 3)
Part B: covering modules 4 to 6 (due at the end of each modules 4, 5, 6)
Step 1: In the Assessment 3 Discussion Forum nursing assignment help, post a comment in regard to ONE discussion topic related to EACH module (Refer to module discussion topics provided by your lecturer).
Discussion Topic 1: Observational Study Designs
What study designs could be used to explore the relationships between work-related factors and mental health?
Different designs might be more useful for exploring different relationships. Please suggest a proposed observational study design for a study which considers the relationship between work overload and mental health.
Why did you choose this study design?
Discussion Topic 2: Experimental Study Design
When would the use of a randomised controlled trial be inappropriate? Give a public health example and outline the reasons why conclusion randomised control trial would not be appropriate in this context.
Module 3
Discussion Topic 1: Comparing Screening and Surveillance
Apart from prostate cancer, are there any other conditions for which the benefits of screening may not outweigh the risks? If you have been involved with any screening or surveillance initiatives, you are encouraged to share your experiences and perspectives
Discussion Topic 2: Comparing Screening and Surveillance
Considering the methods by which surveillance data are collected, what elements of the social context or community in which you live create barriers to or facilitate effective disease surveillance? Feel free to draw from your personal and professional experiences.
Module 6
Discussion Topic 1
How does systematic review differ from the critical appraisal task set for assessment 3? How is it similar?
Discussion Topic 2
How are you going with your critical appraisal? Take this opportunity to compare notes with the other students about what you’ve struggled with and what you feel confident with.
Solution
Module 2
Answer 1
For exploring the relationships between work-related factors and mental health the case-control study design is used. In this type of observational study design researchers select the respondents for the study. With the help of this study, the design researcher gets appropriate data for the subject and helps in developing the best outcomes (Cahill et al., 2021). The case-control design helps in developing the data which is related to the real-life cases and can also observe the respondents behaviour and use it as data. In this design, the participants referred to as control who have no outcome of interest whereas participants referred to as cases who have the outcome of interest. At first, the pollution is defined and studied, cases are defined and selected, controls are defined and selected and exposure is measured. Lastly, the results are analyzed and calculated and link it with the objectives to draw the final conclusion.
Answer 2
For the questions which are related to health promotion research, randomized controlled trials are inappropriate. In the health promotion field, certain questions are developed through research methodologies that are more appropriate than random appropriate trials (Finkelstein et al., 2020). This trial is inappropriate because the test for efficiency is not conducted effectively and results developed from this test are not appropriate. Also, test effectiveness is larger and not cost-effective. The results are not related to real-life treatment. The hypothesis and objectives involved in the RTC are unclear, endpoints have poor selection, selected subject criteria is inappropriate and information provided is not relevant.
References
Cahill, J., Cullen, P., Anwer, S., Wilson, S. & Gaynor, K. (2021). Pilot Work Related Stress (WRS), Effects on Wellbeing and Mental Health, and Coping Methods. The International Journal of Aerospace Psychology, 1-23.
Finkelstein, A., Zhou, A., Taubman, S., & Doyle, J. (2020). Health care hotspotting—a randomized, controlled trial. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(2), 152-162.
Fulmer, R., Joerin, A., Gentile, B., Lakerink, L., & Rauws, M. (2018). Using psychological artificial intelligence (Tess) to relieve symptoms of depression and anxiety: randomized controlled trial. JMIR mental health, 5(4), e9782.
Module 3
TOPIC 1
Screening has become a very regular practice in the health and medication field. Most of the healthcare professionals are of the opinion that the benefits of screening outweigh the cons. Apart from prostate cancer, ovarian cancer is another condition in which the risks of screening outweighs its benefits. The reason is that the ovarian cancer screening might provide false positive-screening tests (Carlson, 2020). False positive might end up as women having surgery when they do not need any. Surgery also leads to anxiety, incurrence of additional costs, loss of work and might even lead to serious complications for many healthy women.
References
Carlson, K. (2020). Patient education: Ovarian cancer screening. Retrieved on 25th March, 2021, from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/ovarian-cancer-screening-beyond-the-basics#H5
TOPIC 2
Surveillance of public health is essentially important and compulsory in almost all the countries across the world. However, despite the benefits that it casts in the society in context to keeping the spread of diseases in check, it is faced with a lot of challenges (World Health Organization, 2017). The inadequacy in the number of health professions is the most serious barrier which is faced at the time of surveillance of public health. Apart from this, lack of proper diagnostic centres for the detection of diseases is another challenge that the regulatory bodies face in keeping the spread of diseases in check by using the instrument of surveillance.
References
World Health Organization. (2017). WHO guidelines on ethical issues in public health surveillance. Retrieved on 25th March, 2021, from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/255721/9789241512657-eng.pdf
Module 6
Discussion Topic 1
In general the genre of systemic review is following a chronological format and the main foundation of this style of review is referring to dates of publications. The critical styled tasks for appraisals are those which also make use of data of publication but these are descending order. Critical appraisal studies make extensive investigation about LR or literature review so that they can come in a conclusion of their quality parameters (Li, 2020, p. 87). All components which exists internally, their important, validation as well general approach is reviewing. Review here focuses over the work and discuses whether researcher has developed a neutral work or not. Critical appraisal is somewhat similar as the aim is to make in-depth analysis in both cases. Secondly both might make use of grey material as references.
Discussion Topic 2
My critical appraisal is going in a positive direction. Using this organised process i am finding out strength and weakness of the research study. I have however struggled to find the weaknesses of this research. Hence to solve it I have compared notes with other fellow students and checked out varied unpolished gray materials as well on the internet. This has helped me develop crucial understanding of the subject from different perspectives. This has also helped me make my own conclusion with a clear approach (Gundogan, Fowler & Agha, 2018, p. 1). A critical thinking approach is as per me helpful in making the study analysis become effective.
References
Gundogan, B., Fowler, A., & Agha, R. (2018). Assessing the compliance of systematic review articles published in leading dermatology journals with the prisma statement guidelines: a systematic review protocol. International Journal of Surgery Protocols, 10-12, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isjp.2018.11.001
Li, S. (2020). Quality control of the peer-review process by forensic sciences research. Forensic Sciences Research, 5(1), 87–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/20961790.2019.1700886
Coursework
PBHL20010 Working and Learning in Cross Cultural Communities Assignment Sample
Question
The first assessment help task is a case study of about 2000 words that you will complete on an individual basis. The case study will require you to choose one of the eight stakeholders and discuss their role in a public health emergency; the nature and direction of their interest based on their position in the community and their function in society; and their actions. You must also choose a specific emergency situation from which you will draw examples to illustrate your discussion. This may be an epidemic of disease (for example- a natural disaster (flood, bushfire, earthquake, etc); or an anthropogenic event (chemical spill, industrial explosion, etc). You must specify the emergency and stakeholder group in the case study. You will also need to use appropriate academic references to support your understanding of stakeholder participation, communication needs, and responsibility.
The stakeholders you may choose from are:
1. Local government
2. Science/health experts
3. Local business interests
4. The media
5. Representatives of the long-term community (people who have lived in a given location for 10 years or more)
6. Representatives of new groups (people who have recently arrived in or moved to a given location)
7. Local health care personnel
8. State (or higher level) government
Your case study must have the following sections: 1) Introduction – identifies the chosen stakeholder, the emergency and gives a general indication of who they are or where is the Public health Event – for the stakeholder group you have chosen, describe their role in a public health emergency; make sure to consider whether their role is official or personally at risk of health impacts and it he other kinds of risk they experience; 3) Risks and Responsibilities – for the group you have chosen, describe the nature of the section; make sure to consider whether the risk is direct or indirect, whether it is a risk to health or another kind of risk, what the specific health or non-health risk involves responsibilities are in relation to the public health emergency and its own and the risks of other stakeholders; 4) Role in Public health Decision-Making – for the group you chose, they contribute to decision-making in the context of a public health emergency; be sure to discuss whether their contribution is official or unofficial, the channel through which decision-making process, and the degree to which their impact is informed by evidence-based and non-evidence-based knowledge; and 5) Conclusion – discuss the position you have chosen in a public health emergency; you may want to consider whether they are actors or bystanders, for example, or use some other classification, but be sure stakeholder group is likely to be affected significantly, the nature of the impact, and why you believe this would occur.
This essay writing help must be written in a formal, academic style (not first person) and must be fully referenced. Harvard referencing is preferred for this unit. If you need help the referencing guides available online and through the Library as soon as possible.
Answer
1.0 Introduction
Public Health professionals are aimed towards protecting the health of the populations. Within a particular Public Health field, they also work to prevent the disease and make sure that the injury of the person does not spread (Harper et al. 2020). When an infectious disease is spreading such as that of coronavirus Public Health professionals work to track and stop the same while making sure that they can keep communities as healthy as possible.
The current reflection is based on my learning and experience of the scenario. It is focused on reflecting the specific experiences and other instances of the learner. The job experience is based in the larger context of community engagement. It highlights my experience of what I have learnt about public health and my job as a public health professional in the public health emergency of a covid-19 pandemic.
2.0 Learning during Scenario
The learning processes within the course of the scenario were extensive. This is so because I participated in scenarios every week and in a group of 5 members. It helped me understand the perspectives of other individuals and gain an idea about how they would view the same situation differently from me.
The process of learning is firstly involved in studying the scenarios and understanding the variables which revolve around the same. We then discussed the scenarios and the complications it presents which enabled us to gain a deeper insight about information that is presented. In this way we got to know how the other person would view the same situation. In this way we were able to understand the scenario completely which made solving answers easier (Rosa et al. 2020).
After the discussion we each picked up a question for answering. I learnt a lot from the information presented in this scenario as well as the perspectives shared by my group members. As an individual, I found it hard to work in a group and participate in group discussions. Due to these scenarios, I was able to develop team working skills along with the ability to participate in a discussion while presenting personal viewpoints and also learning about that of others. I got to know that there are a couple of underlying gaps in my knowledge because the perspective presented by my group members were highly differing and I got to know that a need for future learning exists as I need to strengthen my course knowledge and perform better.
3.0 Reflection on Scenario Experience
The self-analysis highlights that I need to revise the contents of my course and link them with the scenario so that I am able to understand the case is shared within them and answer the questions in a better way. I also need to undertake future learning about how to understand and reflect upon case studies so that I would be able to perform better in real life situations.
In the PBHL20007 unit, I got to know about the persistence of cultural shock within Public Health with specific reference to language and food. Reflected how the students who come from their country to Australia experience cultural shock as it acts as a barrier while adopting food and culture which is highly different from whether they have experienced all their life. Students also feel lonely when they leave their country because they leave behind their family and friends and also take time to make new friends with people who belong to different cultures and have different viewpoints and identities (Banerjee & Firtell 2017).
In this way they find themselves alone whenever they have a problem to encounter with specific reference to academic or personal life. I found this to be resulting in heavy stress which makes it difficult for international students to perform well in university. Differences in study pattern and the required level of academic writing skills also act as a bird in which need to be managed along with handling emotional and psychological health.
In PBHL20008, I got to know how to engage with cross-cultural communities. I research the information before the placement so that I would know my roles and responsibilities. I focused on the Australian indigenous community in the second assignment of this unit which was based on a case study of rural and remote areas. I reflected upon the mental health and physical status of the community members.
I gained an insight that they have poor accessibility to health services and quality food which further possesses a negative impact on their physical and mental health (Takeda & Melby 2017). I also found the patterns of heavy alcohol consumption due to problems such as lack of knowledge and stress. I give solutions so as to make sure that these communities are able to fulfil their cultural needs by increasing their knowledge regarding food and education and engaging with other community members.
4.0 Descriptive Elements of the Scenario
From the scenario, I learnt a lot of important things that improved my existing knowledge base and also allowed me to explore a lot of unexplored ideas and viewpoints. As highlighted earlier, me and my other group members participated in the scenarios every week where we performed various activities. It is vital to note that me and my group members were not able to meet and interact physically so as to fulfil this scenario activities and hence, we created a group over WhatsApp so that we could discuss the contents of the scenario and also reflect upon or learn from the same. My group members were highly considered rated because whenever one individual did not understand something the entire group would remain online and discuss the same way until it was clear to everyone which highlighted interpersonal participation.
In addition to this, I also got to know about its stakeholders within a public health scenario along with the members of the community and the public health professional. The most important insight I gained about the stakeholders was in reference to the responsibilities and roles performed by them in large Public Health events such as with situations of epidemic or pandemic.
These scenarios also help me to understand how to treat people and members of the community who are infected from the infection or illnesses. I gained an insight that I do not need to provide just the medical care for medicines and rather I need to provide them with adequate emotional support so that they do not feel that they are alone in this and rather have emotional support as and when required.
The major consideration here was that I firstly need to determine all the variables present in the condition so that I have all the required information for solving the issue. This is capable of helping me as a public health professional when I would be dealing with people who are affected from a public health event as well as individuals who were not affected. This is so because people who are affected are dealing with illness as well as emotional issues which makes it hard for them to concentrate on the positive aspects and have confidence that they will get better.
On the other hand, people who are not affected live in the constant state of fear and panic because they feel that they would catch the viruses and will not be able to protect themselves within the public health epidemic (Edmonds et al. 2020). This situation was common in the times of covid-19 pandemic because the people who had not contracted the coronavirus lived in a state of panic and hysteria where they were highly protective of themselves and found it hard to live a normal life while taking the required precautions.
It has been identified that the stakeholders of the public health infection control were management, program staff, funding agencies, Public Health professionals, and community members (Glenn et al. 2021).
I (as a public health professional) and other stakeholders were interested in making sure that infection control is being done properly where everyone is performing their jobs in the desired manner while focusing on the interests of the community. The outcome of the situation was collecting swabs for testing people for covid-19 and injecting what scenes to others.
The role of these stakeholders was directed towards making sure that the infection control happened in the desired manner and that each person performing the job was doing it correctly. It is vital to note that operations in public health can be tedious because there is a perfect set of instructions that need to be followed to take a single swab for a test or to inject a vaccine (Calisher et al. 2020).
The group of stakeholders who is the most at risk include public health professionals and community members. The key reason behind the same is that they are in close contact with the virus. The group which is at risk for non-health loss includes funding agencies. Their monetary resources are at stake while managing the public health event.
5.0 Job Experience in Public Health
I have been performing the role of Public Health professional as infection control in the public health emergency of the covid-19 pandemic. My role involved covid swapping and vaccination, PPE spotter. These were focused on controlling the spread of infection in the community and making sure that the stakeholders of Public Health are satisfied. My job did not only have a medical front but also reflected critical importance as me along with other practitioners was working closely with the virus.
During the situation, I felt fearful of contracting the virus myself. This is so because I was closely working while the people were submitting their samples for a test which might or might not be positive but I always felt at risk by performing my job as a public health professional in a public health emergency. Before the situation, I felt that I should do something to contribute to the diversification of the community of Australia and help them make it easier to manage the covid-19 pandemic.
After the situation, I felt that I have done good and worked for the benefit of society in order to promote Public Health. I felt that other people who were present at the scene also had similar feelings about the situation to myself. It can be further evaluated that the things that did not go so well involved me not being able to handle my emotional challenges and feelings of fear while making sure that I am doing my job in the desired manner. I was also not able to manage my academic and personal life while I was engaged in professional activities as a public health practitioner.
Apart from this, I signed up for the job without actually thinking about how I am going to protect myself which led to feelings of anxiety and fear while I was working. It can be analysed that I did not have paid the required attention to the demands of my academic life and emotional health because of which I was not able to handle the stress of the things going around me and they might have experienced Burnout at work. The sense which I can make of the situation now revolves around how if I could have undertaken better time management and stress management the situation would have been better.
Along with this, I think that if I would have developed these skills the situation of Burnout wouldn't have taken place which put me at risk of a public health emergency. I feel that even though I performed my job properly I did not pay the required attention to other aspects of my life which caused emotional distress. I feel that the learning and knowledge which I gained from this experience can be implemented in future situations so that I can handle them in a better way.
6.0 Conclusion
From the reflection, it can be concluded that learning during the scenario enabled me to develop team working skills and ability to participate within group discussions. I also got to know about gaps in my current knowledge and the ways in which I can undertake future learning. The units PBHL20007 and PBHL20008 further contributed to my learnings of cross culture public health. The public health stakeholders were discussed along with their relationships with specific reference to the public health event of covid-19 pandemic.
References
Banerjee, S & Firtell, J 2017, ‘Pedagogical models for enhancing the cross-cultural online public health learning environment’, Health Education Journal, vol.76, no.5, pp.622-631, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Srikanta-Banerjee/publication/317387894_Pedagogical_models_for_enhancing_the_cross-cultural_online_public_health_learning_environment/links/60be3017458515218f9ee08b/Pedagogical-models-for-enhancing-the-cross-cultural-online-public-health-learning-environment.pdf
Calisher, C, Carroll, D, Colwell, R, Corley, R B, Daszak, P, Drosten, C, Enjuanes, L, Farrar, J, Field, H, Golding, J & Gorbalenya, A 2020, ‘Statement in support of the scientists, public health professionals, and medical professionals of China combatting COVID-19’, The Lancet, vol. 395, no. 10226, pp. 42-43, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://escholarship.org/content/qt05h3r4qr/qt05h3r4qr.pdf
Edmonds, J K, Kneipp, S M & Campbell, L 2020, A call to action for public health nurses during the COVID?19 pandemic, ‘Public Health Nursing (Boston, Mass.’), vol.37, no.3, p.323, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7262140/
Glenn, J., Chaumont, C. & Villalobos Dintrans, P 2021, ‘Public health leadership in the times of COVID-19: a comparative case study of three countries’, International Journal of Public Leadership, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 81-94, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJPL-08-2020-0082/full/html
Harper, C A, Satchell, L P, Fido, D & Latzman, R D 2020, ‘Functional fear predicts public health compliance in the COVID-19 pandemic’, International journal of mental health and addiction, pp.1-14, viewed 22nd September 2021, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11469-020-00281-5
Rosa, W E, Gray, T F, Chow, K, Davidson, P M, Dionne-Odom, J N, Karanja, V, Khanyola, J, Kpoeh, J D, Lusaka, J, Matula, S T & Mazanec, P 2020, ‘Recommendations to leverage the palliative nursing role during COVID-19 and future public health crises’, Journal of hospice and palliative nursing: JHPN: the official journal of the Hospice and Palliative Nurses Association, vol.22, no.4, p.260, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc8018720/
Takeda, W &Melby, M K 2017, ‘Spatial, temporal, and health associations of eating alone: A cross-cultural analysis of young adults in urban Australia and Japan’, Appetite, vol.118, pp.149-160, viewed 30th September 2021, https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wakako-Takeda/publication/319113899_Spatial_temporal_and_health_associations_of_eating_alone_A_cross-cultural_analysis_of_young_adults_in_urban_Australia_and_Japan/links/59d6d7700f7e9b42a6aa0a78/Spatial-temporal-and-health-associations-of-eating-alone-A-cross-cultural-analysis-of-young-adults-in-urban-Australia-and-Japan.pdf
Essay
PBHL20009 Assessment 2 Sample
Question:
Your essay must consist of your reflection on the evolving situation that has taken place during the course of term 2 2020 and term 1 2021. The focus of the essay is to show your deepening understanding of issues that may arise during a public health event, especially as they relate to cross-cultural communities like the one we live in, and yourself as a developing practitioner. Your essay should address the following points:
1) A very brief summary of the current pandemic and its effects in the place where you live
2) The actual effects on our cross-cultural community
3) The potential effects of this kind of situation on a cross-cultural community
4) What have you, as a developing public health practitioner learned from experiencing a real-life public health emergency.
Answer:
In recent times COVID 19 pandemics caused by coronavirus which has spread from China and very new to the world and affected the world population drastically. The COVID 19 pandemic impacted on Australia and especially on the population of Sydney. I can see that the economic, social and political situations are very much affected by the virus spread as the contamination of the virus is uncontrollable and higher level of contamination developed a certain amount of panic among people as well. As a developing public health practitioner, I can also experience the psychological impacts among people due to the change in the social processes and rising unemployment issues along with an instable economic situation. I have seen that the COVID 19 pandemic developed several issues and the only way to reduce the impact of the virus was global lockdown and rapid vaccination to build immunity against the virus. However, the virus shown a characteristic of changing its functionality and structure and thus, there are different species have been found till now from the end of 2019 when the virus outbreak occurred from China. Considering all these factors, I have seen that the Australian government and local government of NSW developed the regulation of lockdown especially marking some hotspots where the rate of COVID cases is high (NSW Government, 2021). Sydney have several hotspots, though, due to 80 per cent of population of Sydney have been administered with first dose of vaccine till 20 th September 2021 and the curfew or strict lockdown of the 12 hotspots of Sydney has been lifted (The Guardian 2021). However, as per my knowledge, regulation developed by the government highlighted that if there is any single new case can be found among these areas the lockdown will again be put forward for at least 14 days (The Guardian 2021). As a developing public health practitioner, I think in this dire situation this is the only solution for the people to be safe and reduce the contamination of corona virus.
I can state that the situation of COVID 19 cannot be marked as positive even after almost one and half year of the pandemic impact on the world population. As a developing public health practitioner, I can state that the impact of the pandemic is still present and the regulation of NSW government is strict to improve the situation (NSW Government 2021). The regulations include travelling outside the local area without proper permission and identification of the contamination free situation for any individual which can be visible to me and others still now as in Sydney a truck driver found with the infection and a 31-year-old woman travelling outside the area has been confronted by the police as well (Abc.net.au 2021). Considering all these factors, I can highlight that the regulation of the lockdown and curfew are still implemented by the government for the safety of the local and national population. However, there are 628 cases including 3 deaths due to COVID 19 found in the area of Victoria and the government put forward the regulation regarding vaccination of education staffs till November to continue the educational works as well (Abc.net.au 2021). Hence, as a developing public health practitioner, I can reflect that the policies and regulations can be effective.
However, I think that the empowerment to the people will help them to understand the importance of the policies and regulations. Thus, as per my experience and knowledge I reflect that the empowerment programs for people should be considered with higher priority. However, the requirement of the hand washing, face mask and face shield usage related education to people cannot be neglected and I should try to educate andempower people regarding the use of these factors. I think that the vaccination can provide immunity though developing habit of healthy practices is necessary to reduce the risk of the COVID 19 pandemic. Considering this, I can highlight that hand washing is done through 7 steps as per regulation of WHO and these should be considered to improve the health education of people and also the proper face mask wearing processes should be considered as well for the empowerment process (Who.int, 2021). Moreover, the regular sanitisation is also required to be considered for the safety from the virus and I should also practice that and influence people to do so as well.
People from various cultural backgrounds are being influenced differently by the epidemic. SBS, a multi-ethnic and multilingual broadcaster, claimed that people were being misled by alleged therapies that had no proven impact, such as utilising salt water, garlic, vitamins, and whiskey as home cures. Others were said to be utilising traditional remedies, and certain religious groups were led to think that fervent religiosity would provide them with viral protection. They felt they could disregard government public health recommendations and legislation (SBS, 2020). SBS said that public education initiatives in languages other than English were minimal and ineffective. Better, culturally relevant information, for example, would enhance public messages on
hygiene and physical distance (SBS 2020). COVID-19 also resulted in a rise in racist complaints to the Human Rights Commission. Since the beginning of February, one-third of all complaints have been linked to the virus. These included reports of verbal and physical assault, as well as vandalism (Human Rights Commission 2020), with Chinese individuals being particularly targeted and, as a result, suffering from insecurity, fear, and mental illness (Fang and Yang 2020).
I can also necessarily highlight that the supplies of medication and other products are also delayed due to the lockdown and the imbalanced international situation. Hence, I can reflect that the change in the situation is not possible at this moment properly as the global pandemic situation is not normalised yet. Moreover, as a developing public health practitioner, I can see that the social and psychological situation of people is also not in a proper shape. Hence, I should consider empowerment and educational programs for the people to reduce the impact of the pandemic situation and promoting wellbeing for them. However, the unemployment and the social distancing affected on the economic and psychosocial aspects of people in a drastic manner. Considering all these factors, I can highlight that the importance of the normalisation of the situation through proper strategic implementation should be considered by the government. Though, the impact of the international economic situation and the employment situation are not positive. Hence, based on all these situational contexts of the local area of Sydney and also the national and international context, it is evident that the health care is hampered due to the social determinants of health are impacted drastically.
Moreover, the overwhelming cases of COVID 19 lead to the imbalance in the work force and work load. Other than all these, the lockdown regulations impacted negatively on the supply of medical products as well (van Barneveld et al. 2020).I can state that the impact of COVID 19 on health care department is very much prominent due to the sudden change in the care regulations and demands as well. However, I think that the social and political along with the economic factors that have been adversely affected due to the pandemic developed the negative situation in a more prominent manner. I also realise that the lockdown regulation led to a gap in the social interactions and also impacted on the psychological aspects of people (van Barneveld et al. 2020). Hence, the health care department should be focused on the planning for the effective care delivery to these people as well and I should take part in the proper care delivery planning. Moreover, the technological use of the social media based or the telephonic care delivery processes should be prioritised for the improvement of the situation and also the cost and time reduction for care delivery. The COVID pandemic is going to be tougher in few months as well as the 3 rd wave or the Delta strain of COVID 19 will infect as per the health scientists. Thus, I think it is necessary to state that the consideration of the change in the health care work force or processes should be prioritised for the improved care delivery to the COVID patients as well as the people affected with other comorbidities to maintain the quality of care. The regulations should be strictly followed and it can provide a better situation to cope with the adverse impact of the disease. The prospect of almost 2 years of prolonged impact of a virus on human health in a drastic manner is very much rare situation for health care department (Bateson et al. 2020). Hence, I think that in this sudden and drastic issue the health care department is trying to cope and it can be stated that the international situation impacts more adversely and delays the improvement against the disease or virus.
It is evident to me that with proper infrastructure and work force the health care department can reduce the impact of the disease in a positive manner. The general impacts in the Sydney and Australian contexts are also impacted with the issues of the cross-cultural communities and also the people from other minority groups. It has been seen that the cross-cultural group of people and also the minority people have barriers of language and also cultural differences (Spennemann 2021). As a developing public health practitioner, I think that the linguistic barrier develops gap in the care access and also reduce the chances of proper interaction with the health care professionals or the majority of the population (OECD 2020). Hence, I can reflect that there is a social gap develops which is prominent and negatively impact on the health outcome of these people. Based on this context, I can necessarily highlight that the language-based issues should be reduced through the implementation of the positive communication strategies. The nurses and other health care workers should show empathy and use the non-verbal communication strategies to communicate with these people. I think that as a developing public health practitioner, and other health care professionals along with the people can access the health care appropriately.
The cross-cultural people and also the minority people showed different cultural beliefs and actions in different situations. I can also reflect that the impact of these activities lead to different issues in several situations. Thus, it is necessary to provide proper care and empowerment to these people to follow the regulations of COVID 19 and reduce the impact of the disease on them. In this manner, the situation will be improved and the reduction of the negative consequences can be achieved. The factor of the change also depends on the attitude of the health care workers (OECD 2020). It has been seen that the cross-cultural people are neglected and discriminated by the White population in several cases and it also develops unnecessary communication
gaps and impacts on the health care process. Thus, the consideration of the change in the situation through the empowerment of the health care workers should also be considered for the improvement in the care process (Cui et al. 2021). Thus, as a developing public health practitioner, I can necessarily highlight that the self- actualisation of people is very much important considering the national, local and also international situations of COVID 19. Though, the health care workers should reduce the attitude of discrimination and provide culturally safe and collaborative care to each and every patient needing health related support.
As a health care worker, the COVID 19 pandemic is one of the crucial issues I have faced in my entire career and maintaining the safety of the co-workers, patients and myself should be considered by me at the first place. The aspect of the care delivery and also considering the priorities and needs of the patients are very much important for me. However, in terms of the experience in Sydney as a nursing care professional I understood my duties and the impacts of life threats as well. The COVID 19 pandemic developed a panic among the health care workers as well as among the patients (Bateson et al. 2020). I should also state that I have found that the impact of the cultural differences of people should not affect the care delivery process or health outcome of the patients. Hence, I should promote cultural safety and provide equal care to all the patients. Moreover, I should focus on empowering people regarding the DOs and DON’Ts to avoid the risk of the COVID 19 or other comorbidities of the disease. However, the recent data of the Sydney and other areas of NSW developed a concern and I should focus on helping people to improve their own situation regarding the health outcomes along with the community people as well. The cultural safety should be considered with priority by me as well.
References
Abc.net.au, 2021, ‘Truck driver 'presumed' to have Delta was in WA for two days — as it
happened’, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.abc.net.au/news/2021-09-22/covid-updates-sydney-melbourne-cases-restrictions-border/100481082>
Bateson, D, Lohr, P, Norman, W, Moreau, C, Gemzell-Danielsson, K, Blumenthal, P, Hoggart, L, Li, H, Aiken, A & Black, K, 2020, ‘The impact of COVID-19 on contraception and abortion care policy and practice: experiences from selected countries’, BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health, vol. 46, no. 4, pp.241-243, viewed 26 September < https://srh.bmj.com/content/familyplanning/46/4/241.full.pdf>
Cui, J., Mao, L., Newman, C., Kwan, C. and Lancaster, K., 2020. ‘Managing Risk in the Pro-Empowerment Era of Mental Health Care: A Cross-Cultural Study of Social Work Perspectives in Hong Kong and Sydney’. The British Journal of Social Work, 51(3), pp.831-848, viewed 29 September 2021 < https://academic.oup.com/bjsw/article-abstract/51/3/831/6044335>
Fang, J., Yang, S. (2020). ‘Chinese-Australian family targeted over coronavirus receives outpouring of support, ABC’, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-04-23/chinese-australian-family-racist-coronavirus-racist-attack-speak/12178884>
Health.gov.au, 2021. ‘COVID-19 Vaccine Roll-out Jurisdictions Breakdowns.’, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2021/09/covid-19-vaccine-rollout-update jurisdictional-breakdown-29-september-2021.pdf>
Human Rights Commission. (2020). ‘Where’s all the data on COVID-19 racism?’,
viewed 29 September 2021 < https://humanrights.gov.au/about/news/opinions/wheres-all-data-covid-19-racism>
NSW Government, 2021. ‘Greater Sydney restrictions.’, NSW Government, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.nsw.gov.au/covid-19/rules/greater-sydney>
OECD, 2020. ‘Culture shock: COVID-19 and the cultural and creative sectors.’, OECD. viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/culture-shock-covid-19-and-the-cultural-and-creative-sectors-08da9e0e/>
SBS Australia. (2020). ‘Harmful coronavirus myths are being spread in Australia’s multicultural communities.’, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.sbs.com.au/news/harmful-coronavirus-myths-are-being-spread-in-
australia-s-multicultural-communities>
Spennemann, D., 2021. ‘No Entry into New South Wales: COVID-19 and the Historic and Contemporary Trajectories of the Effects of Border Closures on an Australian Cross-Border Community.’, Land, 10(6), p.610, viewed 29 September 2021 & lt;https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/10/6/610/pdf>
The Guardian, 2021. ‘New NSW Covid lockdown restrictions: update to Sydney, regional NSW and Canberra, ACT coronavirus rules explained.’, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://www.theguardian.com/australia-news/2021/sep/22/new-nsw-covid-lockdown-restrictions-update-to-sydney-regional-nsw-and-canberra-act-coronavirus-rules-explained>
van Barneveld, K., Quinlan, M., Kriesler, P., Junor, A., Baum, F., Chowdhury, A.,Junankar, P., Clibborn, S., Flanagan, F., Wright, C., Friel, S., Halevi, J. and Rainnie, A.,2020. ‘The COVID-19 pandemic: Lessons on building more equal and sustainable societies.’, The Economic and Labour Relations Review, 31(2), pp.133-157, viewed 29 September 2021 <https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1035304620927107>
Who.int, 2021. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Masks. [online] Who.int., viewed 7 October 2021 https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-masks Who.int, 2021. Hand Hygiene: Why, How & When?. [online] Who.int., viewed 7 October
2021
https://www.who.int/gpsc/5may/Hand_Hygiene_Why_How_and_When_Brochure.pdf
Who.int, 2021. World Hand Hygiene Day 2021: Seconds save lives - clean your hands!.[online] Who.int., viewed 7 October 2021 https://www.who.int/campaigns/world-hand-hygiene-day/2021
Research
PUBH6013 Qualitative Research Methods Assignment Sample
Question:
This assessment addresses the following learning outcomes:
c) Apply qualitative research methods through undertaking data collection through, e.g. focus group, interviews, observational methods.
d) Appreciate cultural and ethical considerations for qualitative research in Public Health
e) Understand sampling techniques, bias and rigour as they apply to qualitative research
f) Apply coding and analysis techniques to qualitative data
Instructions:
Analysis: Use the resources in module six to:
1. Code the data that you collect from your interviewees.
2. Develop themes based on your coding.
3. Report on the themes that you’ve identified, supported by relevant quotes from your interviewees. Report this part in the same style as the results section of a qualitative journal article.
Reflection: reflect on your experience of interviewing and analysing the data. What did you do well, and what did you struggle with? What could you learn to do better? What did you learn through this experience?
Answer:
Introduction
The current research is about the reasoning behind the diabetes among the Australian indigenous community. The research question is significant to identify the main reason of Diabetes and its effect on the life-expectancy among the Australian indigenous community. The primary research based on online papers gave a set of organised data but cannot fulfil the criteria of the research on likelihood of diabetes. The likelihood criteria can be derived from interviewing questions on selected participants. The current research proceeds with the data analysis based on interviewing. The interviews have been taken as face-to-face session where the researcher can notice the expression and actions while responding to a question. This will help a researcher to develop coding because the reaction of the respondents help enables researcher to develop their perceptions. While transcribing an interview, the researcher find some physical gesture and give better answer to a question, rather than their verbal expression. In this paper, the development of coding and theme development will be analysed in this way, on the proposed research.
Analysis and findings of interview
The study reflects a participatory action approach for conducting their interview sessions. In these interview sessions, the participants are selected from the local healthcare who have good knowledge on the health of indigenous people. Unlike the primary research, the participatory actions find out some surplus data which can create the challenge of diversion (Crosley & Jansen, 2020). The researcher is able to highlight only the relevant data while developing coding for the research.
Familiarization
The first step of coding is familiarization. It is conducted by transcribing the recording of participants’ interviews (Cristancho & Helmich, 2019). From the interviews of healthcare participants, the research finds out that the Likelihood of diabetes, obesity and hypertension occurs mostly in mid-aged females whereas most of them are pregnant. The same respondent informed that most of the diabetic women are from aboriginal ethnicity. Another participants respondent that he has observed the likelihood of death in diabetes is mostly among Torrens-islanders while the general mortality rate of these community is better than the non-indigenous. It implies that the indigenous people have better life-expectancy rate than the non-indigenous but they are prone to suffer in Chronic disease which slows down the dying process. From another respondent, it is drawn that the indigenous people refuse to take the primary healthcare as they believe in their traditional medicines. A team of respondent who were treating on the narcotic patients informed that the consumptions of alcohol is higher in indigenous patients compared to the non-indigenous populations. It implies that the alcohol can be a major cause in diabetes. After checking all the notes, the coding is developed in this way:
Developing codes
|
Notes taken from interview transcriptions |
Coding |
|
the prevalence of diabetes, obesity and hypertension occurs mostly in mid-aged females. Most of them are pregnant aboriginal women. |
Likelihood of diabetes Likelihood of obesity Likelihood of hypertension Females Mid-aged Pregnant Aboriginal |
|
likelihood of death in diabetes is mostly among Torrens-islanders while the general mortality rate of these community is better than the non-indigenous. |
death in diabetes diabetes likelihood Torrens-islanders mortality rate non-indigenous |
|
indigenous people refuse to take the primary healthcare as they believe in their traditional medicines |
indigenous people primary healthcare refuse believe traditional medicines |
|
the consumptions of alcohol is higher in indigenous patients compared to the non-indigenous populations |
Alcohol consumption Higher indigenous patients non-indigenous populations |
Developing Themes
In the coding process, the research gathers the raw data of Diabetes disease of indigenous people. In the theme developing process, it will reach to the actual meaning derived from the raw data set (Caulfield, 2020). By looking on the patterns of the codes, the study will combine the codes into the theme. The unnecessary codes will be eliminated while the main codes will be categorized by matching their patterns. The eliminated codes can also be combined into a theme but the researcher has to remind that the data which are relevant in regards to the research objective, only taken (Crosley & Jansen, 2020). This indicates an inductive coding while giving importance to the didactive data indicates the didactive coding. Here the data that concludes the research question, ‘the likelihood of diabetes among Australian indigenous populations’, reflects inductive coding. The data those take part in addressing common symptoms of diabetes or alcohol addiction of aboriginal people, captures different broader contexts. These are called didactive coding. The didactive codes can form themes which are not relevant to this current context. For example, the diabetics patients have common diseases like obesity and hypertension. This will create less impact while developing strategies to prevent diabetes. This can be used as symptoms. The reference of females and their age group is important to this research because it will help in medicine research (Radcliffe et al., 2020). Now the study shows how it develops themes by mapping the relationship between codes.
|
Codes |
Themes |
|
· Likelihood of diabetes · Females · Mid-aged · Aboriginal |
Likelihood of diabetes among mid-aged aboriginal females. |
|
· Likelihood of diabetes · Females · Pregnant · Aboriginal |
Likelihood of diabetes among pregnant aboriginal females. |
|
· death in diabetes · diabetes likelihood · Torrens-islanders |
The likelihood of death among Torrens-islanders in diabetes |
|
· indigenous people · primary healthcare · diabetes likelihood |
The primary healthcare of indigenous diabetic patients |
|
· indigenous people · traditional medicines · diabetes likelihood |
The use of traditional medicines in indigenous diabetics. |
|
· Alcohol consumption · indigenous patients · diabetes likelihood |
Alcohol consumption among indigenous diabetic patients |
Result
From the above table it can be shown that the meaningful codes are only used which can answer the problem of this research. It avoids unnecessary themes development like mortality rate among indigenous; mortality rate among diabetics; mortality rate among alcoholic; alcoholic among indigenous; and chronic disease among diabetes. The purpose is to locate the genetic DNA of indigenous and their likelihood of developing diabetes, which is detected through this research.
Reflections
As the research is conducted in a cross-cultural environment, as a researcher I feel it is very necessary to take some ethical consideration of the research. Before making any decision, I should check my biasness to any culture. Through out my research, from data collection to decision making, I am on the track of moral behaviour and justice. I have maintained the respect for all the cultures discussed in this research. Also, I select participants of healthcare from various cultural backgrounds. They were both from Indigenous and non-indigenous background. It helped me to check the consistency of their statement. Also, I tried to put the social context of indigenous people which is often ignored in the health research. I have drawn this from value coding. My research is not bounded within men, rather I have mentioned the special needs of women health in the research of Diabetes (Goins et al, 2020). I felt the inclusion of woman is very necessary in this research as the healthcare of the marginalised woman is overlooked or challenged in Australian society. I have mentioned the need of primary care among diabetes patients as I observed from the transcriptions of participants that the indigenous women often do not get the primary care in the time of child birth. From the conversation of the respondents, I came to know that the social belief among indigenous are profound. They believe in traditional medicines. So, they refuse to take the help of primary healthcare which I have highlighted in my research. I have addressed the habit of drinking among indigenous patients because alcohol can be a major driver of diabetes. I have to consider the ethical challenges of a social research as it is not purely a medical research.
Being a researcher, I am obliged to keep confide the names of the participants, their healthcare organizations and the patient’s personal case history data given by them. During the research I used my personal laptop for recording their video, as I need to watch their physical expressions also. I found it is helpful in this research as most of the participants are from different cultures and languages. Some of them have no clarity of speaking but they try to express the meaning. For this reason, a visual observation is important.
Conclusion
Developing codes and themes are important to make a research question. In this study, we observe only didactive coding which ideates many references. It helps to assess the proposed idea that whether diabetes occur more in indigenous. An inductive coding will answer it by gathering and connecting all the data. An inductive coding helps to reach to the conclusion of a research question and used in getting a research theory out of codes. Though the initial target of coding is to interpret the data and familiarise the data, it also reflects the value coding which indicates the cultural value through the health attitude of indigenous people.While moving from coding to analysation, the core topic qualitative data analysis comes. The researcher analyses the data and locates the code categorization. The categorization and data set of codes combinedly develop themes. The inductive coding gives a proper answer of the research question that there is a genetical connection between Diabetes and Indigenous community.
References
Caulfield, J. (2020). How to do thematic analysis. Scribber. How to Do Thematic Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples (scribbr.com)[5th Aug 2021]
Cristancho, S. M., &Helmich, E. (2019). Rich pictures: a companion method for qualitative research in medical education. Medical Education, 53(9), 916–924. https://doi-org.torrens.idm.oclc.org/10.1111/medu.13890
Crosley, J., & Jansen, D. (2020).Qualitative Data Coding 101:How to code qualitative data, explained simply.Gradcoach. Qualitative Data Coding: Explained Simply (With Examples) - Grad Coach [5th Aug 2021]
Goins, R. T., Jones, J., Schure, M., Winchester, B., & Bradley, V. (2020). Type 2 diabetes management among older American Indians: beliefs, attitudes, and practices. Ethnicity & Health, 25(8), 1055–1071. https://doi-org.torrens.idm.oclc.org/10.1080/13557858.2018.1493092
Radcliffe, P., Canfield, M., Lucas D’Oliveira, A. F. P., Finch, E., Segura, L., Torrens, M., & Gilchrist, G. (2020). Patterns of alcohol use among men receiving treatment for heroin and/or cocaine use in England, Brazil and Spain. A cross-country analysis. Drugs: Education, Prevention & Policy, 27(4), 297–305. https://doi-org.torrens.idm.oclc.org/10.1080/09687637.2019.1658715
Assignment
PUBH6008 Capstone A Applied Research Project in Public Health Assignment Sample
Question:
By the end of module 3, student must provide to their learning facilitator a brief review of the literature on their chosen topic. The literature review must contain key references/theorists/researchers for the public health topic chosen. The literature review assignment must be designed to address the following questions:
• Who are the key theorists/researchers in your public health topic?
• What are the key issues?
• What are the gaps in the existing body of knowledge?
The literature review should provide a basis for justifying a clear research question or hypothesis to be explored further.
You must also indicate the search strategy used for your literature review. For example, what were the key words you searched for, and which key databases or other sources did you use to conduct your literature review? (e.g. CINAHL, Proquest Public Health, Informit, Medline, Google Scholar).
Assessment Criteria:
• Critical and comprehensive review of the literature (70%) Clarity of research question/hypothesis (10%) General assessment criteria (20%):
o Provides a lucid introduction
o Shows a sophisticated understanding of the key issues
o Shows ability to interpret relevant information and literature in relation to chosen topic
o Demonstrates a capacity to explain and apply relevant concepts o Shows evidence of reading beyond the required readings
o Justifies any conclusions reached with well-formed arguments and not merely assertions
o Provides a conclusion or summary o Correctly uses academic writing, presentation and grammar:
- Complies with academic standards of legibility, referencing and bibliographical details (including reference list)
- Writes clearly, with accurate spelling and grammar as well as proper sentence and paragraph construction
- Uses appropriate APA style for citing and referencing research
Answer:
Sexual abuse among children is considered as a widespread public health challenge, acknowledged in all levels of society worldwide. Child sexual abuse (CSA) is a key issue that has been seen to be present in most of the societies in all classes in India. The prevalence is increasing in India at an uncontrolled rate and it is not only affecting health of the victims, but also becoming a public health, social and economic challenge (Srivastava et al., 2017). In this regard, it is the high time to take strong and effective steps to eradicate the issue for safeguarding and securing children’s health. According to WHO, child sexual abuse is referred as the “the involvement of a child in sexual activity that he or she does not fully comprehend, is unable to give informed consent to, or for which the child is not developmentally prepared, or else that violates the laws or social taboos of society” (Behere, 2018). Indian government has implemented a range of preventive activities in the country. The following chapter has been developed for raising significant understanding on the particular issue, by reviewing the existing literatures.
Background of The Study
Violent behavior against women and children is a significantly known public health challenge globally. It includes “physical, psychological, sexual as well as economic violation or maltreatment” against people below 18 years old. CSA or child molestation is a type of child abuse, in which an older adolescent or adult by abusing a child for sexual encouragement (Choudhry et al., 2018). A range of activities includes different types of child sexual abuse, which involves engaging in sexual activities with a non-adult person, child grooming, indecent exposure, as well as child sexual exploitation, involving a child to make child pornography. According to UNICEF, child marriage is “represented perhaps the most prevalent form of sexual abuse and exploitation of girls” (Behere, 2018). The definition by the WHO has been accepted globally that indicates that CSA is the process involving a child through sexual activities, which the victim does not completely comprehend and is incapable to give assent to, or for which the victim is not prepared developmentally and the process that infringes legal and social regulations (Singh et al., 2014). Different types of activities are indicated under this umbrella term, including “attempted intercourse, intercourse, oral-genital contact, exposing children to adult sexual activity or pornography, fondling of genitals directly or through clothing and the abusing the child for pornography or prostitution” (Behere, 2018).
Srivastava et al., (2017) claimed that the dynamics of CSA are dissimilar from adult sexual abuse. It is because; children usually do not disclose the incident of sexual abuse after the occurrence. Thus, the disclosure of the events seems to be a long term procedure, instead of being a single episode, which is usually done in case of adult sexual violence. Thus, it is often started following a physical complaint or behavioral change (Seth, 2015). Instead of such issue, child sexual abuse is a neglected issue. The consequences of the issue are also widespread, including immediate effects like “shock, confusion, fear, guilt, hyper vigilance or dissociation”; to long term effects including “anxiety disorder, depression, suicidal tendency, antisocial personality, substance use, issues in relationship building, interpersonal issues, schizophrenia as well as eating disorder” (Saini, 2013).
Methodology
Research Methods
The method that has been applied for the purpose of the study includes systematic review of literature in collecting data for the study which will use electronic academic database to find literature for the study. Therefore, the research study has been conducted using articles that have been published in different academic databases such as Google Scholar (Ghosh, 2009).
Search Strategy
Search strategy has been formulated by using some keywords for refining the search procedure that includes “child sexual abuse, violence, harassment, prevalence, child safety, consequences, India, globally, factors, prevention, preventive strategies, measures, intervention”. Using these search terms, selected databases have been searched including the “Torrens library” for finding the most appropriate articles in the field of CSA and its preventive measure in India. The researcher mainly gathered data from the articles published in English within the last 10 years. Articles meeting these criteria have been included in the search procedure. The researcher has screened the reference list and relevant reviews of the studies included, along with citation tracking, as required (Tyagi & Karande, 2021).
Findings
Prevalence of Child Sexual Abuse Worldwide
According to the WHO, it is estimated that about 1 billion children within 2 to 17 years old have experience of abuse or violence from physical, emotional, sexual domain. Experiencing such violence has significant negative impact upon health and wellbeing of these children. Globally, prevalence of CSA is increasingly significant (Behere, 2018). In 2002, the WHO has estimated that 150 million females and 73 million males, who are under 18 years old, have experienced CSA. According to UNICEF, most of the abuses are done by people the child knows and trusts. Around 120 million girls within the age of 20, while 1 in 10 children are forced to involve in sex or perform sexual activities, as per the latest report (UNICEF, 2021). It is also revealed that around 90% teenage girls, reporting forced sex indicate that their first executor was someone they knew. Srivastava et al., (2017) highlighted that in a Meta analysis covering studies from 22 different nations, it is found that child sexual abuse is common in 19.7% girl and 7.9% boys. Prevalence is high in African and Asian countries, compared to America and Europe (Collin-Vézina et al., 2013). For instance, the prevalence found in the analysis was 34.4%, 23.9%, 10.1% and 9.2% in Africa, Asia, America and Europe respectively. The study also revealed highest percentage cases in South Africa, for both boys and girls, i.e. 60.9% and 43.7% respectively (Seth & Srivastava, 2017). Currently, for girls, sexual abuse is highly prevalent in North America and Australia, with 20.4% and 28.8% prevalence. However, in these regions, the rate is significantly low for boys. In case of Asia, the prevalence varies from only 6 per cent in Hong Kong to 41 per cent and 29.5 per cent in China for girls and boys respectively. In a study by UNICEF regarding maltreatment of children in East Asia and Pacific, it is reported that physical contact and sexual abuse is varied and it is from 1.7 per cent in Hong Kong to 11.6 per cent in Pacific Island (Jena, 2013). In a recent study on the street children trafficking and sexual abuse in Nepal, Kathmandu, and the findings revealed that 80% sexual exploitation is among friends and the enhancing tourism business in Asia is putting these children at stake regarding sexual abuse (Srivastava et al., 2017). In this regard, it is noteworthy that according to the World Health Organization, India has been reported to have the maximum number of sexually abused children in the world (Carson et al., 2013).
Prevalence of Child Sexual Abuse in India
It is estimated that around 19 per cent of World’s Children resides in India and they are contributing around 42 per cent Indian population (Srivastava et al., 2017). According to a survey by WHO, India has been reported to have the highest number of sexually abused children throughout the world. Tyagi and Karande (2021) highlighted that “Study on Child Abuse India 2007” is among the most known and wide surveys carried out in India by the Ministry of Women and Child Development. In that recent survey, it is revealed that 53.22 per cent children are having sexual abuse, within which, around 21.9 per cent are facing severe outcomes (Srivastava et al., 2017). It is also found from the survey results that the most vulnerable form of sexual abuse among children involves 7 to 13 years old children to adolescent people, including school going children. In India, recent evidences indicate that sexual abuse is faced by every second child in different forms throughout their life, while the severe form of sexual abuse is faced by 1 in every 5 children. Among these child victims, 52.94% have been reported to be boys, while 47.06% are girls (Behere, 2018).
Further, as per the National Crime Record Bureau 2016 statistics, 106 sexual abuse cases are reported daily in India, with highest number of cases in Delhi (1196), then Mumbai (712), Pune (354) and Jaipur (330). The highest sexual abuse cases reported among girls within the age of 0 to 12 years. Madhya Pradesh has reported the highest number of cases yearly, for continuously 6 years, with around 13 cases daily and thus identified as the “rape capital” of India, followed by UP and Maharashtra. In another study including samples from Kerala, it is found among 1614 teenagers, 36% males and 35% females have experience of sexual abuse at some point of their entire life (Choudhry et al., 2018).
Child Sexual Abuse: A Hidden Issue
Chopra et al. (2020), child sex abuse is one of the most prevalent issues in the world and the society, economic status, culture, awareness and other factors are predominantly involved in this issue. In terms of India, the child sex abuse is very much an issue and it is mostly covered, polished or neglected in the country due to the norm of accusing the victim for the situation It has been seen that in India the social structure has changed with time and the situation of joint family to the nuclear families are comprising of parents who are earning both for the family (Tomori et al., 2016). However, Joseph and Bance (2019), when the changes in the attitude or physical conditions develop among these children the parents or other individuals try to hide it to reduce the media exposure or social exposure as the victims are mostly accused in this country or the development of a situation where the child or the victim is stigmatized or unnecessarily harassed by different questions of people (Agarwal et al., 2013). Thus, the situation of awareness is still lacking in the country which develops a huge gap in the process of the reduction of the negative situations for people. However, it is necessary to highlight that the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences 2012 act has been put forward by the government of India and cases after this act have been considered with priority and a number of cases were properly registered under this act and awareness of people has also been changed (indiacode.nic.in, 2021). Though, the covering of these incidents and lack of access in the remote places let the issues run as the past (Edwards et al., 2020). Hence, in India child sexual abuse is prominent though action against these issues have not been properly considered yet and people try to hide it with proper knowledge to maintain the social reputation which ignites the crime ore and more in the country.
Factors Influencing The Issue of Child Sexual Abuse in India
Child sexual abuse in India is a predominant issue and it should be considered for the change in the society. It has been seen that the numbers of child sexual abuse cases in India is high and it is very much concerning for the society as well (Nebhinani et al., 2019). The factors involved in the child sexual abuse are not strictly confined in the psychological abnormality of people. The issues of lack of awareness and proper social functioning can also be marked as the factors that influence the issue (Cockbain & Reynald, 2016). It should be highlighted that the lack of awareness among people about the negative consequences of the post abusive activity is one of the most impacting factors in this process (Seth & Srivastava, 2017). On the other hand, the issue of the patriarchal societal culture developed the situation of hiding and covering the sexual abuse incidents in a higher magnitude. This issue lingers the consideration of not acknowledging human rights and not following the legal and social rules and regulations (Dhawan et al., 2016). Though, the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences 2012 act is present in India, the implementation of the act is very less impactful and the issues are not reducing as well (Indiacode.nic.in, 2021). Moreover, the reporting or registering the child sexual abuse cases are very less as hiding the incidents are the common norm in the country along with the accusation towards the victims. On the other hand, the consideration of the remote places and lack of awareness among people to report the incidents are also prominent factors that let the people who are actively abusing the children roam freely (Sowmya et al., 2016). This is a social issue along with an economic issue as well (Sharma, Bhattacharya & Singh, 2018). The economic instability and imbalance in the society, the child labor is one of the prominent issues of the country and the children working for money are also vulnerable to the child sexual abuse situations (Malhotra & Biswas, 2005).
Moreover, these children are threatened to their lives and the power of the economic support let people influence society. There are different corruptions and legal issues also present which induces the child sexual abuse along other abusive activities to be increased in the country. It is necessary to highlight that despite of a large amount of media exposure and awareness build up processes the abnormal fetish of people and negligence to the social structure or function induces the negative activities of people (Seth & Srivastava, 2017). Thus, it is necessary to highlight that the development of positive awareness among people and strict legal actions can change the situation along with changing the norm of hiding the incidents as well (Chattoraj, 2006). Other than all these, political factors are also involved in this factor as the political leaders linger these issues according to their need and these incidents and legal actions remained inactive when the political leaders are not interested anymore to these incidents and justice for the victims (Tiwari et al., 2018). Thus, the mental support to the victims is not there and people will harass them in a higher magnitude which is also humiliating. All these factors, involve in the negative consequences and people hiding after being abused let the criminal roam freely and the increase in this social crime is also prominent due to this situation (Sharma, 2007).
Health Outcomes of Child Sexual Abuse in India
Child sexual abuse can be seen in India in an extensive amount on the remote area population and even in the urban population along with the rural people as well. The age of the victims are mostly around 3 to 12 years and under the age of 18 years. Thus, it is visible that the inhumanity and cruelness among people to abuse a child below the age of puberty even. However, the health outcome of the children being abused is different (Gaidhane et al., 2016). In most of the cases due to the hiding and covering on the incidents the sexual trauma is developed in case of girls and also the impact of the negative physical pain the trauma regarding intercourse would develop as well. It has also been seen that the impact of the negative physical and mental trauma due to the abusive incidents the children also develop negative abusive behaviors and this impacts on the mental and social activities as well (Dayal et al., 2018). The substance abuse cases increase due to the negative impact of the sexual abuse among the adolescent population as well. In this manner, it is necessary to highlight that the mental impact is more than the physical impacts among the children who are affected with these abusive incidents. On the other hand, the physical trauma and pain is also very much prevalent as there are multiple cases of STDs and pain or other issues regarding the reproductive system among both girls and boys who are affected with any kind of sexual abuse (Roy & Madiki, 2020). Moreover, it is necessary to highlight that the lack of awareness and hiding the incidents lead to other physical issues which can be chronic and develop severe health issues as well. Most importantly, the children under the age of puberty can die as well due to the child sexual abuse cases (Joseph & Patel, 2020). Hence, it is necessary to state that the awareness development and strict legal actions should be considered to improve the situation. However, a large number of cases of child sexual abuse in India are found among the adolescent population and the impact found to be mostly on the mental health state such as depression, anxiety, trauma regarding sexual intercourse and relation development issues along with a higher magnitude of social isolation (Chandran, Bhargava & Kishor, 2018). Thus, the health outcomes of child sexual abuse can be different for different age groups and the awareness regarding all these issues should be considered with higher priority.
Prevention Strategies
Child sexual abuse in India is mostly increased due to the silence and the negative social norms of accusing the victim and their family. It is necessary to state that the consideration of the change in the situation is very much required (Damodaran et al., 2014). The aspect of the awareness among the family members and the society needed to be expanded and the government of India is developing different awareness programs to improve the education and responsibilities of people regarding the prevention of the child sexual abuse cases. The awareness to people to provide support to the family of the victims and also helping them to find justice and voice against this kind of cruel activity (Ramaswamy & Seshadri, 2020). Thus, it is necessary to state that the preventive measures of awareness development can be effective and it is impacting as well. On the other hand, the Children’s Homes, work places and schools are other institutions are the places where the children are being abused mostly and thus the respective institution authorities are provided with the regulations of proper supervision and reduction of these activities as well. Finally, the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 is developed to penalize the abuser with appropriate process (Indiacode.nic.in, 2021). Furthermore, 1098 is the Childline telephone number for the Indian citizens to inform any kind of child abuse activities to the government and the necessary actions will be taken by the government officials if required. All these preventive measures are now carried to reduce the number of child sexual abuse cases in India and make the country healthy (Neherta et al., 2015).
Role of Health Promotion
Child sexual abuse I India is dominant due to the silence and covering up the incidents. In this context, it can be stated that the social norm and culture regarding not speaking about sexual intercourse and these are taboo. Thus, the lack of communication and education among people from the childhood develop the gap and impact negatively on the behavioral and psychological point of view of people. Thus, the health promotion considering the awareness development and providing the social structural and functional factors to the people would be effective in reduction of these malpractices. Thus, the whole idea of health promotion in this context is to develop awareness and educate people to reduce the malpractices and take responsibilities of their actions (Ramaswamy & Seshadri, 2020). It should be highlighted that the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 will be effective on any kind of child sexual abuse case (Indiacode.nic.in, 2021). Furthermore, the people should be aware regarding the reporting of these kinds of activities or incidents to reduce the criminal offense. Thus, the health promotion play the role in awareness and education development regarding the activities, behaviors, legal and regulatory along with reporting related factors. Hence, the health promotion for the reduction of child sexual abuse can be effective.
Legal and Regulatory Interventions
Child sexual abuse is very much prominent in India and it should be controlled properly through legal interventions. In terms of the legal regulations for the child sexual abuse or any kind of child rights are comprehended by the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 (indiacode.nic.in, 2021). However, in terms of cultural and social norms of India the reporting of child sexual abuse have not been done in most of the cases. Thus, the awareness and regulatory mandate should be considered for the improvement in the reporting rate. However, the reported or registered cases are very much effectively considered for the legal actions and the victims would be provided with justice in many cases. However, the legal intervention can provide justice to the victims in terms of legal factors, though the mental and physical trauma due to the abusive incident cannot be healed through this (Seth & Srivastava, 2017).
Gap in Literature
In terms of the child sexual abuse in India there are many data regarding the cases and statistical factors as well. However, in case of the preventive measures, it has been seen that the preventive possible strategies have been identified in several literatures through the impacts of the preventive measures have not been identified in the literatures. It should be stated that the impacts of the preventive measures should be evaluated considering the awareness regarding the issues and also the reporting about the child sexual abuse should be considered as well. The impacts of the cultural and social impacts should be prevented as well. Moreover, sometimes the victims also die due lack of capability to withstand against the incident and the impacts or health issues and thee cases cannot be justified with only legal interventions as the loss cannot be repaid. On the other hand, the legal regulations also included with the reporting facility through telephone as well. Though, the rate of reporting from the victim’s end is very low in India due to social taboo and negative impacts on the mental and social factors. Thus it should be stated that the further researches should be conducted to properly evaluate the preventive factors and their possibilities in reduction of the child sexual abuse in India. The health promotion can develop awareness regarding the consequences of the malpractice among people. The school based health promotions can provide the idea of ‘good touch’, ‘bad touch’ and the private body parts among the children and they can act appropriately. Moreover, teaching the children of different age according to their need of knowledge regarding the abuse related activity, their rights and required activity from their end. Moreover, the parents should focus on supervising their children considering their safety and communicate with them and teach them appropriately to reduce the victimization of the child sexual abuse issues.
Summary
Brief Recap of What We Know About the Topic and What We Don’t
The literature review provided a deep understanding regarding the statistical factors of India considering the child sexual abuse. On the other hand, it should be stated that the literature review also effectively highlighted the social impacts on the child sexual abuse cases and also helped in the understanding about the negative impacts on the life style. It should also be highlighted that the preventive measures and the ideas regarding prevention and awareness development have been discussed in the literatures as well. However, the impacts of the preventive measures have not been properly highlighted in the studies. The literatures effectively pointed out the influencing factors of the child sexual abuse and the possible processes that can change the situation for the country has been identified in this review. However, the in depth research should be conducted for better understanding. Thus, in this situation the children needed to be take care of themselves or they are put under some known people to be taken care of. In this situation, the lack of awareness regarding the consequences and psychological issues of some people makes the children vulnerable and the negative sexual or other kinds of abusive situation develop for these children.
Summary of Key Points
The urbanization and the unstable economic flow in India still encouraging the child labor situations and these children who are working in different shops or other places far from their home or the orphan children as well are vulnerable to the physical and mental along with sexual abusive situations. Furthermore, in India the norms of accusing the victim and also developing a negative impact of neglecting or covering the sexual abuse incidents lead to the non-reporting of the child sexual abuse incidents immediately. The children who are abused mostly hide the incidents and bear with the trauma of mental and physical burden.
Research Question
• How economic inequality as well as rapid urbanization contributes towards child sexual abuse in India?
• What preventive strategies have been implemented in India for preventing incidence of child sexual abuse?

.png)
.png)
.png)



.png)
~5.png)
.png)
~1.png)























































.png)






